TRPV1-Like Immunoreactivity in the Human Locus K, a Distinct Subregion of the Cuneate Nucleus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Sampling
2.2. Immunohistochemistry and Histology
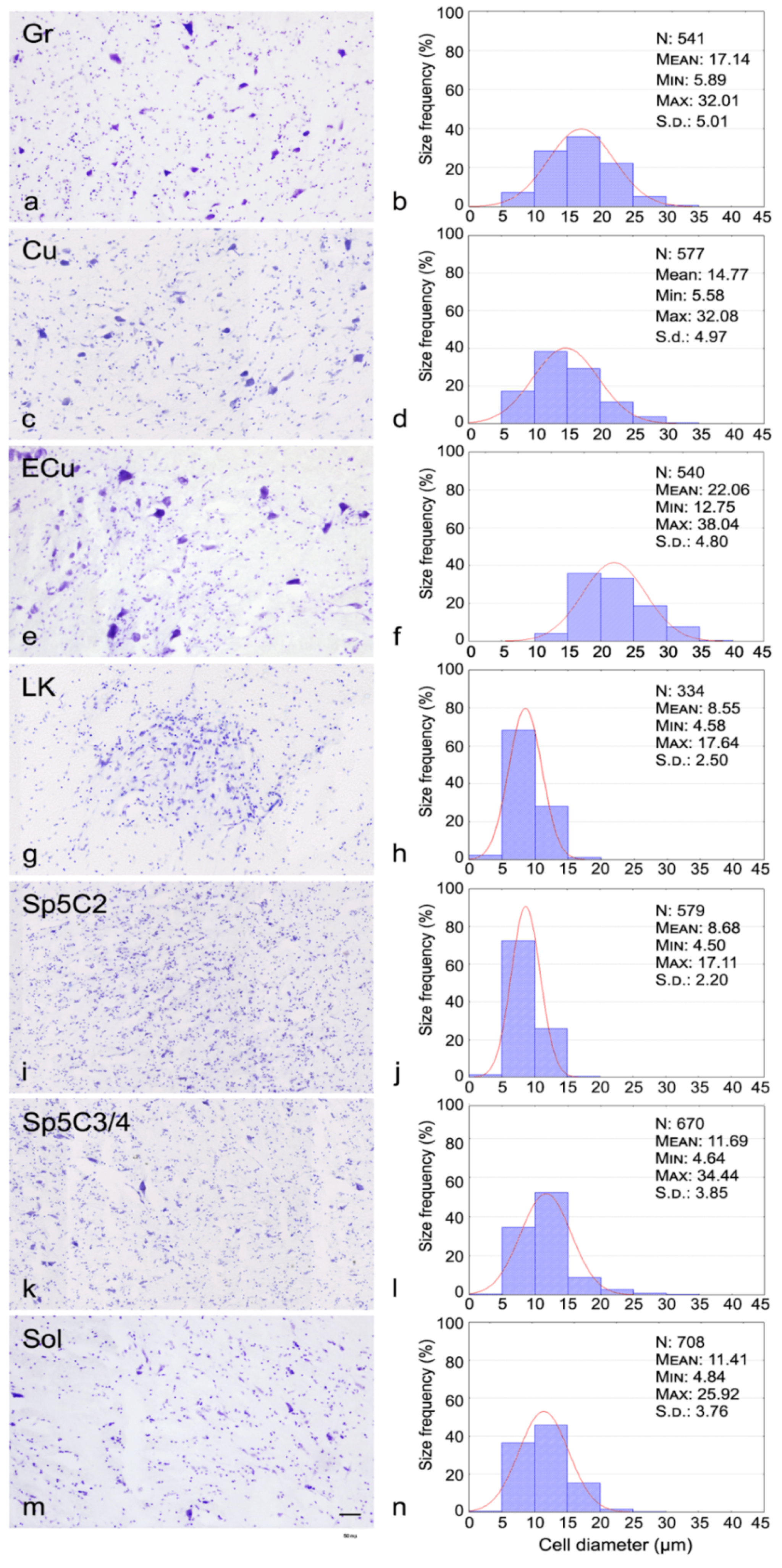
2.3. Morphometric Analysis
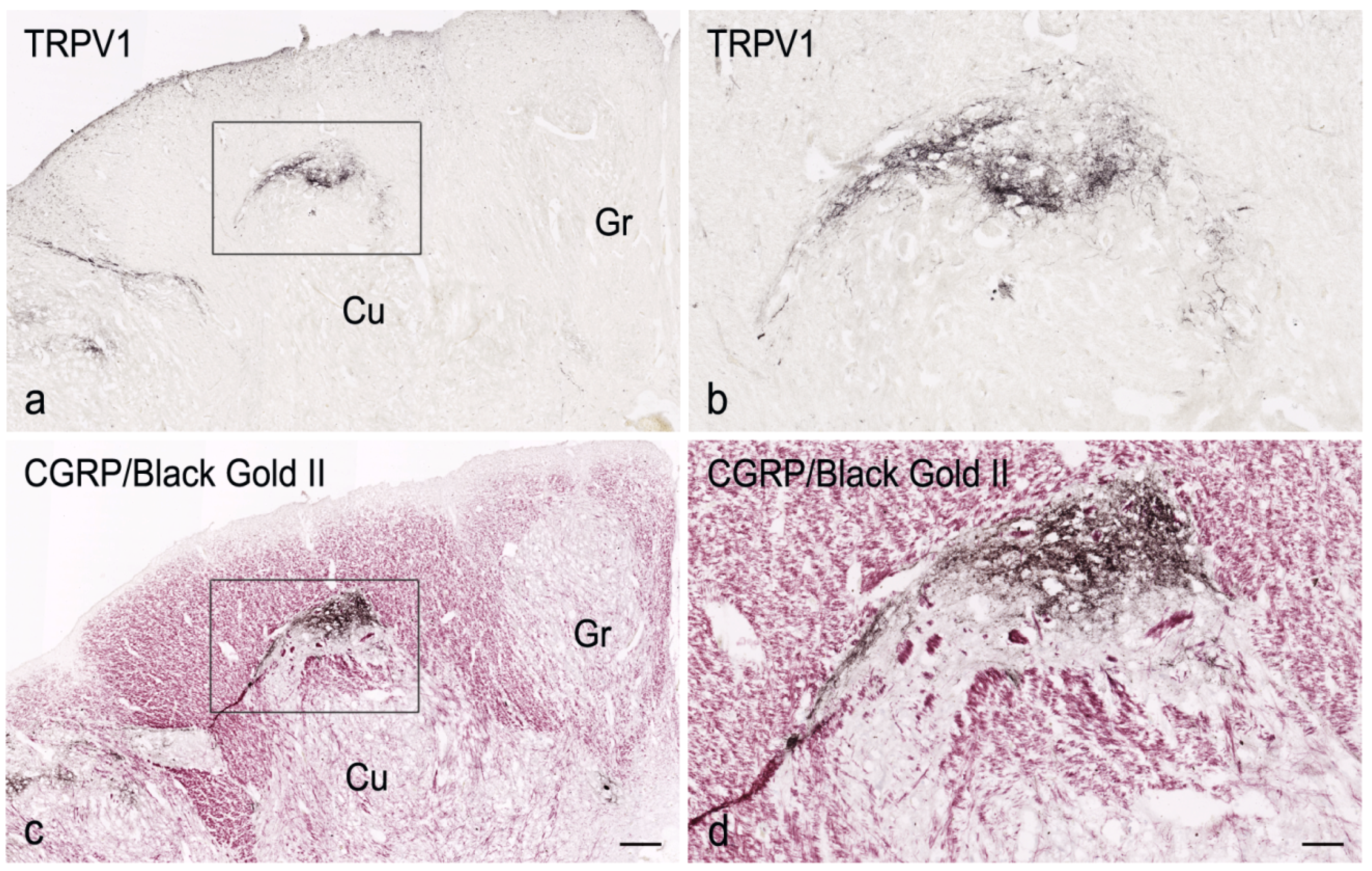
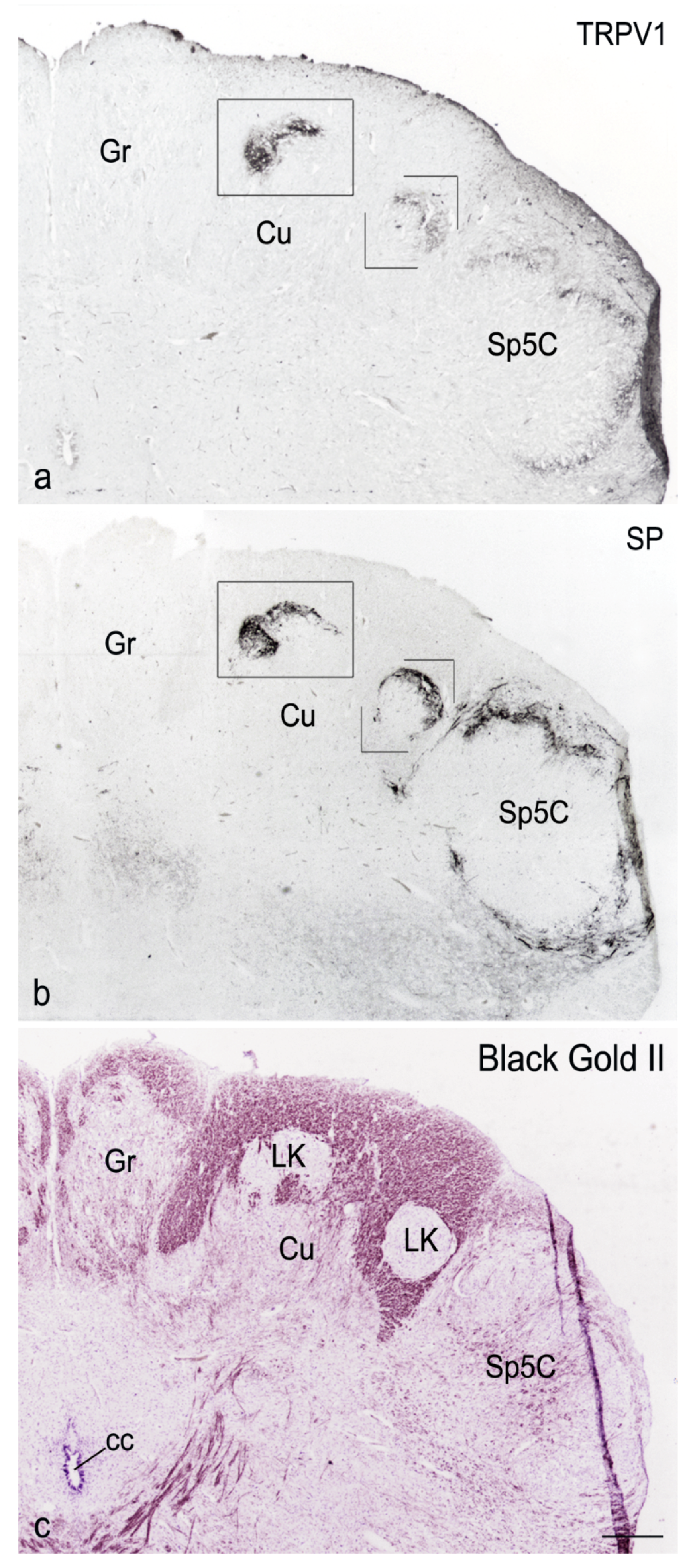
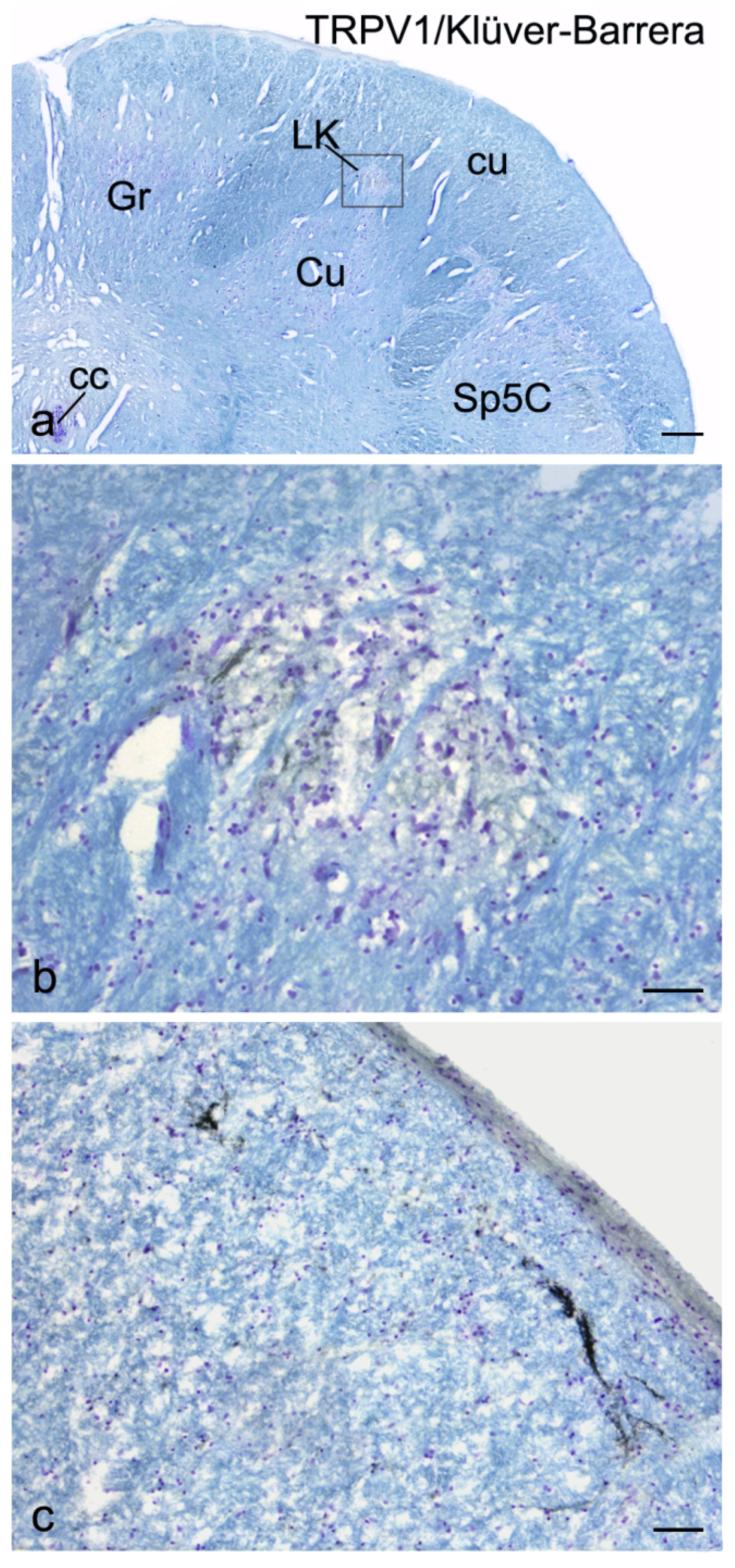
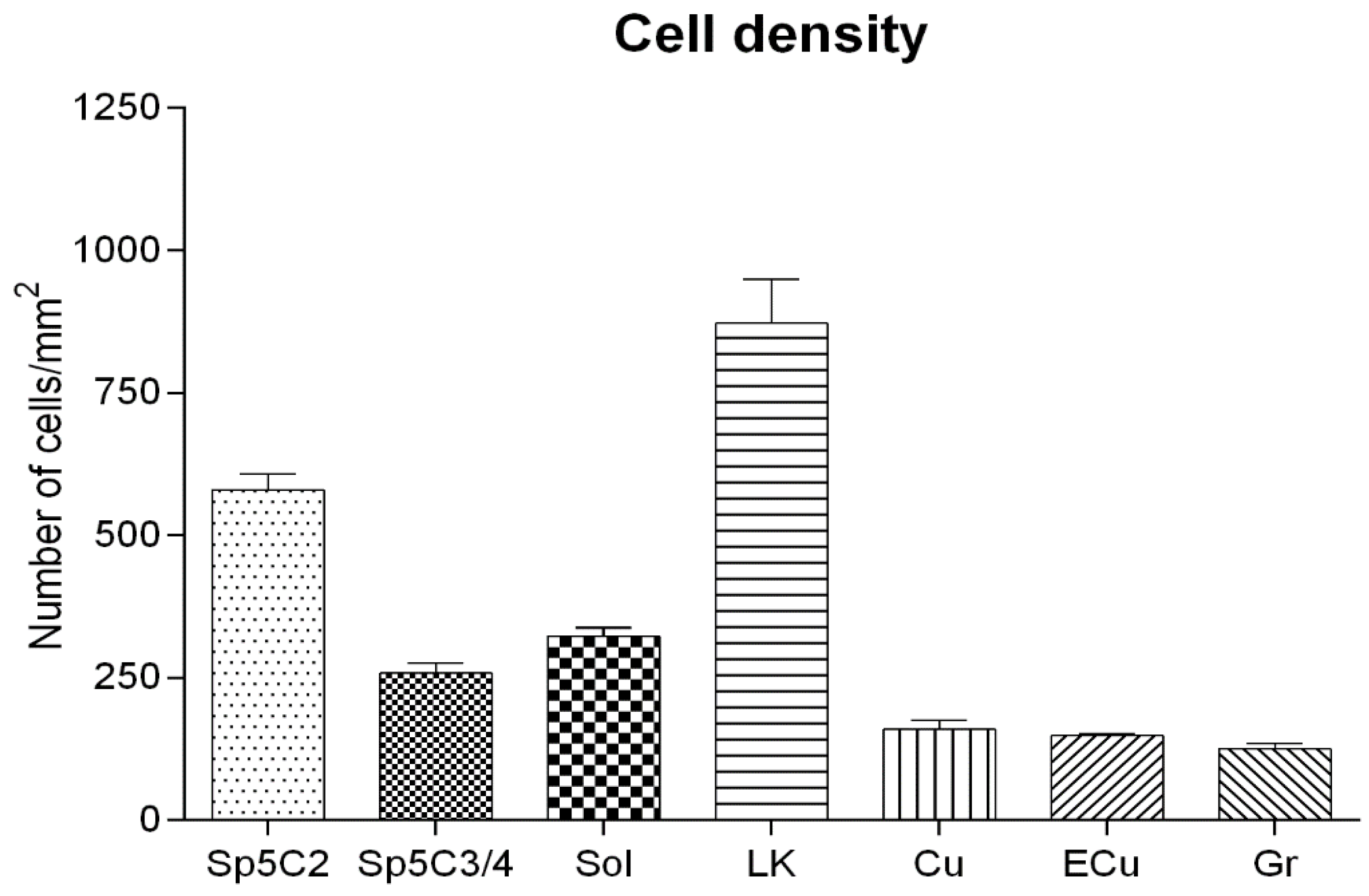
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caterina, M.J.; Schumacher, M.A.; Tominaga, M.; Rosen, T.A.; Levine, J.D.; Julius, D. The capsaicin receptor: A heat-activated ION channel in the pain pathway. Nature 1997, 389, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szallasi, A.; Cortright, D.N.; Blum, C.A.; Eid, S.R. The vanilloid receptor TRPV1: 10 years from channel cloning to antagonist proof-of-concept. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. TRPV1 structures in nanodiscs reveal mechanisms of ligand and lipid action. Nature 2016, 534, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, V.; Rohacs, T. TRPV1: A Target for Rational Drug Design. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y.; Nakazato, E.; Fujiuchi, A.; Hara, T.; Imai, A. Involvement of an increased spinal TRPV1 sensitization through its up-regulation in mechanical allodynia of CCI rats. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, L.; Altier, C. Transient Receptor Potential Channels in neuropathic pain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 32, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gu, L.; Ruan, Y.; Gegen, T.; Yu, L.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, G.; Tang, Z. Pirt together with TRPV1 is involved in the regulation of neuropathic pain. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 4861491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szallasi, A.; Blumberg, P.M. Vanilloid (capsaicin) receptors and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 159–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.W.; Cho, H.; Kwak, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, C.J.; Kang, C.J.; Jung, J.; Cho, S.; Min, K.H.; Suh, Y.G.; et al. Direct activation of capsaicin receptors by products of lipoxygenases: Endogenous capsaicin-like substances. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6155–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bölcskei, K.; Helyes, Z.; Szabó, A.; Sándor, K.; Elekes, K.; Németh, J. Investigation of the role of TRPV1 receptors in acute and chronic nociceptive processes using gene-deficient mice. Pain 2005, 117, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P. The pharmacological challenge to tame the transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) nocisensor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helliwell, R.J.; McLatchie, L.M.; Clarke, M.; Winter, J.; Bevan, S.; McIntyre, P. Capsaicin sensitivity is associated with the expression of the vanilloid (capsaicin) receptor (VR1) mRNA in adult rat sensory ganglia. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 250, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, M.; Caterina, M.J.; Malmberg, A.B.; Rosen, T.A.; Gilbert, H.; Skinner, K.; Raumann, B.E.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron 1998, 21, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.J.; Priestley, J.V. Differential expression of the mRNA for the vanilloid receptor subtype 1 in cells of the adult rat dorsal root and nodose ganglia and its downregulation by axotomy. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezey, E.; Tóth, Z.E.; Cortright, D.N.; Arzubi, M.K.; Krause, J.E.; Elde, R.; Guo, A.; Blumberg, P.M.; Szallasi, A. Distribution of mRNA for vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR1), and VR1-like immunoreactivity, in the central nervous system of the rat and human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3655–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, I.; Emori, Y.; Ninomiya, Y.; Abe, K. A comparative study of three cranial sensory ganglia projecting into the oral cavity: In situ hybridization analyses of neurotrophin receptors and thermosensitive cation channels. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 93, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, H.; Fukunaga, T.; Jin, H.W.; Fujita, M.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Sugimoto, T. VR1-, VRL-1- and P2X3 receptor-immunoreactive innervation of the rat temporomandibular joint. Brain Res. 2004, 1008, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, H.; Sugimoto, T. The co-expression of VR1 and VRL-1 in the rat vagal sensory ganglia. Brain Res. 2003, 980, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Groneberg, D.A.; Peiser, C.; Springer, J.; Joachim, R.A.; Arck, P.C.; Klapp, B.F.; Fischer, A. Nerve growth factor-induced substance P in capsaicin-insensitive vagal neurons innervating the lower mouse airway. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damann, N.; Rothermel, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Hatt, H.; Wetzel, C.H. Chemosensory properties of murine nasal and cutaneous trigeminal neurons identified by viral tracing. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, S.; Quallo, T.; Andersson, D.A. TRPV1. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 222, pp. 207–245. [Google Scholar]
