On the Host Side of the Hepatitis E Virus Life Cycle
Abstract
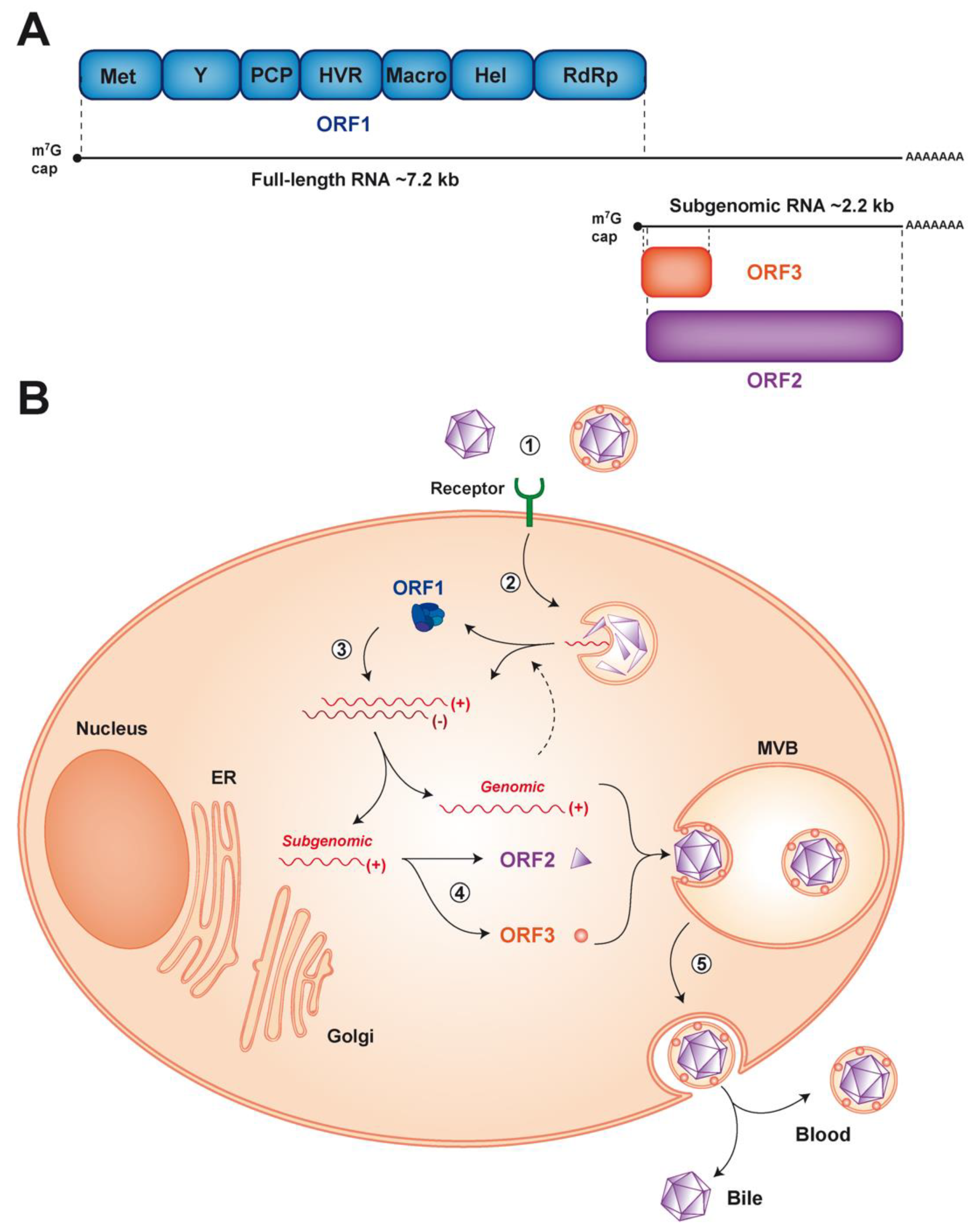
1. Introduction
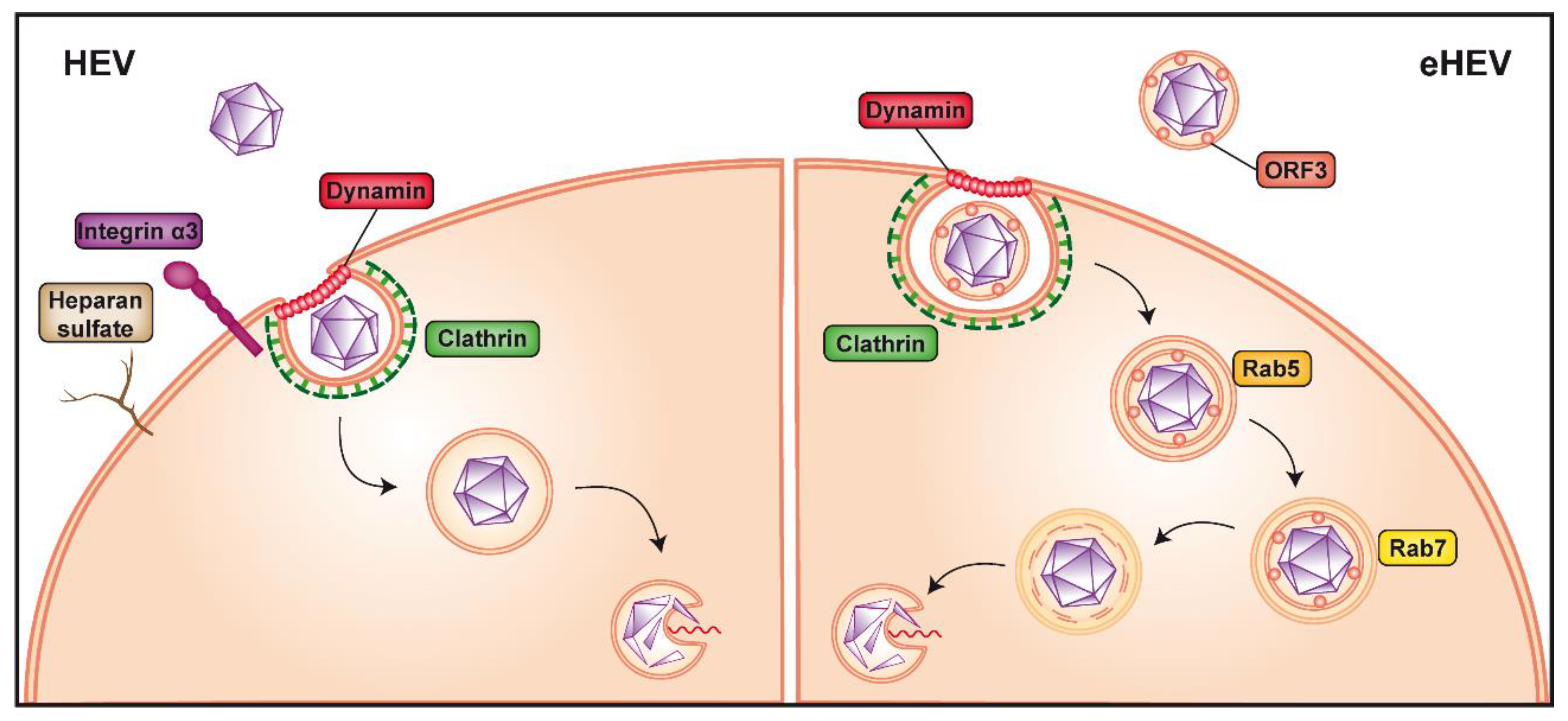
2. HEV Entry
3. Viral RNA Replication
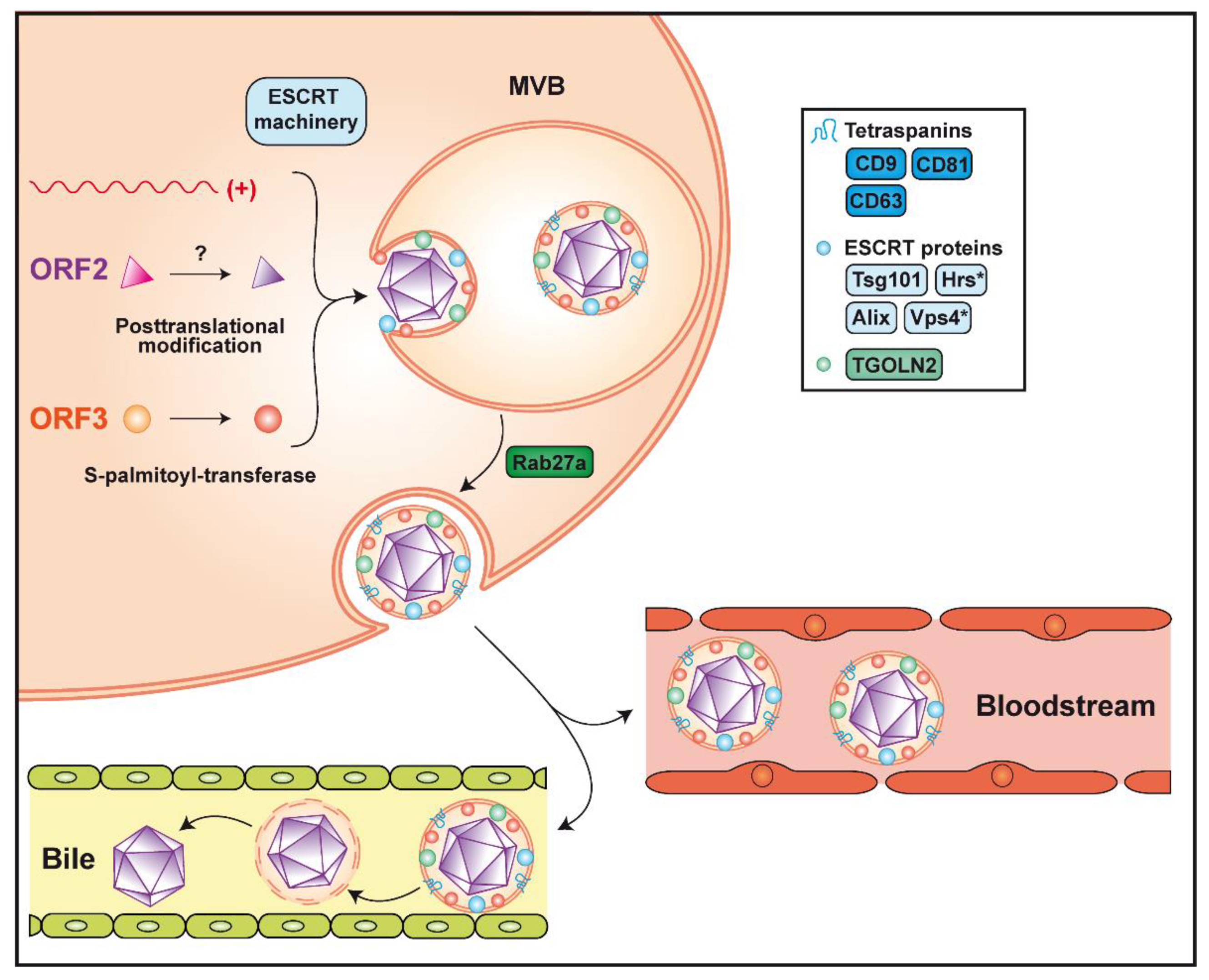
4. Virion Assembly and Infectious Particle Release
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khuroo, M.S. Study of an epidemic of non-A, non-B hepatitis. Possibility of another human hepatitis virus distinct from post-transfusion non-A, non-B type. Am. J. Med. 1980, 68, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayan, M.S.; Andjaparidze, A.G.; Savinskaya, S.S.; Ketiladze, E.S.; Braginsky, D.M.; Savinov, A.P.; Poleschuk, V.F. Evidence for a virus in non-A, non-B hepatitis transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Intervirology 1983, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, G.R.; Purdy, M.A.; Kim, J.P.; Luk, K.C.; Young, L.M.; Fry, K.E.; Bradley, D.W. Isolation of a cDNA from the virus responsible for enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science 1990, 247, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.W.; Smith, M.M.; Guerra, M.E.; Huang, C.C.; Bradley, D.W.; Fry, K.E.; Reyes, G.R. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): Molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 1991, 185, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.; Purdy, M.A. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic infection with camelid hepatitis E virus in a liver transplant recipient who regularly consumes camel meat and milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355.e353–357.e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimgaonkar, I.; Ding, Q.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; El Costa, H.; Schvartz, B.; Peron, J.M.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Rabbit hepatitis E virus infections in humans, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, R.; Fraga, M.; Semela, D.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Rabbit HEV in immunosuppressed patients with hepatitis E acquired in Switzerland. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Wu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, A.J.; Leung, K.H.; Chung, T.W.H.; Chan, J.F.W.; Chan, W.M.; Teng, J.L.L.; et al. Rat hepatitis E virus as cause of persistent hepatitis after liver transplant. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.; Wu, S.; Chew, N.F.; Leung, K.H.; Chan, J.F.; Zhao, P.S.; Chan, W.M.; Poon, R.W.; Tsoi, H.W.; et al. Transmission of rat hepatitis E virus infection to humans in Hong Kong: A clinical and epidemiological analysis. Hepatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiyama, K.; Yamada, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H. Determination of the 5′-terminal sequence of subgenomic RNA of hepatitis E virus strains in cultured cells. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.; Harrison, T.J.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Y. Virus host protein interaction network analysis reveals that the HEV ORF3 protein may interrupt the blood coagulation process. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, C.; Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Mandal, S.D.; Pareek, M.; Kaushik, N.; Srivastava, A.; Saha, S.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; et al. Host-virus protein interaction network reveals the involvement of multiple host processes in the life cycle of hepatitis E virus. mSystems 2018, 3, e00135-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, S.; Yang, C.; Wei, M.; Song, C.; Zheng, Z.; Gu, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N. Homology model and potential virus-capsid binding site of a putative HEV receptor Grp78. J. Mol. Model. 