Circulating Tumor Cell PD-L1 Expression as Biomarker for Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in NSCLC
Abstract
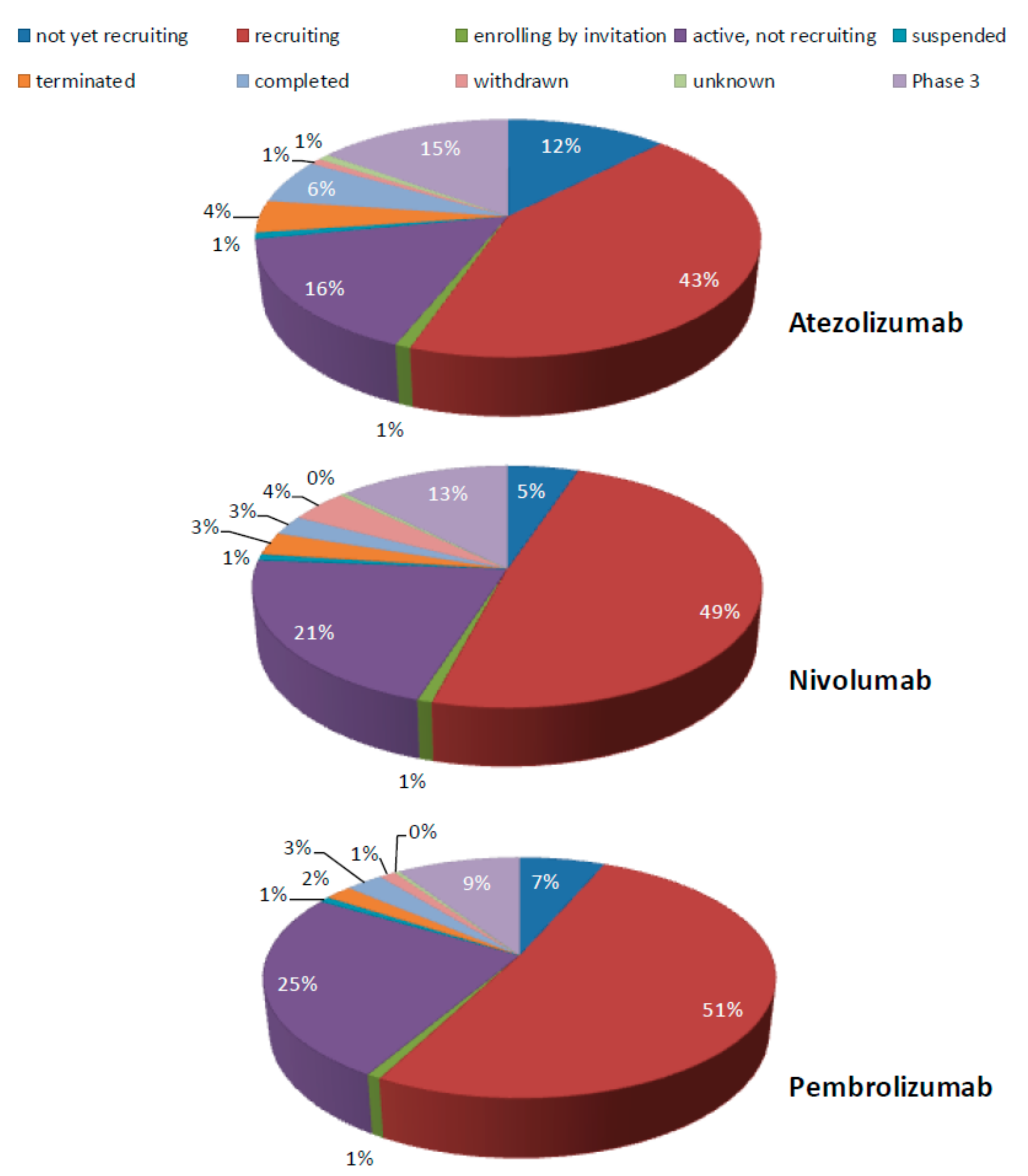
:1. Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): State of the Art
2. Clinical Significance of PD-L1-Positive CTCs in NSCLC
3. The Need for (Pre-)Analytical Standardizations
3.1. The Need for Clinically Applicable CTC Enrichment and Detection Approaches
3.2. The Need for Harmonized Immunostaining Protocols
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crino, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, pd-l1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (keynote-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (oak): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, H.; Law, A.; Hong, S.; Middleton, K. Identifying regulatory posttranslational modifications of pd-l1: A focus on monoubiquitinaton. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the pd1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Reviews. Immunol. 2018, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Gilligan, B.M.; Yuan, J.; Li, T. Current status and perspectives in translational biomarker research for pd-1/pd-l1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First anti-pd-l1 drug approved for nsclc. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, OF1. [CrossRef]
- Sul, J.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Jiang, X.; He, K.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. Fda approval summary: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors express programmed death-ligand 1. Oncologist 2016, 21, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Bylicki, O.; Barazzutti, H.; Paleiron, N.; Margery, J.; Assie, J.B.; Chouaid, C. First-line treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (nsclc) with immune checkpoint inhibitors. BioDrugs Clin. Immunother. Biopharm. Gene Ther. 2019, 33, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, J.; Jabbour, S.K.; Aisner, J. Current state of immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, R.; Lal, R.; Lewanski, C.; Nicolson, M.C.; Ottensmeier, C.H.; Popat, S.; Hodgson, M.; Postmus, P.E. Patient selection for anti-pd-1/pd-l1 therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Implications for clinical practice. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, H.; Li, C.; Fang, J.Y.; Xu, J. Regulation of pd-l1: Emerging routes for targeting tumor immune evasion. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanos, R.; Thierry, A.R. Clinical relevance of liquid biopsy for cancer screening. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, S105–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, B.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Muller, V.; Janni, W.; Fehm, T.; Wallwiener, D.; Pantel, K.; Tewes, M.; Group, D.S. Comparison of the her2, estrogen and progesterone receptor expression profile of primary tumor, metastases and circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Snyder, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Makarov, V.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, W.; Yuan, J.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to pd-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 2015, 348, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, N.; Delaunay, M.; Lusque, A.; Boubekeur, N.; Rouquette, I.; Clermont, E.; Mourlanette, J.; Gouin, S.; Dormoy, I.; Favre, G.; et al. Pd-l1 expression in circulating tumor cells of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer 2018, 120, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasinghe, A.; Kapeleris, J.; Kimberley, R.; Mattarollo, S.R.; Thompson, E.W.; Thiery, J.P.; Kenny, L.