Characteristics of the First Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase with Phytase Activity from a Soil Metagenome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
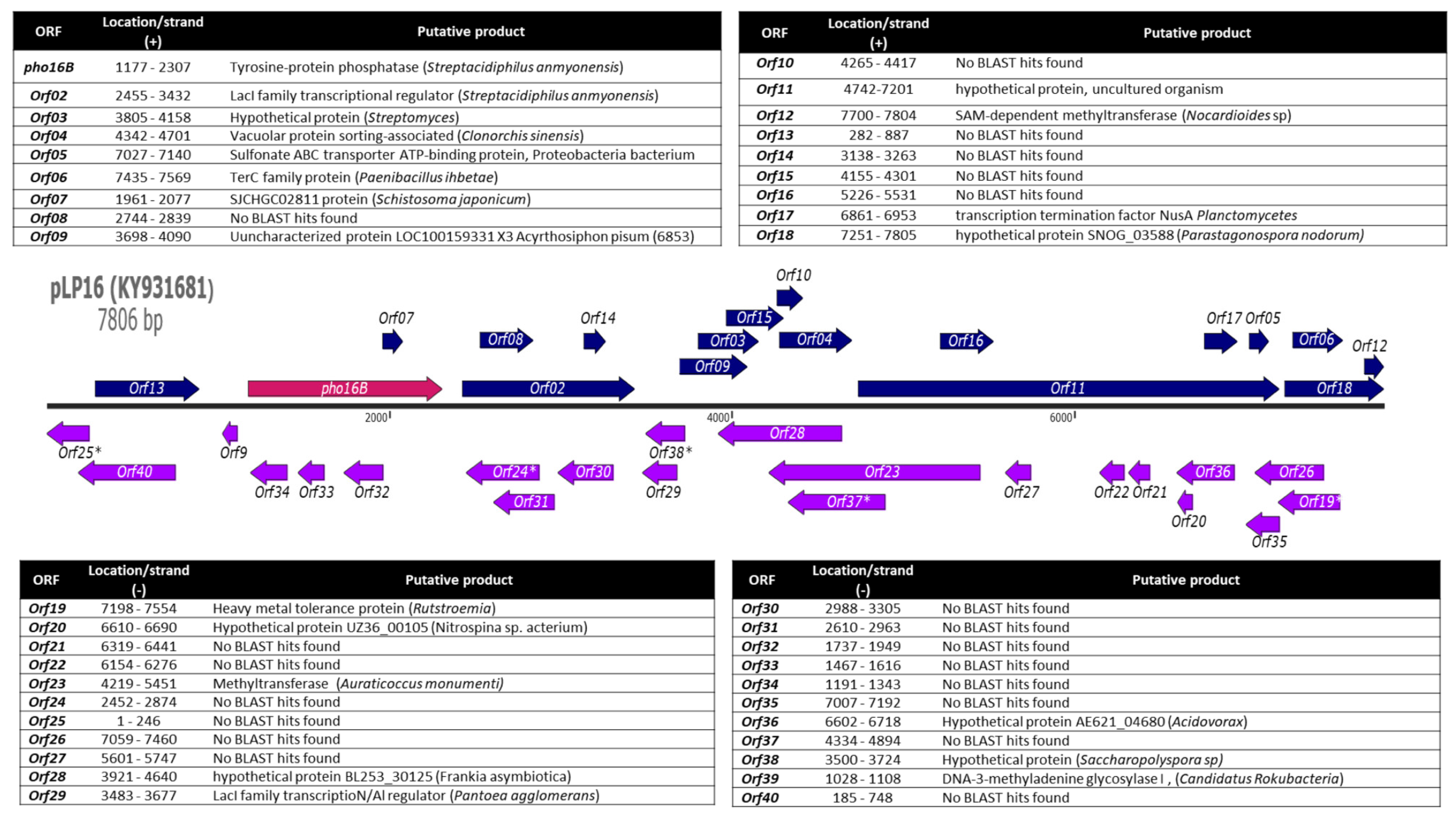
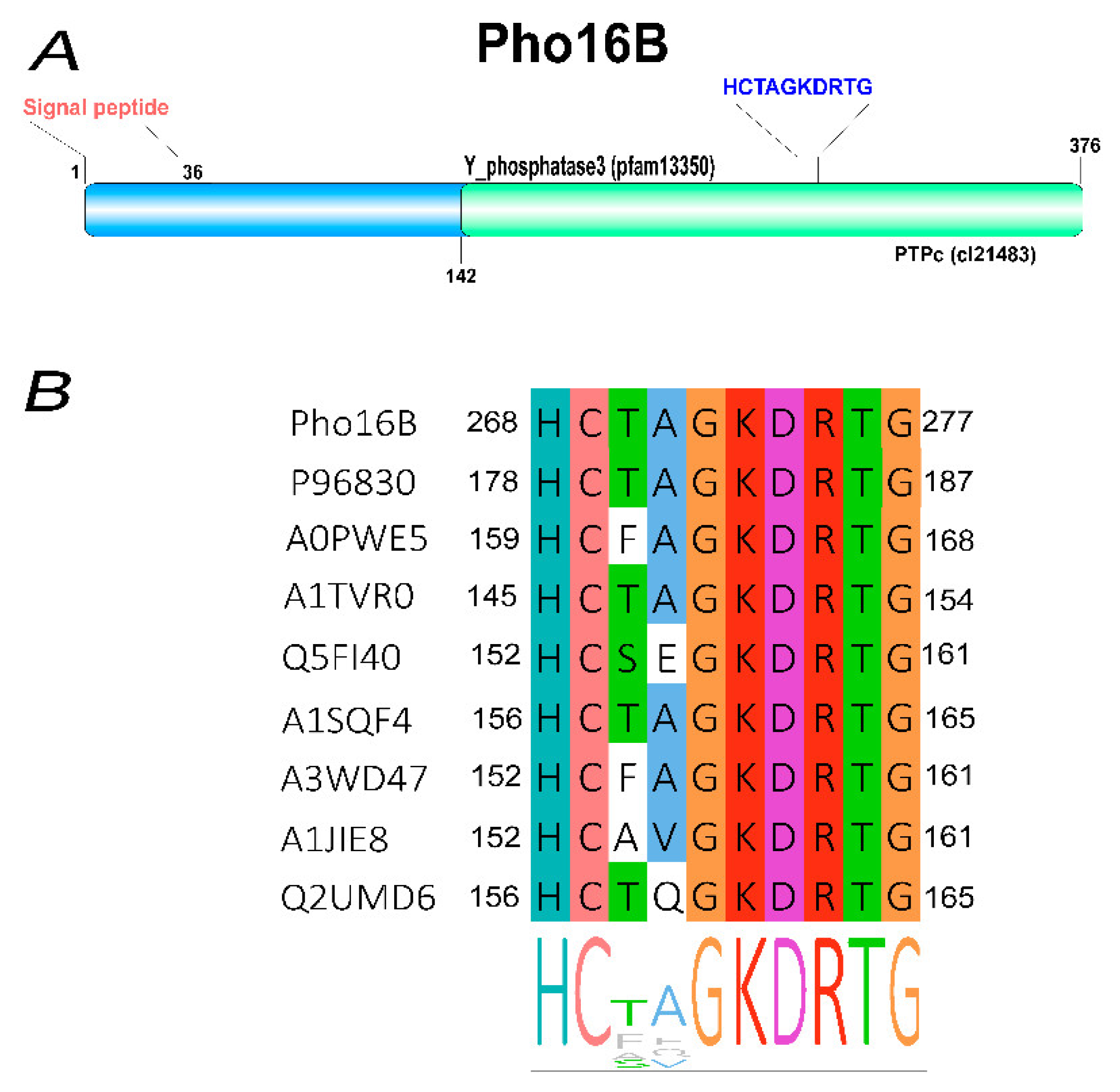
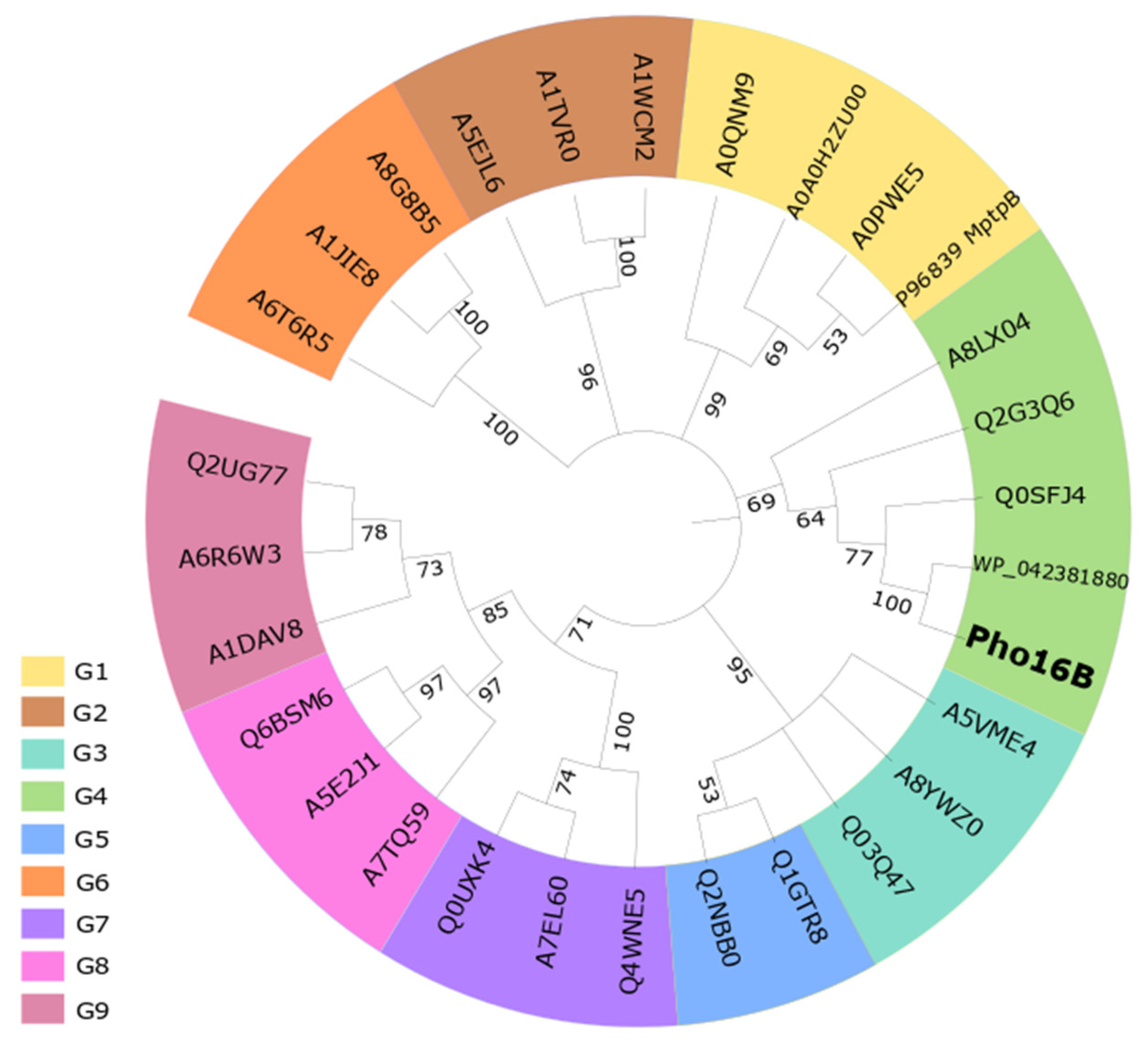
2.1. Identification and In Silico Characterization of the Novel ALP Member Pho16B
2.2. Tertiary Structure Prediction of Pho16B
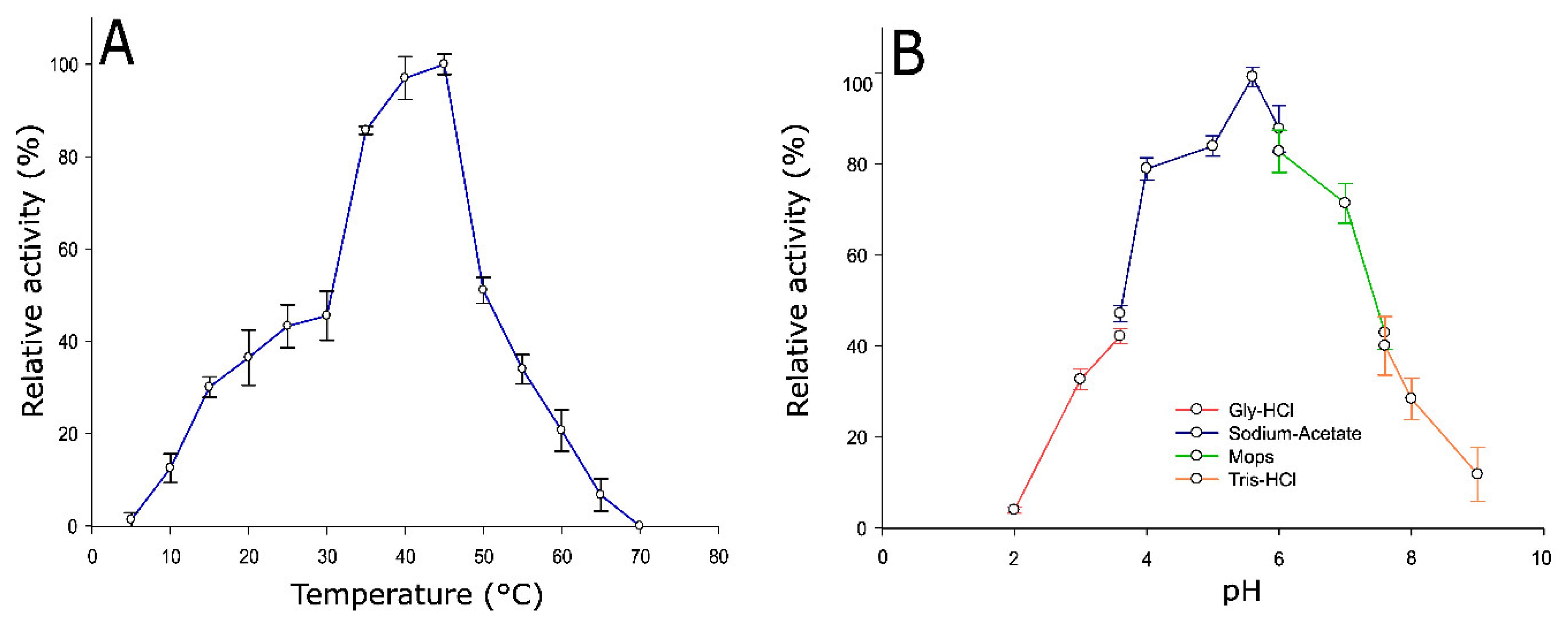
2.3. Optimum Temperature and pH of Pho16B
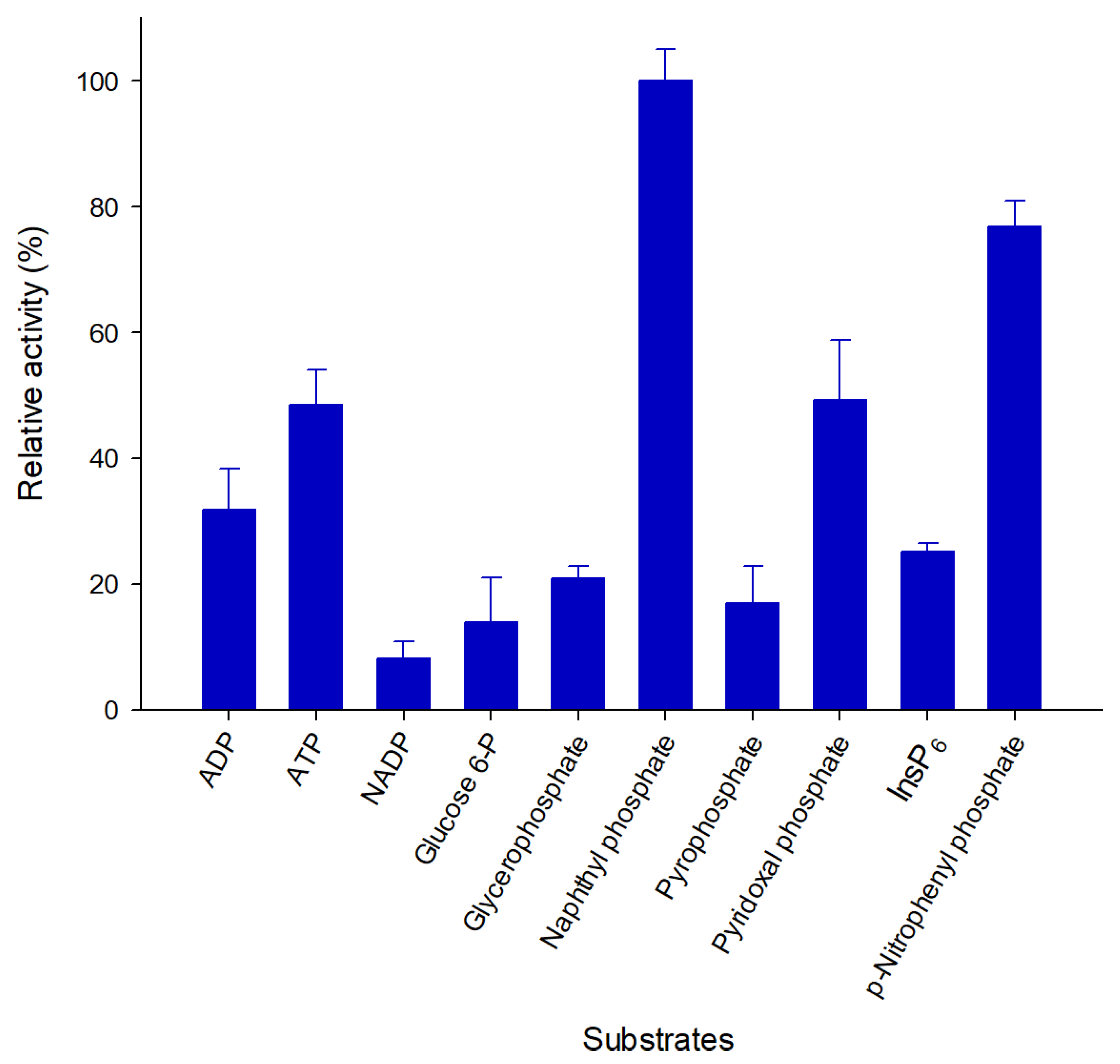
2.4. Pho16B Converts a Broad Range of Substrates
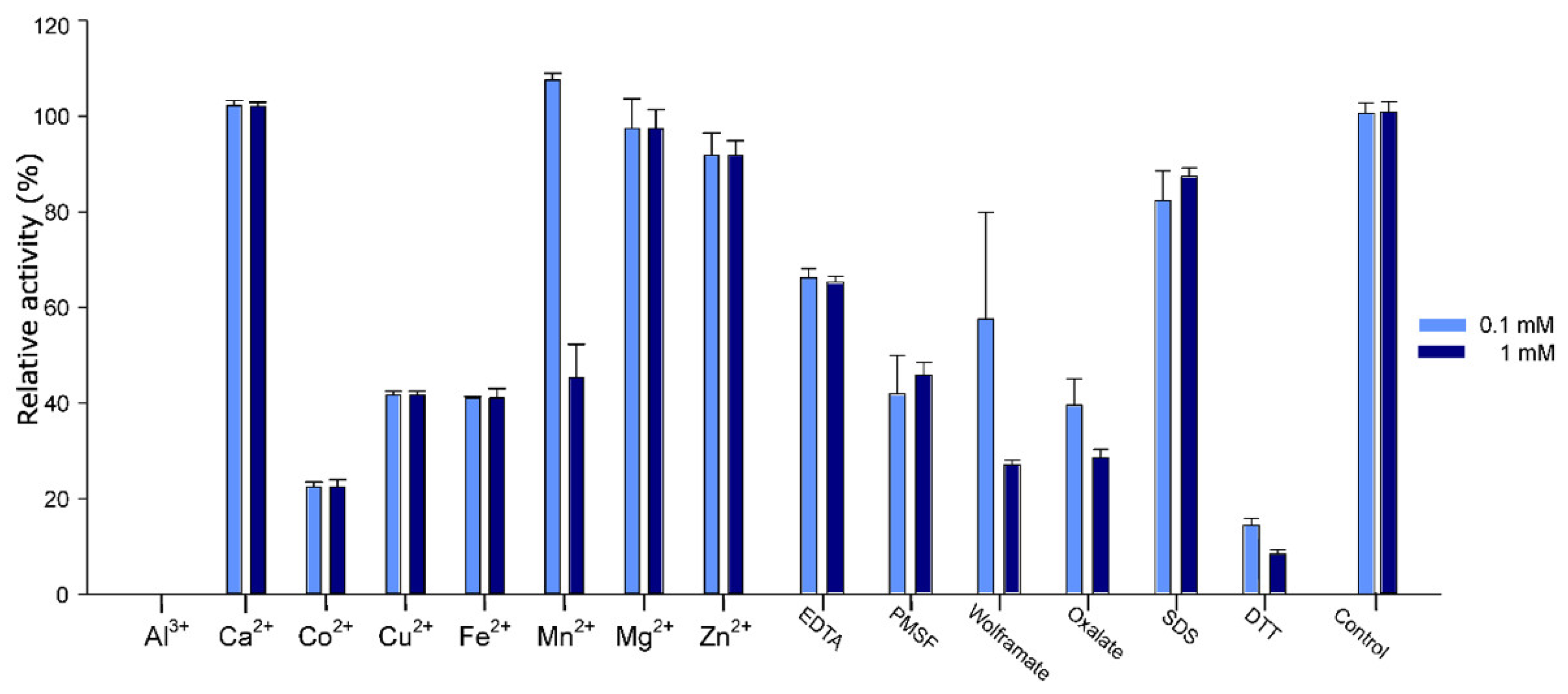
2.5. Effect of Additives on Pho16B Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling, Metagenomic Library Construction, and Function-Based Screening
3.2. Molecular Analysis
3.3. Biochemical Characterization of Pho16B
3.4. Accession Number
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pallen, M.J.; Wren, B.W. Bacterial pathogenomics. Nature 2007, 449, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, R. The metagenomics of soil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søborg, D.A.; Hendriksen, N.B.; Kilian, M.; Christensen, J.H.; Kroer, N. Bacterial human virulence genes across diverse habitats as assessed by in silico analysis of environmental metagenomes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiganis, T.; Bennett, A.M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase function: The substrate perspective. Biochem. J. 2007, 402, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonks, N.K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: From genes, to function, to disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beresford, N.J.; Saville, C.; Bennett, H.J.; Roberts, I.S.; Tabernero, L. A new family of phosphoinositide phosphatases in microorganisms: Identification and biochemical analysis. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, N.; Patel, S.; Armstrong, J.; Szöor, B.; Fordham-Skelton, A.P.; Tabernero, L. Mptpb, a virulence factor from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, exhibits triple-specificity phosphatase activity. Biochem. J. 2007, 406, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, A.A.; Greiner, R.; Selinger, L.B. Kinetics, substrate specificity, and stereospecificity of two new protein tyrosine phosphatase-like inositol polyphosphatases from selenomonas lacticifex. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 86, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Stirnimann, C.U.; Wieser, M.; Frey, D.; Meier, R.; Engelhardt, S.; Li, X.; Capitani, G.; Kammerer, R.A.; Hilbi, H. A type IV translocated Legionella cysteine phytase counteracts intracellular growth restriction by phytate. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34175–34188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, R.F.; Schell, M.J. Back in the water: The return of the inositol phosphates. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.P.; Lewsey, M.G.; Palukaitis, P. Signaling in induced resistance. In Advances in Virus Research; Carr, J.P., Loebenstein, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 76, pp. 57–121. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, E.; Empson, K.L.; Eaton, J.W. Phytic acid. A natural antioxidant. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 11647–11650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Prostate cancer and inositol hexaphosphate: Efficacy and mechanisms. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruder, L.M.; Gruninger, R.J.; Cleland, C.P.; Mosimann, S.C. Bacterial PhyA protein-tyrosine phosphatase-like myo-inositol phosphatases in complex with the Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 and Ins(1,4,5)P3 second messengers. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17302–17311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasakawa, N.; Sharif, M.; Hanley, M.R. Metabolism and biological activities of inositol pentakisphosphate and inositol hexakisphosphate. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullaney, E.J.; Daly, C.B.; Ullah, A.H.J. Advances in phytase research. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 47, pp. 157–199. ISBN 978-0-12-002647-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, J. Phytate (inositol hexakisphosphate) in soil and phosphate acquisition from inositol phosphates by higher plants. A review. Plants 2015, 4, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullaney, E.J.; Ullah, A.H.J. The term phytase comprises several different classes of enzymes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, S.; Knietsch, A.; Scholten, E.; Braun, J.; Lohscheidt, M.; Zelder, O. Biotechnological production and applications of phytases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 68, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushasree, M.V.; Vidya, J.; Pandey, A. Other enzymes: Phytases. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Pandey, A., Negi, S., Soccol, C.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 309–333. [Google Scholar]
- Puhl, A.A.; Gruninger, R.J.; Greiner, R.; Janzen, T.W.; Mosimann, S.C.; Selinger, L.B. Kinetic and structural analysis of a bacterial protein tyrosine phosphatase-like myo-inositol polyphosphatase. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.G.; Weaver, J.D.; Mullaney, E.; Ullah, A.H.; Azain, M.J. Phytase, a new life for an “old” enzyme. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2013, 1, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruninger, R.J.; Dobing, S.; Smith, A.D.; Bruder, L.M.; Selinger, L.B.; Wieden, H.J.; Mosimann, S.C. Substrate binding in protein-tyrosine phosphatase-like inositol polyphosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9722–9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, N.; Almeida, I.; Meneses, C. New bacterial phytase through metagenomic prospection. Molecules 2018, 23, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berini, F.; Casciello, C.; Marcone, G.L.; Marinelli, F. Metagenomics: Novel enzymes from non-culturable microbes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Wu, X.; Xie, L.; Huang, Z.; Peng, W.; Gan, B. Identification and characterization of a mesophilic phytase highly resilient to high-temperatures from a fungus-garden associated metagenome. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2225–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Mooij, M.J.; Barret, M.; Hegarty, P.M.; Harington, C.; Dobson, A.D.; O’Gara, F. Identification of novel phytase genes from an agricultural soil-derived metagenome. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo Villamizar, G.A.; Nacke, H.; Böhning, M.; Herz, K.; Daniel, R. Functional metagenomics reveals an overlooked diversity and novel features of soil-derived bacterial phosphatases and phytases. mBio 2019, 10, e01966-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.-H.; Han, J.-H.; Ko, H.-Y.; Kim, S.B. Streptacidiphilus anmyonensis sp. Nov., Streptacidiphilus rugosus sp. Nov. and Streptacidiphilus melanogenes sp. Nov., acidophilic actinobacteria isolated from pinus soils. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruninger, R.J.; Thibault, J.; Capeness, M.J.; Till, R.; Mosimann, S.C.; Sockett, R.E.; Selinger, B.L.; Lovering, A.L. Structural and biochemical analysis of a unique phosphatase from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus reveals its structural and functional relationship with the protein tyrosine phosphatase class of phytase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Protein structure and function prediction using I-TASSER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2015, 52, 5.8.1–5.8.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-tasser: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, A.A.; Greiner, R.; Selinger, L.B. Stereospecificity of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate hydrolysis by a protein tyrosine phosphatase-like inositol polyphosphatase from Megasphaera elsdenii. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anné, J.; Vrancken, K.; Van Mellaert, L.; Van Impe, J.; Bernaerts, K. Protein secretion biotechnology in gram-positive bacteria with special emphasis on Streptomyces lividans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacke, H.; Will, C.; Herzog, S.; Nowka, B.; Engelhaupt, M.; Daniel, R. Identification of novel lipolytic genes and gene families by screening of metagenomic libraries derived from soil samples of the German Biodiversity Exploratories. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneberg, P.; Draber, P. Regulation of cys-based protein tyrosine phosphatases via reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in mast cells and basophils. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Pandya, C.; Liu, C.; Al-Obaidi, N.F.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L.; Toews Keating, S.; Aono, M.; Love, J.D.; Evans, B.; et al. Panoramic view of a superfamily of phosphatases through substrate profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1974–E1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruninger, R.J.; Selinger, L.B.; Mosimann, S.C. Effect of ionic strength and oxidation on the p-loop conformation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase-like phytase, phyasr. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3783–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Clemens, J.C.; Schubert, H.L.; Stuckey, J.A.; Fischer, M.W.; Hume, D.M.; Saper, M.A.; Dixon, J.E. Expression, purification, and physicochemical characterization of a recombinant Yersinia protein tyrosine phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23759–23766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- George, T.S.; Quiquampoix, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Richardson, A.E. Interactions between phytases and soil constituents: Implications for the hydrolysis of inositol phosphates. In Inositol Phosphates, Linking Agriculture and the Environment; Turner, B.L., Richardson, A.E., Mullaney, E.J., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Bekalu, Z.E.; Madsen, C.K.; Dionisio, G.; Brinch-Pedersen, H. Aspergillus ficuum phytase activity is inhibited by cereal grain components. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, G.Q.; Abdullah, N.; Jalaludin, S.; Ho, Y.W. Purification and characterization of a phytase from Mitsuokella jalaludinii, a bovine rumen bacterium. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12766–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimanova, A.D.; Beinhauer, A.; Valeeva, L.R.; Chastukhina, I.B.; Balaban, N.P.; Shakirov, E.V.; Greiner, R.; Sharipova, M.R. Novel glucose-1-phosphatase with high phytase activity and unusual metal ion activation from soil bacterium Pantoea sp. Strain 3.5.1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.S.; Guimarães, V.M.; de Melo, R.R.; de Rezende, S.T. Isolation of a thermostable acid phytase from Aspergillus niger ufv-1 with strong proteolysis resistance. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Raza, A.; Löfgren, S.; Fernando, M.R.; Ho, Y.-S.; Lou, M.F. Low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase (LMW-PTP) and its possible physiological functions of redox signaling in the eye lens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1774, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, M.P.; Salgado, R.L.; Eller, M.R.; Vidigal, P.M.P.; Fernandes de Carvalho, A. Characterization of a heat-resistant extracellular protease from Pseudomonas fluorescens 07a shows that low temperature treatments are more effective in deactivating its proteolytic activity. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7842–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alliegro, M.C. Effects of dithiothreitol on protein activity unrelated to thiol–disulfide exchange: For consideration in the analysis of protein function with cleland’s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 282, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, M.; Hollander, V.P. Acid phosphatase from rat liver: Purification, crystallization, and properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 6084–6089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gazizova, N.I.; Petrova, N.V.; Karimova, F.G. Effect of tungstate on pea root growth and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 60, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Wemheuer, B.; Korolkow, V.; Wemheuer, F.; Nacke, H.; Schöning, I.; Schrumpf, M.; Daniel, R. Driving forces of soil bacterial community structure, diversity, and function in temperate grasslands and forests. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamizar, G.A.C.; Nacke, H.; Daniel, R. Function-based metagenomic library screening and heterologous expression strategy for genes encoding phosphatase activity. In Metagenomics: Methods and Protocols; Streit, W.R., Daniel, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1539, pp. 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, K.; Parkhill, J.; Crook, J.; Horsnell, T.; Rice, P.; Rajandream, M.