2011, 17, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Holla, P.; Ahmad, I.; Jameel, S. The ATP synthase subunit β (ATP5B) is an entry factor for the hepatitis E virus. bioRxiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Qi, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Asialoglycoprotein receptor facilitates infection of PLC/PRF/5 cells by HEV through interaction with ORF2. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Chandra, V.; Rahman, S.A.; Sehgal, D.; Jameel, S. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are required for cellular binding of the hepatitis E virus ORF2 capsid protein and for viral infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12714–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ambardekar, C.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Z. Distinct entry mechanisms for nonenveloped and quasi-enveloped hepatitis E viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4232–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WuDunn, D.; Spear, P.G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, M.T.; WuDunn, D.; Montgomery, R.I.; Esko, J.D.; Spear, P.G. Cell surface receptors for herpes simplex virus are heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 116, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondor, I.; Ugolini, S.; Sattentau, Q.J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 attachment to HeLa CD4 cells is CD4 independent and gp120 dependent and requires cell surface heparans. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3623–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, H.; Schafer, C.; Adah, M.I.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Toyoda, H.; Kinoshita-Toyoda, A.; Toida, T.; Van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Depla, E.; et al. Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41003–41012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, M.; Natori, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Miyamura, T.; Takeda, N. Genogroup II noroviruses efficiently bind to heparan sulfate proteoglycan associated with the cellular membrane. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, T.; Li, T.C.; Nishimura, Y.; Yoshizaki, S.; Sugiyama, R.; Shimojima, M.; Saijo, M.; Shimizu, H.; Suzuki, R.; Wakita, T.; et al. Integrin alpha3 is involved in non-enveloped hepatitis E virus infection. Virology 2019, 536, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, S.M.; Pramod, N.P.; Wang, F.Z.; Chandran, B. Integrin alpha3beta1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 2002, 108, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Serrano, E.E.; González-López, O.; Das, A.; Lemon, S.M. Cellular entry and uncoating of naked and quasi-enveloped human hepatoviruses. Elife 2019, 8, e43983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, M.Y.; Richman, P.I.; Horton, M.A.; MacDonald, T.T. Expression of the VLA family of integrins in human intestine. J. Pathol. 1990, 160, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, O.; Lhomme, S.; Nayrac, M.; Dubois, M.; Pucelle, M.; Requena, M.; Migueres, M.; Abravanel, F.; Peron, J.M.; Carrere, N.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication in human intestinal cells. Gut 2020, 69, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oechslin, N.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Hepatitis E virus finds its path through the gut. Gut 2020, 69, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melker, A.A.; Sterk, L.M.; Delwel, G.O.; Fles, D.L.; Daams, H.; Weening, J.J.; Sonnenberg, A. The A and B variants of the alpha 3 integrin subunit: Tissue distribution and functional characterization. Lab. Invest. 1997, 76, 547–563. [Google Scholar]
