Abstract
Parallel research on multiple model organisms shows that while some principles of telomere biology are conserved among all eukaryotic kingdoms, we also find some deviations that reflect different evolutionary paths and life strategies, which may have diversified after the establishment of telomerase as a primary mechanism for telomere maintenance. Much more than animals, plants have to cope with environmental stressors, including genotoxic factors, due to their sessile lifestyle. This is, in principle, made possible by an increased capacity and efficiency of the molecular systems ensuring maintenance of genome stability, as well as a higher tolerance to genome instability. Furthermore, plant ontogenesis differs from that of animals in which tissue differentiation and telomerase silencing occur during early embryonic development, and the “telomere clock” in somatic cells may act as a preventive measure against carcinogenesis. This does not happen in plants, where growth and ontogenesis occur through the serial division of apical meristems consisting of a small group of stem cells that generate a linear series of cells, which differentiate into an array of cell types that make a shoot and root. Flowers, as generative plant organs, initiate from the shoot apical meristem in mature plants which is incompatible with the human-like developmental telomere shortening. In this review, we discuss differences between human and plant telomere biology and the implications for aging, genome stability, and cell and organism survival. In particular, we provide a comprehensive comparative overview of telomere proteins acting in humans and in Arabidopsis thaliana model plant, and discuss distinct epigenetic features of telomeric chromatin in these species.
1. Introduction
Telomere biology, whose foundations were laid out in maize and Drosophila at the end of the 1930s and which developed at the molecular level in the 1980s, has flourished enourmously in the last 30 years. This interest in telomere biology follows from the generally attractive links between telomere functions, cell aging mechanisms, and the genesis of severe diseases in humans. Research in recent decades has elucidated the principles of protection of the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes from progressive shortening due to the incomplete replication (end-replication problem) [1] and from their erroneous recognition as unrepaired chromosome breaks (end-protection problem) [2,3,4]. In addition to these basic functions, other potential roles of telomeres have been suggested, such as a trap for reactive oxygen species [5,6]. Telomeres are composed of non-coding repetitive tandem repeats of (TTAGGG)n in humans and the other vertebrates, and (TTTAGGG)n in most plants. During human aging, telomeres in most somatic cells are shortened at each cell division and it is generally assumed that when telomeres reach a critical length, cells enter a senescent state and cell division ceases [7,8]. However, most human individuals do not reach this critical telomere length brink during their life course [8,9], e.g., the mean leukocyte telomere length (LTL) in newborns is 9.5 kb [10] whereas a length of ~5 kb was defined as the ‘telomeric brink’, which denotes a high risk of imminent death, but only 0.78% of people younger than 90 years display an LTL ≤ 5 kb [9]. So it is obvious, that the link between shortened telomeres and human longevity is more complex than mere reaching the critical telomere length. For instance, age-dependent telomere shortening might alter gene expression in sub-telomeric regions (telomere position effect, TPE) or double strand DNA breaks in telomeres might be inefficiently repaired and initiate cell senescence [11,12]. Furthermore, it has been suggested that even a single critically short telomere in a cell can induce cellular senescence, which potentially contributes to organismal senescence [13,14]. In humans, five short telomeres were reported to predict the onset of cell senescence [15].
Although the principles of protection and replication of telomeres are conserved and point to common evolutionary roots of eukaryotes, their implications for cell and organism survival, senescence, and aging are not shared among kingdoms. In particular, plants show specific features of their growth and development, which lead to confusion of terms like lifespan or aging as commonly used and understood in animals. First, a plant’s body plan is not fully established during embryogenesis and all tissues and organs are formed from proliferating meristem cells throughout the adult life. Second, plant growth is modular. Individual modules of the body (branches, flowers, leaves) are dispensable for survival, and their functions can be replaced by tissues newly differentiated from indefinitely proliferating meristems. This results in the enormous developmental plasticity of plants. Moreover, the vegetative meristems can give rise to a new organism, which will be a somatic clone, genetically indistinguishable from the parental organism. Since these general aspects distinguishing plant from animal development and aging have been well-reviewed [16], we will focus here on a more detailed view of peculiarities of plant telomere biology, including its latest developments.
2. Telomerase Core Components
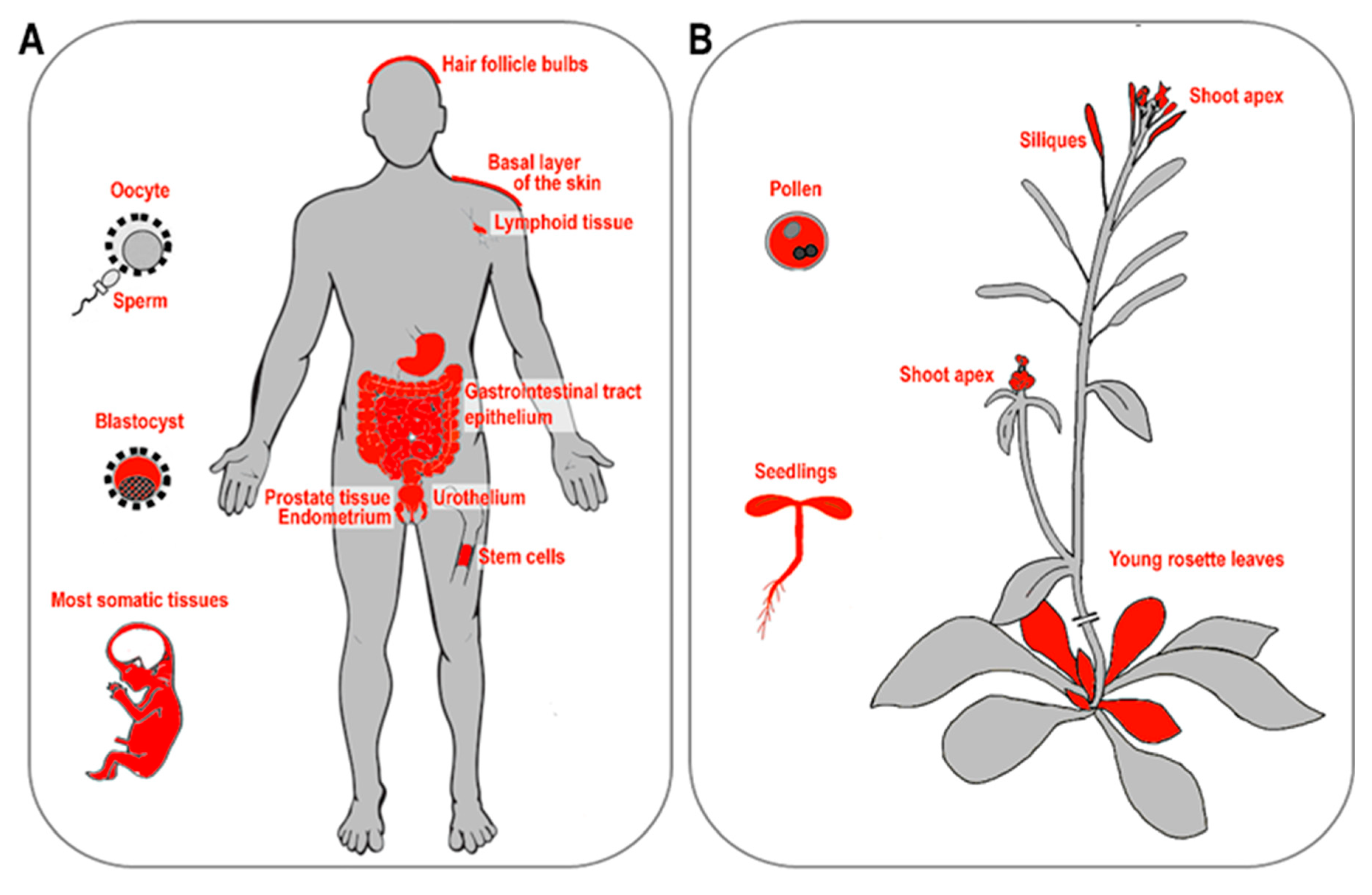
The requirement to finish the incomplete replication of chromosome ends is common for all organisms with linear chromosomes. In eukaryotes, this requirement is commonly solved by a specific nucleoprotein enzyme complex called telomerase, which is considered as an ancestral telomere maintenance system that solves the end-replication problem of linear chromosomes. In humans, telomerase activity is detected in all early developmental stages from oocytes through to blastocyst stage embryos, and increases progressively with advancing embryo stage. Telomerase reaches its highest level in morula and blastocyst stage embryos and then decreases in the inner cell mass stage. In human fetuses—when the embryonic period and organogenesis are finished—telomerase is expressed in tissue-specific stem cells. However, just after birth, telomerase activity in somatic cells is downregulated with the exception of dividing cells (e.g., proliferating cells, T-lymphocytes) [17,18] (Figure 1A).

Figure 1.
Telomerase activity in human and plant tissues. (A) During human embryonic development, high telomerase activity is detected in the blastocyst, but not in mature spermatozoa or oocytes. Highly active telomerase is detected in 16 to 20-week-old human fetuses in most somatic tissues with the exception of brain tissue [18,28]. In adults, low telomerase activity is detected in hair follicule bulbs [29], basal cells of crypt and villi or muconasal basal cells of the gastrointestinal tract, basal keratinocytes of the skin [30], lymphocytes, blood bone marrow, and stem cells [31,32,33], and urothelium [34]. High telomerase activity is detected in prostate tissues and endometrium [30,35]. (B) High telomerase activity is detected in plant pollen, seedling, young rosette leaves, and silliques [21,36,37,38,39]. Likewise, both apical meristems—shoot and root—show high telomerase activity [36,37,38]. Figures adopted from human and Arabidopsis eFP browsers [40].
As seen in mammals, telomeres in plants are maintained by telomerase [19]. Active telomerase is detected in organs and tissues containing highly dividing meristem cells such as seedlings, root tips, young and middle-age leaves, flowers, and floral buds [20,21]. In terminally differentiated tissues (stems, mature leaves), telomerase activity is suppressed (Figure 1B). In some groups of organisms (in particular insects), telomerase has been lost and replaced by telomere-specific retrotransposons (in Drosophila) or tandem arrays of satellite repeats elongated by a gene conversion mechanism (reviewed in References [22,23]). Based on a long-term systematic search, no telomerase-independent exception has been found among vertebrates or land plants despite the variability of telomere DNA observed in land plants [24,25,26,27]. Besides the telomerase-based mechanism of telomere elongation, alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT), which is based on homologous recombination (HR) and may become active upon the loss of telomerase was described in humans as well as in plants (see below).
In yeasts, animals, and plants, telomerase consists of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) protein subunit providing the catalytic activity, and the telomerase RNA (TR) subunit whose short region provides a template for reverse transcription [41,42]. Besides these two core subunits, the telomerase complex comprises several other accessory proteins with diverse roles in telomerase assembly, trafficking, localization, recruitment to telomeres, or the processivity of telomere synthesis [43,44]. During movement of the maturing human telomerase complex through the nucleolus to Cajal bodies and to the telomeres, the TERT catalytical subunit is associated with e.g., HSP90, p23, or pontin. Assembly of human TR, as well as other box C/D or H/ACA small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), is governed by conserved scaffold proteins: dyskerin, NHP2, NOP10, NAF1 in the nucleoplasm, where NAF1 is replaced by GAR1 before the hTR RNP complex reaches the nucleolus. Several orthologues of these conserved scaffold have been identified in plants, e.g., CBF5 (dyskerin), RuvBL1 (pontin), RuvBL2a (reptin), and NAF1. The nucleolar localization of these orthologues suggests potential conservation of the trafficking pathway during telomerase maturation ([45,46,47]; Schorova et al., submitted). Human and plant homologues of proteins associated either with the telomerase protein subunit TERT (Table 1) or the telomerase RNA subunit (Table 2) are listed below.

Table 1.
Comparative overview of proteins associated with the telomerase catalytic subunit TERT.

Table 2.
Comparative overview of proteins associated with the RNA component of telomerase.
Considerable homology in TERT sequences and domain organization exists among organisms, and this homology has frequently been used to identify novel TERTs in genomic or transcriptomic data (reviewed in Reference [125]). Human TERT, as well as the plant TERTs, can be split into the N-terminal part, the central catalytic reverse transcriptase (RT) motifs, and the C-terminal extension (CTE) which is highly conserved among vertebrates as well as among plants. The N-terminal part comprises regions of both low and high similarity, e.g., the structural domains TEN (telomerase essential N-terminal domain) or TRBD (RNA-binding domain). Although most eukaryotes, including humans, harbor a single TERT gene, in the allotetraploid Nicotiana tabacum plant, three transcribed variants of the TERT gene were described, which were inherited from its diploid progenitor species [126].
