The Chalcone Isomerase Family in Cotton: Whole-Genome Bioinformatic and Expression Analyses of the Gossypium barbadense L. Response to Fusarium Wilt Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Identification of CHI Proteins
2.2. Phylogenetic, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motif Analyses
2.3. Chromosomal Position and Synteny Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Promoter and Putative MicroRNA Target Site Analysis
2.5. The Transcriptome of CHI Genes in Cotton
2.6. Plant Materials and Stress Treatments
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Survey and Identification of CHI Genes in Four Cotton Species
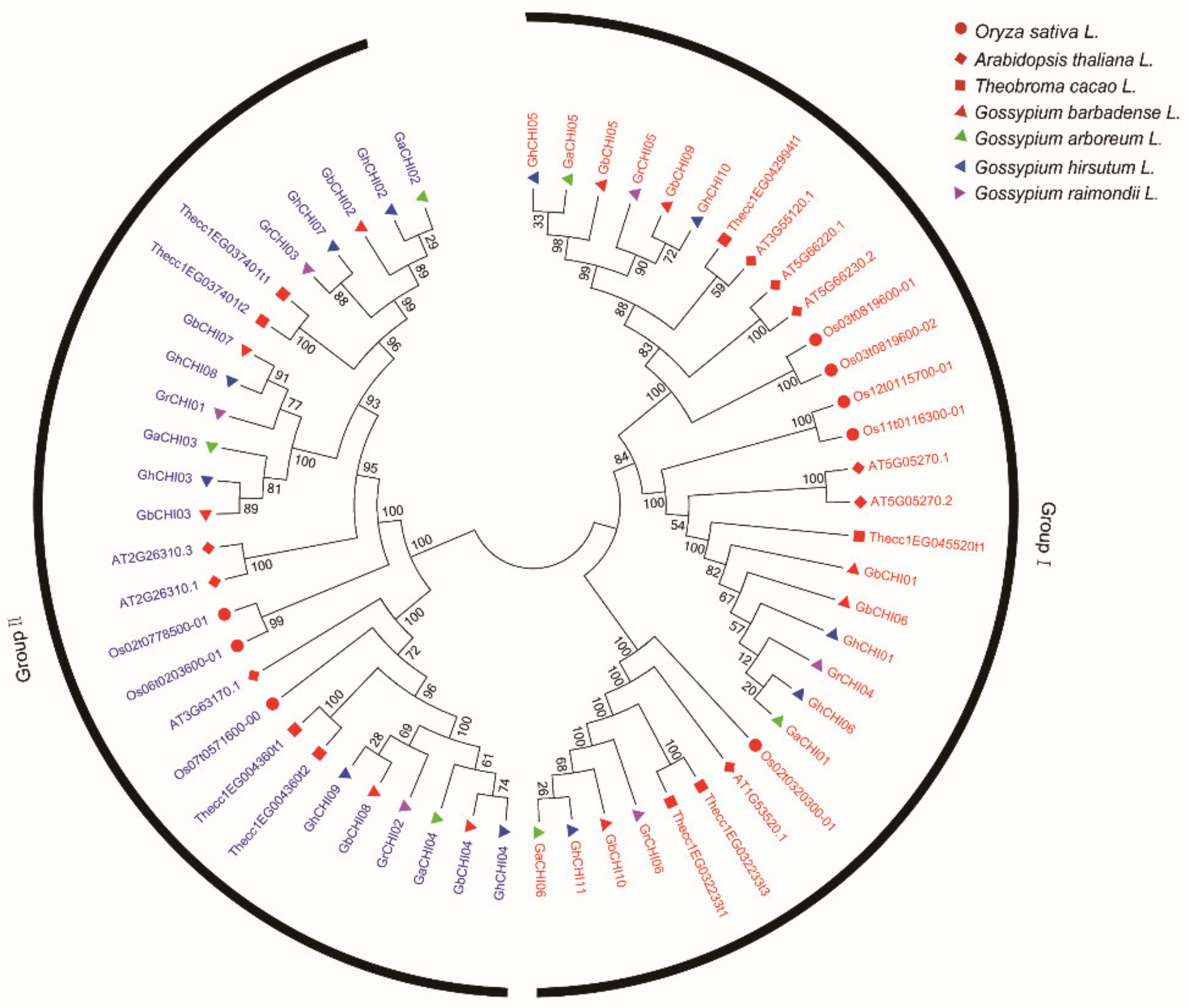
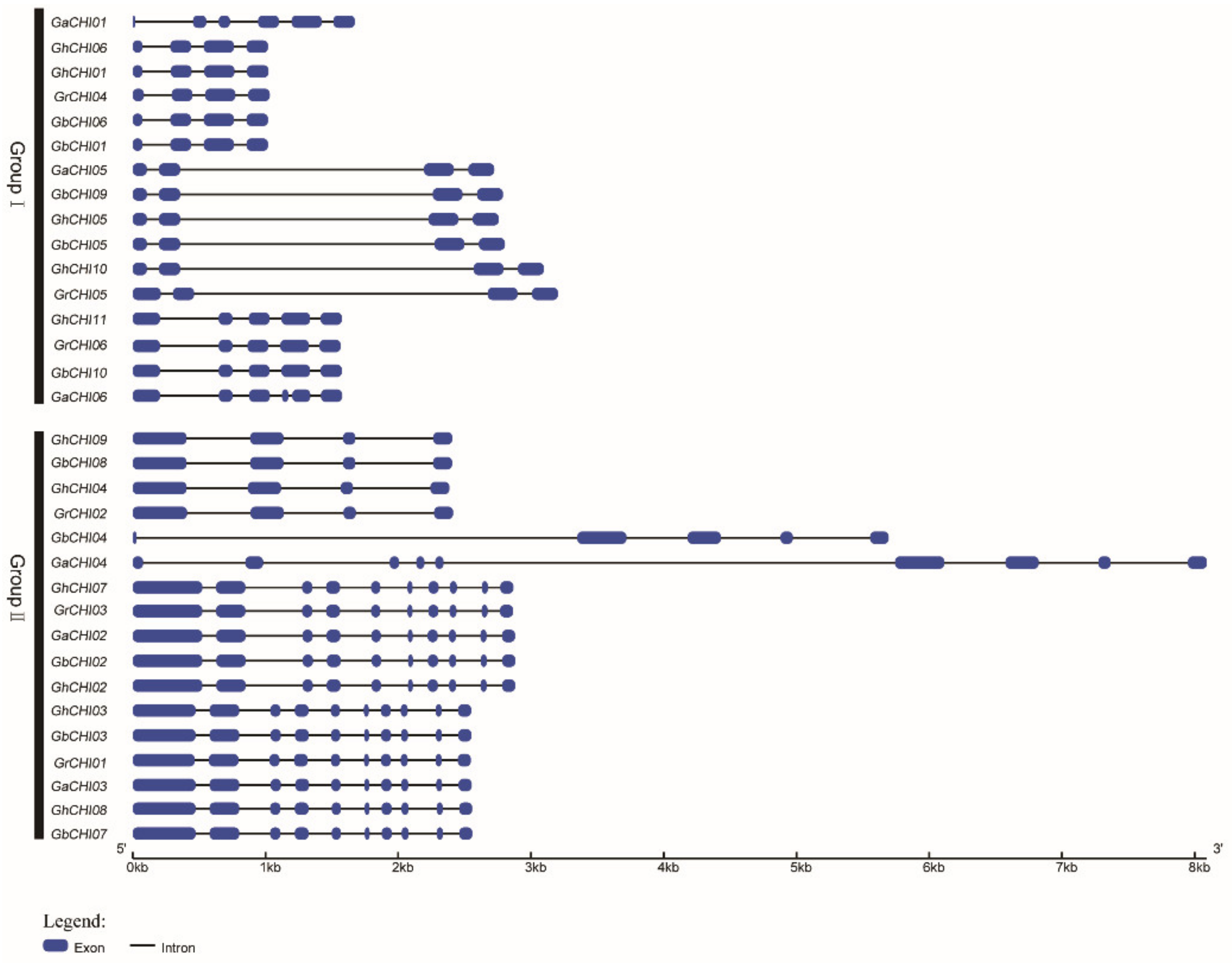
3.2. Phylogenetic Classification, Motif Identification, and Gene Structure
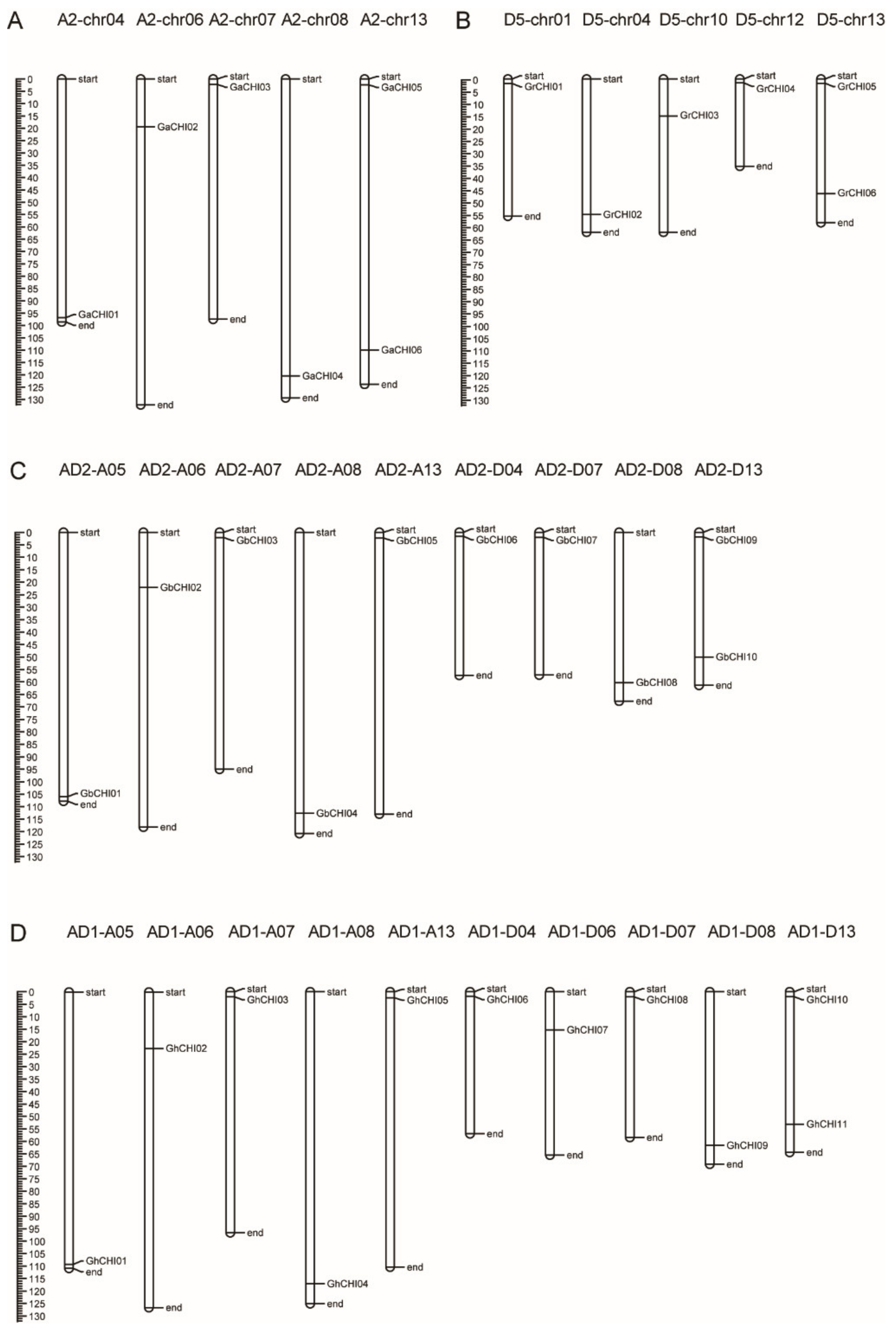
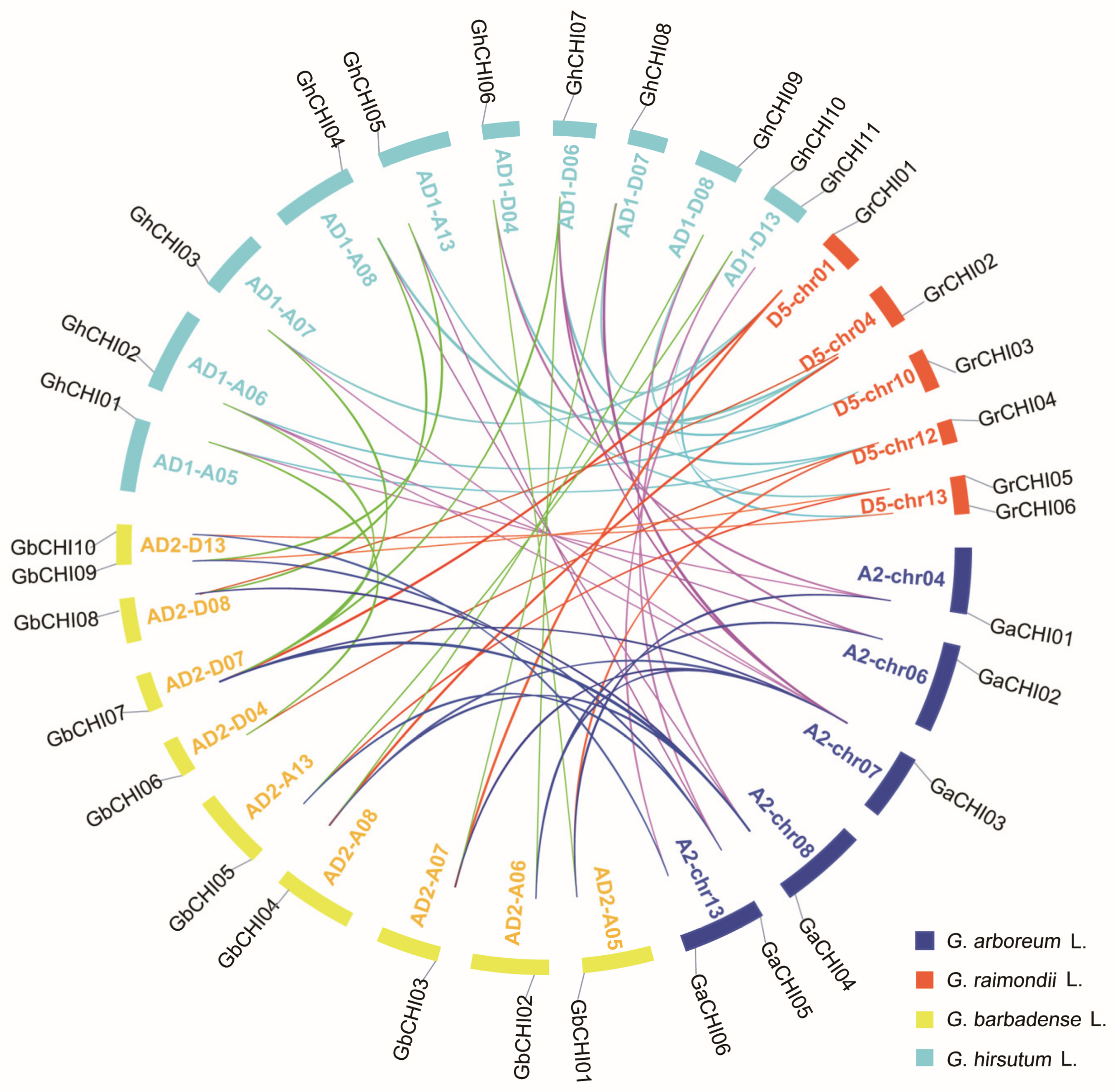
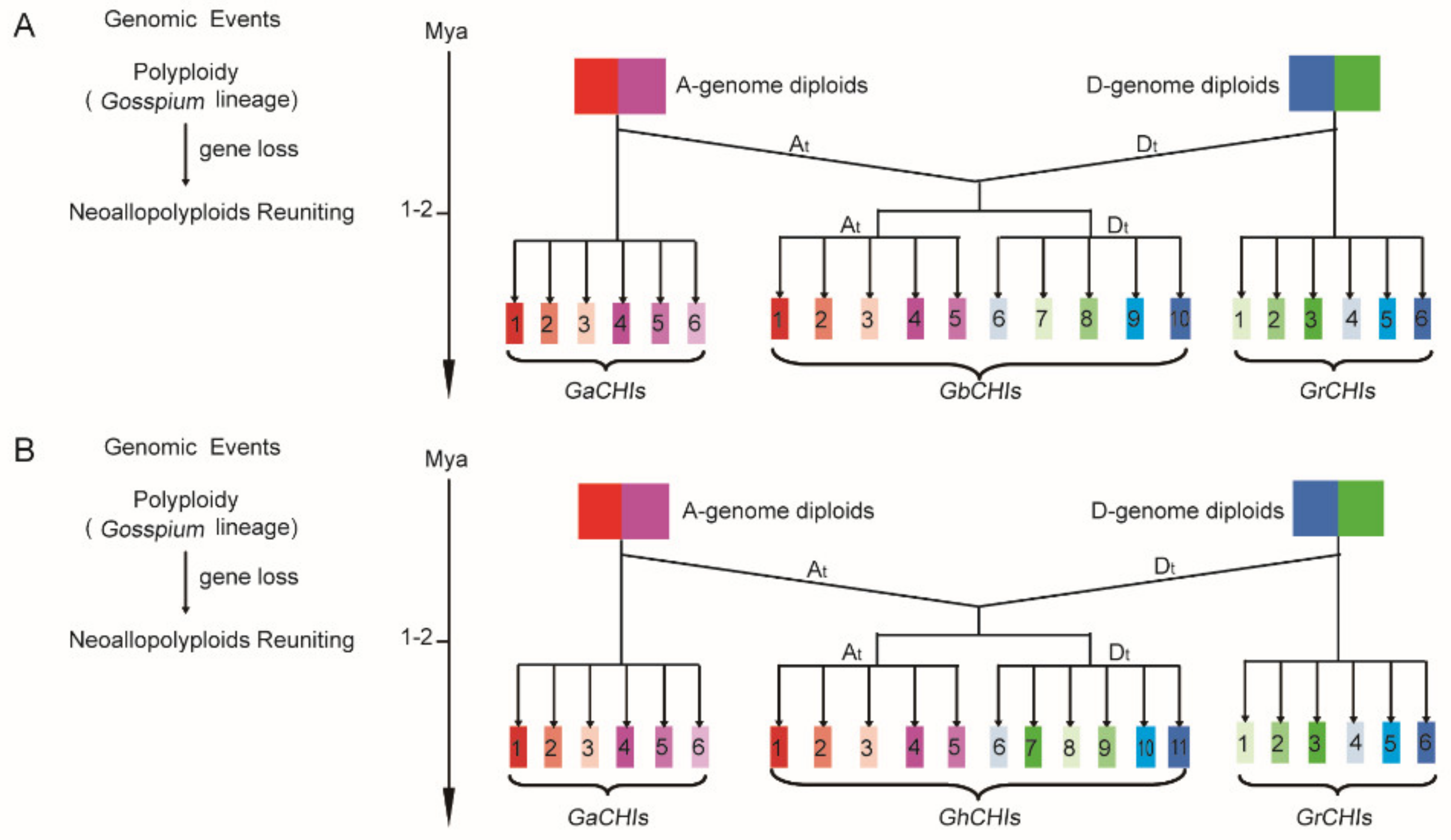
3.3. Chromosomal Distribution and Synteny Analysis of CHI Genes between Gossypium Species
3.4. Contained Multiple Stress-Related Cis-Acting Elements and Prediction of MicroRNA Target Sites
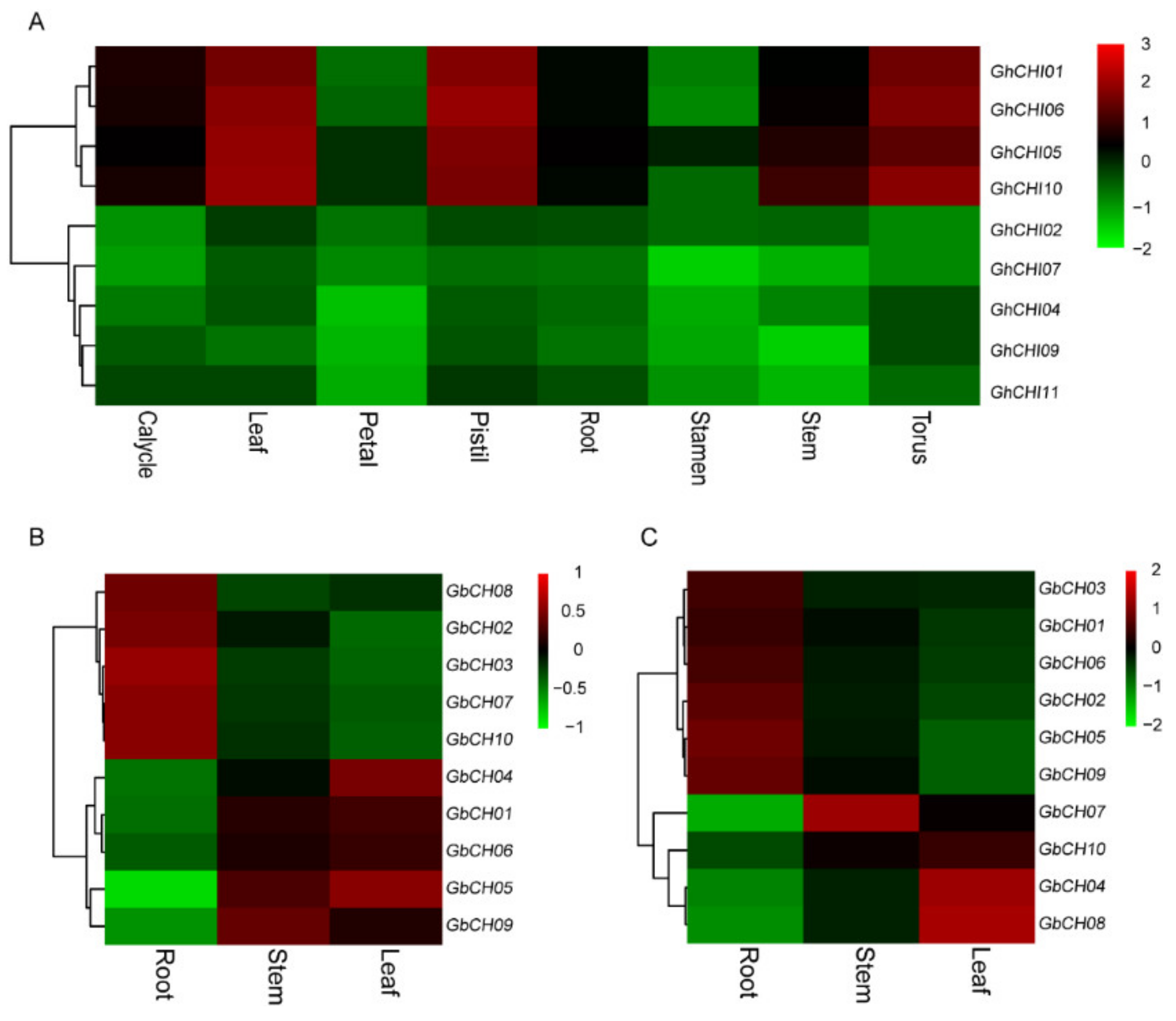
3.5. Expression Analysis of CHI Genes in Cotton
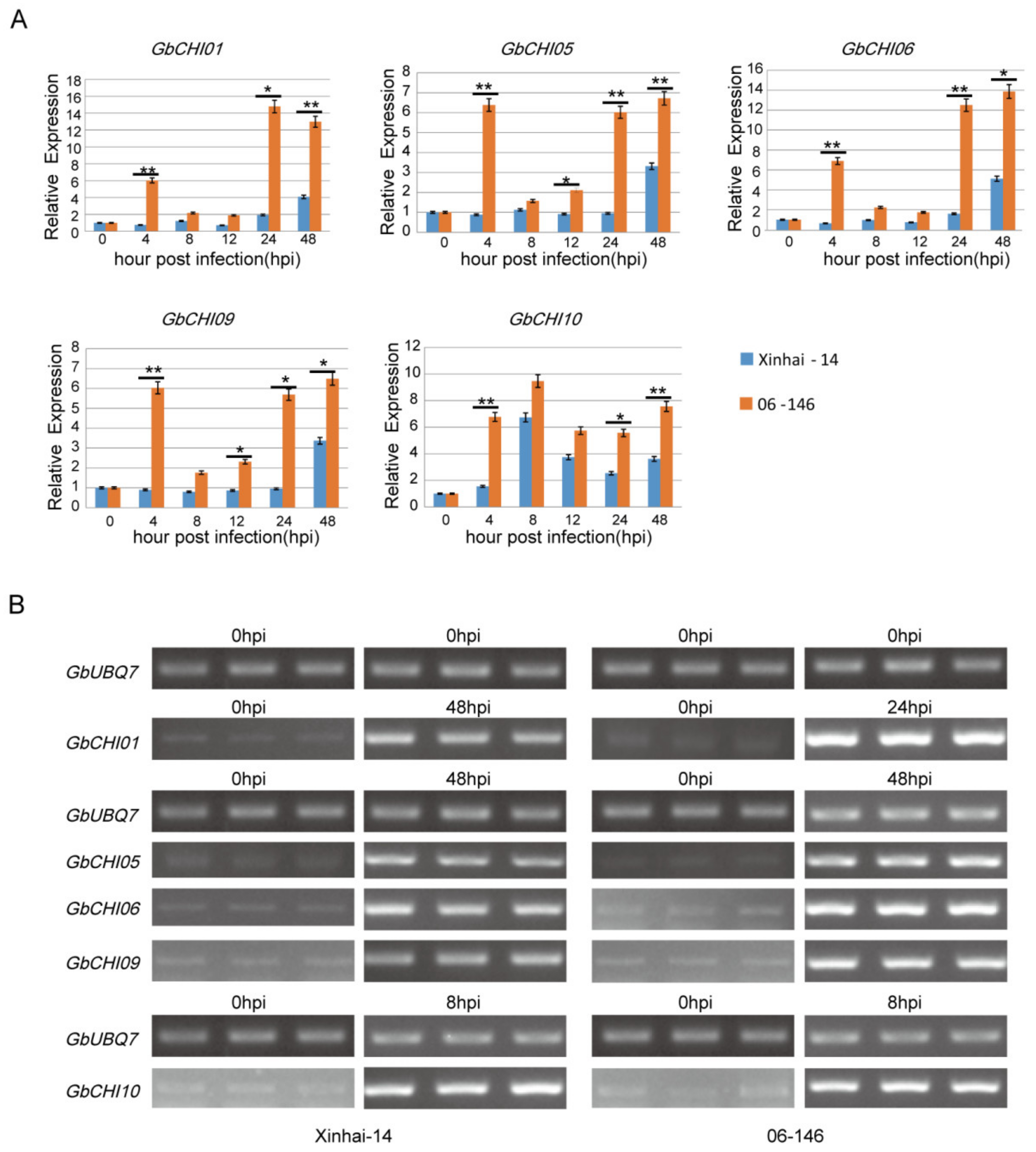
3.6. Transcription Levels of GbCHI Genes under Fusarium Wilt Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHI | chalcone isomerase |
| NJ | neighbor-joining |
| ABA | abscisic acid |
| qRT-PCR RT-PCR | quantitative real-time PCR semiquantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
| WGD | whole-genome duplication |
| GA | gibberellin acid |
| MeJA | methyl jasmonate |
| G. | Gossypium |
| FPKMs | fragments per kilobase per million reads |
References
