Patterns and Constraints in the Evolution of Sperm Individualization Genes in Insects, with an Emphasis on Beetles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Functional Group and Expression Profiles
2.2. Retrieval of Sperm Individualization Gene Orthologs in Insects
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses of Amino Acid Sequences in Insects
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses of Nucleotide Sequences in Beetles
2.5. Estimation of Evolutionary Rates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Analyses Constrained by Gene Interactions
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Datasets: Composition of Sequence Alignments
3.2. Characteristics of Datasets: Gene Duplications
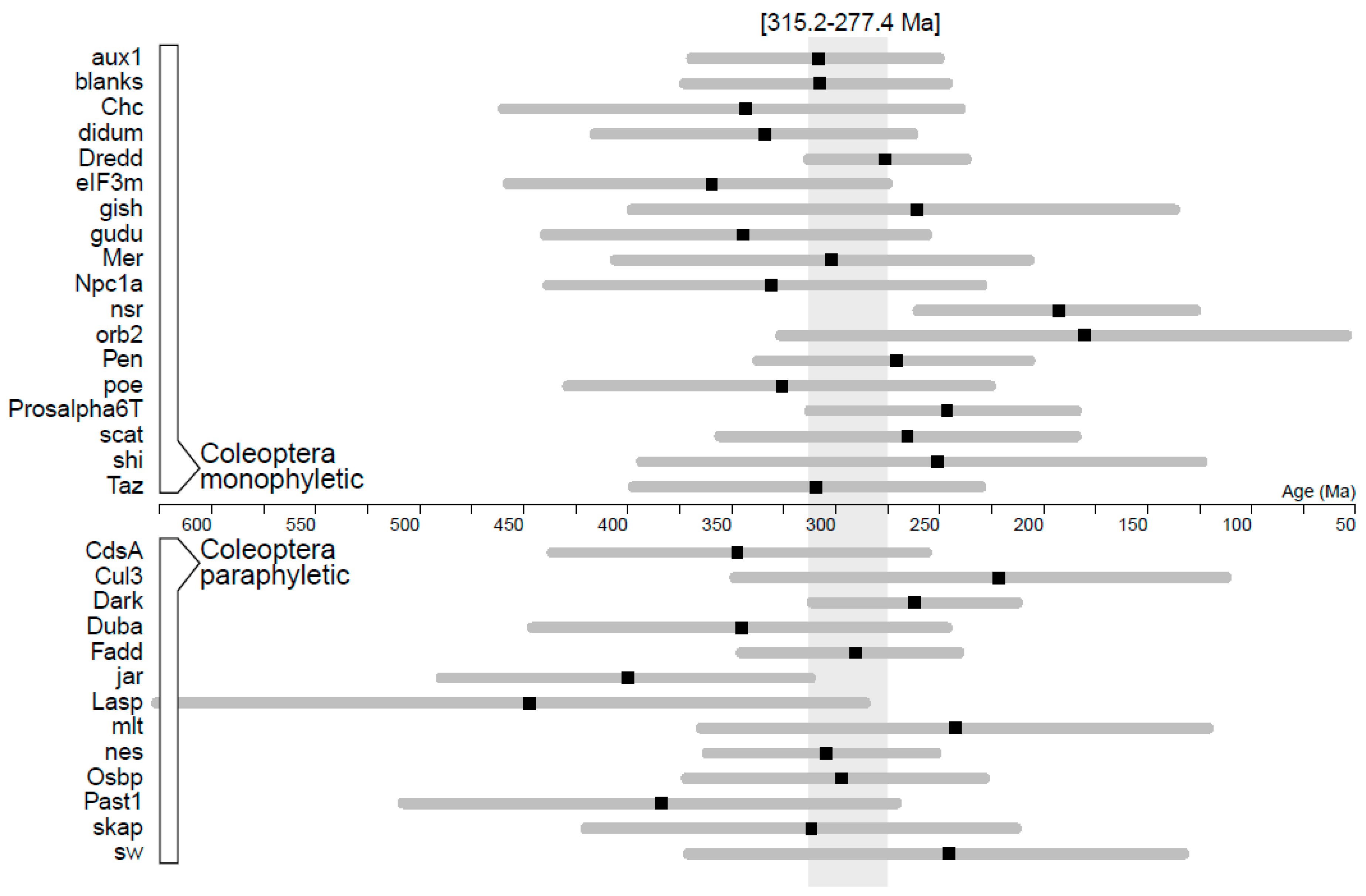
3.3. Evolutionary Rates of Sperm Individualization Genes in Insecta and Coleoptera
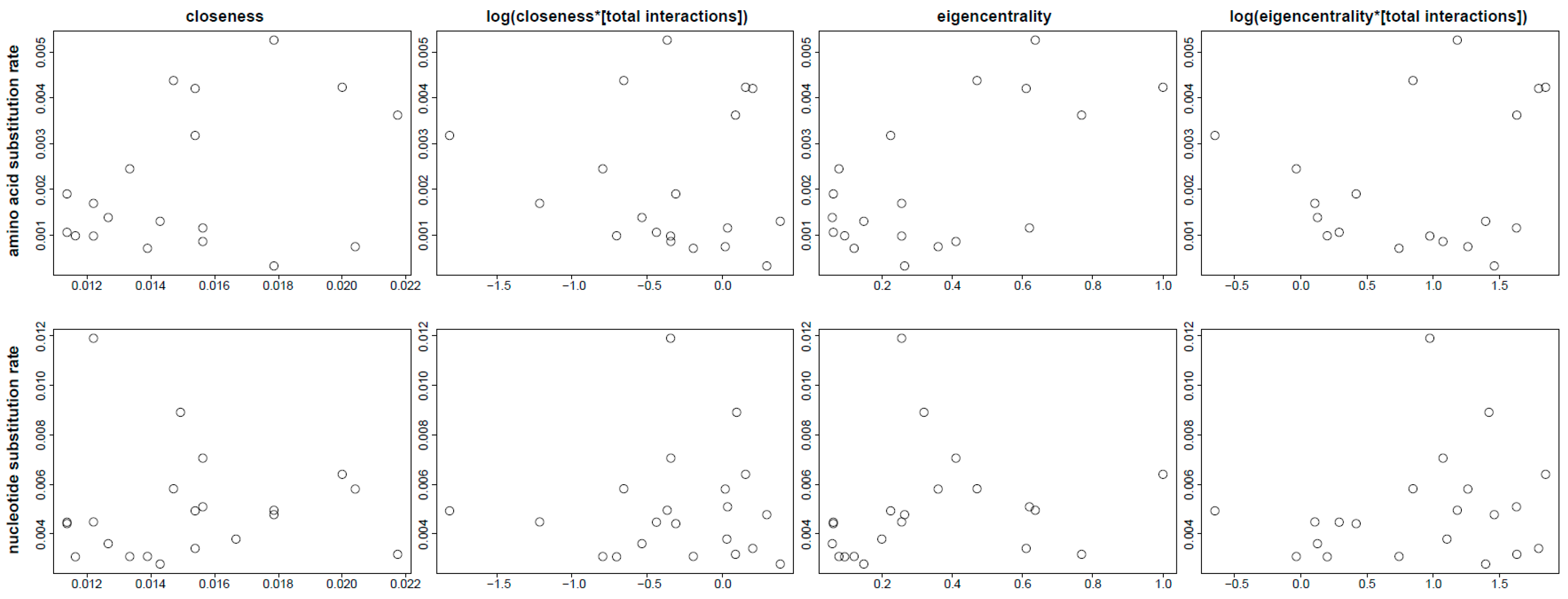
3.4. Analysis of Rate Differences
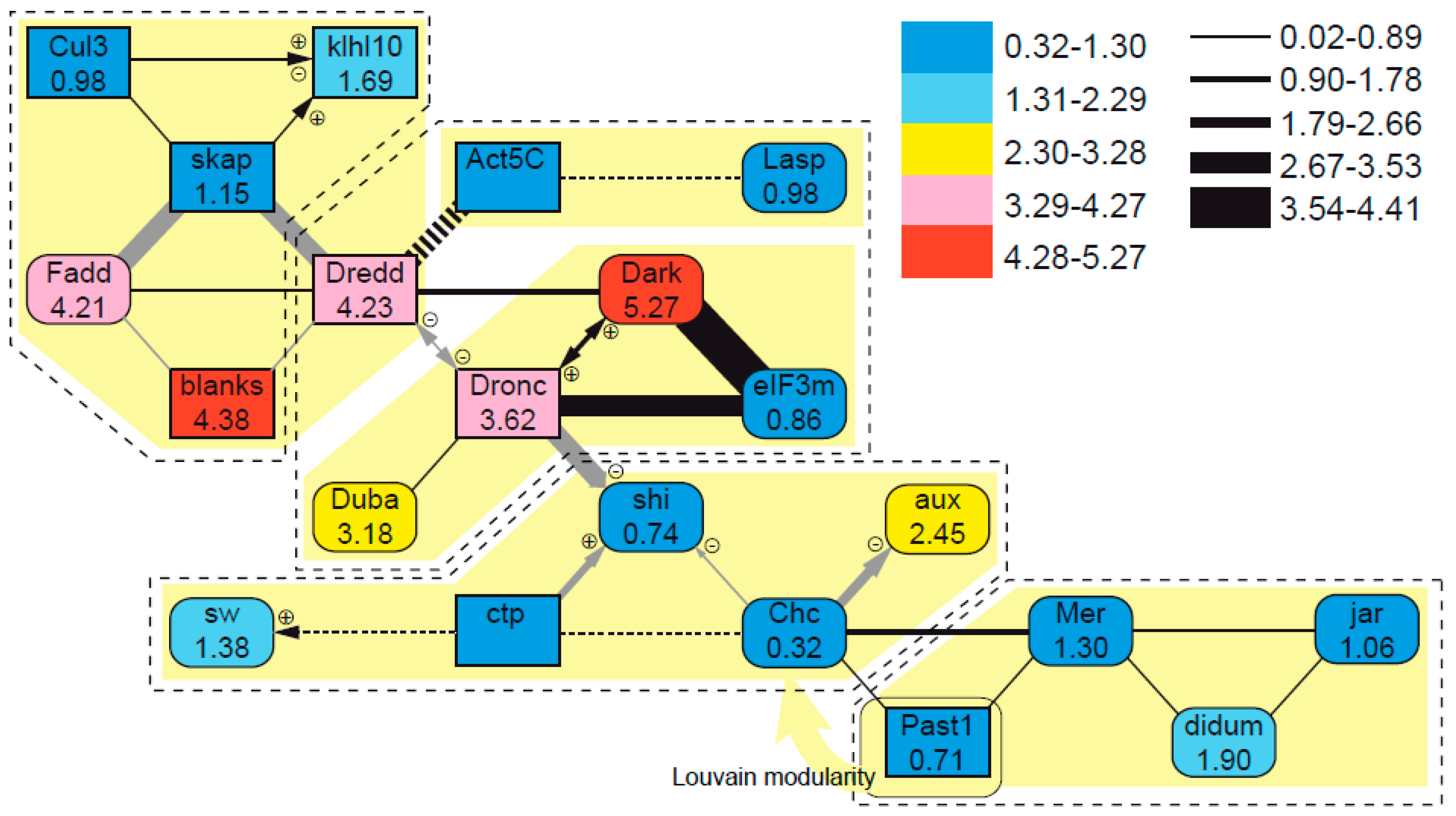
3.5. Evolutionary Patterns in the Sperm Individualization Interaction Network
4. Discussion
4.1. Data Mining Genomic and Transcriptomic Resources: Sequence Quality
4.2. Data Mining Genomic and Transcriptomic Resources: Orthology Assessment
4.3. Evolutionary Dynamics of Sperm Individualization Genes
4.4. Evolutionary Dynamics of Interacting Sperm Individualization Genes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khaitovich, P.; Hellmann, I.; Enard, W.; Nowick, K.; Leinweber, M.; Franz, H.; Weiss, G.; Lachmann, M.; Pääbo, S. Parallel patterns of evolution in the genomes and transcriptomes of humans and chimpanzees. Science 2005, 309, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranz, J.M.; Castillo-Davis, C.I.; Meiklejohn, C.D.; Hartl, D.L. Sex-dependent gene expression and evolution of the Drosophila transcriptome. Science 2003, 300, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graveley, B.R.; Brooks, A.N.; Carlson, J.W.; Duff, M.O.; Landolin, J.M.; Yang, L.; Artieri, C.G.; van Baren, M.J.; Boley, N.; Booth, B.W.; et al. The developmental transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 2011, 471, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Jagadeeshan, S. Sex and speciation: Drosophila reproductive tract proteins—Twenty five years later. Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 191495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.C.; Harrison, P.W.; Mank, J.E. The ontogeny and evolution of sex-biased gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.A.; Nolan, T.; Fischer, B.; Pinder, A.; Crisanti, A.; Russell, S. A comprehensive gene expression atlas of sex- and tissue-specificity in the malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, E.G.; Kirkland, D.; Demuth, J.P. Hyperexpression of the X chromosome in both sexes results in extensive female bias of X-linked genes in the flour beetle. Genome Biol. Evol. 2010, 2, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsch, J.; Ellegren, H. The evolutionary causes and consequences of sex-biased gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telonis-Scott, M.; Kopp, A.; Wayne, M.L.; Nuzhdin, S.V.; McIntyre, L.M. Sex-specific splicing in Drosophila: Widespread occurrence, tissue specificity and evolutionary conservation. Genetics 2009, 181, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, B.; Castelo, R.; Miñana, B.; Peden, E.; Blanchette, M.; Rio, D.C.; Singh, R.; Valcárcel, J. Distinct regulatory programs establish widespread sex-specific alternative splicing in Drosophila melanogaster. RNA 2011, 17, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.P.; Malone, J.H.; Clark, A.G. Disentangling the relationship between sex-biased gene expression and X-linkage. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Cho, D.Y.; Whitworth, C.; Eisman, R.; Phelps, M.; Roote, J.; Kaufman, T.; Cook, K.; Russell, S.; Przytycka, T.; et al. Effects of gene dose, chromatin, and network topology on expression in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranz, J.M.; Parsch, J. Newly evolved genes: Moving from comparative genomics to functional studies in model systems. Bioessays 2012, 34, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallach, M.; Domingues, S.; Betrán, E. Gene duplication and the genome distribution of sex-biased genes. Intl. J. Evol. Biol. 2011, 2011, 989438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Krinsky, B.H.; Long, M.y. New genes as drivers of phenotypic evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Hambuch, T.M.; Parsch, J. Molecular evolution of sex-biased genes in Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pröschel, M.; Zhang, Z.; Parsch, J. Widespread adaptive evolution of Drosophila genes with sex-biased expression. Genetics 2006, 174, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegren, H.; Parsch, J. The evolution of sex-biased genes and sex-biased gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerty, W.; Jagadeeshan, S.; Kulathinal, R.J.; Wong, A.; Ram, K.R.; Sirot, L.K.; Levesque, L.; Artieri, C.G.; Wolfner, M.F.; Civetta, A.; et al. Evolution in the fast lane: Rapidly evolving sex-related genes in Drosophila. Genetics 2007, 177, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Smith, S.A. Orthology inference in nonmodel organisms using transcriptomes and low-coverage genomes: Improving accuracy and matrix occupancy for phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölander, K. Phylogenomic inference of protein molecular function: Advances and challenges. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizán-Rico, H.I.; Gómez-Zurita, J. Testis-specific RNA-Seq of Calligrapha (Chrysomelidae) as a transcriptomic resource for male-biased gene inquiry in Coleoptera. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2017, 17, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grath, S.; Parsch, J. Sex-biased gene expression. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, M.; Nuttall, R.; Edwards, P.; Minor, J.; Naiman, D.; Lü, J.; Doctolero, M.; Vainer, M.; Chan, C.; Malley, J.; et al. A survey of ovary-, tesits-, and soma-biased gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster adults. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizio, J.J.; Hime, G.; Lemmon, S.K.; Bazinet, C. Genetic dissection of sperm individualization in Drosophila melanogaster. Development 1998, 125, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, M.T. Spermatogenesis. In The Development of Drosophila melanogaster; Bate, M., Arias, A.M., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 71–147. [Google Scholar]
- Celniker, S.E.; Dillon, L.A.; Gerstein, M.B.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Henikoff, S.; Karpen, G.H.; Kellis, M.; Lai, E.C.; Lieb, J.D.; MacAlpine, D.M.; et al. Unlocking the secrets of the genome. Nature 2009, 459, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kriventseva, E.V.; Tegenfeldt, F.; Petty, T.J.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Simão, F.A.; Pozdnyakov, I.A.; Ioannidis, P.; Zdobnov, E.M. OrthoDB v8: Update of the hierarchical catalog of orthologs and the underlying free software. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D250–D256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón, T. Large-scale assignment of orthology: Back to phylogenetics? Genome Biol. 2008, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon, S.; Ireland, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Shu, S.Q.; Marshall, B.; Lewis, S. AmiGO: Online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramates, L.S.; Marygold, S.J.; dos Santos, G.; Urbano, J.