The PARP Inhibitor Olaparib Modulates the Transcriptional Regulatory Networks of Long Non-Coding RNAs during Vasculogenic Mimicry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and RNA Extraction
2.2. RNA Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Differential Expression for mRNA and lncRNA
2.5. LncRNA and mRNA Expression Integration
2.6. Olaparib-Modulated lncRNAs in Cancer
2.7. Transcription Factor Binding Sites Analysis
2.8. Predicting lncRNA-Mediated Transcription Changes
3. Results
3.1. Olaparib Modulated lncRNA Expression during Tube Formation on Matrigel
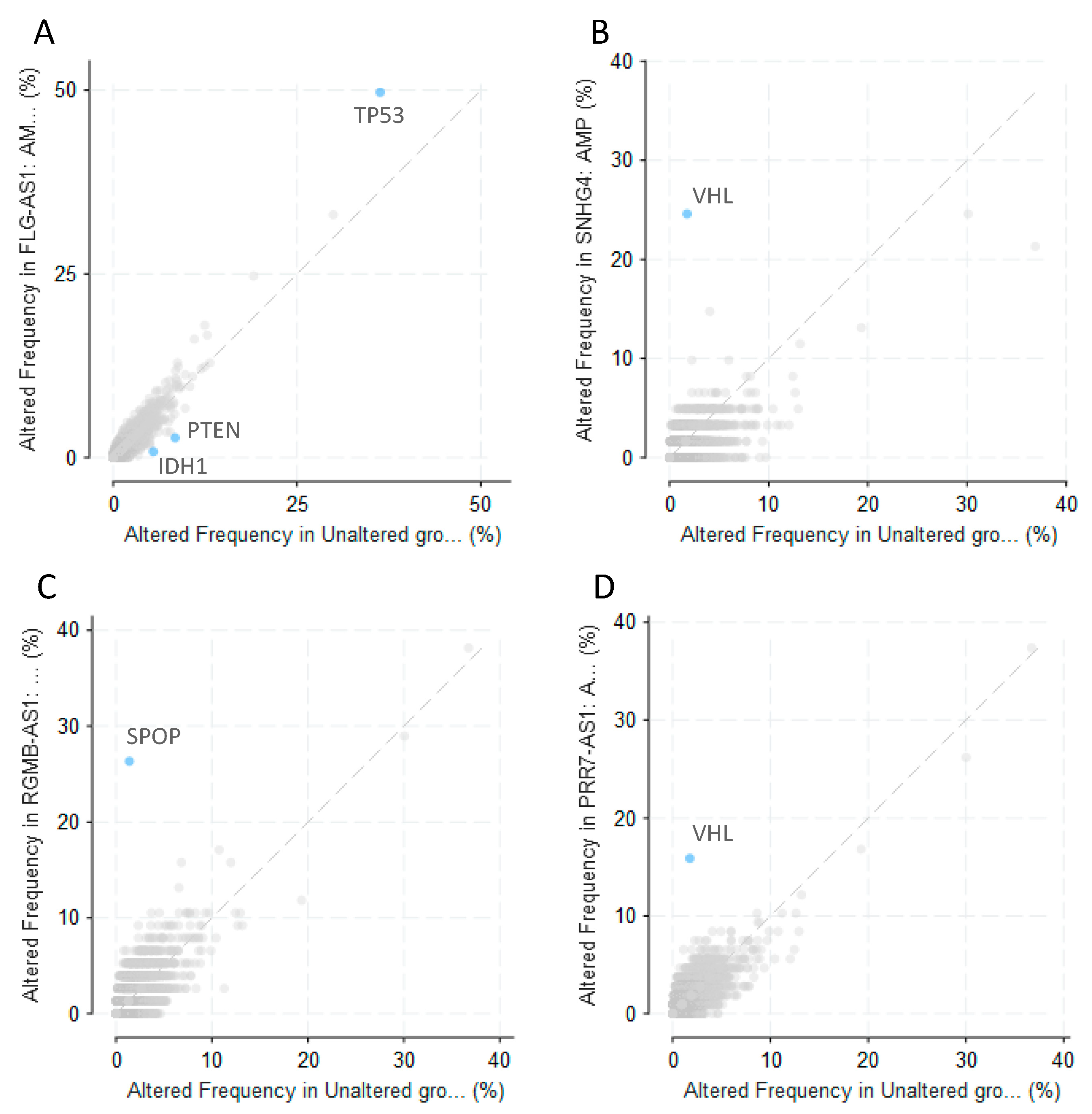
3.2. Olaparib-Modulated lncRNA in the Context of Cancer
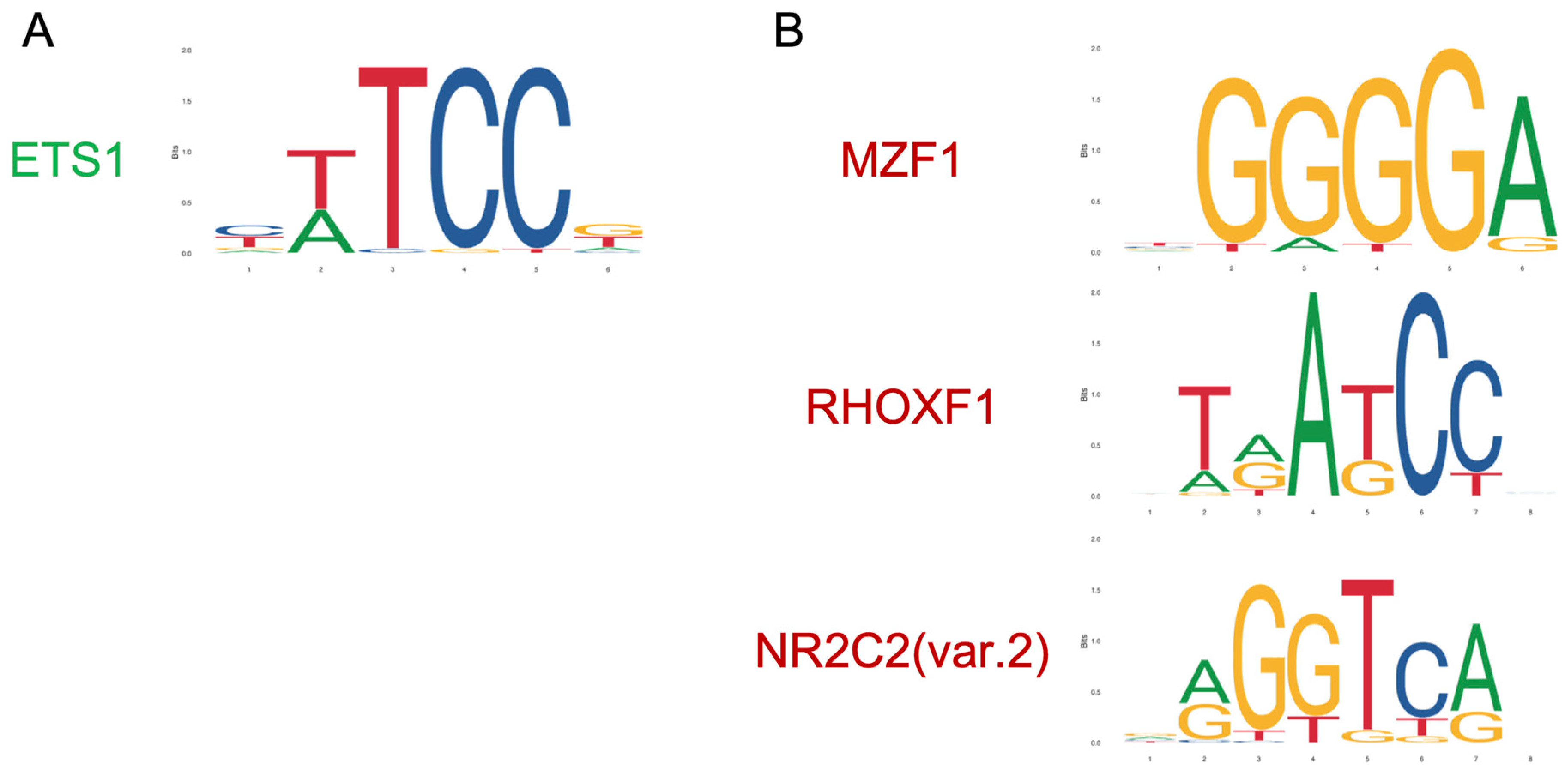
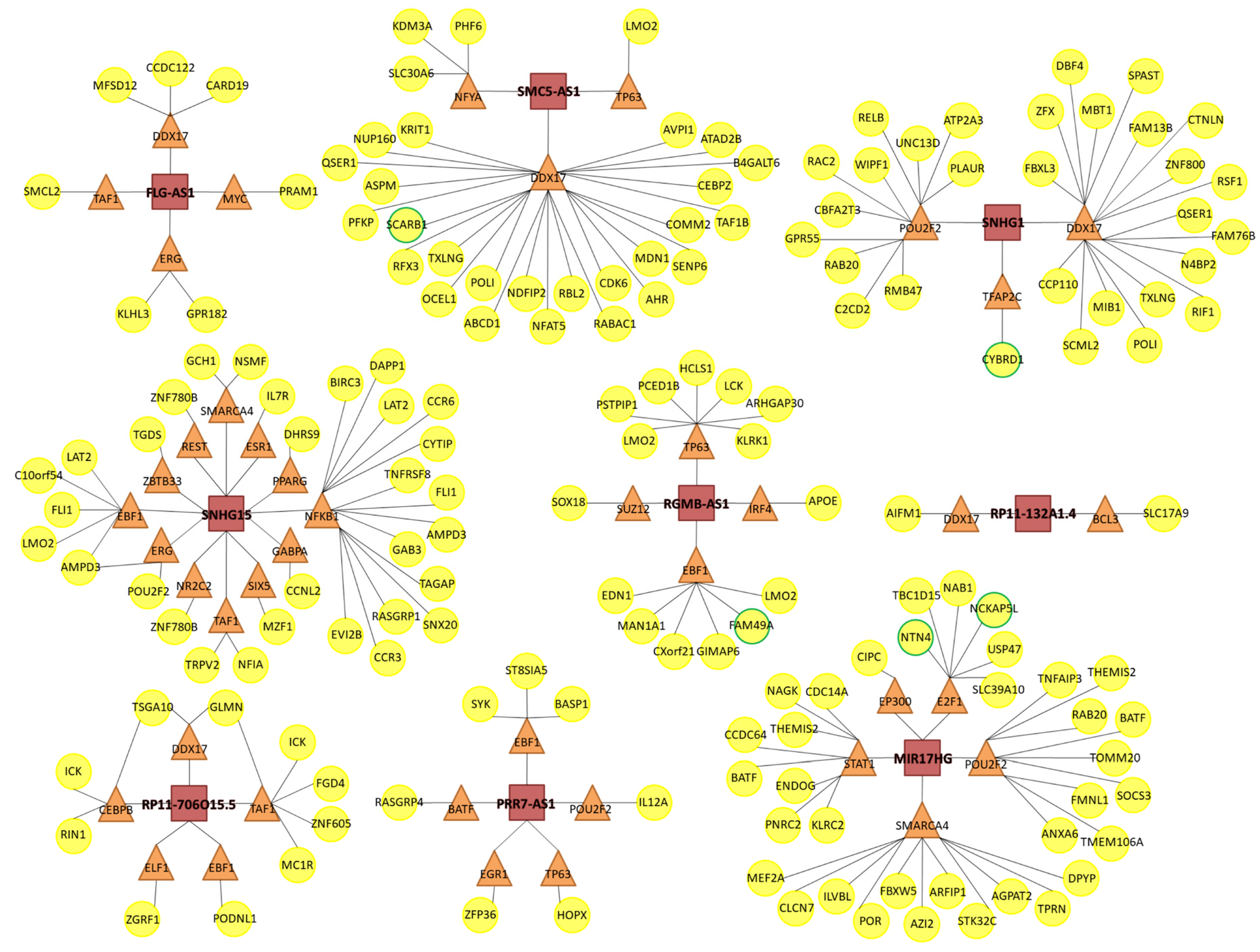
3.3. Transcription Factors Upstream Olaparib-Modulated lncRNA
3.4. Predicted lncRNA-Mediated Transcription Perturbations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, X.; Han, S.; Wu, G.; Latchoumanin, O.; Zhou, G.; Hebbard, L.; George, J.; Qiao, L. Dysregulated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for tumorigenesis, disease progression, and liver cancer stem cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.X.; Koirala, P.; Mo, Y.Y. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Youmans, D.T.; Cech, T.R. How do lncRNAs regulate transcription? Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Bellido, D.; Serrano-Saenz, S.; Fernandez-Cortes, M.; Oliver, F.J. Vasculogenic mimicry signaling revisited: Focus on non-vascular VE-cadherin. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teppan, J.; Barth, D.A.; Prinz, F.; Jonas, K.; Pichler, M.; Klec, C. Involvement of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumor angiogenesis. Non-coding RNA 2020, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Du, P.; Cui, P.; Qin, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qin, L.; Huang, G. LncRNA PVT1 promotes angiogenesis via activating the STAT3/VEGFA axis in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4094–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.R.; Wu, J.S.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. Long noncoding RNAs: Emerging regulators of tumor angiogenesis. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ding, J.; He, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, Z.; Xing, E.Z.; Zhang, C.; Yeh, S. Estrogen receptor β promotes the vasculogenic mimicry (VM) and cell invasion via altering the lncRNA-MALAT1/miR-145-5p/NEDD9 signals in lung cancer. Oncogene 2018, 38, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; Lin, L.; Huang, N.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; Liao, W. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 395, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Shan, B.; Li, B.; Peng, W.; Dong, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhao, W.; He, D.; Duan, M.; et al. The long noncoding RNA LINC00312 induces lung adenocarcinoma migration and vasculogenic mimicry through directly binding YBX1. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Shen, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; et al. ZRANB2/SNHG20/FOXK1 Axis regulates Vasculogenic mimicry formation in glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, M.J.; Seftor, E.A.; Meltzer, P.S.; Gardner, L.M.; Hess, A.R.; Kirschmann, D.A.; Schatteman, G.C.; Seftor, R.E. Expression and functional significance of VE-cadherin in aggressive human melanoma cells: Role in vasculogenic mimicry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8018–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.I.; Peralta-Leal, A.; O’Valle, F.; Rodriguez-Vargas, J.M.; Gonzalez-Flores, A.; Majuelos-Melguizo, J.; Lopez, L.; Serrano, S.; de Herreros, A.G.; Rodriguez-Manzaneque, J.C.; et al. PARP-1 regulates metastatic melanoma through modulation of vimentin-induced malignant transformation. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres-Leon, E.; Nunez-Torres, R.; Rojas, A.M. miARma-Seq: A comprehensive tool for miRNA, mRNA and circRNA analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolayeva, O.; Robinson, M.D. edgeR for differential RNA-seq and ChIP-seq analysis: An application to stem cell biology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1150, 45–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeb, P.D.; Bramardi, S.J.; Steibel, J.P. Assessing Dissimilarity Measures for Sample-Based Hierarchical Clustering of RNA Sequencing Data Using Plasmode Datasets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabalin, A.A. Matrix eQTL: Ultra fast eQTL analysis via large matrix operations. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornes, O.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Khan, A.; van der Lee, R.; Zhang, X.; Richmond, P.A.; Modi, B.P.; Correard, S.; Gheorghe, M.; Baranasic, D.; et al. JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D87–D92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Pan, T.; Sahni, N.; Jin, X.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. LncMAP: Pan-cancer atlas of long noncoding RNA-mediated transcriptional network perturbations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Bellido, D.; Fernandez-Cortes, M.; Rodriguez, M.I.; Serrano-Saenz, S.; Carracedo, A.; Garcia-Diaz, A.; Oliver, F.J. VE-cadherin promotes vasculogenic mimicry by modulating kaiso-dependent gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniotis, A.J.; Folberg, R.; Hess, A.; Seftor, E.A.; Gardner, L.M.; Pe’er, J.