Propagation and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells: A Major Influence of the Long Non-Coding RNA H19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Long Non-Coding RNA H19 and Its Pleiotropic Oncogenic Actions in Different Cancers
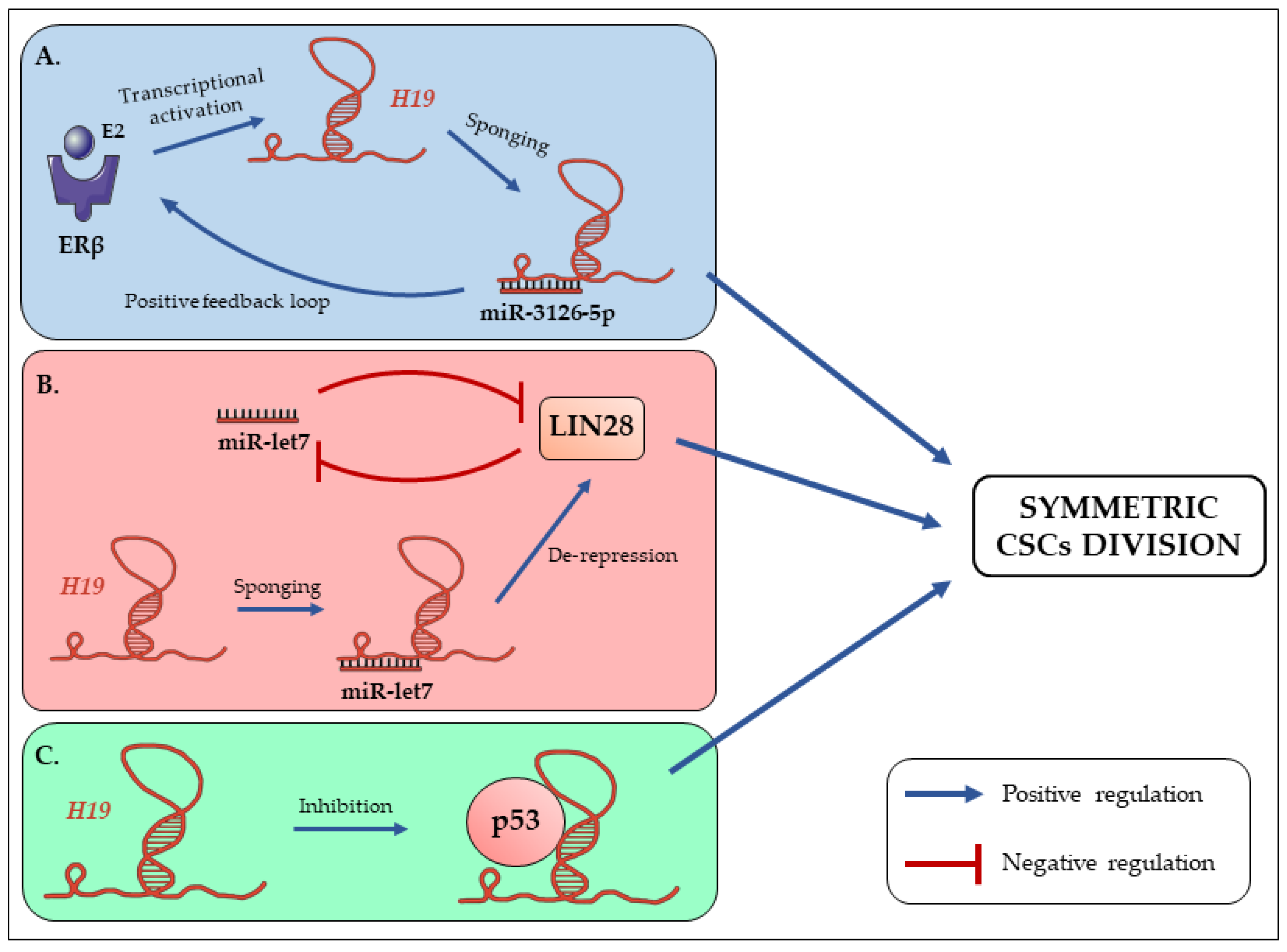
3. The Long Non-Coding RNA H19 Promotes Symmetric Renewal of CSCs
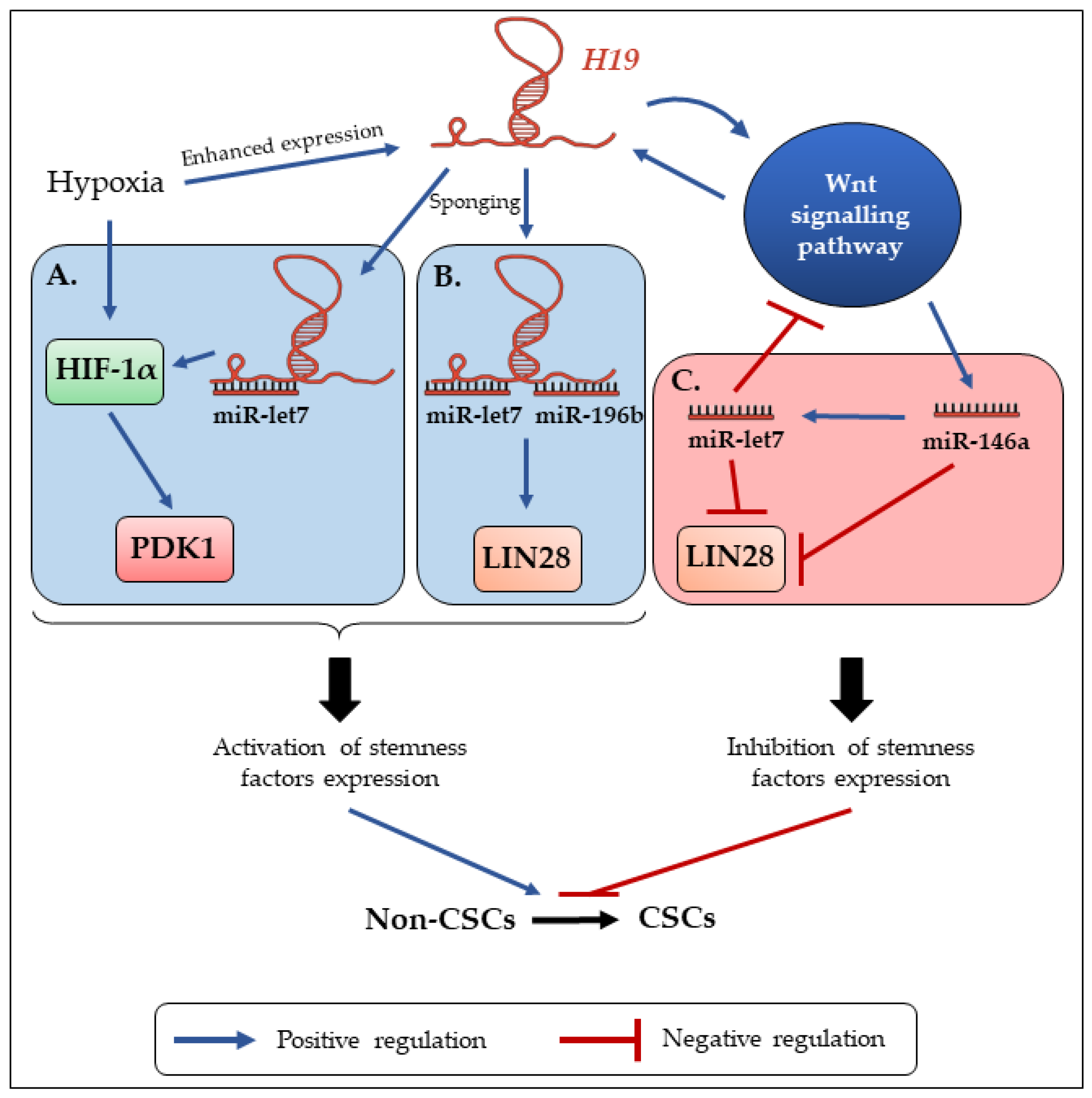
4. H19 Contributes to the Enrichment and Maintenance of CSCs
5. H19 Enhances Drug Resistance of CSCs
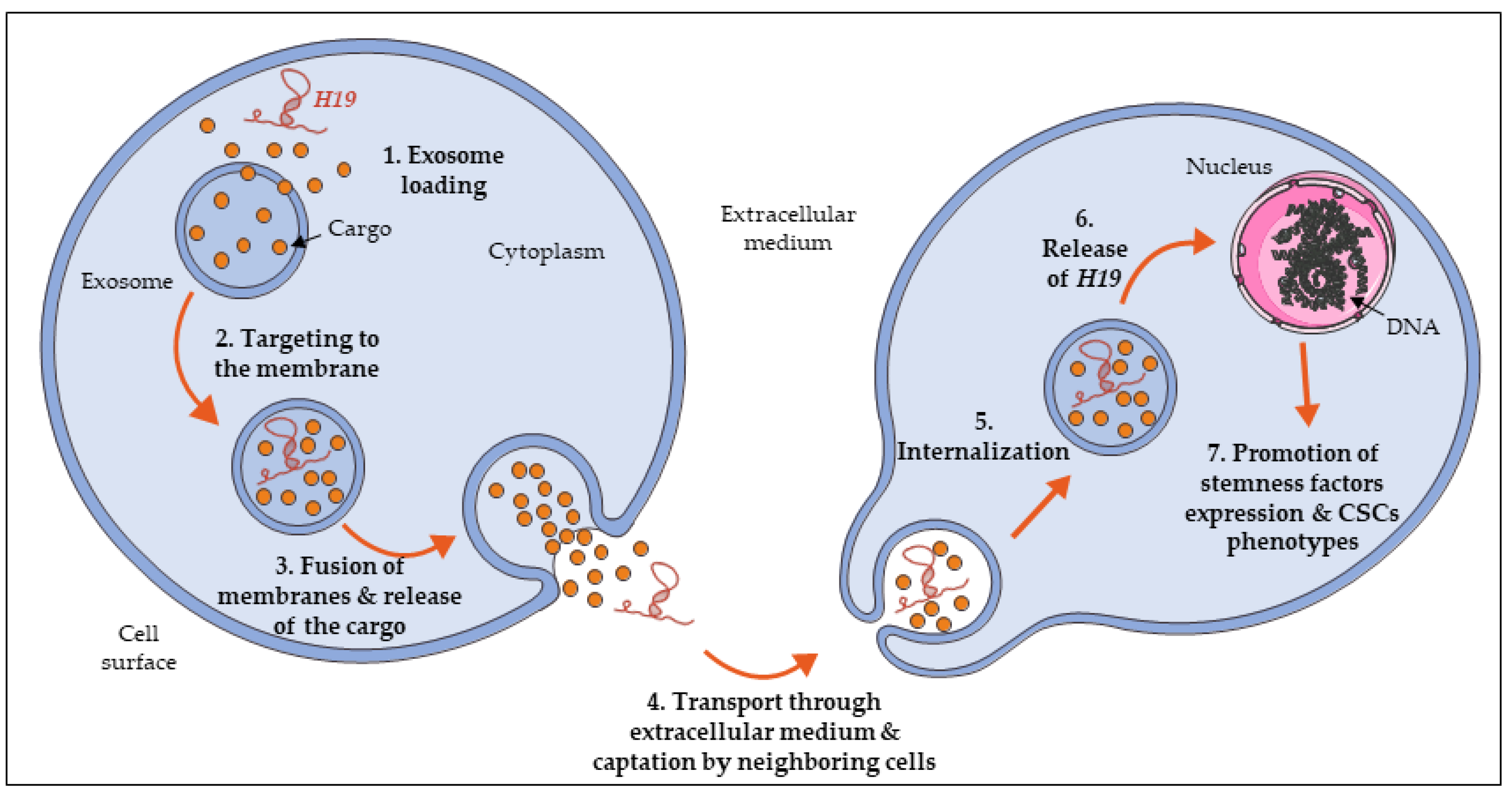
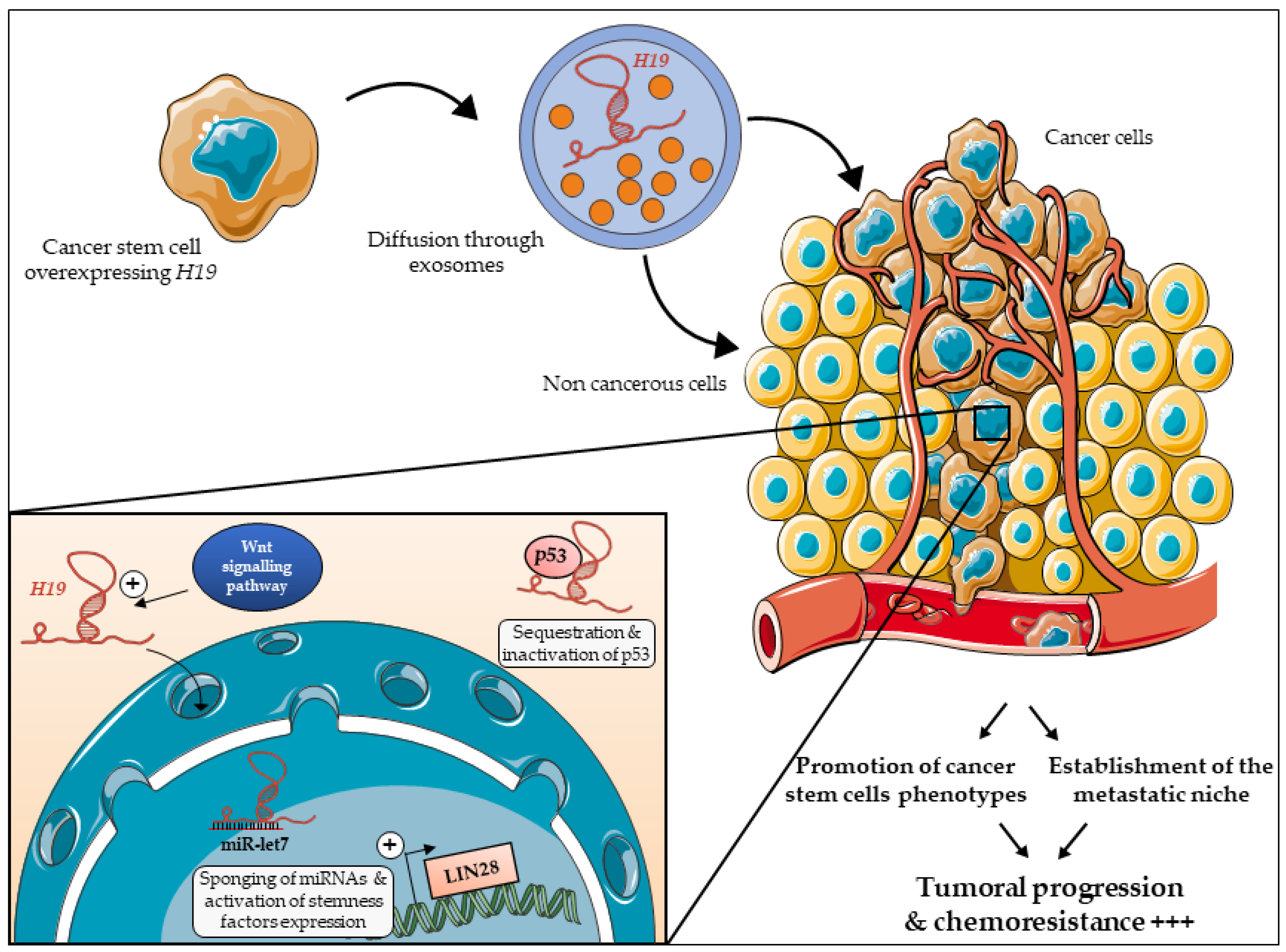
6. H19 Expression Is Propagated in the Tumor Micro-Environment to Promote Stemness
7. Discussion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADT | Androgen deprivation therapy |
| ALDH | Aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| BMP | Bone morphogenetic protein |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| CSC | Cancer stem cell |
| CUDR | Cancer up-regulated drug resistant |
| DMR | Differentially methylated region |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epidermal-to-mesenchymal transition |
| ERβ | Estrogen receptor β |
| GST-π | Glutathione S-transferase-π |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha |
| HMGA2 | High mobility group AT-hook 2 |
| HSC | Hematopoietic stem cells |
| IGF1R | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor |
| IGF2 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 |
| IPS | Induced-pluripotent cells |
| KRAS | V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| LncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| MDR1 | Multidrug resistance 1 |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| PDK1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 |
| PRC2 | Polycomb repressive complex 2 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| RB | Retinoblastoma protein |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RUNX1 | Runt-related transcription factor 1 |
| SC | Stem cell |
| TNM | Tumor node metastasis |
References
- Sugihara, E.; Saya, H. Complexity of cancer stem cells. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, D. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: Functional and mechanistic links. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.-J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Tam, W.L.; Shibue, T.; Kaygusuz, Y.; Reinhardt, F.; Ng Eaton, E.; Weinberg, R.A. Distinct EMT programs control normal mammary stem cells and tumour-initiating cells. Nature 2015, 525, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Marjanovic, N.D.; Lee, T.; Bell, G.; Kleer, C.G.; Reinhardt, F.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Young, R.A.; Weinberg, R.A. Poised chromatin at the ZEB1 promoter enables breast cancer cell plasticity and enhances tumorigenicity. Cell 2013, 154, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacovelli, M.; Frezza, C. Metabolic reprogramming and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3132–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreso, A.; Dick, J.E. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, K.; Ham, S.W.; Kim, H. Cancer stem cell heterogeneity: Origin and new perspectives on CSC targeting. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Desterke, C.; Féraud, O.; Richard, S.; Ferlicot, S.; Verkarre, V.; Patard, J.J.; Loisel-Duwattez, J.; Foudi, A.; Griscelli, F.; et al. iPSC-Derived Embryoid Bodies as Models of c-Met-Mutated Hereditary Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liao, R.; Li, D.; Sun, J. Induced cancer stem cells generated by radiochemotherapy and their therapeutic implications. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17301–17312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Gupta, A.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Chatterji, U. Modulation of SOX2 expression delineates an end-point for paclitaxel-effectiveness in breast cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadec, C.; Vlashi, E.; Donna, L.D.; Dekmezian, C.; Pajonk, F. Radiation-induced reprograming of breast cancer cells. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counter, C.M.; Avilion, A.A.; LeFeuvre, C.E.; Stewart, N.G.; Greider, C.W.; Harley, C.B.; Bacchetti, S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Piatyszek, M.; Prowse, K.; Harley, C.; West, M.; Ho, P.; Coviello, G.; Wright, W.; Weinrich, S.; Shay, J. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Guan, Z.; Ge, Y.; Yang, X.; Cai, J. LncRNAs and their role in cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110685–110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.P. Parallels between artificial reprogramming and the biogenesis of cancer stem cells: Involvement of lncRNAs. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 57, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.Q.; Ahmed, E.I.; Elareer, N.R.; Junejo, K.; Steinhoff, M.; Uddin, S. Role of miRNA-Regulated Cancer Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis of Human Malignancies. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermüller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. RNA Maps Reveal New RNA Classes and a Possible Function for Pervasive Transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Fang, X. A Brief Review on the Human Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Project. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2013, 11, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ENCODE Project Consortium Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 2007, 447, 799–816. [CrossRef]
- Hon, C.-C.; Ramilowski, J.A.; Harshbarger, J.; Bertin, N.; Rackham, O.J.L.; Gough, J.; Denisenko, E.; Schmeier, S.; Poulsen, T.M.; Severin, J.; et al. An atlas of human long non-coding RNAs with accurate 5′ ends. Nature 2017, 543, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. The Diversity of Long Noncoding RNAs and Their Generation. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Chen, Y. Long noncoding RNAs and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Investig. Aging 2016, 11, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Mao, Y.; Ji, J. The link between long noncoding RNAs and depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 73, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.H.; Kaur, S.; Pociot, F. Long non-coding RNAs as novel players in β cell function and type 1 diabetes. Hum. Genom. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long Noncoding RNA and Cancer: A New Paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, M.S.; Zemel, S.; Tilghman, S.M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature 1991, 351, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannan, C.I.; Dees, E.C.; Ingram, R.S.; Tilghman, S.M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabory, A.; Ripoche, M.-A.; Digarcher, A.L.; Watrin, F.; Ziyyat, A.; Forné, T.; Jammes, H.; Ainscough, J.F.X.; Surani, M.A.; Journot, L.; et al. H19 acts as a trans regulator of the imprinted gene network controlling growth in mice. Development 2009, 136, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Wen, X.; Hao, J.; Li, Z.; Ni, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Combined Single-Cell Profiling of lncRNAs and Functional Screening Reveals that H19 Is Pivotal for Embryonic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Development. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 285–298.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, A.; He, X.C.; Thorvaldsen, J.L.; Sugimura, R.; Perry, J.M.; Tao, F.; Zhao, M.; Christenson, M.K.; Sanchez, R.; Yu, J.Y.; et al. Maternal-imprinting at H19-Igf2 locus maintains adult hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Nature 2013, 500, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauderlique-Le Roy, H.; Vennin, C.; Brocqueville, G.; Spruyt, N.; Adriaenssens, E.; Bourette, R.P. Enrichment of Human Stem-Like Prostate Cells with s-SHIP Promoter Activity Uncovers a Role in Stemness for the Long Noncoding RNA H19. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, C.; Li, X.; Jia, L.; Li, W. Long Non-coding RNA H19 Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Epigenetic Modulation of Histone Deacetylases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecerf, C.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. The long non-coding RNA H19: An active player with multiple facets to sustain the hallmarks of cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4673–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kawakami, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Minamoto, T. Long Interspersed Nuclear Element 1 Hypomethylation Is a Marker of Poor Prognosis in Stage IA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2418–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; An, J.; Gui, X.; Li, T.; Lu, D. CUDR promotes liver cancer stem cell growth through upregulating TERT and C-Myc. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40775–40798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berteaux, N.; Lottin, S.; Monté, D.; Pinte, S.; Quatannens, B.; Coll, J.; Hondermarck, H.; Curgy, J.