Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Alantolactone through the Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Cell Coculture
2.3. RNA Extraction and QPCR
- TNF-α F:5′-CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC-3′ and R: 5′-CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG-3′;
- IL-1β F: 5′-GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT-3′ and R: 5′-ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT-3′;
- IL-6 F: 5′-TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC-3′ and R: 5′-TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC-3′;
- iNOS F: 5′-GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA-3′ and R: 5′-GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC-3′;
- COX-2 F: 5′-TGAGCAACTATTCCAAACCAGC-3′ and R: 5′-GCACGTAGTCTTCGATCACTATC-3′;
- β-actin F: 5′-GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG-3′ and R: 5′-CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT-3′
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Immunofluorescent Staining
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Proinflammatory Cytokines, NO, and PGE2 Evaluation
2.10. Animal Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
2.11. Effect on MCAO/R Rat Model
2.12. Histopathological Study
2.13. Proinflammatory Cytokine Evaluation of the MCAO/R Rat Model
2.14. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Ala Suppressed the Proliferation of LPS-Activated BV2 Cells
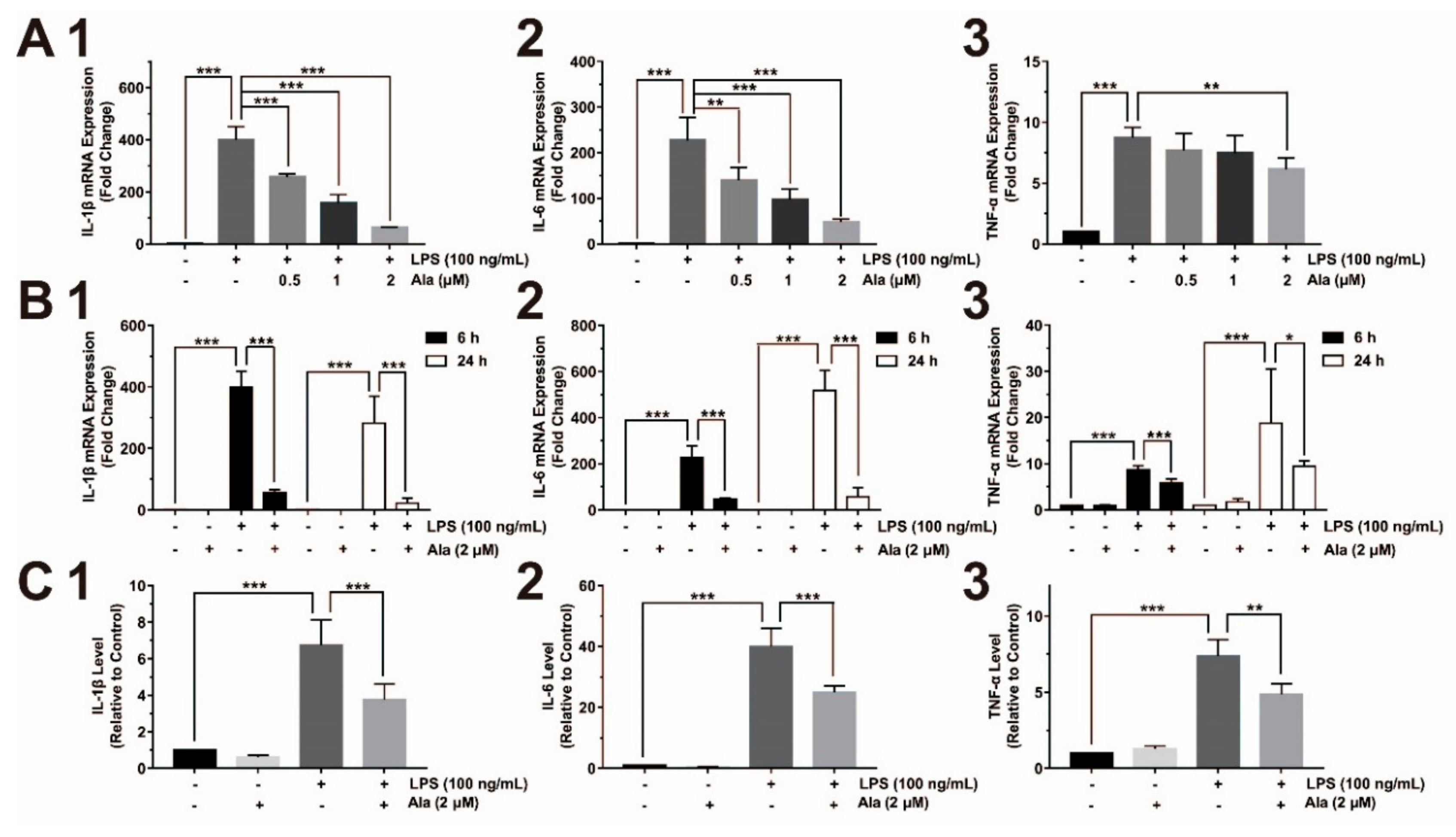
3.2. Ala Attenuated Proinflammatory Cytokine Release from LPS-Activated BV2 Cells
3.3. Effect on COX-2/PGE2 and iNOS/NO Expression
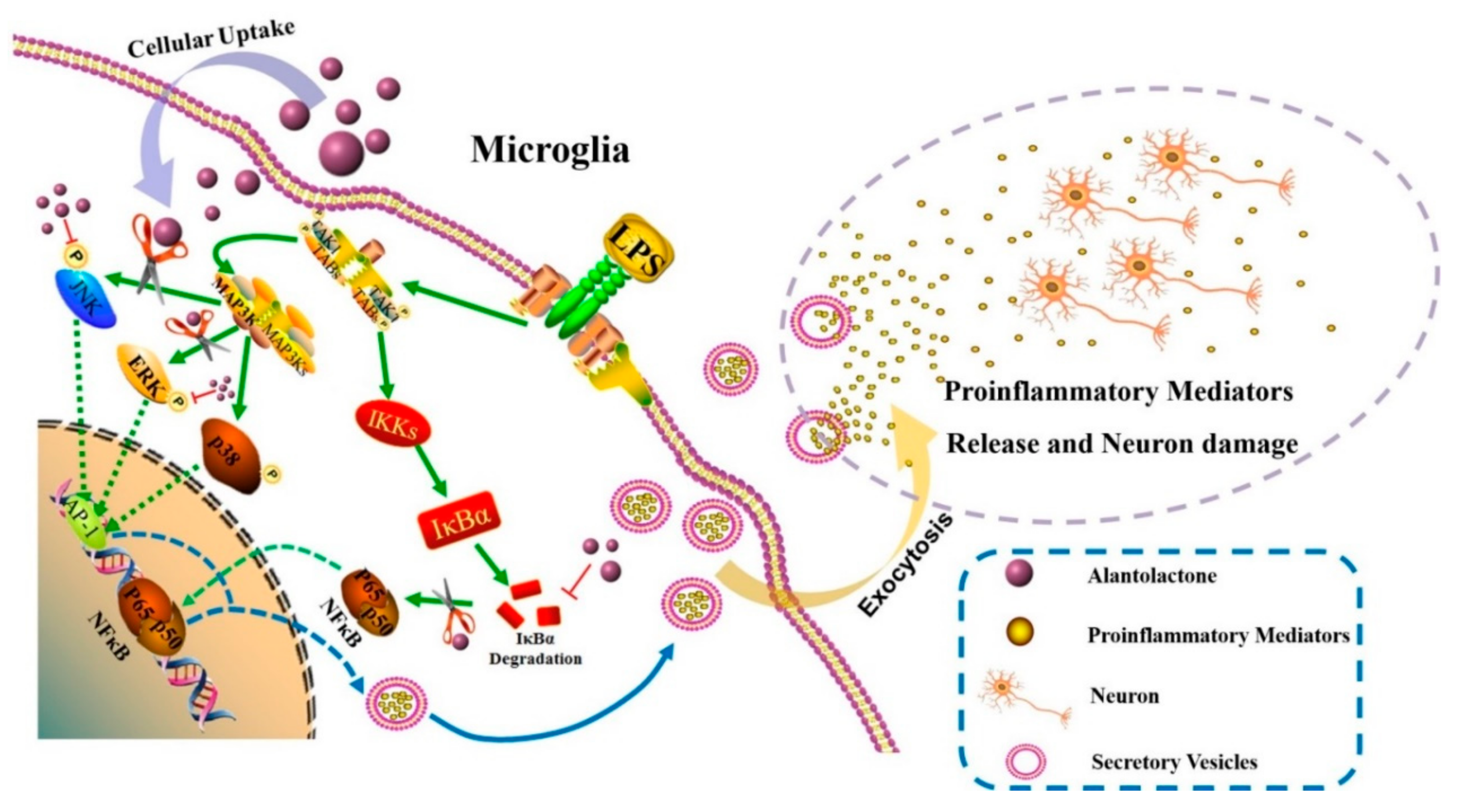
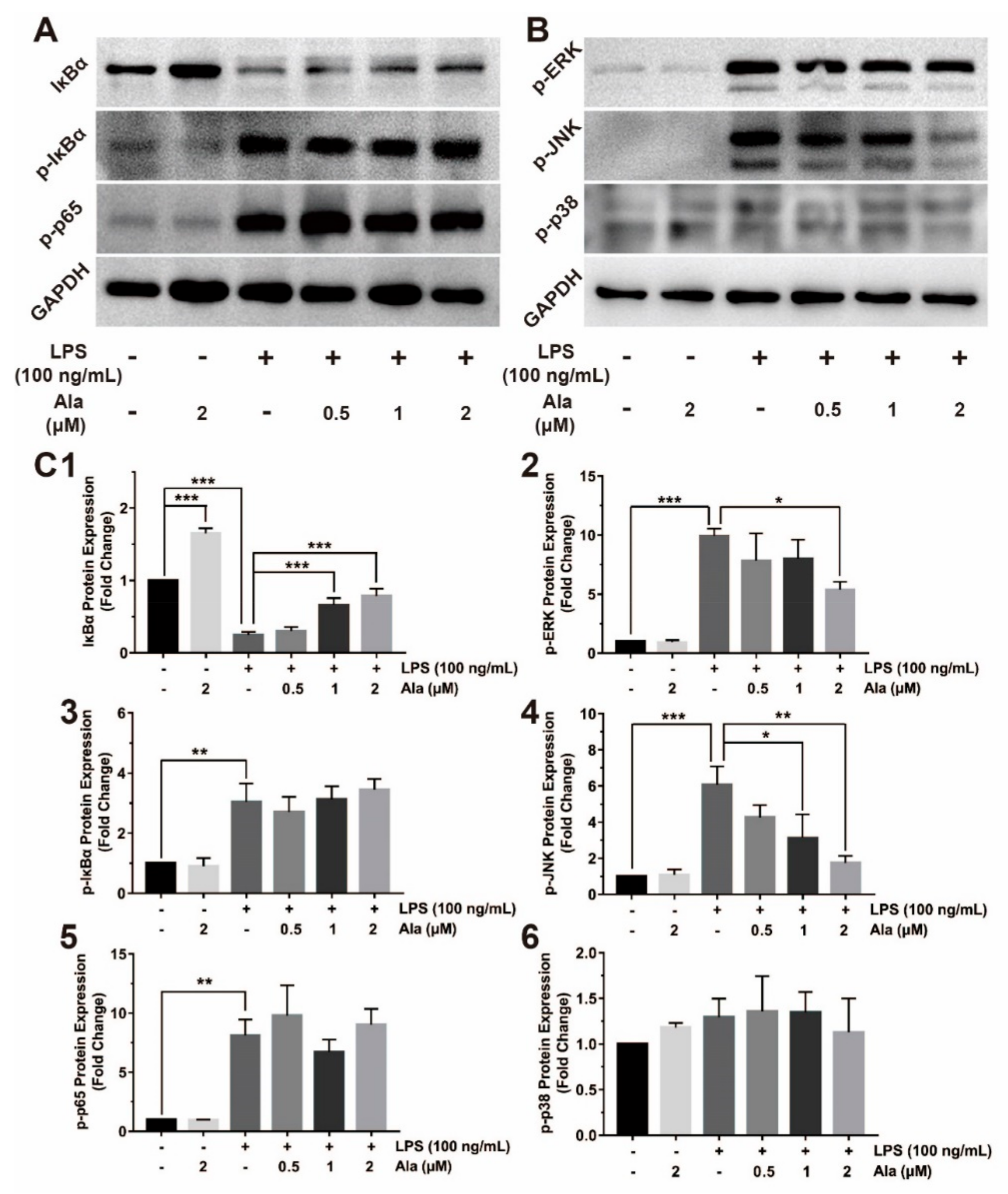
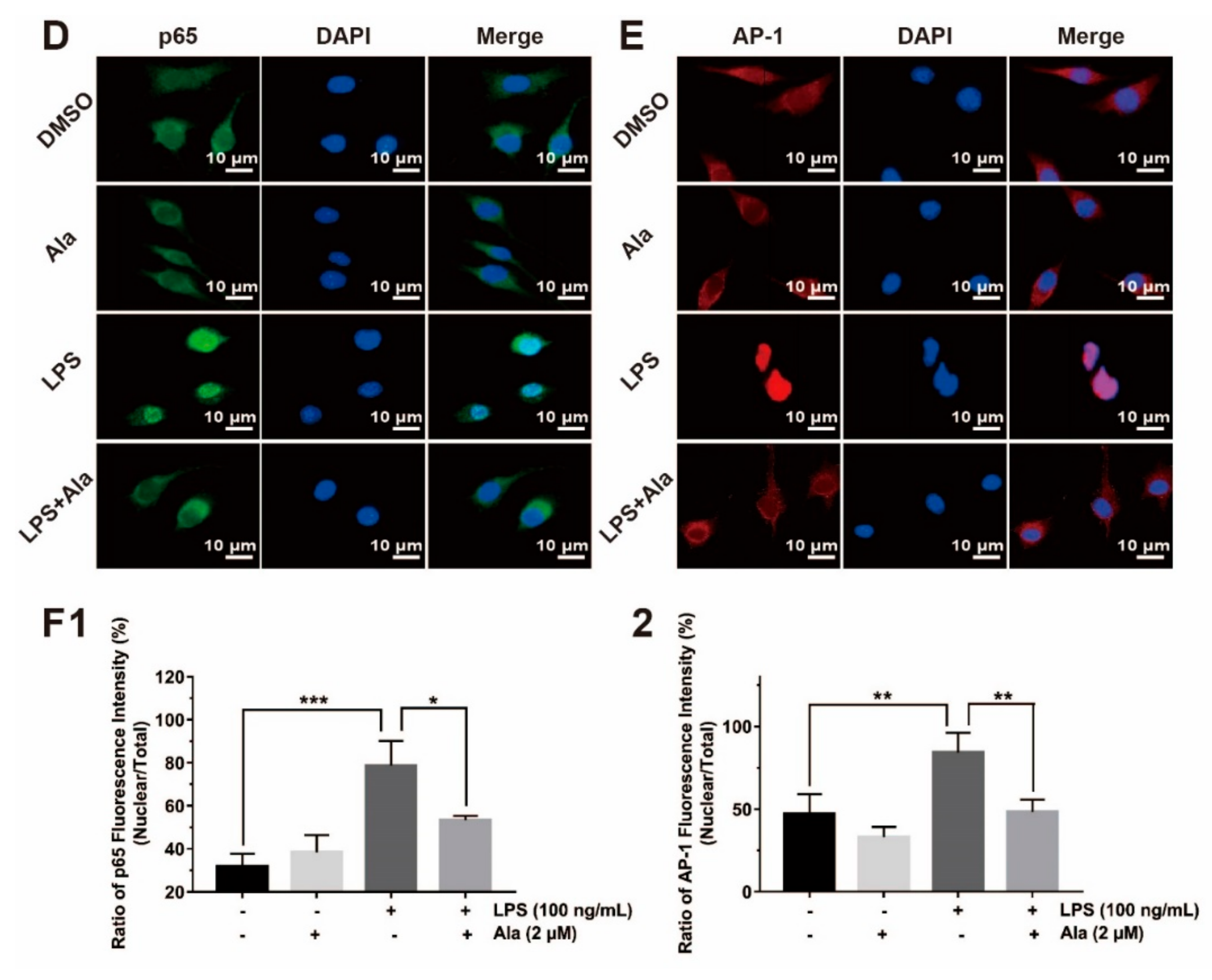
3.4. Effect on NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways
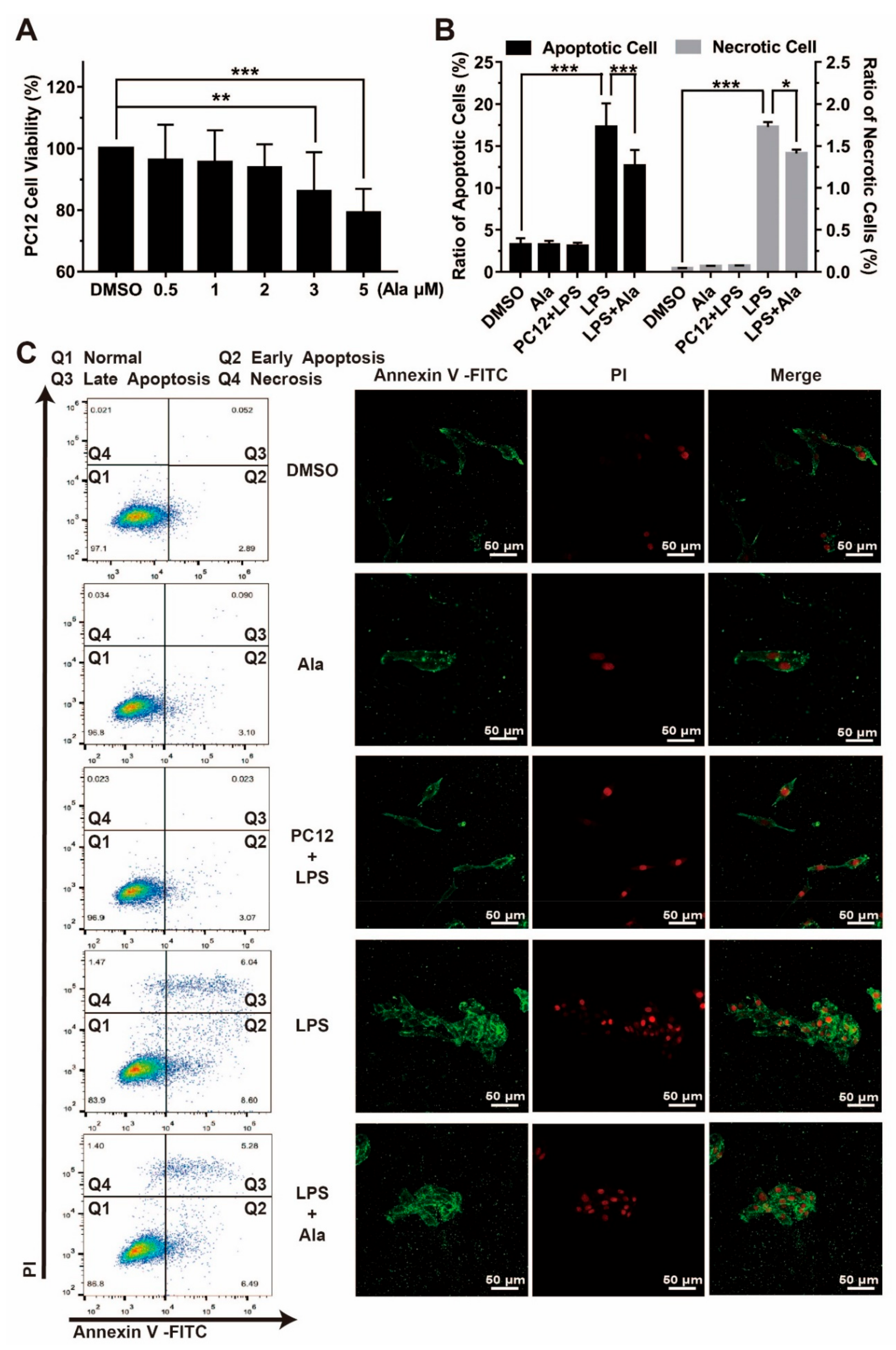
3.5. Effect on Cell Viability in Coculture System of BV2 Cells and PC12 Cells
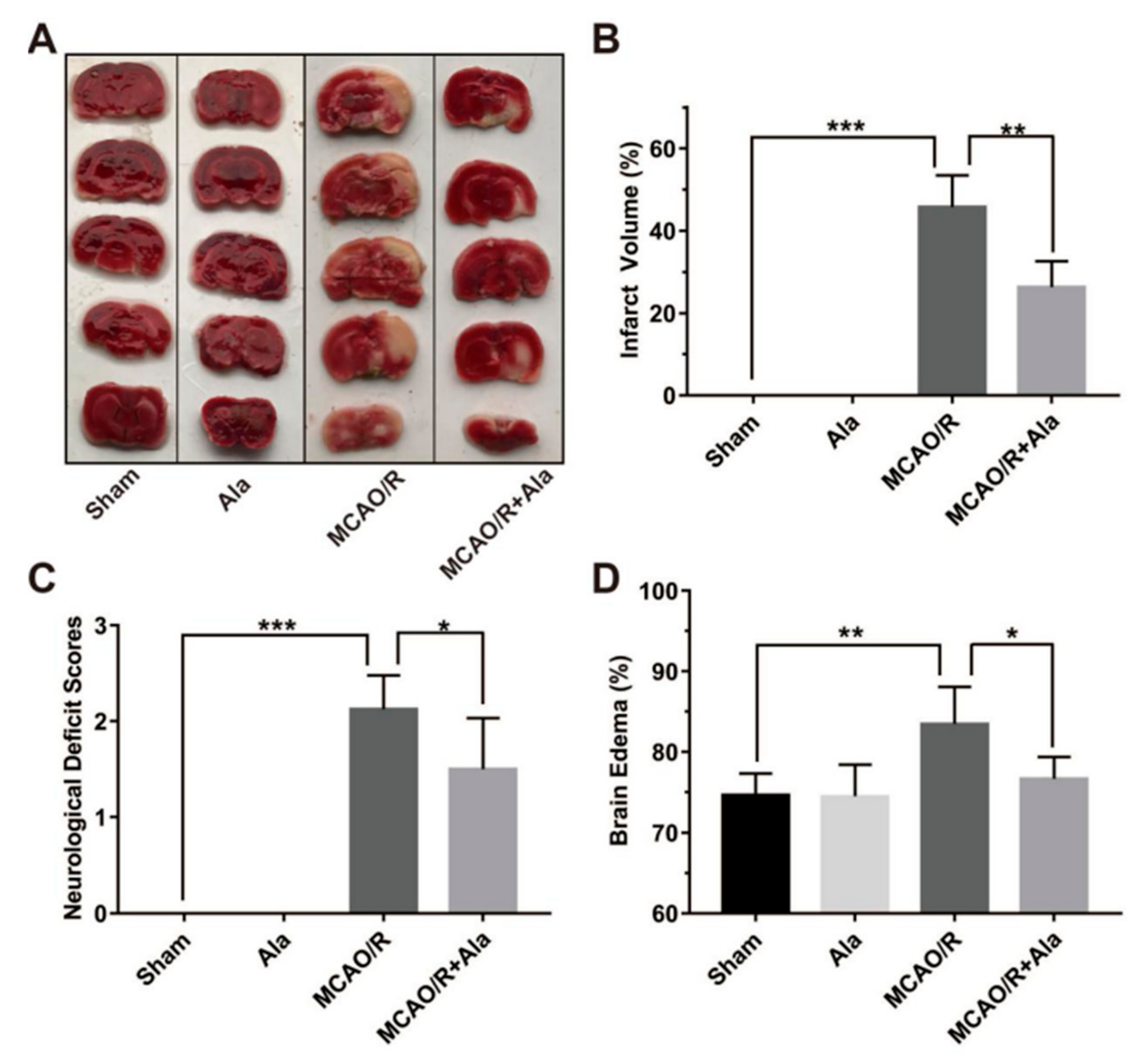
