Abstract
The domain of unknown function (DUF) superfamily encodes proteins of unknown functions in plants. Among them, DUF668 family members in plants possess a 29 amino-acid conserved domain, and this family has not been described previously. Here, we report this plant-specific novel DUF668 gene family containing 12 OsDUF668 genes in rice (Oryza sativa) and 91 DUF668s for the other seven plant species. In our study, DUF668 genes were present in both dicot and monocot plants, indicating that DUF668 is a conserved gene family that originated by predating the dicot–monocot divergence. Based on the gene structure and motif composition, the DUF668 family consists of two distinct clades, I and II in the phylogenetic tree. Remarkably, OsDUF668 genes clustered on the chromosomes merely show close phylogenetic relationships, suggesting that gene duplications or collinearity seldom happened. Cis-elements prediction display that over 80% of DUF668s contain phytohormone and light responsiveness factors. Further comprehensive experimental analyses of the OsDUF668 family are implemented in 22 different tissues, five hormone treatments, seven environmental factor stresses, and two pathogen-defense related stresses. The OsDUF668 genes express ubiquitously in analyzed rice tissues, and seven genes show tissue-specific high expression profiles. All OsDUF668s respond to drought, and some of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes resist to salt, wound, and rice blast with rapidly altered expression patterns. These findings imply that OsDUF668 is essential for drought-enduring and plant defense. Together, our results bring the important role of the DUF668 gene family in rice development and fitness to the fore.
1. Introduction
The structures, functions, and evolution patterns of gene families have hitherto long fascinated plant biologists. Our understanding of the interaction and adaptation to plants with the environment is based on the vast amount of information available for these gene families [1]. Among them, the domain of unknown function (DUF) families refers to a certain kind of protein families with domains of unknown function. Generally, DUF families consist of numerous members, and the entire numbering scheme has extended to DUF2607 from 1997 to 2010 [2]. Multiple attempts have been made to investigate several DUF genes experimentally. For instance, the DUF1 domain (GGDEF) was isolated and detected to stimulate c-di-GMP (cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate) levels as cyclase, and DUF2 (EAL) degrades c-di-GMP as phosphodiesterase conversely in prokaryotes [3]. DUF27, known as the macro domain, possesses the ability to bind the ADP-ribose specifically [4]. Moreover, the DUF283 domain of Dicer proteins was required for siRNA processing in gene silence [5,6]. The DUF538 superfamily was predicted to perform hydrolytic activity towards chlorophyll molecules [7,8]. In addition, the amaranth abiotic stress-induced gene (AhDGR2) encodes a DUF642 protein involved in salt and abscisic acid (ABA) hyper-sensibility in Arabidopsis [9]. The DUF1110 was crystallized and identified as the OsPUB44-interacting protein 1 (PBI1) in rice [10]. The structure of DUF1470 analysis revealed an ABATE domain (PF07336) and suggested its function presumably as the stress-induced transcriptional regulator [11]. Some members of the monocot-specific DUF1618 superfamily were reported to participate in chloroplast biogenesis and photosynthesis pathways [12].
Although some DUF gene families have been characterized, a large set of the DUF members remains unknown, especially in rice, a model monocotyledon benefited from its small genomic size and economic importance. DUF668 domain-containing genes were identified to contain a conserved domain of 29 amino acids (aa). However, there is limited research about this gene family. In plant-pathogen interactions, a dominant or semidominant resistance (R) gene in plant confers resistance to the corresponding avirulence (Avr) peptides from pathogens [13]. Cf-9 is a protein conferring resistance to specific races of tomato C.fulvum through recognition of Avr peptides, and the Avr9/Cf-9 recognition to pathogen invasion has served as an excellent model system to dissect the signaling pathways of plant defense responses [14]. Many signaling components acting downstream of Cf-9, Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes are found to play an important role in this defense process [15]. Several studies have been performed to elaborate on the disease resistance function of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes in solanaceous plants, such as tomato and tobacco, where the studied Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes rapidly respond to Avr9 elicitation and wounding [16,17]. Wounding is usually caused by herbivores and environmental mechanical stresses and opens the way to invasion by microbial pathogens, inducing the plant defense of the dangerous passage [18]. A large number of genes have been found to respond to the wound stress rapidly in Arabidopsis [19]. However, it has not been studied whether Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes in rice respond to the pathogen-defense related stresses like wounds, and even to any other stresses. It will be interesting to explore the possible functions of these rice Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes.
