When the Search for Stemness Genes Meets the Skin Substitute Bioengineering Field: KLF4 Transcription Factor under the Light
Abstract
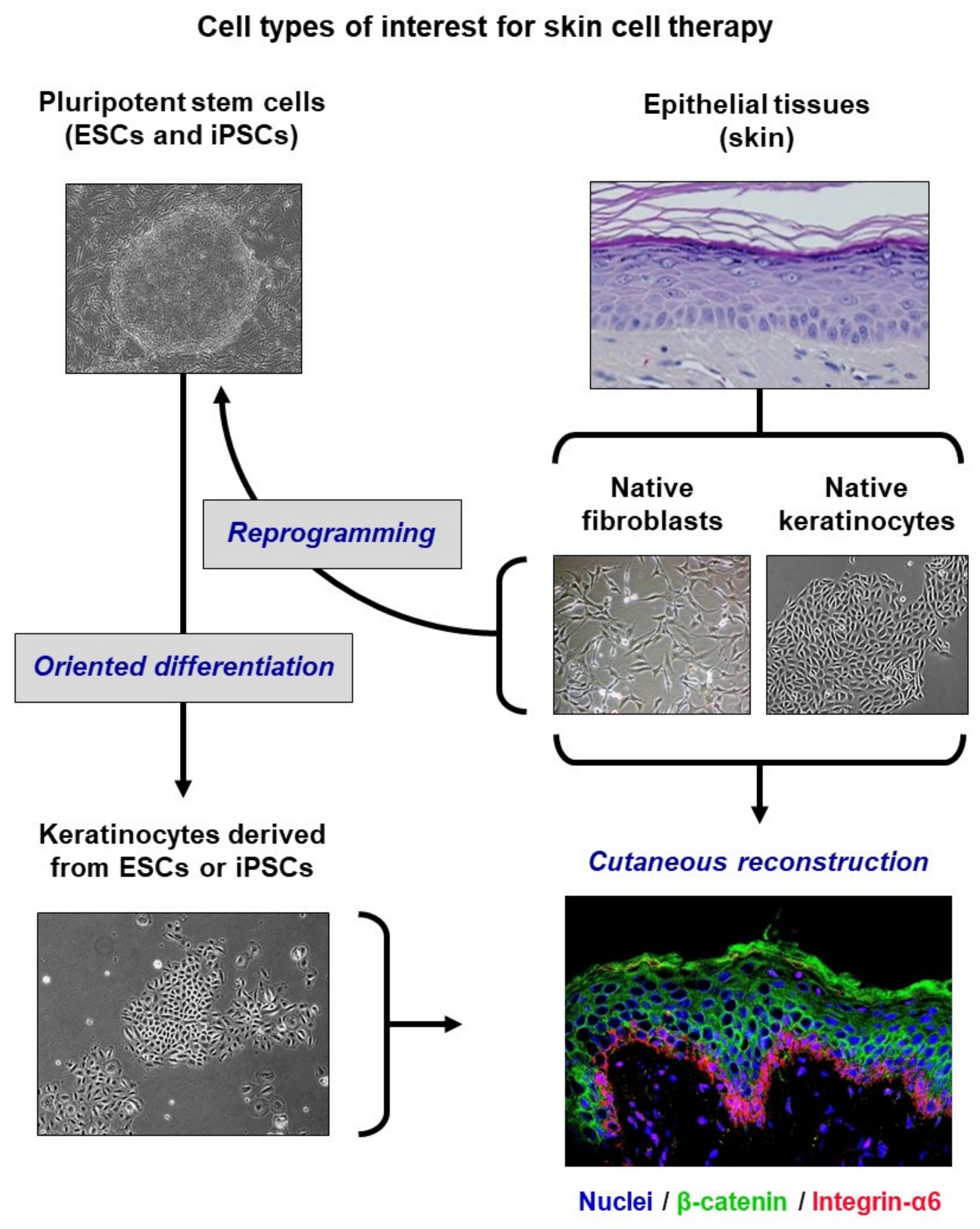
1. Biomedical Context
2. The KLF4 Candidate
3. KLF4 Functions in Native Adult Keratinocytes
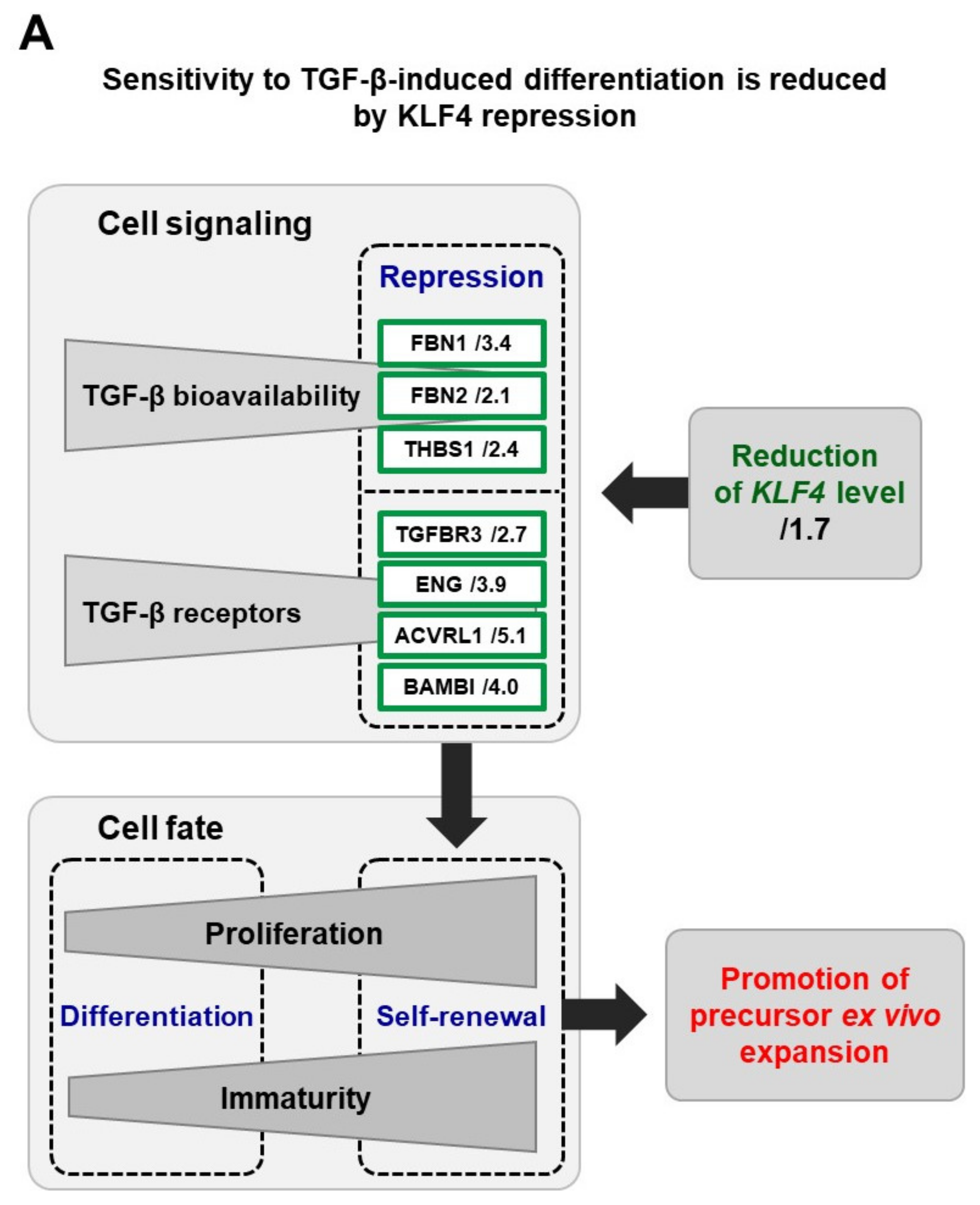
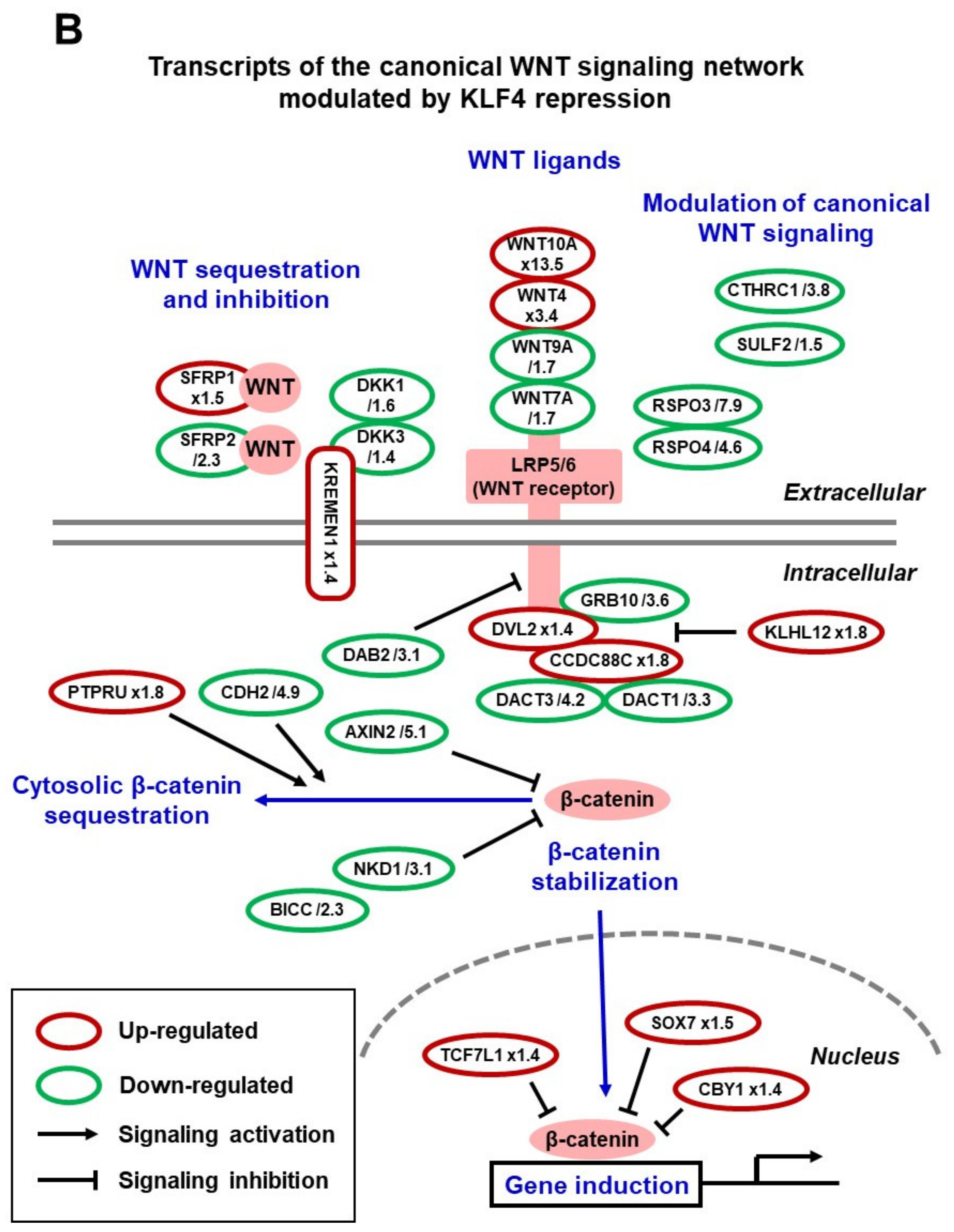
4. Insights into the Mechanisms
5. From Basic Research to Pre-Clinical Models
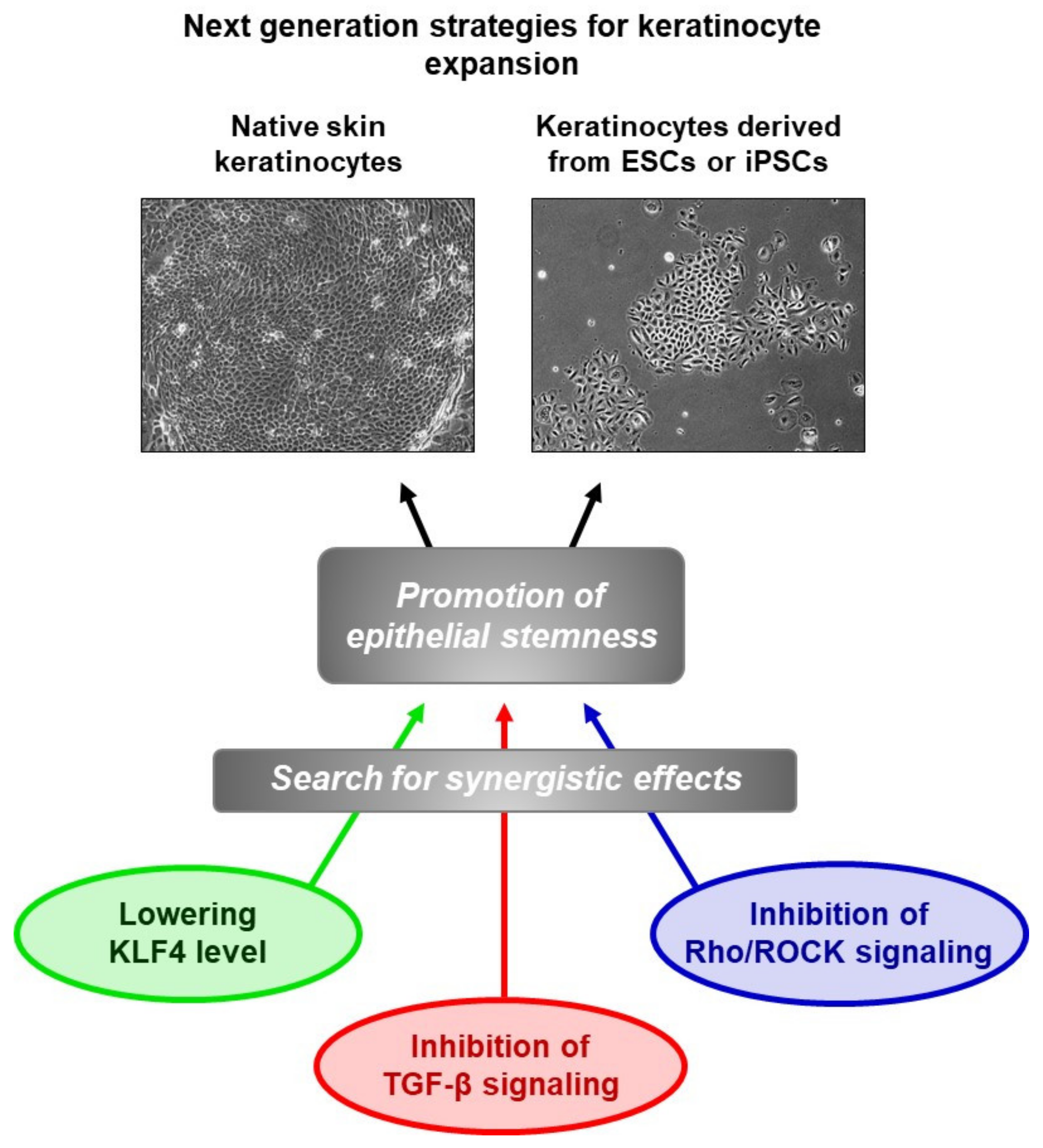
6. Extrapolation to ESC-Derived Keratinocytes
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fortunel, N.O.; Chadli, L.; Coutier, J.; Lemaître, G.; Auvré, F.; Domingues, S.; Bouissou-Cadio, E.; Vaigot, P.; Cavallero, S.; Deleuze, J.-F.; et al. KLF4 inhibition promotes the expansion of keratinocyte precursors from adult human skin and of embryonic-stem-cell-derived keratinocytes. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallico, G.G., III; O’Connor, N.E.; Compton, C.C.; Kehinde, O.; Green, H. Permanent coverage of large burn wounds with autologous cultured human epithelium. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronfard, V.; Rives, J.-M.; Neveux, Y.; Carsin, H.; Barrandon, Y. Long-term regeneration of human epidermis on third degree burns transplanted with autologous cultured epithelium grown on a fibrin matrix. Transplantation 2000, 70, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, T.; Rothoeft, T.; Teig, N.; Bauer, J.W.; Pellegrini, G.; De