Impact of Pre-Analytical Factors on MSI Test Accuracy in Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Multi-Assay Concordance Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
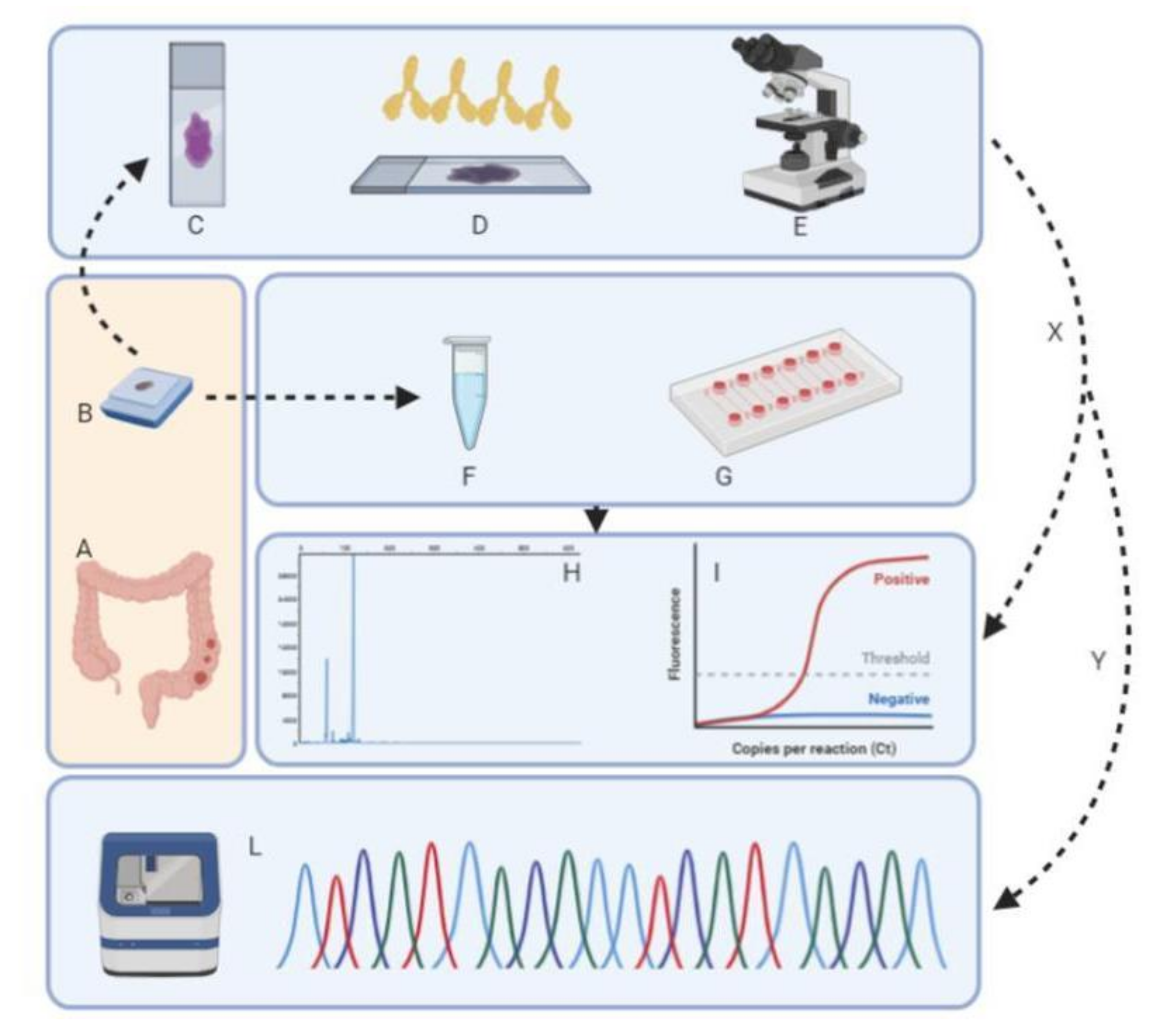
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Qualification
2.4. Microfluidic Analysis for MSI Status Evaluation
2.5. Idylla™ MSI Assay
2.6. Titano MSI Test
3. Results
3.1. MMR and MSI Status on Acellular Mucin
3.2. Sample Stratification by Year
3.3. MMR and MSI Status on Neoplastic Cells
3.4. MMR and MSI Status Based on DNA Quantity and Quality
3.5. Analysis of Discordant Samples due to Low Quality of DNA Integrity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remo, A.; Fassan, M.; Lanza, G. Immunohistochemical evaluation of mismatch repair proteins in colorectal carcinoma: The AIFEG/GIPAD proposal. Pathologica 2016, 108, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luchini, C.; Bibeau, F.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; Singh, N.; Nottegar, A.; Bosse, T.; Miller, R.; Riaz, N.; Douillard, J.Y.; Andre, F.; et al. ESMO recommendations on microsatellite instability testing for immunotherapy in cancer, and its relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumour mutational burden: A systematic review-based approach. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppini, F.; Opocher, E.; Tabori, U.; Mammi, I.; Edwards, M.; Campbell, B.; Kelly, J.; Viel, A.; Quaia, M.; Rivieri, F.; et al. Concomitant IDH wild-type glioblastoma and IDH1-mutant anaplastic astrocytoma in a patient with constitutional mismatch repair deficiency syndrome. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indraccolo, S.; Lombardi, G.; Fassan, M.; Pasqualini, L.; Giunco, S.; Marcato, R.; Gasparini, A.; Candiotto, C.; Nalio, S.; Fiduccia, P.; et al. Genetic, epigenetic, and immunologic profiling of MMR-deficient relapsed glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Panarelli, N.C.; Rennert, H.; Sherr, D.L.; Yantiss, R.K. Neoadjuvant therapy induces loss of MSH6 expression in colorectal carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, A.R.; Hamilton, S.R.; Allegra, C.J.; Grody, W.; Cushman-Vokoun, A.M.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Kopetz, S.E.; Lieu, C.; Lindor, N.M.; Minsky, B.D.; et al. Molecular biomarkers for the evaluation of colorectal cancer: Guideline from the American society for clinical pathology, college of American pathologists, association for molecular pathology, and American society of clinical oncology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 625–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Setton, J.; Lee, N.Y.; Riaz, N.; Powell, S.N. The therapeutic significance of mutational signatures from DNA repair deficiency in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Boland, C.R.; Terdiman, J.P.; Syngal, S.; de la Chapelle, A.; Rüschoff, J.; Fishel, R.; Lindor, N.M.; Burgart, L.J.; Hamelin, R.; et al. Revised Bethesda Guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Nagasaka, T.; Hamelin, R.; Boland, C.R. An optimized pentaplex PCR for detecting DNA mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancers. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9393, Erratum in 2010, 5, 10.1371/annotation/572bb6d3-0315-40b1-a6d7-ce818809b5ea. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, A.; De Luca, C.; Cariou, M.; Vigliar, E.; Barel, F.; Conticelli, F.; Marcorelles, P.; Nousbaum, J.B.; Robaszkiewicz, M.; Samaison, L.; et al. Evaluation of KRAS, NRAS and BRAF mutational status and microsatellite instability in early colorectal carcinomas invading the submucosa (pT1): Towards an in-house molecular prognostication for pathologists? J. Clin. Pathol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaison, L.; Grall, M.; Staroz, F.; Uguen, A. Microsatellite instability diagnosis using the fully automated Idylla™ platform: Feasibility study of an in-house rapid molecular testing ancillary to immunohistochemistry in pathology laboratories. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, F.; Smeraglio, R.; Vacirca, D.; Malapelle, U.; Barberis, M.; Troncone, G. Microsatellite instability evaluation by automated microfluidic electrophoresis: An update. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenthal, M.; Barta, N.; Lohfink, D.; Drebber, U.; Schulze, F.; Dienes, H.P.; Baldus, S.E. Analysis of microsatellite instability in colorectal carcinoma by microfluidic-based chip electrophoresis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupakis, F.; Depetris, I.; Biason, P.; Intini, R.; Prete, A.A.; Leone, F.; Lombardi, P.; Filippi, R.; Spallanzani, A.; Cascinu, S.; et al. Prediction of benefit from checkpoint inhibitors in mismatch repair deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: Role of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Oncologist 2020, 25, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, J.; Schultz, N.; Kuk, D.; Vakiani, E.; Middha, S.; Segal, N.H.; Hechtman, J.F.; Berger, M.F.; Stadler, Z.K.; Weiser, M.R.; et al. Morphological characterization of colorectal cancers in The Cancer Genome Atlas reveals distinct morphology-molecular associations: Clinical and biological implications. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, J.; Holck, S.; Depetris, G.; Greenson, J.K.; Klimstra, D.S. Lynch syndrome-associated neoplasms: A discussion on histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Fam. Cancer 2013, 12, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugen, N.; van Beek, J.J.; de Wilt, J.H.; Nagtegaal, I.D. Insight into mucinous colorectal carcinoma: Clues from etiology. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2963–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remo, A.; Fassan, M.; Vanoli, A.; Bonetti, L.R.; Barresi, V.; Tatangelo, F.; Gafà, R.; Giordano, G.; Pancione, M.; Grillo, F.; et al. Morphology and molecular features of rare colorectal carcinoma histotypes. Cancers 2019, 11, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechtman, J.F.; Middha, S.; Stadler, Z.K.; Zehir, A.; Berger, M.F.; Vakiani, E.; Weiser, M.R.; Ladanyi, M.; Saltz, L.B.; Klimstra, D.S.; et al. Universal screening for microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer in the clinical genomics era: New recommendations, methods, and considerations. Fam. Cancer 2017, 16, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Hubner, R.; Houlston, R.S. Systematic review of microsatellite instability and colorectal cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, T.; Shiu, K.-K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.J.A.; Smith, D.M.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: The phase 3 KEYNOTE-177 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Lonardi, S.; Wong, K.Y.M.; Lenz, H.J.; Gelsomino, F.; Aglietta, M.; Morse, M.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; McDermott, R.; Hill, A.; et al. Durable clinical benefit with nivolumab plus ipilimumab in DNA mismatch repair-deficient/microsatellite instability-high metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overman, M.J.; McDermott, R.; Leach, J.L.; Lonardi, S.; Lenz, H.J.; Morse, M.A.; Desai, J.; Hill, A.; Axelson, M.; Moss, R.A.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Cristescu, R.; Bass, A.J.; Kim, K.M.; Odegaard, J.I.; Kim, K.; Liu, X.Q.; Sher, X.; Jung, H.; Lee, M.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Jin, L.; Wu, G.; Bai, Z.; Wang, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. Prognostic value of the combination of microsatellite instability and BRAF mutation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3911–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Hain, E.; Buhard, O.; Guilloux, A.; Bardier, A.; Kaci, R.; Bertheau, P.; Renaud, F.; Bibeau, F.; Fléjou, J.F.; et al. Association of primary resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic colorectal cancer with misdiagnosis of microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency status. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, J. Immunohistochemistry versus microsatellite instability testing for screening colorectal cancer patients at risk for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer syndrome. Part I. The utility of immunohistochemistry. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours—Digestive System Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019.