In this study, we distinguished 12 DUF668 members in the rice genome, which were subsequently divided into two clades (I and II) based on phylogenetic analysis. The OsDUF668 genes in clade I were annotated as Avr9/Cf-9 exhibited genes. The expression profiles of OsDUF668 genes were investigated in 22 different rice tissues, five hormone treatments, seven environmental factor stresses, and two pathogen-defense related stresses. The possible functions of these OsDUF668 genes were explored and discussed. Our research highlights a novel insight into the evolutionary pattern of the DUF668 family and addresses a better understanding of their functions in rice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the DUF668 Genes
The reference genome sequences of eight plants including Arabidopsis thaliana (Araport11), Brachypodium distachyon (v3.1), Oryza sativa (v7.0), Panicum virgatum (v5.1), Sorghum bicolor (v3.1.1), Setaria italica (v2.2), and Zea mays (Ensembl-18) which were retrieved from the Phytozome database (http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html) and Oryza rufipogpon (OR_W1943) genome database acquired from Ensembl Plants (http://plants.ensembl.org/). The hidden Markov model (HMM) profile (No. PF05003) was downloaded from Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/) [20] and used to identify a proteins database in each species by the hidden Markov model (HMM) in HMMER 3.2.1 software (http://hmmer.org/) [21]. Non-redundant DUF668 proteins were verified by SMART (Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool) (http://smart.embl-heigelberg.de/), and Pfam individually. We searched China’s National Rice Data Center (http://www.ricedata.cn/gene/) to obtain annotation information of OsDUF668s. Finally, physicochemical parameters of the rice DUF668 proteins including theoretical isoelectric points (pI) and molecular weights (MW), were generated by ProtParam tools [22], and the subcellular localizations were predicted via the Plant-PLoc server (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/) [23]. The existence of DUF668 proteins in different organisms was also consulted in the European Bioinformatics Institute database (EMBL-EBI, https://www.ebi.ac.uk/).
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motifs
Multiple amino acid sequences alignments were performed by ClustalW of MEGA 7.0 with default parameters [24]. Unrooted Neighbor-Joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree was constructed using 103 DUF668 genes in eight plants with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The composition of conserved motifs was searched by the MEME (Multiple Em for Motif Elicitation) online tool (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme), setting a maximum number to 20 [25]. The TBtools was used to analyze and visualize gene structure (exon/intron) and conserved motifs of DUF668 genes [26]. The phylogenetic tree was visualized by Evolview v2 (https://evolgenius.info//evolview-v2/) [27].
2.3. Chromosomal Locations, Gene Duplication Events, and Cis-acting Elements Analysis
Coordinates on the reference genome sequence of rice DUF668 genes were obtained from the genome annotation file. Gene duplication events were discriminated by MCScanX software [28]. Locations of OsDUF668 genes were mapped by TBtools [26]. Also, 2 Kb upstream promoter of each rice DUF668 coding sequence was examined, and the cis-acting regulatory element analysis was executed through the PlantCARE dataset (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) [29]. The radar map was generated by R 3.5.1 scripts manually.
2.4. Plant Materials and Treatments
In our case, tissue samples were collected from the Oryza sativa ssp. indica cultivar 93–11 under natural field condition. Altogether, 22 tissues were prepared according to the procedure used by Wang et al. 2016 [30], namely root (R, 12-day-old seedlings), leaf (L, 12-day-old seedlings), sink leaf (SL, unexpanded flag leaf before heading stage), sink flag leaf sheath (SiFLS, before heading stage), flag leaf (FL, one week after heading), source flag leaf sheath (SoFLS, one week after heading), node (N, the first node on the top at panicle stage), internode (IN, part between the first node and the second node on the top at panicle stage), panicle (P5, P10, P15, and P20: panicle grown to the length of 5 cm, 10 cm, 15 cm, and 20 cm, respectively), hull of flower (H1, 1–3 days before flowering), stamen (St, 1–3 days before flowering), pistil (Pi, 1–3 days before flowering ), spikelets (Sp1, Sp5, Sp15, Sp20, at 1, 5, 15, and 20 days after flowering), hull of seed (H2, at 12–15 days after flowering), immature seed (IS, embryo and endosperm at 12–15 days after flowering), and calli (Ca, induced 30 days before subculture). Three biological replicates were implemented. Each sample was collected from over three plants and pooled together. Samples were grounded immediately with liquid nitrogen and stored in TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) at −80 °C for use.
Different experimental treatments were carried out using 12-day-old 93–11 seedlings growing in vermiculite with sterilized water (26 °C, 16-h light/8-h dark). For hormone treatments, seedlings were sprayed with solutions containing 6-benzyl amino purine (6BA) (25 μM), indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) (50 μM), gibberellic acid (GA) (100 μM), salicylic acid (SA) (100 μM), and abscisic acid (ABA) (100 μM), respectively [30,31]. For two environmental factors, heat of 40 °C (H40) and cold of 4 °C (Cold4), the culture temperature of 12-day-old seedlings was separately changed to 40 °C and 4 °C [30,31]. Samples were collected at 0, 1, 3, 6, 12 h after the application of the above treatments. For submergence (Sub), seedlings were submerged in the water with a depth of 5 cm from leaf top to the water surface, and samples were collected at 0, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h after treatment [30]. Seedling samples were collected at 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 12 h for all following treatments. For ultraviolet-B (UV-B), 12-day old seedlings were placed in the 24-h light condition (100 μmol m−2 s−1) supplementing with continuous irradiation of UV-B (500 mWm−2) [30]. As to NaCl, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and drought (Dr) treatments, 12-day-old seedlings were firstly washed off the vermiculite from the roots, and secondly immersed in NaCl solution (200 mM), PEG6000 solution (20%, w/v), and air, respectively [30,32]. For wound stress, seedling leaves were subjected to manual scissors of about nearly one-third of the leaf from the top [30,33]. For rice blast treatment, seedlings were sprayed with 70 ml spore suspension (about 105 conidia ml−1) and inoculated under dark and high-humidity conditions [30,34]. Three biological replicates were performed, with each sample collected from about eight seedlings and pooled together. All samples were grounded immediately with liquid nitrogen, and stored in TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) at −80 °C to preserve full-length RNA.