Compared to the conserved structure of the TERT subunit, TRs show high sequence diversity among more distant organisms, as exemplified by the length differences of TRs in protozoa (159 nt in ciliate Tetrahymena, 2200 nt in Plasmodium), zebrafish (317 nt), mouse (397 nt), human (451 nt), and budding yeasts (1160 nt). Even within yeasts, the homology among TRs is rather low and their lengths range from 930 to more than 2000 nt [42,113,127,128,129,130,131,132,133]. Analogous variance of TR within the plant kingdom is still questionable, since only putative TRs have been predicted in A. thaliana so far [56].
However, several secondary structure motifs in TRs which are essential for telomerase activity are conserved in fungi and animals. Starting from the 5′-end of TR, these include a core-enclosing helix (CEH) formed by pairing the 5’-terminus of TR with the complementary internal TR region, a template boundary element (TBE)—a hairpin defining the end of the sequence recognized by TERT as a template, the template sequence itself, and a pseudoknot [133]. Except for the template sequence, none of these structural elements has been recognized in TER1 in Arabidopsis thaliana, which is the only reported candidate TR among plants so far [56]. With respect to the above-mentioned sequence diversity of plant telomere repeats, it will be interesting to learn whether and how these evolutionary changes are reflected by the corresponding TR subunits. For example, when assuming the phylogeny of Asparagales plants, telomeres switched first from Arabidopsis-like repeats (TTTAGGG)n to human-like repeats (TTAGGG)n in the divergence of the Iridaceae family, and this repeat survived all downstream speciation events until the divergence of the genus Allium, when the human-type repeat was replaced with the unusual (CTCGGTTATGGG)n repeat [24,134,135]. The molecular basis underlying these evolutionary switches in telomere DNA sequences should be sought primarily in the corresponding TRs. We can consider the following possible scenarios. (i) TR remained essentially the same across Asparagales phylogeny and the observed switches in telomere synthesis occurred either as a result of mutations in the template region of TR or in its vicinity, which could have changed the boundaries of the region used as a template, (ii) a different RNA molecule took over the TR function. Experiments are in progress in our laboratory to provide a clear answer to this question.
3. Telomere Chromatin Composition
While the end-replication problem of telomeres is most commonly solved by telomerase, the other essential function of telomeres—their end-protection role (i.e., to distinguish natural chromosome ends from DNA breaks, and to eliminate unwanted repair events at telomeres)—is performed by other proteins associated with telomeres. In humans, these include proteins directly binding telomere DNA either in its double strand part (TRF1, TRF2) or at the single strand overhang (POT1). The other proteins bind telomeres via protein-protein interactions with these proteins (RAP1, TIN2, TPP1), which together form a complex termed shelterin [136,137]. Shelterin components and their interaction partners can inhibit the DNA damage response [138,139,140,141]. In addition to the end-protective function, shelterin components also play other roles as, e.g., the recruitment of telomerase to telomeres, facilitating replication fork movement through telomeres, or formation of telomere loops (t-loops) [142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149]. In particular, t-loops exist as a “closed-state” telomere conformation both in mammalians and plants [146,150]. While t-loop is considered as a structure inaccessible to telomerase, it may provide a template for telomerase-independent ALT (see below).
The composition of shelterin-like complexes shows differences in individual components among vertebrates, while the overall functions remain conserved. Human proteins associated with double and single strand telomeric DNA, together with their plant orthologues, are listed in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.

Table 3.
Comparative overview of proteins associated with telomeric double strand DNA (dsDNA).

Table 4.
Comparative overview of proteins associated with telomeric single strand (ssDNA).
In plants, knowledge of a shelterin-like complex is incomplete. The only proteins with confirmed in vivo telomere localization and function are members of the single-myb-histone family, telomere repeat binding (TRB) proteins, which have been characterised in Arabidopsis thaliana [66,82,151] and their orthologues were identified in other plants ([152]; Schorova et al., submitted). TRB proteins bind specifically telomeric double strand DNA through their myb-like domain of a telobox type [153,154], as well as the human core components of shelterin—TRF1 and TRF2 proteins. While the myb-like domain in TRF1 and TRF2 is localized at the C-terminus, that of TRB proteins occupies the N-terminus. Additionally, TRB proteins contain the centrally located histone-like domain (H1/5) involved in DNA sequence-unspecific DNA-protein interactions, multimerization, and interaction with POT1b (one of the plant POT1 paralogues) [65,151]. This plant-specific protein-domain organization has not been described in animals. TRB proteins bind telomeric DNA in vitro and in vivo, localize to the telomeres in vivo, interact directly with the telomerase TERT subunit, and the deregulation of telomeres was observed in mutant plants [66,68].
TRB proteins are not only components of the terminal complex associated with telomeres/telomerase, but they are also associated in vivo with promoters of translation machinery genes, which mostly contain a short telomeric sequence [67]. It seems that TRB proteins serve as epigenetic regulators that potentially affect the transcription status of thousands of genes by playing a role of recruiting subunits of multiple epigenetically active multi-protein complexes [68,69,70,71,155,156]. These findings are consistent with the observations from yeast or mammals where telomeric proteins (e.g., TRF1, TRF2, and RAP1) are able to localize outside telomeric regions and regulate the transcription of genes involved in metabolism, immunity, and differentiation [157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164].
Surprisingly, no functions in telomere maintenance were found in Arabidopsis orthologues of mammalian TRF proteins (TRFL proteins) where a myb-domain of the telobox type is located C-terminally as in human TRF1 and TRF2 [165]. However, a recent study revealed protein-protein interactions between TRFL2 and TRP1, members of the TRFL family, and TERT from A. thaliana [66,69]. Plant TRFL2 and TRP1 proteins interact with armadillo/β-catenin-like repeat-containing protein (ARM). ARM directly interacts with plant TERT [70] and might be involved in translation initiation or in regulation of recombination-related genes [69]. Moreover, ARM interacts with the chromatin remodeling protein CHR19 (Table 1). ARM, TRB1, POT1a, and CHR19 (but none of the TRFL proteins) were found among proteins that co-purified with Arabidopsis TERT using tandem affinity purification [84]. Association of TERT with proteins that are not essential for telomere maintenance may reflect possible non-telomeric functions of telomerase.
A dual function for telomerase, both telomeric and non-telomeric, is not unique to plants, as mammalian telomerase is involved not only in elongation of telomeres but also non-telomeric activities have been described, including involvement in regulating cellular processes such as apoptosis, proliferation, and cell cycle progression ([166]; reviewed in Reference [167]). Human telomerase and human ARM proteins play a role in the Wnt/APC/β-catenin signaling pathway [168]. A putative human homologue of ARM, ARMC6, interacts with the shelterin protein TRF2 and immuno-precipitates telomerase activity [69].
An additional telomere maintenance component is—somewhat paradoxically—Ku70/80 heterodimer, a DNA repair factor with a high affinity for DNA ends, that plays essential roles in the maintenance of genome integrity in both human and plants cells. In human cells, Ku70/80 heterodimer interacts with the RNA component of telomerase hTR [120] and with catalytic subunit hTERT [94]. In plants, Ku proteins, as well POT1b protein, are associated with TER2. This is a candidate plant TR that is not required for telomere maintenance in A. thaliana [56]. Ku70/80 is, however, important for protection of blunt-ended telomeres and for suppression of ALT (see below).
An integrative updated schematic view based on these and previous studies is depicted in Figure 2. It is obvious that the number of plant telomere-associated and telomerase-associated orthologues (where they exist) is larger in comparison to their mammalian counterparts. The phenomenon of the multiplication of genes of the same family is not surprising, since in many plant families, polyploidy (i.e., whole genome duplication) resulting in retention of multiple gene paralogues may lead to their sub-functionalization, neo-functionalization, or partial or full redundancy [169,170]. In association with the previously mentioned evolutionary divergence of plant telomere DNA repeats toward human-like repeats or unusual telomeric repeats, it will be of interest to learn whether pre-existing components of plant shelterin-like complexes have adapted to the change in DNA sequence (this will be particularly interesting in proteins directly recognizing DNA sequences, such as the TRB or POT1 proteins), or whether some other proteins have replaced their function.
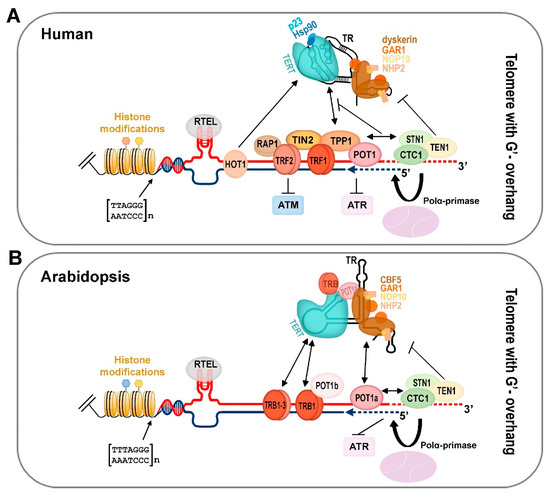
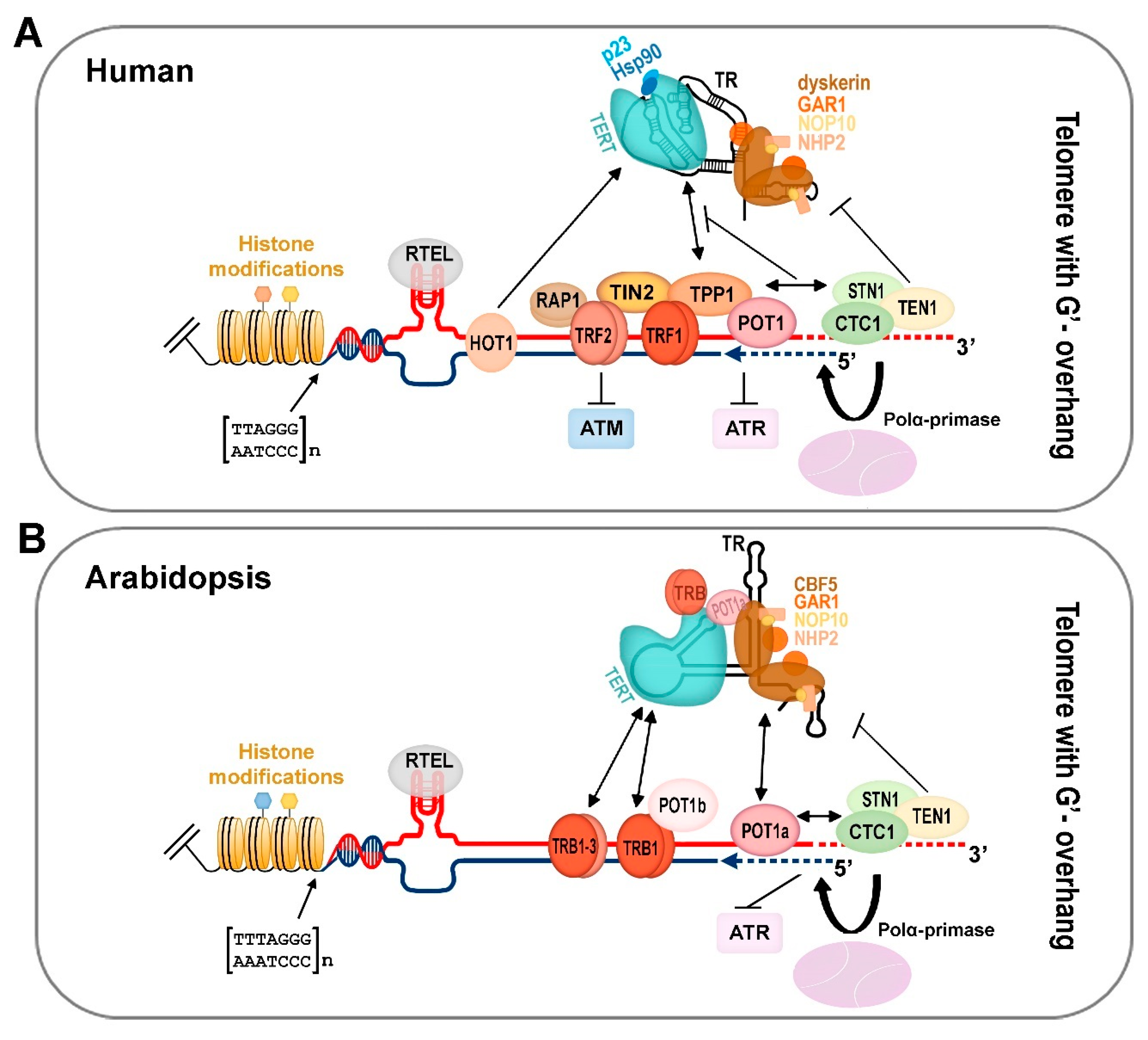
Figure 2.