- Sarode, V.R.; Robinson, L. Screening for lynch syndrome by immunohistochemistry of mismatch repair proteins: Significance of indeterminate result and correlation with mutational studies. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Capo-Chichi, J.M.; Spence, T.; Grenier, S.; Stockley, T.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Serra, S.; Sabatini, P.; Chetty, R. Heterogenous loss of mismatch repair (MMR) protein expression: A challenge for immunohistochemical interpretation and microsatellite instability (MSI) evaluation. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2019, 5, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Kemel, Y.; Shia, J.; Bandlamudi, C.; Mandelker, D.; Middha, S.; Hechtman, J.; Zehir, A.; Dubard-Gault, M.; et al. Microsatellite instability is associated with the presence of lynch syndrome pan-cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| IHC vs. Tape Station 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | IHC | ||
| dMMR | pMMR | Total | |
| MSI-H | 10 (13.7) | 2 (2.7) | 12 (16.4) |
| MSS | 12 (16.4) | 49 (67.1) | 61 (83.6) |
| Total | 22 (30.1) | 51 (69.9) | 73 (100.0) |
| k = 0.48; 95% C.I.: 0.25 to 0.7. | |||
| IHC vs. Idylla™ | |||
| Idylla™ | IHC | ||
| dMMR | pMMR | Total | |
| MSI-H | 18 (24.6) | 1 (1.4) | 19 (26.0) |
| MSS | 4 (5.5) | 50 (68.5) | 54 (74.0) |
| Total | 22 (30.1) | 51 (69.9) | 73 (100.0) |
| k = 0.83; 95% C.I.: 0.69 to 0.97. | |||
| Idylla™ vs. Tape Station 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | Idylla™ | ||
| MSI-H | MSS | Total | |
| MSI-H | 11 (15.0) | 1 (1.4) | 12 (16.4) |
| MSS | 8 (11.0) | 53 (72.6) | 61 (83.6) |
| Total | 19 (26.0) | 54 (74.0) | 73 (100.0) |
| k = 0.64; 95% C.I.: 0.43 to 0.85. | |||
| ≤50% Neoplastic Cells IHC vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 1 (4.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.5) |
| MSS | 4 (18.2) | 17 (77.3) | 21 (95.5) |
| Total | 5 (22.7) | 17 (77.3) | 22 (100.0) |
| k = 0.28; 95% C.I.: −0.16 to 0.72. | |||
| >50% Neoplastic Cells IHC vs. Tape Station 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 9 (17.6) | 2 (3.9) | 11 (21.6) |
| MSS | 8 (15.7) | 32 (62.7) | 40 (78.4) |
| Total | 17 (33.3) | 34 (66.7) | 51 (100.0) |
| k = 0.52; 95% C.I.: 0.26 to 0.77; p-value for difference between k: 0.142. | |||
| ≤50% Neoplastic Cells IHC vs. Idylla™ | |||
| Idylla™ | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 2 (9.1) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (9.1) |
| MSS | 3 (13.6) | 17 (77.3) | 20 (90.9) |
| Total | 5 (22.7) | 17 (77.3) | 22 (100.0) |
| k = 0.51; 95% C.I.: 0.06 to 0.96. | |||
| >50% Neoplastic Cells IHC vs. Idylla™ | |||
| Idylla™ | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 16 (31.4) | 1 (2.0) | 17 (33.3) |
| MSS | 1 (2.0) | 33 (64.7) | 34 (66.7) |
| Total | 17 (33.3) | 34 (66.7) | 51 (100.0) |
| k = 0.91; 95% C.I.: 0.79 to 1; p-value for difference between k: 0.002. | |||
| ≤50% Neoplastic Cells Idylla™ vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | Idylla™ | Total | |
| MSI-H | MSS | ||
| MSI-H | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.2) |
| MSS | 1 (4.2) | 22 (91.7) | 23 (95.8) |
| Total | 2 (8.3) | 22 (91.7) | 24 (100.0) |
| k = 0.65; 95% C.I.: 0.01 to 1. | |||
| >50% Neoplastic Cells Idylla™ vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | Idylla™ | Total | |
| MSI-H | MSS | ||
| MSI-H | 10 (19.6) | 1 (2.0) | 11 (21.6) |
| MSS | 7 (13.7) | 33 (64.7) | 40 (78.4) |
| Total | 17 (33.3) | 34 (66.7) | 51 (100.0) |
| k = 0.61; 95% C.I.: 0.38 to 0.85; p-value for difference between k: 0.913. | |||
| DIN < 4 IHC vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 3 (7.1) | 1 (2.4) | 4 (9.5) |
| MSS | 10 (23.8) | 28 (66.7) | 38 (90.5) |