Rosa, L.; Scaglione, D.; Reichelt, J.; Klausegger, A.; Kneisz, D.; et al. Regeneration of the entire human epidermis using transgenic stem cells. Nature 2017, 551, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenou, H.; Nissan, X.; Larcher, F.; Feteira, J.; Lemaitre, G.; Saidani, M.; Del Rio, M.; Barrault, C.C.; Bernard, F.-X.; Peschanski, M.; et al. Human embryonic stem-cell derivatives for full reconstruction of the pluristratified epidermis: A preclinical study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.; Kiuru, M.; Cairo, M.S.; Christiano, A.M. Generation of keratinocytes from normal and recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8797–8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolundzic, N.; Khurana, P.; Hobbs, C.; Rogar, M.; Ropret, S.; Törmä, H.; Ilic, D.; Liovic, M. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line from an epidermolysis bullosa simplex patient heterozygous for keratin 5 E475G mutation and with the Dowling Meara phenotype. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 37, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunel, N.O.; Martin, M.T. When stemness genes meet skin graft bioengineering: Focus on KLF4. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, N.Y.; Chan, Y.S.; Feng, B.; Lu, X.; Orlov, Y.L.; Moreau, D.; Kumar, P.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J.; Lau, M.S.; et al. A genome-wide RNAi screen reveals determinants of human embryonic stem cell identity. Nature 2010, 468, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, G.L.; Boxer, L.D.; Webster, D.E.; Bussat, R.T.; Qu, K.; Zarnegar, B.J.; Johnston, D.; Siprashvili, Z.; Khavari, P.A. ZNF750 is a p63 target gene that induces KLF4 to drive terminal epidermal differentiation. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segre, J.A.; Bauer, C.; Fuchs, E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Simmons, P.J.; Kaur, P. Identification and isolation of candidate human keratinocyte stem cells based on cell surface phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3902–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachidi, W.; Harfouche, G.; Lemaitre, G.; Amiot, F.; Vaigot, P.; Martin, M.T. Sensing radiosensitivity of human epidermal stem cells. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunel, N.O.; Cadio, E.; Vaigot, P.; Chadli, L.; Moratille, S.; Bouet, S.; Roméo, P.-H.; Martin, M.T. Exploration of the functional hierarchy of the basal layer of human epidermis at the single-cell level using parallel clonal microcultures of keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunel, N.O.; Bouissou-Cadio, E.; Coutier, J.; Martin, M.T. Iterative three-dimensional epidermis bioengineering and xenografting to assess long-term regenerative potential in human keratinocyte precursor cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2109, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, E. Epidermal differentiation and keratin gene expression. J. Cell Sci. Suppl. 