-J.; Dugimont, T.; Adriaenssens, E. H19 mRNA-like Noncoding RNA Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Positive Control by E2F1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29625–29636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Bi, J.; Xue, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhi, K.; Hua, J.; Fang, G. Up-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to proliferation of gastric cancer cells. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Shi, P.; Tian, X.; Guo, Y. Correlation between long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) H19 expression and trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 15, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Guo, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Gong, J.; Li, W. Tumor-released lncRNA H19 promotes gefitinib resistance via packaging into exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3438–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Shen, X.; Jing, R.; Pu, J.; Wang, X.; Ju, S.; Cong, H.; et al. LncRNA H19 overexpression induces bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma by targeting MCL-1 via miR-29b-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Cai, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xue, Y. Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-T.; Ye, H.; Wei, P.-P.; Han, B.-W.; He, B.; Chen, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-Q. LncRNAs H19 and HULC, activated by oxidative stress, promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma through a ceRNA manner. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lian, M.; Ma, H.; Wang, R.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhai, J.; Meng, L.; Feng, L.; Bai, Y.; et al. Competing endogenous RNA network analysis of CD274, IL‑10 and FOXP3 co‑expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3859–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tian, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Du, C.; Xie, X.; Kornmann, M.; Yang, Y. The long noncoding RNA H19 promotes cell proliferation via E2F-1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, J. Long non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.-B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.-S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Imprinted H19 LncRNA Antagonizes Let-7 MicroRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Cullen, B.R. The imprinted H19 noncoding RNA is a primary microRNA precursor. RNA 2007, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xiang, T.; Wu, Q.-F.; Wang, W.-X. Long Noncoding RNA H19-Derived miR-675 Enhances Proliferation and Invasion via RUNX1 in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2016, 23, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, W.P.; Ng, E.K.O.; Ng, S.S.M.; Jin, H.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Kwok, T.T. Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J.M.; Elahi, A.; Clark, C.W.; Wang, J.; Humphries, L.A.; Centeno, B.; Bloom, G.; Fuchs, B.C.; Yeatman, T.; Shibata, D. miR-675 Mediates Downregulation of Twist1 and Rb in AFP-Secreting Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peperstraete, E.; Lecerf, C.; Collette, J.; Vennin, C.; Raby, L.; Völkel, P.; Angrand, P.