- Volpes, R.; van den Oord, J.J.; Desmet, V.J. Distribution of the VLA family of integrins in normal and pathological human liver tissue. Gastroenterology 1991, 101, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpes, R.; van den Oord, J.J.; Desmet, V.J. Integrins as differential cell lineage markers of primary liver tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 142, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Kapur, N.; Thakral, D.; Durgapal, H.; Panda, S.K. Hepatitis E virus enters liver cells through receptor-dependent clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holla, P.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmed, Z.; Jameel, S. Hepatitis E virus enters liver cells through a dynamin-2, clathrin and membrane cholesterol-dependent pathway. Traffic 2015, 16, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubeck, D.; Filman, D.J.; Cheng, N.; Steven, A.C.; Hogle, J.M.; Belnap, D.M. The structure of the poliovirus 135S cell entry intermediate at 10-angstrom resolution reveals the location of an externalized polypeptide that binds to membranes. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7745–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaldesi, M.; Caruso, M.; Sthandier, O.; Amati, P.; Garcia, M.I. Conformational changes of murine polyomavirus capsid proteins induced by sialic acid binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41573–41579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapp, M.; Bienkowska-Haba, M. Viral entry mechanisms: human papillomavirus and a long journey from extracellular matrix to the nucleus. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 7206–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Feng, Z. Hepatitis E virus entry. Viruses 2019, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Korkaya, H.; Zafrullah, M.; Jameel, S.; Lal, S.K. The phosphorylated form of the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus interacts with its non-glycosylated form of the major capsid protein, ORF2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22759–22767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drave, S.A.; Debing, Y.; Walter, S.; Todt, D.; Engelmann, M.; Friesland, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Neyts, J.; Behrendt, P.; Steinmann, E. Extra-hepatic replication and infection of hepatitis E virus in neuronal-derived cells. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.M.; Decker, C.C.; Dao Thi, V.L. Cell culture models for hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouilly, J.; Chen, Q.; Siewiera, J.; Cartron, G.; Levy, C.; Dubois, M.; Al-Daccak, R.; Izopet, J.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N.; El Costa, H. Genotype specific pathogenicity of hepatitis E virus at the human maternal-fetal interface. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knegendorf, L.; Drave, S.A.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Brown, R.J.P.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Resner, K.; Friesland, M.; Khera, T.; Engelmann, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication and interferon responses in human placental cells. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, T.L.; Bruening, J.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E. Cell culture systems for the study of hepatitis E virus. Antiviral Res. 2019, 163, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. Proc/ Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, F.; Xu, L.; Lin, Z.