2.5. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Analysis
Total RNAs of samples were isolated using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen). The first strand of cDNA was synthesized from 5μg of total RNA using the M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega). The quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) was conducted with gene-specific primers (Table S1) in a 96-well plate by Bio-Rad CFX96 real-time PCR system, using 2× SYBR Green Master Mix reagent (Bio-Rad). The thermal cycles were as follows: 95 °C for 5 min; 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, primer-specific annealing temperature for 10 s, and 72 °C for 15 s; and then melt curve from 65 to 95 °C. Reference genes were selected according to each experimental condition, as described in Table S2 [30]. Based on the corresponding reference gene(s), the relative expression levels of OsDUF668 genes were calculated using the Bio-Rad CFX Manager 2.1 software (tissues), and additionally, log2 (experimental treatments).
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of DUF668 Genes in Rice
To identify DUF668 genes in rice, we examined the 29 amino-acid DUF668 conserved domain through the whole rice genome. As a result, we characterized 12 putative non-redundant entries and named all candidates as OsDUF668-1 to OsDUF668-12 according to their chromosomal order, which dispersed unevenly across several chromosomes excluding chromosomes 7–10 (Figure S1). Then, we measured more OsDUF668s to acquire more information about their chromosome locations, mRNA length, number of amino acids (aa), MW, and theoretical pI (Table 1). The encoded protein length of those OsDUF668 genes ranged between 357 and 656 aa; meanwhile, their predicted theoretical pI varied from 6.37 to 10.5. We also predicted the subcellular localization of the rice DUF668 proteins, of which the majority (7/12) was supposed to locate in the chloroplast, while the others to be targeted to the nucleus, peroxisome, cytoplasm, and mitochondrion (Table 1). Of note, we noticed that OsDUF668-1, -4, -5, -6, -9, and -12 were annotated as Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited protein whereas the others were not. In this regard, we tempted to speculate that DUF668 genes in rice could be clustered into two distinct groups.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the putative DUF668 genes in rice.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis, Gene Structure, and Motif Composition of the DUF668s in Eight Plants
To extend our understanding of the DUF668 gene family, we screened out the DUF668 domain in the European Bioinformatics Institute database (EMBL-EBI, https://www.ebi.ac.uk) and found DUF668 genes exist in up to 62 plant organisms excluding animal and other non-plant species (Table S3). We further dissected four model genomes (Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Drosophila melanogaster, and Danio rerio) and none DUF668 was found. Thus, this finding manifested DUF668s might belong to a kind of plant-specific gene family.
Gramineae is known as the fourth largest flowering plant family, and an essential genetic resource consisted of many commercial crops [35]. Apart from O. sativa, we consequently screened DUF668 members through one model dicot A. thaliana genome and six representative graminaceous genomes, including B. distachyon, O. rufipogpon, P. virgatum, S. bicolor, S. italica, and Z. mays. In the above species genomes, 6, 11, 13, 22, 12, 11, and 16 non-redundant DUF668 family members were detected successively (Figure 1A; Table S4). To investigate the evolutionary relationships of the DUF668 family in those Gramineae organisms, we conducted a neighbor joining (NJ)-phylogenetic tree combining with exon/intron structural and conserved motifs analysis. The results showed that all 103 DUF668 proteins could be integrated into the two clades I and II (Figure 1B). Forty-nine and fifty-four DUF668s pertained to clade I and II separately, stating a negligible difference in gene copy number. We noticed that half of the rice OsDUF668s exhibited in clade I, and all of them were Avr9/Cf-9 mediated genes, which confirmed our preceding assumption. Furthermore, these two distinct groups differentiated not only in gene structure but also in motif arrangement. With a few exceptions, DUF668s in clade II had approximately 9–16 exons, in sharp contrast to those in clade I, most of which only possessed one exon (Figure 1C). We identified 20 different conserved motifs (Figure 1D; Table S5). Motif 1, and motif 5 were related to unknown function protein DUF668 and DUF3475, while others have no functional annotation. In general, clade II had more motifs than clade I. Motif 1 was the most common motif, presenting in all DUF668 genes. Besides that, the vast majority of DUF668s included motif 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 20. Motif 9, 10, 13, 15, and 16 were group-specific elements in clade II, as motif 19 mainly existed in clade I. To sum up, the exon-intron structures and motif constituent of the DUF668 genes substantially conformed to their phylogenetic relationships.
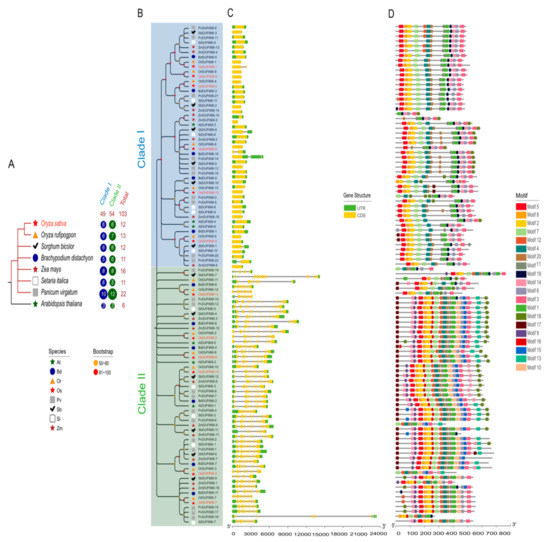
Figure 1.
