Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects, Anthropometric Measurements, and Clinical Assays
2.2. Anthropometry and Clinical Assays
2.3. Collection of Adipose Tissue Biopsies
2.4. Multiplex Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.6. Confocal Microscopy (CM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
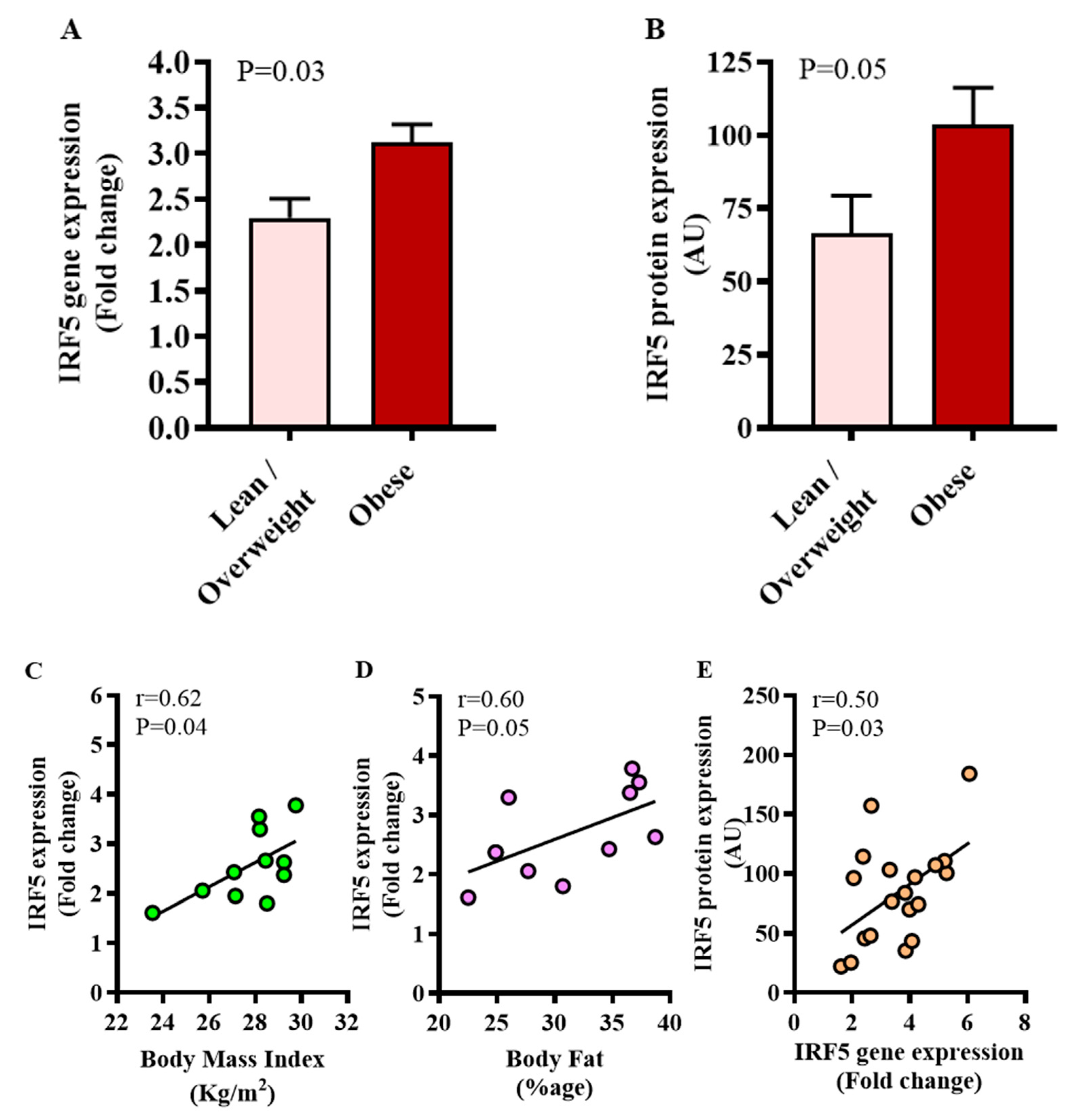
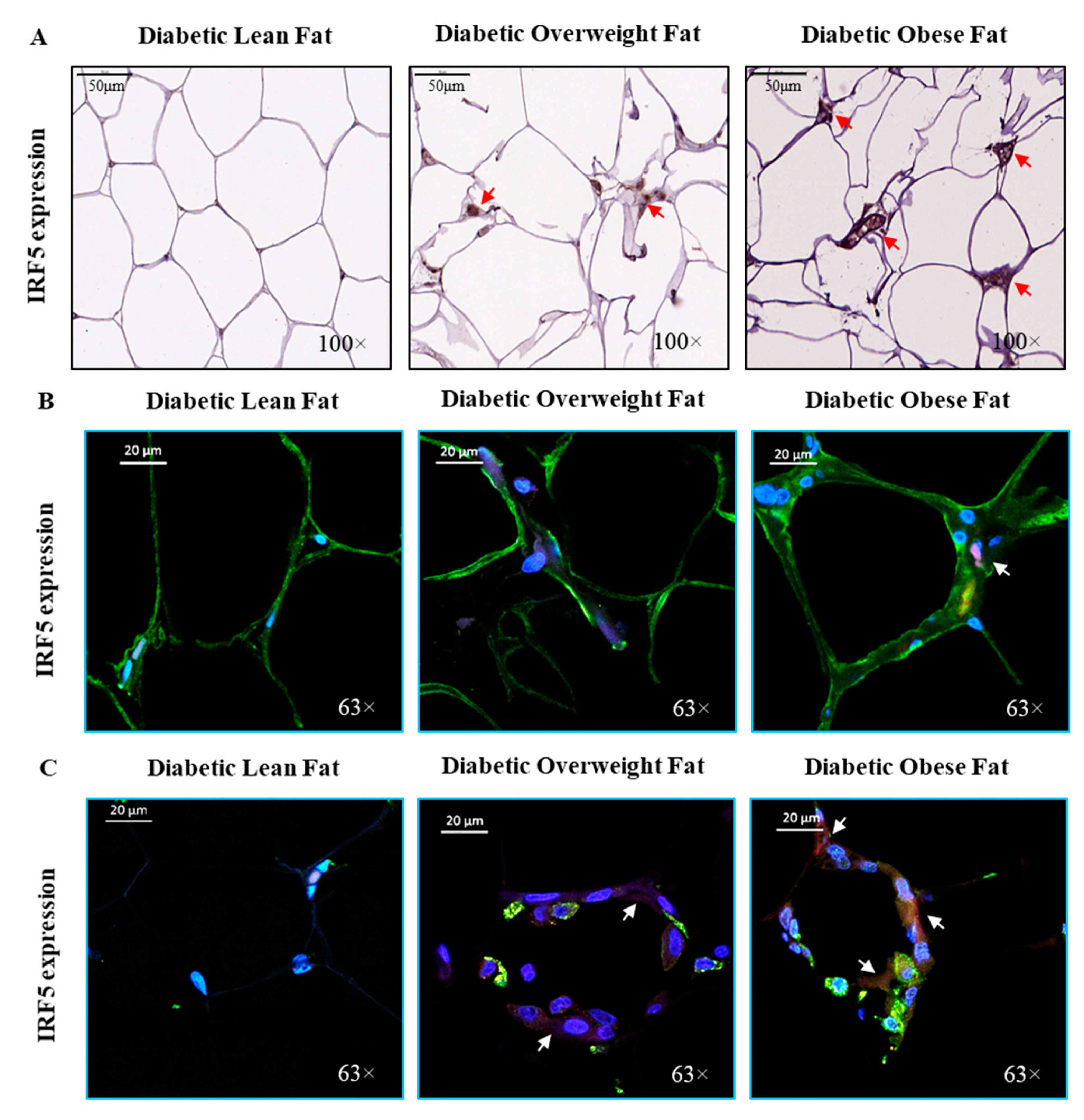
3.1. Increased Adipose Tissue IRF5 Expression in Diabetic Obese Patients
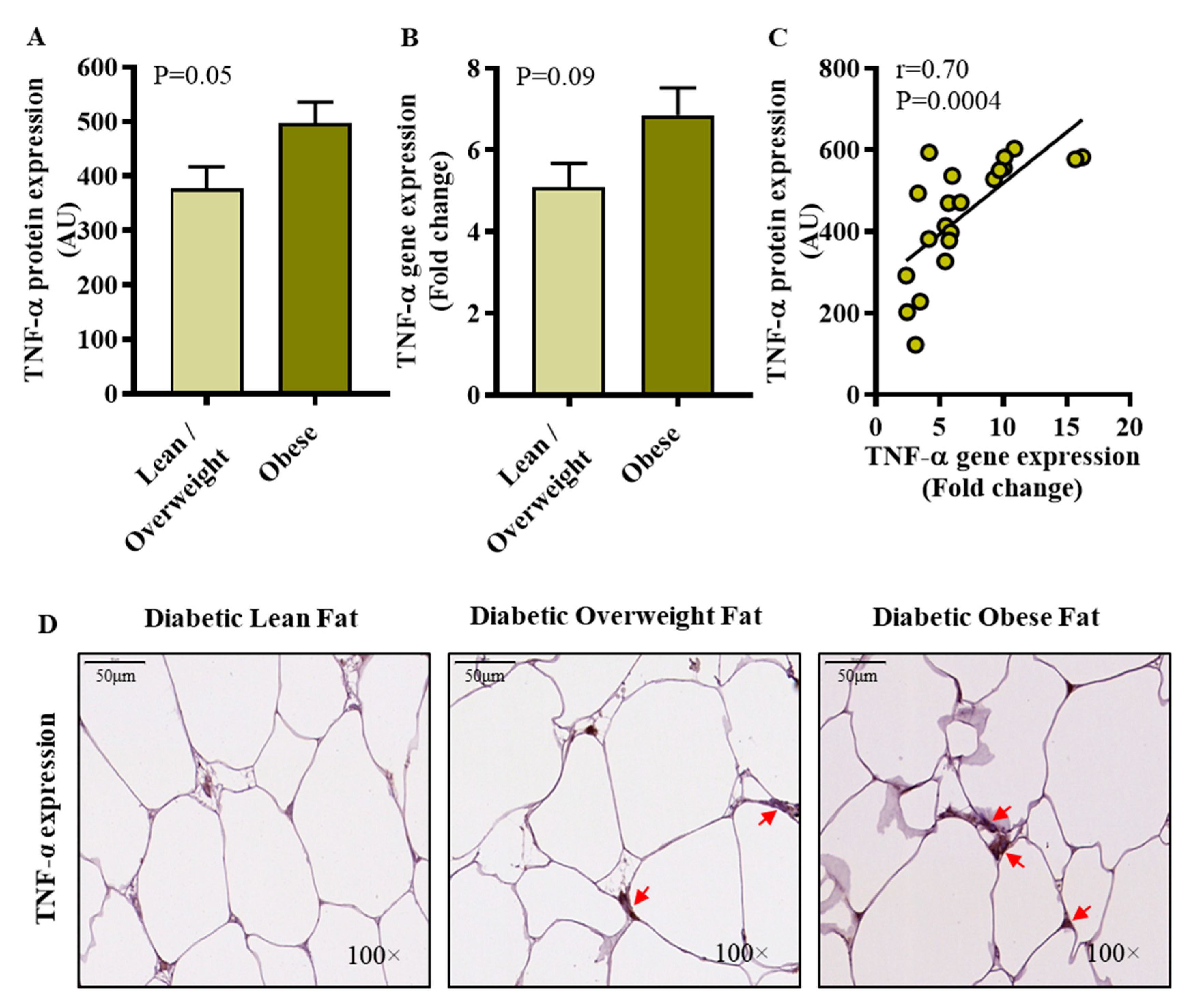
3.2. Elevated Adipose TNF-α Protein Expression in Diabetic Obese Patients Conforms with IRF5 Expression
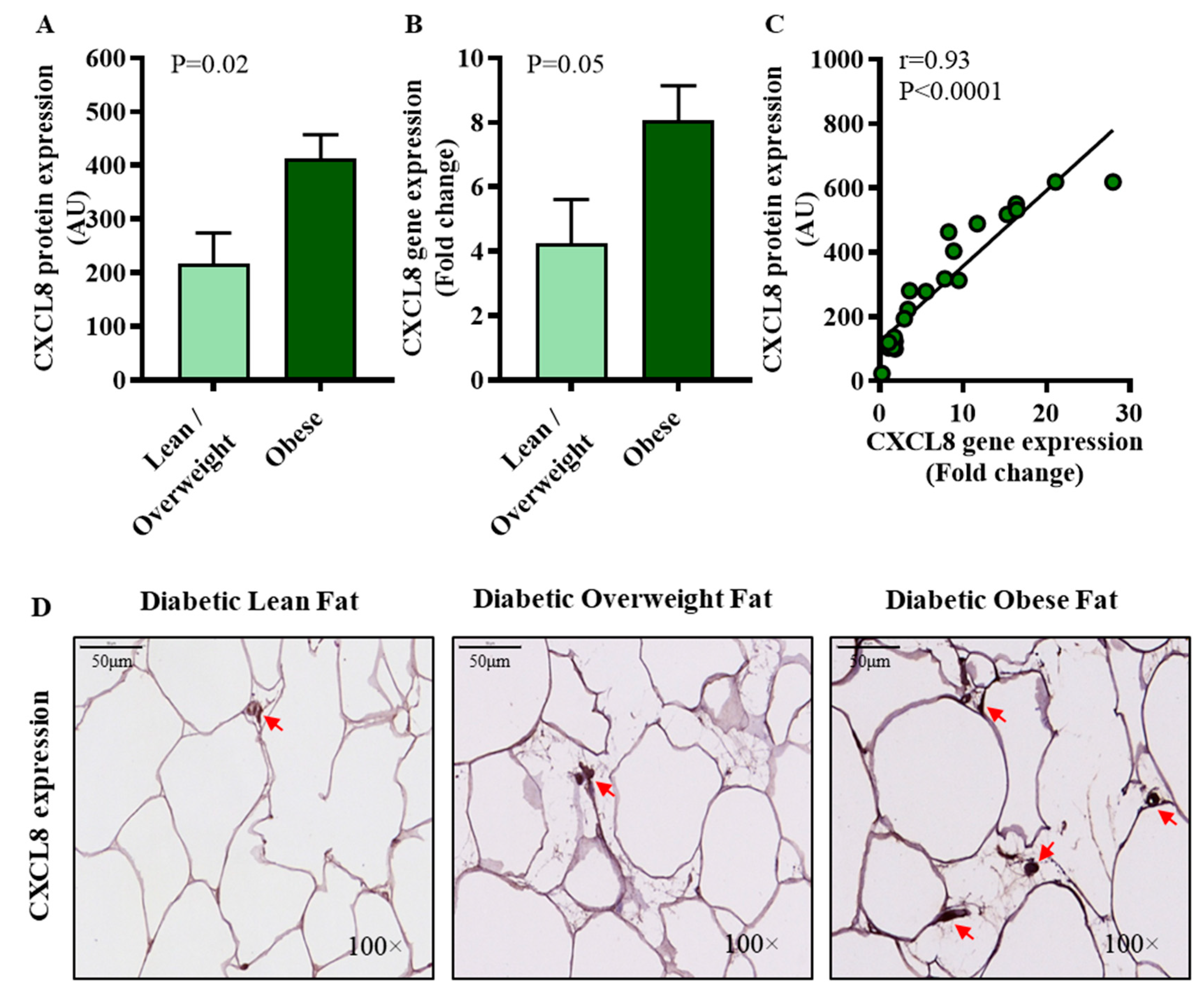
3.3. CXCL8 Expression in Diabetic Obese Individuals Associates Positively with IRF5 Expression in the Adipose Tissue
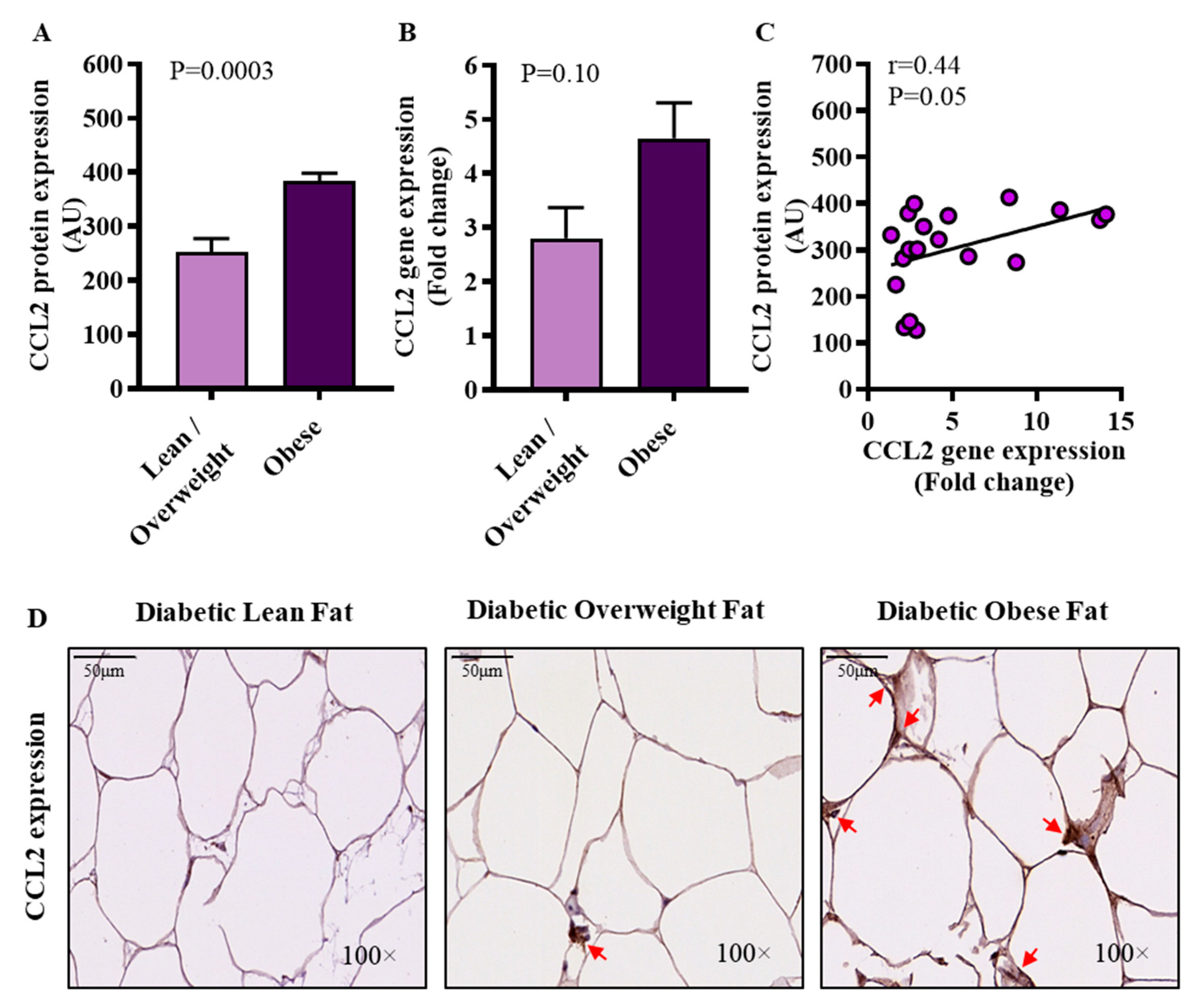
3.4. Increased Adipose CCL2 Protein Expression in Diabetic Obese Patients
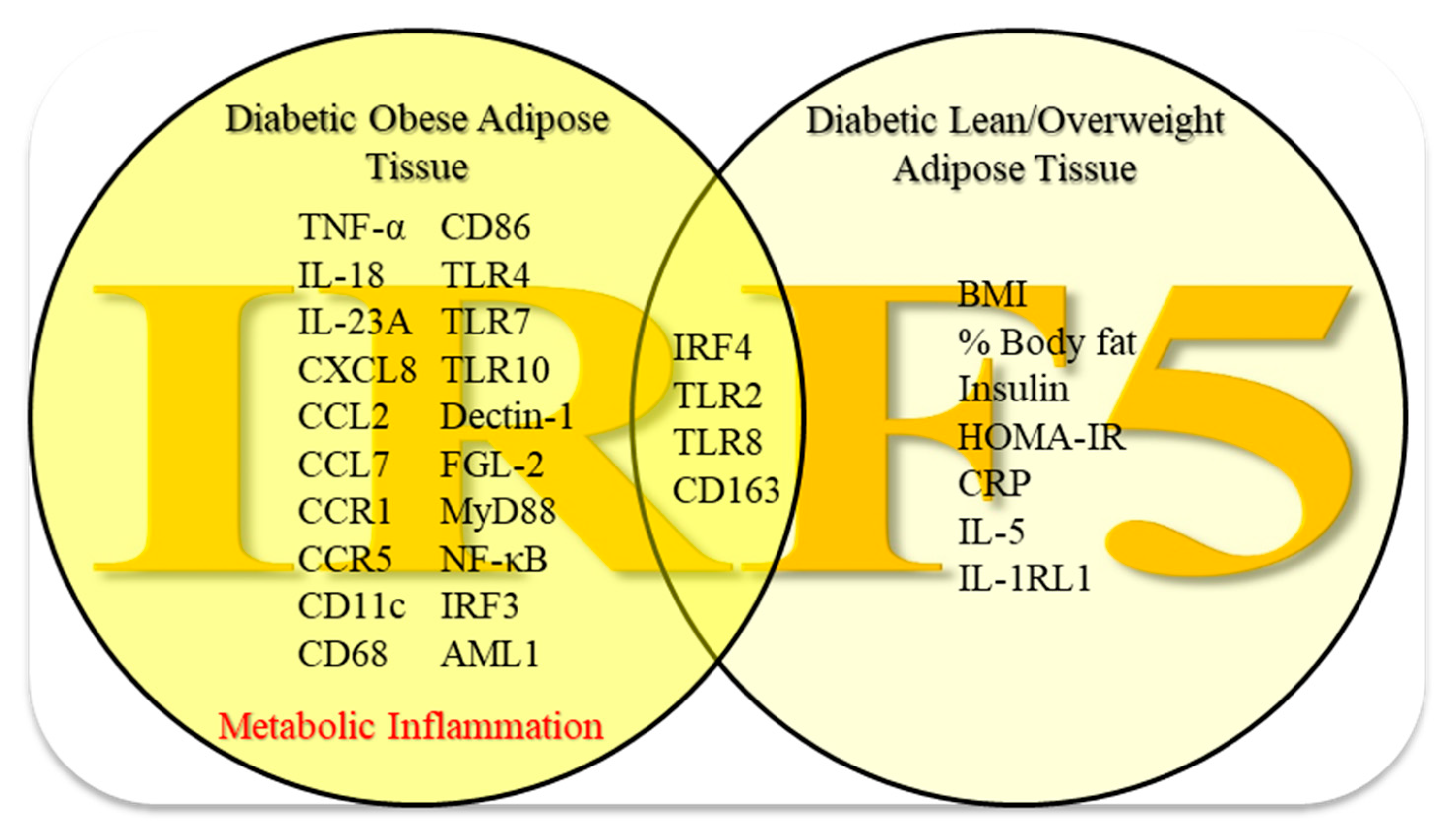
3.5. Relationship of IRF5 Gene Expression with Metabolic Markers and Inflammatory Signature in the Adipose Tissue
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP-1 | Activator protein-1 |
| ATMs | Adipose tissue macrophages |
| AU | Arbitrary unit |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CM | Confocal microscopy |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DAB | 3,3ʹ-diaminobenzidine |
| DAPI | 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| FAM | 6-fluorescein amidite |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IRAK-1 | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 |
| IRFs | Interferon regulatory factors |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MGB | Minor groove binder |
| NFQ | Non-fluorescent quencher |
| PBF | Percent body fat |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| T2D | Type-2 diabetes |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
References
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Greevenbroek, M.M.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Stehouwer, C.D. Obesity-associated low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Causes and consequences. Neth. J. Med. 2013, 71, 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, N.; Garg, A.; Peshock, R.M.; Stray-Gundersen, J.; Grundy, S.M. Relationships of generalized and regional adiposity to insulin sensitivity in men. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 461S–465S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Pessin, J.E. Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2013, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge-Aubry, C.E.; Somm, E.; Giusti, V.; Pernin, A.; Chicheportiche, R.; Verdumo, C.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Burger, D.; Dayer, J.M.; Meier, C.A. Adipose tissue is a major source of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: Upregulation in obesity and inflammation. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruun, J.M.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Regulation of interleukin 8 production and gene expression in human adipose tissue in vitro. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartipy, P.; Loskutoff, D.J. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7265–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, A.; Rumberger, J.M.; Stuart, C.A.; Ruhoff, M.S. Stimulation of lipolysis by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is glucose dependent: Implications for long-term regulation of lipolysis. Diabetes 2004, 53, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, E.; Nguyen, P.; Guenounou, M.; Durlach, V.; Potron, G.; Leutenegger, M. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) are essentially dependent on visceral fat amount in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. 2000, 26, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Arner, P.; Caro, J.F.; Atkinson, R.L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, P.A.; Saghizadeh, M.; Ong, J.M.; Bosch, R.J.; Deem, R.; Simsolo, R.B. The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue. Regulation by obesity, weight loss, and relationship to lipoprotein lipase. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G. Role of fatty acids in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and NIDDM. Diabetes 1997, 46, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, S.K.; Bunkin, D.A.; Greenberg, A.S. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: Depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Thomas, R.; Shihab, P.; Sriraman, D.; Behbehani, K.; Ahmad, R. Obesity Is a Positive Modulator of IL-6R and IL-6 Expression in the Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue: Significance for Metabolic Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Ali, V.; Goodrick, S.; Rawesh, A.; Katz, D.R.; Miles, J.M.; Yudkin, J.S.; Klein, S.; Coppack, S.W. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4196–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, L.; Lalic, N.; Rajkovic, N.; Jotic, A.; Lalic, K.; Milicic, T.; Seferovic, J.; Macesic, M.; Gajovic, J. Hypertension in Obese Type 2 Diabetes Patients is Associated with Increases in Insulin Resistance and IL-6 Cytokine Levels: Potential Targets for an Efficient Preventive Intervention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3586–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Thomas, R.; Kochumon, S.; Sindhu, S. Increased adipose tissue expression of IL-18R and its ligand IL-18 associates with inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2017, 5, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.A. Role of interleukins in obesity: Implications for metabolic disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Thomas, R.; Kochumon, S.; Wilson, A.; Abu-Farha, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. Increased Adipose Tissue Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 in Obesity: Association with Metabolic Inflammation. Cells 2019, 8, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Akhter, N.; Arefanian, H.; Al-Roub, A.A.; Ali, S.; Wilson, A.; Al-Hubail, A.; Al-Beloushi, S.; Al-Zanki, S.; Ahmad, R. Increased circulatory levels of fractalkine (CX3CL1) are associated with inflammatory chemokines and cytokines in individuals with type-2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2017, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochumon, S.; Al-Rashed, F.; Abu-Farha, M.; Devarajan, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Adipose tissue expression of CCL19 chemokine is positively associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.; Lubyova, B.; Pitha, P.M. On the role of IRF in host defense. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002, 22, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, J.; Yan, Q.W.; Schones, D.E.; Kamal, M.; Hsu, C.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Crawford, G.E.; Rosen, E.D. Interferon regulatory factors are transcriptional regulators of adipogenesis. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, C.E.; O’Rahilly, S.; Rochford, J.J. Adipogenesis at a glance. J. Cell Sci 2011, 124, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmas, E.; Toubal, A.; Alzaid, F.; Blazek, K.; Eames, H.L.; Lebozec, K.; Pini, M.; Hainault, I.; Montastier, E.; Denis, R.G.; et al. Irf5 deficiency in macrophages promotes beneficial adipose tissue expansion and insulin sensitivity during obesity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfki, H.; Ben Ali, S.; Bougatef, S.; Ben Ahmed, D.; Haddad, N.; Jmal, A.; Abdennebi, M.; Ben Romdhane, H. Association between C-reactive protein and type 2 diabetes in a Tunisian population. Inflammation 2012, 35, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Al-Mass, A.; Atizado, V.; Al-Hubail, A.; Al-Ghimlas, F.; Al-Arouj, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Dermime, S.; Behbehani, K. Elevated expression of the toll like receptors 2 and 4 in obese individuals: Its significance for obesity-induced inflammation. J. Inflamm. 2012, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Wang, X.; Lantier, L.; Lyubetskaya, A.; Eguchi, J.; Kang, S.; Tenen, D.; Roh, H.C.; Kong, X.; Kazak, L.; et al. IRF3 promotes adipose inflammation and insulin resistance and represses browning. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2839–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, J.; Kong, X.; Tenta, M.; Wang, X.; Kang, S.; Rosen, E.D. Interferon regulatory factor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation through regulation of adipose tissue macrophage polarization. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3394–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, T.L.; Reaven, G.M. Beyond type 2 diabetes: The need for a clinically useful way to identify insulin resistance. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammation and lipid signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanavari, T.; Giannogonas, P.; Karalis, K.P. TNF-alpha and obesity. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Fernandez-Veledo, S.; Kramer, D.K.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Lorenzo, M. Insulin resistance associated to obesity: The link TNF-alpha. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, S.E. The role of TNF-alpha in insulin resistance. Endocrine 2004, 23, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha: A key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.W.; Sokol, C.L.