3.6. Ala Alleviated Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in the MCAO/R Rat Model
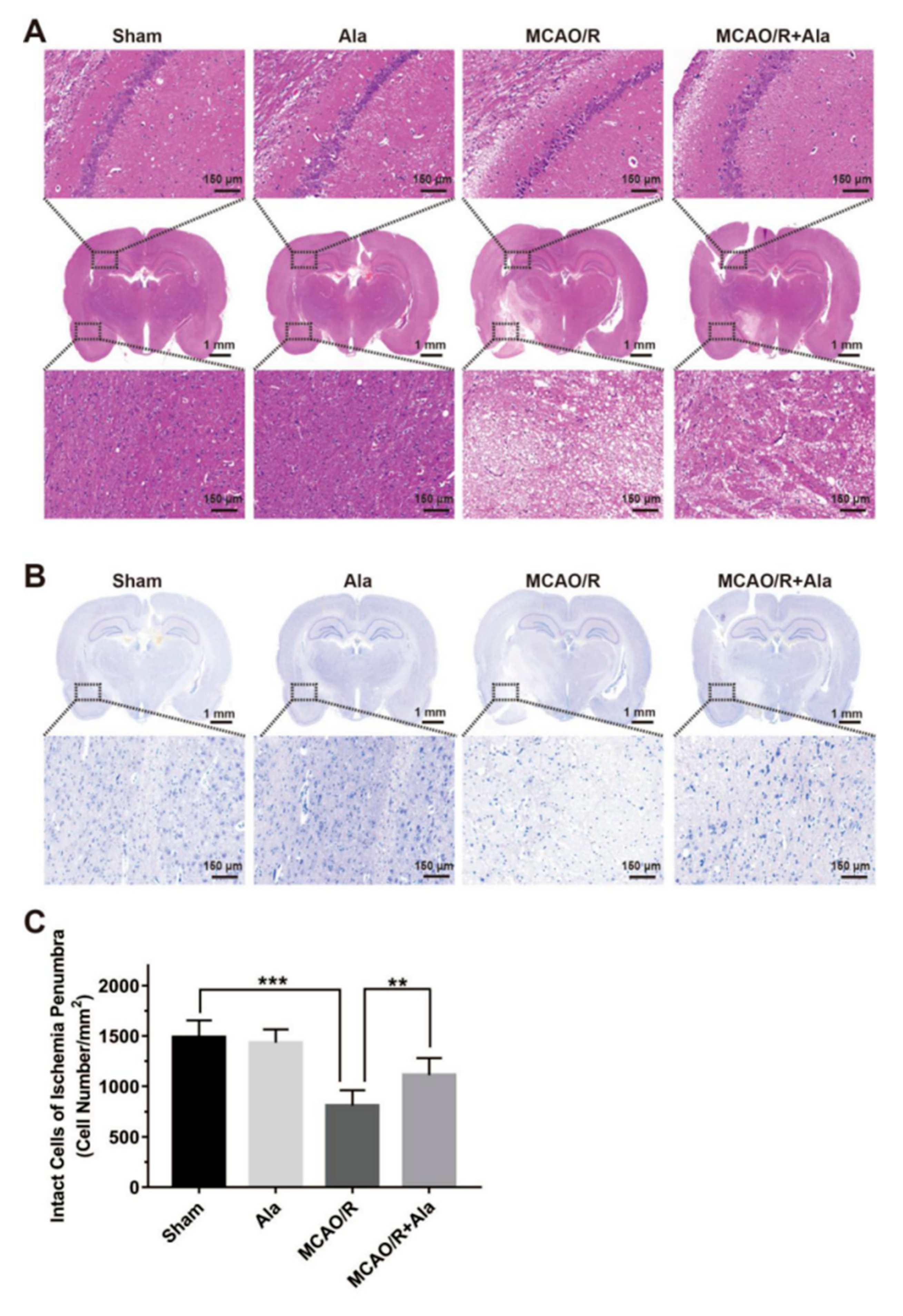
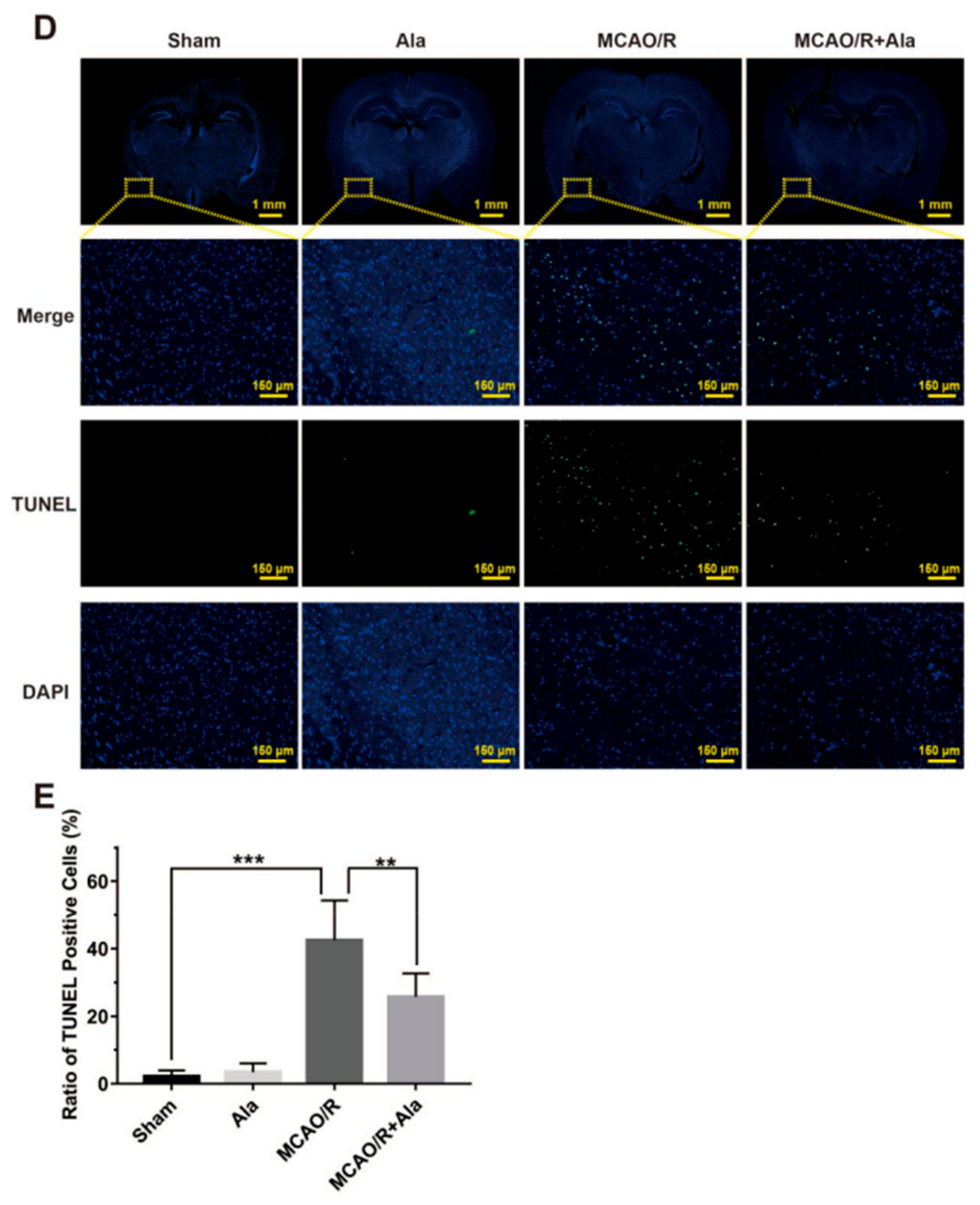
3.7. HE Staining, TUNEL Staining, and Nissl Staining
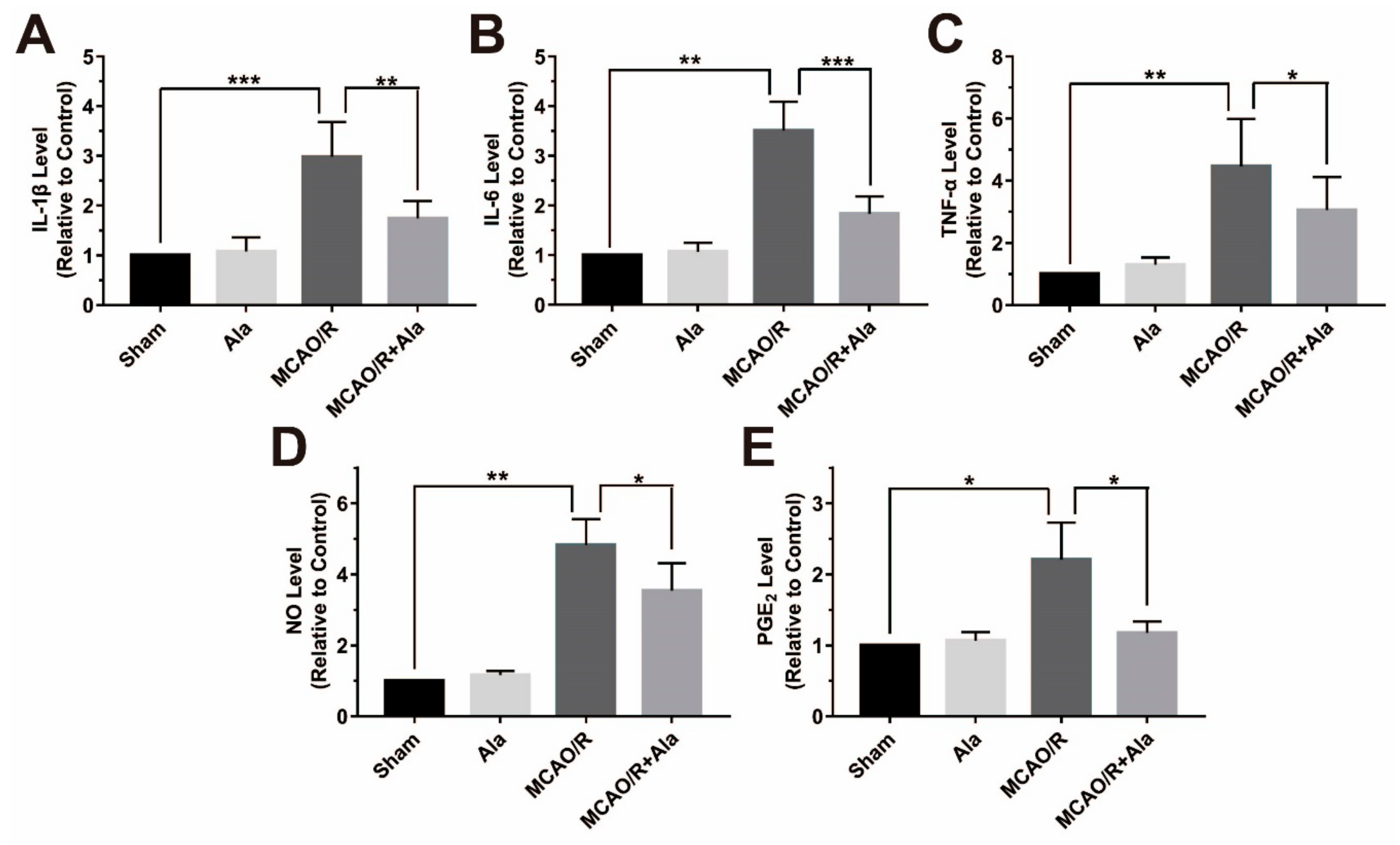
3.8. Proinflammatory Factors in the MCAO/R Rat Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Qin, M.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Ren, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, C.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; et al. A Bioinspired Platform for Effective Delivery of Protein Therapeutics to the Central Nervous System. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1807557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordão, M.J.C.; Sankowski, R.; Brendecke, S.M.; Sugar Locatelli, G.; Tai, Y.-H.; Tay, T.L.; Schramm, E.; Armbruster, S.; Hagemeyer, N.; Groß, O. Single-cell profiling identifies myeloid cell subsets with distinct fates during neuroinflammation. Science 2019, 363, eaat7554. [Google Scholar]
- Arranz, A.M.; De Strooper, B. The role of astroglia in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Suk, K. Emerging roles of protein kinases in microglia-mediated neuroinflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.Z.H.; Kadir, H.A.; Lee, C.L.; Goh, B.H. Neuroprotective properties of Loranthus parasiticus aqueous fraction against oxidative stress-induced damage in NG108-15 cells. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 66, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Tan, L.T.H.; Andy, S.N.; Kamarudin, M.N.A.; Goh, B.H.; Kadir, H.A. Anti-neuroinflammatory Activity of Elephantopus scaber L. via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Inhibition of p38 MAPK Pathway in LPS-Induced Microglia BV-2 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malko, P.; Mortadza, S.A.S.; McWilliam, J.; Jiang, L.-H. TRPM2 Channel in Microglia as a New Player in Neuroinflammation Associated with a Spectrum of Central Nervous System Pathologies. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deczkowska, A.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Weiner, A.; Colonna, M.; Schwartz, M.; Amit, I. Disease-Associated Microglia: A Universal Immune Sensor of Neurodegeneration. Cell 2018, 173, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jin, J.; Chang, M.; Chang, J.-H.; Hu, H.; Zhou, X.; Brittain, G.C.; Stansberg, C.; Torkildsen, Ø.; Wang, X.; et al. Peli1 promotes microglia-mediated CNS inflammation by regulating Traf3 degradation. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.J.; Xu, Z.; Parthasarathy, U.; Drashansky, T.T.; Helm, E.Y.; Zuniga, A.N.; Lorentsen, K.J.; Mansouri, S.; Cho, J.Y.; Edelmann, M.J.; et al. Hectd3 promotes pathogenic Th17 lineage through Stat3 activation and Malt1 signaling in neuroinflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, B.H.; Lambertsen, K.L.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Babcock, A.A.; Von Linstow, C.U.; Meldgaard, M.; Kristensen, B.W.; Deierborg, T.; Finsen, B. Cell therapy centered on IL-1Ra is neuroprotective in experimental stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Das, H. KLF2 in Regulation of NF-κB-Mediated Immune Cell Function and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-D.; Wang, F.; Dai, F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lin, D.; Zhou, B. Development and mechanism investigation of a new piperlongumine derivative as a potent anti-inflammatory agent. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 95, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mei, W.; Chen, J.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, G.; Fan, J. Gamma-secretase inhibitor suppressed Notch1 intracellular domain combination with p65 and resulted in the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway induced by IL-1β and TNF-alpha in nucleus pulposus cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 20, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Lu, J.; Joseph, M.; Aggarwal, R.; Kanji, S.; McMichael, B.K.; Lee, B.S.; Agarwal, S.; Ray-Chaudhury, A.; Iwenofu, O.H.; et al. Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) regulates monocyte differentiation and functions in mBSA and IL-1beta-induced arthritis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Pan, L.; Wu, W.; Yang, D.; Qin, M.; Jia, W.; Xiao, C.; Long, F.; Ge, J.; et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates histone demethylase JMJD3-mediated inflammatory response in LPS-stimulated macrophages and in a mouse model of LPS-induced septic shock. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.-Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H.-F. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2015, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Baig, M.S. NOS1 mediates AP1 nuclear translocation and inflammatory response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Khan, M.; Ali, M.; Li, J.; Li, X. Targeting Apoptosis Pathways in Cancer with Alantolactone and Isoalantolactone. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lan, Y.-L.; Xing, J.-S.; Lan, X.-Q.; Wang, L.-T.; Zhang, B. Alantolactone plays neuroprotective roles in traumatic brain injury in rats via anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptosis pathways. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 368–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.S.; Jin, S.E.; Kim, O.S.; Shin, H.K.; Jeong, S.J. Alantolactone from Saussurea lappa Exerts Antiinflammatory Effects by Inhibiting Chemokine Production and STAT1 Phosphorylation in TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-induced in HaCaT cells. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Cao, X. Alantolactone induces apoptosis and suppresses migration in MCF7 human breast cancer cells via the p38 MAPK, NFκB and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Cheng, W.; Tian, X.; Huo, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Feng, L.; Xing, J.; et al. Alantolactone, a natural sesquiterpene lactone, has potent antitumor activity against glioblastoma by targeting IKKβ kinase activity and interrupting NF-κB/COX-2-mediated signaling cascades. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res 2017, 36, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, F.; Gu, H.; Jiang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhan, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Z. Mxi1-0 regulates the growth of human umbilical vein endothelial cells through extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and interleukin-8 (IL-8)-dependent pathways. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 178831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Supriady, H.; Goh, B.H.; Kadir, H.A. Elephantopus scaber induces apoptosis through ROS-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway in HCT116 human colorectal carcinoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Tang, Y.F.; Yang, M.K.; Huang, X.Z. Dexmedetomidine alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 120, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhu, W.; Sun, L.; Han, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Jiang, W.; Xue, X. Ginsenoside Rb1 administration attenuates focal cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury through inhibition of HMGB1 and inflammation signals. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3020–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Bi, W.; Lu, D.; Zhang, C.; Shu, X.; Lu, D. Luteolin inhibits SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis through suppression of the nuclear transcription factor-κB, mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase B pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cocultured BV2 cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Akashi, K.; Hossain, M.S. PUFA-Plasmalogens Attenuate the LPS-Induced Nitric Oxide Production by Inhibiting the NF-kB, p38 MAPK and JNK Pathways in Microglial Cells. Neuroscience 2019, 397, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Su, S.