Comparison of the gene structure and motif of 103 DUF668 genes in eight plant organisms. (A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree with over 50% bootstrap value above the branch. The clade I and II are displayed in blue and green colors, separately. The different-shaped arcs indicate different species. The names of species are abbreviated to two letters, namely Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), Oryza sativa (Os), Oryza rufipogpon (Or), Panicum virgatum (Pv), Sorghum bicolor (Sb), Setaria italica (Si), and Zea mays (Zm). (B) Motif architectures of all DUF668 genes. Each motif is illustrated with a specific color, and the distribution of identified motifs corresponds to their positions. (C) Exon/introns and untranslated regions (UTRs) of DUF668s. Green boxes denote UTR (untranslated region); yellow boxes denote CDS (coding sequence); black lines denote introns. The length of protein can be estimated using the scale at the bottom. (D) Evolutionary relationship of the DUF668 genes from eight plant species. The right circles show the number of DUF668s in different plant lineages in relative groups. More detailed inspections are provided in Table S4.
3.3. Cis-acting Elements Prediction of DUF668 Genes in Rice
Cis-acting regulatory elements might provide clues for determining gene expression patterns in various organs or under environmental stresses [36]. Previous studies reported a significant positive relationship between response genes and their cis-elements in upstream promoter regions [37,38]. Here, we manifested potential cis-regulatory elements in the 2 Kb upstream regions of the OsDUF668s examined via the PlantCARE database. Thirty-two cis-regulatory elements were detected totally (Figure 2A), which formed eleven subclasses and four main categories as plant growth, abiotic stress, phytohormone responsiveness, and light responsiveness (Figure 2B). The largest subdivision was light responsiveness, which contained 55.5% predicted cis-elements, including AAA-motif (light-responsive element) and AE-box (part of a module for light response) as representatives. A series of regulatory elements participating in plant hormone responsiveness ranked second. Cis-acting factors respond to abscisic acid, auxin, flavonoid, gibberellin, and salicylic acid were involved. Among them, ABRE (related to the abscisic acid response) was covered the largest portion, followed by the TGA-element (auxin-responsive element). In the abiotic stress response category, elements regarding oxygen-deficient induction (GC-motif, ARE) were the most common, followed by those relating to low-temperature responsiveness (LTR) and drought-inducibility (MBS). As for the plant growth regulation category, only two main stress-related cis-acting factors were identified, known as the CAT-box (referred to meristem expression) and O2-site (involved in zein metabolism regulation). Intriguingly, all kinds of cis-regulatory elements distributed widely throughout the promoter regions of OsDUF668 genes, revealing that OsDUF668s may have intricate expression profiles and be crucial in the regulation of rice development and stress resistance.
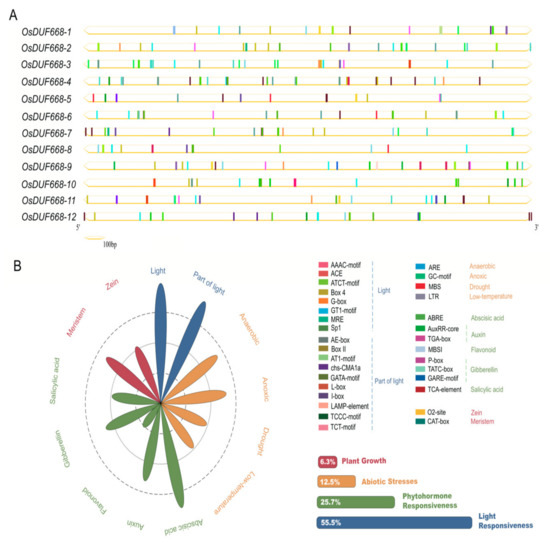
Figure 2.
Identification of cis-acting elements in all the OsDUF668 genes. (A) Distribution of cis-acting elements in 2 Kb upstream of each OsDUF668 gene. The different colored boxes indicate distinct promoter elements. (B) Assessment of different subclass and category proportion in a radar chart. The lengths of the petals are proportional to the number of elements in each subclass qualitatively. Red, orange, green, and blue petals represent plant growth regulation, abiotic stress responses, phytohormone and light responsiveness, respectively.
3.4. Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of OsDUF668s
To further characterize the potential biological function, comprehensive tissue-specific expression analyses of OsDUF668s were investigated using qRT-PCR. As displayed in Figure 3, we detected 11 OsDUF668s except for the undetectable OsDUF668-9 in 22 rice tissues involving in various developmental processes. The results showed that these 11 OsDUF668s were ubiquitously expressed in 22 rice tissues, except for the undetectable OsDUF668-5 in anther and spikelets (Sp20, at 20 days after flowering). OsDUF668-2, -6, -7, and -8 exhibited moderate expression levels and minor expression differences among 22 tissues, except that OsDUF668-6 expressed negligibly in node (N), internode (IN), anther (An), immature seed (IS), and calli (Ca). Comparatively, the rest OsDUF668-1, -3, -4, -5, -10, -11, and -12 showed large expression difference among 22 tissues, presenting discernibly, organ-specific high expression patterns. For example, OsDUF668-1 was negligibly expressed in flag leaf (SL and FL), panicle (P5, P10, P15, and P20), and immature seed (IS), whereas it highly expressed in source flag leaf sheath (SoFLS), node (N) and hull of flower (H1). Additionally, OsDUF668-3 and OsDUF668-10 were expressed highly in more than eight different tissues. These tissue expression patterns suggested OsDUF668s played an influential role in rice growth and development.
