Mertk Interacts with Tim-4 to Enhance Tim-4-Mediated Efferocytosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.2. Plasmids and Antibodies
2.3. Mice
2.4. Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
2.5. Immunostaining
2.6. Efferocytosis Assay
2.7. Proximity Ligation Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
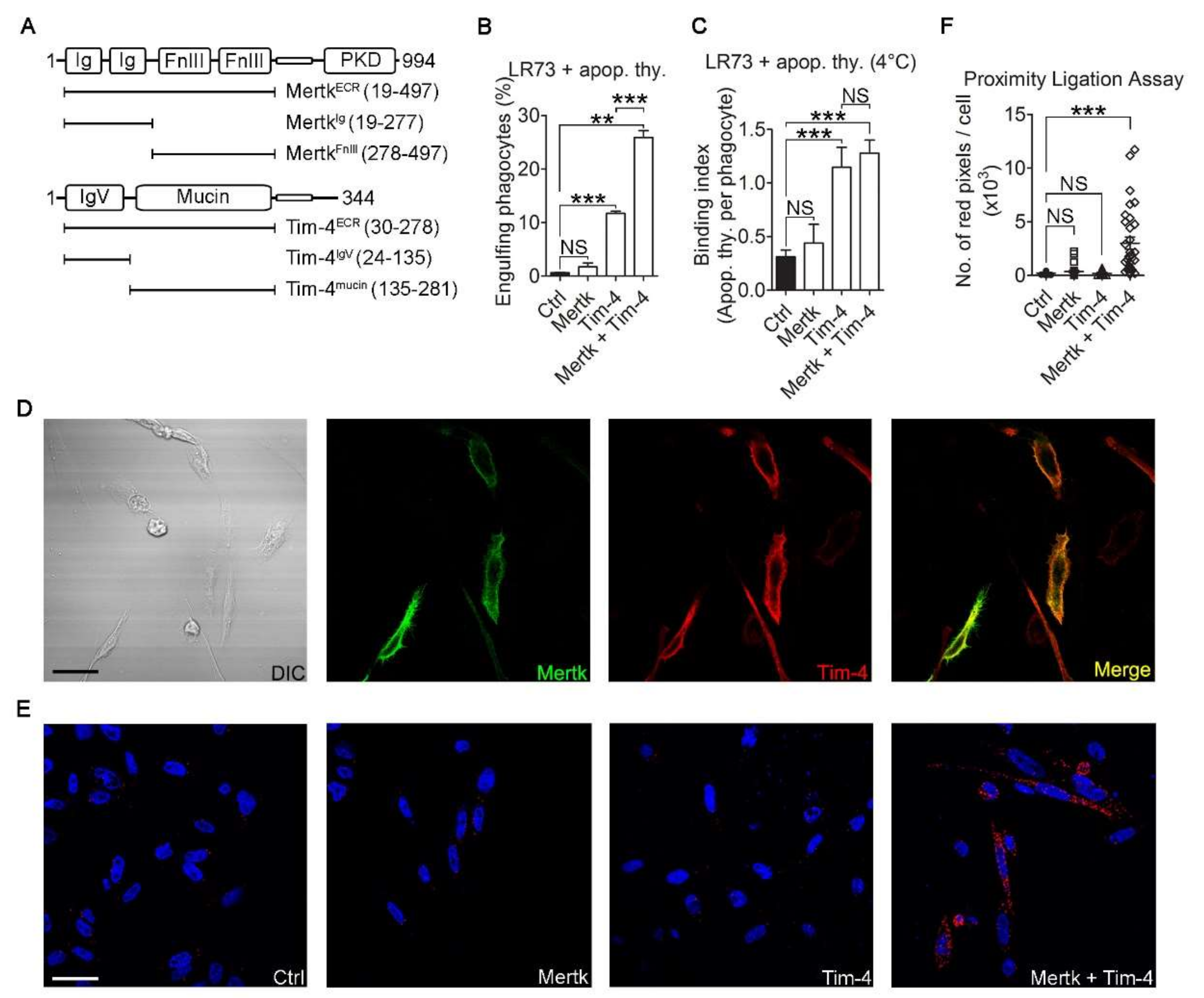
3.1. Tim-4 is Co-Localized with Mertk
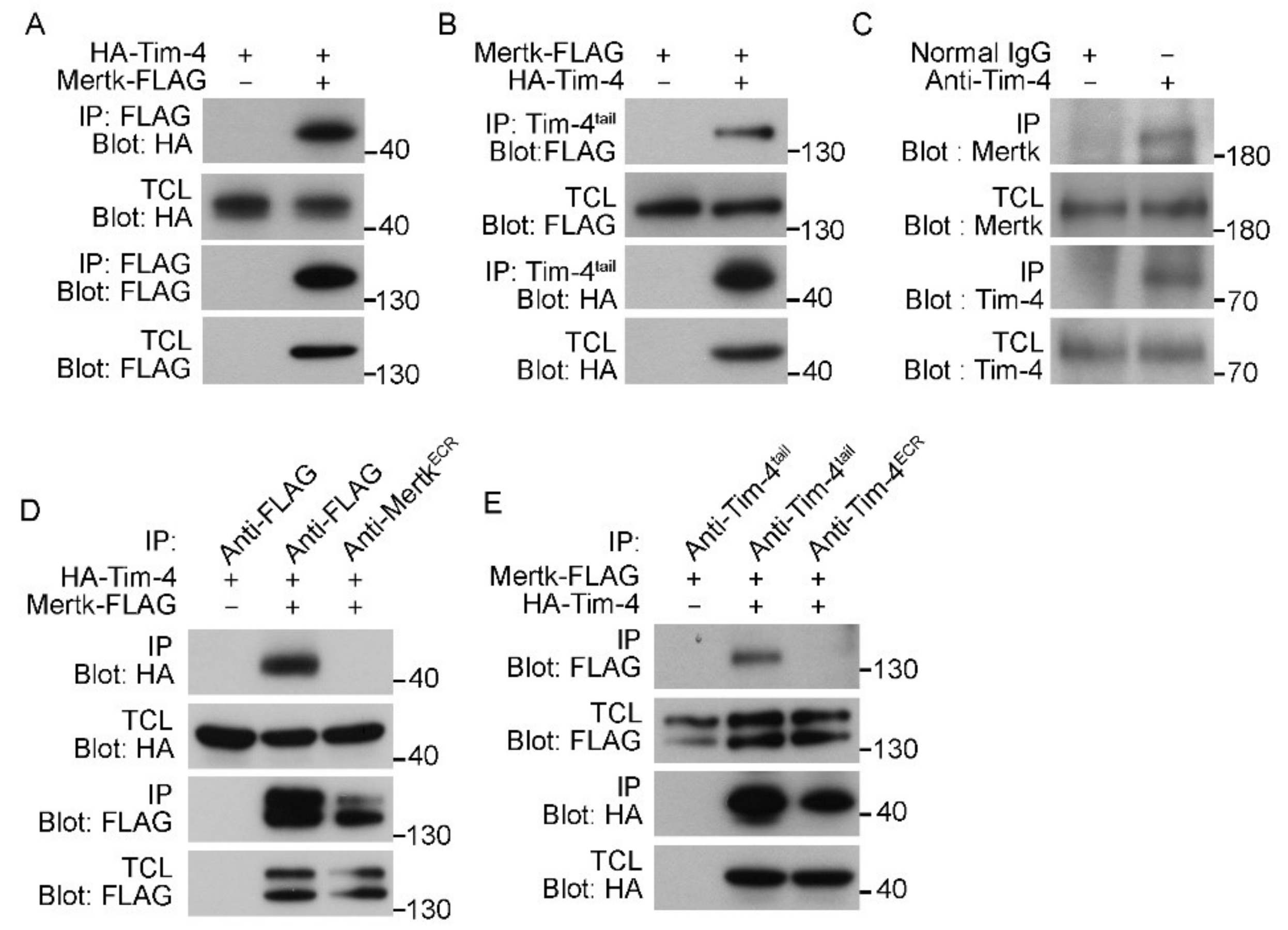
3.2. Tim-4 Interacts with Mertk
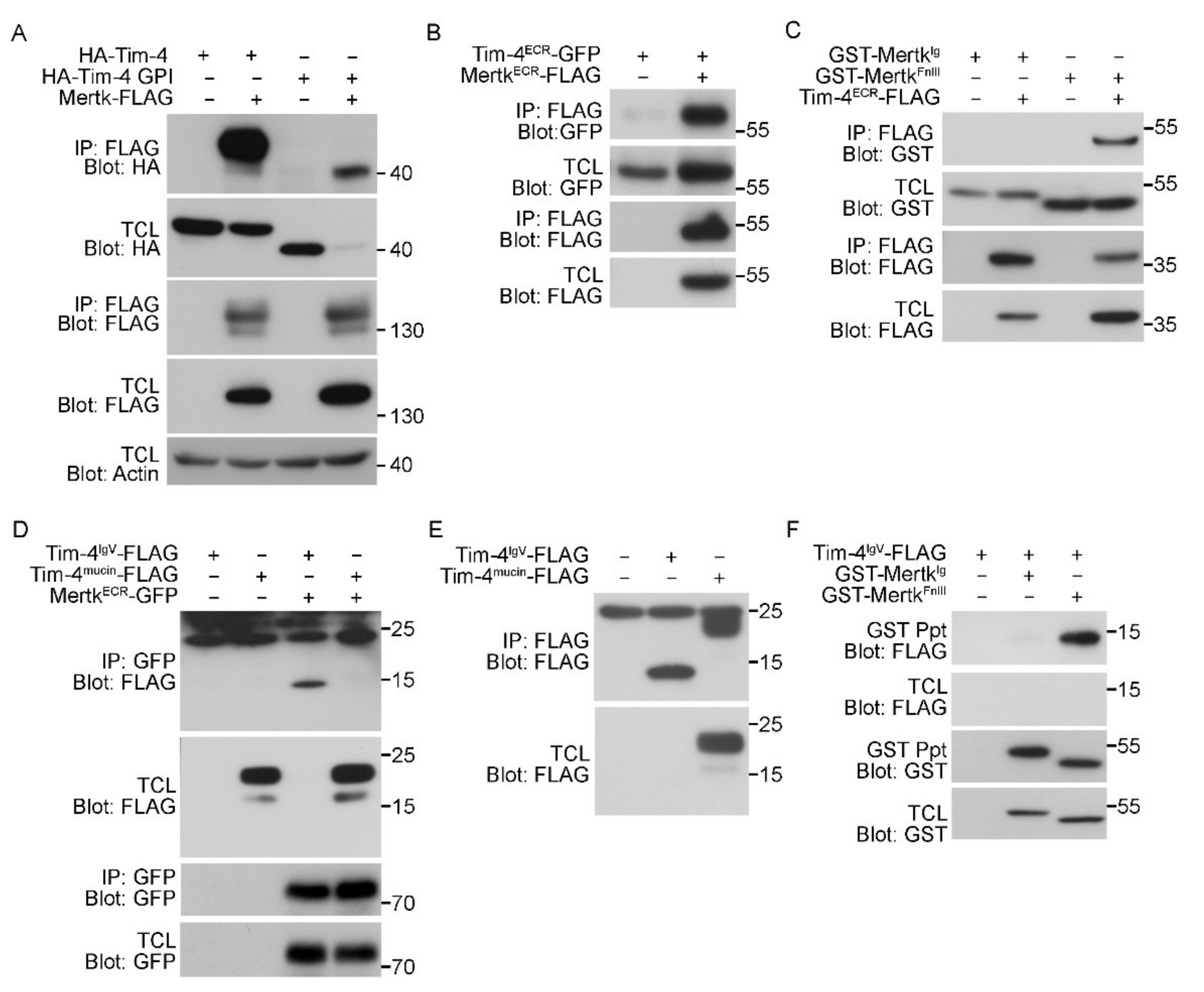
3.3. The IgV Domain of Tim-4 Binds to the Fibronectin Type III Domain of Mertk
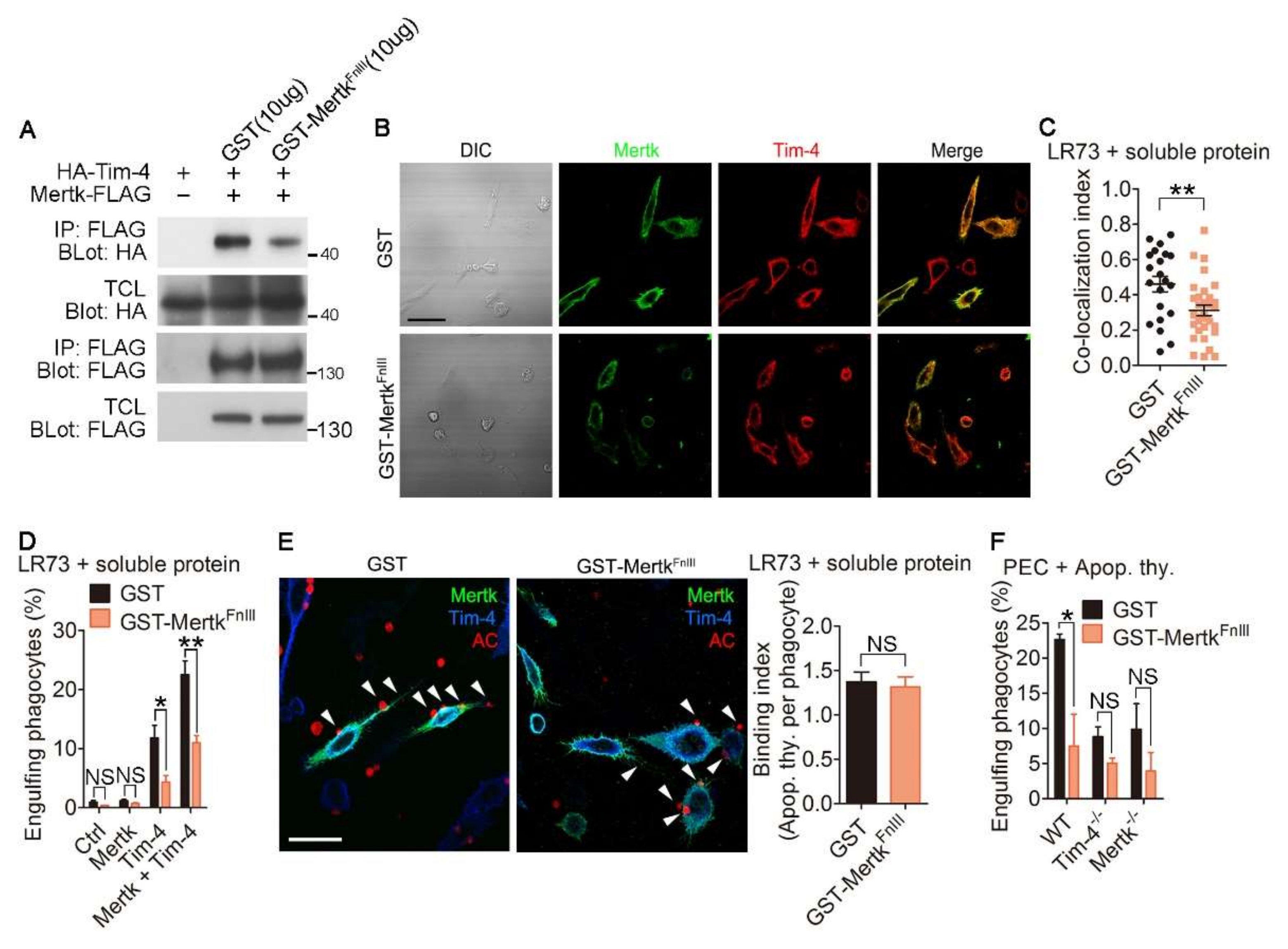
3.4. Disrupting the Interaction between Tim-4 and Mertk Abolishes the Effect of Mertk on Tim-4-Mediated Efferocytosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savill, J.; Dransfield, I.; Gregory, C.; Haslett, C. A blast from the past: Clearance of apoptotic cells regulates immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savill, J.; Fadok, V. Corpse clearance defines the meaning of cell death. Nature 2000, 407, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morioka, S.; Maueroder, C.; Ravichandran, K.S. Living on the Edge: Efferocytosis at the Interface of Homeostasis and Pathology. Immunity 2019, 50, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter-Hufford, A.; Ravichandran, K.S. Clearing the dead: Apoptotic cell sensing, recognition, engulfment, and digestion. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwig, L.P.; Henson, P.M. Clearance of apoptotic cells by phagocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Denning, D.P.; Imanishi, E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Nagata, S. Xk-related protein 8 and CED-8 promote phosphatidylserine exposure in apoptotic cells. Science 2013, 341, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stace, C.L.; Ktistakis, N.T. Phosphatidic acid-and phosphatidylserine-binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadok, V.A.; Bratton, D.L.; Frasch, S.C.; Warner, M.L.; Henson, P.M. The role of phosphatidylserine in recognition of apoptotic cells by phagocytes. Cell Death Differ. 1998, 5, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Owen, K.A.; Ly, K.T.; Park, D.; Black, S.G.; Wilson, J.M.; Sifri, C.D.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Ernst, P.B.; Casanova, J.E. Brain angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1) is a pattern recognition receptor that mediates macrophage binding and engulfment of Gram-negative bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Jung, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, B.H.; Kwon, T.H.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S. Rapid cell corpse clearance by stabilin-2, a membrane phosphatidylserine receptor. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, M.; Tada, K.; Koike, M.; Uchiyama, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Nagata, S. Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 2007, 450, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kubo, H.; Morimoto, K.; Fujino, N.; Suzuki, T.; Takahasi, T.; Yamada, M.; Yamaya, M.; Maekawa, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products binds to phosphatidylserine and assists in the clearance of apoptotic cells. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, A.; Banerjee, S.; Xie, N.; Cui, H.; Davis, K.I.; Friggeri, A.; Fu, M.; Abraham, E.; Liu, G. Identification of TLT2 as an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6381–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.S.; McMahon, E.J.; Pop, S.M.; Reap, E.A.; Caricchio, R.; Cohen, P.L.; Earp, H.S.; Matsushima, G.K. Phagocytosis and clearance of apoptotic cells is mediated by MER. Nature 2001, 411, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanayama, R.; Tanaka, M.; Miwa, K.; Shinohara, A.; Iwamatsu, A.; Nagata, S. Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 2002, 417, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, G.; Burstyn-Cohen, T. TAM receptors and the clearance of apoptotic cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1209, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardai, S.J.; McPhillips, K.A.; Frasch, S.C.; Janssen, W.J.; Starefeldt, A.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Bratton, D.L.; Oldenborg, P.A.; Michalak, M.; Henson, P.M. Cell-surface calreticulin initiates clearance of viable or apoptotic cells through trans-activation of LRP on the phagocyte. Cell 2005, 123, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Hochreiter-Hufford, A.; Ravichandran, K.S. The phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-4 does not mediate direct signaling. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.; Moon, B.; Park, J.; Moon, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.A.; Kim, D.; Min, C.; Lee, D.H.; et al. A scaffold for signaling of Tim-4-mediated efferocytosis is formed by fibronectin. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devitt, A.; Moffatt, O.D.; Raykundalia, C.; Capra, J.D.; Simmons, D.L.; Gregory, C.D. Human CD14 mediates recognition and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nature 1998, 392, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, C.; Toda, S.; Segawa, K.; Nagata, S. Tim4- and MerTK-mediated engulfment of apoptotic cells by mouse resident peritoneal macrophages. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, S.; Hanayama, R.; Nagata, S. Two-step engulfment of apoptotic cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Lee, J.; Moon, H.; Lee, G.; Lee, D.H.; Cho, J.H.; Park, D. Co-receptors are dispensable for tethering receptor-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Canton, J.; Furuya, W.; Glogauer, M.; Grinstein, S. The phosphatidylserine receptor TIM4 utilizes integrins as coreceptors to effect phagocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Karisola, P.; Pena-Cruz, V.; Dorfman, D.M.; Jinushi, M.; Umetsu, S.E.; Butte, M.J.; Nagumo, H.; Chernova, I.; Zhu, B.; et al. TIM-1 and TIM-4 glycoproteins bind phosphatidylserine and mediate uptake of apoptotic cells. Immunity 2007, 27, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, C.; Ballesteros, A.; Martinez-Munoz, L.; Mellado, M.; Kaplan, G.G.; Freeman, G.J.; Casasnovas, J.M. Structures of T cell immunoglobulin mucin protein 4 show a metal-Ion-dependent ligand binding site where phosphatidylserine binds. Immunity 2007, 27, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.H.; Chakravarti, S.; Schlesinger, D.; Illes, Z.; Waldner, H.; Umetsu, S.E.; Kenny, J.; Zheng, X.X.; Umetsu, D.T.; DeKruyff, R.H.; et al. TIM-4 is the ligand for TIM-1, and the TIM-1-TIM-4 interaction regulates T cell proliferation. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.H.; Sabatos, C.A.; Chakravarti, S.; Kuchroo, V.K. The TIM gene family regulates autoimmune and allergic diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, G.J.; Casasnovas, J.M.; Umetsu, D.T.; DeKruyff, R.H. TIM genes: A family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 235, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.M.; Camenisch, T.D.; Lemke, G.; Earp, H.S.; Matsushima, G.K. Macrophages and dendritic cells use different Axl/Mertk/Tyro3 receptors in clearance of apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5635–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, H.; Park, B.; Kim, D.; Joo, Y.E.; Park, D. Intermolecular steric inhibition of Ephexin4 is relieved