Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in T2D Patients Across Clinical Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
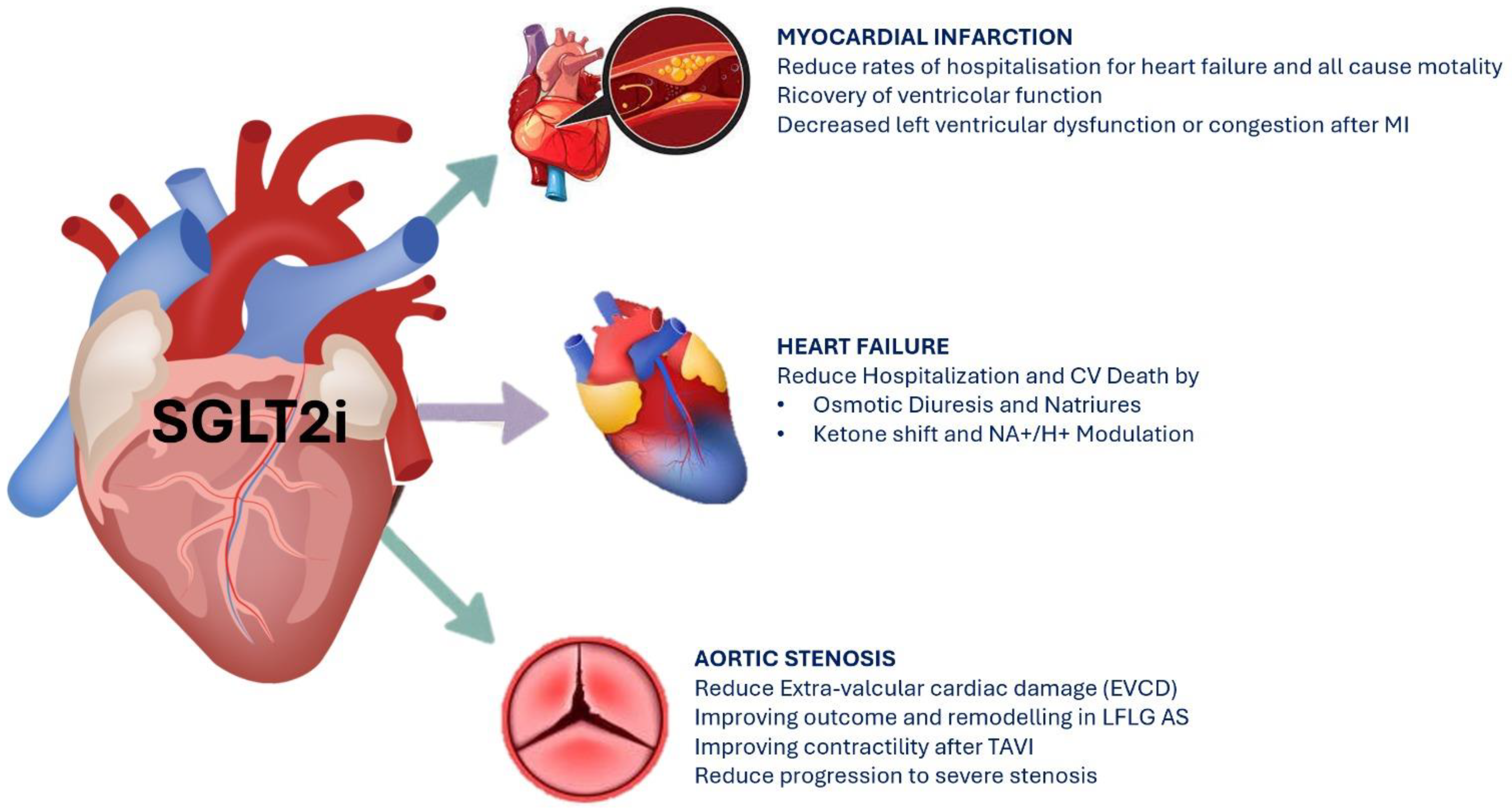
2. Effects of SGLT2i on Cardiovascular Outcomes
2.1. SGLT2i and Acute and Chronic Heart Failure
2.2. SGLT2i and Myocardial Infarction
2.3. SGLT2i and Aortic Stenosis
3. Effects of SGLT2i on Renal Outcomes
SGLT2i and Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Disease
4. Effects of SGLT2i on Electrolytic Balance and Uric Acid
5. Effects of SGLT2i on Body Weight
6. Effects of SGLT2i on Blood Pressure
7. Effects of SGLT2i on Lipid Profile
8. Effects of SGLT2i on Bone Metabolism
9. Effects of SGLT2i on Liver
10. SGLT2i and Cancer
11. Future Perspectives: IBD, Cognitive Impairment, and COPD
12. Euglycemic Ketoacidosis and Post-Surgery
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Standard of Care in Diabetes 2025, Diabetes Care December 2024; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee: Arlington, VA, USA, 2024; Volume 48, pp. S1–S352. [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, C.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Gmyr, V.; Queniat, G.; Moerman, E.; Thévenet, J.; Beaucamps, C.; Delalleau, N.; Popescu, I.; Malaisse, W.J.; et al. Inhibition of the glucose transporter SGLT2 with dapagliflozin in pancreatic alpha cells triggers glucagon secretion. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V. The mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 inhibitors: The star in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardiance. JardianceTM Press Releases; Boehringer Ingelheim: Wan Chai, Hong Kong, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- LLC. InvokanaTM Press Releases; Janssen Research & Development: Raritan, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Steglatro. SteglatroTM Press Releases; Merck: Darmstadt, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Forxiga. ForxigaTM Press Releases; AstraZeneca: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Garg, A.; Tantry, U.S.; Bliden, K.; Gurbel, P.A.; Gulati, M. Cardiovascular Outcomes With Empagliflozin and Dapagliflozin in Patients Without Diabetes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2024, 218, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.S.; Siddiqi, T.J.; Anker, S.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Bhatt, D.L.; Filippatos, G.; Fonarow, G.C.; Greene, S.J.; Januzzi, J.L.; Khan, M.S.; et al. Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Cardiovascular Outcomes Across Various Patient Populations. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 2377–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfella, R.; Scisciola, L.; D’Onofrio, N.; Maiello, C.; Trotta, M.C.; Sardu, C.; Panarese, I.; Ferraraccio, F.; Capuano, A.; Barbieri, M.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) expression in diabetic and non-diabetic failing human cardiomyocytes. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scisciola, L.; Paolisso, P.; Belmonte, M.; Gallinoro, E.; Delrue, L.; Taktaz, F.; Fontanella, R.A.; Degrieck, I.; Pesapane, A.; Casselman, F.; et al. Myocardial sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 expression and cardiac remodelling in patients with severe aortic stenosis: The BIO-AS study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2024, 26, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.M.; Lau, Y.M.; Dhandhania, V.; Cai, Z.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Lai, W.H.; Tse, H.F.; Siu, C.W. Empagliflozin Ammeliorates High Glucose Induced-Cardiac Dysfuntion in Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- von Lewinski, D.; Rainer, P.P.; Gasser, R.; Huber, M.S.; Khafaga, M.; Wilhelm, B.; Haas, T.; Mächler, H.; Rössl, U.; Pieske, B. Glucose-transporter-mediated positive inotropic effects in human myocardium of diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Metabolism 2010, 59, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefits of Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: A State-of-the-Art Review. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kato, E.T.; Silverman, M.G.; Mosenzon, O.; Zelniker, T.A.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Kuder, J.; Murphy, S.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Heart Failure and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2019, 139, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Fitchett, D.; Mattheus, M.; George, J.