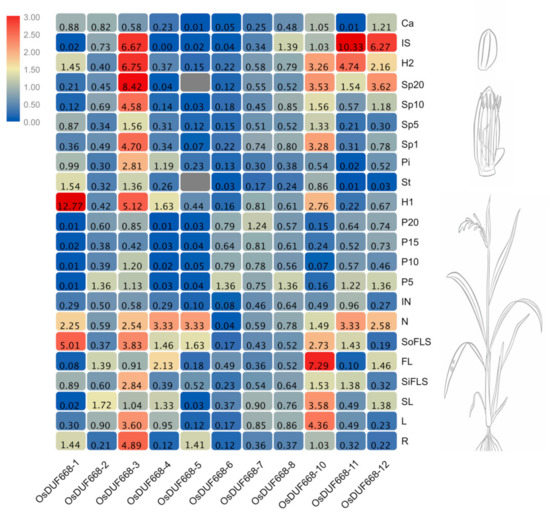
Figure 3.
Relative expression levels of DUF668 genes in rice 22 various tissues. The relative expression levels in the heat map were calculated by the 2−∆∆CT method and represented by the color legend: red indicates high expression level, and blue represents low expression level. The rice morphology diagrams at the right of the heat map were downloaded from Expression Atlas (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gxa/home).
3.5. Expression Profiles of OsDUF668s in Response to Plant Hormone
Plant hormones, including auxin, cytokinin, and ethylene, have a lasting impact on regulating plant architecture and development [39]. In order to explore the possible functions of OsDUF668s in response to hormone stress, we used qRT-PCR to analyze their relative expressions under 6BA, IAA, GA, SA, and ABA treatments (Figure 4). In this study, the two-fold change (|log2| > 1) was considered to be a significant difference for the gene expression under each treatment. Of all 11 OsDUF668s, seven genes merely up-expressed in any treatment, while the remaining four (OsDUF668 -2, -5, -6, and -11) were examined to be elevating expression in at least one treat. For instance, OsDUF668-5 and OsDUF668-6 were both up-regulated following 6BA and IAA conditions. Also, OsDUF668-5 was induced in 3 h treatment of SA. Expression of OsDUF668-2 and OsDUF668-11 were elevated when applying with ABA. By contrast, more genes were down-regulated or suppressed for certain hormone treatments, such as OsDUF668-4 and OsDUF668-1 under all five hormone conditions, OsDUF668-2 and OsDUF668-10 in all five hormone treatments except for ABA, OsDUF668-3 for 6BA, IAA and GA, and OsDUF668-5 for GA and ABA. The results indicated that these OsDUF668 genes might regulate relevant hormone signaling pathways.
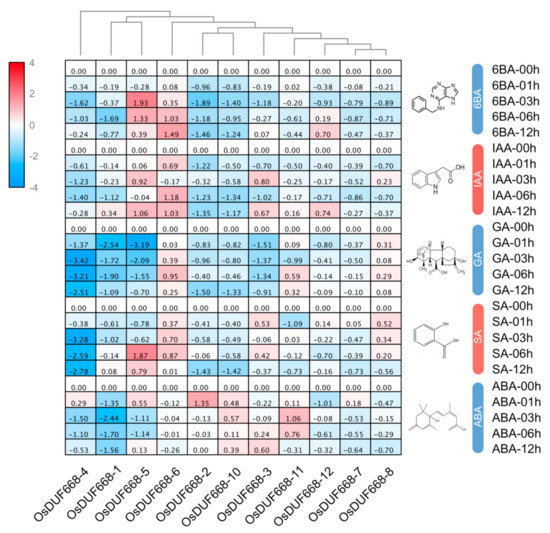
Figure 4.
Relative expression of OsDUF668s under 6BA, IAA, GA, SA, and ABA treatments. 6BA: 6-benzyl amino purine, IAA: indole-3-acetic acid, GA: gibberellic acid, SA: salicylic acid, and ABA: abscisic acid. Expression characteristics of OsDUF668s in response to different phytohormone at four-time points (1, 3, 6, and 12h) were normalized to 0 h treatment. The fold changes values were calculated by the 2−∆∆CT method and log2 and represented in color scale legend at the left of the heat map: red indicated up-regulation and blue showed down-regulated expression.
3.6. Transcriptional Responses of OsDUF668s Facing Environmental Stresses
Plants suffer from a wide variety of environmental stresses under natural conditions during their life span. As a result, we investigated the expression of OsDUF668 genes, responding to seven environmental stresses (Figure 5). Results showed the accumulation of OsDUF668-1, and OsDUF668-4 transcripts occurred within 1h after UVB application. Expression levels of OsDUF668-5 and OsDUF668-11 were elevated under H40 and Sub conditions, separately. Interestingly, all analyzed OsDUF668 genes were found to positively respond to the Dr stress, in which, OsDUF668-1, -2, -4, -5, -10, -11, and -12 showed strong up-regulation of over four times, meanwhile OsDUF668-1, -3, -5, -6, -11 and -12 showed fast elicitation after the 15-min treatment. Moreover, four OsDUF668 genes, OsDUF668-1, -2, -4, and -10 were induced under NaCl stress, and OsDUF668-1 showed fast elicitation after 15-min stress. Only OsDUF668-4 was significantly induced for PEG stress. Additionally, many genes were down-regulated or suppressed under environmental stresses, such as OsDUF668-3, -5, and -11 for UVB, OsDUF668-2, -4, -7, and -10 for H40, all OsDUF668s but OsDUF668-7 or -11 for Cold4, OsDUF668-1, -5, -6, -7, and -12 for Sub, OsDUF668-5 and -11 for NaCl, and OsDUF668-2,- 3, -5, -6, -7, -8, -11, and -12 for PEG stress. In summary, OsDUF668 genes may act as key roles in various environmental fitness.