-M.; Antonazzo, G.; Matthews, B.B.; Rey, A.J.; Tabone, C.J.; Crosby, M.A.; Emmert, D.B.; et al. FlyBase at 25: Looking to the future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D663–D671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalderimis, A.; Lyne, R.; Butano, D.; Contrino, S.; Lyne, M.; Heimbach, J.; Hu, F.; Smith, R.; Stěpán, R.; Sullivan, J.; et al. InterMine: Extensive web services for modern biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W468–W472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdobnov, E.M.; Tegenfeldt, F.; Kuznetsov, D.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Simão, F.A.; Panagiotis, I.; Seppey, M.; Loetscher, A.; Kriventseva, E.V. OrthoDB v9.1: Cataloguing evolutionary and functional annotations for animal, fungal, plant, archaeal, bacterial and viral orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D744–D749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.; Meusemann, K.; Donath, A.; Dowling, D.; Liu, S.; Peters, R.S.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Vasilikopoulos, A.; Zhou, X.; Misof, B.; et al. Orthograph: A versatile tool for mapping coding nucleotide sequences to clusters of orthologous genes. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attrill, H.; Falls, K.; Goodman, J.L.; Millburn, G.H.; Antonazzo, G.; Rey, A.J.; Marygold, S.J. FlyBase Consortium. FlyBase: Establishing a Gene Group resource for Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D786–D792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Murphy, T.; Xia, J.; Caragea, D.; Park, Y.; Beeman, R.W.; Lorenzen, M.D.; Butcher, S.; Manak, J.R.; Brown, S.J. BeetleBase in 2010: Revisions to provide comprehensive genomic information for Tribolium castaneum. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D437–D442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, S.; Zhang, G.; Schiott, M.; Li, C.; Wurm, Y.; Hu, H.F.; Zhou, J.J.; Ji, L.; Qiu, F.; Rasmussen, M.; et al. The genome of the leaf-cutting ant Acromyrmex echinatior suggests key adaptations to advanced social life and fungus farming. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsik, C.G.; Tayal, A.; Diesh, C.M.; Unni, D.R.; Emery, M.L.; Nguyen, H.N.; Hagen, D.E. Hymenoptera Genome Database: Integrating genome annotations in HymenopteraMine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D793–D800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Klopfstein, S.; Vilhelmsen, L.; Schulmeister, S.; Murray, D.L.; Rasnitsyn, A.P. A total-evidence approach to dating with fossils, applied to the early radiation of the Hymenoptera. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 973–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertone, M.A.; Courtney, G.W.; Wiegmann, B.M. Phylogenetics and temporal diversification of the earliest true flies (Insecta: Diptera) based on multiple nuclear genes. Syst. Ent. 2008, 33, 668–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1.6. 2014. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (accessed on 10 March 2015).
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, N.A. wPerm. Permutation Tests. R package version 1.0.1. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=wPerm (accessed on 15 February 2018).
- Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.-J.; Reguly, T.; Boucher, L.; Breitkreutz, A.; Tyers, M. BioGRID: A general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D535–D539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. Int. J. Complex. Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Blondel, V.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. 2008, 10, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, U.; Delling, D.; Gaertler, M.; Görke, R.; Hoefer, M.; Nikoloski, Z.; Wagner, D. On modularity clustering. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2008, 20, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, U. A faster algorithm for betweenness centrality. J. Math. Sociol. 