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Duan, J.A. Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of the combination of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae against focal cerebral ischaemia via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway in MCAO rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peferoen, L.; Kipp, M.; Valk, P.; Noort, J.M.; Amor, S.; Van Der Valk, P.; Van Noort, J.M. Oligodendrocyte-microglia cross-talk in the central nervous system. Immunology 2014, 141, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, J.; Sivakumar, V.; Ling, E.A.; Kaur, C. Amoeboid Microglia in the Periventricular White Matter Induce Oligodendrocyte Damage through Expression of Proinflammatory Cytokines via MAP Kinase Signaling Pathway in Hypoxic Neonatal Rats. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Li, L.; Xie, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Nrf2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through regulating Trx1/TXNIP complex in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 336, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Song, M. Leaves of Raphanus sativus L. Shows Anti-Inflammatory Activity in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages via Suppression of COX-2 and iNOS Expression. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 22, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Jian, Z.; Xiong, X.; Shao, L.; Jin, T.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L. Daphnetin Protects against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice via Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2816056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, J.; Wan, F.; Yang, N.; Jiang, H.; Fang, M.; Xiao, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, J. Tissue kallikrein protects against ischemic stroke by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB and activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.-X.; Ding, Y.-B.; Jin, F.Y.J.; Li, T.; Ma, J.-H.; Qiao, L.-Y.; Pan, W.-Z.; Li, K.-Z. Effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 1770–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Dass, J.F.P. Study of pathway cross-talk interactions with NF-κB leading to its activation via ubiquitination or phosphorylation: A brief review. Gene 2016, 584, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimifard, M.; Maqbool, F.; Moeini-Nodeh, S.; Niaz, K.; Abdollahi, M.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M.; Nabavi, S.F. Targeting the TLR4 signaling pathway by polyphenols: A novel therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Goduni, L.; Takami, Y.; Sharma, N.; Kapil, P.; Jain, M.K.; Mahabeleshwar, G.H. Kruppel-Like Factor 2 Is a Transcriptional Regulator of Chronic and Acute Inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, S.; Chun, E.; Lee, K.-Y. Inhibition of TRAF6 ubiquitin-ligase activity by PRDX1 leads to inhibition of NFKB activation and autophagy activation. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-P.; Gao, F.; Hu, Q.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, G.-H. Vitamin K2 suppresses rotenone-induced microglial activation in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.A.; Roper, K.M.; Bond, J.; Bell, S.M.; Sweeney, S.T.; Morrison, E.E. A MAPK/c-Jun-mediated switch regulates the initial adaptive and cell death responses to mitochondrial damage in a neuronal cell model. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Boil. 2018, 104, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.O.; Byun, J.-E.; Seong, H.