Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats Is Driven by RIP3-Dependent Necroptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
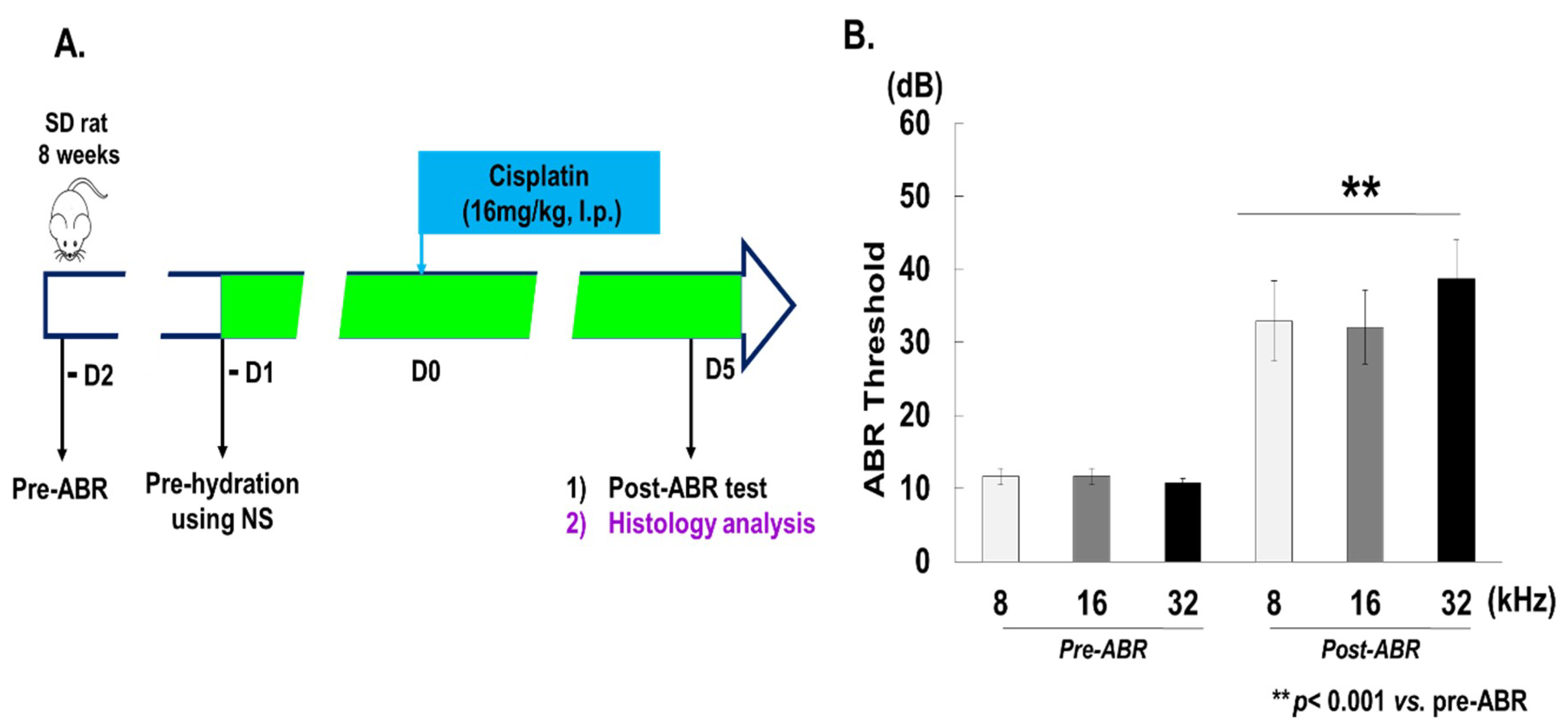
2.1. Experimental Animal Model
2.2. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
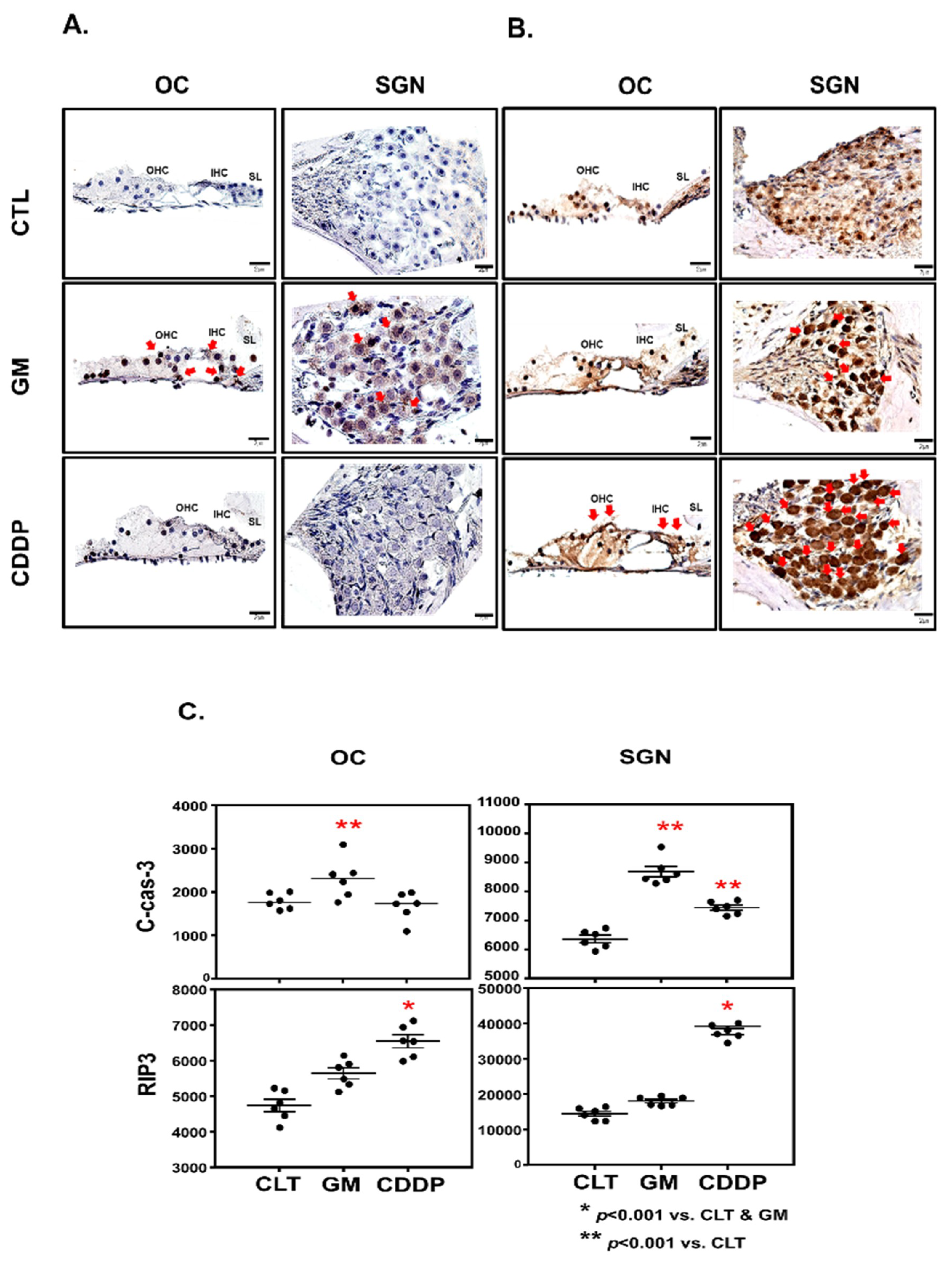
2.3. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Chromogenic Intensity Quantitation
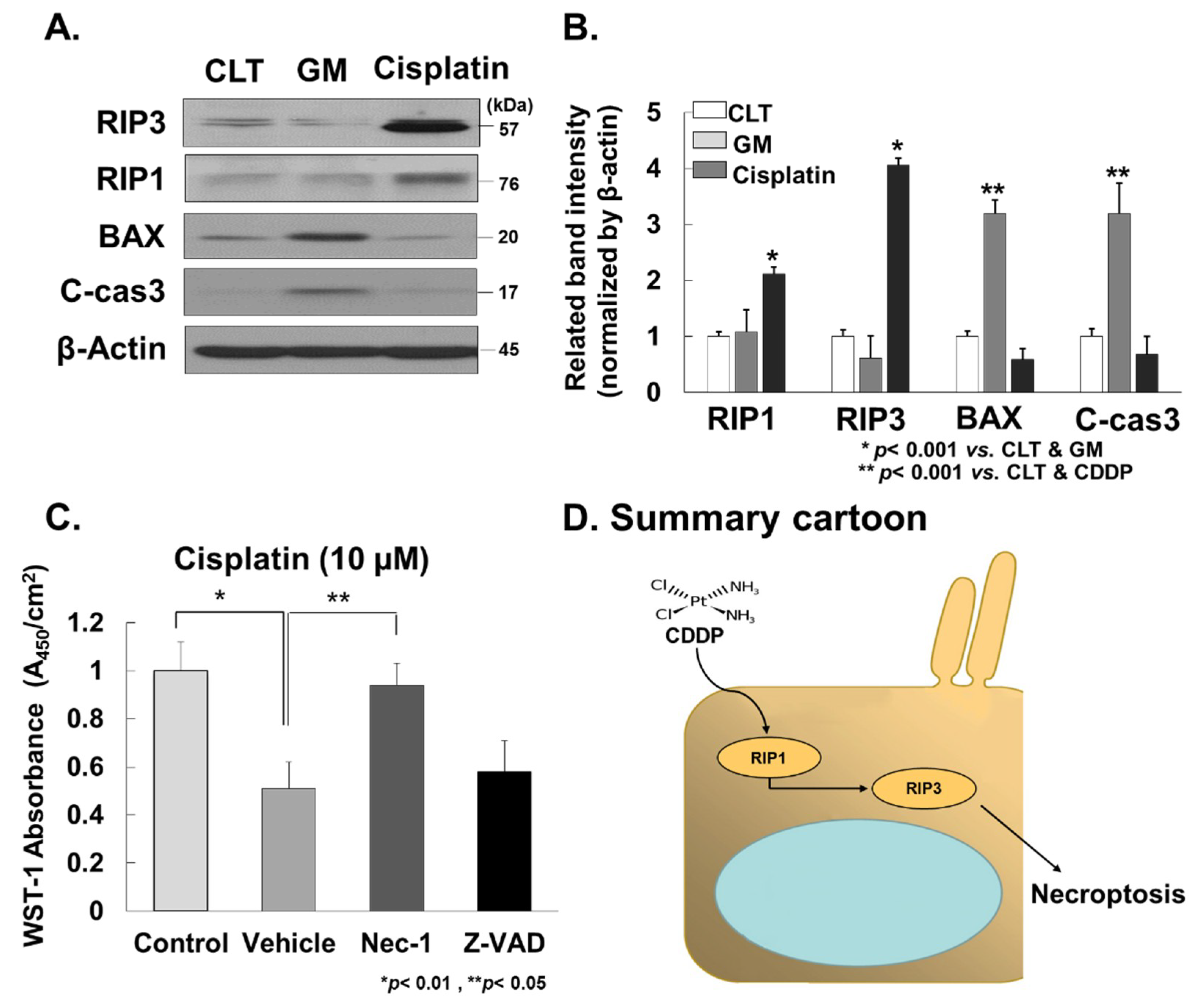
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. In Vitro Experiments
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cisplatin Induces Hearing Loss
3.2. Cisplatin Induces OC and SGNs Injuries
3.3. Cisplatin Increases RIP3 Expression in OC and SGN
3.4. Cisplatin Promotes RIP3-Dependent Necroptosis in Cochlea
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanden Berghe, T.; Vanlangenakker, N.; Parthoens, E.; Deckers, W.; Devos, M.; Festjens, N.; Guerin, C.J.; Brunk, U.T.; Declercq, W.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis, necrosis and secondary necrosis converge on similar cellular disintegration features. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Jitkaew, S.; Zhao, J.; Chiang, H.C.; Choksi, S.; Liu, J.; Ward, Y.; Wu, L.G.; Liu, Z.G. Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Savitz, S.I.; Yang, J.; Degterev, A.; Yuan, J.; Cuny, G.D.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Whalen, M.J. Necrostatin-1 reduces histopathology and improves functional outcome after controlled cortical impact in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedde, M.; Lutz, M.; Carter, N.; Sosna, J.; Jacoby, C.; Vucur, M.; Gautheron, J.; Roderburg, C.; Borg, N.; Reisinger, F.; et al. RIP3, a kinase promoting necroptotic cell death, mediates adverse remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Haig, A.; Pavlosky, A.; Linkermann, A.; Zhang, Z.X.; Jevnikar, A.M. RIPK3-mediated necroptosis promotes donor kidney inflammatory injury and reduces allograft survival. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 2805–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkermann, A.; Green, D.R. Necroptosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, D.; Du, T.T.; Wagner, E.L.; Hwan Choi, J.; Li, S.; Reed, R.; Kim, K.; Freeman, M.; Hashisaki, G.; Lukens, J.R.; et al. Necroptosis and apoptosis contribute to cisplatin and aminoglycoside ototoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2951–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.; Mukherjea, D.