Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Cellular Physiology, Calcium, ROS Signaling, and Metaflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. IRE1α: Structure and Mode of Activation
3. Activation Mechanism of IRE1α during Physiological Stress
4. IRE1α in ER Stress and Its Crosstalk with Other UPR Signal Transducers
5. IRE1α in Cellular Physiological Function
| Physiological Role | Mechanism | Model/Tissue Region | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue growth | Inducing XBP1s dependent function. | Liver | [91] |
| Lipogenesis | Regulates lipogenic gene expression involved in serum cholesterol triglyceride and free fatty acid synthesis. | Liver | [92] |
| Secretory function | IRE1 deletion impaired the insulin, saliva, and antibody secretion. | Exocrine glands, plasma cell, pancreatic acinar and β cells, salivary serous tissues | [93,94,95] |
| Lipid metabolism | IRE1β-mediated RIDD activity on MTP and reduce dyslipidemia. | Mice/Liver | [96,97] |
| Lipid, glucose, and bile acid metabolism | Deletion of hepatic XBP1 disables the bile acid metabolism in mice. | Liver | [94,98] |
| Organelle biogenesis and homeostasis | IRE1/XBP1 increases the synthesis of membrane phospholipids, especially in secretory cells and fibroblasts to carry out their huge task to meet the physiological demand. | Endoplasmic reticulum | [99,100,101] |
| B cell differentiation | XBP1s dependent function, deletion impaired differentiation. | Lymphoid tissue | [102] |
| Eosinophil differentiation | XBP1s dependent function, deletion impaired differentiation. | myeloid tissue granulocyte | [103] |
| Embryogenesis | IRE1α, IRE1β function in mesoderm development, XBP1 dependent pathway. | Human/Xenopus laevis. Mesoderm, gut | [104,105,106] |
| Osteoclastogenesis | IRE1α/XBP1-mediated osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation, induction of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and PTHR. | Osteoblast, Osteoclast | [107,108,109] |
| Immune cell development | IRE1α/XBP1 functions, deletion impaired antigen presentation to T cells, proliferation, and differentiation. Loss of RIDD and XBP1 causes the cDC1 cell death. | Dendritic cells, Lung and small intestine | [110] |
| Cell cycle regulation | IRE1α /XBP1 drives cells from G1 to S-phase through regulation of cyclin A1 and D1, promote compensatory proliferation of β-cells. | Pancreatic β cells | [111,112] |
| Photoreceptor differentiation | IRE1α /RIDD level and increased the delivery of rhodopsin-1 to the rhabdomere. Loss of IRE1α disrupted the rhabdomere morphogenesis and the ER anatomy. | Drosophila compound eye R cells | [113,114] |
| Chondrocyte differentiation | IRE1α negatively regulates chondrocyte differentiation through inhibition of granulin-epithelin precursor (GEP) and by upregulating parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP). | Chondrocyte | [109,115] |
| Dendrite morphogenesis | Perturbation of the IRE1 pathway causes loss of dendritic branches. | Caenorhabditis elegans/neurons | [116,117] |
| Enterocytes | IRE1β inhibited the differentiation of Caco-2 cells into enterocyte-like cells by suppressing microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). | Intestine | [43] |
| Mucous secretion | IRE1β knockout mice are viable, but are more susceptible to colitis. IRE1β is needed to maintain normal transcription rates of mucin genes and genes associated with the development of mucins. | Intestine goblet cells, gut epithelium, airway epithelium | [5,6,118] |
| Metabolic transformation of cells | IRE1/XBP1 pathway contributes to lipogenic gene expression during locational metabolism and lipid metabolism by controlling liver hormone; fibroblast growth factor 21(FGF21). | Mammary gland, Liver, adipocytes | [119,120,121] |
| Tissue regeneration | IRE1/XBP1 through direct regulation of transcription factor STAT3. | Mice/hepatocyte | [122] |
| Hematopoietic cells | IRE1/XBP1 pathway plays a role in cell cycle, differentiation of hematopoietic cell. | Hematopoietic tissue | [123] |
6. Modulation of IRE1α Downstream Activities toward Divergent Cell Fate
7. Intrinsic Modulation of IRE1α by Its Binding Partner and Functional Implication
8. IRE1α in Cellular Signaling: Calcium, ROS
9. Potential Role of IRE1α in Chronic Metabolic Diseases and Its Influence on Metaflammation
9.1. Type 2 Diabetes
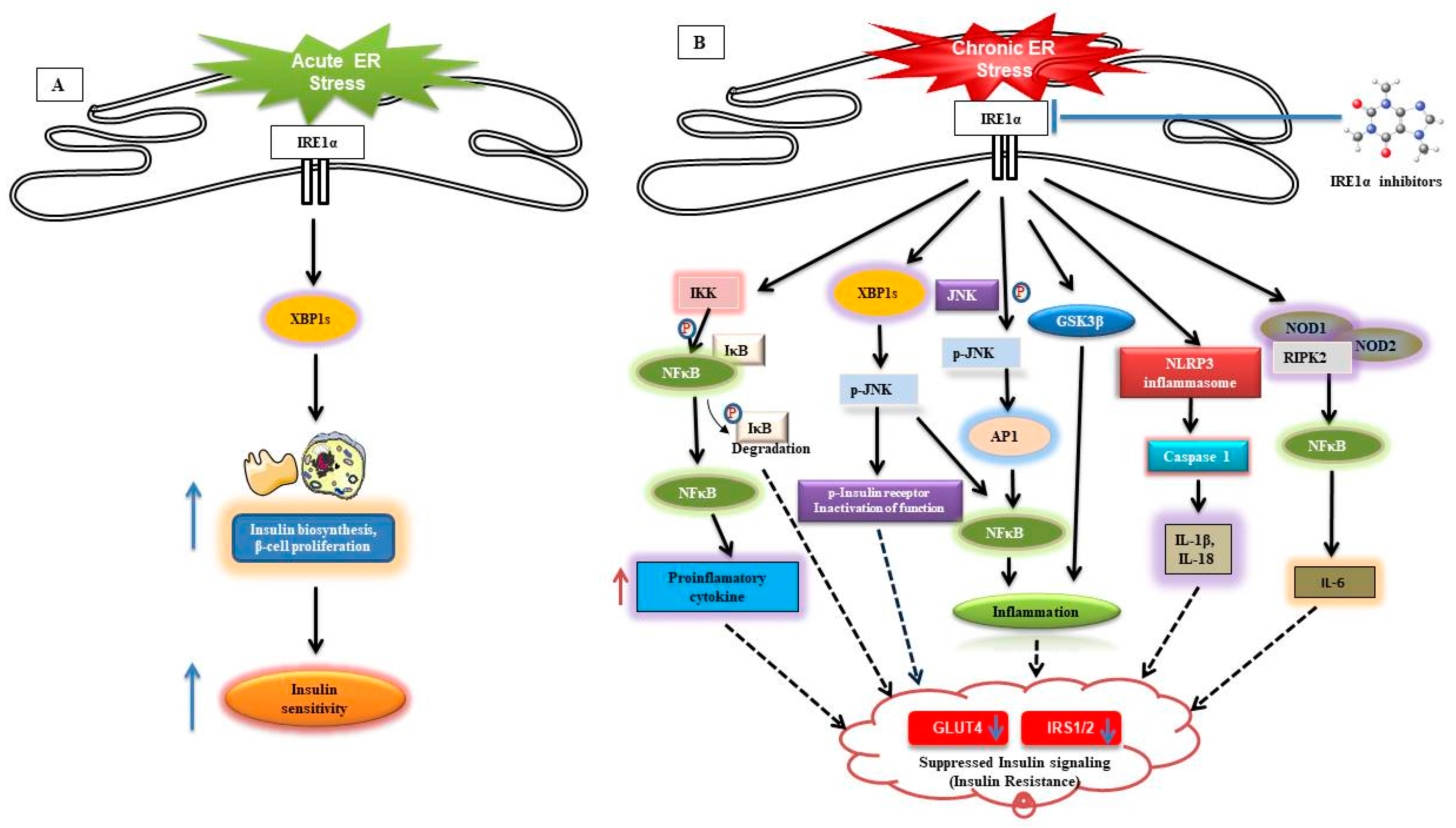
9.2. IRE1α Contribution in Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance and Metaflammation
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| ASK1 | Apoptosis signaling kinase 1 |
| ATF6 | Activating transcription factor 6 |
| ATF4 | Activated transcription factor 4 |
| ATMs | Adipose tissue-recruited macrophages |
| BiP | Binding immunoglobulinprotein |
| CSSR | Core stress-sensing region |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| CIB1 | Calcium and integrin binding protein 1 |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| DR5 | Death receptor 5 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| eif2α | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha |
| ERAD | Endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| IRE1α | Inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase endoribonuclease-1α |
| IP3Rs | Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors |
| ISC | Intestinal stem cell |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| KIRAs | Kinase-Inhibiting RNase Attenuators |
| MHCs | Major histocompatibility complexes |
| MAMs | Mitochondria-associated membranes |
| MTP | Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein |
| MTORC1 | Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| MEFs | Mouse embryonic fibroblasts |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| PP2A | Protein phosphatase 2A |
| PP1C | Protein phosphatase 1C |
| PERK | PRKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase |
| PHLDA3 | Pleckstrin homology-like domain family A, member 3 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RyRs | Ryanodine receptors |
| RACK1 | Receptor for activated C kinase 1 |
| RIDD | Regulated IRE1-dependent decay |
| SERCAs | Sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPases |
| TXNIP | Thioredoxin interacting protein |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
| TRAF2 | TNF receptor-associated factor 2 |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| XBP1 | X-box binding protein 1 |
References
- Nikawa, J.-I.; Yamashita, S. IRE1 encodes a putative protein kinase containing a membrane-spanning domain and is required for inositol phototrophy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.S.; Shamu, C.E.; Walter, P. Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell 1993, 73, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Ma, W.; Gething, M.-J.; Sambrook, J. A transmembrane protein with a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase activity is required for signaling from the ER to the nucleus. Cell 1993, 74, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ron, D.; Walter, P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2007, 8, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, A.; Wang, X.Z.; Novoa, I.; Jungreis, R.; Schlessinger, K.; Cho, J.H.; West, A.B.; Ron, D. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Increased sensitivity to dextran sodium sulfate colitis in IRE1beta-deficient mice. Fac. Opin. Post Publ. Peer Rev. Biomed. Lit. 2016, 107, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.B.; Jones, L.; Brighton, B.; Ehre, C.; Abdulah, L.; Davis, C.W.; Ron, D.; O’neal, W.K.; Ribeiro, C.M.P. The ER stress transducer IRE1beta is required for airway epithelial mucin production. Mucosal. Immunol. 2013, 6, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, D.; Kimata, Y.; Kohno, K.; Iwawaki, T. Activation of mammalian IRE1α upon ER stress depends on dissociation of BiP rather than on direct interaction with unfolded proteins. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagawa, Y.; Hosoda, A.; Sasaka, S.-I.; Tsuru, A.; Kohno, K. RNase domains determine the functional difference between IRE1α and IRE1β. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwawaki, T.; Hosoda, A.; Okuda, T.; Kamigori, Y.; Nomura-Furuwatari, C.; Kimata, Y.; Tsuru, A.; Kohno, K. Translational control by the ER transmembrane kinase/ribonuclease IRE1 under ER stress. Nature 2001, 3, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfon, M.; Zeng, H.; Urano, F.; Till, J.H.; Hubbard, S.R.; Harding, H.P.; Clark, S.G.; Ron, D. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 2002, 415, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Jolicoeur, E.M.; Kuroda, M.; Ron, D. Cloning of mammalian Ire1 reveals diversity in the ER stress responses. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5708–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anelli, T.; Sitia, R. Protein quality control in the early secretory pathway. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, R.J. Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, F.; Wang, X.; Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, P.