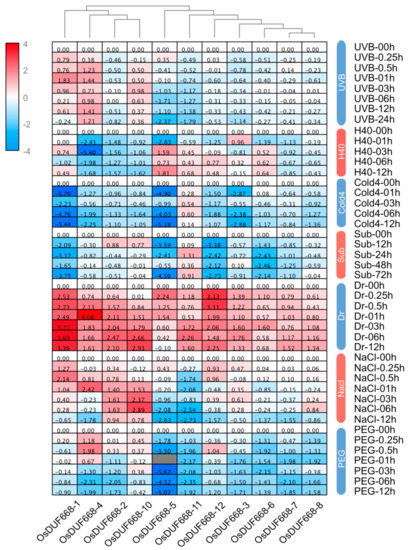
Figure 5.
Expression changes of OsDUF668s under different environmental stresses. The abbreviation represented as following rules, UVB: ultraviolet-B, H40: the heat of 40 °C, Cold4: cold of 4 °C, Sub: submergence, Dr: drought, and PEG: polyethylene glycol.
3.7. Transcriptional Responses of OsDUF668s Facing Pathogen-Defense Related Stresses
Previous studies have reported that Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes play an important role in plant defense for pathogen invasion [14,16]. On the fact that half of the OsDUF668s were annotated as Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes, we implemented qRT-PCR to analyze whether OsDUF668s resisted two pathogen-defense related stresses: wound and rice blast (Figure 6). The results showed that OsDUF668-1, -3, -4, and -5 were significantly elevated following wound and rice blast conditions. Transcripts of those genes were strongly induced in particular with rice blast. OsDUF668-1 showed fast elicitation after 15-min wound stress, meanwhile, OsDUF668-1, -4, and -5 exhibited fast elicitation under 15-min rice blast treatment. In addition, expression levels of OsDUF668-6, -7, -11, and -12 were significantly down-regulated for both pathogen-defense related stresses. The results implied that these OsDUF668 genes might be involved in rice defense for pathogens.
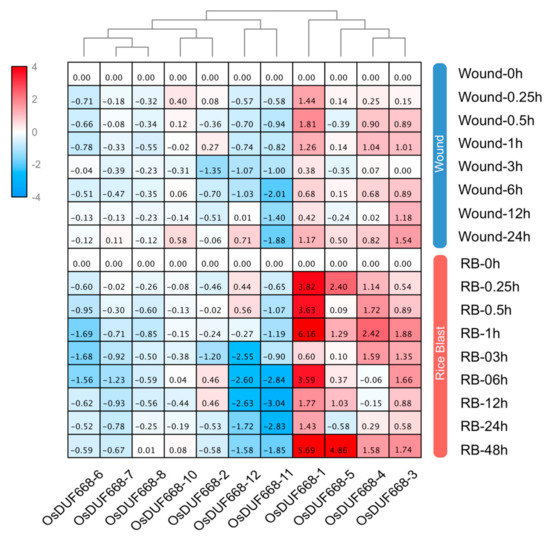
Figure 6.
Expression changes of OsDUF668s under wound and rice blast stresses. The relative expression levels were showed in the heat map from blue to red. 0h was treated as standard control to normalized data. In the heat map, fold changes reflected relative expression values from blue to red, while gray cells represented undetected values. The abbreviation RB meant rice blast.
4. Discussion
In this case, we reported plants to possess a unique set of DUF668 genes from genome-wide identification profiling. A further study distinguished 103 DUF668 genes in the databases of dicot Arabidopsis thaliana and eight representative crops in Gramineae, explicating that the DUF668 family originated in an ancestral plant species before the divergence between monocotyledon and dicotyledon (Figure 1). Thereby, DUF668 has been a conserved gene family for a long evolution. In the monocot grass family (Gramineae), DUF668 family members in each organism were close in number without regard to P. virgatum and Z. mays. One alternative explanation may be that the total number of annotated genes from the Phytozome database in rice (52,425) was in the same range as B. distachyon (52,973), S. bicolor (47,122), B. distachyon (52,973), and S. italica (43,002). Given that Z. mays and P. virgatum had relatively large genome size and a great many genes, the number of DUF668 genes was more than other species consequently. These results indicated similar gene numbers across a broad diversity of economically important grasses. In rice, a multitude of gene family members with high sequence similarity has been observed to cluster on the chromosomes as paralogous pairs [40,41]. However, we identified 12 OsDUF668s and found there were no collinearity relationships among them. It meant that the DUF668 family has still not experienced gene expansion events driven by tandem and segmental duplication. Furthermore, phylogenetic analysis categorized all DUF668 proteins into two distinct lineages differing from the exon-intron association and motif arrangement (Figure 1). All clade I members in rice were the Avr9/Cf-9 mediated protein without sufficient research.
