Human Platelet Lysate as a Functional Substitute for Fetal Bovine Serum in the Culture of Human Adipose Derived Stromal/Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Human Platelet Lysate Preparation
2.3. Adipose Derived Stromal/Stem Cells
2.4. Proliferation Assay
2.5. Colony Forming Unit Assay
2.6. Flow Cytometry Assay
2.7. Differentiation Capacity of ASCs
2.8. Adipogenic Induction
2.9. Osteogenic Induction
2.10. Chondrogenic Induction
2.11. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Platelet Lysate Concentration in Culture Medium on ASC Proliferation
3.2. ASC Surface Immunophenotype as a Function of Medium Composition
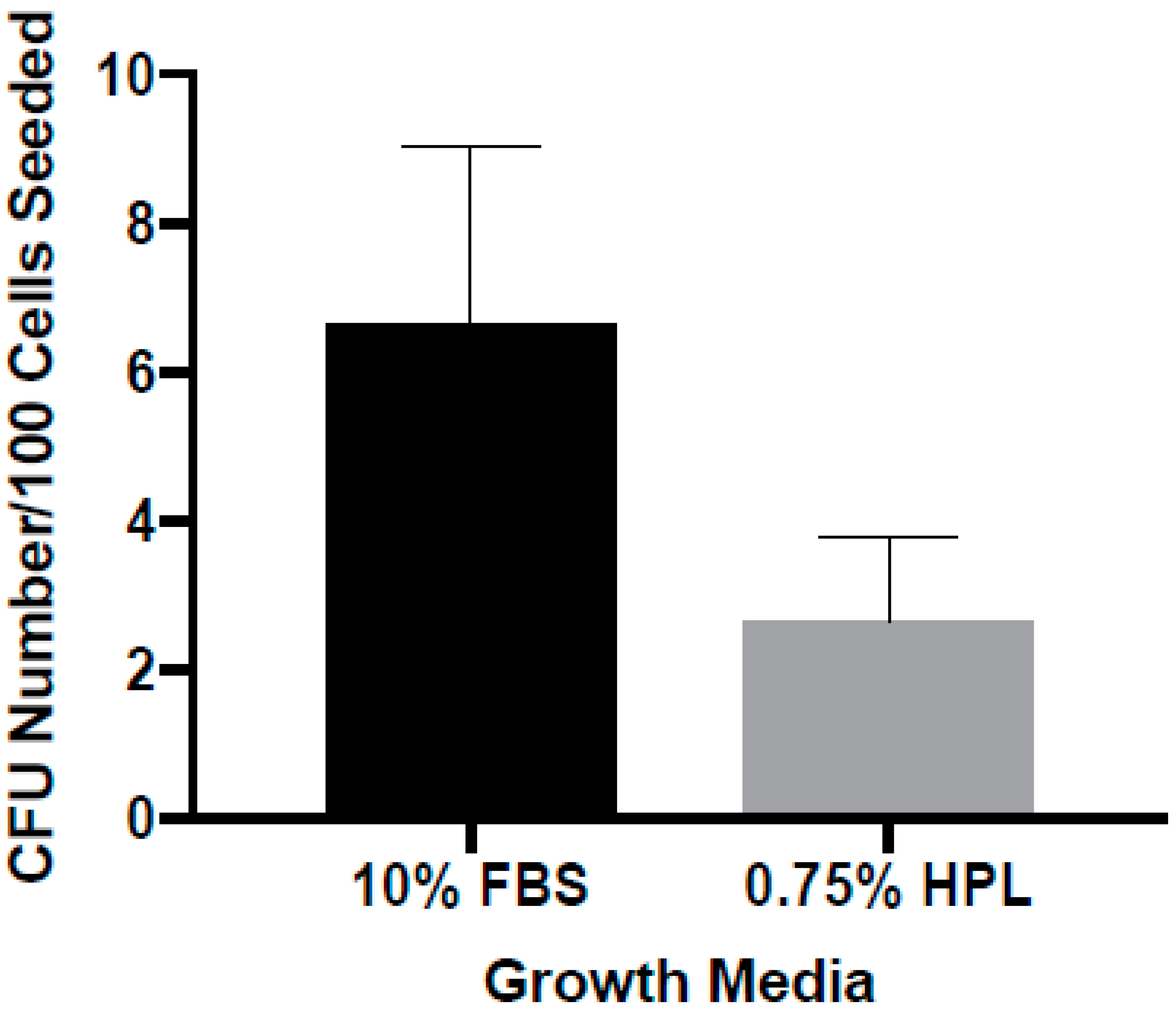
3.3. Colony Forming as a Function of Medium Composition
3.4. Differentiation as a Function of Medium Nutrient Supplement Composition
4. Discussion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gimble, J.M.; Katz, A.J.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilroy, G.E.; Foster, S.J.; Wu, X.; Ruiz, J.; Sherwood, S.; Heifetz, A.; Ludlow, J.W.; Stricker, D.M.; Potiny, S.; Green, P.; et al. Cytokine profile of human adipose-derived stem cells: Expression of angiogenic, hematopoietic, and pro-inflammatory factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, A.J.; Reis, R.L.; Sousa, N.J.; Gimble, J.M. Adipose tissue derived stem cells secretome: Soluble factors and their roles in regenerative medicine. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2010, 5, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, R.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Fu, B.; Yang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, M. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote cell proliferation, migration, and inhibit cell apoptosis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cutaneous wound healing. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 10847–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maumus, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Noel, D. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine applied to rheumatic diseases: Role of secretome and exosomes. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shehada, H.M.A.; Hu, B.; Song, J.; Chen, L. Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, K.R.; Frazier, T.; Rowan, B.G.; Gimble, J.M. Evolution and future prospects of adipose-derived immunomodulatory cell therapeutics. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, R.C.; Loboa, E.G. Our Fat Future: Translating Adipose Stem Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, M.E.; Strong, A.L.; Gimble, J.M.; Bunnell, B.A. Concise Review: Using Fat to Fight Disease: A Systematic Review of Nonhomologous Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cell Therapies. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 1311–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottipamula, S.; Muttigi, M.S.; Kolkundkar, U.; Seetharam, R.N. Serum-free media for the production of human mesenchymal stromal cells: A review. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organizatio. Medicinal and other products and human and animal transmissible spongiform encephalopathies: Memorandum from a WHO meeting. Bull. World Health Organ. 