- Quartu, M.; Carozzi, V.A.; Dorsey, S.G.; Serra, M.P.; Poddighe, L.; Picci, C.R.; Boi, M.A.; Melis, T.I.; Del Fiacco, M.; Meregalli, C.R.; et al. Bortezomib treatment produces nocifensive behavior and changes in the expression of TRPV1, CGRP, and substance P in the rat DRG, spinal cord, and sciatic nerve. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 180428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortright, D.N.; Crandall, M.; Sanchez, J.F.; Zou, T.; Krause, J.E.; White, G. The tissue distribution and functional characterization of human VR1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P. TRPV1 and the gut: From a tasty receptor for a painful vanilloid to a key player in hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 500, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.R.; Rodd, H.D.; Clayton, N.; Davis, J.B.; Boissonade, F.M. Vanilloid receptor 1 expression in human tooth pulp in relation to caries and pain. J. Orofac. Pain 2005, 19, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lauria, G.; Morbin, M.; Lombardi, R.; Capobianco, R.; Camozzi, F.; Pareyson, D.; Manconi, M.; Geppetti, P. Expression of capsaicin receptor immunoreactivity in human peripheral nervous system and in painful neuropathies. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2006, 11, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facer, P.; Smith, G.D.; Benham, C.D.; Chessell, I.P.; Bountra, C.; Sinisi, M.; Birch, R.; Anand, P. Differential expression of the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 and related novel receptors TRPV3, TRPV4 and TRPM8 in normal human tissues and changes in traumatic and diabetic neuropathy. BMC Neurol. 2007, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, U.; Otto, W.R.; Bountra, C.; Chessell, I.; Sinisi, M.; Birch, R.; Anand, P. Cytosine arabinoside affects the heat and capsaicin receptor TRPV1 localisation and sensitivity in human sensory neurons. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 89, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Uddman, R.; Tajti, J.; Kanje, M.; Edvinsson, L. Capsaicin receptor immunoreactivity in the human trigeminal ganglion. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 330, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Poddighe, L.; Picci, C.; Demontis, R.; Del Fiacco, M. TRPV1 receptor in the human trigeminal ganglion and spinal nucleus: Immunohistochemical localization and comparison with the neuropeptides CGRP and SP. J. Anat. 2016, 229, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Z.; Renton, T.; Yiangou, Y.; Zakrzewska, J.; Chessell, I.P.; Bountra, C.; Anand, P. Burning mouth syndrome as a trigeminal small fibre neuropathy: Increased heat and capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in nerve fibres correlates with pain score. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 14, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, M.; Takeda, M.; Honda, K.; Maruno, M.; Katagiri, A.; Satoh-Kuriwada, S.; Shoji, N.; Tsuchiya, M.; Iwata, K. Involvement of peripheral artemin signaling in tongue pain: Possible mechanism in burning mouth syndrome. Pain 2015, 156, 2528–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fiacco, M.; Quartu, M.; Boi, M.; Serra, M.P.; Melis, T.; Boccaletti, R.; Shevel, E.; Cianchetti, C. TRPV1, CGRP and SP in scalp arteries of patients suffering from chronic migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisani, M.; Smart, D.; Gunthorpe, M.J.; Tognetto, M.; Barbieri, M.; Campi, B.; Amadesi, S.; Gray, J.; Jerman, J.C.; Brough, S.J.; et al. Ethanol elicits and potentiates nociceptor responses via the vanilloid receptor-1. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, A.D.; Gerard, N.P.; Brain, S.D. Evidence of a role for NK1 and CGRP receptors in mediating neurogenic vasodilatation in the mouse ear. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chizh, B.A.; O’Donnell, M.B.; Napolitano, A.; Wang, J.; Brooke, A.C.; Aylott, M.C.; Bullman, J.N.; Gray, E.J.; Lai, R.Y.; Williams, P.M.; et al. The effects of the TRPV1 antagonist SB-705498 on TRPV1 receptor-mediated activity and inflammatory hyperalgesia in humans. Pain 2007, 132, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, A.; Graepel, R.; Keeble, J.; Schmidhuber, S.; Clark, N.; Grant, A.; Shah, A.M.; Brain, S.D. A reactive oxygen species-mediated component in neurogenic vasodilatation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 78, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.K.; Kim, M.S.; Fang, Z.; Li, H.Y.; Jung, S.