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S.; Hendrix, M.J. Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: Vasculogenic mimicry. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, R.; Liu, Z.; Kraus, W.L. PARPs and ADP-ribosylation: Recent advances linking molecular functions to biological outcomes. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.I.; Majuelos-Melguizo, J.; Marti Martin-Consuegra, J.M.; Ruiz de Almodovar, M.; Lopez-Rivas, A.; Javier Oliver, F. Deciphering the Insights of Poly(ADP-Ribosylation) in Tumor Progression. Med. Res. Rev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Houck, J.R.; Lohavanichbutr, P.; Chen, C. Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed lncRNAs between oral squamous cell carcinoma and healthy oral mucosa. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31521–31531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Gryder, B.; Woods, W.S.; Subramanian, M.; Jones, M.F.; Li, X.L.; Jenkins, L.M.; Shabalina, S.A.; Mo, M.; Dasso, M.; et al. Prosurvival long noncoding RNA PINCR regulates a subset of p53 targets in human colorectal cancer cells by binding to Matrin 3. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimta, A.A.; Tigu, A.B.; Braicu, C.; Stefan, C.; Ionescu, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. An Emerging Class of Long Non-coding RNA With Oncogenic Role Arises From the snoRNA Host Genes. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, F.; Li, D.; Yang, T. Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 predicts a poor prognosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 80, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, C.; Geng, L.; Tian, T.; Liu, H. Upregulated lncRNA SNHG1 contributes to progression of non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of miR-101-3p and activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17785–17794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Shan, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Jin, W.; Ren, T. Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by up-regulating MTDH via sponging miR-145-5p. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3957–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Yang, W.; Zheng, F.S.; Wang, Y.B.; Lu, J.B. Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 regulates zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 expression by interacting with TAp63 and promotes cell metastasis and invasion in Lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xue, Y.; Ma, J.; Shao, L.; Wang, D.