| Total | 13 (31.0) | 29 (69.0) | 42 (100.0) |
| k = 0.24; 95% C.I.: −0.04 to 0.52. | |||
| DIN ≥ 4 IHC vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 7 (24.1) | 1 (3.4) | 8 (27.6) |
| MSS | 1 (3.4) | 20 (69.0) | 21 (72.4) |
| Total | 8 (27.6) | 21 (72.4) | 29 (100.0) |
| k = 0.83; 95% C.I.: 0.6 to 1; p-value for difference between k: 0.009. | |||
| DIN < 4 IHC vs. Idylla™ | |||
| Idylla™ | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 9 (21.4) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (21.4) |
| MSS | 4 (9.5) | 29 (69.0) | 33 (78.6) |
| Total | 13 (31.0) | 29 (69.0) | 42 (100.0) |
| k = 0.76; 95% C.I.: 0.54 to 0.98. | |||
| DIN ≥ 4 IHC vs. Idylla™ | |||
| Idylla™ | IHC | Total | |
| dMMR | pMMR | ||
| MSI-H | 8 (27.6) | 1 (3.4) | 9 (31.0) |
| MSS | 0 (0.0) | 20 (69.0) | 20 (69.0) |
| Total | 8 (27.6) | 21 (72.4) | 29 (100.0) |
| k = 0.92; 95% C.I.: 0.76 to 1; p-value for difference between k: 0.285 | |||
| DIN < 4 Idylla™ vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | Idylla™ | Total | |
| MSI-H | MSS | ||
| MSI-H | 3 (7.1) | 1 (2.4) | 4 (9.5) |
| MSS | 6 (14.3) | 32 (76.2) | 38 (90.5) |
| Total | 9 (21.4) | 33 (78.6) | 42 (100.0) |
| k = 0.38; 95% C.I.: 0.03 to 0.73. | |||
| DIN ≥ 4 Idylla™ vs. TapeStation 4200 | |||
| TapeStation 4200 | Idylla™ | Total | |
| MSI-H | MSS | ||
| MSI-H | 8 (27.6) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (27.6) |
| MSS | 1 (3.4) | 20 (69.0) | 21 (72.4) |
| Total | 9 (31.0) | 20 (69.0) | 29 (100.0) |
| k = 0.92; 95% C.I.: 0.76 to 1; p-value for difference between k: 0.012 | |||
| Titano | IHC | Idylla™ | TapeStation 4200 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSS | pMMR | MSS | MSI-H |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS * |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS |
| MSS | dMMR | MSS | MSS |
| MSS | dMMR | MSS | MSS |
| MSS | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS * |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS * |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS * |
| MSI | dMMR | MSI-H | MSS * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malapelle, U.; Parente, P.; Pepe, F.; De Luca, C.; Cerino, P.; Covelli, C.; Balestrieri, M.; Russo, G.; Bonfitto, A.; Pisapia, P.; et al. Impact of Pre-Analytical Factors on MSI Test Accuracy in Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Multi-Assay Concordance Study. Cells 2020, 9, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092019
Malapelle U, Parente P, Pepe F, De Luca C, Cerino P, Covelli C, Balestrieri M, Russo G, Bonfitto A, Pisapia P, et al. Impact of Pre-Analytical Factors on MSI Test Accuracy in Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Multi-Assay Concordance Study. Cells. 2020; 9(9):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092019
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalapelle, Umberto, Paola Parente, Francesco Pepe, Caterina De Luca, Pellegrino Cerino, Claudia Covelli, Mariangela Balestrieri, Gianluca Russo, Antonio Bonfitto, Pasquale Pisapia, and et al. 2020. "Impact of Pre-Analytical Factors on MSI Test Accuracy in Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Multi-Assay Concordance Study" Cells 9, no. 9: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092019
APA StyleMalapelle, U., Parente, P., Pepe, F., De Luca, C., Cerino, P., Covelli, C., Balestrieri, M., Russo, G., Bonfitto, A., Pisapia, P., Fiordelisi, F., D’Armiento, M., Bruzzese, D., Loupakis, F., Pietrantonio, F., Triassi, M., Fassan, M., Troncone, G., & Graziano, P. (2020). Impact of Pre-Analytical Factors on MSI Test Accuracy in Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Multi-Assay Concordance Study. Cells, 9(9), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092019