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Park, K.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.B. Functional expression of thermo-transient receptor potential channels in dental primary afferent neurons: Implication for tooth pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17304–17311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, A.; Yiangou, Y.; Facer, P.; Walters, J.R.; Anand, P.; Ghosh, S. Increased capsaicin receptor TRPV1-expressing sensory fibres in irritable bowel syndrome and their correlation with abdominal pain. Gut 2008, 57, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P. Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels as drug targets for diseases of the digestive system. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 131, 142–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Izzo, A.A. The pharmacology of TRP channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 2469–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.-K.; Lee, J.; Duraes, G.; Ro, J.Y. Lipopolysaccharide-induced pulpitis up-regulates TRPV1 in trigeminal ganglia. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, M.R.; Beyer, C.E.; Stahl, S.M. TRPV1 Antagonists and Chronic Pain: Beyond Thermal Perception. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikandar, S.; Dickenson, A.H. Visceral pain: The ins and outs, the ups and downs. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2012, 6, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, E.; Jinnouchi, O.; Nakano, S.; Ohnishi, H.; Kawata, I.; Okamoto, H.; Takeda, N. Aural stimulation with capsaicin ointment improved swallowing function in elderly patients with dysphagia: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, comparative study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, H.; Ara, T.; Fujinami, Y.; Hiraoka, B.Y. Aberrant TRPV1 expression in heat hyperalgesia associated with trigeminal neuropathic pain. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakir, H.M.; Mostafeezur, R.M.; Suzuki, A.; Hitomi, S.; Suzuki, I.; Maeda, T.; Seo, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Lev, S.; et al. Expression of TRPV1 channels after nerve injury provides an essential delivery tool for neuropathic pain attenuation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazerani, P.; Pedersen, N.S.; Staahl, C.; Drewes, A.M.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Subcutaneous Botulinum toxin type A reduces capsaicin-induced trigeminal pain and vasomotor reactions in human skin. Pain 2009, 141, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aykanat, V.; Gentgall, M.; Briggs, N.; Williams, D.; Yap, S.; Rolan, P. Intradermal capsaicin as a neuropathic pain model in patients with unilateral sciatica. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 73, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberberg, A.; Moeller-Bertram, T.; Wallace, M.S. A randomized, double-blind, crossover study to evaluate the depth response relationship of intradermal capsaicin-induced pain and hyperalgesia in healthy adult volunteers. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Sun, X.X.; Locke, E.E.; Henry, M.A.; Hargreaves, K.M. Capsaicin-evoked CGRP release from human dental pulp: A model system for the study of peripheral neuropeptide secretion in normal healthy tissue. Pain 2009, 144, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, L.E.; Ramsey, A.A.; Emrick, J.J.; Janal, M.N.; Gibbs, J.L. Variability in Capsaicin-stimulated Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide Release from Human Dental Pulp. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witting, N.; Svensson, P.; Gottrup, H.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Jensen, T.S. Intramuscular and intradermal injection of capsaicin: A comparison of local and referred pain. Pain 2000, 84, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Yarnitsky, D. Experimental and clinical applications of quantitative sensory tsting applied to skin, muscles and viscera. J. Pain 2009, 10, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, M.K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Svensson, P. Inhibition of motor unit firing during experimental muscle pain in humans. Muscle Nerv. 2000, 23, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J.; Brock, C.; Olesen, A.E.; Andresen, T.; Nilsson, M.; Dickenson, A.H. Unravelling the mystery of capsaicin: A tool to understand and treat pain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 939–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompeiano, O.; Brodal, A. Spinovestibular fibers in the cat; an experimental study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1957, 108, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, A.; Krnjević, K.; Schwartz, S. Micro-iontophoretic studies on neurones in the cuneate nucleus. J. Physiol. 