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; He, Q.; Ruan, X.; et al. SNHG1 promotes malignant biological behaviors of glioma cells via microRNA-154-5p/miR-376b-3p- FOXP2- KDM5B participating positive feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R. lncRNA SNHG1 cooperated with miR-497/miR-195-5p to modify epithelial-mesenchymal transition underlying colorectal cancer exacerbation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 1453–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G.; Lv, M.; Li, D. Up-regulation of lncRNA SNHG1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 111715–111727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Fang, J. Up-regulated lnc-SNHG1 contributes to osteosarcoma progression through sequestration of miR-577 and activation of WNT2B/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Kong, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA SNHG1 inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and invasion by suppressing the Notch-1 signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 6106–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zeng, T.; Li, W.; Wu, H.; Sun, C.; Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Fu, Z.; Yin, Y. Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 activates HOXA1 expression via sponging miR-193a-5p in breast cancer progression. Aging (Albany N. Y.) 2020, 12, 10223–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Feng, F.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lao, L. LncRNA SNHG4 promotes tumour growth by sponging miR-224-3p and predicts poor survival and recurrence in human osteosarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hong, J.; Wijayakulathilaka, W. Long non-coding RNA SNHG4 promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating c-Met via targeting miR-148a-3p. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, P. SP1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA SNHG4 functions as a ceRNA for miR-377 to facilitate prostate cancer progression through regulation of ZIC5. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3916–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Kong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, Z.; Bi, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X. Knockdown of SNHG15 suppresses renal cell carcinoma proliferation and EMT by regulating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.X.; Yin, J.F.; Lin, B.C.; Su, H.F.