Cis-acting elements of light, phytohormone, and abiotic stresses responsiveness presented ubiquitously in the promoter region of OsDUF668, indicating these optical and chemical impact factors may interact to act on the DUF668 regulatory mechanism (Figure 2). Tissue expression profiles showed that the majority of OsDUF668s were ubiquitously expressed in various developmental stages (Figure 3), implying their roles in the whole life cycle of rice. OsDUF668-1, -3, -4, -5, -10, -11, and -12 also exhibited high expression levels in some specific tissues (Figure 3), reflecting the functional tissue specificity of these OsDUF668 genes. The positive response of most OsDUF668 genes to hormones was marginal, regardless of that OsDUF668-5 and OsDUF668-6 were significantly up-regulated in 6BA, IAA, and SA treatments (Figure 4), implying their relevant roles in these hormone pathways. Besides, OsDUF668-1 and OsDUF668-4 positively responded to UVB, elucidating their roles in rice adaption to the solar UV light (Figure 5). A surprising finding was all thje OsDUF668 genes were up-regulated extensively by drought stresses (Figure 5), suggesting that OsDUF668 may be important for rice resistance to drought. Similarly, OsDUF668-1, -2, -4, and -10 were found to positively regulated in NaCl stress (Figure 5), reflecting that the physiological function of these genes were also involved in plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Considering the common positive response of OsDUF668-1, -2, -4, and -10 under drought and NaCl stresses overexpression of these four genes in rice may be effective methods to engineering plant fitness for drought and salinity conditions.
Avr9/Cf-9 elicited genes play key roles in plant-pathogen interactions. Expression levels of Avr9/Cf-9 elicited genes are found to be differentially changed during transcriptome profile analysis of resistance induced by burdock fructooligosaccharide in tobacco [42]. The protein kinase ACIK1 is encoded by an Avr9/Cf-9 elicited gene and is essential for full Cf-9-dependent disease resistance in tomato [17]. The F-Box protein ACRE189/ACIF1, encoded by another Avr9/Cf-9 elicited gene, regulates cell death, and defense response activated during pathogen recognition in tobacco and tomato [16]. In our study, clade I members of OsDUF668 family OsDUF668-1, -4 and -5 expressed highly, and OsDUF668-6 and OsDUF668-12 were down-regulated in wound and rice blast treatments (Figure 6), displaying these Avr9/Cf-9 elicited genes may also mediate response to biotic defense in rice. Moreover, OsDUF668-1, -3, -4, and -5 showed positive response under both wound and rice blast conditions (Figure 6), implying that overexpression of these four genes in rice may help to improve plant defense against pathogens. In addition, a key characteristic of the Avr9/Cf-9 elicited gene is that their expression pattern usually rapidly altered (15 min after elicitation) during the biotic defense response [17]. In rice, corresponding Avr9/Cf-9 elicited genes in DUF668 gene family also exhibited response to Dr (OsDUF668-1, -5, -6, and -12), NaCl (OsDUF668-1), wound (OsDUF668-1) and rice blast (OsDUF668-1, -4, and -5) in a rapid manner of 15 min (Figure 5 and Figure 6), implying the conservation and similarity of regulation and function of Avr9/Cf-9 elicited genes among plant species. However, why and how these Avr9/Cf-9 elicited genes respond so fast still need further study in the plant.
Importantly, the conserved evolutionary property of DUF668 genes in the rice genome and the responses of some members to adverse situations reflected their importance for rice growth and resistance to multiple stresses. Tackling the function of the DUF668s nexus will require more powerful approaches like transgenic experiments. Taken together, we provide a detailed and multi-level view of the DUF668 gene family in rice. This study underlies further work to dissect the evolutionary significance of this gene family and simultaneously accelerates functional research of their roles in rice growth and development as well as the stress response.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/10/12/980/s1, Figure S1: Chromosomal locations of DUF668 genes in rice. Different colors of OsDUF668s represent the members of different subfamilies; Table S1: Primers for qRT-PCR; Table S2: Reference genes for each experimental condition; Table S3: DUF668 gene family number in 62 plant species; Table S4: Summary of information on DUF668 genes from seven other plants; Table S5: Annotation of conserved motifs in DUF668 proteins.
