Infection of Porphyromonas gingivalis Increases Phosphate-Induced Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Infection of Cells with P. gingivalis
2.5. Carboxyfluorescein Succinimidyl Ester (CFSE) Staining
2.6. Induction and Quantification of Calcification
2.7. ARS Staining
2.8. Von Kossa Staining and Quantification
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Immunocytochemistry
2.12. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.13. TUNEL Assay
2.14. Matrix Vesicle Isolation
2.15. Arterial Ring Calcification
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
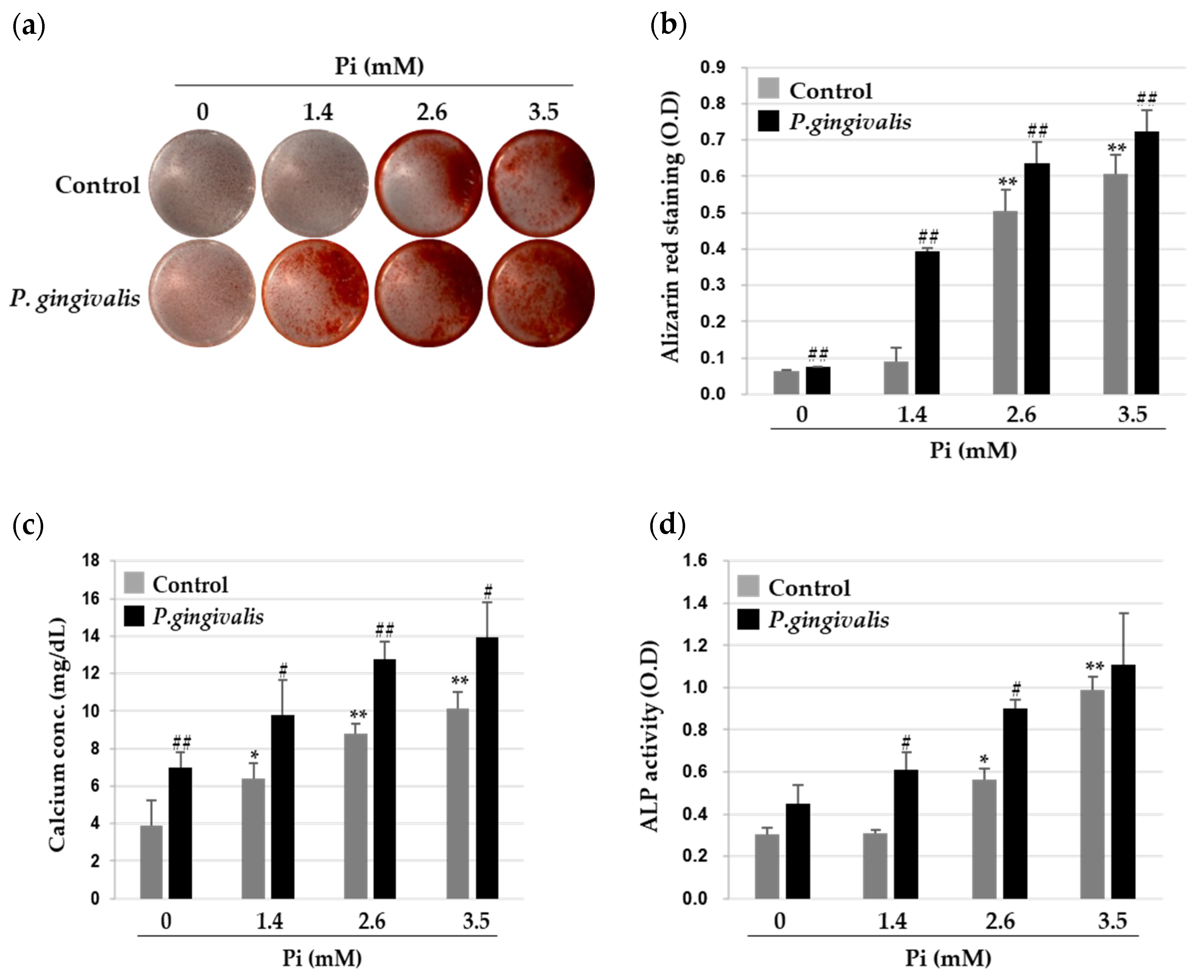
3.1. P. gingivalis Promotes Inorganic Phosphate (Pi)-Induced Calcium Deposition in VSMCs
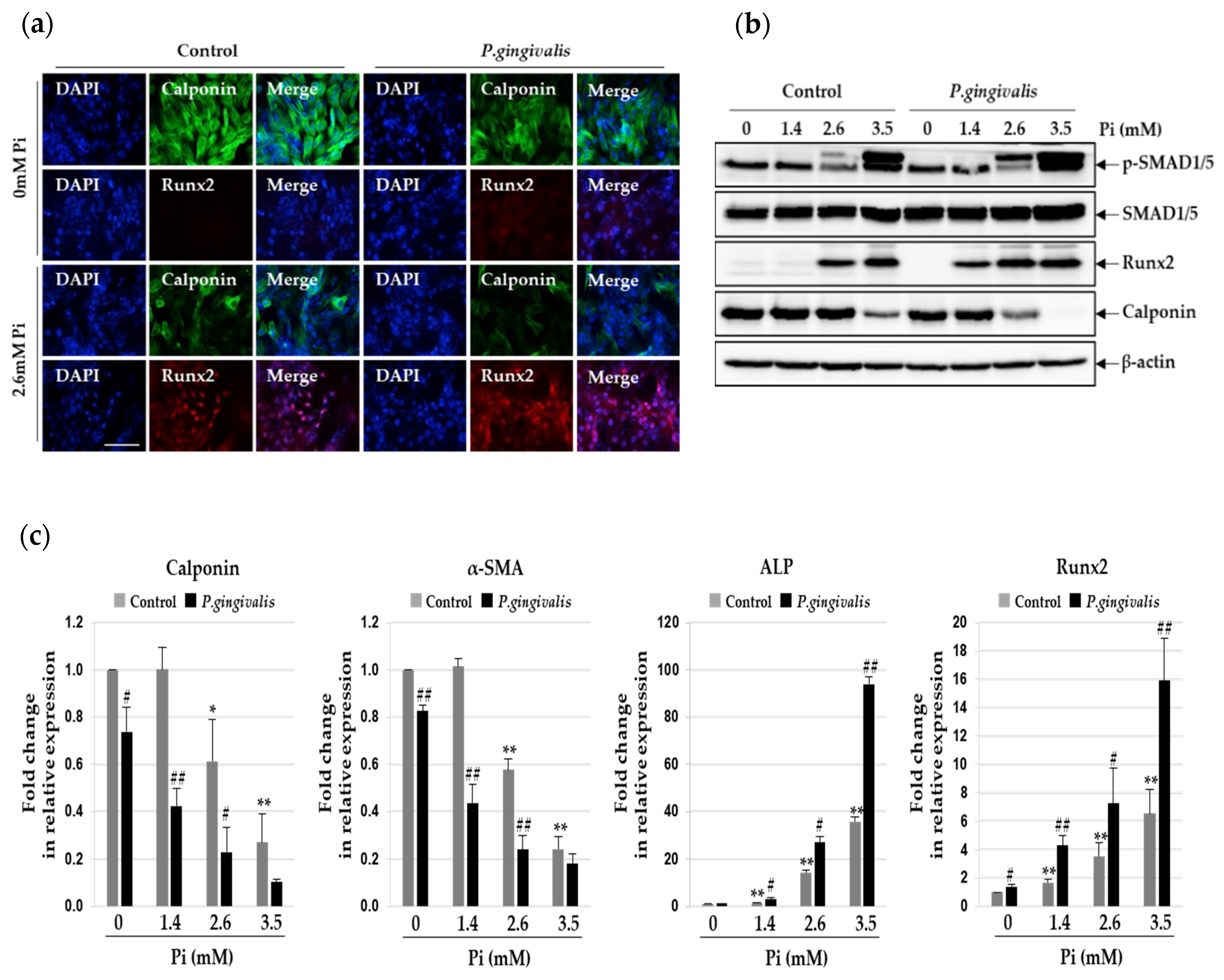
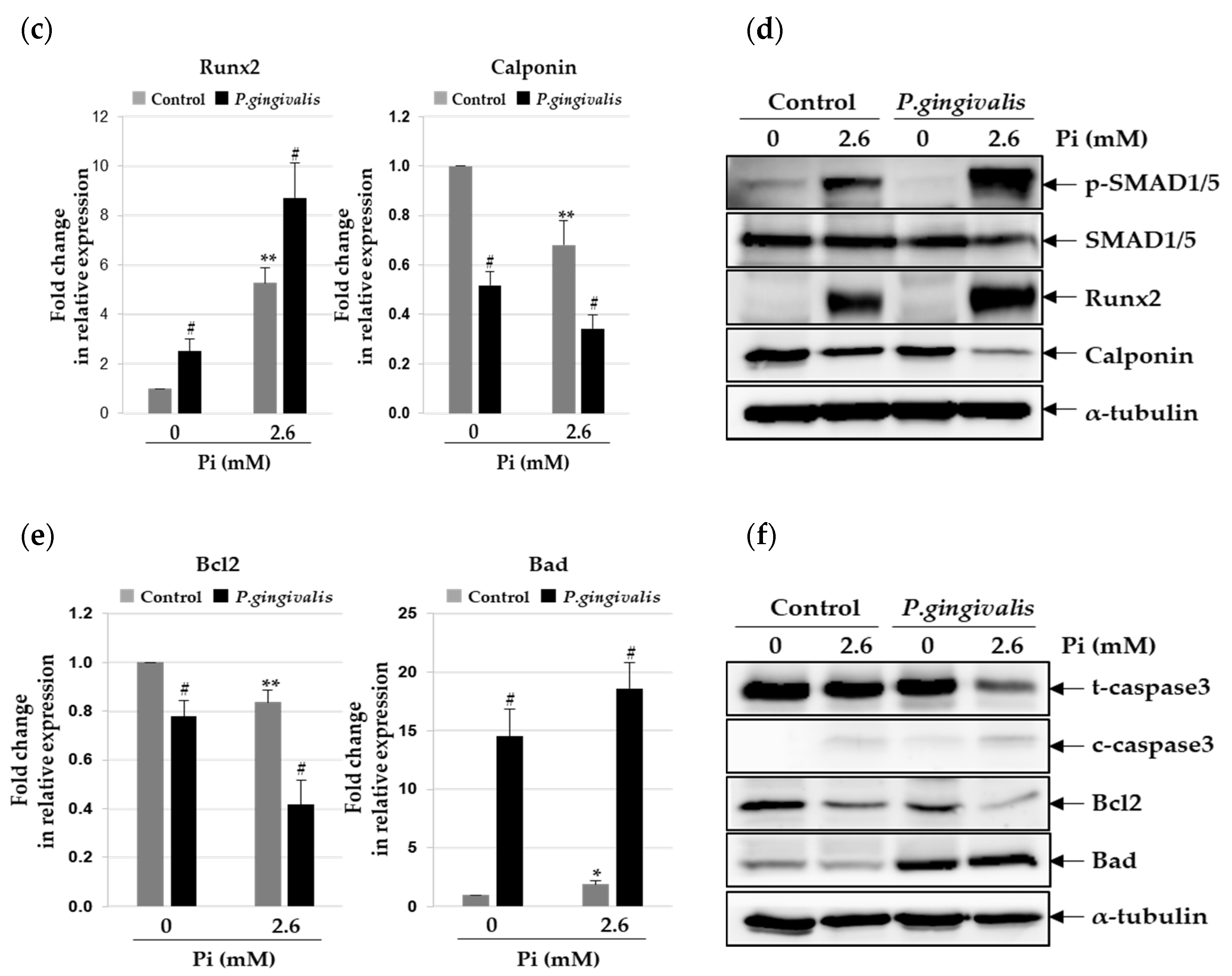
3.2. P.gingivalis Stimulates Pi-Induced Osteogenic Transdifferentiation of VSMCs
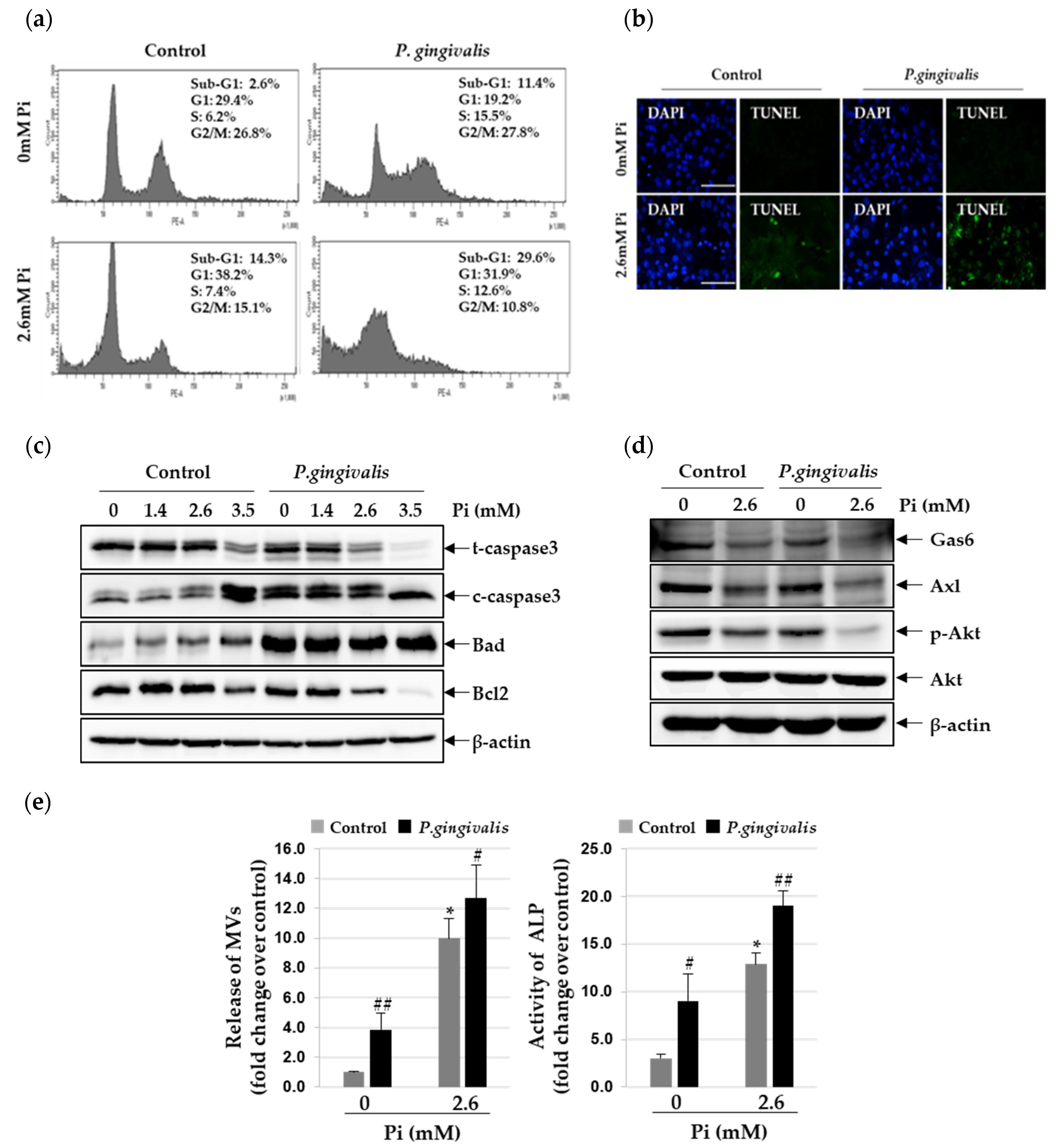
3.3. P. gingivalis Increases Pi-Induced Apoptosis and Matrix Vesicle Release in VSMCs
3.4. P. gingivalis Induces Vascular Calcification in Aortic Culture Ex Vivo
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Offenbacher, S. Periodontal Diseases: Pathogenesis. Ann. Periodontol. 1996, 1, 821–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N. Porphyromonas gingivalis: An invasive and evasive opportunistic oral pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 333, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genco, R.J.; Sanz, M. Clinical and public health implications of periodontal and systemic diseases: An overview. Periodontology 2020, 83, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velsko, I.M.; Chukkapalli, S.S.; Rivera, M.F.; Lee, J.Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, D.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Gangula, P.R.; Lucas, A.R.; Kesavalu, L. Active invasion of oral and aortic tissues by Porphyromonas gingivalis in mice causally links periodontitis and atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Links between atherosclerotic and periodontal disease. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Rementer, C.; Giachelli, C.M. Vascular calcification: An update on mechanisms and challenges in treatment. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 93, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.A. Vascular calcification: Mechanisms of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachelli, C.M. The emerging role of phosphate in vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.W.; Guo, B.; Jia, W.Y.; Jia, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis-derived outer membrane vesicles promote calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells through ERK1/2-RUNX2. FEBS OpenBio 2016, 6, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Chen, S.; Lou, X.; Zhang, P.; Pan, K. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cells activates proliferation and calcification. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschfeld, J.; Kawai, T. Oral inflammation and bacteremia: Implications for chronic and acute systemic diseases involving major organs. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, B.R.; Dunn, W.A., Jr.; Progulske-Fox, A. Porphyromonas gingivalis traffics to autophagosomes in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5698–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, B.R.; Dunn, W.A., Jr.; Progulske-Fox, A. Invasion of human coronary artery cells by periodontal pathogens. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 5792–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.K.; Hwang, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Bae, S.K.; Bae, M.K. Inhibition of gastrin-releasing peptide attenuates phosphate-induced vascular calcification. Cells 2020, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.L.; Joannides, A.J.; Skepper, J.N.; McNair, R.; Schurgers, L.J.; Proudfoot, D.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: A potential mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, S.A.; Speer, M.Y.; Curinga, G.; Yang, H.Y.; Haynes, P.; Aebersold, R.; Schinke, T.; Karsenty, G.; Giachelli, C.M. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic transition associated with calcification: Upregulation of Cbfa1 and downregulation of smooth muscle lineage markers. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazono, K. Signal transduction by bone morphogenetic protein receptors: Functional roles of Smad proteins. Bone 1999, 25, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woeckel, V.J.; Alves, R.D.; Swagemakers, S.M.; Eijken, M.; Chiba, H.; van der Eerden, B.C.; van Leeuwen, J.P. 1Alpha,25-(OH)2D3 acts in the early phase of osteoblast differentiation to enhance mineralization via accelerated production of mature matrix vesicles. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 225, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, D.; Skepper, J.N.; Hegyi, L.; Bennett, M.R.; Shanahan, C.M.; Weissberg, P.L. Apoptosis regulates human vascular calcification in vitro: Evidence for initiation of vascular calcification by apoptotic bodies. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.K.; Kozaki, K.; Iijima, K.; Eto, M.; Nakano, T.; Akishita, M.; Ouchi, Y. Gas6/Axl-PI3K/Akt pathway plays a central role in the effect of statins on inorganic phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 556, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, T.; Ota, H.; Iijima, K.; Son, B.K.; Kahyo, T.; Setou, M.; Ogawa, S.; Ouchi, Y.; Akishita, M. A novel organ culture model of aorta for vascular calcification. Atherosclerosis 2016, 244, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jono, S.; McKee, M.D.; Murry, C.E.; Shioi, A.; Nishizawa, Y.; Mori, K.; Morii, H.; Giachelli, C.M. Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E10–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlieper, G.; Schurgers, L.; Brandenburg, V.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Floege, J. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: An update. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertpimonchai, A.; Rattanasiri, S.; Tamsailom, S.; Champaiboon, C.; Ingsathit, A.; Kitiyakara, C.; Limpianunchai, A.; Attia, J.; Sritara, P.; Thakkinstian, A. Periodontitis as the risk factor of chronic kidney disease: Mediation analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Taylor, G.W.; Manz, M.C.; Kaneko, N.; Imai, S.; Yoshihara, A.; Miyazaki, H. Serum antibody to Porphyromonas gingivalis in chronic kidney disease. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sage, A.P.; Tintut, Y.; Demer, L.L. Regulatory mechanisms in vascular calcification. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, I.K.; Jeon, J.H. Vascular calcification-new insights into its mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencel, P.; Hardouin, P.; Magne, D. Do cytokines induce vascular calcification by the mere stimulation of TNAP activity? Med. Hypotheses 2010, 75, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, S.; Dounousi, E.; Salmas, M.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Liakopoulos, V. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: The role of vitamin K-dependent matrix Gla protein. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, A.; Traghella, I.; Mazzone, A.; Sbrana, S.; Vassalle, C. Vascular and valvular calcification biomarkers. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 95, 73–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ersin Kalkan, R.; Ongoz Dede, F.; Gokmenoglu, C.; Kara, C. Salivary fetuin-A, S100A12, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in periodontal diseases. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turer, C.C.; Balli, U.; Guven, B. Fetuin-A, serum amyloid A and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels in periodontal health and disease. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairo, F.; Gaeta, C.; Dorigo, W.; Oggioni, M.R.; Pratesi, C.; Pini Prato, G.P.; Pozzi, G. Periodontal pathogens in atheromatous plaques. A controlled clinical and laboratory trial. J. Periodontal. Res. 2004, 39, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, N.E.; Larsen, T.; Christiansen, N.; Holmstrup, P.; Schroeder, T.V. Identification of periodontal pathogens in atherosclerotic vessels. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraszthy, V.I.; Zambon, J.J.; Trevisan, M.; Zeid, M.; Genco, R.J. Identification of periodontal pathogens in atheromatous Plaques. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavrini, F.; Sambri, V.; Moter, A.; Servidio, D.; Marangoni, A.; Montebugnoli, L.; Foschi, F.; Prati, C.; Di Bartolomeo, R.; Cevenini, R. Molecular detection of Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis in carotid and aortic atheromatous plaques by FISH: Report of two cases. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozarov, E.V.; Dorn, B.R.; Shelburne, C.E.; Dunn, W.A., Jr.; Progulske-Fox, A. Human atherosclerotic plaque contains viable invasive Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, e17–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, A.C.; Meller, N.; McNamara, C.A. Role of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Elmabsout, A.A.; Khalaf, H.; Basic, V.T.; Jayaprakash, K.; Kruse, R.; Bengtsson, T.; Sirsjo, A. The periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis changes the gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells involving the TGFbeta/Notch signalling pathway and increased cell proliferation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Lin, C.T.; Chien, S.J.; Chang, S.F.; Chen, C.N. Regulation of calcification in human