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, C.Y.; Fei, Z.H. Upregulated expression of long noncoding RNA SNHG15 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through regulates MMP2/MMP9 in patients with GC. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 6801–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Pu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, P.; Hui, B.; Ji, H.; Wang, K. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 inhibits P15 and KLF2 expression to promote pancreatic cancer proliferation through EZH2-mediated H3K27me3. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84153–84167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Qiu, M. Long noncoding RNA SNHG15 promotes human breast cancer proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-211-3p. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeinasab, M.; Bahrami, A.R.; Gonzalez, J.; Marchese, F.P.; Martinez, D.; Mowla, S.J.; Matin, M.M.; Huarte, M. SNHG15 is a bifunctional MYC-regulated noncoding locus encoding a lncRNA that promotes cell proliferation, invasion and drug resistance in colorectal cancer by interacting with AIF. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, T.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Song, J.; Sun, X.; Tang, Y.; Wan, J.; Yu, Y.; et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 interacts with and stabilizes transcription factor Slug and promotes colon cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2018, 425, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lv, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. LncRNA SNHG15 acts as an oncogene in prostate cancer by regulating miR-338-3p/FKBP1A axis. Gene 2019, 705, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Jin, H.; Wu, H.B.; Xu, J.J.; Li, B. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 promotes CDK14 expression via miR-486 to accelerate non-small cell lung cancer cells progression and metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7164–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, R.; Chen, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA RGMB-AS1 Indicates a Poor Prognosis and Modulates Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Lung Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, N.; Xu, L.; Wu, T.; Li, Z. LncRNA RGMB-AS1 Promotes Glioma Growth and Invasion Through miR-1200/HOXB2 Axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 10107–10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, D.; Song, Y. Long Noncoding RNA RGMB-AS1 Acts as a microRNA-574 Sponge Thereby Enhancing the Aggressiveness of Gastric Cancer via HDAC4 Upregulation. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.; Cai, H.; et al. FXR1 promotes the malignant biological behavior of glioma cells via stabilizing MIR17HG. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Tan, L.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Tao, K.; Wang, G.; Shi, W.; Gao, J. MIR17HG-miR-18a/19a axis, regulated by interferon regulatory factor-1, promotes gastric cancer metastasis via Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Meng, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.; Gao, N.; Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Familiari, G.; Relucenti, M.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA MIR17HG Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via miR-17-5p. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4882–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.D. Tumor suppression: Putting p53 in context. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3461–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, M.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: New modes and prospects. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, R.J.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Wilmink, J.W.; van Noorden, C.J.F. Wild-type and mutated IDH1/2 enzymes and therapy responses. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, L.M.; Boulay, K.; Topisirovic, I.; Huot, M.E.; Mallette, F.A. Oncogenic Activities of IDH1/2 Mutations: From Epigenetics to Cellular Signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, C.; Yan, L.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhu, X. The emerging role of SPOP protein in tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Ateeq, B. Molecular Underpinnings Governing Genetic Complexity of ETS-Fusion-Negative Prostate Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, G.; Barbieri, C.E.; Prandi, D.; Blattner, M.; Chae, S.S.; Dahija, A.; Nataraj, S.; Huang, D.; Marotz, C.; Xu, L.; et al. SPOP mutation leads to genomic instability in prostate cancer. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossage, L.; Eisen, T.; Maher, E.R. VHL, the story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, J. The role of the transcription factor Ets1 in carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatenkov, V.A.; Albor, A.; Patel, B.K.; Dreszer, R.; Dritschilo, A.; Notario, V. Regulation of the human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase promoter by the ETS transcription factor. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatenkov, V.A.; Trofimova, I.N.; Rouzaut, A.; McDermott, F.; Dritschilo, A.; Notario, V. Differential regulation of the response to DNA damage in Ewing’s sarcoma cells by ETS1 and EWS/FLI-1. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, A.J.; Choul-Li, S.; Spriet, C.; Idziorek, T.; Vicogne, D.; Drobecq, H.; Dantzer, F.; Villeret, V.; Aumercier, M. The level of Ets-1 protein is regulated by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) in cancer cells to prevent DNA damage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choul-Li, S.; Legrand, A.J.; Bidon, B.; Vicogne, D.; Villeret, V.; Aumercier, M. Ets-1 interacts through a similar binding interface with Ku70 and Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, T.; Prince, T.; Wegiel, B.; Calderwood, S.K. Role and Regulation of Myeloid Zinc Finger Protein 1 in Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Hu, A.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Song, H.; Hong, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of MZF1-AS1/PARP1/E2F1 Axis Inhibits Proline Synthesis and Neuroblastoma Progression. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbulan-Rosenthal, C.M.; Rosenthal, D.S.; Luo, R.; Samara, R.; Espinoza, L.A.; Hassa, P.O.; Hottiger, M.O.; Smulson, M.E. PARP-1 binds E2F-1 independently of its DNA binding and catalytic domains, and acts as a novel coactivator of E2F-1-mediated transcription during re-entry of quiescent cells into S phase. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8460–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Iwasaki, T.; Pyndiah, S.; Cassimere, E.K.; Palani, C.D.; Sakamuro, D. Regulation of E2F1-induced apoptosis by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgmann, J.; Tuttelmann, F.; Dworniczak, B.; Ropke, A.; Song, H.W.; Kliesch, S.; Wilkinson, M.F.; Laurentino, S.; Gromoll, J. The human RHOX gene cluster: Target genes and functional analysis of gene variants in infertile men. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4898–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, C.M.; MacLean, J.A.; Cornwall, G.; Wilkinson, M.F. Two novel human X-linked homeobox genes, hPEPP1 and hPEPP2, selectively expressed in the testis. Gene 2002, 301, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, A.; Feelders, R.A.; Stratakis, C.A.; Nieman, L.K. Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet 2015, 386, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Yang, D.R.; Li, G.; Chang, C. TR4 Nuclear Receptor Different Roles in Prostate Cancer Progression. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yeh, S.; Qiu, X.; Hu, L.; Zeng, J.; Cai, Y.; Zuo, L.; Li, G.; Yang, G.; Chang, C. TR4 nuclear receptor promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and metastasis via altering the miR490-3p/vimentin signals. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5901–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hao, Q.; Prasanth, K.V. Nuclear Long Noncoding RNAs: Key Regulators of Gene Expression. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
