Temporal Dynamics of VEGFA-Induced VEGFR2/FAK Co-Localization Depend on SHB
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. DNA Constructs
2.3. Cell Isolation and Transfection
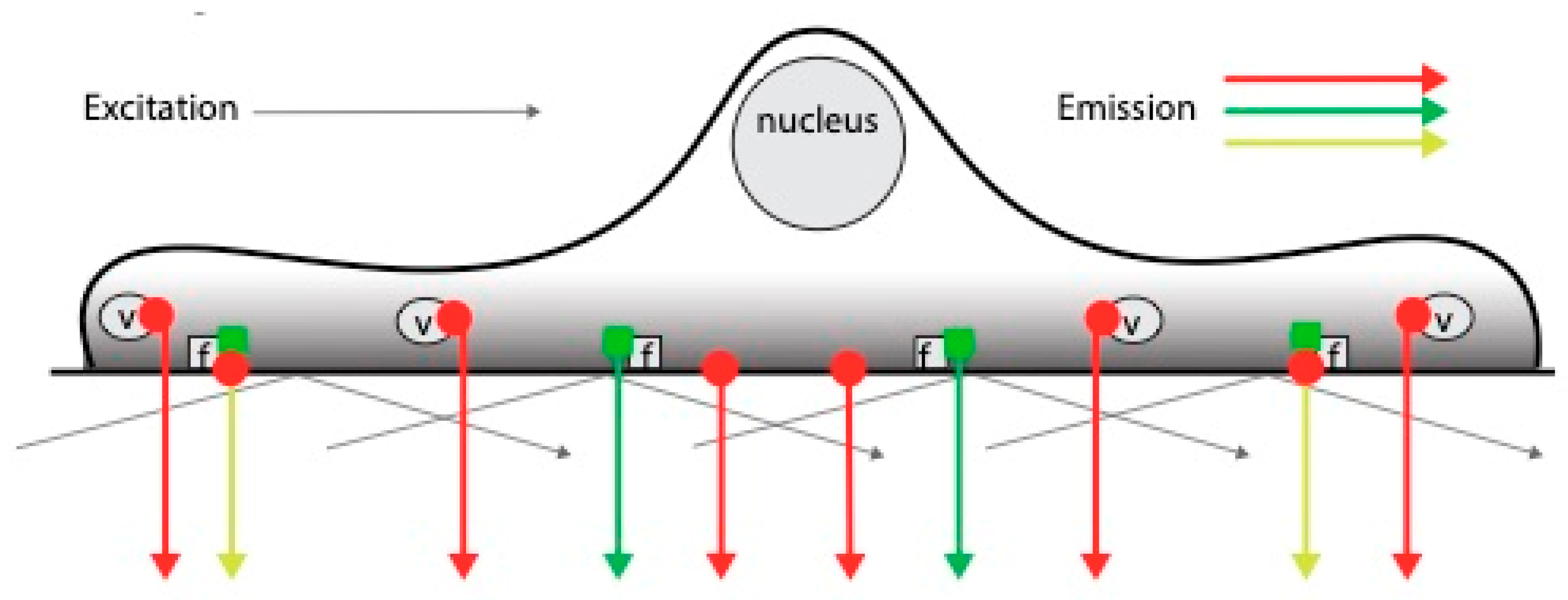
2.4. TIRF Microscopy
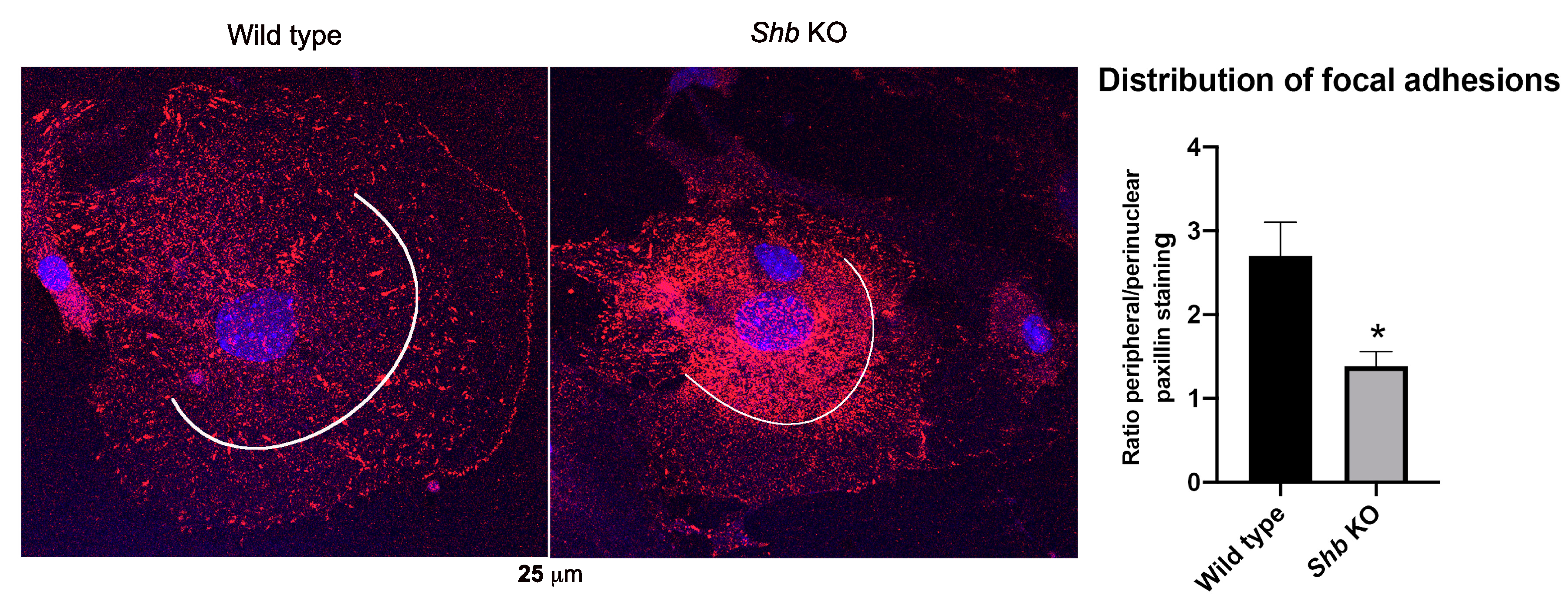
2.5. Paxillin Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
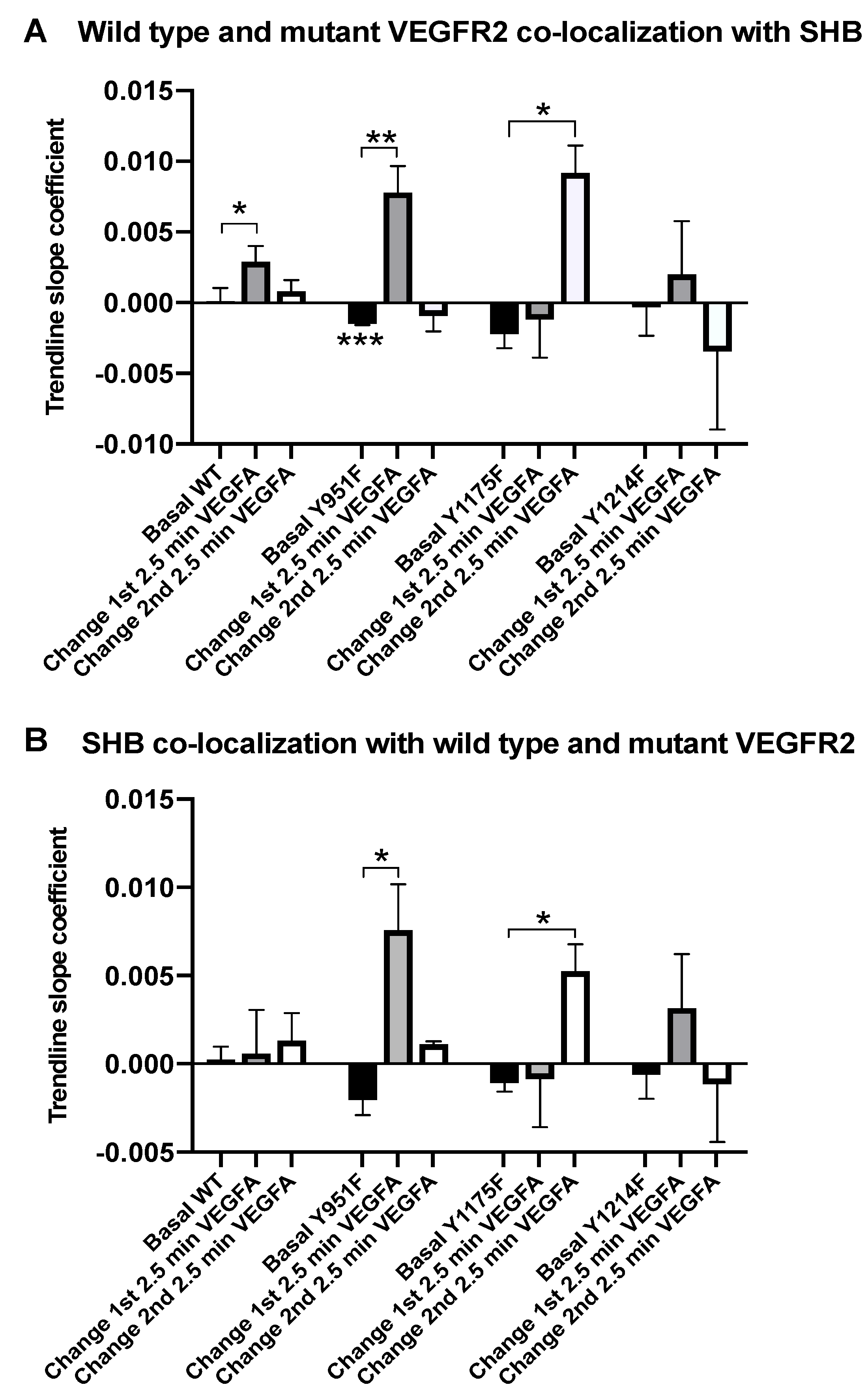
3.1. SHB and VEGFR2 Co-Localization
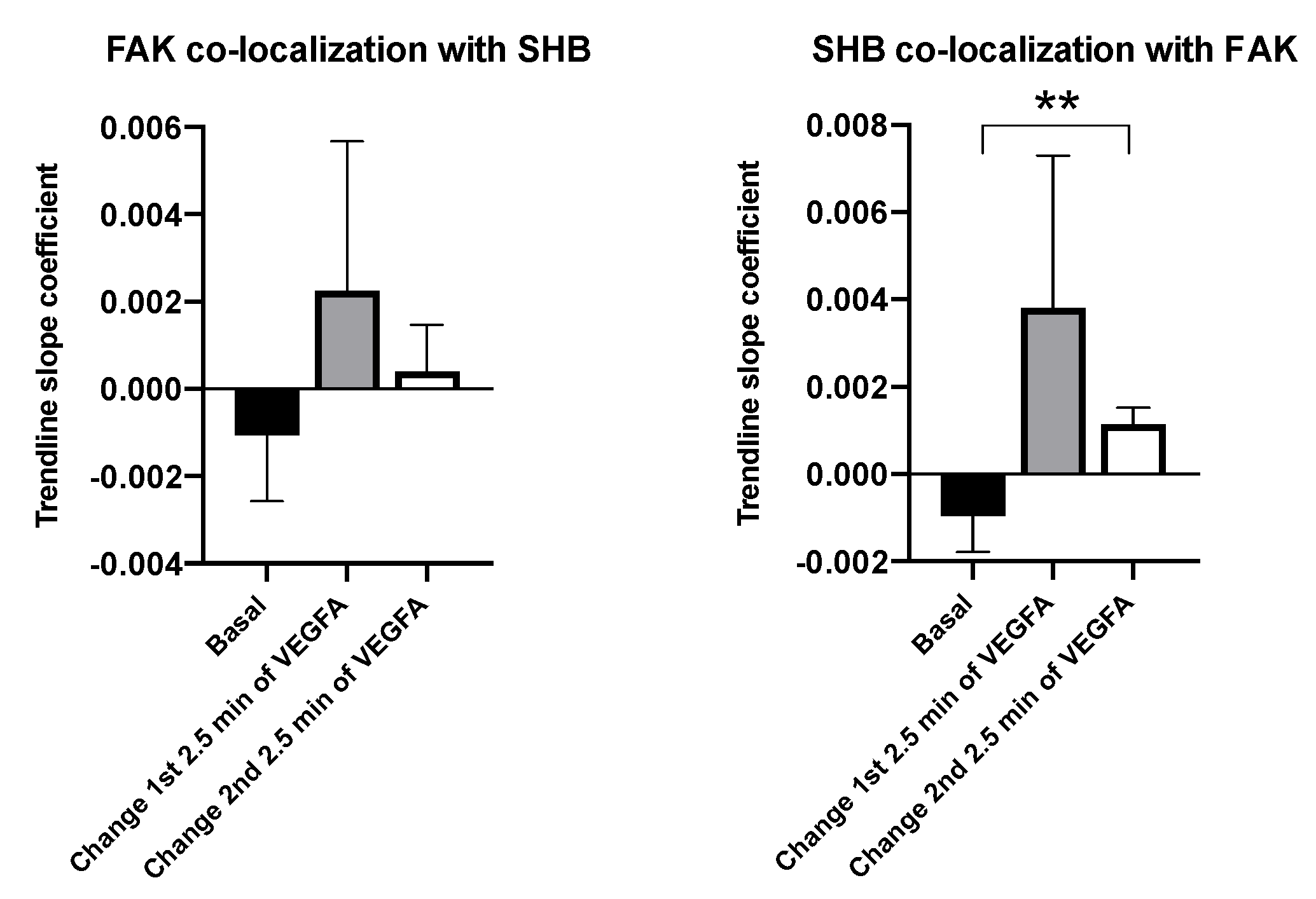
3.2. SHB and FAK Co-Localization
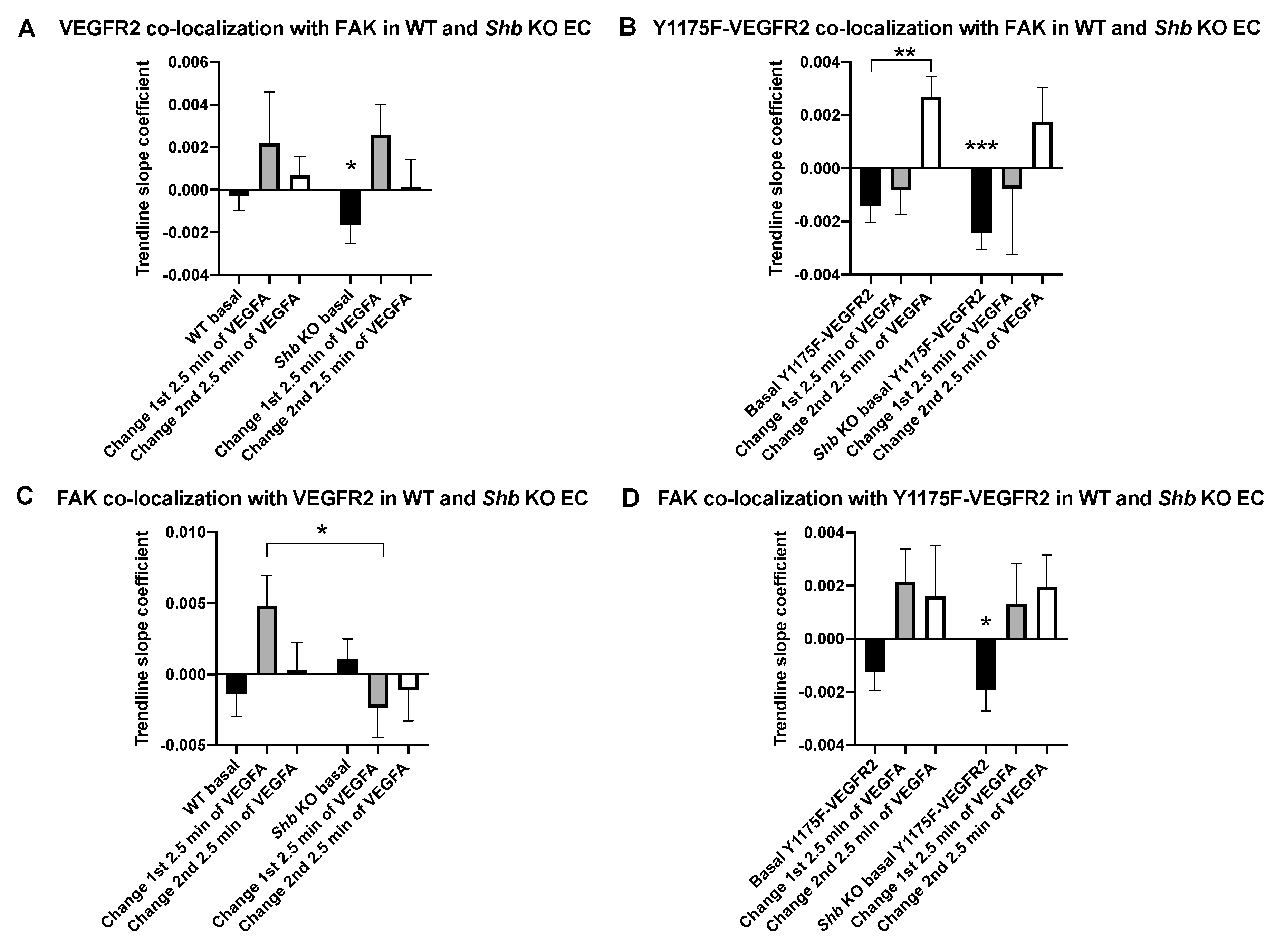
3.3. VEGFR2 and FAK Co-Localization
3.4. Focal Adhesions in Shb KO EC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, R.; Machein, M.; Nicolaus, A.; Hilbig, A.; Wild, C.; Clauss, M.; Plate, K.H.; Breier, G. Inhibition of solid tumor growth by gene transfer of VEGF receptor-1 mutants. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 111, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, R.; Murayama, T.; Silver, M.; Essl, C.; Asahara, T.; Rocken, M.; Breier, G. Tracking adult neovascularization during ischemia and inflammation using Vegfr2-LacZ reporter mice. J. Vasc. Res. 2008, 45, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testini, C.; Smith, R.O.; Jin, Y.; Martinsson, P.; Sun, Y.; Hedlund, M.; Sainz-Jaspeado, M.; Shibuya, M.; Hellstrom, M.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Myc-dependent endothelial proliferation is controlled by phosphotyrosine 1212 in VEGF receptor-2. EMBO Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.L.; Nam, J.O.; Jean, C.; Lawson, C.; Walsh, C.T.; Goka, E.; Lim, S.T.; Tomar, A.; Tancioni, I.; Uryu, S.; et al. VEGF-induced vascular permeability is mediated by FAK. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavora, B.; Batista, S.; Reynolds, L.E.; Jadeja, S.; Robinson, S.; Kostourou, V.; Hart, I.; Fruttiger, M.; Parsons, M.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M. Endothelial FAK is required for tumour angiogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, M.; Jamalpour, M.; Zang, G.; Akerblom, B. The role of the Src Homology-2 domain containing protein B (SHB) in beta cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, R21–R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerblom, B.; Zang, G.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Calounova, G.; Simons, M.; Welsh, M. Heterogeneity among RIP-Tag2 insulinomas allows vascular endothelial growth factor-A independent tumor expansion as revealed by studies in Shb mutant mice: Implications for tumor angiogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersson, G.; Zang, G.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Vagesjo, E.; Simons, M.; Phillipson, M.; Welsh, M. Vascular adaptation to a dysfunctional endothelium as a consequence of Shb deficiency. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funa, N.S.; Kriz, V.; Zang, G.; Calounova, G.; Akerblom, B.; Mares, J.; Larsson, E.; Sun, Y.; Betsholtz, C.; Welsh, M. Dysfunctional microvasculature as a consequence of shb gene inactivation causes impaired tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikpour, M.; Gustafsson, K.; Vagesjo, E.; Seignez, C.; Giraud, A.; Phillipson, M.; Welsh, M. Shb deficiency in endothelium but not in leucocytes is responsible for impaired vascular performance during hindlimb ischaemia. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 2015, 214, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, G.; Gustafsson, K.; Jamalpour, M.; Hong, J.; Genove, G.; Welsh, M. Vascular dysfunction and increased metastasis of B16F10 melanomas in Shb deficient mice as compared with their wild type counterparts. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, G.; Christoffersson, G.; Tian, G.; Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Vagesjo, E.; Phillipson, M.; Barg, S.; Tengholm, A.; Welsh, M. Aberrant association between vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 and VE-cadherin in response to vascular endothelial growth factor-a in Shb-deficient lung endothelial cells. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, K.; Cross, M.; Riley, D.; Welsh, M. The Shb adaptor protein causes Src-dependent cell spreading and activation of focal adhesion kinase in murine brain endothelial cells. Cell. Signal. 2003, 15, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergai, O.V.; Yaruchik, A.M.; Rynditch, A.V. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK1) regulates SHB phosphorylation and its binding with a range of signaling proteins. Biopolym. Cell 2016, 32, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, K.; Cross, M.J.; Rolny, C.; Hagerkvist, R.; Rahimi, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. The adaptor protein shb binds to tyrosine 1175 in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-2 and regulates VEGF-dependent cellular migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22267–22275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenkvist, I.; Dyachok, O.; Tian, G.; Li, J.; Mehrabanfar, S.; Jin, Y.; Birnir, B.; Tengholm, A.; Welsh, M. Absence of Shb impairs insulin secretion by elevated FAK activity in pancreatic islets. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, K.; Heffner, G.; Wenzel, P.L.; Curran, M.; Grawe, J.; McKinney-Freeman, S.L.; Daley, G.Q.; Welsh, M. The Src homology 2 protein Shb promotes cell cycle progression in murine hematopoietic stem cells by regulation of focal adhesion kinase activity. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, K.; Jamalpour, M.; Trinh, C.; Kharas, M.G.; Welsh, M. The Src homology-2 protein Shb modulates focal adhesion kinase signaling in a BCR-ABL myeloproliferative disorder causing accelerated progression of disease. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, V.; Mares, J.; Wentzel, P.; Funa, N.S.; Calounova, G.; Zhang, X.Q.; Forsberg-Nilsson, K.; Forsberg, M.; Welsh, M. Shb null allele is inherited with a transmission ratio distortion and causes reduced viability in utero. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Bohman, S.; Dixelius, J.; Berge, T.; Dimberg, A.; Magnusson, P.; Wang, L.; Wikner, C.; Qi, J.H.; Wernstedt, C.; et al. VEGF receptor-2 Y951 signaling and a role for the adapter molecule TSAd in tumor angiogenesis. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Shuai, H.; Ahooghalandari, P.; Gylfe, E.; Tengholm, A. Glucose controls glucagon secretion by directly modulating cAMP in alpha cells. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampel, A.; Moss, L.; Jones, M.C.; Brunton, V.; Norman, J.C.; Mellor, H. VEGF regulates the mobilization of VEGFR2/KDR from an intracellular endothelial storage compartment. Blood 2006, 108, 2624–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanteti, R.; Batra, S.K.; Lennon, F.E.; Salgia, R. FAK and paxillin, two potential targets in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31586–31601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundby, A.; Franciosa, G.; Emdal, K.B.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Gnosa, S.P.; Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Secher, A.; Maurya, S.R.; Paul, I.; Mendez, B.L.; et al. Oncogenic Mutations Rewire Signaling Pathways by Switching Protein Recruitment to Phosphotyrosine Sites. Cell 2019, 179, 543–560.e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, C.; Sherman, A.; Chen, G.I.; Pasculescu, A.; Poliakov, A.; Hsiung, M.; Larsen, B.; Wilkinson, D.G.; Linding, R.; Pawson, T. Cell-specific information processing in segregating populations of Eph receptor ephrin-expressing cells. Science 2009, 326, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Chida, K.; Shibuya, M. A single autophosphorylation site on KDR/Flk-1 is essential for VEGF-A-dependent activation of PLC-gamma and DNA synthesis in vascular endothelial cells. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, A.R.; Bodrug, N.; Gomez-Escudero, J.; Carter, E.P.; Reynolds, L.E.; Georgiou, P.N.; Fernandez, I.; Lees, D.M.; Kostourou, V.; Alexopoulou, A.N.; et al. Tumor Angiogenesis Is Differentially Regulated by Phosphorylation of Endothelial Cell Focal Adhesion Kinase Tyrosines-397 and -861. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4371–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.J.; Lu, L.; Magnusson, P.; Nyqvist, D.; Holmqvist, K.; Welsh, M.; Claesson-Welsh, L. The Shb adaptor protein binds to tyrosine 766 in the FGFR-1 and regulates the Ras/MEK/MAPK pathway via FRS2 phosphorylation in endothelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2881–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietilä, I.; Van Mourik, D.; Tamelander, A.; Kriz, V.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Tengholm, A.; Welsh, M. Temporal Dynamics of VEGFA-Induced VEGFR2/FAK Co-Localization Depend on SHB. Cells 2019, 8, 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121645
Pietilä I, Van Mourik D, Tamelander A, Kriz V, Claesson-Welsh L, Tengholm A, Welsh M. Temporal Dynamics of VEGFA-Induced VEGFR2/FAK Co-Localization Depend on SHB. Cells. 2019; 8(12):1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121645
Chicago/Turabian StylePietilä, Ilkka, Djenolan Van Mourik, Andreas Tamelander, Vitezslav Kriz, Lena Claesson-Welsh, Anders Tengholm, and Michael Welsh. 2019. "Temporal Dynamics of VEGFA-Induced VEGFR2/FAK Co-Localization Depend on SHB" Cells 8, no. 12: 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121645
APA StylePietilä, I., Van Mourik, D., Tamelander, A., Kriz, V., Claesson-Welsh, L., Tengholm, A., & Welsh, M. (2019). Temporal Dynamics of VEGFA-Induced VEGFR2/FAK Co-Localization Depend on SHB. Cells, 8(12), 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121645