2001, 25, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misof, B.; Liu, S.l.; Meusemann, K.; Peters, R.S.; Donath, A.; Mayer, C.; Frandsen, P.B.; Ware, J.; Flouri, T.; Beutel, R.G.; et al. Phylogenomics resolves the timing and pattern of insect evolution. Science 2014, 346, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI Reference Sequence (RefSeq): A curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D501–D504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimke, W.; O’Donovan, C.; White, O.; Brister, J.R.; Clark, K.; Fedorov, B.; Mizrachi, I.; Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T. Solving the problem: Genome annotation standards before the data deluge. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2011, 5, 168–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, A.; Dehmer, M.; Jurisica, I. Knowledge Discovery and interactive data mining in Bioinformatics -state-of-the-art, future challenges and research directions. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, I1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sturgill, D.; Parisi, M.; Kumar, S.; Oliver, B. Constraint and turnover in sex-biased gene expression in the genus Drosophila. Nature 2007, 450, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, R.; Zhou, Q.; Bachtrog, D. Sex-biased transcriptome evolution in Drosophila. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, D.G.; Kulathinal, R.J.; Singh, R.S. Mammalian sperm proteins are rapidly evolving: Evidence of positive selection in functionally diverse genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeeshan, S.; Singh, R.S. Rapidly evolving genes of Drosophila: Differing levels of selective pressure in testis, ovary, and head tissues between sibling. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Parsch, J. Positive correlation between evolutionary rate and recombination rate in Drosophila genes with male-biased expression. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1945–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.P. Towards a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between sex-biased gene expression and rates of protein-coding sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Grath, S.; von Heckel, K.; Parsch, J. Inter- and intraspecific variation in Drosophila genes with sex-biased expression. Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Werren, J.H.; Clark, A.G. Genetic and epigenetic architecture of sex-biased expression in the jewel wasps Nasonia vitripennis and giraulti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3545–E3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darolti, I.; Wright, A.E.; Pucholt, P.; Berlin, S.; Mank, J.E. Slow evolution of sex-biased genes in the reproductive tissue of the dioecious plant Salix viminalis. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, F.; Windbichler, N.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Cagnetti, A.; D’Amato, R.; Persampieri, T.; Lawniczak, M.K.N.; Nolan, T.; Papathanos, P.A. Rapid evolution of female-biased genes among four species of Anopheles malaria mosquitoes. Genome Res. 2018, 27, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grath, S.; Parsch, J. Rate of amino acid substitution is influenced by the degree and conservation of male-biased transcription over 50 myr of Drosophila evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, D.A.; Bloom, J.D.; Adami, C.; Wilke, C.O.; Arnold, F.H. Why highly expressed proteins evolve slowly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14338–14343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.; Wolfner, M.F. Evolution of Drosophila seminal proteins and their networks. In Rapidly Evolving Genes & Genetic Systems; Singh, R.S., Xu, J.P., Kulathinal, R.