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Otoprotection. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, T.; Steyger, P.S. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 17, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humes, H.D. Insights into ototoxicity. Analogies to nephrotoxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 884, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.R.; Kraemer, D.F.; Neuwelt, E.A. Ototoxicity in children receiving platinum chemotherapy: Underestimating a commonly occurring toxicity that may influence academic and social development. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8588–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaal, R.M.; de Groot, J.C.; Huizing, E.H.; Veldman, J.E.; Smoorenburg, G.F. Dose-dependent effect of 8-day cisplatin administration upon the morphology of the albino guinea pig cochlea. Hear. Res. 2000, 144, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, B.; Ferraresi, A.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G.; Fetoni, A.R. Cisplatin ototoxicity in the guinea pig: Vestibular and cochlear damage. Hear. Res. 2003, 182, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.H.; Schacht, J. Formation of reactive oxygen species following bioactivation of gentamicin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boveris, A.; Chance, B. The mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide. General properties and effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Biochem. J. 1973, 134, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, L.P. Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity and progress in otoprotection. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck. Surg. 2007, 15, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ladrech, S.; Pujol, R.; Brabet, P.; Van De Water, T.R.; Puel, J.L. Caspase inhibitors, but not c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase inhibitor treatment, prevent cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 9217–9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, D.J.; Blakley, B.W. Quantification of sodium thiosulphate protection on cisplatin-induced toxicities. J. Otolaryngol. 