- Nejat, N.; Mantri, N. Plant immune system: Crosstalk between responses to biotic and abiotic stresses the missing link in understanding plant defence. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2017, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.K.; Chapple, C. The origin and evolution of lignin biosynthesis. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Fang, H.; Guo, F.; Li, F.; Chen, A.; Huang, S. Flavonoids as inducers of white adipose tissue browning and thermogenesis: Signalling pathways and molecular triggers. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.X.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, C.J.; Lou, H.X. Identification of chalcone isomerase in the basal land plants reveals an ancient evolution of enzymatic cyclization activity for synthesis of flavonoids. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednar, R.A.; Hadcock, J.R. Purification and characterization of chalcone isomerase from soybeans. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 9582–9588. [Google Scholar]
- Ngaki, M.N.; Louie, G.V.; Philippe, R.N.; Manning, G.; Pojer, F.; Bowman, M.E.; Li, L.; Larsen, E.; Wurtele, E.S.; Noel, J.P. Evolution of the chalcone-isomerase fold from fatty-acid binding to stereospecific catalysis. Nature 2012, 485, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Blyden, E.R.; Robbins, M.P.; van Tunen, A.J.; Mol, J.N. Comparative biochemistry of chalcone isomerases. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 2801–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.C.; Zhang, X.D.; Gao, Z.Q.; Hu, T.; Liu, Y. The research progress of chalcone isomerase (CHI) in plants. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, N.; Aoki, T.; Sato, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Tabata, S.; Ayabe, S.I. A cluster of genes encodes the two types of chalcone isomerase involved in the biosynthesis of general flavonoids and legume-specific 5-deoxy (ISO) flavonoids in Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Huan, S.; Hui, X.; Xiaoxin, T.; Ming, T.; Zhigang, J.; Yi, Y. Chalcone Isomerase a Key Enzyme for Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Ophiorrhiza japonica. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 865. [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara, T.; Sugishita, N.; Ishida-Dei, M.; Okamoto, E.; Kouno, T.; Cano, E.A.; Sasaki, N.; Watanabe, A.; Tasaki, K.; Nishihara, M.; et al. Carnation I locus contains two chalcone isomerase genes involved in orange flower coloration. Breed. Sci. 2018, 68, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, T.; Huang, J.; Lu, X.; Huang, B.; Zheng, Y. The expression of Millettia pinnata chalcone isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae salt-sensitive mutants enhances salt-tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8775–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, P.; Pardo, A.; Fierro, A.; Prieto, H.; Zúñiga, G.E. Molecular characterization of the chalcone isomerase gene family in Deschampsia antarctica. Polar Biol. 2013, 36, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, L.M.; Wang, X.F.; Guo, N.; Zhao, J.; Xing, H. Overexpression of Chalcone Isomerase (CHI) Increases Resistance Against Phytophthora sojae in Soybean. J. Plant Biol. 2018, 61, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, P.F.; Berhow, M.A.; Johnson, E.T. Enhanced pest resistance and increased phenolic production in maize callus transgenically expressing a maize chalcone isomerase-3 like gene. Plant Gene 2018, 13, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.P.; Xia, S.B.; Wang, X.G.; Zhang, J.H.; Qin, H.D.; Zhang, Y.C.; Feng, C.; Bie, S. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Chalcone Synthase and Chalcone Isomerase Encoding Genes in Gossypium hirsutum. Agric. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 2164–4993. [Google Scholar]