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, H.B.; Wall, D.P.; Hirsh, A.E. A simple dependence between protein evolution rate and the number of protein-protein interactions. BMC Evol. Biol. 2003, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, H.B.; Hirsh, A.E.; Steinmetz, L.M.; Scharfe, C.; Feldman, M.W. Evolutionary rate in the protein interaction network. Science 2002, 296, 750–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cork, J.M.; Purugganan, M.D. The evolution of molecular genetic pathways and networks. Bioessays 2004, 26, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. Metabolic networks and their evolution. In Evolutionary Systems Biology; Soyer, O.S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 29–52. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Ponce, D.; Fares, M.A. Evolutionary rate and duplicability in the Arabidopsis thaliana protein-protein interaction network. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Laayouni, H.; Invergo, B.M.; Bertranpetit, J.; Montanucci, L. Metabolic flux is a determinant of the evolutionary rates of enzyme-encoding genes. Evolution 2013, 68, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovelin, R.; Phillips, P.C. Evolutionary rates and centrality in the yeast gene regulatory network. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

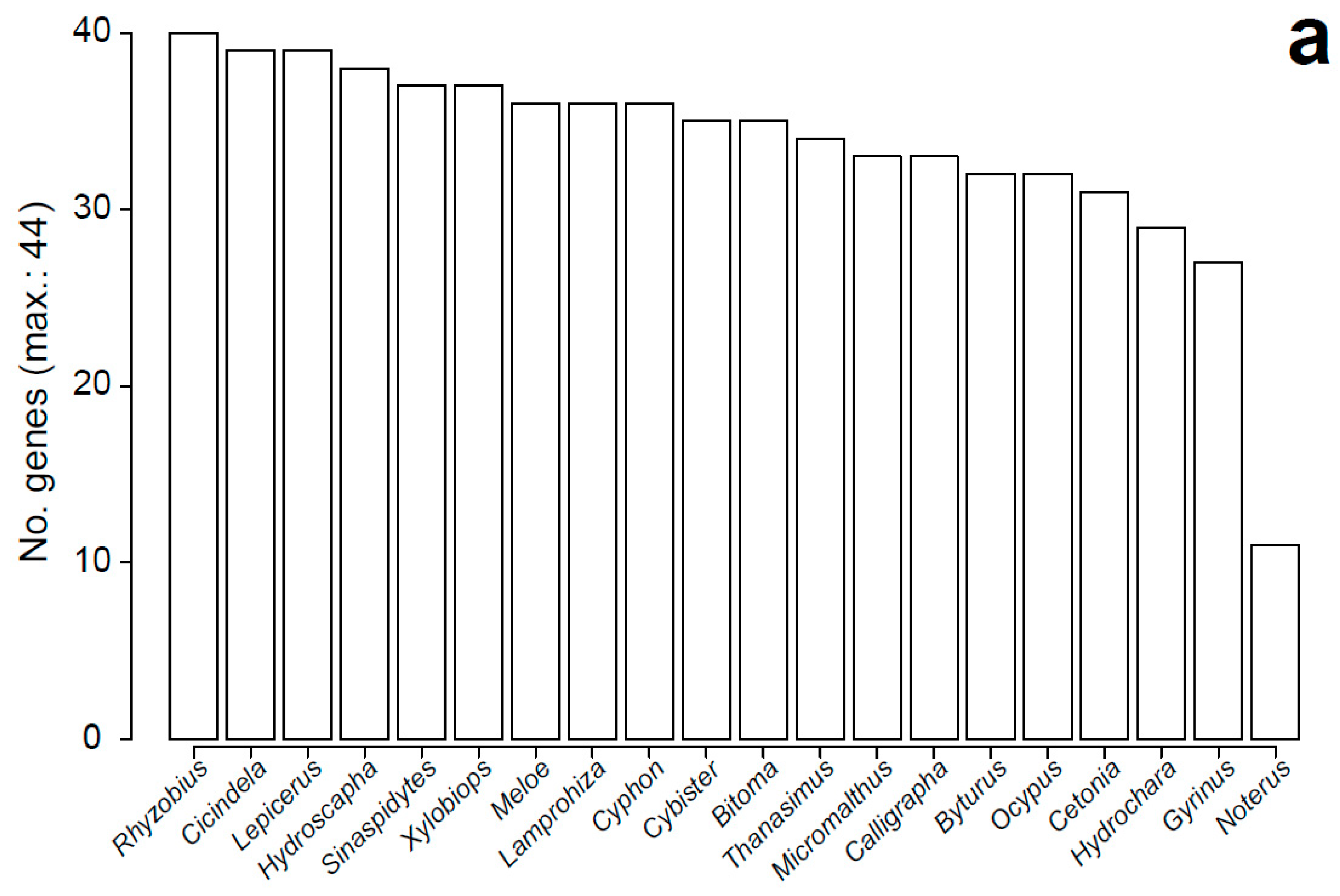
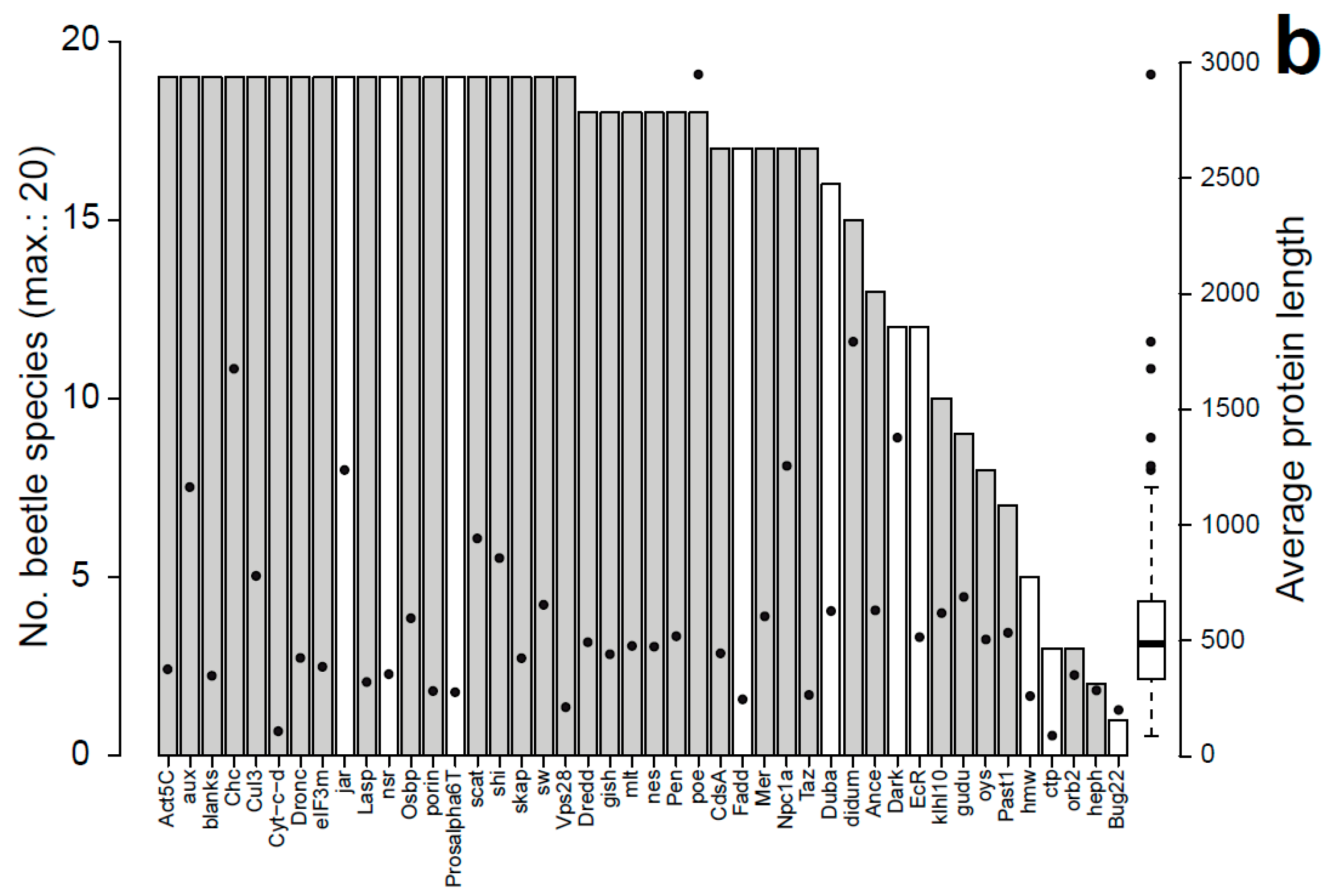
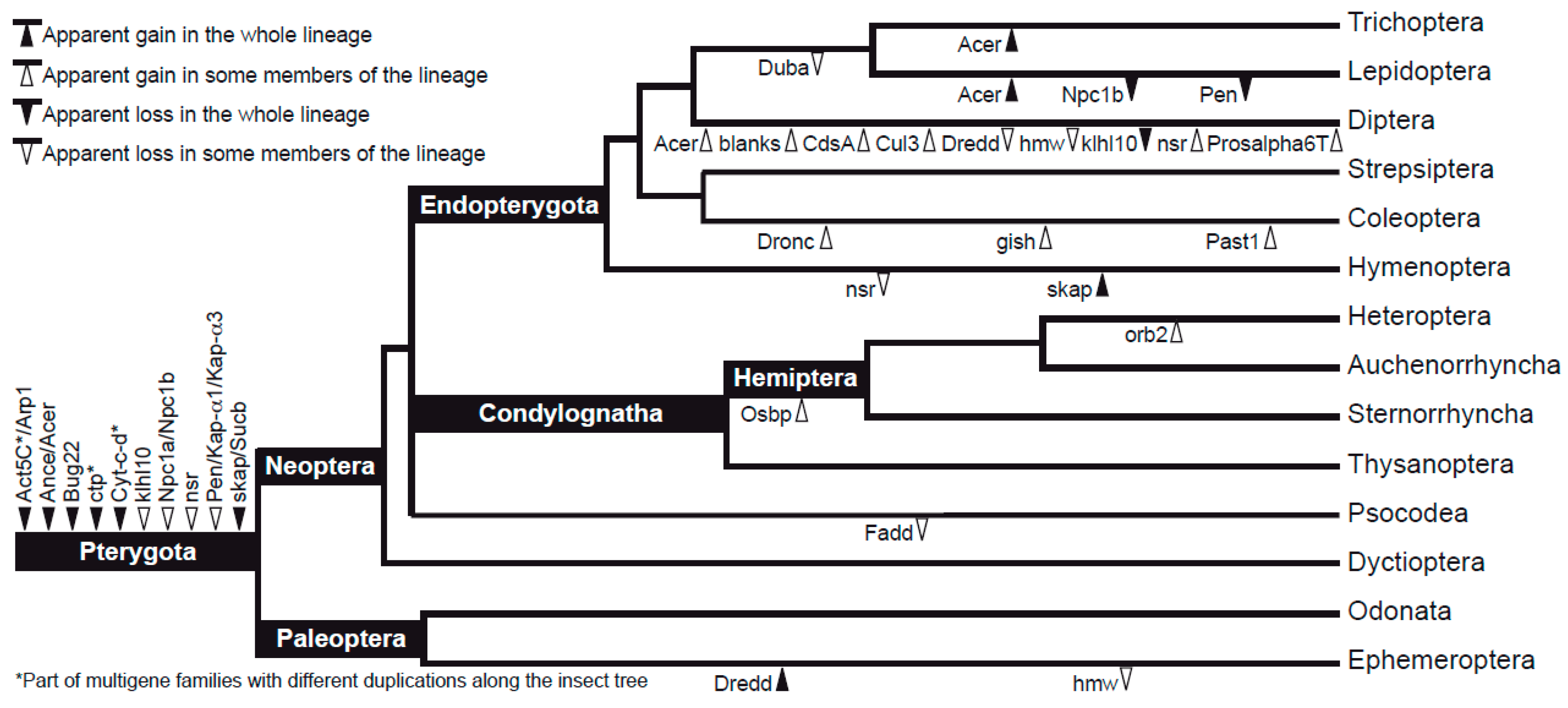
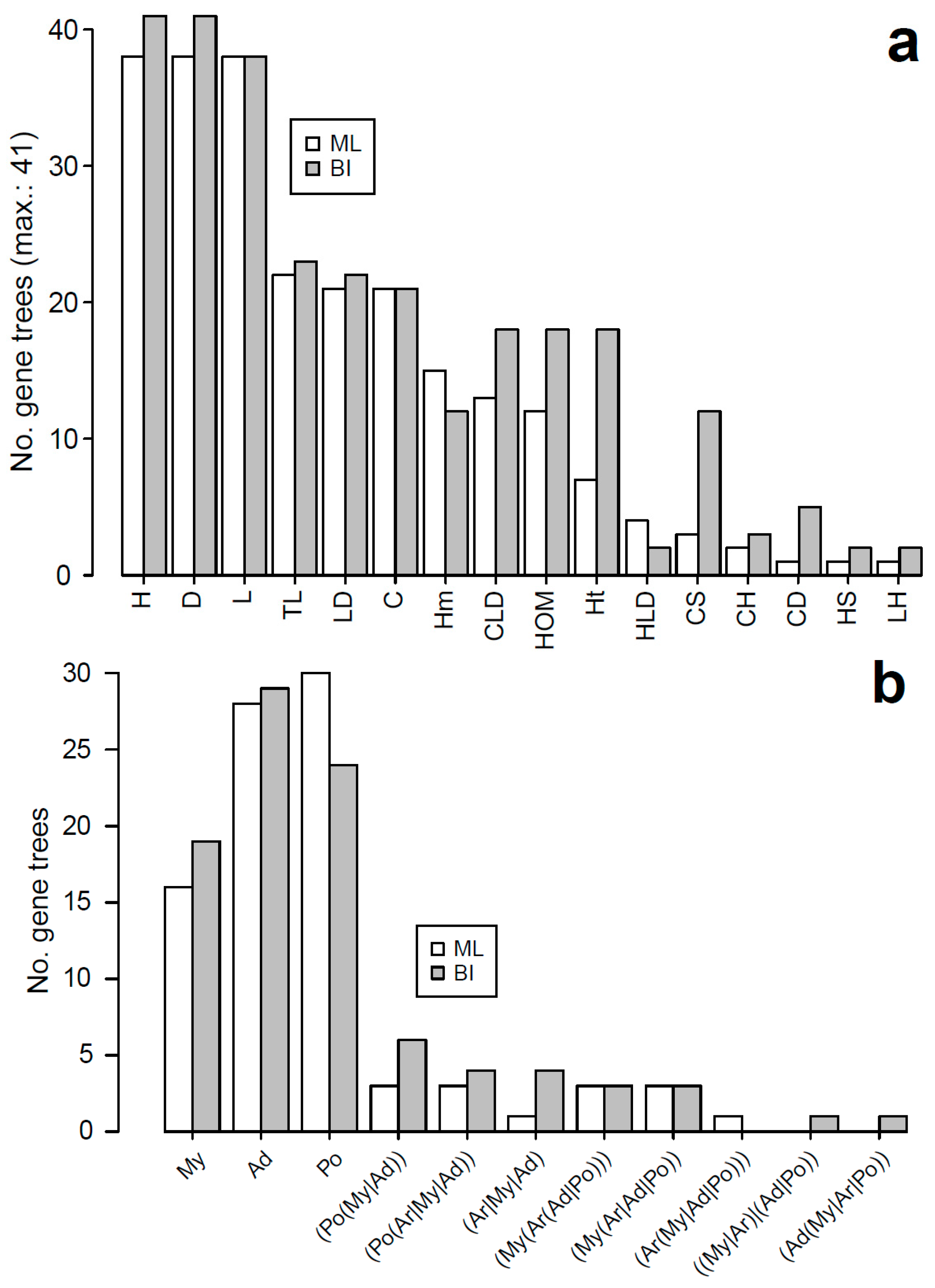
| Gene | FlyBase ID | Function | Expression Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Act5C | FBgn0000042 | cytoskeleton structure | unbiased |
| Ance | FBgn0012037 | peptidase | unbiased |
| aux | FBgn0037218 | ATP binding cofactor of kinase | unbiased |
| blanks | FBgn0035608 | siRNA binding | male biased |
| Bug22 | FBgn0032248 | cilium organization and assembly | unbiased |
| CdsA | FBgn0010350 | enzyme (CDP diglyceride synthetase) | unbiased |
| Chc | FBgn0000319 | coated vesicles structure | unbiased |
| ctp | FBgn0011760 | dynein complex assembly | unbiased |
| Cul3 | FBgn0261268 | protein binding | unbiased |
| Cyt-c-d | FBgn0086907 | electron carrier | male biased |
| Dark | FBgn0263864 | apoptosome assembly | unbiased |
| didum | FBgn0261397 | unconventional myosin | unbiased |
| Dredd | FBgn0020381 | enzyme (caspase) | unbiased |
| Dronc | FBgn0026404 | enzyme (caspase) | unbiased |
| Duba | FBgn0036180 | enzyme (deubiquitinase) | unbiased |
| EcR | FBgn0000546 | transcription factor | unbiased |
| eIF3m | FBgn0033902 | translation initiation factor | unbiased |
| Fadd | FBgn0038928 | protein binding | unbiased |
| gish | FBgn0250823 | enzyme (protein kinase) | unbiased |
| gudu | FBgn0031905 | NA | male biased |
| heph | FBgn0011224 | mRNA binding (translation repression) | unbiased |
| hmw | FBgn0038607 | motile cilium assembly | male biased |
| jar | FBgn0011225 | myosin | unbiased |
| klhl10 | FBgn0040038 | substrate recruiting for ubiquitin ligase complex | male biased |
| Lasp | FBgn0063485 | actin/myosin scaffolding | unbiased |
| Mer | FBgn0086384 | cytoskeletal protein binding | unbiased |
| mlt | FBgn0265512 | microtubule removal | unbiased |
| nes | FBgn0026630 | enzyme (lysophospholipid acyltransferase) | unbiased |
| Npc1a | FBgn0024320 | sterol metabolism | unbiased |
| nsr | FBgn0034740 | dynein complex assembly | male biased |
| orb2 | FBgn0264307 | translation factor | unbiased |
| Osbp | FBgn0020626 | protein binding | unbiased |
| oys | FBgn0033476 | enzyme (lysophospholipid acyltransferase) | unbiased |
| Past1 | FBgn0016693 | membrane assembly | unbiased |
| Pen | FBgn0011823 | protein binding | unbiased |
| poe | FBgn0011230 | calmodulin binding | unbiased |
| porin | FBgn0004363 | membrane channel protein | unbiased |