-A.; Yoon, S.R.; Choi, I.; Jung, H. Thioredoxin-interacting protein-derived peptide (TN13) inhibits LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting p38 MAPK signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawieh, A.; Langley, E.F.; Tomlinson, S. Targeted complement inhibition salvages stressed neurons and inhibits neuroinflammation after stroke in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tu, M.; Gao, W.; Cai, X.; Song, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Jin, C.; Shi, J.; et al. Hollow Prussian Blue Nanozymes Drive Neuroprotection against Ischemic Stroke via Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Counteracting Inflammation, and Suppressing Cell Apoptosis. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2812–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walberer, M.; Jantzen, S.U.; Backes, H.; Rueger, M.A.; Keuters, M.H.; Neumaier, B.; Hoehn, M.; Fink, G.R.; Graf, R.; Schroeter, M. In-Vivo detection of inflammation and neurodegeneration in the chronic phase after permanent embolic stroke in rats. Brain Res. 2014, 1581, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Tan, R. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Alantolactone through the Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Cells 2019, 8, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070739
Tan L, Li J, Wang Y, Tan R. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Alantolactone through the Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Cells. 2019; 8(7):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070739
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Liwei, Jinsheng Li, Yeye Wang, and Rui Tan. 2019. "Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Alantolactone through the Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways" Cells 8, no. 7: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070739
APA StyleTan, L., Li, J., Wang, Y., & Tan, R. (2019). Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Alantolactone through the Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Cells, 8(7), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070739