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; Ayo-Martin, A.C.; van der Kroeg, M.; Zhao, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Hepatitis E virus infects neurons and brains. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Bendall, R.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Xia, N.S.; Ijaz, S.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E. Lancet 2012, 379, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debing, Y.; Moradpour, D.; Neyts, J.; Gouttenoire, J. Update on hepatitis E virology: Implications for clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Huang, W.; Harrison, T.J.; Zhang, H.; Geng, K.; Wang, Y. Detection and assessment of infectivity of hepatitis E virus in urine. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E virus: Chronic infection, extra-hepatic manifestations, and treatment. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2015, 39, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, H.; Perez-Gil, G.; Sampieri, C.L. Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF4A) during viral infections. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sprengers, D.; Metselaar, H.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Requirement of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F complex in hepatitis E virus replication. Antiviral Res. 2015, 124, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glitscher, M.; Himmelsbach, K.; Woytinek, K.; Johne, R.; Reuter, A.; Spiric, J.; Schwaben, L.; Grunweller, A.; Hildt, E. Inhibition of hepatitis E virus spread by the natural compound silvestrol. Viruses 2018, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, D.; Moeller, N.; Praditya, D.; Kinast, V.; Friesland, M.; Engelmann, M.; Verhoye, L.; Sayed, I.M.; Behrendt, P.; Dao Thi, V.L.; et al. The natural compound silvestrol inhibits hepatitis E virus (HEV) replication in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 2018, 157, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenkopf, N.; Lange-Grunweller, K.; Schulte, F.W.; Weisser, A.; Muller, C.; Becker, D.; Becker, S.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grunweller, A. The natural compound silvestrol is a potent inhibitor of Ebola virus replication. Antiviral Res. 2017, 137, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgner, F.; Sabino, C.; Basic, M.; Ploen, D.; Grunweller, A.; Hildt, E. Inhibition of Zika virus replication by silvestrol. Viruses 2018, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henss, L.; Scholz, T.; Grunweller, A.; Schnierle, B.S. Silvestrol inhibits Chikungunya virus replication. Viruses 2018, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C.; Schulte, F.W.; Lange-Grunweller, K.; Obermann, W.; Madhugiri, R.; Pleschka, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grunweller, A. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of the eIF4A inhibitor silvestrol against corona- and picornaviruses. Antiviral Res. 2018, 150, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpe, Y.A.; Lole, K.S. Deubiquitination activity associated with hepatitis E virus putative papain-like cysteine protease. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2088–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Debing, Y.; Jankevicius, G.; Neyts, J.; Ahel, I.; Coutard, B.; Canard, B. Viral macro domains reverse protein ADP-ribosylation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8478–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanade, G.D.; Pingale, K.D.; Karpe, Y.A. Activities of thrombin and factor Xa are essential for replication of hepatitis E virus and are possibly implicated in ORF1 polyprotein processing. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01853-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDesma, R.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus replication. Viruses 2019, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkolnicka, D.; Pollan, A.; Da Silva, N.; Oechslin, N.; Gouttenoire, J.; Moradpour, D. Recombinant hepatitis E viruses harboring tags in the ORF1 protein. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00459-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Archer, N.F.; Bram, Y.; Heller, B.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Identification of the intragenomic promoter controlling hepatitis E virus subgenomic RNA transcription. mBio 2018, 9, e00769-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanade, G.D.; Pingale, K.D.; Karpe, Y.A. Protein interactions network of hepatitis E virus RNA and polymerase with host proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingale, K.D.; Kanade, G.D.; Karpe, Y.A. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins participate in hepatitis E virus (HEV) replication. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 2369–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, A.J.; Gong, L.; Hardy, R.W. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear protein K interacts with Sindbis virus nonstructural proteins and viral subgenomic mRNA. Virology 2007, 367, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit Kneller, E.L.; Connor, J.H.; Lyles, D.S. hnRNPs relocalize to the cytoplasm following infection with vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourai, M.; Lucas-Hourani, M.; Gad, H.H.; Drosten, C.; Jacob, Y.; Tafforeau, L.; Cassonnet, P.; Jones, L.M.; Judith, D.; Couderc, T.; et al. Mapping of Chikungunya virus interactions with host proteins identified nsP2 as a highly connected viral component. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, J.E.; Scolaro, L.A.; Castilla, V. The heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) is a host factor required for dengue virus and Junin virus multiplication. Virus Res. 2015, 203, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poenisch, M.; Metz, P.; Blankenburg, H.; Ruggieri, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Rupp, D.; Rebhan, I.; Diederich, K.; Kaderali, L.; Domingues, F.S.; et al. Identification of hnRNPK as regulator of hepatitis C virus particle production. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Madan, V.; Bartenschlager, R. Hepatitis C virus RNA replication and assembly: Living on the fat of the land. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F.; Rice, C.M. Replication of hepatitis C virus. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, R.; Seron, K.; Ferlin, J.; Feneant, L.; Belouzard, S.; Goueslain, L.; Jackson, C.L.; Dubuisson, J.; Rouillé, Y. Identification of class II ADP-ribosylation factors as cellular factors required for hepatitis C virus replication. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goueslain, L.; Alsaleh, K.; Horellou, P.; Roingeard, P.; Descamps, V.; Duverlie, G.; Ciczora, Y.; Wychowski, C.; Dubuisson, J.; Rouille, Y. Identification of GBF1 as a cellular factor required for hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, G.A.; Feng, Q.; Nikovics, K.; Jackson, C.L.; Ehrenfeld, E. A critical role of a cellular membrane traffic protein in poliovirus RNA replication. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanke, K.H.