1993, 17, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunel, N.O.; Chadli, L.; Bourreau, E.; Cadio, E.; Vaigot, P.; Marie, M.; Deshayes, N.; Rathman-Josserand, M.; Leclaire, J.; Martin, M.T. Cellular adhesion on collagen: A simple method to select human basal keratinocytes which preserves their high growth capacity. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2011, 21 (Suppl. 2), 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Fu, J.; Ray, S.; Huang, S.; Zheng, H.; Ai, W. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is required for maintenance of breast cancer stem cells and for cell migration and invasion. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2161–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.; Mix, E.; Frahm, J.; Glass, A.; Müller, J.; Schmitt, O.; Schmöle, A.-C.; Klemm, K.; Ortinau, S.; Hübner, R.; et al. Small molecule GSK-3 inhibitors increase neurogenesis of human neural progenitor cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 488, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunel, N.O.; Otu, H.H.; Ng, H.H.; Chen, J.; Mu, X.; Chevassut, T.; Li, X.; Joseph, M.; Bailey, C.; Hatzfeld, J.A.; et al. Comment on “‘Stemness’: Transcriptional profiling of embryonic and adult stem cells” and “a stem cell molecular signature”. Science 2003, 302, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, G. ‘Stemness’ genes still elusive. Science 2003, 302, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxer, L.D.; Barajas, B.; Tao, S.; Zhang, J.; Khavari, P.A. ZNF750 interacts with KLF4 and RCOR1, KDM1A, and CTBP1/2 chromatin regulators to repress epidermal progenitor genes and induce differentiation genes. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Tang, J.; Lopez-Pajares, V.; Tao, S.; Qu, K.; Crabtree, G.R.; Khavari, P.A. ACTL6a enforces the epidermal progenitor state by suppressing SWI/SNF-dependent induction of KLF4. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Pajares, V.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Webster, D.E.; Barajas, B.C.; Siprashvili, Z.; Zarnegar, B.J.; Boxer, L.D.; Rios, E.J.; Tao, S.; et al. LncRNA-MAF:MAFB transcription factor network regulates epidermal differentiation. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Park, J.; Feng, A.; Awasthi, P.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Iglesias-Bartolome, R. YAP1/TAZ-TEAD transcriptional networks maintain skin homeostasis by regulating cell proliferation and limiting KLF4 activity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexaline, M.M.; Trouillas, M.; Nivet, M.; Bourreau, E.; Leclerc, T.; Duhamel, P.; Martin, M.T.; Doucet, C.; Fortunel, N.O.; Lataillade, J.