An integrative schematic view of the human and plant terminal telomeric complex. (A) Human active telomerase is associated with Hsp90 and p23 chaperones as well as with TR associated conserved scaffold proteins of box H/ACA small nucleolar RNAs (dyskerin, NHP2, NOP10, GAR1). Mammalian shelterin proteins (TRF1/2, RAP1, TIN2, TPP1, and POT1) modulate access to the telomerase complex and the ATR/ATM-dependent DNA damage response pathway. The CST complex (CTC1-STN1-TEN1) affects telomerase and DNA polymerase α recruitment to the chromosomal termini, and, thus, coordinates G-overhang extension by telomerase with fill-in synthesis of the complementary C-strand (blue dashed line). G-quadruplexes, D-loops, and t-loops during telomere replication are resolved by RTEL helicase. HOT1 directly binds double strand telomere repeats and associates with the active telomerase. Telomere nucleosomes show a shorter periodicity than that in the other parts of chromosomes. For human telomere histone modifications, see Figure 3. (B) Arabidopsis telomerase is associated with TRB proteins as well as with POT1a that interacts with the dyskerin orthologue CBF5. Plants possess all orthologue proteins of conserved scaffold box H/ACA of small nucleolar RNAs (CBF5, GAR1, NOP10, NHP2). Moreover, TRB proteins interact with the telomeric sequence due to the same myb-like binding domain as that in mammalian TRF1/2. TRB proteins interact with TERT and POT1b, and, when localized at chromosomal ends, they are eligible to function as components of the plant shelterin complex. An evolutionarily conserved CST complex is suggested to coordinate the unique requirements for efficient replication of telomeric DNA in plants as well as in other organisms. In addition, plant RTEL contributes to telomere homeostasis. For the sake of clarity, only the situation in telomere with 3′ overhang is depicted. For plant telomere histone modifications, see Figure 3.
Besides the shelterin complex in mammals and its emerging equivalents in plants, there is yet another complex termed CST (CTC1-STN1-TEN1), which is involved in telomere maintenance. This tripartite complex binds the 3′-overhang of the G-rich strand of telomeric DNA and its function in telomere maintenance is conserved in both mammals and plants, and a similar complex exists also in yeast (with Cdc13 instead of CTC1 subunit) [171]. Recently, the roles of individual components of the human CST complex in telomere maintenance were elucidated: while CTC1-STN1 limits telomerase action to prevent G-overhang over-extension, TEN1 is essential for CST function in C-strand fill-in synthesis due to its stabilizing effect on binding the whole CST complex to telomeres and DNA polymerase α engagement in telomere synthesis [172,173]. CST functions, at least in humans, are not limited only to telomeres. CST is also required to avoid replication problem at G-rich sites throughout the genome, likely resolving replication fork stalling [174].
In addition to the telomere-specific proteins, the major part of telomeres is assembled into the nucleosomal chromatin structure which shows a shorter nucleosome periodicity (spacing) than that in the other parts of the chromosomes of the same organism [175,176,177,178,179]. Since shorter telomeres in cultured human cells show a lower nucleosome density than that in cells with longer telomeres, a close relationship was hypothesized between histone density, heterochromatin protein associations, telomere length, and TPE [180]. Interestingly, this feature of telomeric chromatin is conserved at least in vertebrates and plants, and may reflect the specific columnar structure of telomeric chromatin with stacked nucleosomes and weak determination of nucleosome positions by telomeric DNA sequence [181].
4. Telomere Epigenetics
As chromatin structures, telomeres are natural targets for epigenetic modifications. At the DNA level, methylation at carbon 5 of cytosine represents the dominant mark in eukaryotic cells. Methylated cytosines (mCs) are generally enriched in heterochromatic regions of the genome and silenced promoters. Important differences in the sequence contexts, in which mCs are located, exist between animals and plants. In mammalian cells, they are predominantly located in CG doublet motifs, with the symmetry of the sequence crucial for the maintenance of the methylation pattern during DNA replication (reviewed in Reference [199]). A fraction of mCs in non-CG contexts was found in human embryonic cells. This fraction disappears after differentiation and is restored in induced pluripotent stem cells, which shows involvement of distinct methylation patterns in the regulation of gene expression [200]. Also in plants, cytosines in the CG motif are most frequently methylated, but mCs are also commonly placed in non-CG sequences, symmetrical CHG triplets (H=C or A or T), or non-symmetrical CHH motifs (reviewed in Reference [201]). In telomeres, cytosines in non-symmetrical sequence contexts are present in the telomeric C-rich strand, i.e., in CCCTAA repeats in animals and CCCTAAA repeats in plants. Using shotgun bisulfite genomic sequencing, mCs were detected in A. thaliana telomeric repeats with the inner cytosine most frequently methylated [202]. This pattern was confirmed by an independent approach, with high reliability at least in the proximal part of the telomere [203,204], and methylated telomeric cytosines were detected in cultured Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) cells [205] and other plants [206]. Disruption of telomere homeostasis as a consequence of decreased genomic DNA methylation was observed in A. thaliana [203,207] but not in tobacco cells [205], which shows differences in the involvement of DNA methylation in regulation of telomere homeostasis between these model plants (for a more detailed review see Reference [208]).
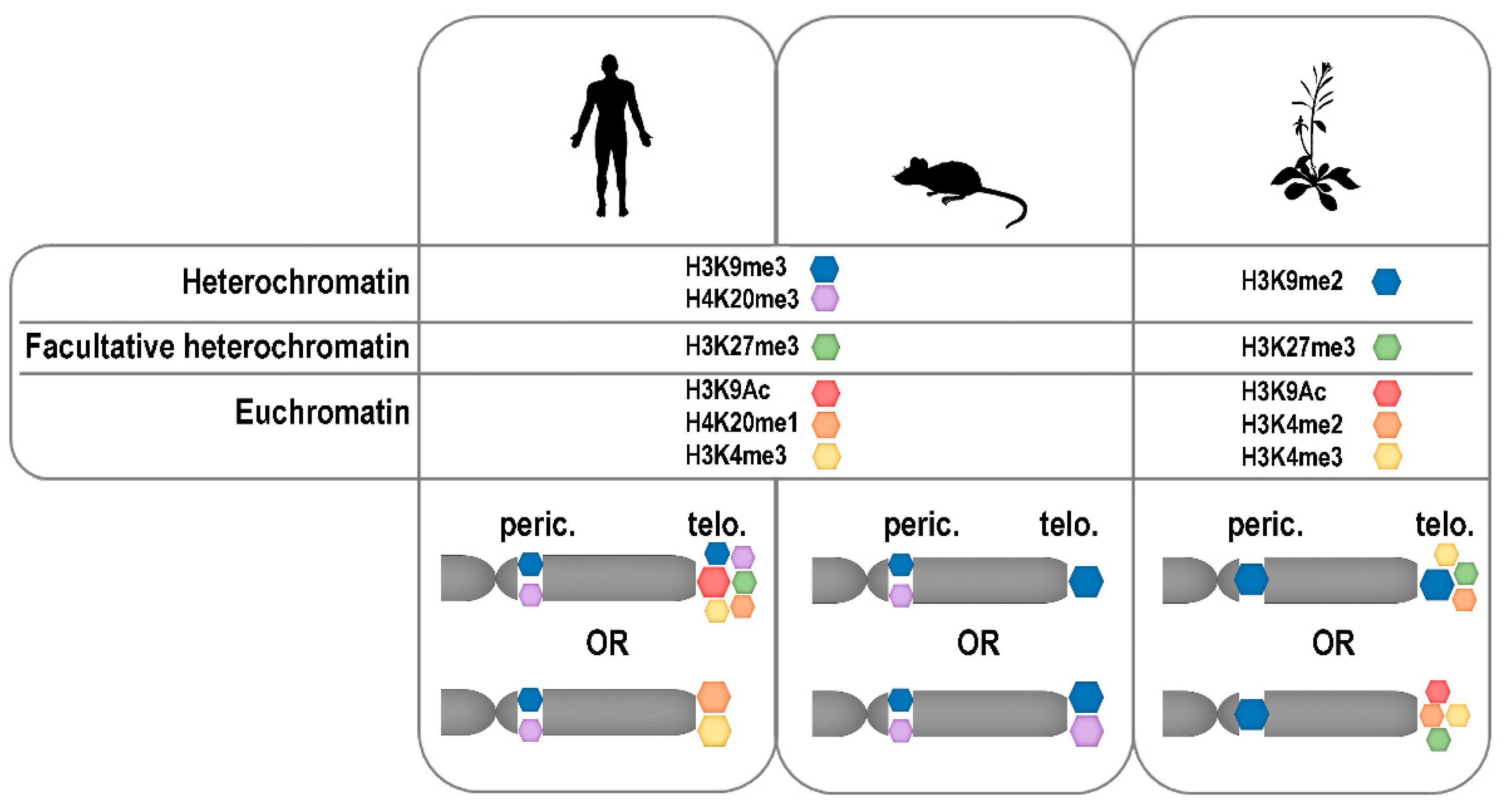
Telomeres formed by mini-satellite repeats were traditionally considered as heterochromatic regions, and, thus, associated with heterochromatin-specific histone marks. Certain differences in histone modifications in heterochromatin have been described between animals and plants. In animals, constitutive heterochromatin is defined by the presence of H3K9me3 (trimethylation of lysine 9 of histone H3) (reviewed in Reference [209]) while in plants, this mark decorates silenced euchromatic genes, and constitutive heterochromatin is associated with H3K9me2 modification [210]. Facultative heterochromatin is enriched in H3K27me3 in cells of representatives of both kingdoms. In agreement with the hypothesis of the heterochromatic character of telomeres, the importance of heterochromatin-specific epigenetic marks for telomere maintenance and genome stability was demonstrated in numerous studies using human and mouse cells as models (reviewed in Reference [211]). On the other hand, data showing a low level of heterochromatin-specific modifications and an abundance of active marks on human telomeric histones have been presented [212,213,214], which shows certain dynamics of the human telomeric chromatin structure. Based on these and other reports, distinct differences exist in telomeric chromatin composition between the most important mammalian models, human and mouse cells, because H3K9me3 density and HP1 enrichment were significantly higher in mouse compared to humans [215,216]. Nevertheless, according to a study utilizing quantitative locus purification [217] the heterochromatic histone modification H4K20me3 is underrepresented at mouse telomeres even though it was previously detected by others at mouse [218,219] and also human [220] telomeres in analyses based on chromatin immuno-precipitation. Further research is necessary to draw final conclusions on the epigenetic nature of mammalian telomeres, especially considering other factors mentioned below.
Plant telomeric chromatin was shown to be associated with both heterochromatin-specific H3K9me2 and euchromatic H3K4me3 marks, with the latter less abundant [204,206,221]. Therefore, the plant telomeric chromatin exhibits a dual epigenetic character. Identification of the H3K27me3 modification, which is typical for facultative heterochromatin, in telomeric histones of A. thaliana [221,222] and N. tabacum [206] was rather surprising. However, it correlates with its presence at human telomeres [215], and with the recent observation that polycomb repressor complex 2-dependent loading of H3K27me3 at human telomeres is essential for the proper establishment of H3K9me3 and H4K20me3 modifications [220]. Nevertheless, H3K27me3 was not detected at mouse telomeres [217]. Thus, although significantly fewer results are available on the epigenetics of telomeric chromatin in plants compared to mammals, interesting similarities as well as differences have already been described and hopefully others will be elucidated based on future studies using different model organisms, including plants with non-canonical telomere sequences [24,25,27,134].
When discussing telomeric chromatin, it is necessary to mention that analysis of epigenetic modifications may be complicated by the presence of non-terminally located telomeric repeats forming interstitial telomeric sequences (ITSs). ITSs are relatively abundant in subtelomeric, pericentromeric, and centromeric regions of most eukaryotic organisms and represent fragile parts of chromosomes, which are prone to rearrangements and recombinations. The detailed compositions of telomeres and ITSs are different. In contrast to telomeres consisting of long tracts of perfect telomeric repeats, ITSs are often degenerated and/or disrupted by non-telomeric sequences. However, ITSs may still contribute to the telomere-specific signal in epigenetic studies, mainly those based on hybridization of membrane-bound DNA. Frequently-used genome-wide sequencing analyses (ChIP-seq and bisulfite sequencing) do not completely solve this problem because telomeres, like other tandem repeats, are difficult to analyze, and even direct analysis of respective read counts (i.e., those comprising perfect telomeric repeats versus those formed by degenerated repeats and non-telomeric sequences) may be ambiguous due to the non-linearity of PCR amplification of repetitive sequences [223]. Both mammalian and plant telomeres are transcribed to long non-coding RNA called TERRA [204,224] and this transcriptional potency could reflect the relatively lower level of compactness of telomeric chromatin compared with heterochromatin. The apparent discrepancy between the association of heterochromatic marks with telomeric histones and the transcriptional activity of telomeres is weakened by the facts that a mechanistic relationship between TERRA transcription and loading of heterochromatic modifications to human telomeres has been described [220], and that in Arabidopsis a certain—maybe dominant—fraction of TERRA is transcribed from ITSs [204], which are purely heterochromatic [225].