| Prosalpha6T | FBgn0032492 | enzyme (protease) | male biased |
| scat | FBgn0011232 | protein binding | female biased |
| shi | FBgn0003392 | GTPase for microtubule motility | unbiased |
| skap | FBgn0037643 | ATP binding enzyme | unbiased |
| sw | FBgn0003654 | dynein complex assembly | unbiased |
| Taz | FBgn0026619 | enzyme (phospholipid transacylase) | unbiased |
| Vps28 | FBgn0021814 | vesicular trafficking | unbiased |
| Suborder Infraorder | Superfamily | Family | Species | Library ID (1KITE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archostemata | Micromalthidae | Micromalthus debilis | INSqzbTABRAAPEI-210 | |
| Adephaga | Aspidytidae | Sinaspidytes wrasei | WHINSnuyTAAARAAPEI-47 | |
| Carabidae | Cicindela hybrida | INShauTBARAAPEI-21 | ||
| Dytiscidae | Cybister lateralimarginalis | INSnfrTADRAAPEI-16 | ||
| Gyrinidae | Gyrinus marinus | INSnfrTBERAAPEI-19 | ||
| Noteridae | Noterus clavicornis | INShkeTALRAAPEI-37 | ||
| Myxophaga | Hydroscaphidae | Hydroscapha redfordi | INSntgTARRAAPEI-208 | |
| Lepiceridae | Lepicerus sp. | INSytvTAJRAAPEI-19 | ||
| Polyphaga | ||||
| “basal Polyphaga” | Scirtoidea | Scirtidae | Cyphon laevipennis | INSjdsTBDRAAPEI-47 |
| Bostrichiformia | Bostrichoidea | Bostrichidae | Xylobiops basilaris | WHANIsrmTMCLRAAPEI-11 |
| Cucujiformia | Chrysomeloidea | Cerambycidae | Anoplophora glabripennisa | - |
| Chrysomelidae | Calligrapha multipunctatab | - | ||
| Leptinotarsa decemlineataa | - | |||
| Cleroidea | Byturidae | Byturus ochraceus | INShkeTAORAAPEI-43 | |
| Cleridae | Thanasimus formicarius | INShkeTCERAAPEI-79 | ||
| Coccinelloidea | Coccinellidae | Rhyzobius pseudopulcher | WHANIsrmTMABRAAPEI-9 | |
| Curculionoidea | Curculionidae | Dendroctonus ponderosaea | - | |
| Tenebrionoidea | Meloidae | Meloe violaceus | INShauTAYRAAPEI-19 | |
| Tenebrionidae | Tribolium castaneuma | - | ||
| Zopheridae | Bitoma cylindrica | WHANIsrmTMAPRAAPEI-39 | ||
| Elateriformia | Buprestoidea | Buprestidae | Agrilus planipennisa | - |
| Elateroidea | Lampyridae | Lamprohiza splendidula | INShkeTCGRAAPEI-87 | |
| Scarabaeiformia | Scarabaeoidea | Scarabaeidae | Cetonia aurata pisana | WHANIsrmTMAVRAAPEI-53 |
| Onthophagus taurusa | - | |||
| Staphyliniformia | Hydrophiloidea | Hydrophilidae | Hydrochara caraboides | INShauTASRAAPEI-13 |
| Staphylinoidea | Staphylinidae | Ocypus brunnipes | INShkeTCMRAAPEI-45 |
| Gene | N | Sp | Single | L | r | n | Length | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Act5C | 517 | 115 | 7 | 376 | 0.60 | - | - | - |
| Ance | 238 | 109 | 30 | 631 | 0.92 | 90 | 621 | LG + G + I |
| aux | 136 | 112 | 94 | 1164 | 1.21 | 126 | 1755 | JTT + G + I + F |
| blanks | 172 | 107 | 71 | 348 | 1.55 | 122 | 719 | JTT + G + I + F |
| Bug22 | 201 | 115 | 36 | 200 | 0.61 | 83 | 270 | LG + G + I |
| CdsA | 118 | 109 | 101 | 445 | 0.76 | 122 | 574 | JTT + G + I + F |
| Chc | 123 | 115 | 110 | 1676 | 0.63 | 130 | 1726 | JTT + G + I |
| ctp | 121 | 98 | 79 | 89 | 0.57 | - | - | - |
| Cul3 | 153 | 116 | 91 | 780 | 0.73 | 133 | 858 | JTT + G + I |
| Cyt-c-d | 148 | 110 | 74 | 108 | 0.65 | - | - | - |
| Dark | 119 | 106 | 94 | 1378 | 1.99 | 112 | 2193 | JTT + G + I + F |
| didum | 126 | 113 | 102 | 1793 | 1.10 | 124 | 2175 | LG + G + I |
| Dredd | 91 | 81 | 75 | 493 | 1.76 | 98 | 676 | JTT + G + I + F |
| Dronc | 128 | 96 | 78 | 425 | 1.67 | 119 | 654 | WAG + G + I + F |
| Duba | 105 | 99 | 93 | 628 | 0.95 | 113 | 1087 | JTT + G + I + F |
| EcR | 121 | 113 | 105 | 515 | 0.83 | 120 | 576 | JTT + G + I |
| eIF3m | 116 | 113 | 111 | 387 | 0.77 | 130 | 394 | JTT + G + I |
| Fadd | 96 | 93 | 90 | 246 | 1.77 | 108 | 353 | JTT + G + I + F |
| gish | 129 | 113 | 99 | 441 | 0.73 | 124 | 401 | JTT + G + I |
| gudu | 125 | 115 | 106 | 689 | 1.01 | 124 | 658 | LG + G + I |
| heph | 206 | 114 | 47 | 285 | 0.78 | 114 | 597 | JTT + G + I + F |