2003, 32, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamers, F.P.; Brakkee, J.H.; Cavalletti, E.; Tedeschi, M.; Marmonti, L.; Pezzoni, G.; Neijt, J.P.; Gispen, W.H. Reduced glutathione protects against cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.C.; Larsen, D.L.; Meech, R.P.; Rybak, L.P.; Hughes, L.F. Glutathione ester but not glutathione protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in a rat model. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2003, 14, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, L.M.; Darin, J.D.; Bianchi, M.D. Protective effects of vitamin C against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and lipid peroxidation in adult rats: A dose-dependent study. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 41, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sha, S.H.; Zotova, E.; Arezzo, J.; Van de Water, T.; Schacht, J. Salicylate protects hearing and kidney function from cisplatin toxicity without compromising its oncolytic action. Lab. Invest. 2003, 82, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.Q.; Zheng, H.W.; Schacht, J.; Sha, S.H. Mitochondrial peroxiredoxin 3 regulates sensory cell survival in the cochlea. PLoS ONE 2013, 23, e61999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, E., Jr. Ototoxic mechanisms. A working hypothesis. Audiology 1973, 12, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, L.G.; Hawkins, J.E., Jr.; Kingsley, T.C.; Black, F.O.; Matz, G.J. Aminoglycoside-induced cochlear pathology in man. Acta. Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1981, 383, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Ototoxicity. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyderman, H.; Sims, N.R.; Tanaka, M.; Fuku, N.; Raghupathi, R.; Thyagarajan, D. The mitochondrial T1095C mutation increases gentamicin-mediated apoptosis. Mitochondrion 2012, 12, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Tian, C.; Kim, J.; Shin, B.; Choo, O.