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Al-Roub, A.; Kochumon, S.; Akther, N.; Thomas, R.; Kumari, M.; Koshy, M.S.; Tiss, A.; Hannun, Y.A.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. The Synergy between Palmitate and TNF-alpha for CCL2 Production Is Dependent on the TRIF/IRF3 Pathway: Implications for Metabolic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3599–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Akhter, N.; Al-Roub, A.; Thomas, R.; Kochumon, S.; Wilson, A.; Koshy, M.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. TNF-alpha in Combination with Palmitate Enhances IL-8 Production via The MyD88- Independent TLR4 Signaling Pathway: Potential Relevance to Metabolic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharieva, E.; Kamenov, Z.; Velikova, T.; Tsakova, A.; El-Darawish, Y.; Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 serum level is elevated in type 2 diabetes and latent autoimmune diabetes. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Borg, D.J.; Harcourt, B.E.; Tong, H.; Sheng, Y.H.; Ng, C.P.; Das, I.; Wang, R.; Chen, A.C.; Loudovaris, T.; et al. Glycemic control in diabetes is restored by therapeutic manipulation of cytokines that regulate beta cell stress. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, I.; Mahata, S.K.; De, R.K. Obesity: An Immunometabolic Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitade, H.; Sawamoto, K.; Nagashimada, M.; Inoue, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sai, Y.; Takamura, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Ginsberg, H.N.; et al. CCR5 plays a critical role in obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by regulating both macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, J.; Kiefer, F.W.; Zeyda, M.; Ludvik, B.; Silberhumer, G.R.; Prager, G.; Zlabinger, G.J.; Stulnig, T.M. CC chemokine and CC chemokine receptor profiles in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue are altered in human obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3215–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Hua, S. Expression Levels of Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 (IRF5) and Related Inflammatory Cytokines Associated with Severity, Prognosis, and Causative Pathogen in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3620–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Blazek, K.; Byrne, A.J.; Perocheau, D.P.