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C. The prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in head and neck and non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5910–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, N.; Li, D.; Wang, R.; Dang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Dynamic change of pd-l1 expression on circulating tumor cells in advanced solid tumor patients undergoing pd-1 blockade therapy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1438111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, M.; Jacot, W.; Pantel, K.; Bartkowiak, K.; Topart, D.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Rossille, D.; Maudelonde, T.; Fest, T.; Alix-Panabieres, C. Frequent expression of pd-l1 on circulating breast cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schehr, J.L.; Schultz, Z.D.; Warrick, J.W.; Guckenberger, D.J.; Pezzi, H.M.; Sperger, J.M.; Heninger, E.; Saeed, A.; Leal, T.; Mattox, K.; et al. High specificity in circulating tumor cell identification is required for accurate evaluation of programmed death-ligand 1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Bai, T.; Takata, K.; Yokobori, T.; Ohnaga, T.; Hisada, T.; Maeno, T.; Bao, P.; Yoshida, T.; Kumakura, Y.; et al. High expression of carcinoembryonic antigen and telomerase reverse transcriptase in circulating tumor cells is associated with poor clinical response to the immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallergi, G.; Vetsika, E.K.; Aggouraki, D.; Lagoudaki, E.; Koutsopoulos, A.; Koinis, F.; Katsarlinos, P.; Trypaki, M.; Messaritakis, I.; Stournaras, C.; et al. Evaluation of pd-l1/pd-1 on circulating tumor cells in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758834017750121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.L.; Adams, D.K.; He, J.; Kalhor, N.; Zhang, M.; Xu, T.; Gao, H.; Reuben, J.M.; Qiao, Y.; Komaki, R.; et al. Sequential tracking of pd-l1 expression and rad50 induction in circulating tumor and stromal cells of lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5948–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, T.H.; Fouladdel, S.; Zhang, Z.; Soni, P.; Qin, A.; Zhao, L.; Azizi, E.; Lawrence, T.S.; Ramnath, N.; et al. Pd-l1 expression in circulating tumor cells increases during radio(chemo)therapy and indicates poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilie, M.; Szafer-Glusman, E.; Hofman, V.; Chamorey, E.; Lalvee, S.; Selva, E.; Leroy, S.; Marquette, C.H.; Kowanetz, M.; Hedge, P.; et al. Detection of pd-l1 in circulating tumor cells and white blood cells from patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janning, M.; Kobus, F.; Babayan, A.; Wikman, H.; Velthaus, J.L.; Bergmann, S.; Schatz, S.; Falk, M.; Berger, L.A.; Bottcher, L.M.; et al. Determination of pd-l1 expression in circulating tumor cells of nsclc patients and correlation with response to pd-1/pd-l1 inhibitors. Cancers 2019, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolazzo, C.; Raimondi, C.; Mancini, M.; Caponnetto, S.; Gradilone, A.; Gandini, O.; Mastromartino, M.; Del Bene, G.; Prete, A.; Longo, F.; et al. Monitoring pd-l1 positive circulating tumor cells in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with the pd-1 inhibitor nivolumab. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, A.; Loges, S.; Pantel, K.; Wikman, H. Detection of circulating tumor cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, C.; Carpino, G.; Nicolazzo, C.; Gradilone, A.; Gianni, W.; Gelibter, A.; Gaudio, E.; Cortesi, E.; Gazzaniga, P. Pd-l1 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in circulating tumor cells from non-small cell lung cancer patients: A molecular shield to evade immune system? Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1315488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, M.; Wong, J.; Che, J.; Matsumoto, M.; Grogan, T.; Elashoff, D.; Garon, E.B.; Goldman, J.W.; Sollier Christen, E.; Di Carlo, D.; et al. Evaluation of pd-l1 expression on vortex-isolated circulating tumor cells in metastatic lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Soria, J.C.; Kowanetz, M.; Fine, G.D.; Hamid, O.; Gordon, M.S.; Sosman, J.A.