1997, 75, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Bandeiras, C.; Cabral, J.M.; Finkelstein, S.N.; Ferreira, F.C. Modeling biological and economic uncertainty on cell therapy manufacturing: The choice of culture media supplementation. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.R.; Lopez, M.J.; Borneman, J.N.; Spencer, N.D.; Anderson, P.A.; Gimble, J.M. Immunogenicity of allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells in a rat spinal fusion model. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesimaki, K.; Lindroos, B.; Tornwall, J.; Mauno, J.; Lindqvist, C.; Kontio, R.; Miettinen, S.; Suuronen, R. Novel maxillary reconstruction with ectopic bone formation by GMP adipose stem cells. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, D.H.; Graham, J. Stimulation of human tumor colony formation by platelet lysate. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1983, 102, 973–986. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, D.H.; Graham, J.; Paskevich, M.C.; Quinn, P.G. Influence of platelet lysate on colony formation of human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1983, 3, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blande, I.S.; Bassaneze, V.; Lavini-Ramos, C.; Fae, K.C.; Kalil, J.; Miyakawa, A.A.; Schettert, I.T.; Krieger, J.E. Adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cell expansion in animal serum-free medium supplemented with autologous human platelet lysate. Transfusion 2009, 49, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castegnaro, S.; Chieregato, K.; Maddalena, M.; Albiero, E.; Visco, C.; Madeo, D.; Pegoraro, M.; Rodeghiero, F. Effect of platelet lysate on the functional and molecular characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from adipose tissue. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2011, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessels, C.; Durandt, C.; Pepper, M.S. Comparison of human platelet lysate alternatives using expired and freshly isolated platelet concentrates for adipose-derived stromal cell expansion. Platelets 2019, 30, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glovinski, P.V.; Herly, M.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Svalgaard, J.D.; Borup, R.; Talman, M.M.; Elberg, J.J.; Kolle, S.T.; Drzewiecki, K.T.; Fischer-Nielsen, A. Overcoming the bottleneck of platelet lysate supply in large-scale clinical expansion of adipose-derived stem cells: A comparison of fresh versus three types of platelet lysates from outdated buffy coat-derived platelet concentrates. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haack-Sorensen, M.; Juhl, M.; Follin, B.; Harary Sondergaard, R.; Kirchhoff, M.; Kastrup, J.; Ekblond, A. Development of large-scale manufacturing of adipose-derived stromal cells for clinical applications using bioreactors and human platelet lysate. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2018, 78, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildner, F.; Eder, M.J.; Hofer, K.; Aberl, J.; Redl, H.; van Griensven, M.; Gabriel, C.; Peterbauer-Scherb, A. Human platelet lysate successfully promotes proliferation and subsequent chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells: A comparison with articular chondrocytes. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, A.M.; Davenport, M.; Verrier, S.; Droeser, R.; Alini, M.; Bocelli-Tyndall, C.; Schaefer, D.J.; Martin, I.; Scherberich, A. Platelet lysate as a serum substitute for 2D static and 3D perfusion culture of stromal vascular fraction cells from human adipose tissue. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaijkens, B.A.; Niessen, H.W.; Prins, H.J.; Krijnen, P.A.; Kokhuis, T.J.; de Jong, N.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Kamp, O.; Helder, M.N.; Musters, R.J.; et al. Human platelet lysate as a fetal bovine serum substitute improves human adipose-derived stromal cell culture for future cardiac repair applications. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 348, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.T.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Kuo, Y.P.; Su, C.Y.; Burnouf, T. Expansion of adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal progenitors in serum-free medium supplemented with virally inactivated allogeneic human platelet lysate. Transfusion 2011, 51, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojahn Kolle, S.F.; Oliveri, R.S.; Glovinski, P.V.; Kirchhoff, M.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Elberg, J.J.; Andersen, P.S.; Drzewiecki, K.T.; Fischer-Nielsen, A. Pooled human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum-investigating the proliferation rate, chromosome stability and angiogenic potential of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells intended for clinical use. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewa, D.; Stiehl, T.; Schellenberg, A.; Bokermann, G.; Joussen, S.; Koch, C.; Walenda, T.; Pallua, N.; Marciniak-Czochra, A.; Suschek, C.V.; et al. Expansion of adipose mesenchymal stromal cells is affected by human platelet lysate and plating density. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Tong, J.B.; Yang, X.X.; Zhao, J.L.; Zheng, Q.F.; Zhao, G.B.; Ma, Z.J. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue under xeno-free conditions for cell therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wu, X.; Dietrich, M.A.; Polk, P.; Scott, L.K.; Ptitsyn, A.A.; Gimble, J.M. Yield and characterization of subcutaneous human adipose-derived stem cells by flow cytometric and adipogenic mRNA analyzes. Cytotherapy 2010, 12, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Floyd, Z.E.; Wu, X.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Gimble, J.M. Isolation of human adipose-derived stem cells from lipoaspirates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 702, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Floyd, Z.E.; Wu, X.; Hebert, T.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Buehrer, B.M.; Gimble, J.M. Adipogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 702, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hicok, K.C.; Du Laney, T.V.; Zhou, Y.S.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Hitt, D.C.; Cooper, L.F.; Gimble, J.M. Human adipose-derived adult stem cells produce osteoid in vivo. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, B.T.; Diekman, B.O.; Gimble, J.M.; Guilak, F. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells and their induction to a chondrogenic phenotype. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1294–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzebach, S.; Dietz, L.; Kluter, H.; Thierse, H.J.; Bieback, K. Functional and differential proteomic analyses to identify platelet derived factors affecting ex vivo expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieback, K. Platelet lysate as replacement for fetal bovine serum in mesenchymal stromal cell cultures. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2013, 40, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, C.; Ernou, I.; Zhang, Y.; Llense, J.R.; Begot, L.; Holy, X.; Lataillade, J.J. Platelet lysates promote mesenchymal stem cell expansion: A safety substitute for animal serum in cell-based therapy applications. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 205, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieback, K.; Hecker, A.; Kocaomer, A.; Lannert, H.; Schallmoser, K.; Strunk, D.; Kluter, H. Human alternatives to fetal bovine serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Donor | Race | Age | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|
| L111110W | AA | 55 | 24.56 |
| L110411W | C | 66 | 25.28 |
| L110822W | C | 56 | 26.62 |
| L100401T | C | 41 | 23.73 |
| L100723W | C | 22 | 23.59 |
| L100910W | C | 44 | 24.89 |
| L145 | AA | 39 | 31.75 |
| Average | 46.14 ± 14.35 | 25.77 ± 2.82 |
| Antibody | FBS | HPL |
|---|---|---|
| CD29 PE-A | 93.97 ± 3.56 | 81.80 ± 29.50 |
| CD105 PE-A | 95.66 ± 3.66 | 90.47 ± 10.52 |
| CD45 PE-A | –0.1 ± 0.82 | 0.02 ± 0.37 |
| CD34 PE-A | 2.98 ± 2.35 | 0.89 ± 0.47 |
| CD31 PE-A | 0.53 ± 1.19 | 0.23 ± 0.27 |
| CD73 PE-A | 93.69 ± 5.10 | 92.74 ± 6.44 |
| CD90 BV605-A | 93.66 ± 3.08 | 99.15 ± 0.75 |
| IgG PE-A | 0.32 ± 0.19 | −0.10 ± 0.37 |
| PE-A | 0.74 ± 0.79 | 0.33 ± 0.65 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cowper, M.; Frazier, T.; Wu, X.; Curley, J.L.; Ma, M.H.; Mohiuddin, O.A.; Dietrich, M.; McCarthy, M.; Bukowska, J.; Gimble, J.M. Human Platelet Lysate as a Functional Substitute for Fetal Bovine Serum in the Culture of Human Adipose Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070724
Cowper M, Frazier T, Wu X, Curley JL, Ma MH, Mohiuddin OA, Dietrich M, McCarthy M, Bukowska J, Gimble JM. Human Platelet Lysate as a Functional Substitute for Fetal Bovine Serum in the Culture of Human Adipose Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. Cells. 2019; 8(7):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070724
Chicago/Turabian StyleCowper, Mathew, Trivia Frazier, Xiying Wu, J. Lowry Curley, Michelle H. Ma, Omair A. Mohiuddin, Marilyn Dietrich, Michelle McCarthy, Joanna Bukowska, and Jeffrey M. Gimble. 2019. "Human Platelet Lysate as a Functional Substitute for Fetal Bovine Serum in the Culture of Human Adipose Derived Stromal/Stem Cells" Cells 8, no. 7: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070724
APA StyleCowper, M., Frazier, T., Wu, X., Curley, J. L., Ma, M. H., Mohiuddin, O. A., Dietrich, M., McCarthy, M., Bukowska, J., & Gimble, J. M. (2019). Human Platelet Lysate as a Functional Substitute for Fetal Bovine Serum in the Culture of Human Adipose Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. Cells, 8(7), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070724



.png)