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Belov, G.A.; Feng, Q.; Duijsings, D.; Jackson, C.L.; Ehrenfeld, E.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. GBF1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Arf, is crucial for coxsackievirus B3 RNA replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11940–11949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Du, J.; Jin, Q. Class I ADP-ribosylation factors are involved in enterovirus 71 replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, R.; Ankavay, M.; Lebsir, N.; Gouttenoire, J.; Jackson, C.L.; Wychowski, C.; Moradpour, D.; Dubuisson, J.; Rouille, Y.; Cocquerel, L. Identification of GBF1 as a cellular factor required for hepatitis E virus RNA replication. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheije, M.H.; Raaben, M.; Mari, M.; Te Lintelo, E.G.; Reggiori, F.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Rottier, P.J.; de Haan, C.A. Mouse hepatitis coronavirus RNA replication depends on GBF1-mediated ARF1 activation. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Li, T.C.; Mayazaki, N.; Simon, M.N.; Wall, J.S.; Moore, M.; Wang, C.Y.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T.; Miyamura, T.; et al. Structure of hepatitis E virion-sized particle reveals an RNA-dependent viral assembly pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33175–33183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Matsuura, Y. Structure of hepatitis E viral particle. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; St Claire, M.; Yu, C.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Mutations within potential glycosylation sites in the capsid protein of hepatitis E virus prevent the formation of infectious virus particles. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F.; et al. Hepatitis E virus lifecycle and identification of 3 forms of the ORF2 capsid protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211.e218–223.e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Z. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of ORF2 in hepatitis E virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankavay, M.; Montpellier, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Saliou, J.M.; Wychowski, C.; Saas, L.; Duvet, S.; Aliouat-Denis, C.M.; Farhat, R.; de Masson d’Autume, V.; et al. New insights into the ORF2 capsid protein, a key player of the hepatitis E virus lifecycle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenggenhager, D.; Gouttenoire, J.; Malehmir, M.; Bawohl, M.; Honcharova-Biletska, H.; Kreutzer, S.; Semela, D.; Neuweiler, J.; Hurlimann, S.; Aepli, P.; et al. Visualization of hepatitis E virus RNA and proteins in the human liver. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, S.; Zafrullah, M.; Ozdener, M.H.; Panda, S.K. Expression in animal cells and characterization of the hepatitis E virus structural proteins. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafrullah, M.; Ozdener, M.H.; Kumar, R.; Panda, S.K.; Jameel, S. Mutational analysis of glycosylation, membrane translocation, and cell surface expression of the hepatitis E virus ORF2 protein. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4074–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.; Torian, U.; Purcell, R.H. ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is not required for replication, virion assembly, or infection of hepatoma cells in vitro. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10457–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Nagashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is essential for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, N.; Marion, O.; Dubois, M.; Allart, S.