-A.; Barrell, B. Artemis: Sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Church, D.M.; Federhen, S.; Lash, A.E.; Madden, T.L.; Pontius, J.U.; Schuler, G.D.; Schriml, L.M.; Sequeira, E.; Tatusova, T.A.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. Interproscan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Zheng, C.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Lanczycki, C.J.; et al. CDD: Conserved domains and protein three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D348–D352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstencroft, K.J.; Stevens, R.; Tabernero, L.; Brass, A. Phosphabase: An ontology-driven database resource for protein phosphatases. Proteins 2005, 58, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. Signalp 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, P.; Ng, K.L.; Krogh, A. Fast and sensitive taxonomic classification for metagenomics with kaiju. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boratyn, G.M.; Camacho, C.; Cooper, P.S.; Coulouris, G.; Fong, A.; Ma, N.; Madden, T.L.; Matten, W.T.; McGinnis, S.D.; Merezhuk, Y.; et al. Blast: A more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W29–W33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Scheremetjew, M.; Denise, H.; Potter, S.; Tarkowska, A.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Pesseat, S.; Boland, M.A.; Hunter, F.M.I.; et al. EBI metagenomics in 2017: Enriching the analysis of microbial communities, from sequence reads to assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D726–D735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Muscle: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. Mega X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-Tasser suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-Tasser server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. LB (Luria-Bertani) Liquid Medium; Cold Spring Harbor Protocols: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. M9 Minimal Medium (Standard); Cold Spring Harbor Protocols: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, J.K.; Lahti, R.J. A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 113, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, R. Purification and properties of a phytate-degrading enzyme from Pantoea agglomerans. Protein J. 2004, 23, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomori, G. Preparation of buffers for use in enzyme studies. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1955; Volume 1, pp. 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tabernero, L.; Aricescu, A.R.; Jones, E.Y.; Szedlacsek, S.E. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: Structure-function relationships. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Substrate | Km (mM) | kcat (min−1) | Kcat/Km (s−1mM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| InsP6 | 1.290 ± 0.38 | 5.48 ± 0.7 | 70.43 ± 4.4 |
| Naphthyl phosphate | 0.966 ± 0.18 | 14.64 ± 1.52 | 238.73 ± 14.52 |
| p-Nitrophenylphosphate | 1.026 ± 0.14 | 19.73 ± 2.8 | 316.89 ± 32.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo Villamizar, G.A.; Nacke, H.; Griese, L.; Tabernero, L.; Funkner, K.; Daniel, R. Characteristics of the First Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase with Phytase Activity from a Soil Metagenome. Genes 2019, 10, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020101
Castillo Villamizar GA, Nacke H, Griese L, Tabernero L, Funkner K, Daniel R. Characteristics of the First Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase with Phytase Activity from a Soil Metagenome. Genes. 2019; 10(2):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020101
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo Villamizar, Genis Andrés, Heiko Nacke, Laura Griese, Lydia Tabernero, Katrina Funkner, and Rolf Daniel. 2019. "Characteristics of the First Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase with Phytase Activity from a Soil Metagenome" Genes 10, no. 2: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020101
APA StyleCastillo Villamizar, G. A., Nacke, H., Griese, L., Tabernero, L., Funkner, K., & Daniel, R. (2019). Characteristics of the First Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase with Phytase Activity from a Soil Metagenome. Genes, 10(2), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020101