| hmw | 78 | 76 | 74 | 260 | 1.38 | 80 | 925 | JTT + G + I + F |
| jar | 131 | 111 | 97 | 1238 | 0.86 | 129 | 1375 | JTT + G + I + F |
| klhl10 | 214 | 109 | 54 | 619 | 0.96 | 113 | 630 | LG + G + I |
| Lasp | 113 | 105 | 97 | 321 | 0.79 | 121 | 298 | JTT + G + I |
| Mer | 120 | 112 | 105 | 605 | 0.87 | 129 | 686 | JTT + G + I |
| mlt | 124 | 112 | 103 | 477 | 1.10 | 130 | 651 | LG + G + I + F |
| nes | 122 | 112 | 104 | 474 | 1.21 | 128 | 472 | LG + G + I + F |
| Npc1a | 216 | 116 | 23 | 1256 | 0.98 | 124 | 1435 | LG + G + I |
| nsr | 317 | 115 | 38 | 355 | 0.92 | 129 | 563 | JTT + G + I |
| orb2 | 115 | 106 | 98 | 351 | 0.62 | 105 | 293 | JTT + G + I |
| Osbp | 158 | 112 | 79 | 597 | 0.91 | 130 | 1094 | JTT + G + I |
| oys | 121 | 108 | 97 | 505 | 1.03 | 115 | 463 | LG + G + I |
| Past1 | 124 | 114 | 104 | 534 | 0.66 | 120 | 564 | LG + G + I |
| Pen | 342 | 116 | 7 | 519 | 0.83 | 121 | 593 | LG + G + I + F |
| poe | 183 | 115 | 84 | 2949 | 1.08 | 129 | 3846 | JTT + G + I + F |
| porin | 124 | 108 | 98 | 282 | 0.86 | 127 | 286 | LG + G + I + F |
| Prosalpha6T | 126 | 108 | 91 | 277 | 0.77 | 125 | 312 | LG + G + I + F |
| scat | 130 | 116 | 103 | 942 | 1.11 | 133 | 1233 | JTT + G + I |
| shi | 133 | 113 | 94 | 857 | 0.67 | 132 | 1005 | LG + G + I |
| skap | 247 | 116 | 8 | 424 | 0.80 | 128 | 476 | LG + G + I |
| sw | 125 | 115 | 109 | 655 | 0.80 | 133 | 755 | JTT + G + I |
| Taz | 105 | 102 | 99 | 265 | 0.91 | 118 | 303 | LG + G + I + F |
| Vps28 | 135 | 112 | 94 | 212 | 0.72 | 131 | 213 | LG + G + I |
| Gene | B/D/N | Substitution Rate (×10−3) | ucld.stdev | Age Coleoptera |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hmw | 1/0/0 | 9.67 ± 1.349 | 2.972 | - |
| Dark | 0/0/1 | 5.27 ± 0.282 | 0.418 | 264.2 [214.3–314.2] |
| blanks | 1/1/1 | 4.38 ± 0.382 | 0.483 | 310.6 [248.2–376.1] |
| Dredd | 0/0/1 | 4.23 ± 0.219 | 0.309 | 278.4 [239.2–315.8] |
| Fadd | 0/0/1 | 4.21 ± 0.277 | 0.345 | - |
| Dronc | 0/1/1 | 3.62 ± 0.221 | 0.391 | 379.8 [339.5–426.0] b |
| Duba | 0/0/1 | 3.18 ± 0.257 | 0.566 | 348.2 [248.5–450.2] b |
| nsr | 1/1/0 | 3.00 ± 0.279 | 0.672 | 194.1 [127.4–262.5] |
| Bug22 | 0/1/0 | 2.82 ± 0.278 | 0.559 | - |
| scat | 1/0/0 | 2.73 ± 0.259 | >3 a | 267.8 [185.8–359.0] |
| aux | 0/0/1 | 2.45 ± 0.154 | 0.386 | 311.0 [252.3–372.7] |
| nes | 0/0/0 | 2.27 ± 0.130 | 0.423 | 307.2 [253.7–365.2] b |
| poe | 0/0/0 | 2.10 ± 0.174 | >3 a | 328.7 [227.3–433.1] |
| Osbp | 0/1/0 | 2.05 ± 0.180 | 0.601 | 299.6 [230.3–375.4] b |
| Npc1a | 0/1/0 | 1.91 ± 0.157 | >3 a | 334.2 [231.5–442.6] |
| didum | 0/0/1 | 1.90 ± 0.126 | 0.511 | 337.0 [264.9–419.9] |
| Pen | 0/1/0 | 1.78 ± 0.120 | 0.531 | 273.2 [208.2–340.5] |
| klhl10 | 1/1/1 | 1.69 ± 0.124 | 0.816 | - |
| Prosalpha6T | 1/1/0 | 1.68 ± 0.151 | 0.559 | 248.5 [185.6–315.1] |
| oys | 0/0/0 | 1.57 ± 0.127 | 0.558 | - |
| gudu | 1/0/0 | 1.45 ± 0.115 | 0.553 | 347.7 [258.1–444.1] |
| Ance | 0/1/0 | 1.42 ± 0.099 | 0.396 | - |
| sw | 0/0/1 | 1.38 ± 0.171 | 3.712 | 247.5 [133.2–374.3] |
| Taz | 0/0/0 | 1.33 ± 0.111 | 0.607 | 312.2 [231.9–401.0] |
| Mer | 0/0/1 | 1.30 ± 0.130 | 0.936 | 304.5 [208.4–409.9] |
| skap | 0/1/1 | 1.15 ± 0.116 | 0.557 | 314.4 [214.9–424.3] b |
| CdsA | 0/0/0 | 1.15 ± 0.103 | 0.629 | 350.5 [258.6–440.6] b |
| jar | 0/0/1 | 1.06 ± 0.086 | 0.482 | 403.2 [315.0–494.6] b |
| porin | 0/0/0 | 0.99 ± 0.106 | 0.779 | - |
| Lasp | 0/0/1 | 0.98 ± 0.138 | 0.930 | 451.5 [288.4–633.0] b |
| Cul3 | 0/1/1 | 0.98 ± 0.130 | 3.798 | 223.1 [112.6–351.7] b |
| EcR | 0/0/0 | 0.93 ± 0.091 | 0.789 | - |
| heph | 0/0/0 | 0.90 ± 0.118 | 3.919 | - |
| eIF3m | 0/0/1 | 0.86 ± 0.084 | 0.480 | 363.0 [277.4–462.1] |
| shi | 0/0/1 | 0.74 ± 0.092 | 3.847 | 253.2 [124.3–397.0] |
| Past1 | 0/1/1 | 0.71 ± 0.069 | 0.713 | 387.4 [273.0–513.2] b |
| Vps28 | 0/0/0 | 0.63 ± 0.079 | 0.822 | - |
| gish | 0/1/0 | 0.47 ± 0.070 | 4.174 | 262.9 [137.6–401.9] |