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Chapuy-Regaud, S. Vectorial release of hepatitis E virus in polarized human hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Wu, X.; Belote, R.L.; Andreo, U.; Takacs, C.N.; Fernandez, J.P.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Prallet, S.; Decker, C.C.; Fu, R.M.; et al. Stem cell-derived polarized hepatocytes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrullah, M.; Ozdener, M.H.; Panda, S.K.; Jameel, S. The ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is a phosphoprotein that associates with the cytoskeleton. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 9045–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjit, M.; Oberoi, R.; Kumar, R.; Lal, S.K. Enhanced alpha1 microglobulin secretion from hepatitis E virus ORF3-expressing human hepatoma cells is mediated by the tumor susceptibility gene 101. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8135–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai; Tanaka, T.; Yamada, K.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. A PSAP motif in the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is necessary for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai, S.; Tanaka, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Yasuda, J.; Okamoto, H. Tumour susceptibility gene 101 and the vacuolar protein sorting pathway are required for the release of hepatitis E virions. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrus, J.E.; von Schwedler, U.K.; Pornillos, O.W.; Morham, S.G.; Zavitz, K.H.; Wang, H.E.; Wettstein, D.A.; Stray, K.M.; Cote, M.; Rich, R.L.; et al. Tsg101 and the vacuolar protein sorting pathway are essential for HIV-1 budding. Cell 2001, 107, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Serrano, J.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. HIV-1 and Ebola virus encode small peptide motifs that recruit Tsg101 to sites of particle assembly to facilitate egress. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietri, M.; Radulovic, M.; Stenmark, H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, S.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanggis; Nishizawa, T.; Kouki, T.; Yashiro, T.; Okamoto, H. Hepatitis E virus egress depends on the exosomal pathway, with secretory exosomes derived from multivesicular bodies. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai, S.; Tanggis; Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. The membrane on the surface of hepatitis E virus particles is derived from the intracellular membrane and contains trans-Golgi network protein 2. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Primadharsini, P.P.; Okamoto, H. Characterization of the quasi-enveloped hepatitis E virus particles released by the cellular exosomal pathway. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00822-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Harrison, T.J.; Huang, W.; Zhao, C.; Kong, W.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y. Hepatitis E virus produced from cell culture has a lipid envelope. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouttenoire, J.; Pollan, A.; Abrami, L.; Oechslin, N.; Mauron, J.; Matter, M.; Oppliger, J.; Szkolnicka, D.; Dao Thi, V.L.; van der Goot, F.G.; et al. Palmitoylation mediates membrane association of hepatitis E virus ORF3 protein and is required for infectious particle secretion. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovic, S.; Blanc, M.; van der Goot, F.G. What does S-palmitoylation do to membrane proteins? FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Dubois, M.; Plisson-Chastang, C.; Bonnefois, T.; Lhomme, S.