Extracellular Juxtamembrane Motif Critical for TrkB Preformed Dimer and Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Construction of Expression Vectors
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Primary Neuron Culture
2.5. Transient and Stable Transfection
2.6. Native PAGE and Western Blotting
2.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.8. Protein Expression and Purification
3. Results
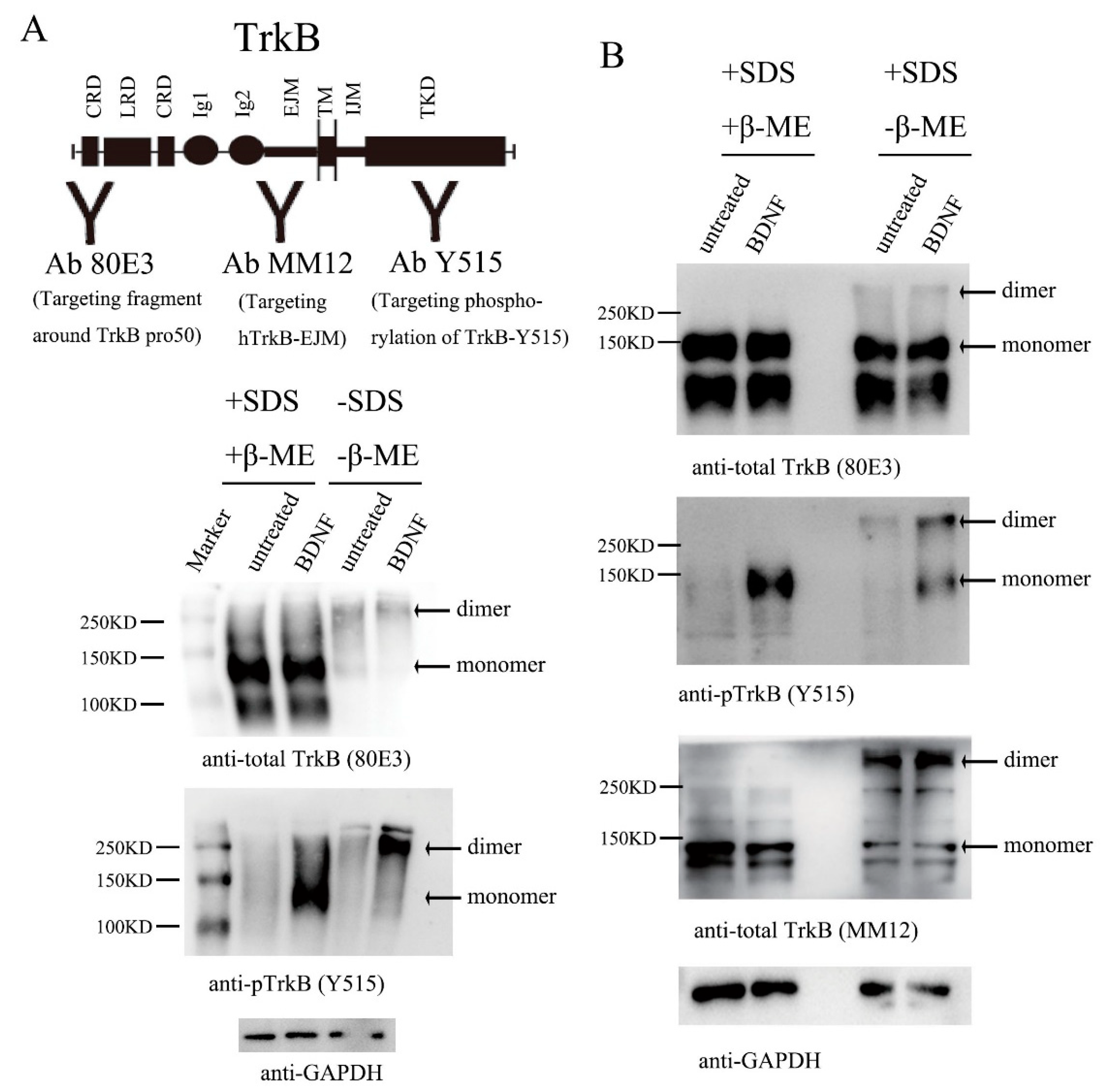
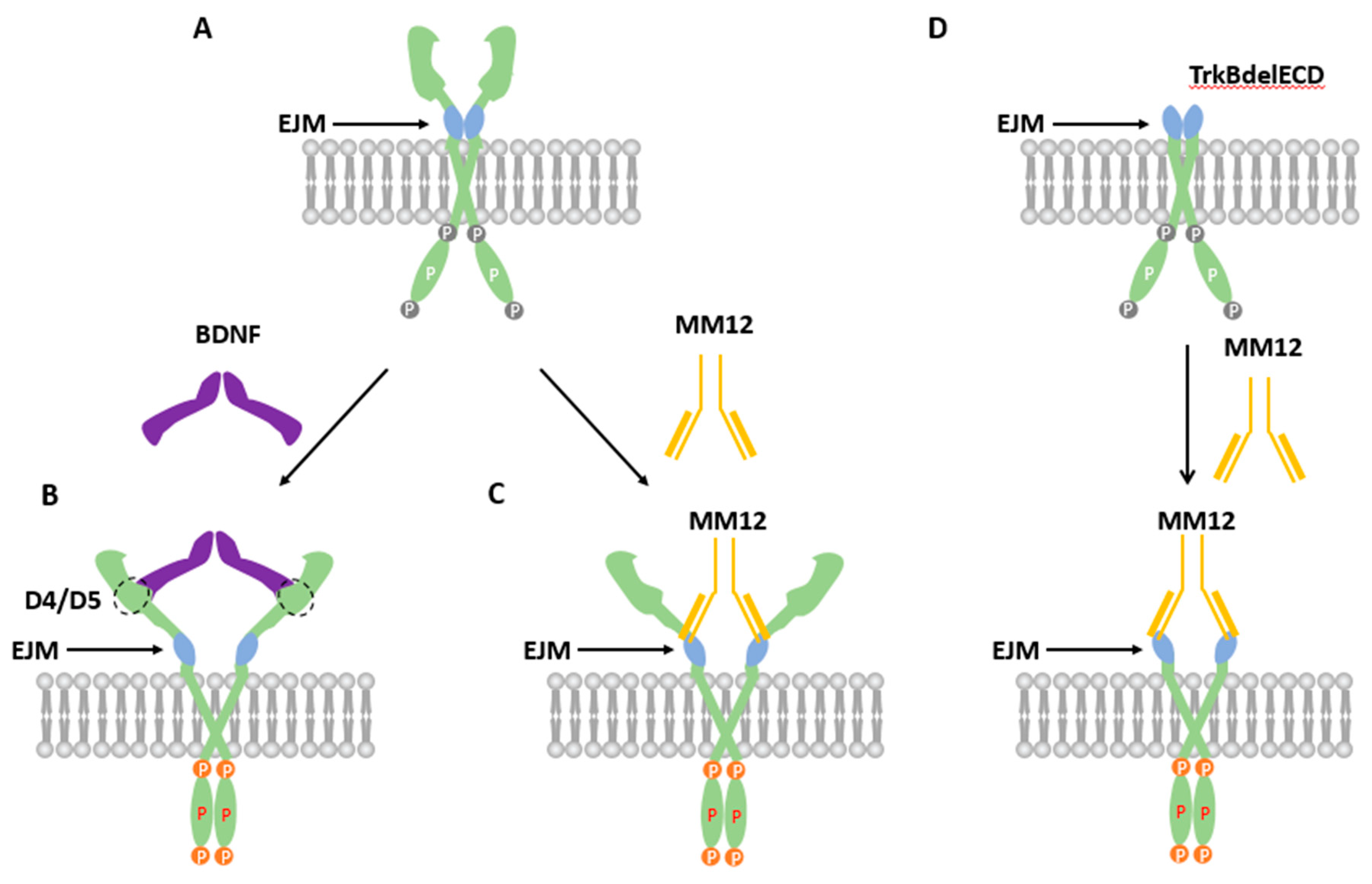
3.1. Endogenous TrkB Is Expressed Largely as Preformed Dimers in Cultured Primary Neurons
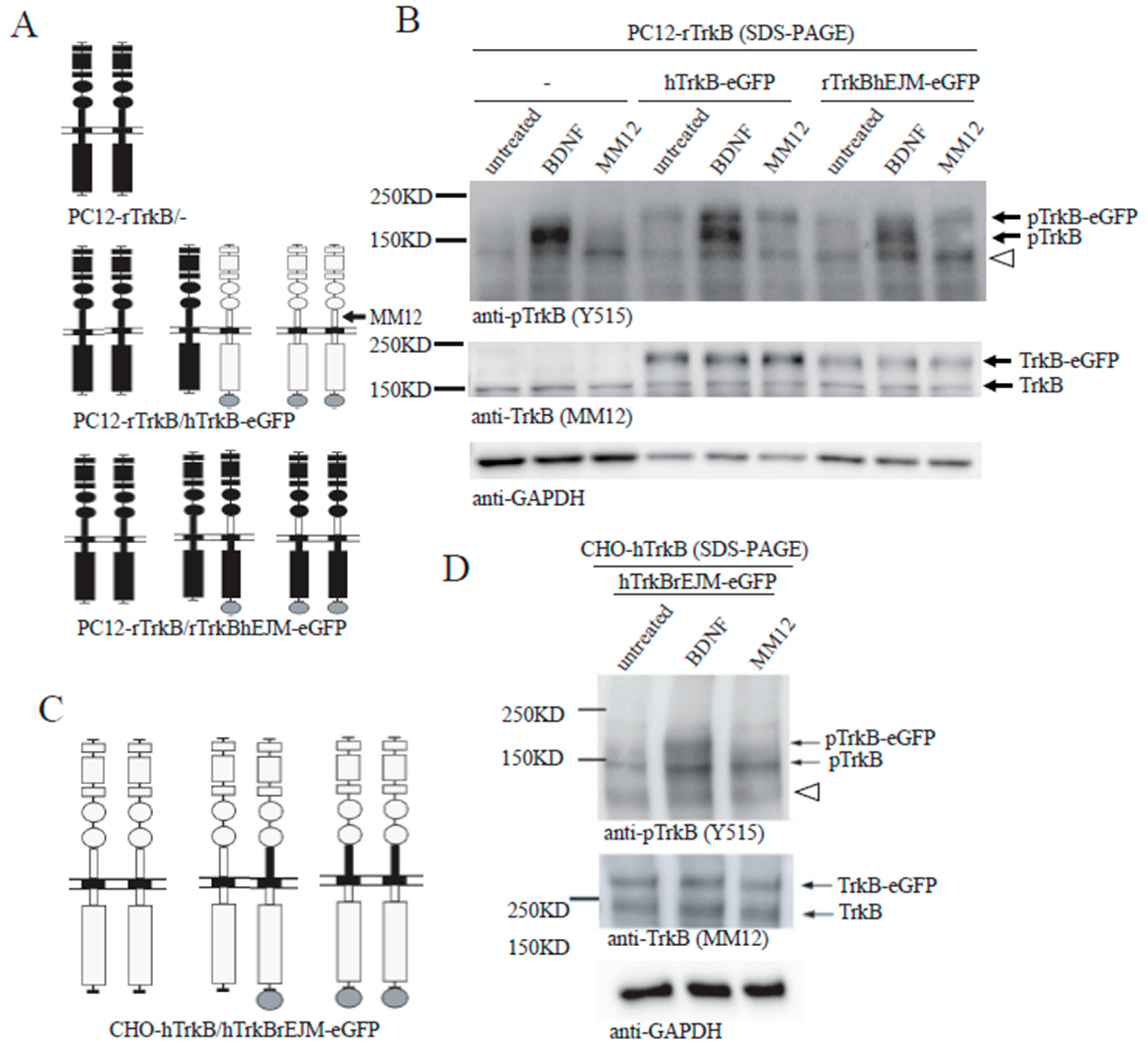
3.2. TrkB EJM Inhibits the Formation of Preformed Dimers
3.3. Binding of TrkB EJM by a TrkB Antibody Activates Preformed Dimers
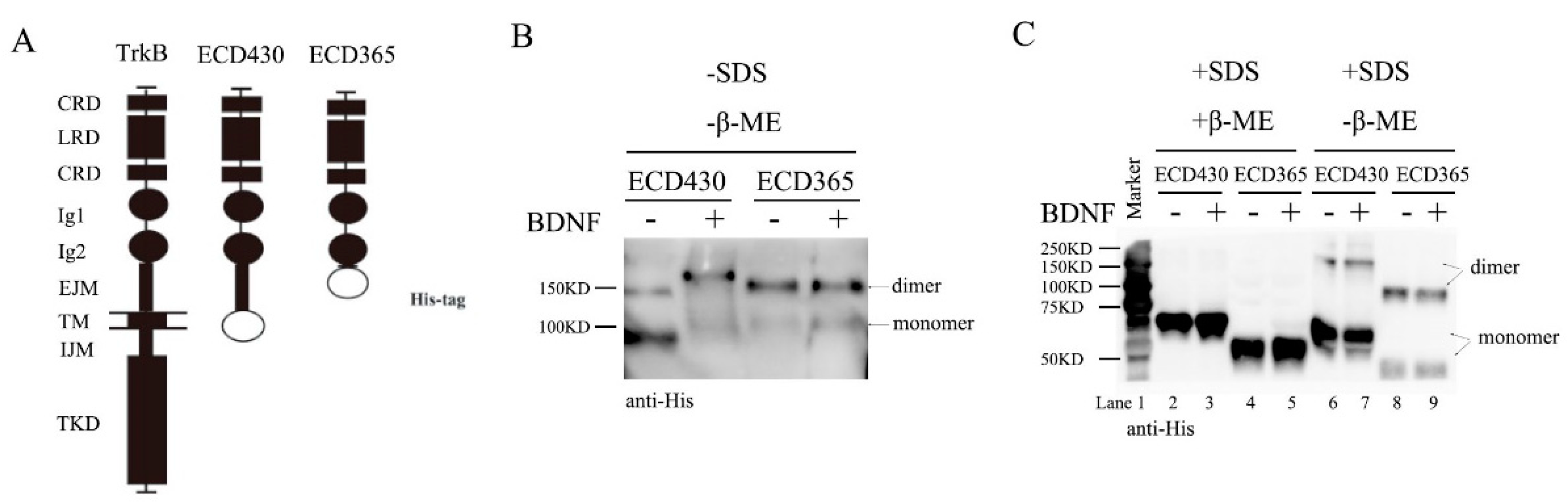
3.4. TrkB ECD Does not Inhibit TrkB Activation
3.5. Binding of both Monomers by a Ligand Is Required for Preformed TrkB Dimer Activation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Vilček, J. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 163, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.J.; Goldenring, J.R.; Asher, V.A.; Modlin, I.M. Effects of epidermal growth factor on signal transduction in rabbit parietal cells. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1990, 258, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circolo, A.; Pierce, G.F.; Katz, Y.; Strunk, R.C. Antiinflammatory effects of polypeptide growth factors. Platelet-derived growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor inhibit the cytokine-induced expression of the alternative complement pathway activator factor B in human fibroblasts. J. Boil. Chem. 1990, 265, 5066–5071. [Google Scholar]
- Massoglia, S.; Gray, A.; Dull, T.J.; Munemitsu, S.; Kun, H.J.; Schlessinger, J.; Ullrich, A. Epidermal growth factor receptor cytoplasmic domain mutations trigger ligand-independent transformation. Mol. Cell. Boil. 1990, 10, 3048–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minichiello, L. TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biarc, J.; Chalkley, R.J.; Burlingame, A.L.; Bradshaw, R.A. Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling--a proteomic perspective. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2011, 51, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriki, T.; Maruyama, H.; Maruyama, I.N. Activation of preformed EGF receptor dimers by ligand-induced rotation of the transmembrane domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 311, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sharma, K.D.; Takahashi, T.; Iwamoto, R.; Mekada, E. Ligand-independent Dimer Formation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Is a Step Separable from Ligand-induced EGFR Signaling. Mol. Boil. Cell 2002, 13, 2547–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, A.H.A.; Walker, F.; Orchard, S.G.; Henderson, C.; Fuchs, D.; Rothacker, J.; Nice, E.C.; Burgess, A.W. Ligand-induced Dimer-Tetramer Transition during the Activation of the Cell Surface Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-A Multidimensional Microscopy Analysis. J. Boil. Chem. 2005, 280, 30392–30399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teramura, Y.; Ichinose, J.; Takagi, H.; Nishida, K.; Yanagida, T.; Sako, Y. Single-molecule analysis of epidermal growth factor binding on the surface of living cells. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Sudhaharan, T.; Koh, R.M.L.; Hwang, L.C.; Ahmed, S.; Maruyama, I.N.; Wohland, T. Investigation of the Dimerization of Proteins from the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Family by Single Wavelength Fluorescence Cross-Correlation Spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saffarian, S.; Li, Y.; Elson, E.L.; Pike, L.J. Oligomerization of the EGF Receptor Investigated by Live Cell Fluorescence Intensity Distribution Analysis. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, R.-H.; Maruyama, I.N. All EGF(ErbB) receptors have preformed homo- and heterodimeric structures in living cells. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bader, A.N.; Hofman, E.G.; Voortman, J.; Henegouwen, P.M.V.B.E.; Gerritsen, H.C. Homo-FRET Imaging Enables Quantification of Protein Cluster Sizes with Subcellular Resolution. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.S.; Ilagan, M.X.G.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Pike, L.J. Luciferase Fragment Complementation Imaging of Conformational Changes in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 7474–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wohland, T.; Ma, X. EGFR activation monitored by SW-FCCS in live cells. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-S.; Leahy, D.J. Structure of the Extracellular Region of HER3 Reveals an Interdomain Tether. Science 2002, 297, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.M.; Berger, M.B.; Mendrola, J.M.; Cho, H.-S.; Leahy, D.J.; Lemmon, M.A. EGF Activates Its Receptor by Removing Interactions that Autoinhibit Ectodomain Dimerization. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyain, S.; Longo, P.A.; Li, S.; Ferguson, K.M.; Leahy, D.J. The extracellular region of ErbB4 adopts a tethered conformation in the absence of ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 15024–15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, K.M. A structure-based view of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor regulation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 37, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, T.P.; McKern, N.M.; Lou, M.; Elleman, T.C.; Adams, T.E.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Zhu, H.J.; Walker, F.; Frenkel, M.J.; Hoyne, P.A.; et al. Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell 2002, 110, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiso, H.; Ishitani, R.; Nureki, O.; Fukai, S.; Yamanaka, M.; Kim, J.; Saito, K.; Shirouzu, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Initiative, R.S.G. Crystal Structure of the Complex of Human Epidermal Growth Factor and Receptor Extracellular Domains. Cell 2002, 110, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Zanca, D.; Oskam, R.; Mitra, G.; Copeland, T.; Barbacid, M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol. Cell. Boil. 1989, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soppet, D.; Escandon, E.; Maragos, J.; Middlemas, D.S.; Raid, S.W.; Blair, J.; Burton, L.E.; Stanton, B.R.; Kaplan, D.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell 1991, 65, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.J.; Nye, S.H.; Hantzopoulos, P.; Macchi, M.J.; Squinto, S.P.; Goldfarb, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D. TrkB mediates BDNF/NT-3-dependent survival and proliferation in fibroblasts lacking the low affinity NGF receptor. Cell 1991, 66, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.; Hempstead, B.; Martin-Zanca, D.; Chao, M.; Parada, L. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science 1991, 252, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, T.; Kothe, M.; Liu, J.; Dupuy, A.; Rak, A.; Berne, P.; Davis, S.; Gladysheva, T.; Valtre, C.; Crenne, J.; et al. The Crystal Structures of TrkA and TrkB Suggest Key Regions for Achieving Selective Inhibition. J. Mol. Boil. 2012, 423, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbacid, M. Structural and Functional Properties of the TRK Family of Neurotrophin Receptors. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1995, 766, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Boil. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, D.R.; Martin-Zanca, D.; Parada, L.F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature 1991, 350, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Tapley, P.; Barbacid, M. Nerve growth factor mediates signal transduction through trk homodimer receptors. Neuron 1992, 9, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, C.; Ilag, L.; Murray-Rust, J.; Persson, H. An extended surface of binding to Trk tyrosine kinase receptors in NGF and BDNF allows the engineering of a multifunctional pan-neurotrophin. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesmann, C.; Ultsch, M.H.; Bass, S.H.; De Vos, A.M. Crystal structure of nerve growth factor in complex with the ligand-binding domain of the TrkA receptor. Nature 1999, 401, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Maruyama, I.N. Nerve growth factor receptor TrkA exists as a preformed, yet inactive, dimer in living cells. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Maruyama, I.N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor receptor TrkB exists as a preformed dimer in living cells. J. Mol. Signal. 2012, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artim, S.C.; Mendrola, J.M.; Lemmon, M.A. Assessing the range of kinase autoinhibition mechanisms in the insulin receptor family. Biochem. J. 2012, 448, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.; You, H.; Chen, Y.; Chu, P.; Hu, M.; Shen, J.; Guo, W.; Xie, C.; Lu, B. MagR Alone Is Insufficient to Confer Cellular Calcium Responses to Magnetic Stimulation. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, J.C.; Condé, B.; Hempstead, B.L.; Chao, M.V.; Martin-Zanca, D.; Pérez, P. TrkA Immunoglobulin-Like Ligand Binding Domains Inhibit Spontaneous Activation of the Receptor. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2000, 20, 5908–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, I.N. Mechanisms of Activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Monomers or Dimers. Cells 2014, 3, 304–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahavi, E.E.; Steinberg, N.; Altman, T.; Chein, M.; Joshi, Y.; Gradus-Pery, T.; Perlson, E. The receptor tyrosine kinase TrkB signals without dimerization at the plasma membrane. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaao4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Hristova, K. Dimerization of the Trk receptors in the plasma membrane: effects of their cognate ligands. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3669–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewitt, J.; Ochoa, V.; Urschitz, J.; Elston, M.; Moisyadi, S.; Nishi, R. Constitutively active TrkB confers an aggressive transformed phenotype to a neural crest-derived cell line. Oncogene 2014, 33, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasia, A.; Barker, P.A.; Chao, M.V.; Hempstead, B.L. Detection of p75NTR Trimers: Implications for Receptor Stoichiometry and Activation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11911–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, M.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Kenchappa, R.S.; Simi, A.; Karaca, E.; Reversi, A.; Choi, S.; Bothwell, M.; Mingarro, I.; Friedman, W.J.; et al. Activation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor through conformational rearrangement of disulphide-linked receptor dimers. Neuron 2009, 62, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haniu, M.; Talvenheimo, J.; Le, J.; Katta, V.; Welcher, A.; Rohde, M. Extracellular Domain of Neurotrophin Receptor trkB: Disulfide Structure, N-Glycosylation Sites, and Ligand Binding. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 322, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Sun, D.; Shao, J.; Chen, Y.; Pang, K.; Guo, W.; Lu, B. Extracellular Juxtamembrane Motif Critical for TrkB Preformed Dimer and Activation. Cells 2019, 8, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080932
Shen J, Sun D, Shao J, Chen Y, Pang K, Guo W, Lu B. Extracellular Juxtamembrane Motif Critical for TrkB Preformed Dimer and Activation. Cells. 2019; 8(8):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080932
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jianying, Dang Sun, Jingyu Shao, Yanbo Chen, Keliang Pang, Wei Guo, and Bai Lu. 2019. "Extracellular Juxtamembrane Motif Critical for TrkB Preformed Dimer and Activation" Cells 8, no. 8: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080932
APA StyleShen, J., Sun, D., Shao, J., Chen, Y., Pang, K., Guo, W., & Lu, B. (2019). Extracellular Juxtamembrane Motif Critical for TrkB Preformed Dimer and Activation. Cells, 8(8), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080932