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Coupling of Stress in the ER to Activation of JNK Protein Kinases by Transmembrane Protein Kinase IRE1. Science 2000, 287, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y. The Protein Kinase/Endoribonuclease IRE1alpha That Signals the Unfolded Protein Response Has a Luminal N-terminal Ligand-independent Dimerization Domain. J. Boil. Chem. 2002, 277, 18346–18356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, C.Y.; Back, S.H.; Clark, R.L.; Peisach, D.; Xu, Z.; Kaufman, R.J. The crystal structure of human IRE1 luminal domain reveals a conserved dimerization interface required for activation of the unfolded protein response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14343–14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, D.; Kimata, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Kohno, K. An essential dimer-forming subregion of the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor Ire1. Biochem. J. 2005, 391, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, A.; Wang, Y. Cdc37/Hsp90 protein-mediated regulation of IRE1alpha protein activity in endoplasmic reticulum stress response and insulin synthesis in INS-1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6266–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prischi, F.; Nowak, P.R.; Carrara, M.; Ali, M.M.U. Phosphoregulation of Ire1 RNase splicing activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Korennykh, A.V.; Behrman, S.L.; Walter, P. Mammalian endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1 signals by dynamic clustering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16113–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamu, C.E.; Walter, P. Oligomerization and phosphorylation of the Ire1p kinase during intracellular signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 3028–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, B.M.; Walter, P. Unfolded Proteins Are Ire1-Activating Ligands That Directly Induce the Unfolded Protein Response. Science 2011, 333, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korennykh, A.; Egea, P.F.; A Korostelev, A.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Stroud, R.M.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Walter, P. Cofactor-mediated conformational control in the bifunctional kinase/RNase Ire1. BMC Boil. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, K.P.K.; Harding, H.P.; Haynes, C.M.; Price, J.; Sicheri, F.; Ron, D. Flavonol Activation Defines an Unanticipated Ligand-Binding Site in the Kinase-RNase Domain of IRE1. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, E.S.; Perera, B.G.K.; Igbaria, A.; Morita, S.; Prado, K.; Thamsen, M.; Caswell, D.; Macias, H.; et al. Allosteric inhibition of the IRE1α RNase preserves cell viability and function during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell 2014, 158, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, D.; Chevalier, M.W.; Aragón, T.; Van Anken, E.; Vidal, S.E.; El-Samad, H.; Walter, P. BiP Binding to the ER-Stress Sensor Ire1 Tunes the Homeostatic Behavior of the Unfolded Protein Response. PLoS Boil. 2010, 8, e1000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, Y.; Ishiwata-Kimata, Y.; Ito, T.; Hirata, A.; Suzuki, T.; Oikawa, D.; Takeuchi, M.; Kohno, K. Two regulatory steps of ER-stress sensor Ire1 involving its cluster formation and interaction with unfolded proteins. J. Cell Boil. 2007, 179, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hendershot, L.M.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nature 2000, 2, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, Y.; Kimata, Y.I.; Shimizu, Y.; Abe, H.; Farcasanu, I.C.; Takeuchi, M.; Rose, M.D.; Kohno, K. Genetic Evidence for a Role of BiP/Kar2 That Regulates Ire1 in Response to Accumulation of Unfolded Proteins. Mol. Boil. Cell 2003, 14, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, Y.; Oikawa, D.; Shimizu, Y.; Ishiwata-Kimata, Y.; Kohno, K. A role for BiP as an adjustor for the endoplasmic reticulum stress-sensing protein Ire1. J. Cell Boil. 2004, 167, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA Is Induced by ATF6 and Spliced by IRE1 in Response to ER Stress to Produce a Highly Active Transcription Factor. Cell 2001, 107, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onn, A.; Ron, D. Modeling the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Struct. Mol. Boil. 2010, 17, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorner, A.; Wasley, L.; Kaufman, R. Overexpression of GRP78 mitigates stress induction of glucose regulated proteins and blocks secretion of selective proteins in Chinese hamster ovary cells. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, K.; Normington, K.; Sambrook, J.; Gething, M.J.; Mori, K. The promoter region of the yeast KAR2 (BiP) gene contains a regulatory domain that responds to the presence of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Cell. Boil. 1993, 13, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrara, M.; Prischi, F.; Nowak, P.R.; Kopp, M.C.; Ali, M.M.U. Noncanonical binding of BiP ATPase domain to Ire1 and Perk is dissociated by unfolded protein CH1 to initiate ER stress signaling. eLife 2015, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, D.; Kimata, Y.; Kohno, K. Self-association and BiP dissociation are not sufficient for activation of the ER stress sensor Ire1. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promlek, T.; Ishiwata-Kimata, Y.; Shido, M.; Sakuramoto, M.; Kohno, K.; Kimata, Y. Membrane aberrancy and unfolded proteins activate the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor Ire1 in different ways. Mol. Boil. Cell 2011, 22, 3520–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credle, J.J.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Papa, F.R.; Stroud, R.M.; Walter, P. On the mechanism of sensing unfolded protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18773–18784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korennykh, A.V.; Egea, P.F.; Korostelev, A.A.; Finer-Moore, J.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Stroud, R.M.; Walter, P. The unfolded protein response signals through high-order assembly of Ire1. Nature 2008, 457, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, R. Structural Basis for Regulation of RNA-Binding Proteins by Phosphorylation. ACS Chem. Boil. 2015, 10, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagoz, G.E.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Lee, C.P.; Chu, F.; Walter, P. An unfolded protein-induced conformational switch activates mammalian IRE1. eLife 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.H.; Li, H.; Yasumura, U.; Cohen, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Panning, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Lavail, M.M.; Walter, P. IRE1 Signaling Affects Cell Fate During the Unfolded Protein Response. Science 2007, 318, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, K.; Khatun, I.; Hussain, M.M. NR2F1 and IRE1beta suppress microsomal triglyceride transfer protein expression and lipoprotein assembly in undifferentiated intestinal epithelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2009, 30, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Queiroz, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.-C.; Ron, D.; Hussain, M.M. Increased intestinal lipid absorption caused by Ire1beta deficiency contributes to hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, D.; Kitamura, A.; Kinjo, M.; Iwawaki, T. Direct Association of Unfolded Proteins with Mammalian ER Stress Sensor, IRE1β. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathuranyanon, R.; Tsukamoto, T.; Takeuchi, A.; Ishiwata-Kimata, Y.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Kohno, K.; Kimata, Y. Tight regulation of the unfolded protein sensor Ire1 by its intramolecularly antagonizing subdomain. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwata-Kimata, Y.; Promlek, T.; Kohno, K.; Kimata, Y. BiP-bound and nonclustered mode of Ire1 evokes a weak but sustained unfolded protein response. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhou, L.; Okoro, E.U.; Fan, G.; Ramaswamy, R.; Yang, H. Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Lipoproteins Induce Foam Cell Formation by Activation of PERK-EIF-2α Signaling Cascade. J. Bioanal. Biomed. 2010, 2, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locker, N.; E Easton, L.; Lukavsky, P.J. HCV and CSFV IRES domain II mediate eIF2 release during 80S ribosome assembly. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Murthy, R.; Wood, B.; Song, B.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.; Malhi, H.; Kaufman, R.J. ER stress signalling through eIF2α and CHOP, but not IRE1α, attenuates adipogenesis in mice. Diabetology 2013, 56, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Kimmig, P.; Mendez, A.S.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Walter, P.; Ashkenazi, A. Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science 2014, 345, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, M.; Huang, C.; Snider, M.D.; Komar, A.A.; Tanaka, J.; Kaufman, R.J.; Krokowski, D.; Hatzoglou, M. A Novel Feedback Loop Regulates the Response to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress via the Cooperation of Cytoplasmic Splicing and mRNA Translation. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2012, 32, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Malhotra, J.; Hassler, J.R.; Back, S.H.; Wang, G.; Chang, L.; Xu, W.; Miao, H.; Leonardi, R.; et al. The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1α prevents ER stress-induced hepatic steatosis. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1357–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Zeng, L.; Yi, W.; Liu, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Ju, Z.; Cong, Y. A critical role of DDRGK1 in endoplasmic reticulum homoeostasis via regulation of IRE1α stability. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugea, A.; Tischler, D.; Nguyen, J.; Gong, J.; Gukovsky, I.; French, S.W.; Gorelick, F.S.; Pandol, S.J. Adaptive unfolded protein response attenuates alcohol-induced pancreatic damage. Gastroenterology 2010, 140, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Read, D.E.; Hetz, C.; Samali, A.; Gupta, S. PERK regulated miR-424(322)-503 cluster fine-tunes activation of IRE1 and ATF6 during Unfolded Protein Response. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuru, A.; Imai, Y.; Saito, M.; Kohno, K. Novel mechanism of enhancing IRE1α-XBP1 signalling via the PERK-ATF4 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, J.-S.; Cho, S.; Min, S.-H.; Kimball, S.R.; Lee, A.-H. IRE1α-Dependent Decay of CReP/Ppp1r15b mRNA Increases Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α Phosphorylation and Suppresses Protein Synthesis. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2015, 35, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Haze, K.; Yanagi, H.; Yura, T.; Mori, K. Identification of the cis-acting endoplasmic reticulum stress response element responsible for transcriptional induction of mammalian glucose-regulated proteins. Involvement of basic leucine zipper transcription factors. J. Boil. Chem. 1998, 273, 33741–33749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Arenzana, N.; Tirasophon, W.; Kaufman, R.J.; Prywes, R. Activation of ATF6 and an ATF6 DNA binding site by the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J. Boil. Chem. 2000, 275, 27013–27020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.-J.; Xiong, Z.; Lu, X.; Ye, M.; Han, X.; Jiang, R. ATF6 upregulates XBP1S and inhibits ER stress-mediated apoptosis in osteoarthritis cartilage. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Tirasophon, W.; Shen, X.; Michalak, M.; Prywes, R.; Okada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Mori, K.; Kaufman, R.J. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genome Res. 2002, 16, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, A.; Oku, M.; Mori, K.; Yoshida, H. Unconventional splicing of XBP1 mRNA occurs in the cytoplasm during the mammalian unfolded protein response. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, M.; Chevet, E.; Tavernier, J.; Gerlo, S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimata, Y.; Yamada, S.; Kohno, K.; Ishiwata-Kimata, Y. Yeast unfolded protein response pathway regulates expression of genes for anti-oxidative stress and for cell surface proteins. Genes Cells 2005, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C.; Martinon, F.; Rodriguez, D.; Glimcher, L.H. The Unfolded Protein Response: Integrating Stress Signals through the Stress Sensor IRE1α. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1219–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, Y.; Mishiba, K.-I.; Suzuki, E.; Shimada, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Koizumi, N. Arabidopsis IRE1 catalyses unconventional splicing of bZIP60 mRNA to produce the active transcription factor. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Ogawa, N.; Kawahara, T.; Yanagi, H.; Yura, T. mRNA splicing-mediated C-terminal replacement of transcription factor Hac1p is required for efficient activation of the unfolded protein response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4660–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liang, F.-X.; Wang, X. A synthetic biology approach identifies the mammalian UPR RNA ligase RtcB. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Mishiba, K.-I.; Koizumi, N. Arabidopsis tRNA ligase completes the cytoplasmic splicing of bZIP60 mRNA in the unfolded protein response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkin, J.; Henkel, T.; Nielsen, A.F.; Minnich, M.; Popow, J.; Kaufmann, T.; Heindl, K.; Hoffmann, T.; Busslinger, M.; Martínez, J. The mammalian tRNA ligase complex mediates splicing of XBP1 mRNA and controls antibody secretion in plasma cells. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2922–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popow, J.; Jurkin, J.; Schleiffer, A.; Martínez, J. Analysis of orthologous groups reveals archease and DDX1 as tRNA splicing factors. Nature 2014, 511, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poothong, J.; Tirasophon, W.; Kaufman, R.J. Functional analysis of the mammalian RNA ligase for IRE1 in the unfolded protein response. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.K.; Cheng, C.L.; Bingman, C.A.; Phillips, G.N.; Raines, R.T. A tRNA splicing operon: Archease endows RtcB with dual GTP/ATP cofactor specificity and accelerates RNA ligation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 3931–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollien, J.; Lin, J.H.; Li, H.; Stevens, N.; Walter, P.; Weissman, J.S. Regulated Ire1-dependent decay of messenger RNAs in mammalian cells. J. Cell Boil. 2009, 186, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Sen, U.; Vrati, S. Regulated IRE1-dependent decay pathway is activated during Japanese encephalitis virus-induced unfolded protein response and benefits viral replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, S.L.; Jayewickreme, T.R.; Molony, R.D.; Iwawaki, T.; Landis, C.S.; Lindenbach, B.D.; Iwasaki, A. IRE1α promotes viral infection by conferring resistance to apoptosis. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaai7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estornes, Y.; A Aguileta, M.; Dubuisson, C.; De Keyser, J.; Goossens, V.; Kersse, K.; Samali, A.; Vandenabeele, P.; Bertrand, M.J.M. RIPK1 promotes death receptor-independent caspase-8-mediated apoptosis under unresolved ER stress conditions. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.; Lewis, J.; Neckers, L.; Liu, Z. Tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced activation of the MAP kinase JNK. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y.; Lim, S.W.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.G. PHLDA3 overexpression in hepatocytes by endoplasmic reticulum stress via IRE1–Xbp1s pathway expedites liver injury. Gut 2015, 65, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Davis, R.J. JNK phosphorylation of Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2432–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, C. Requirement of JNK for Stress- Induced Activation of the Cytochrome c-Mediated Death Pathway. Science 2000, 288, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Nakajima, S.; Saito, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Katoh, R.; Kitamura, M. mTORC1 serves ER stress-triggered apoptosis via selective activation of the IRE1–JNK pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 19, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, J.A.; Schwarze, S.R. IRE1α controls cyclin A1 expression and promotes cell proliferation through XBP-1. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 15, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencer, W.I.; DeLuca, H.; Grey, M.J.; Cho, J.A. Innate immunity at mucosal surfaces: The IRE1-RIDD-RIG-I pathway. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, J.-P.; Austgen, K.; Nishino, M.; Coakley, K.M.; Hagen, A.R.; Han, D.; Papa, F.R.; Oakes, S.A. Caspase-2 Cleavage of BID Is a Critical Apoptotic Signal Downstream of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2008, 28, 3943–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, J.-P.; Wang, L.; Han, D.; Wang, E.S.; Huskey, N.E.; Lim, L.; Truitt, M.; McManus, M.T.; Ruggero, D.; Goga, A.; et al. IRE1 Cleaves Select microRNAs During ER Stress to Derepress Translation of Proapoptotic Caspase-2. Science 2012, 338, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, D.T.; Hegde, R.S. Regulation of basal cellular physiology by the homeostatic unfolded protein response. J. Cell Boil. 2010, 189, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwawaki, T.; Akai, R.; Yamanaka, S.; Kohno, K. Function of IRE1 alpha in the placenta is essential for placental development and embryonic viability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16657–16662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimold, A.M.; Etkin, A.; Clauss, I.; Perkins, A.; Friend, D.S.; Zhang, J.; Horton, H.F.; Scott, A.; Orkin, S.H.; Byrne, M.C.; et al. An essential role in liver development for transcription factor XBP-1. Genome Res. 2000, 14, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.-H.; Scapa, E.F.; Cohen, D.E.; Glimcher, L.H. Regulation of Hepatic Lipogenesis by the Transcription Factor XBP1. Science 2008, 320, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwawaki, T.; Akai, R.; Kohno, K. IRE1α Disruption Causes Histological Abnormality of Exocrine Tissues, Increase of Blood Glucose Level, and Decrease of Serum Immunoglobulin Level. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.-H.; Chu, G.C.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Glimcher, L.H. XBP-1 is required for biogenesis of cellular secretory machinery of exocrine glands. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, K.L.; Fonseca, S.G.; Ishigaki, S.; Nguyen, L.X.; Foss, E.; Bortell, R.; Rossini, A.A.; Urano, F. Regulation of insulin biosynthesis in pancreatic beta cells by an endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein kinase IRE1. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Dai, K.; Seimon, T.; Jungreis, R.; Oyadomari, M.; Kuriakose, G.; Ron, D.; Tabas, I.; Hussain, M.M. IRE1β Inhibits Chylomicron Production by Selectively Degrading MTP mRNA. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.-S.; Hur, K.Y.; Tarrio, M.; Ruda, V.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Koteliansky, V.; Lichtman, A.H.; Iwawaki, T.; Glimcher, L.H.; et al. Silencing of lipid metabolism genes through IRE1α-mediated mRNA decay lowers plasma lipids in mice. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Henkel, A.S.; Lecuyer, B.E.; Hubchak, S.C.; Schipma, M.J.; Zhang, E.; Green, R.M. Hepatic deletion of X-box binding protein 1 impairs bile acid metabolism in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 58, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriburi, R.; Bommiasamy, H.; Buldak, G.L.; Robbins, G.R.; Frank, M.; Jackowski, S.; Brewer, J.W. Coordinate Regulation of Phospholipid Biosynthesis and Secretory Pathway Gene Expression in XBP-1(S)-induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Biogenesis. J. Boil. Chem. 2007, 282, 7024–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.E.; Kinkel, S.; Kim, D. Physiological IRE-1-XBP-1 and PEK-1 Signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans Larval Development and Immunity. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-W.; Zeng, X.; Rhim, T.; Ron, D.; Ryoo, H.D. The requirement of IRE1 and XBP1 in resolving physiological stress during Drosophila development. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimold, A.M.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Manis, J.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E.; Gravallese, E.M.; Friend, D.; Grusby, M.J.; Alt, F.; Glimcher, L.H. Plasma cell differentiation requires the transcription factor XBP-1. Nature 2001, 412, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettigole, S.E.; Lis, R.; Adoro, S.; Lee, A.-H.; Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F.; Glimcher, L.H. The transcription factor XBP1 is selectively required for eosinophil differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, X.-X.; Feng, J.-J.; Yin, C.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Wang, N.; Yuan, L. Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α is required for gut development in Xenopus lavies embryos. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Li, X.; Feng, J.; Yin, C.; Yuan, F.; Wang, X. IRE1α is essential for Xenopus pancreas development. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 28, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, L.; Cao, Y.; Oswald, F.; Knochel, W. IRE1beta is required for mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Mech. Dev. 2008, 125, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmonda, T.; Miyauchi, Y.; Ghosh, R.; Yoda, M.; Uchikawa, S.; Takito, J.; Morioka, H.; Nakamura, M.; Iwawaki, T.; Chiba, K.; et al. The IRE1α–XBP1 pathway is essential for osteoblast differentiation through promoting transcription of Osterix. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmonda, T.; Yoda, M.; Iwawaki, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakamura, M.; Mikoshiba, K.; Toyama, Y.; Horiuchi, K. IRE1alpha/XBP1-mediated branch of the unfolded protein response regulates osteoclastogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3269–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmonda, T.; Yoda, M.; Mizuochi, H.; Morioka, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Urano, F.; Toyama, Y.; Horiuchi, K. The IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway positively regulates parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor expression and is involved in pth-induced osteoclastogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakoshi, N.N.; Pypaert, M.; Glimcher, L.H. The transcription factor XBP-1 is essential for the development and survival of dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yang, L.; Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, P.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, M.; Jia, W.; Wang, X.; et al. The IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway regulates metabolic stress-induced compensatory proliferation of pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gaspard, J.P.; Mizukami, Y.; Li, J.; Graeme-Cook, F.; Chung, D.C. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in pancreatic beta-cells in vivo results in islet hyperplasia without hypoglycemia. Diabetes 2005, 54, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, D.; Cairrao, M.D.F.; Zeng, X.; Pires, E.; Coelho, A.V.; Ron, D.; Ryoo, H.D.; Domingos, P.M. Xbp1-independent Ire1 signaling is required for photoreceptor differentiation and rhabdomere morphogenesis in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chikka, M.R.; Xia, H.; Ready, D.F. Ire1 supports normal ER differentiation in developing Drosophila photoreceptors. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.-J.; Jiang, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Han, X.; Liu, C.-J. Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by IRE1α depends on its enzymatic activity. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Howell, A.S.; Dong, X.; A Taylor, C.; Cooper, R.C.; Zhang, J.; Zou, W.; Sherwood, D.R.; Shen, K. The unfolded protein response is required for dendrite morphogenesis. eLife 2015, 4, 06963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, Y.; Coleman, A.J.; Celestrin, K.; Cohen-Berkman, M.; Biederer, T.; Henis-Korenblit, S.; Bülow, H. Reduced Insulin/Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Mitigates Defective Dendrite Morphogenesis in Mutants of the ER Stress Sensor IRE-1. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, A.; Fujimoto, N.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, M.; Nakamura, D.; Iwano, M.; Iwawaki, T.; Kadokura, H.; Ron, D.; Kohno, K. Negative feedback by IRE1beta optimizes mucin production in goblet cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Misch, E.S.; Yang, L.; Hummasti, S.; Inouye, K.E.; Lee, A.-H.; Bierie, B.; Hotamisligil, G.S. The role of adipocyte XBP1 in metabolic regulation during lactation. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yan, C.; Fang, Q.-C.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.-P.; Shan, B.; Liu, J.-Q.; Li, H.-T.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is Regulated by the IRE1α-XBP1 Branch of the Unfolded Protein Response and Counteracts Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-induced Hepatic Steatosis. J. Boil. Chem. 2014, 289, 29751–29765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Zenno, A.; Shi, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, L. The IRE1α-XBP1 Pathway of the Unfolded Protein Response Is Required for Adipogenesis. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Wu, Y.; Yan, C.; Jiang, S.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Jia, W.; et al. Role for the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1α in liver regenerative responses. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kanno, Y.; Ishibashi, S.; Takahara, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Nakamura, T. Anti-apoptotic function of Xbp1 as an IL-3 signaling molecule in hematopoietic cells. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Shi, W.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L. Structural insights into IRE1 functions in the unfolded protein response. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Lerner, A.G.; Walle, L.V.; Upton, J.-P.; Xu, W.; Hagen, A.; Backes, B.J.; Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. IRE1alpha kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell 2009, 138, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, H.C.; Tong, M.; Wang, L.; Meza-Acevedo, R.; Gobillot, T.; Lebedev, I.; Gliedt, M.J.; Hari, S.B.; Mitra, A.K.; Backes, B.J.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Allosteric Inhibition of IRE1α with ATP-Competitive Ligands. ACS Chem. Boil. 2016, 11, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Perera, B.G.K.; Hari, S.B.; Bhhatarai, B.; Backes, B.J.; Seeliger, M.A.; Schürer, S.C.; Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R.; Maly, D.J. Divergent allosteric control of the IRE1α endoribonuclease using kinase inhibitors. Nat. Methods 2012, 8, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.; Ding, L.-W.; Sun, Q.-Y.; Torres-Fernandez, L.A.; Tan, S.Z.; Xiao, J.; Lim, S.L.; Garg, M.; Lee, K.L.; Kitajima, S.; et al. Selective inhibition of unfolded protein response induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4881–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Ruan, S.; Wang, M.; Ye, D.; Fan, N.; Meng, Q.; Tian, B.; Huang, T. A novel chemical, STF-083010, reverses tamoxifen-related drug resistance in breast cancer by inhibiting IRE1/XBP1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40692–40703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufanli, O.; Telkoparan-Akillilar, P.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Kocaturk, B.; Onat, U.I.; Hamid, S.M.; Cimen, I.; Walter, P.; Weber, C.; Erbay, E. Targeting IRE1 with small molecules counteracts progression of atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1395–E1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Niwa, M.; Koong, A. Targeting the IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the unfolded protein response in human diseases. Semin. Cancer Boil. 2015, 33, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Upton, J.