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 is a specific marker of inflammatory macrophages in vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 245804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.N.; Jiang, D.S.; Li, H. Interferon regulatory factors: At the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1852, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.M.; Asquith, D.L.; Hueber, A.J.; Anderson, L.A.; Holmes, W.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Xu, D.; Sattar, N.; McInnes, I.B.; Liew, F.Y. Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, L.; Ferraz, J.C. Role of pro- and anti-inflammatory phenomena in the physiopathology of type 2 diabetes and obesity. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Nguyen, K.D.; Goh, Y.P. Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat. Reviews. Immunol. 2011, 11, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, M.; Coats, B.R.; Hisert, K.B.; Hagman, D.; Mutskov, V.; Peris, E.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Kuzma, J.N.; Larson, I.; Billing, P.S.; et al. Metabolic dysfunction drives a mechanistically distinct proinflammatory phenotype in adipose tissue macrophages. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, L.; Lumeng, C.N. Properties and functions of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity. Immunology 2018, 155, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzaid, F.; Lagadec, F.; Albuquerque, M.; Ballaire, R.; Orliaguet, L.; Hainault, I.; Blugeon, C.; Lemoine, S.; Lehuen, A.; Saliba, D.G.; et al. IRF5 governs liver macrophage activation that promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice and humans. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e88689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Byrne, A.J.; Blazek, K.; Saliba, D.G.; Pease, J.E.; Perocheau, D.; Feldmann, M.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 controls both acute and chronic inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, T. Obesity activates toll-like receptor-mediated proinflammatory signaling cascades in the adipose tissue of mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Atizado, V.; Sindhu, S. Increased adipose tissue expression of TLR8 in obese individuals with or without type-2 diabetes: Significance in metabolic inflammation. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akhter, N.; Madhoun, A.; Arefanian, H.; Wilson, A.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Shenouda, S.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R.; Sindhu, S. Oxidative Stress Induces Expression of the Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) 2 and 4 in the Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Implications for Metabolic Inflammation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Akhter, N.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Wilson, A.; Shenouda, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Increased Expression of the Innate Immune Receptor TLR10 in Obesity and Type-2 Diabetes: Association with ROS-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, A.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Aguiar, C.F.; Amano, M.T.; Lee, J.; Miyagi, M.T.; Latancia, M.T.; Braga, T.T.; da Silva, M.B.; Ignacio, A.; et al. Dectin-1 Activation Exacerbates Obesity and Insulin Resistance in the Absence of MyD88. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2272–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguine, J.; Barton, G.M. MyD88: A central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Nikolaus, S.; Hampe, J. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1998, 42, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal. Transduct Target. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, S.S. NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: A pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res. 2001, 3, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamukcu, B.; Lip, G.Y.; Shantsila, E. The nuclear factor--kappa B pathway in atherosclerosis: A potential therapeutic target for atherothrombotic vascular disease. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, A.J.; Luo, C.; Zhou, W.; Hu, J.K.; Daniele, S.G.; Wang, J.; Sheng, J.; et al. CDK6 inhibits white to beige fat transition by suppressing RUNX1. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Diabetic Lean/Overweight | Diabetic Obese |
|---|---|---|
| Total number (N) | 11 (7 male, 4 female) | 35 (19 male, 16 female) |
| Age (Yrs.) | 53.43 ± 1.15 | 52.34 ± 1.70 |
| Body mass index (BMI) (kg/m2) | 27.55 ± 0.46 | 33.83 ± 0.42 |
