Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Clinical Samples
2.4. RT-qPCR of mRNA and miRNA
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. ELISA Assay
2.7. Analysis of the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) Dataset
2.8. Transient Transfection
2.9. Plasmid Construction and Luciferase Assays
2.10. Tube Formation Assay
2.11. Transwell Migration Assay
2.12. Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay
2.13. In Vivo Matrigel Plug Assay
2.14. Experimental OA Model
2.15. Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) Imaging
2.16. Histological Analysis
2.17. Statistics
3. Results
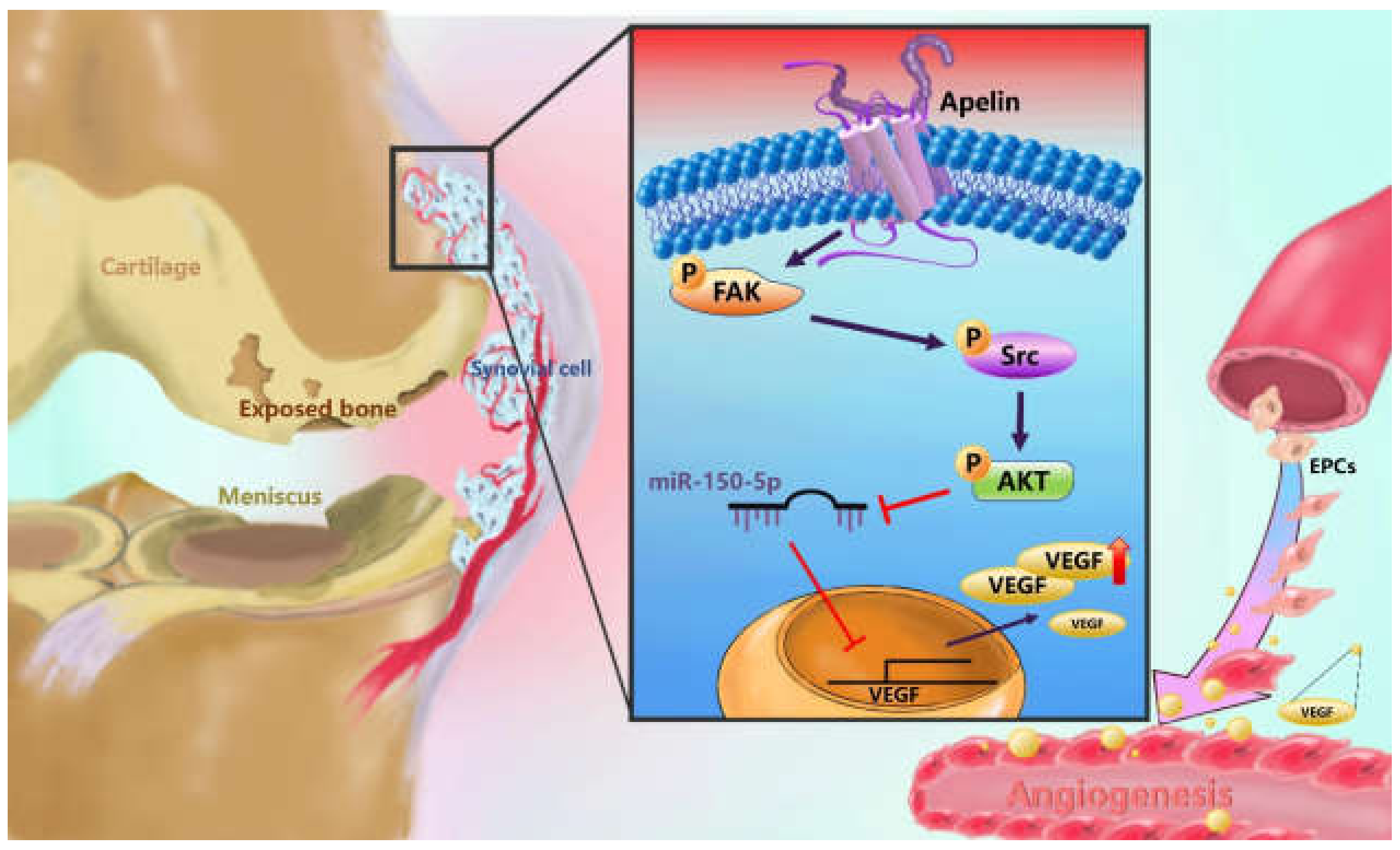
3.1. Apelin Expression is Positively Associated with VEGF Expression Among the OA Patients
3.2. APLN Stimulates VEGF Expression and Facilitates Angiogenesis
3.3. APLN Stimulates VEGF Expression via the Phosphorylation of FAK/Src/Akt
3.4. APLN Enhances VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-150-5p Synthesis
3.5. Infection of shAPLN Reduces VEGF-Mediated Angiogenesis
3.6. Infection of shAPLN Mitigates in Vivo Severity of OA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuo, S.J.; Liu, S.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Hsu, H.C.; Tang, C.H. TGF-beta1 enhances FOXO3 expression in human synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting miR-92a through AMPK and p38 pathways. Aging 2019, 11, 4075–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H. Research of Pathogenesis and Novel Therapeutics in Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Wu, T.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Chung, J.G.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Yin, M.C.; et al. Soya-cerebroside reduces IL-1 beta-induced MMP-1 production in chondrocytes and inhibits cartilage degradation: Implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Food Agr. Immunol. 2019, 30, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotin, Y.; Pesesse, L.; Lambert, C. Targeting the synovial angiogenesis as a novel treatment approach to osteoarthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet Dis. 2014, 6, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.J.; Liu, S.C.; Su, C.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Tang, C.H. Implications of Angiogenesis Involvement in Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.M.; Huang, C.Y.; Tang, C.H. Characteristics of resistin in rheumatoid arthritis angiogenesis. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramoff, B.; Caldera, F.E. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med. Clin. North Am. 2020, 104, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.J.; Liu, S.C.; Huang, C.C.; Kuo, S.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Tang, C.H. Associations between Adipokines in Arthritic Disease and Implications for Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cao, J.; Chen, L. Apelin/APJ system: A novel therapeutic target for oxidative stress-related inflammatory diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krist, J.; Wieder, K.; Kloting, N.; Oberbach, A.; Kralisch, S.; Wiesner, T.; Schon, M.R.; Gartner, D.; Dietrich, A.; Shang, E.; et al. Effects of weight loss and exercise on apelin serum concentrations and adipose tissue expression in human obesity. Obes. Facts 2013, 6, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.F.; Chen, W.P.; Tang, J.L.; Bao, J.P.; Wu, L.D. Apelin plays a catabolic role on articular cartilage: In vivo and in vitro studies. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunduzova, O.; Alet, N.; Delesque-Touchard, N.; Millet, L.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Muller, C.; Dray, C.; Schaeffer, P.; Herault, J.P.; Savi, P.; et al. Apelin/APJ signaling system: A potential link between adipose tissue and endothelial angiogenic processes. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 4146–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.F.; Tang, J.L.; Chen, W.P.; Bao, J.P.; Wu, L.D. Increased apelin serum levels and expression in human chondrocytes in osteoarthritic patients. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Su, C.M.; Hsu, C.J.