aortic smooth muscle cells infected with high-glucose-treated Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4759–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamster, I.B.; Ahlo, J.K. Analysis of gingival crevicular fluid as applied to the diagnosis of oral and systemic diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1098, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G. Gingival crevicular fluid as a periodontal diagnostic indicator-II: Inflammatory mediators, host-response modifiers and chair side diagnostic aids. J. Med. Life 2013, 6, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camerlingo, C.; d’Apuzzo, F.; Grassia, V.; Perillo, L.; Lepore, M. Micro-Raman spectroscopy for monitoring changes in periodontal ligaments and gingival crevicular fluid. Sensors 2014, 14, 22552–22563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.-J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Park, H.-R.; Kim, H.-J.; Bae, S.-K.; Bae, M.-K. Infection of Porphyromonas gingivalis Increases Phosphate-Induced Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122694
Park H-J, Kim Y, Kim M-K, Park H-R, Kim H-J, Bae S-K, Bae M-K. Infection of Porphyromonas gingivalis Increases Phosphate-Induced Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122694
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyun-Joo, Yeon Kim, Mi-Kyoung Kim, Hae-Ryoun Park, Hyung-Joon Kim, Soo-Kyung Bae, and Moon-Kyoung Bae. 2020. "Infection of Porphyromonas gingivalis Increases Phosphate-Induced Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells" Cells 9, no. 12: 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122694
APA StylePark, H.-J., Kim, Y., Kim, M.-K., Park, H.-R., Kim, H.-J., Bae, S.-K., & Bae, M.-K. (2020). Infection of Porphyromonas gingivalis Increases Phosphate-Induced Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cells, 9(12), 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122694




