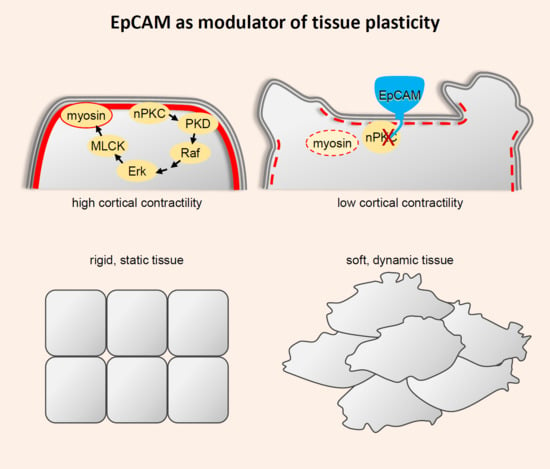
EpCAM as Modulator of Tissue Plasticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Features of EpCAM
3. EpCAM Function in Cell Signalling and Proliferation
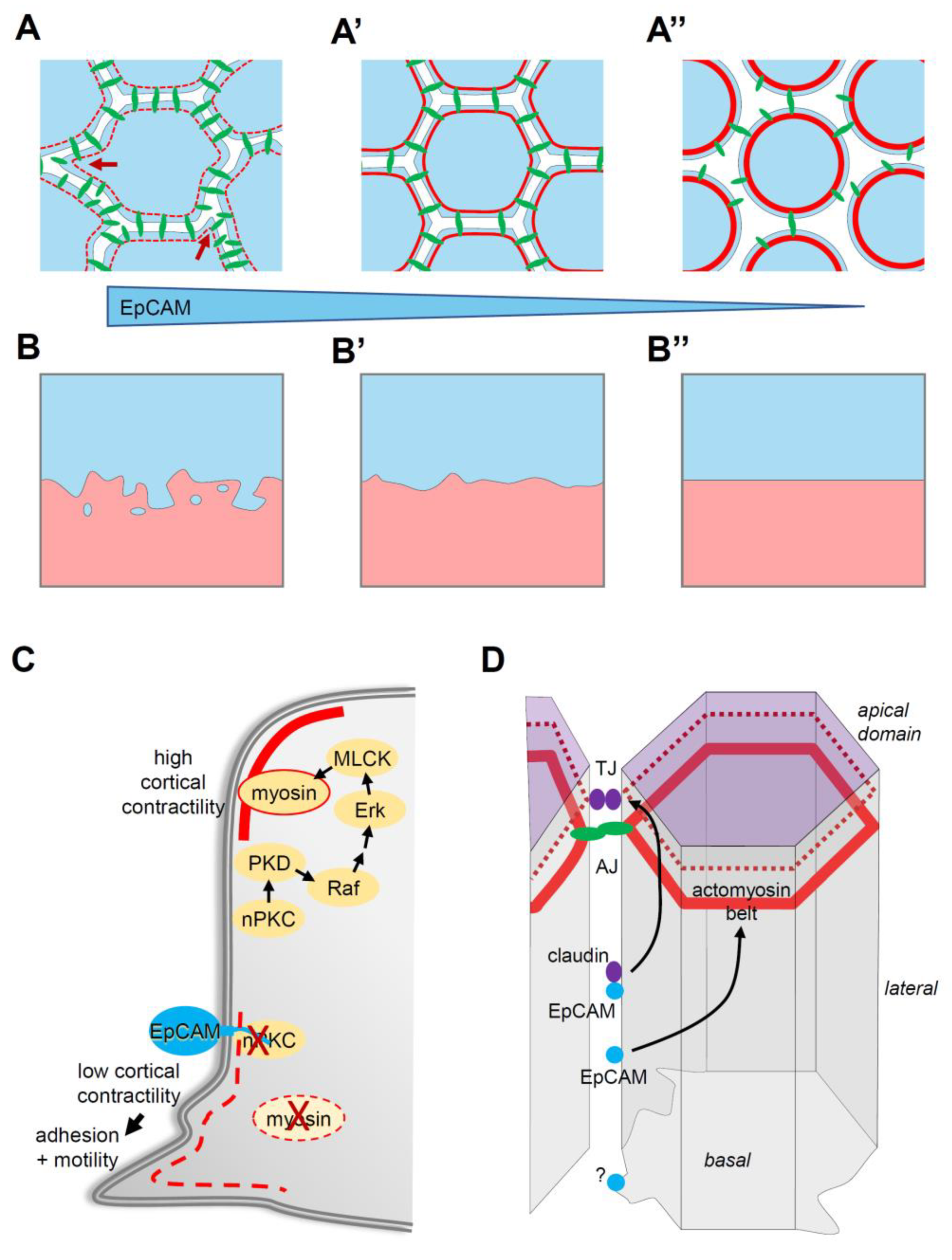
4. EpCAM Function in Tissue Morphogenesis
4.1. EpCAM and Embryonic Development
4.2. EpCAM Acts through PKC Signalling
4.3. EpCAM Pro-Adhesive and Pro-Migratory Activity through Control of Myosin
4.4. The EpCAM-nPKC-Myosin Pathway
4.5. EpCAM Function in Intestinal Homeostasis
5. Perspectives: From Here, Now Where Do We Go?
5.1. Is EpCAM Specifically Controlling Cortical Tension?
5.2. How Much Specificity Can Be Achieved by Controlling Multifunctional Components?
5.3. Regulation
5.4. EpCAM Morphogenetic Function and Cancer
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipinski, M.; Parks, D.R.; Rouse, R.V.; Herzenberg, L.A. Human trophoblast cell-surface antigens defined by monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 5147–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzpis, M.; McLaughlin, P.M.J.; de Leij, L.M.F.H.; Harmsen, M.C. Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule: More than a Carcinoma Marker and Adhesion Molecule. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, A.R.; Tolcos, M.; Hooper, S.B.; Cole, T.J.; Wallace, M.J. Trop2: From development to disease. Dev. Dyn. 2015, 244, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, V.; Crisa, L.; Beattie, G.M.; Mally, M.I.; Lopez, A.D.; Fannon, A.; Ptasznik, A.; Inverardi, L.; Ricordi, C.; Deerinck, T.; et al. KSA antigen Ep-CAM mediates cell-cell adhesion of pancreatic epithelial cells: Morphoregulatory roles in pancreatic islet development. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 140, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, C.J.; van Krieken, J.H.; Janssen-van Rhijn, C.M.; Litvinov, S.V. Expression of Ep-CAM in normal, regenerating, metaplastic, and neoplastic liver. J. Pathol. 1999, 188, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, A.D.; Zhan, F.; Bellone, S.; Palmieri, M.; Cane, S.; Bignotti, E.; Anfossi, S.; Gokden, M.; Dunn, D.; Roman, J.J.; et al. Gene expression profiles in primary ovarian serous papillary tumors and normal ovarian epithelium: Identification of candidate molecular markers for ovarian cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, S.V.; Bakker, H.A.; Gourevitch, M.M.; Velders, M.P.; Warnaar, S.O. Evidence for a role of the epithelial glycoprotein 40 (Ep-CAM) in epithelial cell-cell adhesion. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1994, 2, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, S.V.; Velders, M.P.; Bakker, H.A.; Fleuren, G.J.; Warnaar, S.O. Ep-CAM: A human epithelial antigen is a homophilic cell–cell adhesion molecule. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzar, M.; Bakker, H.A.; Briaire-de-Bruijn, I.H.; Fleuren, G.J.; Warnaar, S.O.; Litvinov, S.V. Cytoplasmic tail regulates the intercellular adhesion function of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 4833–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzar, M.; Winter, M.J.; de Boer, C.J.; Litvinov, S.V. The biology of the 17-1A antigen (Ep-CAM). J. Mol. Med. 1999, 77, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzar, M.; Briaire-de Bruijn, I.H.; Rees-Bakker, H.A.M.; Prins, F.A.; Helfrich, W.; de Leij, L.; Riethmuller, G.; Alberti, S.; Warnaar, S.O.; Fleuren, G.J.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Repeats Mediate Lateral and Reciprocal Interactions of Ep-CAM Molecules in Homophilic Adhesions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 2570–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ripani, E.; Sacchetti, A.; Corda, D.; Alberti, S. Human Trop-2 is a tumor-associated calcium signal transducer. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 76, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Lenarcic, B.; Pavsic, M. Current View on EpCAM Structural Biology. Cells 2020, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, C.; Munz, M.; Kieu, C.; Mack, B.; Breinl, P.; Wollenberg, B.; Lang, S.; Zeidler, R.; Gires, O. Tumor-specific glycosylation of the carcinoma-associated epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM in head and neck carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2003, 193, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, M.; Fellinger, K.; Hofmann, T.; Schmitt, B.; Gires, O. Glycosylation is crucial for stability of tumour and cancer stem cell antigen EpCAM. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5195–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaye, M.N.; Hou, Q.; Basu, S.; Teheux, F.; Pucci, F.; Rooman, M. A comprehensive computational study of amino acid interactions in membrane proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.S.; Klingbeil, P.; Schnolzer, M.; Zoller, M. CD44 variant isoforms associate with tetraspanins and EpCAM. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 297, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claas, C.; Wahl, J.; Orlicky, D.J.; Karaduman, H.; Schnolzer, M.; Kempf, T.; Zoller, M. The tetraspanin D6.1A and its molecular partners on rat carcinoma cells. Biochem. J. 2005, 389, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balzar, M.; Prins, F.A.; Bakker, H.A.; Fleuren, G.J.; Warnaar, S.O.; Litvinov, S.V. The structural analysis of adhesions mediated by Ep-CAM. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 246, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, S.V.; Balzar, M.; Winter, M.J.; Bakker, H.A.; Briaire-de Bruijn, I.H.; Prins, F.; Fleuren, G.J.; Warnaar, S.O. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) modulates cell-cell interactions mediated by classic cadherins. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Kim, S.J.; Kaake, R.M.; Bencina, M.; Krogan, N.; Sali, A.; Pavsic, M.; Lenarcic, B. EpCAM homo-oligomerization is not the basis for its role in cell-cell adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Koch, M.; Nubel, T.; Ladwein, M.; Antolovic, D.; Klingbeil, P.; Hildebrand, D.; Moldenhauer, G.; Langbein, L.; Franke, W.W.; et al. A complex of EpCAM, claudin-7, CD44 variant isoforms, and tetraspanins promotes colorectal cancer progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nubel, T.; Preobraschenski, J.; Tuncay, H.; Weiss, T.; Kuhn, S.; Ladwein, M.; Langbein, L.; Zoller, M. Claudin-7 regulates EpCAM-mediated functions in tumor progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.J.; Mannan, P.; Lu, M.; Udey, M.C. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) regulates claudin dynamics and tight junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12253–12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Takechi, M.; Kiyonari, H.; Shioi, G.; Tamura, A.; Tsukita, S. Intestinal deletion of Claudin-7 enhances paracellular organic solute flux and initiates colonic inflammation in mice. Gut 2015, 64, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, A.I.M.; Kim, H.; Riedel-Kruse, I.H. Regulation of epithelial migration by epithelial cell adhesion molecule requires its Claudin-7 interaction domain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Maeda, T.; Tamura, A.; Nakamura, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shiratori, H.; Yashiro, K.; Tsukita, S.; Hamada, H. EpCAM contributes to formation of functional tight junction in the intestinal epithelium by recruiting claudin proteins. Dev. Biol. 2012, 371, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetzel, D.; Denzel, S.; Mack, B.; Canis, M.; Went, P.; Benk, M.; Kieu, C.; Papior, P.