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, S.W.; Liu, S.C.; Chen, W.C.; Fuh, L.J.; Tang, C.H. CCN1 Promotes VEGF Production in Osteoblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-126 Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Sun, L.; Li, J.J.; An, C.H. Elevated VEGF levels contribute to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fontenla, C.; Calaza, M.; Evangelou, E.; Valdes, A.M.; Arden, N.; Blanco, F.J.; Carr, A.; Chapman, K.; Deloukas, P.; Doherty, M.; et al. Assessment of osteoarthritis candidate genes in a meta-analysis of nine genome-wide association studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 66, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetan, N.; Honsawek, S.; Tanavalee, A.; Yuktanandana, P.; Meknavin, S.; Ngarmukos, S.; Tanpowpong, T.; Parkpian, V. Relationship of plasma and synovial fluid vascular endothelial growth factor with radiographic severity in primary knee osteoarthritis. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipaleenmaki, H. Regulation of Bone Metabolism by microRNAs. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swingler, T.E.; Niu, L.; Smith, P.; Paddy, P.; Le, L.; Barter, M.J.; Young, D.A.; Clark, I.M. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cong, L.; Zhu, Y.; Tu, G. A bioinformatic analysis of microRNAs role in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2017, 25, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.J.; Yang, W.H.; Liu, S.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Tang, C.H. Transforming growth factor beta1 enhances heme oxygenase 1 expression in human synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting microRNA 519b synthesis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.M.; Hsu, C.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Tang, C.H. Resistin Promotes Angiogenesis in Endothelial Progenitor Cells Through Inhibition of MicroRNA206: Potential Implications for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, J.A.; Wang, S.W.; Peng, C.Y.; Cheng, H.C.; Tang, C.H. Endothelin-1 promotes vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-P.; Wang, S.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chung, J.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Yin, M.-C.; et al. Glucocerebroside reduces endothelial progenitor cell-induced angiogenesis. Food Agr. Immunol. 2019, 30, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Wang, S.W.; Lin, Y.M.; Tang, C.H. Interleukin-1beta induces fibroblast growth factor 2 expression and subsequently promotes endothelial progenitor cell angiogenesis in chondrocytes. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-P.; Wang, S.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Lin, L.-W.; Tsai, F.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Li, T.-M.; Tang, C.-H. Soya-cerebroside inhibits VEGF-facilitated angiogenesis in endothelial progenitor cells. Food Agr. Immunol. 2020, 31, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-P.; Chen, P.-C.; Wang, S.-W.; Fong, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chung, J.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Hsu, Y.-M.; et al. Plumbagin suppresses endothelial progenitor cell-related angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J. Func. Foods 2019, 52, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Hsu, C.J.; Fong, Y.C. The CCL5/CCR5 axis promotes interleukin-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Tang, C.H. Glucose suppresses IL-1beta-induced MMP-1 expression through the FAK, MEK, ERK, and AP-1 signaling pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Chiou, P.C.; Chen, P.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Huang, W.C.; Chao, C.C.; Tang, C.H. Melatonin reduces lung cancer stemness through inhibiting of PLC, ERK, p38, beta-catenin, and Twist pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.C.; Tzeng, H.E.; Huang, C.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, P.C.; Chang, A.C.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. WISP-1 positively regulates angiogenesis by controlling VEGF-A expression in human osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, E.K.; Akpinar, M.Y.; Dogan, O.; Goktas, Z.; Sapmaz, F.P.; Simsek, G.G.; Uzman, M.; Nazligul, Y. Clinical Significance of Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor, Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Progranulin Levels in Patients with Gastric Cancer and Gastric Precancerous Lesions. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2019, 50, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.M.; Wang, I.C.; Liu, S.C.; Sun, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.W.; Lee, H.P.; Tseng, W.P.; Tang, C.H. Hypoxia induced mitogenic factor (HIMF) triggers angiogenesis by increasing interleukin-18 production in myoblasts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.H.; Tsai, H.C.; Cheng, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Xu, G.H.; Wang, S.W.