Water-Soluble closo-Docecaborate-Containing Pteroyl Derivatives Targeting Folate Receptor-Positive Tumors for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Methods
2.2. MTT Assay
2.3. Cell Uptake Study
2.4. Immunofluorescence
3. Results
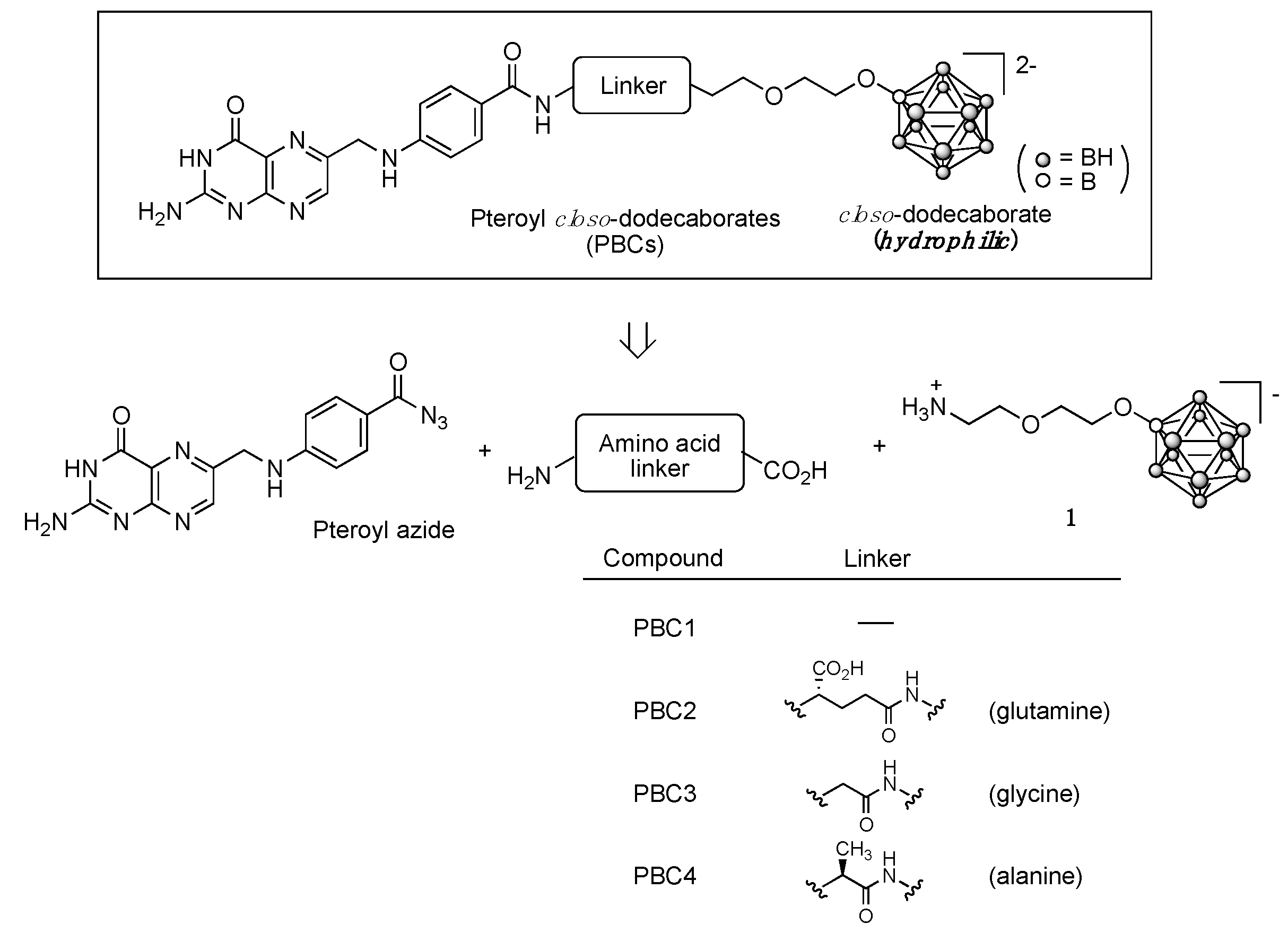
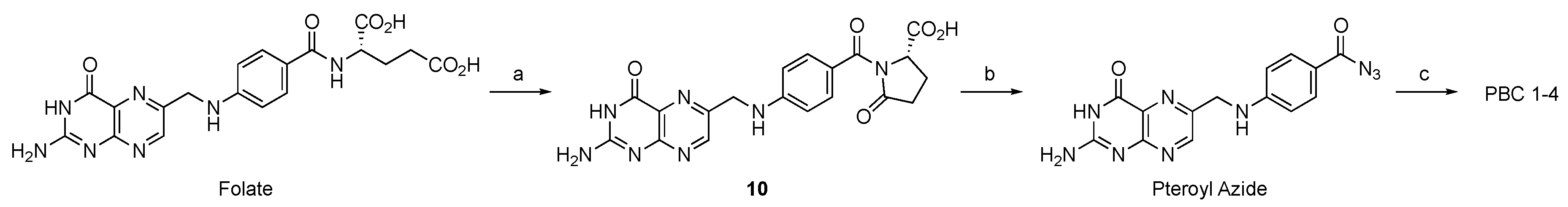
3.1. Design and Synthesis of Pteroyl Closo-Dodecaborates
3.2. Cytotoxicity of PBCs
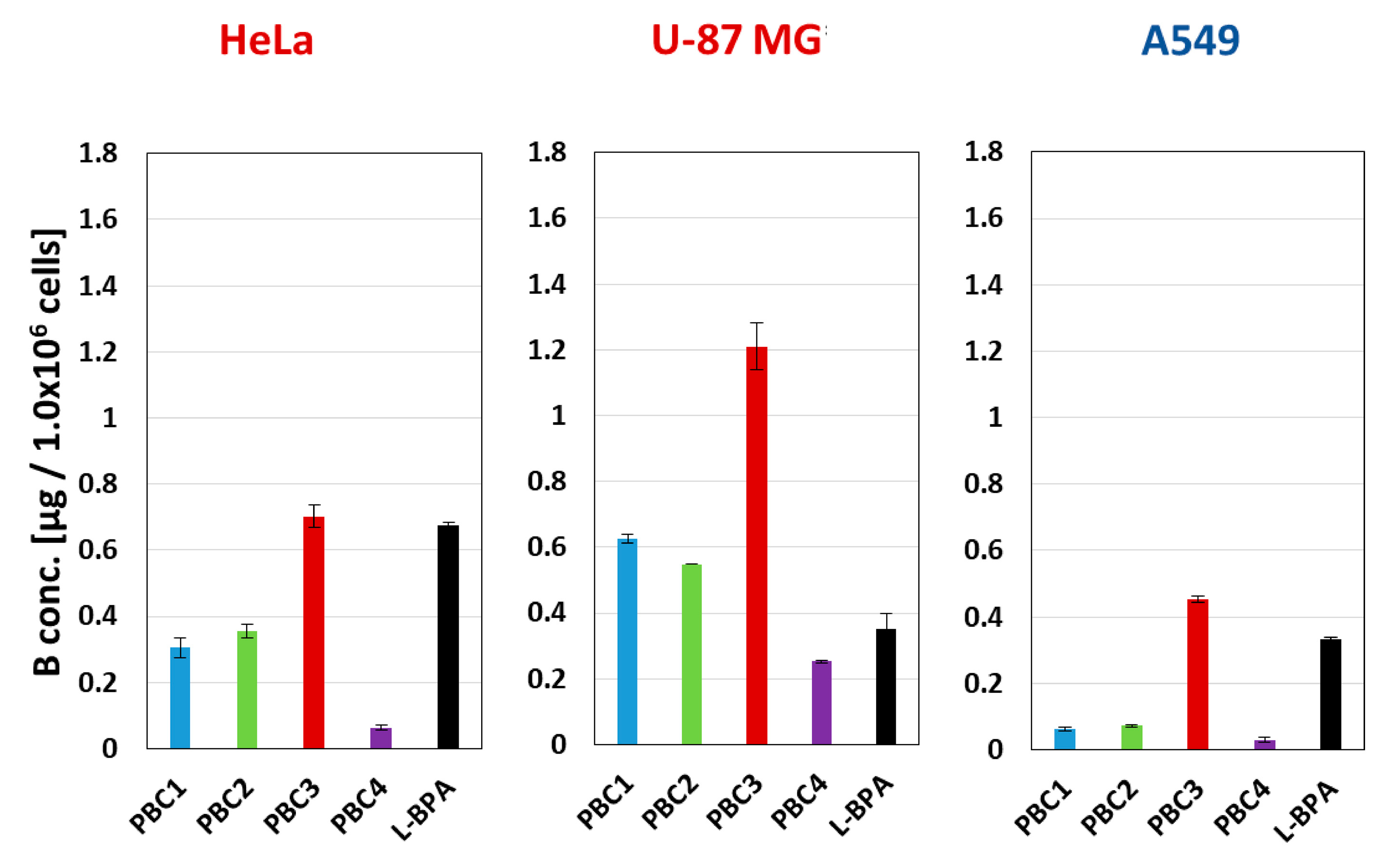
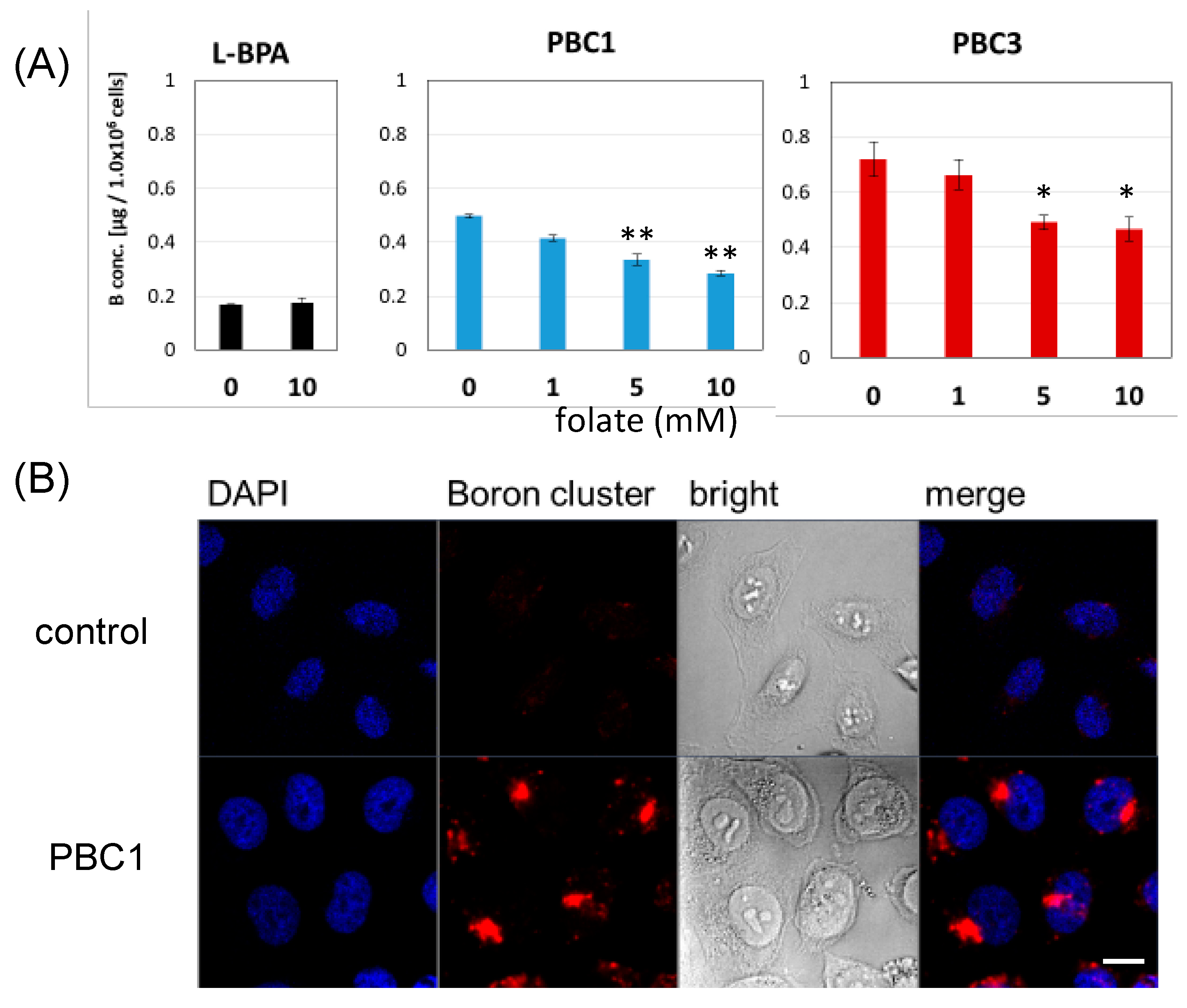
3.3. Cellular Uptake and Distribution of PBCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soloway, A.H.; Tjarks, W.; Barnum, B.A.; Rong, F.G.; Barth, R.F.; Codogni, I.M.; Wilson, J.G. The Chemistry of Neutron Capture Therapy. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1515–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakai, K.; Matsumura, A. Boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2008, 262, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Blue, T.E.; Gahbauer, R.A. A design study of an accelerator-based epithermal neutron source for boron neutron capture therapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 1989, 165, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yanch, J.C.; Zhou, X.L.; Shefer, R.E.; Klinkowstein, R.E. Accelerator-Based Epithermal Neutron Beam Design for Neutron-Capture Therapy. Med. Phys. 1992, 19, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.A.; Beynon, T.D. A design study for an accelerator-based epithermal neutron beam for BNCT. Phys. Med. Biol. 1995, 40, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Kashino, G.; Yong, L.; Masunaga, S.; Kinashi, Y.; Mitsumoto, T.; Yajima, S.; Tsutsui, H.; et al. Impact of accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy (AB-BNCT) on the treatment of multiple liver tumors and malignant pleural mesothelioma. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; Yoshinaga, H.; Mitsumoto, T.; Maruhashi, A.; Ono, K.; Sakurai, Y. A phantom experiment for the evaluation of whole body exposure during BNCT using cyclotron-based epithermal neutron source (C-BENS). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1830–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartelli, D.; Capoulat, M.E.; Bergueiro, T.J.; Gagetti, L.; Anzorena, M.S.; del Grosso, M.P.; Baldo, M.; Castell, W.; Padulo, J.; Sandin, J.C.S.; et al. Present status of accelerator-based BNCT: Focus on developments in Argentina. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 106, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Imamichi, S.; Masumoto, K.; Ito, M.; Wakita, A.; Okamoto, H.; Nishioka, S.; Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Abe, Y.; et al. Evaluation of radioactivity in the bodies of mice induced by neutron exposure from an epi-thermal neutron source of an accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy system. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2017, 93, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Josephson, L.; Liang, S.H.; Zhang, M.-R. Boron agents for neutron capture therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 405, 213139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, Y.; Honda, C.; Ichihashi, M.; Obara, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Fukuda, H.; Karashima, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Kanda, K.; Yoshino, K. Treatment of malignant melanoma by single thermal neutron capture therapy with melanoma-seeking 10B-compound. Lancet 1989, 2, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, A.; Sauerwein, W.A.; Coderre, J.A. Mechanisms of transport of p-borono-phenylalanine through the cell membrane in vitro. Radiat. Res. 2000, 153, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detta, A.; Cruickshank, G.S. L-amino acid transporter-1 and boronophenylalanine-based boron neutron capture therapy of human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, L.B.; Gregory, J.F., 3rd. Folate metabolism and requirements. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsue, H.; Rothberg, K.G.; Takashima, A.; Kamen, B.A.; Anderson, R.G.; Lacey, S.W. Folate receptor allows cells to grow in low concentrations of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6006–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, M.A.; Elwood, P.C.; Portillo, R.M.; Antony, A.C.; Najfeld, V.; Finley, A.; Waxman, S.; Kolhouse, J.F. Influence on immunoreactive folate-binding proteins of extracellular folate concentration in cultured human cells. J. Clin. Invest. 1988, 81, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stover, P.J. Physiology of folate and vitamin B12 in health and disease. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, S3¨CS12 discussion S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, L.E. The role of folate receptor alpha in cancer development, progression and treatment: Cause, consequence or innocent bystander? Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudimack, J.; Lee, R.J. Targeted drug delivery via the folate receptor. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2000, 41, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.; Bax, H.J.; Josephs, D.H.; Ilieva, K.M.; Pellizzari, G.; Opzoomer, J.; Bloomfield, J.; Fittall, M.; Grigoriadis, A.; Figini, M.; et al. Targeting folate receptor alpha for cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52553–52574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.M.; Kularatne, S.A.; Myers, C.H.; Gagare, P.; Norshi, M.; Liu, X.; Singhal, S.; Low, P.S. Evaluation of novel tumor-targeted near-infrared probe for fluorescence-guided surgery of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9637−9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Low, P.S. Folate-targeted therapies for cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6811–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Q.; Wang, H.; Shukla, S.; Sekido, M.; Adams, D.M.; Tjarks, W.; Barth, R.F.; Lee, R.J. Boron-containing folate receptor-targeted liposomes as potential delivery agents for neutron capture therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Wu, G.; Chatterjee, M.; Yang, W.; Sekido, M.; Diop, L.A.; Muller, R.; Sudimack, J.J.; Lee, R.J.; Barth, R.F.