- Winkel, S.B. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and effects of stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierziak, J.; Wojtasik, W.; Kostyn, K.; Czuj, T.; Szopa, J.; Kulma, A. Crossbreeding of transgenic flax plants overproducing flavonoids and glucosyltransferase results in progeny with improved antifungal and antioxidative properties. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.A.; Kapulnik, Y. Plant isoflavonoids, pathogens and symbionts. Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Paterson, A.H. Genomes for jeans: Cotton genomics for engineering superior fiber. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, T. Molecular linkage map of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L.) with a haploid population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, A.H.; Wendel, J.F.; Gundlach, H.; Guo, H.; Jenkins, J.; Jin, D.; Llewellyn, D.; Showmaker, K.C.; Shu, S.; Udall, J.; et al. Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature 2012, 492, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.B.; Wang, Z.W.; Li, F.G.; Ye, W.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Song, G.L.; Yue, Z.; Cong, L.; Shang, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Huang, G.; He, S.; Yang, Z.; Sun, G.; Ma, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Resequencing of 243 diploid cotton accessions based on an updated A genome identifies the genetic basis of key agronomic traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, W.; Niu, Y.; Ju, L.; Deng, J.; Zhao, T.; Lian, J.; et al. Gossypium barbadense and Gossypium hirsutum genomes provide insights into the origin and evolution of allotetraploid cotton. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Ke, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z. Genome-wide identification of cyclophilin genes in Gossypium hirsutum and functional characterization of a CYP with antifungal activity against Verticillium dahlia. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Liang, C.; Meng, Z.; Sun, G.; Meng, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, R. CottonFGD: An integrated functional genomics database for cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, C.J.; de Castro, E.; Cerutti, L.; Cuche, B.A.; Hulo, N.; Bridge, A.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I. New and continuing developments at PROSITE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D344–D347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, C.H.; Hwang, J.K. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berri, S.; Abbruscato, P.; Faivre-Rampant, O.; Brasileiro, A.C.; Fumasoni, I.; Satoh, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Mizzi, L.; Morandini, P.; Pè, M.E.; et al. Characterization of WRKY co-regulatory networks in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Baker, M.E.; Elkan, C.P. An artificial intelligence approach to motif discovery in protein sequences: Application to steroid dehydrogenases. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 62, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2019, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xia, R.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various biological data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. BioRxiv 2018, 289600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, M.; Torrents, D.; Bork, P. PAL2NAL: Robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W609–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higo, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Korenaga, T. Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X. psRNA Target: A plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W155–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.; Xu, W.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.W.; Yi, X.; Yao, D.X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Provart, N.J.; et al. ccNET: Database of co-expression networks with functional modules for diploid and polyploid Gossypium. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1090–D1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, D.; Hu, M.; Dong, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Shen, F. The Catalase Gene Family in Cotton: Genome-Wide Characterization and Bioinformatics Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.L.; Wu, P.H.; Qu, Y.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, Q.J. Analysis and evluation of Fusarium wilt resistance for diferent populations in Sea island cotton (Gossypium Barbadense). Mol. Plant Breed. 2015, 13, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.G.; Fan, G.Y.; Wang, K.B.; Sun, F.M.; Yuan, Y.L.; Song, G.L.; Li, Q.; Ma, Z.; Lu, C.; Zou, C.; et al. Genome sequence of the cultivated cotton Gossypium arboretum. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensheimer, M.; Mushegian, A. Chalcone isomerase family and fold: No longer unique to plants. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, L.; Subramanian, S.; Matsuno, M.; Yu, O. Partial reconstruction of flavonoid and isoflavonoid biosynthesis in yeast using soybean type I and type II chalcone isomerase. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, H.J.; Hu, Y.; Lu, G.; Yang, C.Q.; Chen, J.D.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, D.Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Gossypium barbadense genome sequence provides insight into the evolution of extra-long staple fiber and specialized metabolites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 2000, 290, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belak, Z.R.; Pickering, J.A.; Gillespie, Z.E.; Audette, G.F.; Eramian, M.; Mitchell, J.A.; Bridger, J.M.; Kusalik, A.; Eskiw, C.H. Genes responsive to rapamycin and serum deprivation are clustered on chromosomes and undergo re-organization within local chromatin environments. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.Z.; Wang, J.S.; Zhao, C.Z.; Guan, H.S.; Hou, L.; Li, C.; Xia, H.; Wang, X. Molecular cloning, expression, and evolution analysis of type II CHI gene from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Dev. Genes Evol. 2015, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, F.; Xu, J.H.; Tannier, E.; Abrouk, M.; Guilhot, N.; Pont, C.; Messing, J.; Salse, J. Ancestral grass karyotype reconstruction unravels new mechanisms of genome shuffling as a source of plant evolution. Genome Res. 2012, 20, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.P.; Whitton, J. Polyploid incidence and evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2000, 34, 401–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.L. Evolution of duplicate gene expression in polyploid and hybrid plants. J. Hered. 2007, 98, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, J.F.; Brubaker, C.; Alvarez, I.; Cronn, R.; Stewart, J.M.; Paterson, A.H. Evolution and natural history of the cotton genus. Genet. Genom. Cotton 2009, 3, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Shen, F. Identification of miRNAs and their targets in cotton inoculated with Verticillium dahliae by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14749–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, X.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Qiu, B.; Ge, F. A transcriptome analysis uncovers Panax notoginseng resistance to Fusarium solani induced by methyl jasmonate. Genes Genom. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.P.; Bai, Y.C.; Gao, F.; Li, C.L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Gene cloning and expression level of chalcone isomerase during florescence and content of flavonoids in Fagopyrum dibotrys. Zhong Cao Yao 2013, 44, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Korsangruang, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Saito, K.; Prathanturarug, S. Cloning of gene encoding