At this stage of knowledge, it is difficult or even impossible to formulate any general conclusion on the epigenetic nature of telomeric chromatin (Figure 3). Without any doubt, the specific structure of telomeres is crucial for the maintenance of genome integrity. Telomeres are rigid enough to prevent repair and recombination at chromosome ends and to restrict telomere accessibility for telomerase, but open enough to be transcribed and, at least in a specific time window of the cell cycle, accessible to telomerase. Moreover, in disagreements about telomeric “heterochromatin” or “euchromatin”, contribution of non-histone players, mainly shelterin proteins, to the telomeric chromatin compaction should be reflected (reviewed in Reference [226]). Why not admit, that telomeric chromatin is so specific that it does not fit into the existing criteria and that these should be widened? This suggestion is strengthened by the finding that other non-genic parts of the human genome, originally thought to be uniformly heterochromatic, are associated with different combinations of histone marks [213]. It is well possible that the epigenetic state of telomeres is more dynamic than previously thought and shows tissue-specific, cell-cycle specific, and developmental stage-specific changes. This would not only explain the diverse results of the above studies, but would be consistent with our current understanding of the epigenetics of other chromosome regions.
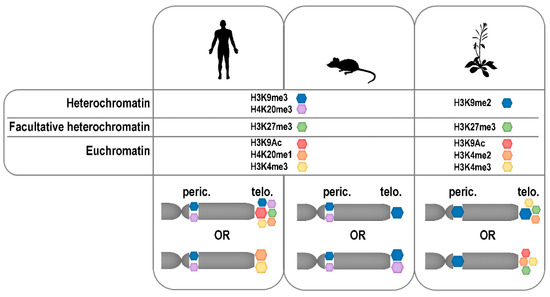
Figure 3.
Modifications of mammalian and plant telomere (telo.) and pericentromere (peric.) histones. The relative enrichments of selected epigenetic modifications of telomeric and pericentromeric histones in human, mouse and Arabidopsis are schematically depicted according to data presented in References [204,212,213,215,217,218,219,220,221,222,225].
5. Telomere 3′-Overhangs, Blunt Ends, and Loops
Telomeres in vertebrates, in particular humans, possess 3′-overhangs at both chromosome ends. These overhangs are of different sizes on lagging versus leading strands [227]. In human telomeres a G-overhang is prevalent whose length varies from several tens to 280 nt [228,229,230]. Likewise, a 5′ C-rich overhang is present at the telomeres of human chromosomes, being far more prevalent in tumor cells using ALT (see below) [231]. This is not the case in Arabidopsis thaliana, Silene latifolia, and other angiosperm plants, which lack telomere overhangs or possess only short 1–3 nt overhangs at about half of their telomeres [232,233]. The telomere whose 3′- end is being synthesized in a given cell cycle by leading strand synthesis remains blunt-ended likely due to protection against end-processing by a specific exonuclease. This protection is dependent on the Ku70/80 heterodimer [233]. The role of the Ku complex in plant telomere protection was also suggested by our earlier studies, which indicated Ku as an interaction partner of AtTRP1, one of the TRF-like proteins in A. thaliana ([82]; see Reference [155] for a review). An analogous interaction between the shelterin components TRF2 and Ku70 was observed earlier in human cells [77]. Due to the asymmetry (non-equivalence) of plant telomeres, a different set of proteins may protect the telomere whose 3′-end serves as a template in “incomplete” lagging strand synthesis and can be elongated by telomerase. Protection of blunt-ended telomeres in Arabidopsis by the Ku70/80 complex seems paradoxical considering the presumed end-protective function of telomeres on one hand, and a key role of the Ku complex in non-homologous end-joining repair of double strand DNA breaks on the other hand. A possible solution of this enigma was suggested recently by a study which indicated different binding modes of the Ku complex to dsDNA breaks and to telomeres. Both functions were dissected using Ku mutants with impaired ability to translocate along DNA. While Ku sliding is not required for its association with plant telomeres, it is essential for its involvement in the non-homologous end joining pathway of DNA repair [101]. The presence of blunt-ended telomeres is, however, not common to all plants. For example, in the moss Physcomitrella patens, both telomeres of a chromosome possess overhangs and, correspondingly, lack of the Ku complex components shows no effect on telomere maintenance or end protection [234]. The Ku70/80 complex was also reported to be a negative regulator of telomerase function in Arabidopsis [99]. In addition to telomere elongation by telomerase, an extension of telomere G-strand overhangs was observed in Ku mutants, which suggests a role of Ku70/80 in C-rich telomeric strand maintenance [235].
Besides telomerase, eukaryotic cells can also utilize a back-up mechanism of telomere maintenance—ALT—which is based on homologous recombination (HR) [236]. This telomerase-independent mechanism is activated in a number of human tumors, in human cells immortalized in culture, and also in normal somatic tissues [237]. In plants, the ALT mechanism is activated in mutants with telomerase dysfunction and possibly also during the earliest stages of normal plant development [238]. ALT relies on the formation of terminal telomeric loops (t-loops) [146], which parallels the first steps of HR. The eventual resolution of these t-loops and aberrant HR at telomeres generates not only telomeres of highly heterogeneous lengths but also extrachromosomal t-circles, which are the known hallmarks of ALT. In mutant plants that are deficient for components of the Ku70/80 complex, induction of t-circle formation was observed at telomeres but not at other regions rich in DNA repeats. Despite ongoing terminal deletions arising from excision of t-circles in mutant plants, the telomeres remain functional, which indicates an efficient telomere healing by telomerase [239].
Another interesting protein connecting telomeric loops and circles with DNA recombination and telomere replication is RTEL1. This was originally described in Caenorhabditis elegans as a functional homologue of the yeast Srs2 protein, which removes Rad51 from single strand DNA. Therefore, it prevents the homology search step of HR and helps to protect the cell from inappropriate HR (for review, see Reference [240]). Furthermore, in C. elegans, the RTEL1 helicase suppresses inappropriate recombination events by promoting disassembly of D-loop recombination intermediates, and the loss of its function results in increased genome instability [241]. In addition to its regulatory role in HR, RTEL1 acts in telomere maintenance in mammalian telomerase-positive cells [242]. This function was explained by the function of RTEL1 in opening t-loops, which blocked inappropriate excision of large telomere regions—the process known as telomere rapid deletion. To promote this t-loop unwinding, RTEL1 is recruited to telomeres in the S-phase by the telomeric protein TRF2 [186].
In addition to its role in t-loop stability, mouse RTEL1 can dissolve G4-DNA structures, which otherwise block replication fork progression and the extension of telomeres by telomerase [243]. Importantly, the role of RTEL1 in telomere dynamics was clearly confirmed by the finding that its mutation is causative for Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome, which is a severe form of dyskeratosis congenita, predisposing to bone-marrow failure and cancer. This disease is characterised by short telomeres and genome instability [244,245,246]. A recent report revealed that reversed replication forks occurring in telomeres of RTEL1-deficient cells is due to compromised telomere replication aberrantly recruiting telomerase, which prevents the restart of reversed replication forks at telomeres and leads to critically short telomeres [247]. In this context, telomerase paradoxically contributes to telomere shortening by stabilizing stalled replication forks at chromosome ends.
In addition, the A. thaliana RTEL1 homolog suppresses HR and is involved in processing DNA replication intermediates and interstrand and intrastrand DNA cross-links. Deficiency of the Arabidopsis RTEL1 triggers a SOG1-dependent replication checkpoint in response to DNA crosslinks [248]. Similarly to the situation in mammals, the Arabidopsis RTEL1 contributes to telomere homeostasis. The concurrent loss of RTEL1 and TERT accelerates telomere shortening, which results in a developmental arrest after four generations [249] compared to 10 generations in single-mutant tert plants [250]. This observation indicates a role of RTEL1 in ALT, which otherwise partially compensates for the loss of TERT [238]. In agreement with these results, it was recently demonstrated that RAD51-dependent homologous recombination participates in ALT in A. thaliana [251]. This is not surprising when considering the essential role of RAD51 in HR, and HR as a major molecular mechanism of ALT. However, the authors further showed that this role of RAD51 is dependent on RTEL1 helicase, which possibly functions in dissolution of the D-loop after telomere replication. In P. patens, RTEL1 has been found among genes, which are up-regulated after γ-irradiation. RTEL1 knockout resulted in a severe growth deficiency, which was independent of the presence of bleomycin [252], and the authors hypothesized that this growth phenotype might be the result of telomere deficiency. Thus, the functions of RTEL1 seem widely conserved. In conclusion, the requirement for RTEL1 in multiple pathways to preserve plant genome stability can be explained by its putative role in the destabilization of DNA loop structures such as D-loops and t-loops, which aligns with previous studies in mammalian systems.
6. Cellular Aging and the Immortal DNA Strand Hypothesis
Cellular aging is characterized by progressive loss of physiological integrity that leads to impaired function and genomic instability and ultimately to a functional decline at the tissue and organ level. Telomere attrition during cell aging is classified as one of the several major hallmarks of aging—together with, e.g., genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, or altered intercellular communication [7]. In Metazoa, there is no universal pattern of telomere erosion [253], and, in some animals, the progressive telomere shortening with age has not been observed [254]. Nevertheless, telomere length is typically inversely correlated with lifespan, while telomerase expression co-evolved with body size [255]. A connection between cellular aging and replicative telomere shortening is widely accepted and experimentally validated in both humans and plants. Importantly, under normal conditions (in wild type plants) this type of cellular aging is prevented by telomerase activity in dividing cells [20,21,38]. The associations between telomere length and age-related disease and mortality in humans have been proven in several studies (reviewed in References [8,256,257]). However, telomere length of humans is not a determinant of aging but rather a marker able to explain life expectancy and disease risk.
In animals, the distribution of cellular age varies among tissues and cell compartments, including progenitor cell compartments, depending on the influx of stem cells and the dynamics of self-renewal and differentiation of progenitor cells. In particular, the mode of cell division of progenitor cells may be: (i) symmetric self-renewal, in which progenitor cell division results in two daughter progenitor cells (one generation older) remaining in the compartment, (ii) symmetric differentiation, resulting in two differentiated cells which leave the progenitor cell compartment, or (iii) asymmetric division resulting in one progenitor and one differentiated cell. Importantly, cellular age distributions between healthy and cancerous tissues may inform dynamic changes within the hierarchical tissue structure, i.e., an acquired increased self-renewal capacity in certain tumors [258]. In this connection, it is of interest to mention the hypothesis of the immortal DNA strand [259]. This hypothesis proposes that adult stem cells segregate their template and newly synthesized DNA strands non-randomly, preferentially retaining parental DNA strands in each division. This way, adult stem cells pass mutations resulting from replication errors onto non-stem cell daughter cells that differentiate and terminate division. Adult stem cells could thus reduce the accumulation of mutations and the associated deterioration of gene functions with each cell cycle. Moreover, this strategy would also slow down replicative telomere shortening. Thus, two major factors of cellular and organismal aging could be substantially limited if immortal DNA strand segregation operates in progenitor cells. Several studies have supported this hypothesis up to now. For example, using sequential pulses of halogenated thymidine analogues, high frequencies of segregation of older and younger template strands during proliferative expansion of mouse muscle stem cells was observed [260]. Template strand co-segregation was strongly associated with asymmetric cell divisions yielding daughters with divergent fates. Daughter cells inheriting the older templates retained a more immature phenotype, whereas daughters inheriting the newer templates acquired a more differentiated phenotype. It will be of interest to learn if the validity of this hypothesis is more general, and specifically to elucidate the molecular mechanism of non-random DNA segregation in asymmetric cell division. This principle may also be functional in meristem cell division and differentiation. While replicative telomere shortening is efficiently counteracted by telomerase in wild type plants (see above), reduction of accumulation of mutations would be extremely beneficial when considering e.g., trees sustaining their growth for centuries. Low telomere loss per plant generation has been found in telomerase-deficient Arabidopsis mutants [250], which indicates a possible involvement of non-random DNA strand segregation in addition to ALT [238]. Unfortunately, the application of sequential pulse labeling in planta is technically too demanding, and any direct evidence for the immortal DNA strand hypothesis is, thus, missing in plants.
7. Concluding Remarks
Currently available data show remarkably conserved principles in telomere biology across eukaryotes, which is consistent with an association of telomere and telomerase emergence with the earliest steps of their evolution. At the same time, however, a number of specific features and exceptions cannot be ignored since they point to limitations of our wider understanding of these principles. Among a number of open questions to be answered, elucidation of the structure of telomeric chromatin (telochromatin), including its epigenetic and higher-order dynamics, with high spatial and temporal resolution is needed in various model systems. Furthermore, the biological relevance of non-canonical structures formed by telomeric DNA should be addressed mainly under in vivo conditions. Such studies are timely due to recent fast progress in adequate technical tools, including e.g., super-resolution and cryo-electron microscopy.