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of folate receptor-targeted boronated PAMAM dendrimers as potential agents for neutron capture therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 14, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilli, C.; Grandi, S.; Ciana, A.; Guidetti, G.F.; Malara, A.; Abbonante, V.; Cansolino, L.; Tomasi, C.; Balduini, A.; Fagnoni, M.; et al. Biocompatibility of functionalized boron phosphate (BPO4) nanoparticles for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) application. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofani, G.; Raffa, V.; Menciassi, A.; Cuschieri, A. Folate Functionalized Boron Nitride Nanotubes and their Selective Uptake by Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells: Implications for their Use as Boron Carriers in Clinical Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.H.; Marino, A.; Rocca, A.; Liakos, I.; Nitti, S.; Athanassiou, A.; Mattoli, V.; Mazzolai, B.; de Sousa, E.M.B.; Ciofani, G. Folate-grafted boron nitride nanotubes: Possible exploitation in cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 481, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Bakeine, G.J.; Krol, S.; Ferrari, C.; Clerici, A.M.; Zonta, C.; Cansolino, L.; Ballarini, F.; Bortolussi, S.; Stella, S.; et al. Design, development and characterization of multi-functionalized gold nanoparticles for biodetection and targeted boron delivery in BNCT applications. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenbach, K.; Schieferstein, H.; Grunewald, C.; Iffland, D.; Reffert, L.M.; Hampel, G.; Schütz, C.; Bings, N.; Ross, T. Synthesis and evaluation of boron folates for Boron-Neutron-Capture-Therapy (BNCT). Radiochim. Acta 2015, 103, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, K.