-O.; Winter, M.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P.; et al. Enhancement of Breast Cancer Cell Aggressiveness by lncRNA H19 and its Mir-675 Derivative: Insight into Shared and Different Actions. Cancers 2020, 12, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, S.J.; Kimble, J. Asymmetric and symmetric stem-cell divisions in development and cancer. Nature 2006, 441, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Xiao, G.-D.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Wang, J.-C.; Xu, C.-W.; Qin, S.; Ren, H.; Tang, S.-C.; Sun, X. H19 regulation of oestrogen induction of symmetric division is achieved by antagonizing Let-7c in breast cancer stem-like cells. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.; Lottin, S.; Dugimont, T.; Fauquette, W.; Coll, J.; Dupouy, J.P.; Boilly, B.; Curgy, J.J. Steroid hormones modulate H19 gene expression in both mammary gland and uterus. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4460–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, M.; Chai, H.-F.; Peng, F.; Meng, Y.-T.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Zou, H.; Liang, Q.-L.; Li, M.-M.; Mao, K.-G.; et al. Estrogen receptor β upregulated by lncRNA-H19 to promote cancer stem-like properties in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, J.; Menezes, M.R.; Cao, S.; Hagan, J.P. The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Tang, S.-C.; Xiao, G.; Sun, X.; Li, G.; Du, N.; Liu, D.; Ren, H. MiR-146a promotes the asymmetric division and inhibits the self-renewal ability of breast cancer stem-like cells via indirect upregulation of Let-7. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insinga, A.; Cicalese, A.; Faretta, M.; Gallo, B.; Albano, L.; Ronzoni, S.; Furia, L.; Viale, A.; Pelicci, P.G. DNA damage in stem cells activates p21, inhibits p53, and induces symmetric self-renewing divisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicalese, A.; Bonizzi, G.; Pasi, C.E.; Faretta, M.; Ronzoni, S.; Giulini, B.; Brisken, C.; Minucci, S.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Pelicci, P.G. The Tumor Suppressor p53 Regulates Polarity of Self-Renewing Divisions in Mammary Stem Cells. Cell 2009, 138, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rübe, C.E.; Fricke, A.; Widmann, T.A.; Fürst, T.; Madry, H.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Rübe, C. Accumulation of DNA Damage in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells during Human Aging. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Lu, C.; Hu, W.; Sun, Y.; Levine, A.J. Multiple roles of p53-related pathways in somatic cell reprogramming and stem cell differentiation. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5635–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigarella, C.L.; Liang, R.; Ghaffari, S. Stem cells and the impact of ROS signaling. Development 2014, 141, 4206–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Padi, S.K.R.; Bearss, J.J.; Pandey, R.; Okumura, K.; Beltran, H.; Song, J.H.; Kraft, A.S.; Olive, V. PIM protein kinases regulate the level of the long noncoding RNA H19 to control stem cell gene transcription and modulate tumor growth. Mol. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Fu, J.; Ma, T.; Yan, B.; Gao, R.; An, Z.; Wang, D. LncRNA H19-elevated LIN28B promotes lung cancer progression through sequestering miR-196b. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiao, P.; Ning, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Yu, W.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J. Macrophages-induced long noncoding RNA H19 up-regulation triggers and activates the miR-193b/MAPK1 axis and promotes cell aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Wang, J.-H.; Fan, W.-J.; Meng, Y.-T.; Li, M.-M.; Li, T.-T.; Cui, B.; Wang, H.-F.; Zhao, Y.; An, F.; et al. Glycolysis gatekeeper PDK1 reprograms breast cancer stem cells under hypoxia. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, T.-T.; Wang, K.-L.; Xiao, G.-Q.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhao, H.-D.; Kang, Z.-J.; Fan, W.-J.; Zhu, L.-L.; Li, M.; et al. H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Finniss, S.; Cazacu, S.; Xiang, C.; Brodie, Z.; Mikkelsen, T.; Poisson, L.; Shackelford, D.B.; Brodie, C. Repurposing phenformin for the targeting of glioma stem cells and the treatment of glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56456–56470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Fleur, L.; Johansson, A.-C.; Roberg, K. A CD44high/EGFRlow Subpopulation within Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines Shows an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype and Resistance to Treatment. PLoS ONE 2012, e44071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, A.-P.; Lièvre, M.; Thomas, C.; Hinkal, G.; Ansieau, S.; Puisieux, A. Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaenssens, E.; Lottin, S.; Berteaux, N.; Hornez, L.; Fauquette, W.; Fafeur, V.; Peyrat, J.-P.; Le Bourhis, X.; Hondermarck, H.; Coll, J.; et al. Cross-Talk between Mesenchyme and Epithelium Increases H19 Gene Expression during Scattering and Morphogenesis of Epithelial Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 275, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T.M.; McBride, W.H.; Pajonk, F. The Response of CD24 −/low /CD44 + Breast Cancer–Initiating Cells to Radiation. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lewis, M.T.; Huang, J.; Gutierrez, C.; Osborne, C.K.; Wu, M.-F.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Pavlick, A.; Zhang, X.; Chamness, G.C.; et al. Intrinsic Resistance of Tumorigenic Breast Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri-Sacca, M.; Bartucci, M.; De Maria, R. DNA Damage Repair Pathways in Cancer Stem Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestier, C.; Hur, M.H.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Monville, F.; Dutcher, J.; Brown, M.; Jacquemier, J.; Viens, P.; Kleer, C.G.; Liu, S.; et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadec, C.; Vlashi, E.; Bhuta, S.; Lai, C.; Mischel, P.; Werner, M.; Henke, M.; Pajonk, F. Tumor cells with low proteasome subunit expression predict overall survival in head and neck cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Kang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Chen, J.