-P.; Hagen, A.R.; Callahan, J.; Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. A kinase inhibitor activates the IRE1α RNase to confer cytoprotection against ER stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; He, G.-T.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.-B. IRE1α Signaling Pathways Involved in Mammalian Cell Fate Determination. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woehlbier, U.; Hetz, C. Modulating stress responses by the UPRosome: A matter of life and death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, F.; Schmid, J.; Dussmann, H.; Concannon, C.G.; Prehn, J.H.M. Imaging of single cell responses to ER stress indicates that the relative dynamics of IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/ATF4 signalling rather than a switch between signalling branches determine cell survival. Cell Death Differ 2015, 22, 1502–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Beatty, A.; Han, X.; Ji, Y.; Ma, X.; Adelstein, R.S.; Yates, J.R.; Kemphues, K.; Qi, L. Nonmuscle Myosin IIB Links Cytoskeleton to IRE1α Signaling during ER Stress. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, S.; Urano, F.; Min, W. AIP1 Is Critical in Transducing IRE1-mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response. J. Boil. Chem. 2008, 283, 11905–11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletto, D.; Eletto, D.; Dersh, D.; Gidalevitz, T.; Argon, Y. Protein disulfide isomerase A6 controls the decay of IRE1α signaling via disulfide-dependent association. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Nguyen, D.T.; Stuible, M.; Dubé, N.; Tremblay, M.L.; Chevet, E. Protein-tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Potentiates IRE1 Signaling during Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J. Boil. Chem. 2004, 279, 49689–49693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzi, F.; Gerlo, S.; Grieco, F.A.; Juusola, M.; Balhuizen, A.; Lievens, S.; Gysemans, C.; Bugliani, M.; Mathieu, C.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Ubiquitin D Regulates IRE1alpha/c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) Protein-dependent Apoptosis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12040–12056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisbona, F.; Rojas-Rivera, D.; Thielen, P.; Zamorano, S.; Todd, D.; Martinon, F.; Glavic, A.; Kress, C.; Lin, J.H.; Walter, P.; et al. BAX Inhibitor-1 Is a Negative Regulator of the ER Stress Sensor IRE1α. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, D.; Rojas-Rivera, D.; Rodríguez, D.A.; Groenendyk, J.; Kohler, A.; Lebeaupin, C.; Ito, S.; Urra, H.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Hazari, Y.; et al. Interactome Screening Identifies the ER Luminal Chaperone Hsp47 as a Regulator of the Unfolded Protein Response Transducer IRE1α. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 238–252.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Deepti, A.; Deegan, S.; Lisbona, F.; Hetz, C.; Samali, A. HSP72 Protects Cells from ER Stress-induced Apoptosis via Enhancement of IRE1α-XBP1 Signaling through a Physical Interaction. PLoS Boil. 2010, 8, e1000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcu, M.G.; Doyle, M.; Bertolotti, A.; Ron, D.; Hendershot, L.; Neckers, L.M. Heat Shock Protein 90 Modulates the Unfolded Protein Response by Stabilizing IRE1α. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2002, 22, 8506–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, T.; Oono, K.; Yui, D.; Gomi, F.; Katayama, T.; Tohyama, M.; Imaizumi, K. Activation of Caspase-12, an Endoplastic Reticulum (ER) Resident Caspase, through Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-associated Factor 2-dependent Mechanism in Response to the ER Stress. J. Boil. Chem. 2001, 276, 13935–13940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oono, K. JAB1 participates in unfolded protein responses by association and dissociation with IRE1. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Mao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, M.; You, J.; Ding, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xie, N.; Lin, X.; et al. A Crucial Role for RACK1 in the Regulation of Glucose-Stimulated IRE1 Activation in Pancreatic Cells. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Yao, W.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wang, F.; Aikhionbare, F.O.; Hill, N.L.; et al. IRE1-RACK1 axis orchestrates ER stress preconditioning-elicited cytoprotection from ischemia/reperfusion injury in liver. J. Mol. Cell Boil. 2015, 8, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Kebache, S.; Fazel, A.; Wong, H.N.; Jenna, S.; Emadali, A.; Lee, E.-H.; Bergeron, J.J.; Kaufman, R.J.; LaRose, L.; et al. Nck-dependent Activation of Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase-1 and Regulation of Cell Survival during Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Boil. Cell 2004, 15, 4248–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ye, Z.; Gu, X.; Wong, C.K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bay, W.P.; Victor, C.Y.; Li, P.; et al. RNF13, a RING finger protein, mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through the inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE1alpha)/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8726–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwa, M.; Chang, P. PARP16 is a tail-anchored endoplasmic reticulum protein required for the PERK- and IRE1α-mediated unfolded protein response. Nature 2012, 14, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Bernasconi, P.; Fisher, J.; Lee, A.-H.; Bassik, M.C.; Antonsson, B.; Brandt, G.S.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Schinzel, A.; Glimcher, L.H.; et al. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK Modulate the Unfolded Protein Response by a Direct Interaction with IRE1. Science 2006, 312, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Rodriguez, D.; Zamorano, S.; Lisbona, F.; Rojas-Rivera, D.; Urra, H.; Cubillos-Ruiz, J.R.; Armisen, R.; Henriquez, D.R.; Cheng, E.H.; Letek, M.; et al. BH3-only proteins are part of a regulatory network that control the sustained signalling of the unfolded protein response sensor IRE1α. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2322–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzi, F.; Gerlo, S.; Grieco, F.A.; Nardelli, T.R.; Lievens, S.; Gysemans, C.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Mathieu, C.; Tavernier, J.; et al. A Combined “Omics” Approach Identifies N-Myc Interactor as a Novel Cytokine-induced Regulator of IRE1α Protein and c-Jun N-terminal Kinase in Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Boil. Chem. 2014, 289, 20677–20693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Polymenis, M. Dcr2 targets Ire1 and downregulates the unfolded protein response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Teng, J. Cab45S inhibits the ER stress-induced IRE1-JNK pathway and apoptosis via GRP78/BiP. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Lee, S.-M.; Chen, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.D.; Kannan, K.; A Ortmann, R.; Fang, D. Synoviolin promotes IRE1 ubiquitination and degradation in synovial fibroblasts from mice with collagen-induced arthritis. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G.-C.; Moon, S.U.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, H.-S.; Han, H.D.; Kim, K.-H. PRKCSH contributes to tumorigenesis by selective boosting of IRE1 signaling pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Hayashi, T.; Hayashi, E.; Su, T.-P. Sigma-1 Receptor Chaperone at the ER-Mitochondrion Interface Mediates the Mitochondrion-ER-Nucleus Signaling for Cellular Survival. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, A.; Plumb, R.; Appathurai, S.; Mariappan, M. The Sec61 translocon limits IRE1α signaling during the unfolded protein response. eLife 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, R.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Appathurai, S.; Mariappan, M. A functional link between the co-translational protein translocation pathway and the UPR. eLife 2015, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkaew, D.; Chattopadhyay, A.; King, M.D.; Chunhacha, P.; Liu, Z.; Stevenson, H.L.; Chen, Y.; Sinthujaroen, P.; McDougal, O.M.; Fujise, K. Fortilin binds IRE1α and prevents ER stress from signaling apoptotic cell death. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urra, H.; Henriquez, D.R.; Cánovas, J.; Villarroel-Campos, D.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Pulgar, E.; Molina, E.; Hazari, Y.M.; Limia, C.M.; Alvarez-Rojas, S.; et al. IRE1α governs cytoskeleton remodelling and cell migration through a direct interaction with filamin A. Nature 2018, 20, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, S.; Villalta, S.A.; Feldman, H.C.; Register, A.C.; Rosenthal, W.; Hoffmann-Petersen, I.T.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Ghosh, R.; Wang, L.; Colon-Negron, K.; et al. Targeting ABL-IRE1alpha Signaling Spares ER-Stressed Pancreatic beta Cells to Reverse Autoimmune Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carafoli, E. Calcium signaling: A tale for all seasons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlach, A.; Klappa, P.; Kietzmann, T. The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Folding, Calcium Homeostasis, Signaling, and Redox Control. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1391–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezprozvanny, I. The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. Cell Calcium. 2005, 38, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Sorrentino, V. Molecular genetics of ryanodine receptors Ca2+-release channels. Cell Calcium 2002, 32, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, J.M. Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium pumps: Recent advances in our understanding of structure/function and biology (Review). Mol. Membr. Boil. 2000, 17, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squier, M.K.T.; Sehnert, A.J.; Sellins, K.S.; Malkinson, A.M.; Takano, E.; Cohen, J.J. Calpain and calpastatin regulate neutrophil apoptosis. J. Cell Physiol. 1999, 178, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-G.; Pathan, N.; Ethell, I.M.; Krajewski, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Shibasaki, F.; McKeon, F.; Bobo, T.; Franke, T.F.; Reed, J.C. Ca2+-Induced Apoptosis Through Calcineurin Dephosphorylation of BAD. Science 1999, 284, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Zhu, H.; Morishima, N.; Li, E.; Xu, J.; Yankner, B.A.; Yuan, J. Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-β. Nature 2000, 403, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennigs, J.K.; Burhenne, N.; Stähler, F.; Winnig, M.; Wälter, B.; Meyerhof, W.; Schmale, H. Sweet taste receptor interacting protein CIB1 is a general inhibitor of InsP3-dependent Ca2+releasein vivo. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.W.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, J.K.; Kang, Y.-H.; Chae, J.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, S.E.; Baik, J.-H.; et al. CIB1 functions as a Ca2+-sensitive modulator of stress-induced signaling by targeting ASK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17389–17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.M.; Byun, J.; Roh, S.-E.; Kim, S.J.; Mook-Jung, I. Reduced IRE1α mediates apoptotic cell death by disrupting calcium homeostasis via the InsP3 receptor. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassik, M.C.; Scorrano, L.; A Oakes, S.; Pozzan, T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Phosphorylation of BCL-2 regulates ER Ca2+ homeostasis and apoptosis. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, J.M.; Sakurikar, N.; E Alford, S.; Chu, R.; Chambers, T.C. Critical role of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein phosphorylation in mitotic death. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Ichijo, H.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 is phosphorylated and inactivated by an ASK1/Jun N-terminal protein kinase pathway normally activated at G(2)/M. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 8469–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Pattingre, S.; Sinha, S.; Bassik, M.; Levine, B. JNK1-Mediated Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 Regulates Starvation-Induced Autophagy. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.E.B.; Olsen, J.C.; Fulcher, N.B.; Wolfgang, M.C.; O’Neal, W.K.; Ribeiro, C.M.P. Airway Epithelial Inflammation-induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Store Expansion Is Mediated by X-box Binding Protein-1. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 14904–14913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Su, T.-P. Sigma-1 Receptor Chaperones at the ER- Mitochondrion Interface Regulate Ca2+ Signaling and Cell Survival. Cell 2007, 131, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-A.; Groenendyk, J.; Michalak, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress associated responses in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2014, 1843, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouaville, L.S.; Pinton, P.; Bastianutto, C.; Rutter, G.A.; Rizzuto, R. Regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis by calcium: Evidence for a long-term metabolic priming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13807–13812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras-Sureda, A.; Jaña, F.; Urra, H.; Durand, S.; Mortenson, D.E.; Sagredo, A.; Bustos, G.; Hazari, Y.; Ramos-Fernández, E.; Sassano, M.L.; et al. Non-canonical function of IRE1α determines mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum composition to control calcium transfer and bioenergetics. Nature 2019, 21, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2008, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Back, S.H.; Hur, J.; Lin, Y.-H.; Gildersleeve, R.; Shan, J.; Yuan, C.L.; Krokowski, D.; Wang, S.; Hatzoglou, M.; et al. ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nature 2013, 15, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX Family of ROS-Generating NADPH Oxidases: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, L.D.; Xu, S.; Choi, S.-K.; Ha, C.-M.; Thoudam, T.; Cha, S.-K.; Wiederkehr, A.; Wollheim, C.B.; Lee, I.-K.; Park, K.-S. Oxidative stress and calcium dysregulation by palmitate in type 2 diabetes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, R.; Hayakawa, T.; Takeda, K.; Ichijo, H. Therapeutic targets in the ASK1-dependent stress signaling pathways. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2012, 88, 434–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, F.; Xie, J.; Zhang, D.; Han, Y.; Wang, C. Polypeptide from Chlamys farreri suppresses ultraviolet-B irradiation-induced apoptosis through restoring ER redox homeostasis, scavenging ROS generation, and suppressing the PERK-eIF2a-CHOP pathway in HaCaT cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Boil. 2015, 151, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Han, D.; Petrovic, L.M.; Kaplowitz, N. c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK)-dependent Acute Liver Injury from Acetaminophen or Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Requires Mitochondrial Sab Protein Expression in Mice. J. Boil. Chem. 2011, 286, 35071–35078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, S.; A Than, T.; Fernándezcheca, J.C.; Kaplowitz, N. JNK interaction with Sab mediates ER stress induced inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Ryoo, H.D.; Jasper, H. Integration of UPRER and Oxidative Stress Signaling in the Control of Intestinal Stem Cell Proliferation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.X.; Tanaka, L.Y.; Wosniak, J.; Laurindo, F.R. Mechanisms and Implications of Reactive Oxygen Species Generation During the Unfolded Protein Response: Roles of Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidoreductases, Mitochondrial Electron Transport, and NADPH Oxidase. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2409–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, A.G.; Upton, J.-P.; Praveen, P.; Ghosh, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Igbaria, A.; Shen, S.; Nguyen, V.; Backes, B.J.; Heiman, M.; et al. IRE1α induces thioredoxin-interacting protein to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote programmed cell death under irremediable ER stress. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuaita, B.H.; Burkholder, K.M.; Boles, B.R.; O’Riordan, M.X. The Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1α Augments Bacterial Killing through Sustained Oxidant Production. mBio 2015, 6, 00705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Antioxidants in human health and disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1996, 16, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishanina, T.; Libiad, M.; Banerjee, R. Biogenesis of reactive sulfur species for signaling by hydrogen sulfide oxidation pathways. Nat. Methods 2015, 11, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, A.M.; Kohr, M.J.; Murphy, E. S-Nitrosylation: Specificity, Occupancy, and Interaction with Other Post-Translational Modifications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourihan, J.M.; Mazzeo, L.E.M.; Fernandez-Cardenas, L.P.; Blackwell, T.K. Cysteine Sulfenylation Directs IRE-1 to Activate the SKN-1/Nrf2 Antioxidant Response. Mol Cell 2016, 63, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanekura, K.; Ma, X.; Murphy, J.T.; Zhu, L.J.; Diwan, A.; Urano, F. IRE1 prevents endoplasmic reticulum membrane permeabilization and cell death under pathological conditions. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassler, J.R.; Scheuner, D.L.; Wang, S.; Han, J.; Kodali, V.K.; Li, P.; Nguyen, J.; George, J.S.; Davis, C.; Wu, S.P.; et al. The IRE1alpha/XBP1s Pathway Is Essential for the Glucose Response and Protection of beta Cells. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Saito, M.; Kohno, K. Pathogenic Mechanism of Diabetes Development Due to Dysfunction of Unfolded Protein Response. Yakugaku Zasshi 2016, 136, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, A.-H.; Heidtman, K.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Glimcher, L.H. Dual and opposing roles of the unfolded protein response regulated by IRE1α and XBP1 in proinsulin processing and insulin secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8885–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.; Luzuriaga, J.; Maxwell, E.L.; West, P.K.; Bensellam, M.; Laybutt, D.R. The balance between adaptive and apoptotic unfolded protein responses regulates beta-cell death under ER stress conditions through XBP1, CHOP and JNK. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2015, 413, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-M.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, K. Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1 Facilitates Diabetic Wound Healing Through Modulating MicroRNAs. Diabetes 2016, 66, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-Q.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Chan, S.M.; Li, S.-P.; Jo, E.; Leung, S.-L.; Molero, J.C.; Ye, J.-M. IRE1 impairs insulin signaling transduction of fructose-fed mice via JNK independent of excess lipid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allagnat, F.; Christulia, F.; Ortis, F.; Pirot, P.; Lortz, S.; Lenzen, S.; Eizirik, D.L.; Cardozo, A.K. Sustained production of spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces pancreatic beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis. Diabetology 2010, 53, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Harg, J.M.; Van Heest, J.C.; Bangel, F.N.; Patiwael, S.; Van Weering, J.R.; Scheper, W. The UPR reduces glucose metabolism via IRE1 signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2017, 1864, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P. Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) and Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Fu, N.; Yang, P. MiR-17 Downregulation by High Glucose Stabilizes Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein and Removes Thioredoxin Inhibition on ASK1 Leading to Apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 150, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Y.; Gu, H.; Reece, E.A.; Fang, S.; Gabbay-Benziv, R.; Aberdeen, G.; Yang, P. Ask1 Gene Deletion Blocks Maternal Diabetes–Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Developing Embryo by Disrupting the Unfolded Protein Response Signalosome. Diabetes 2014, 64, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hou, X.-F.; Wang, G.; Zhong, Q.-X.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.-H.; Yang, N.; Gu, J.-F.; Wang, C.-F.; Zhang, L.; et al. Terpene glycoside component from Moutan Cortex ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-related inflammatory responses. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Liu, J.; Ni, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Suppression of XBP1S Mediates High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Extracellular Matrix Synthesis in Renal Mesangial Cell and Kidney of Diabetic Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Huang, L.; Pang, Q.; Nie, L.; Mu, J.; Yuan, F.; Feng, B. ER stress triggers MCP-1 expression through SET7/9-induced histone methylation in the kidneys of db/db mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2014, 306, F916–F925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Ying, W.; Nandi, S.S.; Bandyopadhyay, G.K.; Patel, K.K.; Mahata, S.K. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An Immunometabolic Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Inflammatory Basis of Metabolic Disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, U. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Links Obesity, Insulin Action, and Type 2 Diabetes. Science 2004, 306, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirosumi, J.; Tuncman, G.; Chang, L.; Görgün, C.Z.; Uysal, K.T.; Maeda, K.; Karin, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 2002, 420, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, D.M.; Calixto, M.C.; Sollon, C.; Alexandre, E.C.; Tavares, E.B.G.; Naime, A.C.A.; Anhê, G.F.; Antunes, E. High-fat diet-induced obesity impairs insulin signaling in lungs of allergen-challenged mice: Improvement by resveratrol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, J.K.; Flier, J.S. Attenuation of leptin and insulin signaling by SOCS proteins. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, P.; Van Obberghen, E. SOCS proteins causing trouble in insulin action. Acta Physiol. 2007, 192, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-H.; Bazuine, M.; Lumeng, C.N.; Geletka, L.M.; Mowers, J.; White, N.M.; Ma, J.-T.; Zhou, J.; Qi, N.; Westcott, D.; et al. The Protein Kinase IKKɛ Regulates Energy Balance in Obese Mice. Cell 2009, 138, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Han, Z.; Couvillon, A.D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Exton, J.H. Autocrine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Links Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to the Membrane Death Receptor Pathway through IRE1α-Mediated NF-κB Activation and Down-Regulation of TRAF2 Expression. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2006, 26, 3071–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Ma, R.C.; Chan, J.C.N.; Xu, H.; Xu, G. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide impairs insulin signaling via inducing adipocyte inflammation in glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide receptor-overexpressing adipocytes. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, S.M.; Ghosh, S.; Tantiwong, P.; Meka, C.R.; Eagan, P.; Jenkinson, C.P.; Cersosimo, E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Coletta, D.K.; Sriwijitkamol, A.; et al. Elevated Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression and Signaling in Muscle From Insulin-Resistant Subjects. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, J.; Lu, A.; Sun, C.; Chung, J.; Ueki, K.; Ozcan, U. The regulatory subunits of PI3K, p85α and p85β, interact with XBP-1 and increase its nuclear translocation. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Aleman, J.; Ueki, K.; Luo, J.; Asano, T.; Kaneto, H.; Stephanopoulos, G.; Cantley, L.C.; Kahn, C.R. The p85α Regulatory Subunit of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Potentiates c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase-Mediated Insulin Resistance. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2007, 27, 2830–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Sakaki, K.; Saunders, T.L.; Rutkowski, D.T.; Back, S.H.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Activates Cleavage of CREBH to Induce a Systemic Inflammatory Response. Cell 2006, 124, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Tang, L.; Sun, H.; Guo, H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress preconditioning antagonizes low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammation in human mesangial cells through upregulation of XBP1 and suppression of the IRE1alpha/IKK/NF-kappaB pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammoun, H.L.; Chabanon, H.; Hainault, I.; Luquet, S.H.; Magnan, C.; Koike, T.; Ferre, P.; Foufelle, F. GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak, M.J.; Lee, A.-H.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Guigni, B.A.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Glimcher, L.H.; Shulman, G.I. Dissociation of inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE1α)-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation from hepatic insulin resistance in conditional X-box-binding protein-1 (XBP1) knock-out mice. J. Boil. Chem. 2011, 287, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrema, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lee, J.; Hernandez, M.A.S.; Shulman, G.I.; Ozcan, U. XBP1s Is an Anti-lipogenic Protein. J. Boil. Chem. 2016, 291, 17394–17404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Joe, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jeong, S.O.; Pae, H.-O.; Ryter, S.W.; Surh, Y.-J.; Chung, H.T. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced IRE1alpha activation mediates cross-talk of GSK-3beta and XBP-1 to regulate inflammatory cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4498–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Calay, E.S.; Fan, J.; Arduini, A.; Kunz, R.C.; Gygi, S.P.; Yalcin, A.; Fu, S.; Hotamisligil, G.S. S-Nitrosylation links obesity-associated inflammation to endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction. Science 2015, 349, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, C.; Xia, Z.; Dai, J.; Shao, M.; Zhao, F.; He, S.; Yang, L.; et al. The metabolic ER stress sensor IRE1α suppresses alternative activation of macrophages and impairs energy expenditure in obesity. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könner, A.C.; Brüning, J.C. Toll-like receptors: Linking inflammation to metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Chen, X.; Lee, A.-H.; Glimcher, L.H. TLR activation of the transcription factor XBP1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, G.; Shan, Q.; Lu, J.; Fan, S.; Sun, C.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Su, W.; et al. Troxerutin Attenuates Enhancement of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis by Inhibiting NOD Activation-Mediated Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Treated Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Deng, T.; Peterson, L.; Yu, R.; Lin, J.; Hamilton, D.J.; Reardon, P.R.; Sherman, V.; Winnier, G.E.; Zhan, M.