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Gettinger, S.N.; et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-pd-l1 antibody mpdl3280a in cancer patients. Nature 2014, 515, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Koh, J.; Kim, S.; Go, H.; Jeon, Y.K.; Chung, D.H. Clinicopathological analysis of pd-l1 and pd-l2 expression in pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison with tumor-infiltrating t cells and the status of oncogenic drivers. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Rozeboom, L.; Rivard, C.J.; Ellison, K.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Yu, H.; Zhou, C.; Hirsch, F.R. Pd-1, pd-l1 protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer and their relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, M.H.D.; Bender, S.; Krahn, T.; Schlange, T. Ctdna and ctcs in liquid biopsy-current status and where we need to progress. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolz, D.; Hauch, S.; Schlumpberger, M.; Guenther, K.; Voss, T.; Sprenger-Haussels, M.; Oelmuller, U. Liquid biopsy preservation solutions for standardized pre-analytical workflows-venous whole blood and plasma. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2018, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farace, F.; Massard, C.; Vimond, N.; Drusch, F.; Jacques, N.; Billiot, F.; Laplanche, A.; Chauchereau, A.; Lacroix, L.; Planchard, D.; et al. A direct comparison of cellsearch and iset for circulating tumour-cell detection in patients with metastatic carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Hou, J.M.; Sloane, R.; Lancashire, L.; Priest, L.; Nonaka, D.; Ward, T.H.; Backen, A.; Clack, G.; Hughes, A.; et al. Analysis of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using epithelial marker-dependent and -independent approaches. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2012, 7, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Kenmotsu, H.; Koh, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Naito, T.; Takahashi, T.; Murakami, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuya, A.; et al. Size-based isolation of circulating tumor cells in lung cancer patients using a microcavity array system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, E.R.; Villalobos, P.; Mino, B.; Rodriguez-Canales, J. Comparison of different antibody clones for immunohistochemistry detection of programmed cell death ligand 1 (pd-l1) on non-small cell lung carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2018, 26, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliffe, M.J.; Sharpe, A.; Midha, A.; Barker, C.; Scott, M.; Scorer, P.; Al-Masri, H.; Rebelatto, M.C.; Walker, J. Agreement between programmed cell death ligand-1 diagnostic assays across multiple protein expression cutoffs in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3585–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheel, A.H.; Baenfer, G.; Baretton, G.; Dietel, M.; Diezko, R.; Henkel, T.; Heukamp, L.C.; Jasani, B.; Johrens, K.; Kirchner, T.; et al. Interlaboratory concordance of pd-l1 immunohistochemistry for non-small-cell lung cancer. Histopathology 2018, 72, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.; Le Stang, N.; Rouquette, I.; Cazes, A.; Badoual, C.; Pinot-Roussel, H.; Tixier, L.; Danel, C.; Damiola, F.; Damotte, D.; et al. Multicenter harmonization study for pd-l1 ihc testing in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimm, D.L.; Han, G.; Taube, J.M.; Yi, E.S.; Bridge, J.A.; Flieder, D.B.; Homer, R.; West, W.W.; Wu, H.; Roden, A.C.; et al. A prospective, multi-institutional, pathologist-based assessment of 4 immunohistochemistry assays for pd-l1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Patients | Blood Tube | CTC-Enrichment System | Antibody Clone | Therapy | Clinical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schehr et al. [23] | 19 | EDTA | Immunomagnetic depletion, Dynabeads-based | MIH1 (BD) | 1st line TX: Radio-/ Chemotherapy, TKIs Current: ICIs | - |
| Bao et al. [24] | 15 | EDTA | Size-based (in-house produced chip) | * | 1st line TX: Chemo Current: Nivolumab | - |