Studies of repair processes at telomeres and of telomerase regulation belong to the hot topics in this field, since this knowledge can clearly be applied to promote protection of genome stability. In this respect, plants are indispensable due to the natural telomerase-competent character of their cells which allows us to examine mechanisms of repression and activation of telomerase in association with proliferation, differentiation, and dedifferentiation of plant cells. This knowledge is essential for understanding carcinogenesis and is potentially applicable to tumor therapy and cell rejuvenation.
Author Contributions
P.P.S., M.F. and J.F. contributed to this paper with a literature review, drafting the paper, and approval of the final version.
Funding
This work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation (projects 16-01137S and 17-09644S), by the project SYMBIT, reg. number: CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000477 financed by the ERDF, and by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under the projects CEITEC 2020 (LQ1601) and INTER-COST (LTC17077).
Acknowledgments
We thank to Ladislav Dokládal and Ronald Hancock for reviewing and discussing the MS prior to submission.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Olovnikov, A.M. Principle of marginotomy in template synthesis of polynucleotides. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1971, 201, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, H.J. The remaking of chromosomes. Collect. Net. 1938, 13, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- McClintock, B. The fusion of broken chromosome ends of sister half-chromatids following chromatid breakage at meiotic anaphases. Mo. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Bull. 1938, 290, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- McClintock, B. The stability of broken ends of chromosomes in Zea mays. Genetics 1941, 26, 234–282. [Google Scholar]
- Von Zglinicki, T. Oxidative stress shortens telomeres. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzl, F.; Cornils, J.S.; Smith, S.; Moodley, Y.; Ruf, T. Telomere dynamics in free-living edible dormice (Glis glis): The impact of hibernation and food supply. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.J.P. Questioning causal involvement of telomeres in aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenstrup, T.; Kark, J.D.; Verhulst, S.; Thinggaard, M.; Hjelmborg, J.V.B.; Dalgard, C.; Kyvik, K.O.; Christiansen, L.; Mangino, M.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Telomeres and the natural lifespan limit in humans. Aging US 2017, 9, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Factor-Litvak, P.; Susser, E.; Kezios, K.; McKeague, I.; Kark, J.D.; Hoffman, M.; Kimura, M.; Wapner, R.; Aviv, A. Leukocyte Telomere Length in Newborns: Implications for the Role of Telomeres in Human Disease. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, J.D.; Ludlow, A.T.; Batten, K.; Magdinier, F.; Stadler, G.; Wagner, K.R.; Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Telomere position effect: Regulation of gene expression with progressive telomere shortening over long distances. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2464–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorelli, S.; Passos, J.F. Telomeres and Cell Senescence—Size Matters Not. Ebiomedicine 2017, 21, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, P.; Luciano, P.; Runge, K.W.; Lisby, M.; Geli, V.; Gilson, E.; Teixeira, M.T. A two-step model for senescence triggered by a single critically short telomere. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemann, M.T.; Strong, M.A.; Hao, L.Y.; Greider, C.W. The shortest telomere, not average telomere length, is critical for cell viability and chromosome stability. Cell 2001, 107, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, Z.; Cesare, A.J.; Huschtscha, L.I.; Neumann, A.A.; Reddel, R.R. Five dysfunctional telomeres predict onset of senescence in human cells. Embo Rep. 2012, 13, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.M.; Riha, K. Telomeres, aging, and plants: From weeds to Methuselah—A mini-review. Gerontology 2011, 57, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsov, E.V. Telomerase and primary T cells: Biology and immortalization for adoptive immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.; Hiyama, E.; Grotzer, M.A. Telomere Maintenance as Therapeutic Target in Embryonal Tumours. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, J.; Kovarik, A.; Kralovics, R. Telomerase activity in plant cells. Febs Lett. 1996, 391, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, J.; Fulneckova, J.; Hulanova, M.; Berkova, K.; Riha, K.; Matyasek, R. Plant cells express telomerase activity upon transfer to callus culture, without extensively changing telomere lengths. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 260, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.S.; McKnight, T.D.; Shippen, D.E. Characterization and developmental patterns of telomerase expression in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14422–14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, J.; Sykorova, E.; Leitch, A.R. Telomeres in evolution and evolution of telomeres. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, E.J. Are Drosophila telomeres an exception or the rule? Genome Biol. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, P.; Peska, V.; Sitova, Z.; Fulneckova, J.; Dvorackova, M.; Gogela, R.; Sykorova, E.; Hapala, J.; Fajkus, J. Allium telomeres unmasked: The unusual telomeric sequence (CTCGGTTATGGG)(n) is synthesized by telomerase. Plant J. 2016, 85, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peska, V.; Fajkus, P.; Fojtova, M.; Dvorackova, M.; Hapala, J.; Dvoracek, V.; Polanska, P.; Leitch, A.R.; Sykorova, E.; Fajkus, J. Characterisation of an unusual telomere motif (TTTTTTAGGG)n in the plant Cestrum elegans (Solanaceae), a species with a large genome. Plant J. 2015, 82, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peska, V.; Sitova, Z.; Fajkus, P.; Fajkus, J. BAL31-NGS approach for identification of telomeres de novo in large genomes. Methods 2017, 114, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Cao, H.X.; Jovtchev, G.; Neumann, P.; Novak, P.; Fojtova, M.; Vu, G.T.H.; Macas, J.; Fajkus, J.; Schubert, I.; et al. Centromere and telomere sequence alterations reflect the rapid genome evolution within the carnivorous plant genus Genlisea. Plant J. 2015, 84, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, W.E.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Rainey, W.E.; Byrd, W.; Shay, J.W. Telomerase activity in human germline and embryonic tissues and cells. Dev. Genet. 1996, 18, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, R.D.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W.; Taylor, R.S. Telomerase activity concentrates in the mitotically active segments of human hair follicles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 108, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyama, E.; Hiyama, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Shay, J.W. Immunohistochemical detection of telomerase (hTERT) protein in human cancer tissues and a subset of cells in normal tissues. Neoplasia 2001, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyama, E.; Hiyama, K. Telomere and telomerase in stem cells. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyama, K.; Hirai, Y.; Kyoizumi, S.; Akiyama, M.; Hiyama, E.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Shay, J.W.; Ishioka, S.; Yamakido, M. Activation of Telomerase in Human-Lymphocytes and Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 3711–3715. [Google Scholar]
- Yui, J.; Chiu, C.P.; Lansdorp, P.M. Telomerase activity in candidate stem cells from fetal liver and adult bone marrow. Blood 1998, 91, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, H.; Kyo, S.; Kanaya, T.; Takakura, M.; Inoue, M.; Namiki, M. Expression of human telomerase subunits and correlation with telomerase activity in urothelial cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Kyo, S.; Takakura, M.; Kohama, T.; Inoue, M. Telomerase activity in human endometrium. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Jureckova, J.F.; Sykorova, E.; Hafidh, S.; Honys, D.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtova, M. Tissue-specific expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase gene variants in Nicotiana tabacum. Planta 2017, 245, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrocka, A.; Sykorova, E.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtova, M. Developmental silencing of the AtTERT gene is associated with increased H3K27me3 loading and maintenance of its euchromatic environment. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, K.; Fajkus, J.; Siroky, J.; Vyskot, B. Developmental control of telomere lengths and telomerase activity in plants. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachova, D.; Fojtova, M.; Dvorackova, M.; Mozgova, I.; Lermontova, I.; Peska, V.; Schubert, I.; Fajkus, J.; Sykorova, E. Structure-function relationships during transgenic telomerase expression in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 149, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.; Vinegar, B.; Nahal, H.; Ammar, R.; Wilson, G.V.; Provart, N.J. An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” Browser for Exploring and Analyzing Large-Scale Biological Data Sets. PLoS ONE 2007, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a Specific Telomere Terminal Transferase-Activity in Tetrahymena Extracts. Cell 1985, 43, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. A Telomeric Sequence in the Rna of Tetrahymena Telomerase Required for Telomere Repeat Synthesis. Nature 1989, 337, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Feigon, J. Progress in Human and Tetrahymena Telomerase Structure Determination. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2017, 46, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.D.; Tam, J.; Wu, R.A.; Greber, B.J.; Toso, D.; Nogales, E.; Collins, K. Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2018, 557, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lermontova, I.; Schubert, V.; Bornke, F.; Macas, J.; Schubert, I. Arabidopsis CBF5 interacts with the H/ACA snoRNP assembly factor NAF1. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendle, A.F.; Clark, G.P.; Boon, R.; Lewandowska, D.; Lam, Y.W.; Andersen, J.; Mann, M.; Lamond, A.I.; Brown, J.W.S.; Shaw, P.J. Proteomic analysis of the Arabidopsis nucleolus suggests novel nucleolar functions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, P.; Collier, S.; Bush, M.; Shaw, P.; Doonan, J.H. Arabidopsis POT1A interacts with TERT-V(18), an N-terminal splicing variant of telomerase. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.M.; Morin, G.B.; Chapman, K.B.; Weinrich, S.L.; Andrews, W.H.; Lingner, J.; Harley, C.B.; Cech, T.R. Telomerase catalytic subunit homologs from fission yeast and human. Science 1997, 277, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, K.; Liu, H.T.; Tamura, K.; Takahashi, H. Molecular cloning and characterization of AtTERT, a telomerase reverse transcriptase homolog in Arabidopsis thaliana. Febs Lett. 1999, 457, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P.; Cech, T.R. Pot1, the putative telomere end-binding protein in fission yeast and humans. Science 2001, 292, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghtaling, B.R.; Cuttonaro, L.; Chang, W.; Smith, S. A dynamic molecular link between the telomere length regulator TRF1 and the chromosome end protector TRF2. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Safari, A.; O’Connor, M.S.; Chan, D.W.; Laegeler, A.; Qin, J.; Zhou, S.Y. PTOP interacts with POT1 and regulates its localization to telomeres. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Z.S.; Hockemeyer, D.; Krutchinsky, A.N.; Loayza, D.; Hooper, S.M.; Chait, B.T.; de Lange, T. POT1-interacting protein PIP1: A telomere length regulator that recruits POT1 to the TIN2/TRF1 complex. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Redon, S.; Lingner, J. The human CST complex is a terminator of telomerase activity. Nature 2012, 488, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, A.; Murata, M. Alternative splicing of Pot1 (Protection of telomere)-like genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Genet. Syst. 2005, 80, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Kannan, K.; Tseng, L.; Shippen, D.E. Two RNA subunits and POT1a are components of Arabidopsis telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Nelson, A.D.L.; Shippen, D.E. Dyskerin is a component of the Arabidopsis telomerase RNP required for telomere maintenance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2332–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Beilstein, M.A.; Shippen, D.E. Evolution of Arabidopsis protection of telomeres 1 alters nucleic acid recognition and telomerase regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 9821–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steensel, B.; de Lange, T. Control of telomere length by the human telomeric protein TRF1. Nature 1997, 385, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kaminker, P.; Campisi, J. TIN2, a new regulator of telomere length in human cells. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Z.S.; de Lange, T. TIN2 is a tankyrase 1 PARP modulator in the TRF1 telomere length control complex. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P. The Pin2/TRF1-interacting: Protein PinX1 is a potent telomerase inhibitor. Cell 2001, 107, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, X.D. MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 and ATM function as co-mediators of TRF1 in telomere length control. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrumpfova, P.; Kuchar, M.; Mikova, G.; Skrisovska, L.; Kubicarova, T.; Fajkus, J. Characterization of two Arabidopsis thaliana myb-like proteins showing affinity to telomeric DNA sequence. Genome 2004, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrumpfova, P.P.; Kuchar, M.; Palecek, J.; Fajkus, J. Mapping of interaction domains of putative telomere-binding proteins AtTRB1 and AtPOT1b from Arabidopsis thaliana. Febs Lett. 2008, 582, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrumpfova, P.P.; Vychodilova, I.; Dvorackova, M.; Majerska, J.; Dokladal, L.; Schorova, S.; Fajkus, J. Telomere repeat binding proteins are functional components of Arabidopsis telomeres and interact with telomerase. Plant J. 2014, 77, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrumpfova, P.P.; Vychodilova, I.; Hapala, J.; Schorova, S.; Dvoracek, V.; Fajkus, J. Telomere binding protein TRB1 is associated with promoters of translation machinery genes in vivo. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Krause, K.; Yang, T.T.; Dongus, J.A.; Zhang, Y.J.; Turck, F. Telobox motifs recruit CLF/SWN-PRC2 for H3K27me3 deposition via TRB factors in Arabidopsis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokladal, L.; Benkova, E.; Honys, D.; Dupl’akova, N.; Lee, L.Y.; Gelvin, S.B.; Sykorova, E. An armadillo-domain protein participates in a telomerase interaction network. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Cho, M.H. Telomere-binding protein regulates the chromosome ends through the interaction with histone deacetylases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4610–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.M.; Zhang, C.J.; Hou, X.M.; Shao, C.R.; Lu, Y.J.; Zhou, J.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; He, X.J. The PEAT protein complexes are required for histone deacetylation and heterochromatin silencing. Embo J. 2018, 37, e98770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steensel, B.; Smogorzewska, A.; de Lange, T. TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions. Cell 1998, 92, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.; Sfeir, A.; de Lange, T. Taking apart Rap1 An adaptor protein with telomeric and non-telomeric functions. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.; Hu, C.; Broton, C.; Chen, Y.; Lei, M.; Chang, S. NBS1 Phosphorylation Status Dictates Repair Choice of Dysfunctional Telomeres. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.S.; Safari, A.; Liu, D.; Qin, J.; Zhou, S.Y. The human Rap1 protein complex and modulation of telomere length. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 28585–28591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.T.; van Overbeek, M.; Donigian, J.R.; Baciu, P.; de Lange, T.; Lei, M. A shared docking motif in TRF1 and TRF2 used for differential recruitment of telomeric proteins. Science 2008, 319, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Jung, D.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, I. Interaction of human Ku70 with TRF2. Febs Lett. 2000, 481, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.; Wu, J.; Schreiber, V.; Dunlap, J.; Dantzer, F.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Y. PARP1 is a TRF2-associated poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase and protects eroded telomere. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, F.; Giraud-Panis, M.J.; Jaco, I.; Ame, J.C.; Schultz, I.; Blasco, M.; Koering, C.E.; Gilson, E.; Menissier-de Murcia, J.; de Murcia, G.; et al. Functional interaction between poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 (PARP-2) and TRF2: PARP activity negatively regulates TRF2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Mitchell, T.R.H.; Zhu, X.D. Human XPF controls TRF2 and telomere length maintenance through distinctive mechanisms. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2008, 129, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Wang, C.T.; Ho, C.H. A plant gene encoding a Myb-like protein that binds telomeric GGTTTAG repeats in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16511–16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchar, M.; Fajkus, J. Interactions of putative telomere-binding proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana: Identification of functional TRF2 homolog in plants. Febs Lett. 2004, 578, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamysheva, Z.N.; Surovtseva, Y.V.; Vespa, L.; Shakirov, E.V.; Shippen, D.E. A C-terminal Myb extension domain defines a novel family of double-strand telomeric DNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47799–47807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majerska, J.; Schrumpfova, P.P.; Dokladal, L.; Schorova, S.; Stejskal, K.; Oboril, M.; Honys, D.; Kozakova, L.; Polanska, P.S.; Sykorova, E. Tandem affinity purification of AtTERT reveals putative interaction partners of plant telomerase in vivo. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.A.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Cha, J.S.; Khadka, P.; Cho, H.S.; Chung, K. Akt-mediated phosphorylation increases the binding affinity of hTERT for importin alpha to promote nuclear translocation. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2287–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurts, S.; Masutomi, K.; Delgermaa, L.; Arai, K.; Oishi, N.; Mizuno, H.; Hayashi, N.; Hahn, W.C.; Murakami, S. Nucleolin interacts with telomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51508–51515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontvianne, F.; Abou-Ellail, M.; Douet, J.; Comella, P.; Matia, I.; Chandrasekhara, C.; DeBures, A.; Blevins, T.; Cooke, R.; Medina, F.J.; et al. Nucleolin Is Required for DNA Methylation State and the Expression of rRNA Gene Variants in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontvianne, F.; Carpentier, M.C.; Durut, N.; Pavlistova, V.; Jaske, K.; Schorova, S.; Parrinello, H.; Rohmer, M.; Pikaard, C.S.; Fojtova, M.; et al. Identification of Nucleolus-Associated Chromatin Domains Reveals a Role for the Nucleolus in 3D Organization of the A. thaliana Genome. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Meng, Z.J.; Mason, P.J.; Veenstra, T.D.; Artandi, S.E. Identification of ATPases pontin and reptin as telomerase components essential for holoenzyme assembly. Cell 2008, 132, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, B.F.; Boyes, D.C.; Ellerstrom, M.; Siefers, N.; Wiig, A.; Kauffman, S.; Grant, M.R.; Dangl, J.L. An evolutionarily conserved mediator of plant disease resistance gene function is required for normal Arabidopsis development. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannone, R.J.; McDonald, H.W.; Hurst, G.B.; Shen, R.F.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Y. The Protein Network Surrounding the Human Telomere Repeat Binding Factors TRF1, TRF2, and POT1. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.; Wu, F.H.; Hsu, C.T.; Shen, S.C.; Yeh, H.Y.; Liao, D.C.; Fang, M.J.; Liu, N.T.; Yen, Y.C.; Dokladal, L.; et al. Screening a cDNA Library for Protein-Protein Interactions Directly in Planta. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1746–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappei, D.; Butter, F.; Benda, C.; Scheibe, M.; Draskovic, I.; Stevense, M.; Novo, C.L.; Basquin, C.; Araki, M.; Araki, K.; et al. HOT1 is a mammalian direct telomere repeat-binding protein contributing to telomerase recruitment. Embo J. 2013, 32, 1681–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.H.; Ford, L.P.; Lenertz, L.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Human Ku70/80 associates physically with telomerase through interaction with hTERT. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47242–47247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, V.L.; Schild-Poulter, C. The Ku heterodimer: Function in DNA repair and beyond. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 763, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundock, P.; van Attikum, H.; Hooykaas, P. Increased telomere length and hypersensitivity to DNA damaging agents in an Arabidopsis KU70 mutant. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3395–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riha, K.; Watson, J.M.; Parkey, J.; Shippen, D.E. Telomere length deregulation and enhanced sensitivity to genotoxic stress in Arabidopsis mutants deficient in Ku70. Embo J. 2002, 21, 2819–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.E.; Waterworth, W.M.; Story, G.W.; Sunderland, P.A.; Jiang, Q.; Bray, C.M. Disruption of the Arabidopsis AtKu80 gene demonstrates an essential role for AtKu80 protein in efficient repair of DNA double-strand breaks in vivo. Plant J. 2002, 31, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, M.E.; Jalut, N.; White, C.I. Telomerase dependence of telomere lengthening in Ku80 mutant Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Nelson, A.D.L.; Boltz, K.A.; Kannan, K.; She, X.T.; Shippen, D.E. An alternative telomerase RNA in Arabidopsis modulates enzyme activity in response to DNA damage. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2512–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valuchova, S.; Fulnecek, J.; Prokop, Z.; Stolt-Bergner, P.; Janouskova, E.; Hofr, C.; Riha, K. Protection of Arabidopsis blunt-ended telomeres is mediated by a physical association with the Ku heterodimer. Plant Cell 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, S.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Baur, J.; Tesmer, V.M.; Dy, M.; Ouellette, M.; Trager, J.B.; Morin, G.B.; Toft, D.O.; Shay, J.W.; et al. Functional requirement of p23 and Hsp90 in telomerase complexes. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhong, D.B.; Monteiro, A. Comparative genomics and evolution of the HSP90 family of genes across all kingdoms of organisms. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Sullivan, W.; Felts, S.J.; Prasad, B.D.; Toft, D.O.; Krishna, P. Characterization of plant p23-like proteins for their co-chaperone activities. Cell Stress Chaperones 2010, 15, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortman, M.J.; Johnson, E.M.; Bergemann, A.D. Mechanism of DNA binding and localized strand separation by Pur alpha and comparison with Pur family member, Pur beta. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2005, 1743, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermoud, J.E.; Rowbotham, S.P.; Varga-Weisz, P.D. Keeping chromatin quiet How nucleosome remodeling restores heterochromatin after replication. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 4017–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, M.; Scheid, O.M. DNA Damage Repair in the Context of Plant Chromatin. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; St-Sauveur, V.G.; Bergeron, D.; Dupuis-Sandoval, F.; Scott, M.S.; Bachand, F. A Polyadenylation-Dependent 3′ End Maturation Pathway Is Required for the Synthesis of the Human Telomerase RNA. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokladal, L.; Honys, D.; Rana, R.; Lee, L.Y.; Gelvin, S.B.; Sykorova, E. cDNA Library Screening Identifies Protein Interactors Potentially Involved in Non-Telomeric Roles of Arabidopsis Telomerase. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Su, L.; Yue, H.W.; Yin, X.L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.L.; Kung, H.F.; Xu, Z.G.; Miao, J.Y. HMBOX1 interacts with MT2A to regulate autophagy and apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.Y.; Luo, Z.H.; Jiang, S.; Li, F.; Han, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, W.B.; Liu, D.; et al. The telomere-associated homeobox-containing protein TAH1/HMBOX1 participates in telomere maintenance in ALT cells. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3982–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamartine, J.; Seri, M.; Cinti, R.; Heitzmann, F.; Creaven, M.; Radomski, N.; Jost, E.; Lenoir, G.M.; Romeo, G.; Sylla, B.S. Molecular cloning and mapping of a human cDNA (PA2G4) that encodes a protein highly homologous to the mouse cell cycle protein p38-2G4. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1997, 78, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.L.; Funk, W.D.; Wang, S.S.; Weinrich, S.L.; Avilion, A.A.; Chiu, C.P.; Adams, R.R.; Chang, E.; Allsopp, R.C.; Yu, J.H.; et al. The Rna Component of Human Telomerase. Science 1995, 269, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Graham, M.E.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Bache, N.; Robinson, P.J.; Reddel, R.R. Protein composition of catalytically active human telomerase from immortal cells. Science 2007, 315, 1850–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, N.S.; Knight, S.W.; Vulliamy, T.J.; Klauck, S.M.; Wiemann, S.; Mason, P.J.; Poustka, A.; Dokal, I. X-linked dyskeratosis congenita is caused by mutations in a highly conserved gene with putative nucleolar functions. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henras, A.; Henry, Y.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C.; Noaillac-Depeyre, J.; Gelugne, J.P.; Caizergues-Ferrer, M. Nhp2p and Nop10p are essential for the function of H/ACA snoRNPs. Embo J. 1998, 17, 7078–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Shin, S.; Okui, K.; Nakamura, Y. Cloning and mapping of a human novel cDNA (NHP2L1) that encodes a protein highly homologous to yeast nuclear protein NHP2. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1996, 72, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, N.J.; Gottschalk, A.; Neubauer, G.; Kastner, B.; Fabrizio, P.; Mann, M.; Luhrmann, R. Cbf5p, a potential pseudouridine synthase, and Nhp2p, a putative RNA-binding protein, are present together with Gar1p in all H BOX/ACA-motif snoRNPs and constitute a common bipartite structure. RNA 1998, 4, 1549–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatica, A.; Dlakic, M.; Tollervey, D. Naf1p is a box H/ACA snoRNP assembly factor. RNA 2002, 8, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, N.S.Y.; Yu, Y.P.; Pohorelic, B.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Beattie, T.L. Human Ku70/80 interacts directly with hTR, the RNA component of human telomerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, A.N.; Collins, K. The 5′ Guanosine Tracts of Human Telomerase RNA Are Recognized by the G-Quadruplex Binding Domain of the RNA Helicase DHX36 and Function To Increase RNA Accumulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.H.; Segal, M.; Boyraz, B.; Guinan, E.; Hofmann, I.; Cahan, P.; Tai, A.K.; Agarwal, S. Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN) mediates 3′-end maturation of the telomerase RNA component. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, Y.; Johnson, M.A.; Lidder, P.; Vogel, J.T.; van Erp, H.; Green, P.J. AtPARN is an essential poly(A) ribonuclease in Arabidopsis. Gene 2004, 328, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Abreu, E.B.; Meng, Z.J.; McCann, K.E.; Terns, R.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Terns, M.P.; Artandi, S.E. A Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Protein Required for Cajal Body Localization and Telomere Synthesis. Science 2009, 323, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykorova, E.; Fajkus, J. Structure-function relationships in telomerase genes. Biol. Cell 2009, 101, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykorova, E.; Fulneckova, J.; Mokros, P.