-J. Bioengineering a human plasma-based epidermal substitute with efficient grafting capacity and high content in clonogenic cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lee, H.J.; Shrivastava, A.; Wang, R.; McQuiston, T.J.; Challberg, S.S.; Pollok, B.A.; Wang, T. Long-term in vitro expansion of epithelial stem cells enabled by pharmacological inhibition of PAK1-ROCK-myosin II and TGF-β signaling. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 598–610.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fortunel, N.O.; Martin, M.T. When the Search for Stemness Genes Meets the Skin Substitute Bioengineering Field: KLF4 Transcription Factor under the Light. Cells 2020, 9, 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102188
Fortunel NO, Martin MT. When the Search for Stemness Genes Meets the Skin Substitute Bioengineering Field: KLF4 Transcription Factor under the Light. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102188
Chicago/Turabian StyleFortunel, Nicolas O., and Michèle T. Martin. 2020. "When the Search for Stemness Genes Meets the Skin Substitute Bioengineering Field: KLF4 Transcription Factor under the Light" Cells 9, no. 10: 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102188
APA StyleFortunel, N. O., & Martin, M. T. (2020). When the Search for Stemness Genes Meets the Skin Substitute Bioengineering Field: KLF4 Transcription Factor under the Light. Cells, 9(10), 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102188