Author Contributions
Z.W. and Y.L. conceptualized and guided this study research. H.Z. performed statistical analyses and validation, and wrote partial manuscript. H.Z. wrote a partial manuscript. R.G. performed the qRT-PCR experiment. Q.W. and X.H. prepared the materials. J.L. and Y.H. helped in data consolidation and manuscript revision.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Project (2016YFD0100400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31760380, 31860359, 31560387), and the Science and Technology Projects of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (GJJ170247).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ohta, T. Evolution of gene families. Gene 2000, 259, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Coggill, P.; Finn, R.D. DUFs: Families in search of function. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2010, 66, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simm, R.; Morr, M.; Kader, A.; Nimtz, M.; Römling, U. GGDEF and EAL domains inversely regulate cyclic di-GMP levels and transition from sessibility to motility. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, G.I.; Kustatscher, G.; Buhecha, H.R.; Allen, M.D.; Pugieux, C.; Sait, F.; Bycroft, M.; Ladurner, A.G. The macro domain is an ADP-ribose binding module. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlakić, M. DUF283 domain of dicer proteins has a double-stranded RNA-binding fold. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2711–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Chen, F.; Huan, X.; Machida, S.; Song, J.; Yuan, Y.A. Structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana DCL4 DUF283 domain reveals a noncanonical double-stranded RNA-binding fold for protein—Protein interaction. Rna 2010, 16, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, A. DUF538 protein superfamily is predicted to be chlorophyll hydrolyzing enzymes in plants. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2016, 22, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, A. Chlorophyll binding ability of non-chloroplastic DUF538 protein superfamily in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeros-Suárez, P.A.; Massange-Sánchez, J.A.; Sánchez-Segura, L.; Martínez-Gallardo, N.A.; Espitia Rangel, E.; Gómez-Leyva, J.F.; Délano-Frier, J.P. AhDGR2, an amaranth abiotic stress-induced DUF642 protein gene, modifies cell wall structure and composition and causes salt and ABA hyper-sensibility in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 2017, 245, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Yamashita, E.; Inoue, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Nakagawa, A.; Kawasaki, T.; Kojima, C. Plant-specific DUF1110 protein from Oryza sativa: Expression, purification and crystallization. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Struct. Biol. Commun. 2016, 72, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakolitsa, C.; Bateman, A.; Jin, K.K.; McMullan, D.; Krishna, S.S.; Miller, M.D.; Abdubek, P.; Acosta, C.; Astakhova, T.; Axelrod, H.L.; et al. The structure of Jann-2411 (DUF1470) from Jannaschia sp. at 1.45 Å resolution reveals a new fold (the ABATE domain) and suggests its possible role as a transcription regulator. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2010, 66, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shen, R.; Chen, L.T.; Liu, Y.G. Characterization of a novel DUF1618 gene family in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.B.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Sessa, G. Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heese, A.; Ludwig, A.A.; Jones, J.D.G. Rapid phosphorylation of a syntaxin during the Avr9/Cf-9-race-specific signaling pathway. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2406–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, W.E.; Rowland, O.; Piedras, P.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Jones, J.D.G. cDNA-AFLP reveals a striking overlap in race-specific resistance and wound response gene expression profiles. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Burg, H.A.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Rowland, O.; Lo, J.; Rallapalli, G.; MacLean, D.; Takken, F.L.W.; Jones, J.D.G. The F-box protein ACRE189/ACIF1 regulates cell death and defense responses activated during pathogen recognition in tobacco and tomato. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 697–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, O.; Ludwig, A.A.; Merrick, C.J.; Baillieul, F.; Tracy, F.E.; Durrant, W.E.; Fritz-Laylin, L.; Nekrasov, V.; Sjölander, K.; Yoshioka, H.; et al. Functional analysis of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes identifies a protein kinase, ACIK1, that is essential for full Cf-9-dependent disease resistance in tomato. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savatin, D.V.; Gramegna, G.; Modesti, V.; Cervone, F. Wounding in the plant tissue: The defense of a dangerous passage. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, J.W.; Coughlan, S.; Hudson, M.E.; Covington, M.F.; Kaspi, R.; Banu, G.; Harmer, S.L.; Dehesh, K. Mechanical stress induces biotic and abiotic stress responses via a novel cis-element. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H. Bin Cell-PLoc: A package of web servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME Suite: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xia, R.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools, a toolkit for biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Chen, W.H.; Hu, S. Evolview v2: An online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W236–W241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, K.; An, B.; Deng, X.; Li, Y. Reliable selection and holistic stability evaluation of reference genes for rice under 22 different experimental conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 179, 753–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Nijhawan, A.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiong, L. Comprehensive expression profiling analysis of OsIAA gene family in developmental processes and in response to phytohormone and stress treatments. Planta 2009, 229, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazman, M.; Sühnel, M.; Schäfer, S.; Zumsteg, J.; Lesot, A.; Beltran, F.; Marquis, V.; Herrgott, L.; Miesch, L.; Riemann, M.; et al. Characterization of jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) hormonal catabolic pathways in rice upon wounding and salt stress. Rice 2019, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q. Identification and characterization of a new blast resistance gene located on rice chromosome 1 through linkage and differential analyses. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, P.M. Poaceae (Gramineae). Encycl. Life Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, B.M.; Ehlting, J.; Hamberger, B.; Douglas, C.J. Multiple cis-regulatory elements regulate distinct and complex patterns of developmental and wound-induced expression of Arabidopsis thaliana 4CL gene family members. Planta 2006, 224, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, D.; Brunnemann, R.; Selbig, J. The regulatory code for transcriptional response diversity and its relation to genome structural properties in A. thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Cheng, X.; Cao, Y.; Su, X.; Manzoor, M.A.; Gao, J.; Cai, Y.; Lin, Y. Zinc finger-homeodomain transcriptional factors (ZHDs) in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Genome-wide identification and expression analysis in fiber development. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, K.; Przedniczek, K. Comprehensive insight into gibberellin-and jasmonate-mediated stamen development. Genes 2019, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; An, B.; Zhong, H.; Yang, J.; Kong, W.; Li, Y. A novel insight into functional divergence of the MST gene family in rice based on comprehensive expression patterns. Genes 2019, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Kong, W.; Gong, Z.; Fang, X.; Deng, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Evolutionary analyses reveal diverged patterns of SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-like (Spl) gene family in Oryza genus. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Chen, K.; Zhang, P. Transcriptome profile analysis of resistance induced by burdock fructooligosaccharide in tobacco. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).