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Choung, Y.H. Autophagic flux, a possible mechanism for delayed gentamicin-induced ototoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 1, 41356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Berghe, T.; Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P. An outline of necrosome triggers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2137–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, K.; Dong, K.; Mookhtiar, A.K.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.C.; Yuan, J. PELI1 functions as a dual modulator of necroptosis and apoptosis by regulating ubiquitination of RIPK1 and mRNA levels of c-FLIP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 7, 11944–11949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, P.; Savoca, M.; Castaneda, M.P.; Park, M.S.; Esteban-Cruciani, N.; Kalinec, G.; Kalinec, F. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in auditory cells: Role of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Hear. Res. 2002, 174, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.H.; Boo, S.H.; Chung, M.K.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, Y.S.; Hong, S.H. Proapoptotic effects of NF-kappaB on cisplatin-induced cell death in auditory cell line. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008, 128, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.W.; Chen, J.; Sha, S.H. Receptor-interacting protein kinases modulate noise-induced sensory hair cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 29, e1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Lee, B.D.; Chae, S.W.; Chi, J.; Kwon, S.K.; Song, J.J. Protective effect of NecroX, a novel necroptosis inhibitor, on gentamicin-induced ototoxicity. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 76, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.J.; Yue, B.; Zhang, P.Z.; Chen, X.D.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.Q.; Chen, Y.; et al. The role of RIP3 mediated necroptosis in ouabain-induced spiral ganglion neurons injuries. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 22, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Mukherjea, D.; Sheehan, K.; Jajoo, S.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Short interfering RNA against STAT1 attenuates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in the rat by suppressing inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 21, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, F.J.; Ramakrishnan, L. TNF dually mediates resistance and susceptibility to mycobacteria via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Cell 2013, 25, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, N.