| mlt | 0/0/0 | 0.42 ± 0.523 | 3.268 | 244.6 [121.4–368.1] b |
| Chc | 0/0/1 | 0.32 ± 0.035 | 0.700 | 346.6 [242.1–464.4] |
| orb2 | 0/1/0 | 0.24 ± 0.035 | 1.414 | 180.4 [52.1–328.6] |
| Gene | N | L | Model | Substitution Rate (×10−3) | ucld.stdev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cul3 | 25 | 2196 | TN93 + G + I | 11.90 ± 2.603 | 2.707 |
| gish | 24 | 1197 | GTR + G + I | 9.34 ± 1.981 | 2.821 |
| Act5C | 15 | 1128 | GTR + G + I | 8.91 ± 2.232 | 2.839 |
| scat | 25 | 1974 | GTR + G + I | 7.26 ± 1.397 | 2.958 |
| eIF3m | 25 | 1155 | GTR + G + I | 7.06 ± 1.394 | 2.872 |
| poe | 23 | 3291 | GTR + G + I | 6.90 ± 1.322 | 2.844 |
| Dredd | 23 | 732 | GTR + G + I | 6.41 ± 1.255 | 3.012 |
| CdsA | 21 | 1323 | GTR + G + I | 6.35 ± 1.229 | 2.954 |
| blanks | 25 | 672 | GTR + G + I | 5.82 ± 1.172 | 2.994 |
| shi | 25 | 2610 | GTR + G + I | 5.81 ± 1.161 | 2.918 |
| skap | 24 | 1302 | GTR + G + I | 5.09 ± 0.984 | 3.033 |
| Dark | 14 | 1863 | GTR + G + I | 4.96 ± 0.905 | 2.947 |
| Duba | 20 | 858 | GTR + G + I | 4.93 ± 0.997 | 2.916 |
| Prosalpha6T | 25 | 822 | GTR + G + I | 4.90 ± 0.959 | 3.041 |
| Chc | 22 | 4944 | GTR + G + I | 4.78 ± 0.410 | 0.270 |
| klhl10 | 14 | 1779 | GTR + G + I | 4.48 ± 0.849 | 2.952 |
| jar | 25 | 3393 | GTR + G + I | 4.47 ± 0.840 | 3.005 |
| didum | 21 | 5073 | GTR + G + I | 4.41 ± 0.817 | 3.029 |
| oys | 14 | 1347 | GTR + G + I | 4.41 ± 0.839 | 3.019 |
| ctp | 8 | 267 | GTR + G | 3.79 ± 1.107 | 0.232 |
| mlt | 24 | 1248 | GTR + G + I | 3.61 ± 0.464 | 0.474 |
| sw | 25 | 1455 | GTR + G + I | 3.61 ± 0.347 | 0.344 |
| Taz | 23 | 774 | GTR + G + I | 3.52 ± 0.278 | 0.340 |
| Fadd | 19 | 228 | GTR + G + I | 3.41 ± 0.495 | 0.463 |
| nsr | 24 | 780 | GTR + G + I | 3.39 ± 0.464 | 0.409 |
| orb2 | 8 | 834 | GTR + G + I | 3.36 ± 0.834 | 0.477 |
| Npc1a | 23 | 3756 | GTR + G + I | 3.32 ± 0.280 | 0.255 |
| Dronc | 24 | 954 | GTR + G + I | 3.17 ± 0.265 | 0.221 |
| EcR | 17 | 1278 | GTR + G + I | 3.13 ± 0.396 | 0.382 |
| Vps28 | 26 | 573 | GTR + G + I | 3.12 ± 0.509 | 0.169 |
| Osbp | 25 | 1881 | GTR + G + I | 3.09 ± 0.285 | 0.365 |
| Past1 | 13 | 1566 | GTR + G + I | 3.09 ± 0.344 | 0.186 |
| aux | 18 | 2130 | GTR + G + I | 3.09 ± 0.295 | 0.252 |
| Lasp | 25 | 423 | GTR + G + I | 3.08 ± 0.495 | 0.110 |
| gudu | 15 | 1848 | GTR + G + I | 2.93 ± 0.280 | 0.450 |
| Pen | 24 | 1440 | GTR + G + I | 2.92 ± 0.252 | 0.296 |
| porin | 25 | 849 | GTR + G + I | 2.78 ± 0.393 | 0.499 |
| Mer | 23 | 1701 | GTR + G + I | 2.78 ± 0.260 | 0.329 |
| Ance | 18 | 1716 | GTR + G + I | 2.59 ± 0.198 | 0.299 |
| hmw | 8 | 201 | GTR + G | 2.57 ± 0.457 | 0.118 |
| nes | 25 | 1317 | GTR + G + I | 2.08 ± 0.171 | 0.538 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vizán-Rico, H.I.; Mayer, C.; Petersen, M.; McKenna, D.D.; Zhou, X.; Gómez-Zurita, J. Patterns and Constraints in the Evolution of Sperm Individualization Genes in Insects, with an Emphasis on Beetles. Genes 2019, 10, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100776
Vizán-Rico HI, Mayer C, Petersen M, McKenna DD, Zhou X, Gómez-Zurita J. Patterns and Constraints in the Evolution of Sperm Individualization Genes in Insects, with an Emphasis on Beetles. Genes. 2019; 10(10):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100776
Chicago/Turabian StyleVizán-Rico, Helena I., Christoph Mayer, Malte Petersen, Duane D. McKenna, Xin Zhou, and Jesús Gómez-Zurita. 2019. "Patterns and Constraints in the Evolution of Sperm Individualization Genes in Insects, with an Emphasis on Beetles" Genes 10, no. 10: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100776
APA StyleVizán-Rico, H. I., Mayer, C., Petersen, M., McKenna, D. D., Zhou, X., & Gómez-Zurita, J. (2019). Patterns and Constraints in the Evolution of Sperm Individualization Genes in Insects, with an Emphasis on Beetles. Genes, 10(10), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100776