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. CTGF promotes osteosarcoma angiogenesis by regulating miR-543/angiopoietin 2 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Huang, Y.W.; Wang, S.W.; Huang, Y.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; Huang, B.F.; Xu, G.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Amphiregulin enhances VEGF-A production in human chondrosarcoma cells and promotes angiogenesis by inhibiting miR-206 via FAK/c-Src/PKCdelta pathway. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.M.; Chiang, Y.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Hsu, C.J.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Osteopontin Promotes Oncostatin M Production in Human Osteoblasts: Implication of Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3355–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Cheng, J.H.; Chou, W.Y.; Hsu, S.L.; Chen, J.H.; Huang, C.Y. Changes of articular cartilage and subchondral bone after extracorporeal shockwave therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Chou, W.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Hsieh, C.C.; Fong, Y.C.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes VEGF-C-dependent lymphangiogenesis by suppressing miR-624-3p in human chondrosarcoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasson, S.S.; Chambers, M.G.; Van Den Berg, W.B.; Little, C.B. The OARSI histopathology initiative—Recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2010, 18, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhu, C.; Qiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Ji, H.; Miao, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. MiR-503 suppresses hypoxia-induced proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells by targeting Apelin. Peptides 2018, 105, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahara, H. Current Status and Strategy of microRNA Research for Cartilage Development and Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. J. Bone Metab. 2016, 23, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Wang, S.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Tang, C.H. Leptin induces oncostatin M production in osteoblasts by downregulating miR-93 through the Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15778–15790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L. Down-Regulation of MiR-150 Alleviates Inflammatory Injury Induced by Interleukin 1 via Targeting Kruppel-Like Factor 2 in Human Chondrogenic Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.W.; Buckwalter, J.A.; Martin, J.A. Inhibition of cell-matrix adhesions prevents cartilage chondrocyte death following impact injury. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ellman, M.; Muddasani, P.; Wang, J.H.; Cs-Szabo, G.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Im, H.J. Prostaglandin E2 and its cognate EP receptors control human adult articular cartilage homeostasis and are linked to the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar-Lesmes, P.; Perramon, M.; Jimenez, W. Roles of the Hepatic Endocannabinoid and Apelin Systems in the Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridvand, Y.; Bagherpour-Hassanlouei, N.; Nozari, S.; Nasiri, N.; Rajabi, H.; Ghaffari, S.; Nouri, M. 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 activates Apelin/APJ system and inhibits the production of adhesion molecules and inflammatory mediators in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Cheng, K.K.; Hoo, R.L.; Siu, P.M.; Yau, S.Y. The Novel Perspectives of Adipokines on Brain Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-H.; Kuo, S.-J.; Liu, S.-C.; Wang, S.-W.; Tsai, C.-H.; Fong, Y.-C.; Tang, C.-H. Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2020, 9, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030594
Wang Y-H, Kuo S-J, Liu S-C, Wang S-W, Tsai C-H, Fong Y-C, Tang C-H. Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2020; 9(3):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030594
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu-Han, Shu-Jui Kuo, Shan-Chi Liu, Shih-Wei Wang, Chun-Hao Tsai, Yi-Chin Fong, and Chih-Hsin Tang. 2020. "Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts" Cells 9, no. 3: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030594
APA StyleWang, Y.-H., Kuo, S.-J., Liu, S.-C., Wang, S.-W., Tsai, C.-H., Fong, Y.-C., & Tang, C.-H. (2020). Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells, 9(3), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030594