1967, 192, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.J. The release of amino acids with proposed neurotransmitter function from the cuneate and gracile nuclei of the rat in vivo. Brain Res. 1974, 67, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustioni, A.; Schmechel, D.E.; Cheema, S.; Fitzpatrick, D. Glutamic acid decarboxylase-containing neurons in the dorsal column nuclei of the cat. Somatosens. Res. 1984, 1, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westman, J. Light and electron microscopical studies of the GABA innervation of the dorsal column nuclei and the lateral cervical nucleus in the primate species Macaca fascicularis and Papio anubis. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 1989, 94, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biasi, S.; Rustioni, A. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of excitatory amino acids in the somatosensory system. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1990, 38, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, R.; Westman, J. Quantitative analysis of the feline dorsal column nuclei and their GABAergic and non-GABAergic neurons. Anat. Embryol. 1991, 184, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biasi, S.; Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L.; Bernardi, P.; Valtschanoff, J.G.; Weinberg, R.J. Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical characterization of primary afferent terminals in the rat cuneate nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 347, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popratiloff, A.; Valtschanoff, J.G.; Rustioni, A.; Weinberg, R.J. Colocalization of GABA and glycine in the rat dorsal column nuclei. Brain Res. 1996, 706, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Shieh, J.Y.; Wen, C.Y. Afferent synaptic contacts on glycine-immunoreactive neurons in the rat cuneate nucleus. Synapse 2001, 41, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, Z.; Sherriff, F.E. Distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactive axons and terminals in the rat and ferret brainstem. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 314, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomqvist, A.; Broman, J. Serotoninergic innervation of the dorsal column nuclei and its relation to cytoarchitectonic subdivisions: An immunohistochemical study in cats and monkeys (Aotus trivirgatus). J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 327, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqbool, A.; Batten, T.F.; Berry, P.A.; McWilliam, P.N. Distribution of dopamine-containing neurons and fibres in the feline medulla oblongata: A comparative study using catecholamine-synthesizing enzyme and dopamine immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience 1993, 53, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fiacco, M.; Dessi, M.L.; Atzori, M.G.; Levanti, M.C. Substance P in the human brainstem. Preliminary results of its immunohistochemical localization. Brain Res. 1983, 264, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fiacco, M.; Dessì, M.L.; Levanti, M.C. Topographical localization of substance P in the human post-mortem brainstem. An immunohistochemical study in the newborn and adult tissue. Neuroscience 1984, 12, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigr, F.; Najimi, M.; Leduque, P.; Charnay, Y.; Jordan, D.; Chayvialle, J.A.; Tohyama, M.; Kopp, N. Anatomical distribution of somatostatin immunoreactivity in the infant brainstem. Neuroscience 1989, 29, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, J.W.; Lange, W. Immunohistochemical mapping of neurophysins and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the human brainstem and cervical spinal cord. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1991, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveñas, R.; Martin, F.; Belda, M.; Smith, V.; Salinas, P.; Rivada, E.; Gonzalez-Baron, S. Mapping of neurokinin-like immunoreactivity in the human brainstem. BMC Neurosci. 2003, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveñas, R.; Martín, F.; Salinas, P.; Rivada, E.; Smith, V.; Aguilar, L.A.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z.; Narváez, J.A.; Tramu, G. An immunocytochemical mapping of methionine-enkephalin-Arg(6)-Gly(7)-Leu(8) in the human brainstem. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simantov, R.; Kuhar, M.J.; Uhl, G.R.; Snyder, S.H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: Immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 2167–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuello, A.C.; Kanazawa, I. The distribution of substance P immunoreactive fibers in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 178, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungdahl, A.; Hökfelt, T.; Nilsson, G. Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat—I. Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience 1978, 3, 861–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.; Elde, R. The distribution of enkephalin immunoreactive fibers and terminals in the monkey central nervous system: An immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 1982, 7, 1049–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath-Verrier, M.; Dietl, M.; Arluison, M.; Cesselin, F.; Bourgoin, S.; Hamon, M. Localization of Met-enkephalin-like immunoreactivity within pain-related nuclei of cervical spinal cord, brainstem and midbrain in the cat. Brain Res. Bull. 1983, 11, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, O.; Hökfelt, T.; Elde, R.P. Immunohistochemical distribution of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the adult rat. Neuroscience 1984, 13, 265–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Takami, K.; Shiosaka, S.; Emson, P.C.; Hillyard, C.J.; Girgis, S.; MacIntyre, I.; Tohyama, M. Topographic localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat brain: An immunohistochemical analysis. Neuroscience 1985, 15, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.R.; McIntosh, C.H.; Buchan, A.M.; Brown, J.C. Central somatostatin systems revealed with monoclonal antibodies. J. Comp. Neurol. 1985, 238, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skofitsch, G.; Jacobowitz, D.M. Immunohistochemical mapping of galanin-like neurons in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 1985, 6, 509–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofitsch, G.; Jacobowitz, D.M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: Detailed immunohistochemical distribution in the central nervous system. Peptides 1985, 6, 721–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber-Pierce, E.; Lichentenstein, E.; Feldman, S.C. The somatostatin systems of the guinea-pig brainstem. Neuroscience 1985, 15, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, T.; Hökfelt, T.; Rökaeus, A. Distribution of galanin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1986, 248, 475–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, L.; Sternini, C.; Brecha, N.C.; Mantyh, P.W. Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in relation to the rat central somatosensory projection. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 273, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordower, J.H.; Le, H.K.; Mufson, E.J. Galanin immunoreactivity in the primate central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 319, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Meister, B.; Elde, R.; Verge, V.M.; Hökfelt, T. Large calibre primary afferent neurons projecting to the gracile nucleus express neuropeptide Y after sciatic nerve lesions: An immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1993, 5, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rossum, D.; Hanisch, U.K.; Quirion, R. Neuroanatomical localization, pharmacological characterization and functions of CGRP, related peptides and their receptors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 649–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fiacco, M.; Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Demontis, R.; Poddighe, L.; Picci, C.; Melis, T. The human cuneate nucleus contains discrete subregions whose neurochemical features match those of the relay nuclei for nociceptive information. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 219, 2083–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fiacco, M.; Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Follesa, P.; Lai, M.L.; Bachis, A. Topographical localization of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the human brain stem: An immunohistochemical study of prenatal, neonatal and adult brains. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2002, 23, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Lai, M.L.; Del Fiacco, M. GAP-43 in the spinal trigeminal and dorsal column nuclei of the newborn and adult man: Immunohistochemical distribution and comparison with that of the neuropeptides SP and CGRP. Ital. J. Anat. Embryol. 1995, 100, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Ferretti, M.T.; Lai, M.L.; Del Fiacco, M. Tissue distribution of Ret, GFRalpha-1, GFRalpha-2 and GFRalpha-3 receptors in the human brainstem at fetal, neonatal and adult age. Brain Res. 2007, 1173, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Sestu, N.; Lai, M.L.; Del Fiacco, M. Tissue distribution of neurturin, persephin and artemin in the human brainstem at fetal, neonatal and adult age. Brain Res. 2007, 1143, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Ibba, V.; Melis, T.; Del Fiacco, M. Polysialylated-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM) in the human trigeminal ganglion and brainstem at prenatal and adult ages. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, M.P.; Quartu, M.; Poddighe, L.; Picci, C.; Melis, T.; Del Fiacco, M. Locus K: A novel territory of the human dorsal column nuclei. In Proceedings of the 23th National Congress of Gruppo Italiano per lo S tudio della Neuromorfologia, Cagliari, Italy, 22–23 November 2013; PAGE Press: Pavia, Italy, 2013; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, M.P.; Quartu, M.; Boi, M.; Poddighe, L.; Melis, T.; Picci, C.; Del Fiacco, M. Locus K: Cuneate subnuclear regions in human dorsal column nuclei with neurochemical, cyto- and myeloarchitectural features of protopathic sensory nuclei. In Proceedings of the 9th FENS Forum of Neuroscience, Milan, Italy, 5–9 July 2014; Volume 7, p. 2773. [Google Scholar]