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, J. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of RIP3-dependent protein phosphorylation in the course of TNF-induced necroptosis. Proteomics 2014, 14, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hang, W.; Yin, Z.X.; Liu, G.; Chen, J.; Werle, K.D.; Quan, C.S.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase protects against necroptosis via regulation of Keap1-PGAM5 complex. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Ren, G.L.; Gao, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.D.; Wu, W.F.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. NADPH oxidase 4 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via ROS-mediated programmed cell death and inflammation. Lab. Invest. 2018, 98, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.-J.; Kang, H.; Lee, Y.Y.; Choo, O.-S.; Jang, J.H.; Park, S.-H.; Moon, J.-S.; Choi, S.J.; Choung, Y.-H. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats Is Driven by RIP3-Dependent Necroptosis. Cells 2019, 8, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050409
Choi M-J, Kang H, Lee YY, Choo O-S, Jang JH, Park S-H, Moon J-S, Choi SJ, Choung Y-H. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats Is Driven by RIP3-Dependent Necroptosis. Cells. 2019; 8(5):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050409
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Mi-Jin, Hyunsook Kang, Yun Yeong Lee, Oak-Sung Choo, Jeong Hun Jang, Sung-Hee Park, Jong-Seok Moon, Seong Jun Choi, and Yun-Hoon Choung. 2019. "Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats Is Driven by RIP3-Dependent Necroptosis" Cells 8, no. 5: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050409
APA StyleChoi, M.-J., Kang, H., Lee, Y. Y., Choo, O.-S., Jang, J. H., Park, S.-H., Moon, J.-S., Choi, S. J., & Choung, Y.-H. (2019). Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats Is Driven by RIP3-Dependent Necroptosis. Cells, 8(5), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050409