by Elmo1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, C.; Yanagihashi, Y.; Segawa, K.; Nagata, S. MERTK tyrosine kinase receptor together with TIM4 phosphatidylserine receptor mediates distinct signal transduction pathways for efferocytosis and cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 7221–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, B.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.-A.; Min, C.; Moon, H.; Kim, D.; Yang, S.; Moon, H.; Jeon, J.; Joo, Y.-E.; et al. Mertk Interacts with Tim-4 to Enhance Tim-4-Mediated Efferocytosis. Cells 2020, 9, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071625
Moon B, Lee J, Lee S-A, Min C, Moon H, Kim D, Yang S, Moon H, Jeon J, Joo Y-E, et al. Mertk Interacts with Tim-4 to Enhance Tim-4-Mediated Efferocytosis. Cells. 2020; 9(7):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071625
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Byeongjin, Juyeon Lee, Sang-Ah Lee, Chanhyuk Min, Hyunji Moon, Deokhwan Kim, Susumin Yang, Heera Moon, Jaeseon Jeon, Young-Eun Joo, and et al. 2020. "Mertk Interacts with Tim-4 to Enhance Tim-4-Mediated Efferocytosis" Cells 9, no. 7: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071625
APA StyleMoon, B., Lee, J., Lee, S.-A., Min, C., Moon, H., Kim, D., Yang, S., Moon, H., Jeon, J., Joo, Y.-E., & Park, D. (2020). Mertk Interacts with Tim-4 to Enhance Tim-4-Mediated Efferocytosis. Cells, 9(7), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071625