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Munz, M.; et al. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gires, O.; Pan, M.; Schinke, H.; Canis, M.; Baeuerle, P.A. Expression and function of epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM: Where are we after 40 years? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Perez, A.; Mack, B.; Maetzel, D.; Kremling, H.; Eggert, C.; Harreus, U.; Gires, O. EpCAM regulates cell cycle progression via control of cyclin D1 expression. Oncogene 2013, 32, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, T.; Goldstein, A.S.; Cai, H.; Drake, J.M.; Huang, J.; Witte, O.N. Regulated proteolysis of Trop2 drives epithelial hyperplasia and stem cell self-renewal via beta-catenin signaling. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachmeister, M.; Bobowski, K.D.; Hogl, S.; Dislich, B.; Fukumori, A.; Eggert, C.; Mack, B.; Kremling, H.; Sarrach, S.; Coscia, F.; et al. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis and degradation of murine epithelial cell adhesion molecule mEpCAM. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chanou, A.; Kranz, G.; Pan, M.; Kohlbauer, V.; Ettinger, A.; Gires, O. Membrane-associated epithelial cell adhesion molecule is slowly cleaved by gamma-secretase prior to efficient proteasomal degradation of its intracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaktanis, T.; Kremling, H.; Pavsic, M.; von Stackelberg, R.; Mack, B.; Fukumori, A.; Steiner, H.; Vielmuth, F.; Spindler, V.; Huang, Z.; et al. Cleavage and cell adhesion properties of human epithelial cell adhesion molecule (HEPCAM). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24574–24591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Schinke, H.; Luxenburger, E.; Kranz, G.; Shakhtour, J.; Libl, D.; Huang, Y.; Gaber, A.; Pavsic, M.; Lenarcic, B.; et al. EpCAM ectodomain EpEX is a ligand of EGFR that counteracts EGF-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition through modulation of phospho-ERK1/2 in head and neck cancers. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankpal, N.V.; Fleming, T.P.; Sharma, P.K.; Wiedner, H.J.; Gillanders, W.E. A double-negative feedback loop between EpCAM and ERK contributes to the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3706–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Werner, S.; Pantel, K. Biology and clinical relevance of EpCAM. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, K.; Zhu, J.; Heneghan, M.B.; Hanson, J.C.; Morasso, M.I.; Tessarollo, L.; Mackem, S.; Udey, M.C. Abnormal placental development and early embryonic lethality in EpCAM-null mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.; Lattanzio, R.; La Sorda, R.; Dini, F.; Tiboni, G.M.; Piantelli, M.; Alberti, S. mTrop1/Epcam knockout mice develop congenital tufting enteropathy through dysregulation of intestinal E-cadherin/beta-catenin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghzal, N.; Vogt, E.; Reintsch, W.; Fraser, J.S.; Fagotto, F. The tumor associated EpCAM regulates morphogenetic movements through intracellular signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 119, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagotto, F. The cellular basis of tissue separation. Development 2014, 141, 3303–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklbauer, R.; Parent, S.E. Forces driving cell sorting in the amphibian embryo. Mech. Dev. 2017, 144, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagotto, F. Tissue segregation in the early vertebrate embryo. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghzal, N.; Kayali, H.A.; Rohani, N.; Kajava, A.V.; Fagotto, F. EpCAM Controls Actomyosin Contractility and Cell Adhesion by Direct Inhibition of PKC. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slanchev, K.; Carney, T.J.; Stemmler, M.P.; Koschorz, B.; Amsterdam, A.; Schwarz, H.; Hammerschmidt, M. The Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule EpCAM Is Required for Epithelial Morphogenesis and Integrity during Zebrafish Epiboly and Skin Development. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villablanca, E.J.; Renucci, A.; Sapede, D.; Lec, V.; Soubiran, F.; Sandoval, P.C.; Dambly-Chaudiere, C.; Ghysen, A.; Allende, M.L. Control of cell migration in the zebrafish lateral line: Implication of the gene “tumour-associated calcium signal transducer,” tacstd. Dev. Dyn 2006, 235, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, O.; David, R.; Ninomiya, H.; Winklbauer, R. Large-scale mechanical properties of Xenopus embryonic epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4000–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, L.; Zarour, E.; Kashkooli, L.; Francois, P.; Fagotto, F. Sorting at embryonic boundaries requires high heterotypic interfacial tension. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkooli, L.; Rozema, D.; Espejo-Ramirez, L.; Lasko, P.; Fagotto, F. Ectoderm to mesoderm transition by downregulation of actomyosin contractility. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagnanam, M.; Mueller, J.L.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Nelson, S.F.; Turner, D.; Zlotkin, S.H.; Pencharz, P.B.; Ngan, B.Y.; Libiger, O.; et al. Identification of EpCAM as the gene for congenital tufting enteropathy. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.; Gaston, C.; Magescas, J.; Duvauchelle, B.; Canioni, D.; Sengmanivong, L.; Mayeux, A.; Michaux, G.; Campeotto, F.; Lemale, J.; et al. Contractile forces at tricellular contacts modulate epithelial organization and monolayer integrity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.J.; Lu, M.; Feng, X.; Nakato, G.; Udey, M.C. Matriptase Cleaves EpCAM and TROP2 in Keratinocytes, Destabilizing Both Proteins and Associated Claudins. Cells 2020, 9, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Keely, P.J. Mechanical signaling through the cytoskeleton regulates cell proliferation by coordinated focal adhesion and Rho GTPase signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyes, J.; Ganesan, A.; Molinar-Inglis, O.; Hamidzadeh, A.; Zhang, J.; Ling, M.; Trejo, J.; Levchenko, A.; Zhang, J. Signaling diversity enabled by Rap1-regulated plasma membrane ERK with distinct temporal dynamics. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J. PKD at the crossroads of DAG and PKC signaling. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2006, 27, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trerotola, M.; Jernigan, D.L.; Liu, Q.; Siddiqui, J.; Fatatis, A.; Languino, L.R. Trop-2 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by modulating beta(1) integrin functions. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3155–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trerotola, M.; Ganguly, K.K.; Fazli, L.; Fedele, C.; Lu, H.; Dutta, A.; Liu, Q.; De Angelis, T.; Riddell, L.W.; Riobo, N.A.; et al. Trop-2 is up-regulated in invasive prostate cancer and displaces FAK from focal contacts. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14318–14328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Isaji, T.; Zhang, G.; Qi, F.; Duan, C.; Fukuda, T.; Gu, J. EpCAM associates with integrin and regulates cell adhesion in cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Feng, X.; Lu, M.; Morimura, S.; Udey, M.C. Matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM destabilizes claudins and dysregulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavsic, M.; Guncar, G.; Djinovic-Carugo, K.; Lenarcic, B. Crystal structure and its bearing towards an understanding of key biological functions of EpCAM. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, S.; Takeda, K. ERK signalling as a regulator of cell motility. J. Biochem. 2017, 162, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degirmenci, U.; Wang, M.; Hu, J. Targeting Aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Ye, J.; Deng, F.; Wang, Q.J. Protein kinase D signaling in cancer: A friend or foe? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Full Name/Alternate Name | Functions/Comments | Kinase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytoskeleton | |||
| ADD1 | adducin 1 | assembly of spectrin–actin network | PKCδ |
| ARHGAP3 | β2 chimaerin | RacGAP | PKCδ |
| Arhgef15 | ephexin-5 | RhoGEF | PKCε |
| CENTA1 | ADAP1 | ArfGAP | PKCε |
| CFL1 | cofilin 1 | actin turnover | PKD |
| CORO1B | coronin 1B | PKCε | |
| CTTN | cortactin | actin organization | PKCδ, PKD |
| DLC1 | deleted in liver cancer 1 | RhoGAP | PKD |
| GIT1 | ArfGAP, adhesion and migration | PKD | |
| HAX1 | HCLS1-associated protein X-1 | regulates Arp2/3 recruitment to cortex | PKCδ |
| IQGAP1 | binds activated CDC42, scaffold protein | PKCε | |
| LCP1 | L-plastin | actin-binding protein | PKCδ |
| LIMK2 | LIM kinase 2 | PKCδ | |
| MYPC3 | myosin-binding protein C | PKCδ | |
| MARK2 | Ser/Thr-protein kinase | cell polarity, microtubule dynamics | PKD |
| MIIP | migration/invasion-inhib prot | PKCε | |
| PAK4 | p21-activated kinase 4 | activated by cdc42 and Rac1 | PKCδ, PKD |
| PIP5K1B | PIP5 kinase 1β | Rac1-dep. reorganization actin filaments | PKCδ |
| PLCB3 | phospholipase C-β-3 | PKCε | |
| PLD2 | phospholipase D2 | signal-induced cytoskeletal regulation | PKCδ |
| Plekhg5 | RhoGEF | PKD | |
| PPP1R14A,B | PP1 regulatory subunit14A,B | myosin regulation | PKCδ,ε,PKD |
| PREX1 | RacGEF | Rac activator | PKCδ |
| PRKD | PKD | PKCδ,ε | |
| RASGRP3 | GEF for Ras and Rap1 | PKCδ | |
| REM1 | actin cytoskeletal reorganization | PKD | |
| Rhotekin | Rho effector | PKD | |
| Src | Src kinase | PKCδ | |
| SHH3 | phosphatase Slingshot homolog 1 | cofilin activation | PKD |
| TAGLN | Transgelin | actin cross-linking/gelling protein | PKCδ |
| VASP | actin nucleator | PKD | |
| Cell–Cell and Cell–Matrix Adhesion | |||
| CDH2 | N-cadherin | PKD | |
| CIB1 | calcium and integrin-binding protein 1 | PKD | |
| CTNNB1 | β-catenin | PKCδ,ε,PKD | |
| ITGB1 | Integrin β1 | PKCη | |
| ITGB2 | Integrin β2 | PKCδ,ε | |
| ITGB4 | Integrin β4 | PKD | |
| PTPRA | recept tyr phosphatase α | integrin–Src–PAK–Rac signalling | PKCδ |
| PXN | paxillin | major integrin–actin cross-linker | PKCδ |
| SDC4 | syndecan-4 | cell surface proteoglycan/binds fibronectin | PKCδ |
| Tight Junctions | |||
| OCLN | occludin | Core component | PKCε |
| Tjp1,2 | ZO1,2 | adaptor, linker to actin, signalling | PKCε |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fagotto, F. EpCAM as Modulator of Tissue Plasticity. Cells 2020, 9, 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092128
Fagotto F. EpCAM as Modulator of Tissue Plasticity. Cells. 2020; 9(9):2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092128
Chicago/Turabian StyleFagotto, François. 2020. "EpCAM as Modulator of Tissue Plasticity" Cells 9, no. 9: 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092128
APA StyleFagotto, F. (2020). EpCAM as Modulator of Tissue Plasticity. Cells, 9(9), 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092128