| Body fat (%) | 31.88 ± 1.61 | 37.59 ± 0.97 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 8.28 ± 0.67 | 8.74 ± 0.50 |
| Fasting plasma insulin (mIU/L) | 24.63 ± 8.13 | 25.68 ± 4.37 |
| Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (Glucose×Insulin/22.5) | 5.47 ± 1.82 | 9.25 ± 1.49 |
| Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (%) | 7.53 ± 0.51 | 8.24 ± 0.24 |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) (pg/mL) | 6.41 ± 1.19 | 5.46 ± 0.78 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.80 ± 0.48 | 4.99 ± 0.20 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.11 ± 0.10 | 1.18 ± 0.05 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.89 ± 0.40 | 2.93 ± 0.19 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.76 ± 0.25 | 1.84 ± 0.24 |
| Hypertension (N) | 4 | 17 |
| Hyperlipidemia (N) | 2 | 6 |
| Therapy | Metformin, Lipitor, Diamicron, Zocor, NovoRapid, Concor, Insulin, Aldomet, Lantus, Diovan | Metformin, Lipitor, Diamicron, Lantus, NovoRapid, Concor, Insulin, Aldomet, Tenormin, Zestril |
| Marker Type | Diabetic Lean/Overweight | Diabetic Obese |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical/metabolic markers |
|
|
| Inflammatory cytokines/chemokines or chemokine receptors |
|
|
| Monocyte/macrophage markers |
|
|
| TLR/non-TLR innate immune markers |
|
|
| TLR-associated signaling molecules and transcription factors |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sindhu, S.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Bennakhi, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients. Cells 2020, 9, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030730
Sindhu S, Kochumon S, Thomas R, Bennakhi A, Al-Mulla F, Ahmad R. Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients. Cells. 2020; 9(3):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030730
Chicago/Turabian StyleSindhu, Sardar, Shihab Kochumon, Reeby Thomas, Abdullah Bennakhi, Fahd Al-Mulla, and Rasheed Ahmad. 2020. "Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients" Cells 9, no. 3: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030730
APA StyleSindhu, S., Kochumon, S., Thomas, R., Bennakhi, A., Al-Mulla, F., & Ahmad, R. (2020). Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients. Cells, 9(3), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030730