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; von Eynatten, M.; Zinman, B. Empagliflozin and clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, established cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. Circulation 2018, 137, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Pal, R.; Nair, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S. SGLT2 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes in heart failure with mildly reduced and preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Indian Heart J. 2023, 75, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Docherty, K.F.; Claggett, B.L.; Jhund, P.S.; de Boer, R.A.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; PLam, C.S.; Martinez, F.; et al. SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Patients with Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of 5 Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Lancet 2022, 400, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Reddy, Y.N.V.; Braun, A.; Sorimachi, H.; Omar, M.; Popovic, D.; Alogna, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Carter, R. Cardiac and Metabolic Effects of Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: The CAMEO-DAPA Trial. Circulation 2023, 148, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Vargas-Delgado, A.P.; Requena-Ibanez, J.A.; Garcia-Ropero, A.; Mancini, D.; Pinney, S.; Macaluso, F.; Sartori, S.; Roque, M.; Sabatel-Perez, F.; et al. Randomized Trial of Empagliflozin in Nondiabetic Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; Angermann, C.E.; Teerlink, J.R.; Collins, S.P.; Kosiborod, M.; Biegus, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Nassif, M.E.; Psotka, M.A.; Tromp, J.; et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: A multinational randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.E.P.; Veiga, T.M.A.; e Silva, A.C.S.; Gewehr, D.M.; Dagostin, C.S.; Fernandes, A.; Nasi, G.; Cardoso, R. Cardiovascular and renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitor initiation in acute heart failure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2023, 112, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Vickneson, K.; Singh, J.S. SGLT2-inhibitors; more than just glycosuria and diuresis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 26, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Coronel, R.; Hollmann, M.W.; Weber, N.C.; Zuurbier, C.J. Direct cardiac effects of SGLT2 inhibitors. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Di Salvo, J.; Epifani, R.; Marfella, R.; Docimo, G.; et al. An Overview of the Cardiorenal Protective Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Herat, L.; Schlaich, M.P.; Matthews, V. The Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Heart and Kidneys Regardless of Diabetes Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldafas, R.; Crabtree, T.; Alkharaiji, M.; Vinogradova, Y.; Idris, I. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2) in frail or older people with type 2 diabetes and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2024, 53, afad254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Marco, C.; Iannantuoni, F.; Hermo-Argibay, A.; Devos, D.; Salazar, J.D.; Víctor, V.M.; Rovira-Llopis, S. Cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists through effects on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 213, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Lewinski, D.; Kolesnik, E.; Tripolt, N.J.; Pferschy, P.N.; Benedikt, M.; Wallner, M.; Alber, H.; Berger, R.; Lichtenauer, M.; Saely, C.H.; et al. Empagliflozin in acute myocardial infarction: The EMMY trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4421–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosén, H.C.; Mohammad, M.A.; Jernberg, T.; James, S.; Oldgren, J.; Erlinge, D. SGLT2 inhibitors for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after myocardial infarction: A nationwide observation registry study from SWEDEHEART. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 45, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- James, S.; Erlinge, D.; Storey, R.F.; McGuire, D.K.; de Belder, M.; Eriksson, N.; Andersen, K.; Austin, D.; Arefalk, G.; Carrick, D.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Myocardial Infarction without Diabetes or Heart Failure. NEJM Evid. 2024, 3, EVIDoa2300286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Udell, J.A.; Jones, W.S.; Anker, S.D.; Petrie, M.C.; Harrington, J.; Mattheus, M.; Seide, S.; Zwiener, I.; Amir, O.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Heart Failure Outcomes after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Insights from the EMPACT-MI Trial. Circulation 2024, 149, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolisso, P.; Belmonte, M.; Gallinoro, E.; Scarsini, R.; Bergamaschi, L.; Portolan, L.; Armillotta, M.; Esposito, G.; Moscarella, E.; Benfari, G.; et al. SGLT2-inhibitors in diabetic patients with severe aortic stenosis and cardiac damage undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shah, H.; Fanaroff, A.C.; Nathan, A.S.; Parise, H.; Lutz, J.; Sugeng, L.; Bellumkonda, L.; Redfors, B.; et al. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on the Progression of Aortic Stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2025, 18, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposeiras-Roubin, S.; Amat-Santos, I.J.; Rossello, X.; Ferreiro, R.G.; Bermúdez, I.G.; Otero, D.L.; Nombela-Franco, L.; Gheorghe, L.; Diez, J.L.; Zorita, C.B.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kasichayanula, S.; Chang, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Liu, X.; Yamahira, N.; LaCreta, F.P.; Imai, Y.; Boulton, D.W. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dapagliflozin, a novel selective inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2, in Japanese subjects without and with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.C.; Rieg, T.; Miracle, C.; Mansoury, H.; Whaley, J.; Vallon, V.; Singh, P. Acute and chronic effects of SGLT2 blockade on glomerular and tubular function in the early diabetic rat. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R75–R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.; Soleymanlou, N.; Har, R.; Fagan, N.; Johansen, O.; Woerle, H.-J.; von Eynatten, M.; Broedl, U.C. The effect of empagliflozin on arterial stiffness and heart rate variability in subjects with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solini, A.; Giannini, L.; Seghieri, M.; Vitolo, E.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, L.; Maria Bruno, R. Dapagliflozin acutely improves endothelial dysfunction, reduces aortic stiffness and renal resistive index in type 2 diabetic patients: A pilot study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M.; Garofalo, C.; Faga, T.; Michael, A.; Ielapi, N.; Grande, R.; Sapienza, P.; de Franciscis, S.; Mastroroberto, P.; et al. The association of matrix metalloproteinases with chronic kidney disease and peripheral vascular disease: A light at the end of the tunnel? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.H.; Park, E.-G.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.G.; Hahn, S.; Kim, N.H. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, E.J.; Muskiet, M.H.; van Baar, M.J.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; Emanuel, A.L.; Bozovic, A.; Danser, A.J.; Geurts, F.; Hoorn, E.J.; et al. The renal hemodynamic effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin are caused by post-glomerular vasodilatation rather than pre-glomerular vasoconstriction in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes in the randomized, double-blind RED trial. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakisaka, M.; Yoshinari, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Nakamura, S.; Asano, T.; Himeno, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Doi, Y.; Fujishima, M. Na+-dependent glucose uptake and collagen synthesis by cultured bovine retinal pericytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997, 1362, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakisaka, M.; Nagao, T.; Yoshinari, M. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Plays as a Physiological Glucose Sensor and Regulates Cellular Contractility in Rat Mesangial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schaub, J.A.; AlAkwaa, F.M.; McCown, P.J.; Naik, A.S.; Nair, V.; Eddy, S.; Menon, R.; Otto, E.A.; Demeke, D.; Hartman, J.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors mitigate kidney tubular metabolic and mTORC1 perturbations in youth-onset type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e164486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, X.; Song, S.; Zou, W.; Yang, Q.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, C. Inhibition of SGLT2 protects podocytes in diabetic kidney disease by rebalancing mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hua, R.; Ding, N.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, T. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients on SGLT2 Inhibitors Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: A Propensity-Matched Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 918167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Yang, C.; Lan, M.; Zhang, C.; Hu, X.; Jin, P.; Liu, D. Protective Effect of SGLT2i on Contrast-Induced AKI after Angiography in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Coronary Syndrome: A 6-Year Ambispective Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4996814 (accessed on 28 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Paolisso, P.; Bergamaschi, L.; Cesaro, A.; Gallinoro, E.; Gragnano, F.; Sardu, C.; Mileva, N.; Foà, A.; Armillotta, M.; Sansonetti, A.; et al. Impact of SGLT2-inhibitors on contrast-induced acute kidney injury in diabetic patients with acute myocardial infarction with and without chronic kidney disease: Insight from SGLT2-I AMI PROTECT registry. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Z.S.; Jamili, M.J.; Ensan, B.; Donyadideh, G.; Shahri, B.; Eshraghi, H.; Darroudi, S.; Moohebati, M. Short-term effects of empagliflozin on preventing contrast induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, a randomised trial. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, G.; Marchi, E.; Allinovi, M.; Lugli, G.; Biagiotti, L.; Di Muro, F.M.; Valenti, R.; Muraca, I.; Tomberli, B.; Ciardetti, N.; et al. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Heart Failure on Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Undergoing Radiocontrast Agent Invasive Procedures: A Propensity-Matched Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, X.X.; Levi, J.; Luo, Y.; Myakala, K.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Qiu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Grenz, A.; Lucia, S.; et al. SGLT2 Protein Expression Is Increased in Human Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5335–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Johnson, E.J.; Tuttle, K.R. SGLT2 Inhibition for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarman, P.R.; Mather, H.M. Diabetes may be independent risk factor for hyperkalaemia. BMJ. 2003, 327, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazella, M.A. Drug-induced hyperkalemia: Old culprits and new offenders. Am. J. Med. 2000, 109, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raebel, M.A.; Ross, C.; Xu, S.; Roblin, D.W.; Cheetham, C.; Blanchette, C.M.; Saylor, G.; Smith, D.H. Diabetes and drug-associated hyperkalemia: Effect of potassium monitoring. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2010, 25, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciolo, G.; De Pascalis, A.; Capelli, I.; Gasperoni, L.; Di Lullo, L.; Bellasi, A.; La Manna, G. Mineral and Electrolyte Disorders With SGLT2i Therapy. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kohan, D.E.; Fioretto, P.; Tang, W.; List, J.F. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavin, Y.; Mansfield, T.A.; Ptaszynska, A.; Johnsson, K.; Parikh, S.; Johnsson, E. Effect of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on potassium levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pooled analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Zhai, S.; Song, Y. Elevated serum magnesium associated with SGLT2 inhibitor use in type 2 diabetes patients: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2546–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, M.R.; Kline, I.; Xie, J.; Edwards, R.; Usiskin, K. Effect of canagliflozin on serum electrolytes in patients with type 2 diabetes in relation to estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2014, 30, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.E.; Mende, C.; Vijapurkar, U.; Sha, S.; Davies, M.J.; Desai, M. Effects of canagliflozin on serum magnesium in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A post hoc analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. SGLT2 inhibitors produce cardiorenal benefits by promoting adaptive cellular reprogramming to induce a state of fasting mimicry: A paradigm shift in understanding their mechanism of action. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Fatal reprogramming of nutrient surplus signaling O-GlcNAcylation the evolution of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 34, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. SGLT2 inhibitors: Role in protective reprogramming of cardiac nutrient transport and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, D.; Kawaguchi, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Koga, H.; Torimura, T. Effects of canagliflozin on growth and metabolic reprograming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Multi-omics analysis of metabolomics and absolute quantification proteomics (iMPAQT). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, A.S.Y.; Leong, S.; Teo, Y.N.; Syn, N.L.X.; See, R.M.; Wee, C.F.; Chong, E.Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, M.Y.; Yeo, T.-C.; et al. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum urate levels in patients with and without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-regression of 43 randomized controlled trials. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2022, 13, 20406223221083509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehner, W.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Zannad, F.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Salsali, A.; Kaempfer, C.; Brueckmann, M.; Pocock, S.J.; et al. Uric acid and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition with empagliflozin in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The EMPEROR-reduced trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.-C.; Hung, P.-H.; Hsiao, P.-J.; Wu, L.-Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Wu, M.-J.; Shieh, J.-J.; Chung, C.-J. Association of Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 Inhibitor Use for Type 2 Diabetes and Incidence of Gout in Taiwan. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2135353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brown, E.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Barber, T.M.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Weight loss variability with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: Mechanistic possibilities. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; Weinstein, R.; Law, G.; Canovatchel, W. Canagliflozin: Effects in overweight and obese subjects without diabetes mellitus. Obesity 2013, 22, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.; Bailey, C.; Rigney, U.; Blak, B.; Beekman, W.; Emmas, C. Glycated hemoglobin, body weight and blood pressure in type 2 diabetes patients initiating dapagliflozin treatment in primary care: A retrospective study. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Muscelli, E.; Frascerra, S.; Baldi, S.; Mari, A.; Heise, T.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.-J. Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, I.; Narko, K.; Zeller, C.; Green, A.; Salsali, A.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.J.; EMPA-REG BP Investigators. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care 2014, 38, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanidas, E.; Papadopoulos, D.P.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Grassos, C.; Velliou, M.; Barbetseas, J. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors Across the Spectrum of Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.W.; Huang, C.C. Pleiotropic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1086672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maliha, G.; Townsend, R.R. SGLT2 inhibitors: Their potential reduction in blood pressure. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 9, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.A.; Mansfield, T.A.; Cain, V.A.; Iqbal, N.; Parikh, S.; Ptaszynska, A. Blood pressure and glycaemic effects of dapagliflozin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes on combination antihypertensive therapy: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, P.N.; Barreto, J.; Kimura-Medorima, S.T.; Breder, I.; Nadruz, W.; Sposito, A.C. Dapagliflozin reduces the white coat effect on systolic blood pressure of patients with type 2 diabetes: A post-hoc analysis from the ADDENDA-BHS 2 trial. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2024, 41, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Poelgeest, E.P.; Handoko, M.L.; Muller, M.; van der Velde, N.; EUGMS Task & Finish Group on Fall-Risk-Increasing Drugs. Diuretics, SGLT2 inhibitors and falls in older heart failure patients: To prescribe or to deprescribe? A clinical review. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 14, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sternlicht, H.; Bakris, G.L. Hypertension: SGLT2 inhibitors: Not just another glucose-lowering agent. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 12, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briasoulis, A.; Al Dhaybi, O.; Bakris, G.L. SGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Hypertension. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on the Sympathetic Nervous System and Blood Pressure. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. Mechanistic effects of SGLT2 inhibition on blood pressure in diabetes. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowie, M.R.; Fisher, M. SGLT2 inhibitors: Mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit beyond glycaemic control. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bechmann, L.E.; Emanuelsson, F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Benn, M. SGLT2-inhibition increases total, LDL, and HDL cholesterol and lowers triglycerides: Meta-analyses of 60 randomized trials, overall and by dose, ethnicity, and drug type. Atherosclerosis 2023, 394, 117236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhao, Y. Effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0279889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Storgaard, H.; Gluud, L.L.; Bennett, C.; Grøndahl, M.F.; Christensen, M.B.