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Yoon, C.M. Synthesis of a new amphiphilic ortho-carborane as a potential BNCT agent: 4-[N,N-formyl-(ortho-carboranylmethyl)-amino]benzoyl-L-glutamic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4821–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, T.; Morita, N.; Kamitani, N.; Kumada, H.; Ono, K.; Hiratsuka, J.; Harada, T. Boron neutron capture therapy for advanced salivary gland carcinoma in head and neck. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014, 19, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ke, J.; Zhou, X.E.; Yi, W.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Li, J.; Yong, E.L.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K. Structural basis for molecular recognition of folic acid by folate receptors. Nature 2013, 500, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, M.; Wallace-Povirk, A.; Karim, M.A.; Wilson, M.R.; O’Connor, C.; White, K.; Kushner, J.; Polin, L.; George, C.; Hou, Z.; et al. Tumor Targeting with Novel Pyridyl 6-Substituted Pyrrolo[2¨C- d]Pyrimidine Antifolates via Cellular Uptake by Folate Receptor alpha and the Proton-Coupled Folate Transporter and Inhibition of De Novo Purine Nucleotide Biosynthesis. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2027–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Smith, M.D.; Lantrip, D.A.; Wang, S.; Fuchs, P.L. Efficient Syntheses of Pyrofolic Acid and Pteroyl Azide, Reagents for the Production of Carboxyl-Differentiated Derivatives of Folic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10004–10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semioshkin, A.; Nizhnik, E.; Godovikov, I.; Starikova, Z.; Bregadze, V. Reactions of oxonium derivatives of [B12H12]2− with amines: Synthesis and structure of novel B12-based ammonium salts and amino acids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 692, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Kikuchi, S.; Kawai, K.; Ishii, S.; Sato, S. closo-Dodecaborate-conjugated human serum albumins: Preparation and in vivo selective boron delivery to tumor. Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemitsu, T.; Kawabata, S.; Fukumura, M.; Futamura, G.; Hiramatsu, R.; Nonoguchi, N.; Nakagawa, F.; Takata, T.; Tanaka, H.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Folate receptor-targeted novel boron compound for boron neutron capture therapy on F98 glioma-bearing rats. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2019, 58, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | IC50 (mM) b | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | U87MG | A549 | |
| PBC 1 | 2.00 ± 0.31 | 1.79 ± 0.46 | 3.03 ± 0.12 |
| PBC 2 | 2.04 ± 0.05 | 2.29 ± 0.37 | 1.86 ± 0.11 |
| PBC 3 | 2.53 ± 0.54 | 1.67 ± 0.16 | 1.15 ± 0.15 |
| PBC 4 | 1.51 ± 0.47 | 1.57 ± 0.72 | 2.08 ± 0.24 |
| L-BPA | >10 | >10 | >10 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakagawa, F.; Kawashima, H.; Morita, T.; Nakamura, H. Water-Soluble closo-Docecaborate-Containing Pteroyl Derivatives Targeting Folate Receptor-Positive Tumors for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071615
Nakagawa F, Kawashima H, Morita T, Nakamura H. Water-Soluble closo-Docecaborate-Containing Pteroyl Derivatives Targeting Folate Receptor-Positive Tumors for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells. 2020; 9(7):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071615
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakagawa, Fumiko, Hidehisa Kawashima, Taiki Morita, and Hiroyuki Nakamura. 2020. "Water-Soluble closo-Docecaborate-Containing Pteroyl Derivatives Targeting Folate Receptor-Positive Tumors for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy" Cells 9, no. 7: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071615
APA StyleNakagawa, F., Kawashima, H., Morita, T., & Nakamura, H. (2020). Water-Soluble closo-Docecaborate-Containing Pteroyl Derivatives Targeting Folate Receptor-Positive Tumors for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells, 9(7), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071615