chalcone isomerase (CHI) from P. candollei and expression of genes involved isoflavonoid biosynthesis pathway in seedling plants. Planta Med. 2010, 76, P018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, V.; Lattanzio, V.M.; Cardinali, A. Role of phenolics in the resistance mechanisms of plants against fungal pathogens and insects. Phytochemistry 2006, 661, 23–67. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban, M.; Miao, Y.; Ullah, A.; Khan, A.Q.; Menghwar, H.; Khan, A.H.; Ahmed, M.M.; Tabassum, M.A.; Zhu, L. Physiological and molecular mechanism of defense in cotton against Verticillium dahlia. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zu, Q.-L.; Qu, Y.-Y.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.-J. The Chalcone Isomerase Family in Cotton: Whole-Genome Bioinformatic and Expression Analyses of the Gossypium barbadense L. Response to Fusarium Wilt Infection. Genes 2019, 10, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121006
Zu Q-L, Qu Y-Y, Ni Z-Y, Zheng K, Chen Q, Chen Q-J. The Chalcone Isomerase Family in Cotton: Whole-Genome Bioinformatic and Expression Analyses of the Gossypium barbadense L. Response to Fusarium Wilt Infection. Genes. 2019; 10(12):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121006
Chicago/Turabian StyleZu, Qian-Li, Yan-Ying Qu, Zhi-Yong Ni, Kai Zheng, Qin Chen, and Quan-Jia Chen. 2019. "The Chalcone Isomerase Family in Cotton: Whole-Genome Bioinformatic and Expression Analyses of the Gossypium barbadense L. Response to Fusarium Wilt Infection" Genes 10, no. 12: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121006
APA StyleZu, Q.-L., Qu, Y.-Y., Ni, Z.-Y., Zheng, K., Chen, Q., & Chen, Q.-J. (2019). The Chalcone Isomerase Family in Cotton: Whole-Genome Bioinformatic and Expression Analyses of the Gossypium barbadense L. Response to Fusarium Wilt Infection. Genes, 10(12), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121006