-L. High expression of long non-coding RNA H19 is required for efficient tumorigenesis induced by Bcr-Abl oncogene. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, L.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Zou, X. Ectopic expressed long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to malignant cell behavior of ovarian cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10082–10091. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, N.; Li, X.; Pan, H.; Li, C.; Ren, S.; Su, C.; Cai, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. Correlation of long non-coding RNA H19 expression with cisplatin-resistance and clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, X.; Zang, R.; Zhang, E.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, E.; Shao, L.; Li, A.; Yang, N.; Han, X.; et al. LncRNA H19 confers chemoresistance in ERα-positive breast cancer through epigenetic silencing of the pro-apoptotic gene BIK. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81452–81462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, P.; Sun, X.; Xu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhan, R. Suppressing H19 Modulates Tumorigenicity and Stemness in U251 and U87MG Glioma Cells. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, G.; Xu, Q.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Hou, Y. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3932–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Liao, Y.; Gong, D.; Zhao, X.; Ji, W. Effect of long non-coding RNA H19 on oxidative stress and chemotherapy resistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, W.P.; Wong, T.W.L.; Cheung, A.H.H.; Co, C.N.N.; Kwok, T.T. Induction of drug resistance and transformation in human cancer cells by the noncoding RNA CUDR. RNA 2007, 13, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, J.; Nguyen, E.; Liu, Q.; Bouyer, C.; Adriaenssens, E.; Hilal, G.; Ségal-Bendirdjian, E. Telomerase regulation by the long non-coding RNA H19 in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, R.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and protein that promote tumor growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Nitadori-Hoshino, A.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Sugimoto, H.; O’Connell, J.T.; Kato, N.; Villanueva, A.; Vidal, A.; Qiu, L.; Vitkin, E.; Perelman, L.T.; Melo, C.A.; et al. Cancer Exosomes Perform Cell-Independent MicroRNA Biogenesis and Promote Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xia, K.; Chang, Y.; et al. Emerging role of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, H.; Wei, M.; Zha, W.; Guan, S.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F. MSC-Secreted Exosomal H19 Promotes Trophoblast Cell Invasion and Migration by Downregulating let-7b and Upregulating FOXO1. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2019, 19, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Luan, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhai, A.; Bi, C. The MSC-Derived Exosomal lncRNA H19 Promotes Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers by Upregulating PTEN via MicroRNA-152-3p. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2019, 19, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Gurley, E.C.; Liang, G.; Chen, W.; Lai, G.; et al. Cholangiocyte-Derived Exosomal Long Noncoding RNA H19 Promotes Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Cholestatic Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1317–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conigliaro, A.; Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Saieva, L.; Buccheri, S.; Dieli, F.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M.; et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Yuan, W.; Gao, Z. Determination of Serum Exosomal H19 as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Bladder Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 9307–9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzi-Molan, A.; Babashah, S.; Bakhshinejad, B.; Atashi, A.; Taha, M.F. Down-regulation of the non-coding RNA H19 and its derived miR-675 is concomitant with up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 during neural-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Song, X.; Liu, J. Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yin, C.; Dang, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhang, G. Identification of the long non-coding RNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Li, Q.; Pan, J.; Li, L.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y. Expression level of long noncoding RNA H19 in plasma of patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer and its clinical significance. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 14, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lecerf, C.; Peperstraete, E.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. Propagation and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells: A Major Influence of the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Cells 2020, 9, 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122613
Lecerf C, Peperstraete E, Le Bourhis X, Adriaenssens E. Propagation and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells: A Major Influence of the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122613
Chicago/Turabian StyleLecerf, Clément, Evodie Peperstraete, Xuefen Le Bourhis, and Eric Adriaenssens. 2020. "Propagation and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells: A Major Influence of the Long Non-Coding RNA H19" Cells 9, no. 12: 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122613
APA StyleLecerf, C., Peperstraete, E., Le Bourhis, X., & Adriaenssens, E. (2020). Propagation and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells: A Major Influence of the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Cells, 9(12), 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122613