- Rustioni, A.; Weinberg, R.J. The somatosensory system. In Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Integrated Systems of the CNS, Part II; Björklund, A., Hökfelt, T., Swanson, L.W., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. (Biomedical Division): Amsterdam, Holland, 1989; Volume 7, pp. 219–321. ISBN 0444812326, 9780444812322. [Google Scholar]
- Broman, J. Neurotransmitters in subcortical somatosensory pathways. Anat. Embryol. 1994, 189, 181–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.; Vulchanova, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Elde, R. Immunocytochemical localization of the vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1): Relationship to neuropeptides, the P2X3 purinoceptor and IB4 binding sites. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtschanoff, J.G.; Rustioni, A.; Guo, A.; Hwang, S.J. Vanilloid receptor VR1 is both presynaptic and postsynaptic in the superficial laminae of the rat dorsal horn. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 436, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.J.; Oh, J.M.; Valtschanoff, J.G. Expression of the vanilloid receptor TRPV1 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons supports different roles of the receptor in visceral and cutaneous afferents. Brain Res. 2005, 1047, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špicarová, D.; Paleček, J. The role of spinal cord vanilloid (TRPV1) receptors in pain modulation. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57 (Suppl. 3), S69–S77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.C.; Oh, J.M.; Hwang, S.J.; Shigenaga, Y.; Valtschanoff, J.G. Expression of vanilloid receptor TRPV1 in the rat trigeminal sensory nuclei. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 478, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doly, S.; Fischer, J.; Salio, C.; Conrath, M. The vanilloid receptor-1 is expressed in rat spinal dorsal horn astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 357, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Willcockson, H.H.; Valtschanoff, J.G. Influence of the vanilloid receptor TRPV1 on the activation of spinal cord glia in mouse models of pain. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 220, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Back, S.K.; Davies, A.J.; Jeong, H.; Jo, H.J.; Chung, G.; Na, H.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; et al. TRPV1 in GABAergic interneurons mediates neuropathic mechanical allodynia and disinhibition of the nociceptive circuitry in the spinal cord. Neuron 2012, 74, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.J.; Valtschanoff, J.G. Vanilloid receptor VR1-positive afferents are distributed differently at different levels of the rat lumbar spinal cord. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 349, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K. Postnatal excitability development and innervation by functional transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) terminals in neurons of the rat spinal sacral dorsal commissural nucleus: An electrophysiological study. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6033–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandadi, S.; Roufogalis, B.D. ThermoTRP channels in nociceptors: Taking a lead from capsaicin receptor TRPV1. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.H.; McDougall, S.J.; Fawley, J.A.; Andresen, M.C. TRPV1 marks synaptic segregation of multiple convergent afferents at the rat medial solitary tract nucleus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, L.A.; Coggeshall, R.E. Unmyelinated axons in the Posterior funiculi. Science 1981, 211, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.S.; Coggeshall, R.E. Unmyelinated primary afferent fibers in dorsal funiculi of cat sacral spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1985, 238, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.; Langford, L.A.; Coggeshall, R.E. Primary afferent and propriospinal fibers in the rat dorsal and dorsolateral funiculi. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987, 263, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeill, D.L.; Chung, K.; Carlton, S.M.; Coggeshall, R.E. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunostained axons provide evidence for fine primary afferent fibers in the dorsal and dorsolateral funiculi of the rat spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 272, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamatani, M.; Senba, E.; Tohyama, M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-containing primary afferent fibers in the dorsal column of the rat. Brain Res. 1989, 495, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.T.; Coggeshall, R.E.; Lee, W.T.; Chung, K. Long ascending unmyelinated primary afferent axons in the rat dorsal column: Immunohistochemical localizations. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 108, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Kawai, Y.; Fukuoka, T.; Senba, E.; Miki, K. Substance P induced by peripheral nerve injury in primary afferent sensory neurons and its effect on dorsal column nucleus neurons. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 7633–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Noguchi, K. Calcitonin gene-related peptide increase in the rat spinal dorsal horn and dorsal column nucleus following peripheral nerve injury: Up-regulation in a subpopulation of primary afferent sensory neurons. Neuroscience 1998, 82, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustioni, A. Spinal neurons project to the dorsal column nuclei of rhesus monkeys. Science 1976, 196, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, W.D.; Coggeshall, R.E. Sensory Mechanisms of the Spinal Cord; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Mu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, A.; Yue, Y. NK-1-receptor-mediated lesion of spinal post-synaptic dorsal column neurons might improve intractable visceral pain of cancer origin. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 76, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, F.; De Biasi, S.; Giuffrida, R.; Rustioni, A. Substance P containing projections in the dorsal columns of rats and cats. Neuroscience 1990, 34, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Gatscher, S.; Sure, U.; Bertalanffy, H. The punctate midline myelotomy concept for visceral cancer pain control–case report and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2002, 79, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paleček, J. The Role of Dorsal Columns Pathway in Visceral Pain. Physiol. Res. 2004, 53 (Suppl. 1), S125–S130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pomonis, J.D.; Harrison, J.E.; Mark, L.; Bristol, D.R.; Valenzano, K.J.; Walker, K. N-(4-Tertiarybutylphenyl)-4-(3-cholorphyridin-2-yl)tetrahydropyrazine-1 (2H)-carbox-amide (BCTC), a novel, orally effective vanilloid receptor 1 antagonist with analgesic properties: II. In vivo characterization in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Honore, P.; Zhong, C.; Gauvin, D.; Mikusa, J.; Hernandez, G.; Chandran, P.; Gomtsyan, A.; Brown, B.; Bayburt, E.K.; et al. TRPV1 receptors in the CNS play a key role in broad-spectrum analgesia of TRPV1 antagonists. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 9385–9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culshaw, A.J.; Bevan, S.; Christiansen, M.; Copp, P.; Davis, A.; Davis, C.; Dyson, A.; Dziadulewicz, E.K.; Edwards, L.; Eggelte, H.; et al. Identification and biological characterization of 6-aryl-7-isopropylquinazolinones as novel TRPV1 antagonists that are effective in models of chronic pain. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaraughty, S.; Chu, K.L.; Brown, B.S.; Zhu, C.Z.; Zhong, C.; Joshi, S.K.; Honore, P.; Faltynek, C.R.; Jarvis, M.F. Contributions of central and peripheral TRPV1 receptors to mechanically evoked and spontaneous firing of spinal neurons in inflamed rats. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 3158–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paré, M.; Elde, R.; Mazurkiewicz, J.E.; Smith, A.M.; Rice, F.L. The Meissner corpuscle revised: A multiafferented mechanoreceptor with nociceptor immunochemical properties. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7236–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Senba, E.; Tohyama, M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in Meissner’s corpuscles of rats: An immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res. 1988, 453, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsgaard, C.J.; Jonsson, C.E.; Hökfelt, T.; Cuello, A.C. Localization of substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the human digital skin. Experientia 1983, 39, 1018–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, K.; Yasumasa, S.; Hiromoto, I.; Hironubu, I. Sensory nerve supply in the human subacromial bursa. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 1996, 5, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; de Petrocellis, L.; Pryce, G.; Baker, D.; Guglielmotti, V.; Di Marzo, V. Immunohistochemical localization of cannabinoid type 1 and vanilloid transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 receptors in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 2006, 139, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liapi, A.; Wood, J.N. Extensive co-localization and heteromultimer formation of the vanilloid receptor-like protein TRPV2 and the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in the adult rat cerebral cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, S.; Bisogno, T.; de Novellis, V.; Palazzo, E.; Cristino, L.; Valenti, M.; Petrosino, S.; Guglielmotti, V.; Rossi, F.; Di Marzo, V. Elevation of endocannabinoid levels in the ventrolateral periaqueductal grey through inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase affects descending nociceptive pathways via both cannabinoid receptor type 1 and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.C.; Davis, J.B.; Benham, C.D. [3H]Resiniferatoxin autoradiography in the CNS of wild-type and TRPV1 null mice defines TRPV1 (VR-1) protein distribution. Brain Res. 2004, 995, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, I.; Sántha, P.; Jancsó, G.; Urbán, L. The role of the vanilloid (capsaicin) receptor (TRPV1) in physiology and pathology. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 500, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, E.; Rossi, F.; Maione, S. Role of TRPV1 receptors in descending modulation of pain. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 286 (Suppl. 1), S79–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, A.; Boczán, J.; Kedei, N.; Lizanecz, E.; Bagi, Z.; Papp, Z.; Édes, I.; Csiba, L.; Blumberg, P.M. Expression and distribution of vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) in the adult rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 135, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Ohtori, S.; Takahashi, K.; Ino, H.; Douya, H.; Ozawa, T.; Saito, T.; Moriya, H. Expression and co-expression of VR1, CGRP, and IB4-binding glycoprotein in dorsal root ganglion neurons in rats: Differences between the disc afferents and the cutaneous afferents. Spine 2005, 30, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case | Age | Sex | Primary Cause of Death | Post-Mortem Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fetus 21 w.g. | F | Cardiorespiratory failure | 29 |
| 2 | Pre-term newborn 6 d (25 w.g.) | F | Pneumonitis | 25 |
| 3 | Pre-term newborn 1 d (34 w.g.) | M | Cardiorespiratory failure | 29 |
| 4 | Pre-term newborn (38 w.g.) | M | Cardiorespiratory failure | 38 |
| 5 | Full-term newborn (40 w.g.) | M | Cardiorespiratory failure | 28 |
| 6 | Full-term newborn 1 d | M | Cardiorespiratory failure | 24 |
| 7 | Full-term newborn 2 d | F | Persistence of fetal circulation | 38 |
| 8 | Full-term newborn 7 d | F | Cardiorespiratory failure | 27 |
| 9 | Adult 44 y | M | Stabbing | 40 |
| 10 | Adult 53 y | F | Cardiorespiratory failure | 31 |
| 11 | Adult 56 y | F | Cardiomyopathy | 34 |
| 12 | Adult 71 y | M | Renal failure | 25 |
| Nuclei | Summary | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sp5C3/4 vs. Sol | * | 0.0267 |
| Sp5C3/4 vs. LK | ** | 0.0033 |
| Sp5C2 vs. LK | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sp5C2 vs. Cu | ns | 0.5456 |
| Sp5C2 vs. ECu | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sp5C2 vs. Gr | ns | 0.1186 |
| Sp5C3/4 vs. Cu | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sp5C3/4 vs. ECu | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sp5C3/4 vs. Gr | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sol vs. LK | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sol vs. Cu | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sol vs. ECu | **** | <0.0001 |
| Sol vs. Gr | **** | <0.0001 |
| LK vs. Cu | **** | <0.0001 |
| LK vs. ECu | **** | <0.0001 |
| LK vs. Gr | **** | <0.0001 |
| Cu vs. ECu | ns | 0.9998 |
| Cu vs. Gr | ns | 0.9203 |
| ECu vs. Gr | ns | 0.9771 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Fiacco, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Poddighe, L.; Demontis, R.; Carai, A.; Quartu, M. TRPV1-Like Immunoreactivity in the Human Locus K, a Distinct Subregion of the Cuneate Nucleus. Cells 2018, 7, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070072
Del Fiacco M, Serra MP, Boi M, Poddighe L, Demontis R, Carai A, Quartu M. TRPV1-Like Immunoreactivity in the Human Locus K, a Distinct Subregion of the Cuneate Nucleus. Cells. 2018; 7(7):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070072
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Fiacco, Marina, Maria Pina Serra, Marianna Boi, Laura Poddighe, Roberto Demontis, Antonio Carai, and Marina Quartu. 2018. "TRPV1-Like Immunoreactivity in the Human Locus K, a Distinct Subregion of the Cuneate Nucleus" Cells 7, no. 7: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070072
APA StyleDel Fiacco, M., Serra, M. P., Boi, M., Poddighe, L., Demontis, R., Carai, A., & Quartu, M. (2018). TRPV1-Like Immunoreactivity in the Human Locus K, a Distinct Subregion of the Cuneate Nucleus. Cells, 7(7), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070072