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of human adipocytes implicates the NOD-like receptor pathway in obesity-induced adipose inflammation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 394, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keestra-Gounder, A.M.; Byndloss, M.X.; Seyffert, N.; Young, B.M.; Chávez-Arroyo, A.; Tsai, A.Y.; Cevallos, S.A.; Winter, M.G.; Pham, O.H.; Tiffany, C.R.; et al. NOD1 and NOD2 signalling links ER stress with inflammation. Nature 2016, 532, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Gris, D.; Lei, Y.L.; Jha, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.T.-H.; Brickey, W.J.; Ting, J.P.-Y. Fatty acid-induced NLRP3-ASC inflammasome activation interferes with insulin signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimen, I.; Kocaturk, B.; Koyuncu, S.; Tufanli, O.; Onat, U.I.; Yıldırım, A.D.; Apaydın, O.; Şeyma, D.; Aykut, Z.G.; Nguyen, U.T.; et al. Prevention of atherosclerosis by bioactive palmitoleate through suppression of organelle stress and inflammasome activation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 358ra126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, Y.-H.; Adijiang, A.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Burk, D.; Ravussin, A.; Dixit, V.D. Elimination of the NLRP3-ASC inflammasome protects against chronic obesity-induced pancreatic damage. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4039–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Peng, J.; An, H.; He, Q.; Boronina, T.; Guo, S.; White, M.F.; Cole, P.A.; He, L. Endotoxemia-mediated activation of acetyltransferase P300 impairs insulin signaling in obesity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; He, L. IRS posttranslational modifications in regulating insulin signaling. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 60, R1–R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IRE1α Binding Partner | Function of IRE1α Binding Partner | Functional Implication | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMIIB (Non muscle myosin IIB) | A Cytoskeleton myosin protein | Interacts with IRE1α and regulates its oligomerization and activation. In addition, recruits other regulatory molecules to oligomerized foci. | [136] |
| AIP1 | Apoptotic signaling transducer | AIP1-IRE1α association enhances IRE1 dimerization and its downstream JNK/XBP1 activation. | [137] |
| PDIA6 | Chaperonic protein of ER that inhibits aggregation of misfolded proteins | PDIA6 attenuates the activity of IRE1α. PDIA6, an ER resident protein disulfide isomerase. Negatively regulates IRE1α by binding to its luminal domain at cysteine 148, if it is oxidized, IRE1α will be activated. PDIA6-deficient cells hyperrespond to ER stress with sustained autophosphorylation of IRE1α and increased XBP1s, pJNK. | [138] |
| PTP-1B | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B | In the absence of PTP-1B, ER stress-induced IRE1α downstream activities were impaired, especially XBP1 splicing and JNK activation. | [139] |
| UbD | Ubiquitin-like modifier family member | UbD regulates IRE1α/c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway. It provides a negative feedback on cytokine-induced activation of the IRE1α/JNK pro-apoptotic pathway in cytokine-exposed beta cells, but did not change cytokine-induced XBP1 splicing. | [140] |
| TMBIM6 | ER localized antiapoptotic protein, also known as Bax inhibitor-1 (BI-1) | This has been implicated in the negative modulation of XBP1 splicing activity through interacting with a cytosolic region of IRE1α. | [141] |
| Hsp47 | Heat shock protein | Hsp47 binds directly to the IRE1 ER luminal domain with high affinity, eliminating BiP from the complex to allow IRE1α oligomerization for optimal signaling. | [142] |
| HSP72 | Heat shock protein | Overexpression of HSP72, survival effect of HSP72 under ER stress is mediated by enhanced XBP1splicing and its target genes. Regulation of UPR by HSP72 is by formation of stable protein complex with IRE1α. | [143] |
| HSP90 | Heat shock protein | HSP90 stabilizes IRE1α by preventing the proteasomal degradation, and treatment of HSP90 inhibitor decreases IRE1α protein stability. | [144] |
| JIK | c-Jun N-terminal inhibitory kinase | IRE1α and TRAF2 complex induce apoptotic signal through c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and activation of caspase-12. | [145] |
| JAB1 | Jun activation domain-binding protein-1 | Mutant JAB1 down-regulates the UPR signaling pathway through tight binding with IRE1alpha. | [146] |
| RACK1 | Receptor for activated C-kinase 1 | Interacts with IRE1α and plays a role in dephosphorylation of IRE1α by protein phosphatase (PP2A). Furthermore, IRE1α and RACK1 association may contribute in this process of antiapoptosis by phosphorylating AMPK and Bcl-2 through enhancing autophagy. | [147,148] |
| Nck | SH2/SH3 adaptor protein | Nck and IRE1α association in immune T cells have a critical role in ER-stressed activation of MAPK pathway and cell survival. | [149] |
| RNF13 | RING finger protein | RNF13 knockdown cells showed resistance to apoptosis and JNK activation triggered by ER stress. Conversely, overexpression of RNF13 induces JNK activation and caspase-dependent apoptosis. | [150] |
| PARP16/ARTD15 | Poly ADP-ribose polymerases/ADP-ribosyl transferase D proteins | PARP16 is an upstream regulator, and modification increases its kinase and the endonuclease activity of IRE1α. | [151] |
| BAX/BAK | Pro-apoptotic protein | BAX and BAK directly interact at cytosolic domain of IRE1α during stress condition and promote the stabilized IRE1α activity. | [152] |
| BIM/PUMA | Pro-apoptotic protein | BIM and PUMA have also been linked to IRE1α regulation by direct binding with IRE1α via their BH3 domain in stress-dependent manner. Cells deficient in both BIM and PUMA exhibited reduced splicing of XBP-1 and RIDD. | [153] |
| NMI | N-Myc interactor | Interacts and modulates IRE1α especially in pancreatic beta cell. It negatively regulates the IRE1α-mediated JNK activation and further the cell death. | [154] |
| DCR2 | Dose-dependent cell-cycle regulator 2 | Physically interacts with phosphorylated IRE1α and causes dephosphorylation and IRE1 deactivation. | [155] |
| Cab45S | A member of the CREC family | Negatively regulates RNAse activity of IRE1α and prevents more spliced forms of X-box-binding protein 1 mRNA at the early stage of stress and further phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase induced apoptosis. | [156] |
| SYVN1 | Functions in ER-associated degradation process | Coexpression of IRE1 and SYVN1 increased IRE1 degradation and ubiquitination. | [157] |
| DDRGK1 | DDRGK domain-containing protein 1 | Interaction of DDRGK1 with IRE1α counteracts ubiquitination and subsequently inhibits the ERAD-mediated degradation of IRE1α. | [55] |
| PRKCSH | Protein kinase C substrate 80K-H | In ER stress condition, PRKCH steps up ER stress-mediated autophosphorylation and oligomerization of IRE1 through mutual interaction followed by XBP1 splicing and MAPK activation which contribute to tumorigenesis. | [158] |
| Sigma-1 receptor | Unique ligand-regulated molecular chaperone in the ER. | Under ER stress conditions, interacts with and stabilizes IRE1α and enhances cell survival through prolonged activation of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway, especially in cancer cell survival. | [159] |
| Sec61 | Channel-forming translocon complex | Forms a hetero-oligomeric complex with IRE1α upon ER stress. It recruits XBP1u and aids in splicing. The Sec61-IRE1α complex defines the extent of IRE1α activity and may determine cell fate decisions during ER stress conditions. | [160,161] |
| Fortilin | Pro-survival molecule | Interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of IRE1α, inhibits both kinase and RNase activities, and protects cells from apoptotic cell death. | [162] |
| Filamin A | Actin crosslinking factor involved in the remodeling of cytoskeletons | Through a novel domain located at the distal C-terminal region, monomeric IRE1α interacts physically with Filamine A. A pro-migratory stimulus causes dimerization of IRE1α, increasing Filamin A binding and PKCα recruitment. Phosphorylation of Filamine A by PKCα at S2152 improves actin cytoskeleton remodeling and cell migration in different animal species | [163] |
| ABL kinase | Tyrosine-protein kinase | ABL kinase interaction enhances IRE1α RNase activity and potentiates its apoptosis signaling pathway. | [164] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riaz, T.A.; Junjappa, R.P.; Handigund, M.; Ferdous, J.; Kim, H.-R.; Chae, H.-J. Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Cellular Physiology, Calcium, ROS Signaling, and Metaflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051160
Riaz TA, Junjappa RP, Handigund M, Ferdous J, Kim H-R, Chae H-J. Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Cellular Physiology, Calcium, ROS Signaling, and Metaflammation. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051160
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiaz, Thoufiqul Alam, Raghu Patil Junjappa, Mallikarjun Handigund, Jannatul Ferdous, Hyung-Ryong Kim, and Han-Jung Chae. 2020. "Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Cellular Physiology, Calcium, ROS Signaling, and Metaflammation" Cells 9, no. 5: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051160
APA StyleRiaz, T. A., Junjappa, R. P., Handigund, M., Ferdous, J., Kim, H.-R., & Chae, H.-J. (2020). Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Cellular Physiology, Calcium, ROS Signaling, and Metaflammation. Cells, 9(5), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051160