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtova, M.; Peska, V. Three TERT genes in Nicotiana tabacum. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, K.; Pearson, M.; Grate, L.; Sterne-Weiler, T.; Deans, J.; Donohue, J.P.; Ares, M. Structural RNAs of known and unknown function identified in malaria parasites by comparative genomics and RNA analysis. RNA 2007, 13, 1923–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, C.J.; Zakian, V.A. Identification and characterization of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe TER1 telomerase RNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, J.; Box, J.A.; Bunch, J.T.; Baumann, P. TER1, the RNA subunit of fission yeast telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.Y.; Mosig, A.; Qi, X.; Li, Y.; Stadler, P.F.; Chen, J.J.L. Structure and function of the smallest vertebrate telomerase RNA from teleost fish. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachouri-Lafond, R.; Dujon, B.; Gilson, E.; Westhof, E.; Fairhead, C.; Teixeira, M.T. Large telomerase RNA, telomere length heterogeneity and escape from senescence in Candida glabrata. Febs Lett. 2009, 583, 3605–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunisova, S.; Elboher, E.; Nosek, J.; Gorkovoy, V.; Brown, Y.; Lucier, J.F.; Laterreur, N.; Wellinger, R.J.; Tzfati, Y.; Tomaska, L. Identification and comparative analysis of telomerase RNAs from Candida species reveal conservation of functional elements. RNA-A Publ. RNA Soc. 2009, 15, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldl, M.; Thiel, B.C.; Ochsenreiter, R.; Holzenleiter, A.; de Araujo Oliveira, J.V.; Walter, M.; Wolfinger, M.T.; Stadler, P.F. TERribly Difficult: Searching for Telomerase RNAs in Saccharomycetes. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykorova, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Kunicka, Z.; Chase, M.W.; Bennett, M.D.; Fajkus, J.; Leitch, A.R. Telomere variability in the monocotyledonous plant order Asparagales. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykorova, E.; Fajkus, J.; Meznikova, M.; Lim, K.Y.; Neplechova, K.; Blattner, F.R.; Chase, M.W.; Leitch, A.R. Minisatellite telomeres occur in the family Alliaceae but are lost in Allium. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lange, T. Shelterin: The protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, T. What I got wrong about shelterin. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10453–10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, W.; de Lange, T. How Shelterin Protects Mammalian Telomeres. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfeir, A.; de Lange, T. Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem. Science 2012, 336, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibe, T.; Zimmermann, M.; de Lange, T. TPP1 Blocks an ATR-Mediated Resection Mechanism at Telomeres. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Lottersberger, F.; Buonomo, S.B.; Sfeir, A.; de Lange, T. 53BP1 Regulates DSB Repair Using Rif1 to Control 5 ‘ End Resection. Science 2013, 339, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, A.B.; Hofr, C.; Cech, T.R. Contributions of the TEL-patch Amino Acid Cluster on TPP1 to Telomeric DNA Synthesis by Human Telomerase. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latrick, C.M.; Cech, T.R. POT1-TPP1 enhances telomerase processivity by slowing primer dissociation and aiding translocation. Embo J. 2010, 29, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, J.; Bell, C.F.; Weidenfeld, I.; Zaug, A.J.; Leinwand, L.A.; Cech, T.R. The TEL patch of telomere protein TPP1 mediates telomerase recruitment and processivity. Nature 2012, 492, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.C.; Cech, T.R. Human telomerase: Biogenesis, trafficking, recruitment, and activation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.D.; Comeau, L.; Rosenfield, S.; Stansel, R.M.; Bianchi, A.; Moss, H.; de Lange, T. Mammalian telomeres end in a large duplex loop. Cell 1999, 97, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansel, R.M.; de Lange, T.; Griffith, J.D. T-loop assembly in vitro involves binding of TRF2 near the 3’ telomeric overhang. Embo J. 2001, 20, 5532–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfeir, A.; Kosiyatrakul, S.T.; Hockemeyer, D.; MacRae, S.L.; Karlseder, J.; Schildkraut, C.L.; de Lange, T. Mammalian Telomeres Resemble Fragile Sites and Require TRF1 for Efficient Replication. Cell 2009, 138, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.S.; Stern, J.L.; Sfeir, A.; Kartawinata, M.; de Lange, T.; Zhu, X.D.; Bryan, T.M. ATM and ATR Signaling Regulate the Recruitment of Human Telomerase to Telomeres. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesare, A.J.; Quinney, N.; Willcox, S.; Subramanian, D.; Griffith, J.D. Telomere looping in P-sativum (common garden pea). Plant J. 2003, 36, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgova, I.; Schrumpfova, P.P.; Hofr, C.; Fajkus, J. Functional characterization of domains in AtTRB1, a putative telomere-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marian, C.O.; Bordoli, S.J.; Goltz, M.; Santarella, R.A.; Jackson, L.P.; Danilevskaya, O.; Beckstette, M.; Meeley, R.; Bass, H.W. The maize Single myb histone 1 gene, Smh1, belongs to a novel gene family and encodes a protein that binds telomere DNA repeats in vitro. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1336–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilaud, T.; Koering, C.E.; BinetBrasselet, E.; Ancelin, K.; Pollice, A.; Gasser, S.M.; Gilson, E. The telobox, a Myb-related telomeric DNA binding motif found in proteins from yeast, plants and human. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peska, V.; Schrumpfova, P.P.; Fajkus, J. Using the Telobox to Search for Plant Telomere Binding Proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2011, 12, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrumpfova, P.P.; Schorova, S.; Fajkus, J. Telomere- and Telomerase-Associated Proteins and Their Functions in the Plant Cell. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 851. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Hartwig, B.; James, G.V.; Schneeberger, K.; Turck, F. Complementary Activities of TELOMERE REPEAT BINDING Proteins and Polycomb Group Complexes in Transcriptional Regulation of Target Genes. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mai, M.; Wagner, K.D.; Michiels, J.F.; Ambrosetti, D.; Borderie, A.; Destree, S.; Renault, V.; Djerbi, N.; Giraud-Panis, M.J.; Gilson, E.; et al. The Telomeric Protein TRF2 Regulates Angiogenesis by Binding and Activating the PDGFR beta Promoter. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutilina, R.I.; Oei, S.L.; Buchlow, G.; Yau, P.M.; Zalensky, A.O.; Zalenskaya, I.A.; Bradbury, E.M.; Tomilin, N.V. A negative regulator of telomere-length protein TRF1 is associated with interstitial (TTAGGG)n blocks in immortal Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Thanasoula, M.; Carlos, A.R.; Gomez-Lopez, G.; Tejera, A.M.; Schoeftner, S.; Dominguez, O.; Pisano, D.G.; Tarsounas, M.; Blasco, M.A. Mammalian Rap1 controls telomere function and gene expression through binding to telomeric and extratelomeric sites. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, R.H. RAP, RAP, open up! New wrinkles for RAP1 in yeast. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Iachettini, S.; Salvati, E.; Zizza, P.; Maresca, C.; D’Angelo, C.; Benarroch-Popivker, D.; Capolupo, A.; del Gaudio, F.; Cosconati, S.; et al. SIRT6 interacts with TRF2 and promotes its degradation in response to DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonet, T.; Zaragosi, L.E.; Philippe, C.; Lebrigand, K.; Schouteden, C.; Augereau, A.; Bauwens, S.; Ye, J.; Santagostino, M.; Giulotto, E.; et al. The human TTAGGG repeat factors 1 and 2 bind to a subset of interstitial telomeric sequences and satellite repeats. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Renault, V.M.; Jamet, K.; Gilson, E. Transcriptional outcome of telomere signalling. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Pazin, M.J.; Schwartz, C.M.; Becker, K.G.; Wersto, R.P.; Dilley, C.M.; Mattson, M.P. Nontelomeric TRF2-REST Interaction Modulates Neuronal Gene Silencing and Fate of Tumor and Stem Cells. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulcher, N.; Riha, K. Using Centromere Mediated Genome Elimination to Elucidate the Functional Redundancy of Candidate Telomere Binding Proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Genet. 2016, 6, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrault, S.D.; Hornsby, P.J.; Betts, D.H. Global gene expression response to telomerase in bovine adrenocortical cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerska, J.; Sykorova, E.; Fajkus, J. Non-telomeric activities of telomerase. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.I.; Venteicher, A.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Jun, S.; Shkreli, M.; Chang, W.; Meng, Z.J.; Cheung, P.; Ji, H.; et al. Telomerase modulates Wnt signalling by association with target gene chromatin. Nature 2009, 460, 66–U77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeling, M. Bias in Plant Gene Content Following Different Sorts of Duplication: Tandem, Whole-Genome, Segmental, or by Transposition. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandakova, T.; Lysak, M.A. Chromosomal Phylogeny and Karyotype Evolution in x=7 Crucifer Species (Brassicaceae). Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2559–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.M.; Boltz, K.A.; Chaiken, M.F.; Stewart, J.A.; Beilstein, M.A.; Shippen, D.E. Evolution of CST function in telomere maintenance. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.Y.; Hsu, S.J.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Wang, Y.Y.; Diao, J.J.; Price, C.M. CTC1-STN1 terminates telomerase while STN1-TEN1 enables C-strand synthesis during telomere replication in colon cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.Y.; Hsu, S.J.; Kasbek, C.; Chaiken, M.; Price, C.M. CTC1-mediated C-strand fill-in is an essential step in telomere length maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4281–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.A.; Wang, F.; Chaiken, M.F.; Kasbek, C.; Chastain, P.D.; Wright, W.E.; Price, C.M. Human CST promotes telomere duplex replication and general replication restart after fork stalling. Embo J. 2012, 31, 3537–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoyan, J.K.; Lejnine, S.; Makarov, V.L.; Langmore, J.P. Condensation of rat telomere-specific nucleosomal arrays containing unusually short DNA repeats and histone H1. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18485–18493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejnine, S.; Makarov, V.L.; Langmore, J.P. Conserved Nucleoprotein Structure at the Ends of Vertebrate and Invertebrate Chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2393–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, V.L.; Lejnine, S.; Bedoyan, J.; Langmore, J.P. Nucleosomal Organization of Telomere-Specific Chromatin in Rat. Cell 1993, 73, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommerup, H.; Dousmanis, A.; Delange, T. Unusual Chromatin in Human Telomeres. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 5777–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajkus, J.; Kovarik, A.; Kralovics, R.; Bezdek, M. Organization of Telomeric and Subtelomeric Chromatin in the Higher-Plant Nicotiana tabacum. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1995, 247, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejardin, J.; Kingston, R.E. Purification of Proteins Associated with Specific Genomic Loci. Cell 2009, 136, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajkus, J.; Trifonov, E.N. Columnar packing of telomeric nucleosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, N.; de Lange, T. A TRF1-controlled common fragile site containing interstitial telomeric sequences. Chromosoma 2012, 121, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Karow, J.K.; Hickson, I.D.; Maizels, N. The Bloom’s syndrome helicase unwinds G4 DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27587–27592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muftuoglu, M.; Wong, H.K.; Imam, S.Z.; Wilson, D.M.; Bohr, V.A.; Opresko, P.L. Telomere repeat binding factor 2 interacts with base excision repair proteins and stimulates DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase beta. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumi, Y.; Ezura, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yugawa, T.; Narisawa-Saito, M.; Kiyono, T.; Ohta, S.; Obuse, C.; Fujita, M. Involvement of human ORC and TRF2 in pre-replication complex assembly at telomeres. Genes Cells 2008, 13, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarek, G.; Vannier, J.B.; Panier, S.; Petrini, J.H.J.; Boulton, S.J. TRF2 Recruits RTEL1 to Telomeres in S Phase to Promote T-Loop Unwinding. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlseder, J.; Hoke, K.; Mirzoeva, O.K.; Bakkenist, C.; Kastan, M.B.; Petrini, J.H.J.; de Lange, T. The telomeric protein TRF2 binds the ATM kinase and can inhibit the ATM-dependent DNA damage response. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.G.; Chung, I.K.; Kang, B.G.; Cho, M.H. Sequence-specific binding property of Arabidopsis thaliana telomeric DNA binding protein 1 (AtTBP1). Febs Lett. 2001, 503, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfrew, K.B.; Song, X.Y.; Lee, J.R.; Arora, A.; Shippen, D.E. POT1a and Components of CST Engage Telomerase and Regulate Its Activity in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, H.D.M.; Tsang, A.R.; Lobb, D.A.; Beattie, T.L. Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Q169 Is Essential for Telomerase Function In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganduri, S.; Lue, N.F. STN1-POLA2 interaction provides a basis for primase-pol alpha stimulation by human STN1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9455–9466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Nabetani, A.; Shimamura, S.; Tamura, M.; Yonehara, S.; Saito, M.; Ishikawa, F. RPA-like Mammalian Ctc1-Stn1-Ten1 Complex Binds to Single-Stranded DNA and Protects Telomeres Independently of the Pot1 Pathway. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derboven, E.; Ekker, H.; Kusenda, B.; Bulankova, P.; Riha, K. Role of STN1 and DNA Polymerase alpha in Telomere Stability and Genome-Wide Replication in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehy, K.A.; Lee, J.R.; Song, X.Y.; Renfrew, K.B.; Shippen, D.E. MERISTEM DISORGANIZATION1 Encodes TEN1, an Essential Telomere Protein That Modulates Telomerase Processivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Leehy, K.; Warrington, R.T.; Lamb, J.C.; Surovtseva, Y.V.; Shippen, D.E. STN1 protects chromosome ends in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19815–19820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surovtseva, Y.V.; Churikov, D.; Boltz, K.A.; Song, X.Y.; Lamb, J.C.; Warrington, R.; Leehy, K.; Heacock, M.; Price, C.M.; Shippen, D.E. Conserved Telomere Maintenance Component 1 Interacts with STN1 and Maintains Chromosome Ends in Higher Eukaryotes. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.H.; Kwon, C.; Lee, M.M.; Chung, I.K. Single-stranded DNA binding factor AtWHY1 modulates telomere length homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 49, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.; Chung, I.K. Interaction of an Arabidopsis RNA-binding protein with plant single-stranded telomeric DNA modulates telomerase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12812–12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zhang, Y. DNA Methylation in Mammals. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a019133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Dowen, R.H.; Hawkins, R.D.; Hon, G.; Tonti-Filippini, J.; Nery, J.R.; Lee, L.; Ye, Z.; Ngo, Q.M.; et al. Human DNA methylomes at base resolution show widespread epigenomic differences. Nature 2009, 462, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. The epigenetic landscape of plants. Science 2008, 320, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokus, S.J.; Feng, S.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Merriman, B.; Haudenschild, C.D.; Pradhan, S.; Nelson, S.F.; Pellegrini, M.; Jacobsen, S.E. Shotgun bisulphite sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome reveals DNA methylation patterning. Nature 2008, 452, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogrocka, A.; Polanska, P.; Majerova, E.; Janeba, Z.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtova, M. Compromised telomere maintenance in hypomethylated Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 2919–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrbsky, J.; Akimcheva, S.; Watson, J.M.; Turner, T.L.; Daxinger, L.; Vyskot, B.; Aufsatz, W.; Riha, K. siRNA-Mediated Methylation of Arabidopsis Telomeres. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majerova, E.; Fojtova, M.; Mozgova, I.; Bittova, M.; Fajkus, J. Hypomethylating drugs efficiently decrease cytosine methylation in telomeric DNA and activate telomerase without affecting telomere lengths in tobacco cells. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majerova, E.; Mandakova, T.; Vu, G.T.H.; Fajkus, J.; Lysak, M.A.; Fojtova, M. Chromatin features of plant telomeric sequences at terminal vs. internal positions. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.Y.; Shippen, D.E. DDM1 guards against telomere truncation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojtova, M.; Fajkus, J. Epigenetic Regulation of Telomere Maintenance. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 143, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransz, P.; ten Hoopen, R.; Tessadori, F. Composition and formation of heterochromatin in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chromosome Res. 2006, 14, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudier, F.; Ahmed, I.; Berard, C.; Sarazin, A.; Mary-Huard, T.; Cortijo, S.; Bouyer, D.; Caillieux, E.; Duvernois-Berthet, E.; Al-Shikhley, L.; et al. Integrative epigenomic mapping defines four main chromatin states in Arabidopsis. Embo J. 2011, 30, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeftner, S.; Blasco, M.A. A ‘higher order’ of telomere regulation: Telomere heterochromatin and telomeric RNAs. Embo J. 2009, 28, 2323–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubiles, M.D.; Barroso, S.; Vaquero-Sedas, M.I.; Enguix, A.; Aguilera, A.; Vega-Palas, M.A. Epigenetic features of human telomeres. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, J.A.; Wang, Z.B.; Schones, D.E.; Zhao, K.; DeSalle, R.; Zhang, M.Q. Determination of enriched histone modifications in non-genic portions of the human genome. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, R.J.; Kubicek, S.; Schreiber, S.L.; Karlseder, J. Reduced histone biosynthesis and chromatin changes arising from a damage signal at telomeres. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoult, N.; Van Beneden, A.; Decottignies, A. Telomere length regulates TERRA levels through increased trimethylation of telomeric H3K9 and HP1 alpha. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cao, M.; O’Sullivan, R.; Peters, A.H.F.M.; Jenuwein, T.; Blasco, M.A. Epigenetic regulation of telomere length in mammalian cells by the Suv39h1 and Suv39h2 histone methyltransferases. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksouk, N.; Barth, T.K.; Ziegler-Birling, C.; Olova, N.; Nowak, A.; Rey, E.; Mateos-Langerak, J.; Urbach, S.; Reik, W.; Torres-Padilla, M.E.; et al. Redundant Mechanisms to Form Silent Chromatin at Pericentromeric Regions Rely on BEND3 and DNA Methylation. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, R.; Gonzalo, S.; Jaco, I.; SChotta, G.; Klatt, P.; Jenuwein, T.; Blasco, M.A. Suv4-20h deficiency results in telomere elongation and derepression of telomere recombination. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, S.; Jaco, I.; Fraga, M.F.; Chen, T.P.; Li, E.; Esteller, M.; Blasco, M.A. DNA methyltransferases control telomere length and telomere recombination in mammalian cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.J.; Lopez-Silanes, I.; Megias, D.; Fraga, M.F.; Castells-Garcia, A.; Blasco, M.A. TERRA recruitment of polycomb to telomeres is essential for histone trymethylation marks at telomeric heterochromatin. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovakova, P.P.; Magdolenova, A.; Konecna, K.; Rajecka, V.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtova, M. Telomere elongation upon transfer to callus culture reflects the reprogramming of telomere stability control in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero-Sedas, M.I.; Luo, C.Y.; Vega-Palas, M.A. Analysis of the epigenetic status of telomeres by using ChIP-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut-Karslioglu, A.; Perrera, V.; Scaranaro, M.; de la Rosa-Velazquez, I.A.; van de Nobelen, S.; Shukeir, N.; Popow, J.; Gerle, B.; Opravil, S.; Pagani, M.; et al. A transcription factor-based mechanism for mouse heterochromatin formation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzalin, C.M.; Reichenbach, P.; Khoriauli, L.; Giulotto, E.; Lingner, J. Telomeric repeat-containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science 2007, 318, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero-Sedas, M.I.; Gamez-Arjona, F.M.; Vega-Palas, M.A. Arabidopsis thaliana telomeres exhibit euchromatic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardat, M.; Dejardin, J. Telomere chromatin establishment and its maintenance during mammalian development. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.H.; Du, Q.; Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Human telomeres have different overhang sizes at leading versus lagging strands. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino-Reale, G.; Pascale, E.; Battiloro, E.; Starace, G.; Verna, R.; D’Ambrosio, E. The length of telomeric G-rich strand 3 ‘-overhang measured by oligonucleotide ligation assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.L.; Hirose, Y.; Langmore, J.P. Long G tails at both ends of human chromosomes suggest a C strand degradation mechanism for telomere shortening. Cell 1997, 88, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, W.E.; Tesmer, V.M.; Huffman, K.E.; Levene, S.D.; Shay, J.W. Normal human chromosomes have long G-rich telomeric overhangs at one end. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 2801–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oganesian, L.; Karlseder, J. Mammalian 5’ C-Rich Telomeric Overhangs Are a Mark of Recombination-Dependent Telomere Maintenance. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, K.; McKnight, T.D.; Fajkus, J.; Vyskot, B.; Shippen, D.E. Analysis of the G-overhang structures on plant telomeres: Evidence for two distinct telomere architectures. Plant J. 2000, 23, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazda, A.; Zellinger, B.; Rossler, M.; Derboven, E.; Kusenda, B.; Riha, K. Chromosome end protection by blunt-ended telomeres. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fojtova, M.; Sykorova, E.; Najdekrova, L.; Polanska, P.; Zachova, D.; Vagnerova, R.; Angelis, K.J.; Fajkus, J. Telomere dynamics in the lower plant Physcomitrella patens. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 87, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, K.; Shippen, D.E. Ku is required for telomeric C-rich strand maintenance but not for end-to-end chromosome fusions in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, T.M.; Englezou, A.; DallaPozza, L.; Dunham, M.A.; Reddel, R.R. Evidence for an alternative mechanism for maintaining telomere length in human tumors and tumor-derived cell lines. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.A.; Watson, C.M.; Noble, J.R.; Pickett, H.A.; Tam, P.P.L.; Reddel, R.R. Alternative lengthening of telomeres in normal mammalian somatic cells. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckova, E.; Friml, J.; Schrumpfova, P.P.; Fajkus, J. Role of alternative telomere lengthening unmasked in telomerase knock-out mutant plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 66, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellinger, B.; Akimcheva, S.; Puizina, J.; Schirato, M.; Riha, K. Ku suppresses formation of telomeric circles and alternative telomere lengthening in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpenshif, Y.; Bernstein, K.A. From yeast to mammals: Recent advances in genetic control of homologous recombination. DNA Repair 2012, 11, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.J.; Youds, J.L.; Ward, J.D.; McIlwraith, M.J.; O’Neil, N.J.; Petalcorin, M.I.R.; Martin, J.S.; Collis, S.J.; Cantor, S.B.; Auclair, M.; et al. RTEL1 Maintains Genomic Stability by Suppressing Homologous Recombination. Cell 2008, 135, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uringa, E.J.; Lisaingo, K.; Pickett, H.A.; Brind’Amour, J.; Rohde, J.H.; Zelensky, A.; Essers, J.; Lansdorp, P.M. RTEL1 contributes to DNA replication and repair and telomere maintenance. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2782–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier, J.B.; Pavicic-Kaltenbrunner, V.; Petalcorin, M.I.R.; Ding, H.; Boulton, S.J. RTEL1 Dismantles T Loops and Counteracts Telomeric G4-DNA to Maintain Telomere Integrity. Cell 2012, 149, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guen, T.; Jullien, L.; Schertzer, M.; Lefebvre, A.; Kermasson, L.; de Villartay, J.P.; Londono-Vallejo, A.; Revy, P. RTEL1 (regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1), a DNA helicase essential for genome stability. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Vannier, J.B.; Sarek, G.; Boulton, S.J. RTEL1: Functions of a disease-associated helicase. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, G.; Revy, P.; Schertzer, M.; Londono-Vallejo, A.; Callebaut, I. The C-terminal extension of human RTEL1, mutated in Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome, contains Harmonin-N-like domains. Proteins-Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 82, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, P.; Kotsantis, P.; Borel, V.; Bellelli, R.; Panier, S.; Boulton, S.J. Stabilization of Reversed Replication Forks by Telomerase Drives Telomere Catastrophe. Cell 2018, 172, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.B.; Cools, T.; Kalhorzadeh, P.; Heyman, J.; De Veylder, L. Deficiency of the Arabidopsis Helicase RTEL1 Triggers a SOG1-Dependent Replication Checkpoint in Response to DNA Cross-Links. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recker, J.; Knoll, A.; Puchta, H. The Arabidopsis thaliana Homolog of the Helicase RTEL1 Plays Multiple Roles in Preserving Genome Stability. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4889–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, K.; McKnight, T.D.; Griffing, L.R.; Shippen, D.E. Living with genome instability: Plant responses to telomere dysfunction. Science 2001, 291, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Charbonnel, C.; Amiard, S.; White, C.I.; Gallego, M.E. RAD51 and RTEL1 compensate telomere loss in the absence of telomerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2432–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisugi, Y.; Whitaker, J.W.; Cuming, A.C. The Transcriptional Response to DNA-Double-Strand Breaks in Physcomitrella patens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.; Wapstra, E.; Friesen, C. Ectothermic telomeres: it’s time they came in from the cold. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzl, F.; Smith, S.; Cornils, J.S.; Aydinonat, D.; Bieber, C.; Ruf, T. Telomeres are elongated in older individuals in a hibernating rodent, the edible dormouse (Glis glis). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.M.V.; Ryder, O.A.; Houck, M.L.; Charter, S.J.; Walker, W.; Forsyth, N.R.; Austad, S.N.; Venditti, C.; Pagel, M.; Shay, J.W.; et al. Comparative biology of mammalian telomeres: Hypotheses on ancestral states and the roles of telomeres in longevity determination. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Lingner, J. Impact of oxidative stress on telomere biology. Differentiation 2018, 99, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.W.; Rane, G.; Dai, X.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Samy, R.P.; Lai, M.K.P.; Kappei, D.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G. Ageing and the telomere connection: An intimate relationship with inflammation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 25, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottcher, M.A.; Dingli, D.; Werner, B.; Traulsen, A. Replicative cellular age distributions in compartmentalized tissues. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J. Mutation Selection and Natural-History of Cancer. Nature 1975, 255, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conboy, M.J.; Karasov, A.O.; Rando, T.A. High incidence of non-random template strand segregation and asymmetric fate determination in dividing stem cells and their progeny. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).