Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease Associated to Oxaliplatin: An Entity to Think about It
Abstract
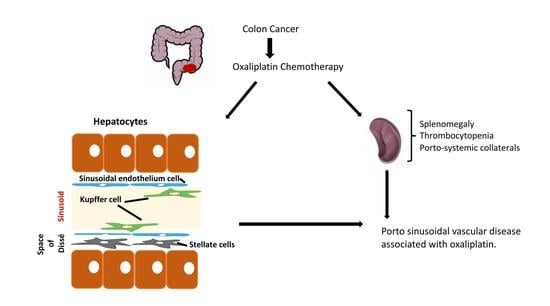
1. Introduction
2. Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease Associated to Oxaliplatin
2.1. Oxaliplatin and Liver Damage
2.2. When Should It Be Suspected?
2.3. How Can We Diagnose It?
2.3.1. Non Invasive Diagnosis
Laboratory
Imagin
Elastography
2.3.2. Invasive Diagnosis
Liver Biopsy
Hepatic Vein Catheterization
Endoscopic Findings
2.4. Management of the Disease
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular diseases of the liver. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Llahí, M.; Albillos, A.; Bañares, R.; Berzigotti, A.; García-Criado, M.Á.; Genescà, J.; Hernández-Gea, V.; Llop-Herrera, E.; Masnou-Ridaura, H.; Mateo, J.; et al. Enfermedades vasculares del hígado. Guías Clínicas de la Sociedad Catalana de Digestología y de la Asociación Española para el Estudio del Hígado. Gastroenterol. Y. Hepatol. 2017, 40, 538–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, J.N.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Valla, D.C.; Janssen, H.L.; García-Pagán, J.C. Idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillaire, S.; Bonte, E.; Denninger, M.-H.; Casadevall, N.; Cadranel, J.-F.; Lebrec, D.; Valla, D.; Degott, C. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension in the West: A re-evaluation in 28 patients. Gut 2002, 51, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gottardi, A.; Rautou, P.E.; Schouten, J.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Leebeek, F.; Trebicka, J.; Murad, S.D.; Vilgrain, V.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Nery, F.; et al. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: Proposal and description of a novel entity. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019, 4, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eapen, C.E.; Nightingale, P.; Hubscher, S.G.; Lane, P.J.; Plant, T.; Velissaris, D.; Elias, E. Non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension: Associated gut diseases and prognostic factors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siramolpiwat, S.; Seijo, S.; Miquel, R.; Berzigotti, A.; Darnell, A.; Turon, F.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Criado, A.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Garcia-Pagán, J.C.; et al. Idiopathic portal hypertension: Natural history and long-term outcome. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Chawla, Y.K.; Baijal, S.S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Jafri, W.; Lesmana, L.A.; Mazumder, D.G.; Omata, M.; Qureshi, H.; et al. Noncirrhotic portal fibrosis/idiopathic portal hypertension: APASL recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Hepatol. Int. 2007, 1, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-E.; Miquel, R.; Blanco, J.-L.; Laguno, M.; Bruguera, M.; Abraldes, J.-G.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.-C. Idiopathic Portal Hypertension in Patients With HIV Infection Treated With Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, S.; Sari, S.; Yilmaz, G.; Stiegler, A.L.; Boggon, T.J.; Jain, D.; Akyol, G.; Dalgiç, B.; Gunel, M.; Lifton, R.P. Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, T.; Boni, C.; Mounedji-Boudiaf, L.; Matilde Navarro, M.; Tabernero, J.; Hickish, T.; Topham, C.; Zaninelli, M.; Clingan, P.; Bridgewater, J.; et al. Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorinas Adjuvant Treatment for Colon Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Wu, H.; Gu, K. Oxaliplatin-Based Regimen is Superior to Cisplatin-Based Regimen in Tumour Remission as First-line Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoize, B.; Madoulet, C. Particular aspects of platinum compounds used at present in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2002, 42, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauthey, J.-N.; Pawlik, T.M.; Ribero, D.; Wu, T.-T.; Zorzi, D.; Hoff, P.M.; Xiong, H.Q.; Eng, C.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; et al. Chemotherapy Regimen Predicts Steatohepatitis and an Increase in 90-Day Mortality After Surgery for Hepatic Colorectal Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arotçarena, R.; Calès, V.; Berthélemy, P.; Parent, Y.; Malet, M.; Etcharry, F.; Ferrari, S.; Pariente, A. Severe sinusoidal lesions: A serious and overlooked complication of oxaliplatin-containing chemotherapy? Gastroentérol. Clin. Biol. 2006, 30, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Audard, V.; Sartoretti, P.; Roth, A.D.; Brezault, C.; Le Charpentier, M.; Dousset, B.; Morel, P.; Soubrane, O.; Chaussade, S.; et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastaticcolorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Wang, H.E.; Majno, P.; Tanabe, K.; Zhu, A.X.; Brezault, C.; Soubrane, O.; Abdalla, E.K.; Mentha, G.; et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and nodular regenerative hyperplasia are frequent oxaliplatin-associated liver lesions and partially prevented by bevacizumab in patients with hepatic colorectal metastasis. Histopathology 2010, 56, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, M.L.; Wakefield, S.J.; Ford, H.C. Hepatocyte membrane injury and bleb formation following low dose comfrey toxicity in rats. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1993, 74, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Canta, A.; Pozzi, E.; Carozzi, V.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN). Toxics 2015, 3, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, J.H.; Alattar, M.L.; Fogelman, D.R.; Overman, M.J.; Agarwal, A.; Maru, D.M.; Coulson, R.L.; Charnsangavej, C.; Vauthey, J.N.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Portal Hypertension Associated With Oxaliplatin Administration: Clinical Manifestations of Hepatic Sinusoidal Injury. Clin. Color. Cancer 2009, 8, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, T.O.; Farris, A.B.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Subramanian, R.M.; Kim, H.S. Oxaliplatin-Induced Hepatoportal Sclerosis, Portal Hypertension, and Variceal Bleeding Successfully Treated With Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2012, 11, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouquet, A.; Benoist, S.; Julié, C.; Penna, C.; Beauchet, A.; Rougier, P.; Nordlinger, B. Risk factors for chemotherapy-associated liver injuries: A multivariate analysis of a group of 146 patients with colorectal metastases. Surgery 2009, 145, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicherts, D.A.; De Haas, R.J.; Sebagh, M.; Ciacio, O.; Levi, F.; Paule, B.; Giacchetti, S.; Guettier, C.; Azoulay, D.; Castaing, D.; et al. Regenerative nodular hyperplasia of the liver related to chemotherapy: Impact on outcome of liver surgery for colorectal metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 18, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Maru, D.M.; Charnsangavej, C.; Loyer, E.M.; Wang, H.; Pathak, P.; Eng, C.; Hoff, P.M.; Vauthey, J.N.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Oxaliplatin-mediated increase in spleen size as a biomarker for the development of hepatic sinusoidal injury. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2549–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Takeyama, S.; Morioka, C.; Sawai, M.; Toyohara, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Yoshiji, H.; Yamao, J.; et al. Development of nodular regenerative hyperplasia (NRH) with portal hypertension following the administration of oxaliplatin for the recurrence of colon cancer. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, D.; Djonov, V.; Zamir, G.; Bala, M.; Safadi, R.; Sklair-Levy, M.; Keshet, E. A Transgenic Model for Conditional Induction and Rescue of Portal Hypertension Reveals a Role of VEGF-Mediated Regulation of Sinusoidal Fenestrations. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Mann, J.; Vasilaki, A.; Mathers, J.; Burt, A.; Oakley, F.; White, S.; Mann, D. Pathogenesis of FOLFOX induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in a murine chemotherapy model. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Ferrarotto, R.; Raghav, K.; George, B.; Qiao, W.; Machado, K.K.; Saltz, L.B.; Mazard, T.; Vauthey, J.N.; Hoff, P.M.; et al. The Addition of Bevacizumab to Oxaliplatin-Based Chemotherapy: Impact Upon Hepatic Sinusoidal Injury and Thrombocytopenia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Gea, V.; Baiges, A.; Turon, F.; Garcia-Pagán, J.C. Idiopathic Portal Hypertension. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Seijo, S.; Lozano, J.J.; Alonso, C.; Reverter, E.; Miquel, R.; Abraldes, J.G.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Garcia-Criado, A.; Berzigotti, A.; Castro, A.; et al. Metabolomics Discloses Potential Biomarkers for the Noninvasive Diagnosis of Idiopathic Portal Hypertension. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Sarin, S.K. Multimodality imaging of obliterative portal venopathy: What every radiologist should know. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20140653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzigotti, A. Non-invasive evaluation of portal hypertension using ultrasound elastography. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanless, I.R. Micronodular transformation (nodular regenerative hyperplasia) of the liver: A report of 64 cases among 2,500 autopsies and a new classification of benign hepatocellular nodules. Hepatology 1990, 11, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, J.P.; Huet, P.M.; Joly, J.G.; Marleau, D.; Côté, J.; Légaré, A.; Lafortune, M.; Lavoie, P.; Viallet, A. Idiopathic portal hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1976, 61, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Chumbalkar, V.; Ells, P.F.; Bonville, D.J.; Lee, H. Prevalence of histological features of idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension in general population: A retrospective study of incidental liver biopsies. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, B.L.; Surana, P.; Kapuria, D.; Vittal, A.; Levy, E.; Kleiner, D.E.; Koh, C.; Heller, T. Portal Pressure in Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension: To Measure or Not to Measure. Hepatology 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, S.; Reverter, E.; Miquel, R.; Berzigotti, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Bosch, J.; García-Pagán, J.C. Role of hepatic vein catheterisation and transient elastography in the diagnosis of idiopathic portal hypertension. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, S.; Di Martino, M.; Minozzi, M.; Nardelli, S.; Cortesi, E.; Riggio, O. Incidence of portal hypertension in patients exposed to oxaliplatin. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.K.; Gupta, N.; Jha, S.K.; Agrawal, A.; Mishra, S.R.; Sharma, B.C.; Kumar, A. Equal Efficacy of Endoscopic Variceal Ligation and Propranolol in Preventing Variceal Bleeding in Patients With Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension. Gastroenterol. 2010, 139, 1238–1245.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, J.; Garcia-Pagán, J.C.; Albillos, A.; Turon, F.; Ferreira, C.; Tellez, L.; Nault, J.-C.; Carbonell, N.; Cervoni, J.-P.; Rehim, M.A.; et al. Role of the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of severe complications of portal hypertension in idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, S.; Ichikawa, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Motohara, T.; Fukuda, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Interventional radiologic treatment for idiopathic portal hypertension. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1999, 22, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessier, A.; Darwish-Murad, S.; Hernandez-Guerra, M.; Consigny, Y.; Fabris, F.; Trebicka, J.; Heller, J.; Morard, I.; Lasser, L.; Langlet, P.; et al. Acute portal vein thrombosis unrelated to cirrhosis: A prospective multicenter follow-up study. Hepatology 2010, 51, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzu, V.; Elias, J.E.; Duckworth, A.; Davies, S.; Brais, R.; Kumararatne, D.S.; Gimson, A.E.S.; Griffiths, W.J.H. Liver transplantation in adults with liver disease due to common variable immunodeficiency leads to early recurrent disease and poor outcome. Liver Transplant. 2018, 24, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Clinical Signs of Portal Hypertension (Any One of the Following †) • Splenomegaly or hypersplenism • Esophageal varices • Ascites (non-malignant) • Minimally increased hepatic venous pressure gradient • Portovenous collaterals |
| Exclusion of Cirrhosis on Liver Biopsy |
| Exclusion of chronic liver disease causing cirrhosis or non-cirrhotic portal hypertension ‡ • Chronic viral hepatitis B or C • Non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis • Autoimmune hepatitis • Hereditary hemochromatosis • Wilson’s disease • Primary biliary cholangitis |
| Exclusion of Conditions Causing Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension • Congenital liver fibrosis • Sarcoidosis • Schistosomiasis |
| Patent Portal and Hepatic Veins (Doppler Ultrasound or CT Scanning) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puente, A.; Fortea, J.I.; Del Pozo, C.; Huelin, P.; Cagigal, M.L.; Serrano, M.; Cabezas, J.; Arias Loste, M.T.; Iruzubieta, P.; Cuadrado, A.; et al. Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease Associated to Oxaliplatin: An Entity to Think about It. Cells 2019, 8, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121506
Puente A, Fortea JI, Del Pozo C, Huelin P, Cagigal ML, Serrano M, Cabezas J, Arias Loste MT, Iruzubieta P, Cuadrado A, et al. Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease Associated to Oxaliplatin: An Entity to Think about It. Cells. 2019; 8(12):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121506
Chicago/Turabian StylePuente, Angela, Jose Ignacio Fortea, Carmen Del Pozo, Patricia Huelin, Maria Luisa Cagigal, Marina Serrano, Joaquin Cabezas, Maria Teresa Arias Loste, Paula Iruzubieta, Antonio Cuadrado, and et al. 2019. "Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease Associated to Oxaliplatin: An Entity to Think about It" Cells 8, no. 12: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121506
APA StylePuente, A., Fortea, J. I., Del Pozo, C., Huelin, P., Cagigal, M. L., Serrano, M., Cabezas, J., Arias Loste, M. T., Iruzubieta, P., Cuadrado, A., Llerena, S., Lopez, C., Fábrega, E., & Crespo, J. (2019). Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease Associated to Oxaliplatin: An Entity to Think about It. Cells, 8(12), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121506