| Kallergi et al. [25] | 30 | EDTA | Size-based (ISET) | B7-H1 (NB) | 1st line TX: None Current: Chemo-naïve | After 3 cycles of chemo, ~19% increase PD-L1+ CTCs |
| Adams et al. [26] | 41 | CellSave | Size-based (CellSieve Microfiltration Assay) | B7-H1 (R&D) | 1st line TX: Chemo Current: Radiotherapy | Slightly better outcome in patients with high PD-L1 expression |
| Wang et al. [27] | 13 | EDTA | Microfluidic graphene oxide (GO) Chip | 29E.2A3 (BL) | 1st line TX: None Current: Radio-/ Chemotherapy | PD-L1+ patients had a shorter PFS compared to PD-L1− patients |
| Ilié et al. [28] | 106 | - | Size-based (ISET) | SP142 (VT) | 1st line TX: None Current: Chemo-naïve (93%), neoadjuvant chemo (7%) | Slightly better outcome in patients with PD-L1+ CTCs |
| Janning et al. [29] | 89 | EDTA and/or Cell Save | EpCAM-based (CellSearch®), size-based (ParsortixTM) | D84TX (CS) | Current: Radio-/ chemotherapy, surgery, TKIs, ICIs | Increase in PD-L1+ CTCs upon disease progression; no change or decrease in responding patients |
| Nicolazzo et al. [30] | 24 | CellSave | EpCAM-based (CellSearch) | B7-H1 (R&D) | 1st line TX: na Current: Nivolumab | Poor clinical outcome |
| Guibert et al. [19] | 96 pre-, 24 post- therapy | - | Size-based (ISET) | D8TX4 (CS) | 1st line TX: Chemo Current: Nivolumab | More non-responders to Nivolumab if ≥1% PD-L1+ CTCs |
| Kulasinghe et al. [20] | 33 | EDTA or Streck | Size-based (ClearCell FX) | n/a (Abcam) | 1st line TX: Radio-/ Chemotherapy Current: Nivolumab | None |
| Dhar et al. [33] | 22 | EDTA | Size-based (Vortex HT chip) | #4059 (PS),29E.2A3 (BL), MIH1 (BD) | 1st line TX: na Current: ICIs | Slightly better outcome for patients with >50% PD-L1+ CTCs |
| Study | Antibody Clone | Company | PD-L1 + Tumor Cell Cut-Off | Patients | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parra et al. [42] | E1L3N, E1J2J | Cell Signaling | ≥1% | 185 + (cell lines) | E1L3N, E1J2J, SP142, 28-8, 22C3, 5H11 and SP263: comparable staining patterns on membranes; SP263: higher IHC score |
| 22C3, 28-8 | Dako | ||||
| SP263, SP142 | Ventana | ||||
| 5H11 | Not commercialized | ||||
| Ratcliffe et al. [43] | 22C3, 28-8 | Dako | ≥1%, ≥10%, ≥25%, ≥50% | 493 | All assays show concordant staining patterns |
| SP263 | Ventana | ||||
| Scheel et al. [44] | E1L3N | Cell Signaling | ≥1%, ≥50% | 21 | 22C3, 28-8 and SP263: concordant staining patterns; SP142 as outlier |
| 22C3, 28-8 | Dako | ||||
| SP263, SP142 | Ventana | ||||
| Adam et al. [45] | E1L3N | Cell Signaling | ≥1%, ≥5%, ≥25%, ≥50% | 41 | 28-8, 22C3, SP263, E1L3N: highly concordant; SP142 as outlier |
| 22C3, 28-8 | Dako | ||||
| SP263, SP142 | Ventana | ||||
| Rimm et al. [46] | E1L3N | Cell Signaling | ≥1%, ≥5%, ≥50% | 90 | SP142: significant lower PD-L1 IHC score; 22C3: significant reduction in PD-L1 staining; 28-8 and E1L3N concordant |
| 22C3, 28-8 | Dako | ||||
| SP142 | Ventana |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kloten, V.; Lampignano, R.; Krahn, T.; Schlange, T. Circulating Tumor Cell PD-L1 Expression as Biomarker for Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in NSCLC. Cells 2019, 8, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080809
Kloten V, Lampignano R, Krahn T, Schlange T. Circulating Tumor Cell PD-L1 Expression as Biomarker for Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in NSCLC. Cells. 2019; 8(8):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080809
Chicago/Turabian StyleKloten, Vera, Rita Lampignano, Thomas Krahn, and Thomas Schlange. 2019. "Circulating Tumor Cell PD-L1 Expression as Biomarker for Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in NSCLC" Cells 8, no. 8: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080809
APA StyleKloten, V., Lampignano, R., Krahn, T., & Schlange, T. (2019). Circulating Tumor Cell PD-L1 Expression as Biomarker for Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in NSCLC. Cells, 8(8), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080809