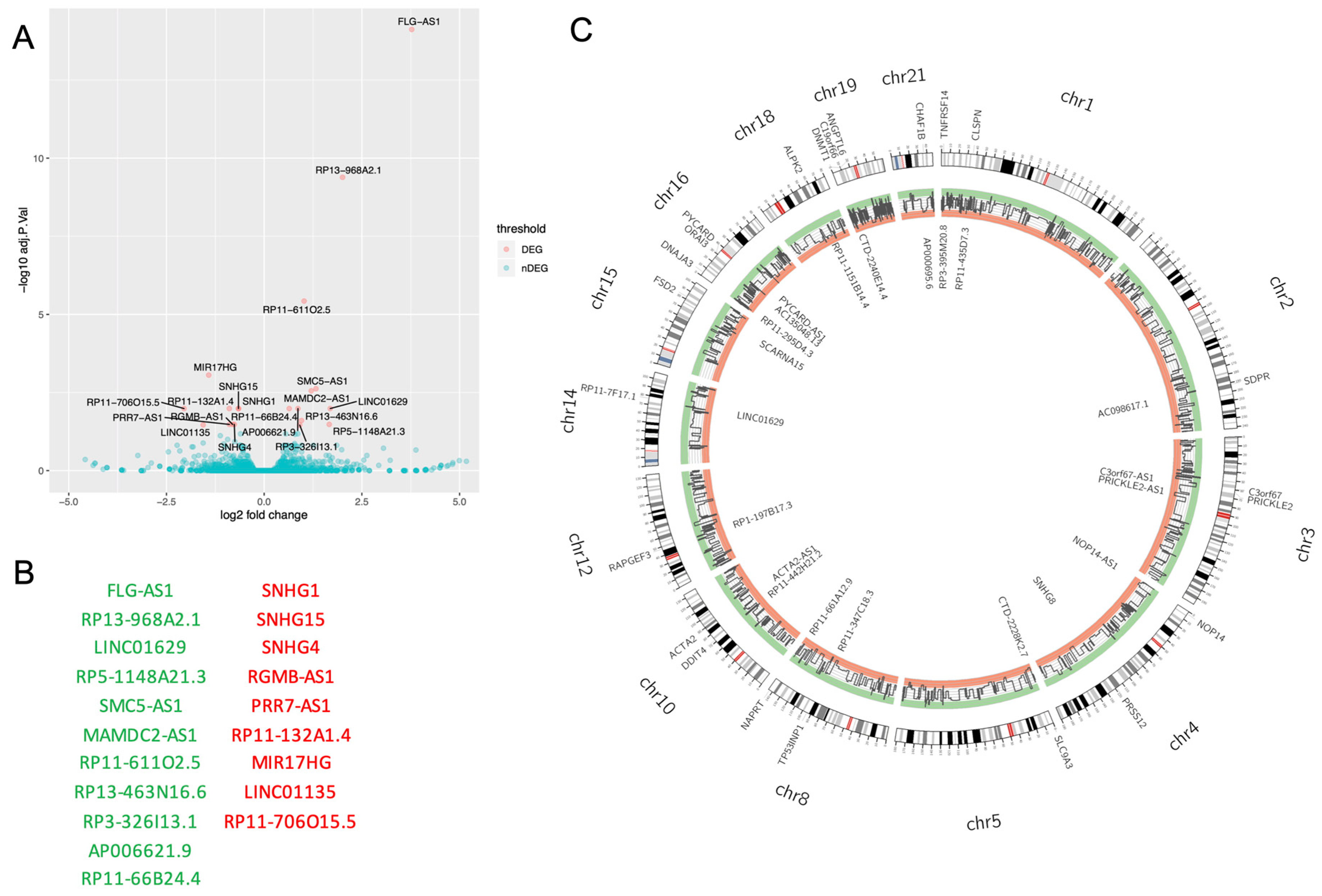
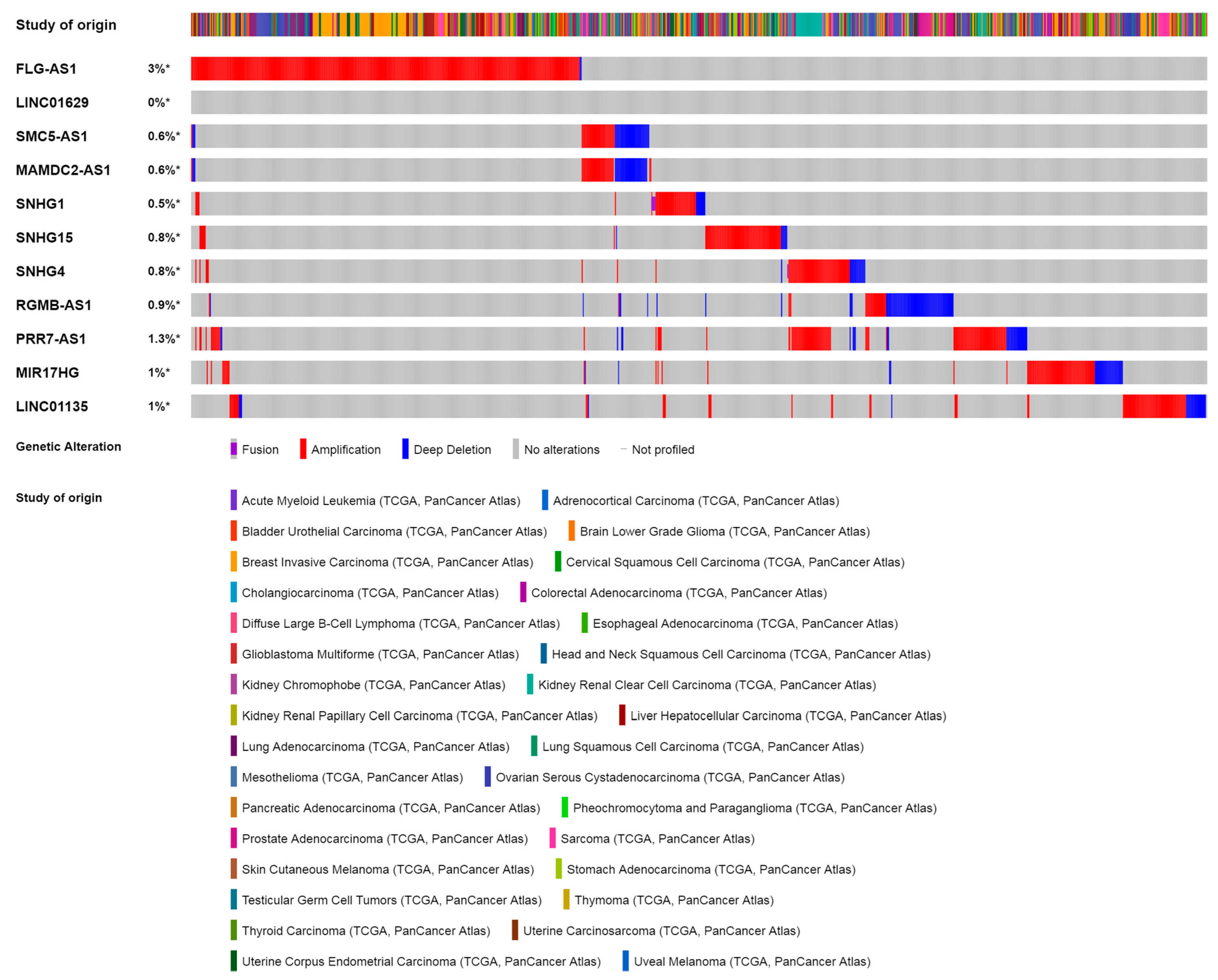
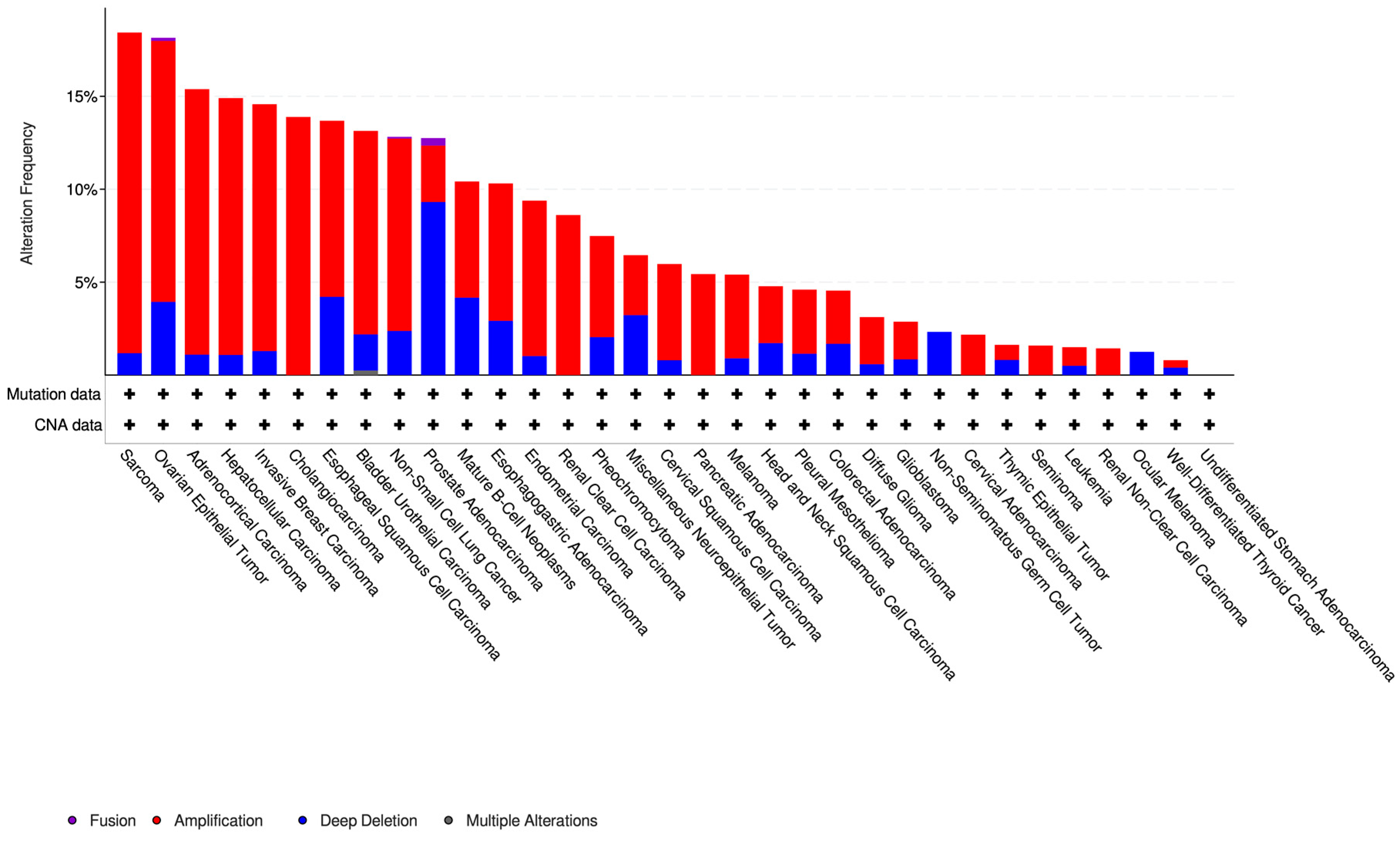
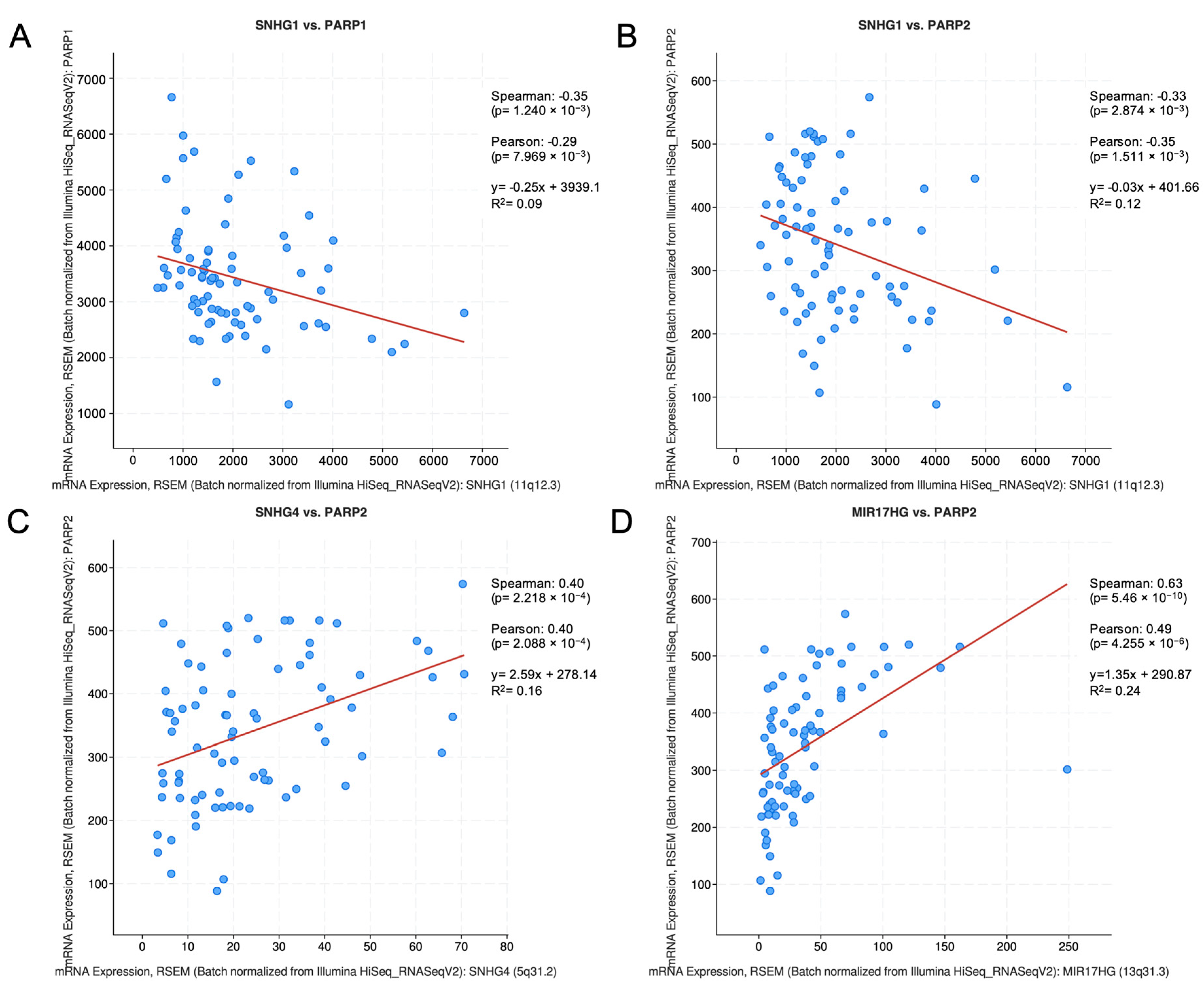
| A | B | Neither | A Not B | B Not A | Both | Log2 Odds Ratio | p-Value | q-Value | Tendency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMC5-AS1 | MAMDC2-AS1 | 10,119 | 3 | 2 | 65 | >3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | Co-occurrence |
| SNHG4 | PRR7-AS1 | 10,018 | 34 | 93 | 44 | >3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | Co-occurrence |
| RGMB-AS1 | PRR7-AS1 | 9962 | 90 | 128 | 9 | 2.96 | <0.001 | <0.001 | Co-occurrence |
| SNHG4 | RGMB-AS1 | 10,019 | 71 | 92 | 7 | >3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | Co-occurrence |
| SNHG1 | PRR7-AS1 | 10,002 | 50 | 131 | 6 | >3 | <0.001 | 0.001 | Co-occurrence |
| FLG-AS1 | PRR7-AS1 | 9693 | 359 | 122 | 15 | 1.731 | <0.001 | 0.001 | Co-occurrence |
| SMC5-AS1 | RGMB-AS1 | 10,027 | 63 | 94 | 5 | >3 | <0.001 | 0.004 | Co-occurrence |
| FLG-AS1 | LINC01135 | 9720 | 362 | 95 | 12 | 1.762 | <0.001 | 0.004 | Co-occurrence |
| PRR7-AS1 | MIR17HG | 9950 | 131 | 102 | 6 | 2.16 | 0.003 | 0.02 | Co-occurrence |
| MAMDC2-AS1 | RGMB-AS1 | 10,027 | 63 | 95 | 4 | 2.744 | 0.004 | 0.022 | Co-occurrence |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Cortés, M.; Andrés-León, E.; Oliver, F.J. The PARP Inhibitor Olaparib Modulates the Transcriptional Regulatory Networks of Long Non-Coding RNAs during Vasculogenic Mimicry. Cells 2020, 9, 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122690
Fernández-Cortés M, Andrés-León E, Oliver FJ. The PARP Inhibitor Olaparib Modulates the Transcriptional Regulatory Networks of Long Non-Coding RNAs during Vasculogenic Mimicry. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122690
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Cortés, Mónica, Eduardo Andrés-León, and Francisco Javier Oliver. 2020. "The PARP Inhibitor Olaparib Modulates the Transcriptional Regulatory Networks of Long Non-Coding RNAs during Vasculogenic Mimicry" Cells 9, no. 12: 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122690
APA StyleFernández-Cortés, M., Andrés-León, E., & Oliver, F. J. (2020). The PARP Inhibitor Olaparib Modulates the Transcriptional Regulatory Networks of Long Non-Coding RNAs during Vasculogenic Mimicry. Cells, 9(12), 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122690