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; You, B.; Simoneau, S.; Gleizes, P.E.; Flan, B.; et al. Characterization of the lipid envelope of exosome encapsulated HEV particles protected from the immune response. Biochimie 2017, 141, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahar, H.S.; Bao, X.; Casola, A. Exosomes and their role in the life cycle and pathogenesis of RNA viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 3204–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Debing, Y.; Chen, K.; Van Der Laan, L.J.; Neyts, J.; Janssen, H.L.; Metselaar, H.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Calcineurin inhibitors stimulate and mycophenolic acid inhibits replication of hepatitis E virus. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Liu, P.; Takacs, C.N.; Xiang, K.; Andrus, L.; Gouttenoire, J.; Moradpour, D.; Rice, C.M. Pan-genotype hepatitis E virus replication in stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 663.e7–674.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meertens, L.; Hafirassou, M.L.; Couderc, T.; Bonnet-Madin, L.; Kril, V.; Kummerer, B.M.; Labeau, A.; Brugier, A.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; et al. FHL1 is a major host factor for Chikungunya virus infection. Nature 2019, 574, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kim, A.S.; Fox, J.M.; Nair, S.; Basore, K.; Klimstra, W.B.; Rimkunas, R.; Fong, R.H.; Lin, H.; Poddar, S.; et al. Mxra8 is a receptor for multiple arthritogenic alphaviruses. Nature 2018, 557, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Perez, J.T.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Benitez, A.; Kandasamy, M.; Lee, Y.; Andrade, J.; tenOever, B.; Manicassamy, B. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screen identifies host factors essential for influenza virus replication. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.B.; Ohlson, M.B.; Eitson, J.L.; Kumar, A.; McDougal, M.B.; Boys, I.N.; Mar, K.B.; De La Cruz-Rivera, P.C.; Douglas, C.; Konopka, G.; et al. A CRISPR screen identifies IFI6 as an ER-resident interferon effector that blocks flavivirus replication. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Lin, D.L.; McMullan, L.K.; Shrivastava-Ranjan, P.; Bergeron, E.; Lo, M.K.; Welch, S.R.; Nichol, S.T.; Tai, A.W.; et al. A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase as a potential antiviral target for Ebola virus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’Kovski, P.; Gerber, M.; Kelly, J.; Pfaender, S.; Ebert, N.; Braga Lagache, S.; Simillion, C.; Portmann, J.; Stalder, H.; Gaschen, V.; et al. Determination of host proteins composing the microenvironment of coronavirus replicase complexes by proximity-labeling. Elife 2019, 8, e42037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oechslin, N.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. On the Host Side of the Hepatitis E Virus Life Cycle. Cells 2020, 9, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051294
Oechslin N, Moradpour D, Gouttenoire J. On the Host Side of the Hepatitis E Virus Life Cycle. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051294
Chicago/Turabian StyleOechslin, Noémie, Darius Moradpour, and Jérôme Gouttenoire. 2020. "On the Host Side of the Hepatitis E Virus Life Cycle" Cells 9, no. 5: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051294
APA StyleOechslin, N., Moradpour, D., & Gouttenoire, J. (2020). On the Host Side of the Hepatitis E Virus Life Cycle. Cells, 9(5), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051294