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Benefits and Harms of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Huggins, L.-A.; Scerbo, D.; Obunike, J.; Mullick, A.E.; Rothenberg, P.L.; Di Prospero, N.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Goldberg, I.J. Mechanism of Increased LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) and Decreased Triglycerides With SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2) Inhibition. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, F.E.; Gusarova, V.; O’Dushlaine, C.; Gottesman, O.; Trejos, J.; Hunt, C.; Van Hout, C.V.; Habegger, L.; Buckler, D.; Lai, K.-M.V.; et al. Inactivating Variants in ANGPTL4 and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Landfors, F.; Henneman, P.; Chorell, E.; Nilsson, S.K. Drug-target Mendelian randomization analysis supports lowering plasma ANGPTL3, ANGPTL4, and APOC3 levels as strategies for reducing cardiovascular disease risk. Eur. Heart J. Open 2024, 4, oeae035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myocardial Infarction Genetics and CARDIoGRAM Exome Consortia Investigators. Coding Variation in ANGPTL4, LPL, and SVEP1 and the Risk of Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Willer, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sengupta, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Gustafsson, S.; Kanoni, S.; Ganna, A.; Chen, J.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Mora, S.; et al. Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eller-Vainicher, C.; Cairoli, E.; Grassi, G.; Grassi, F.; Catalano, A.; Merlotti, D.; Falchetti, A.; Gaudio, A.; Chiodini, I.; Gennari, L. Pathophysiology and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Bone Fragility. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7608964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Russo, G.T.; Giandalia, A.; Romeo, E.L.; Nunziata, M.; Muscianisi, M.; Ruffo, M.C.; Catalano, A.; Cucinotta, D. Fracture Risk in Type 2 Diabetes: Current Perspectives and Gender Differences. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 1615735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Manavalan, J.S.; Cremers, S.; Dempster, D.W.; Zhou, H.; Dworakowski, E.; Kode, A.; Kousteni, S.; Rubin, M.R. Circulating osteogenic precursor cells in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3240–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hygum, K.; Starup-Linde, J.; Harslof, T.; Vestergaard, P.; Langdahl, B.L. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Diabetes mellitus, a state of low bone turnover—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, R137–R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Clay Bunn, R.; Nyman, J.S.; Rettiganti, M.R.; Cockrell, G.E.; Wahl, E.C.; Uppuganti, S.; Lumpkin CKJr Fowlkes, J.L. SGLT2 inhibitor therapy improves blood glucose but does not prevent diabetic bone disease in diabetic DBA/2J male mice. Bone 2015, 82, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Nyman, J.S.; Bunn, R.C.; Uppuganti, S.; Thompson, K.L.; Lumpkin, C.K.; Kalaitzoglou, E.; Fowlkes, J.L. The impact of SGLT2 inhibitors, compared with insulin, on diabetic bone disease in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Bone 2016, 94, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, C.; Wang, X.; David, V.; Quaggin, S.E.; Isakova, T.; Martin, A. Long-Term Effects of Sglt2 Deletion on Bone and Mineral Metabolism in Mice. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Skeith, M.D.; Healey, L.A.; Cutler, R.E. Effect of phloridzin on uric acid excretion in man. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1970, 219, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, M.A.; Petrykiv, S.I.; Laverman, G.D.; van Herwaarden, A.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Bakker, S.J.; Heerspink, H.J.; de Borst, M.H. Effects of dapagliflozin on circulating markers of phosphate homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilezikian, J.P.; Watts, N.B.; Usiskin, K.; Polidori, D.; Fung, A.; Sullivan, D.; Rosenthal, N. Evaluation of Bone Mineral Density and Bone Biomarkers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Canagliflozin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ljunggren, Ö.; Bolinder, J.; Johansson, L.; Wilding, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; Sjöström, C.D.; Sugg, J.; Parikh, S. Dapagliflozin has no effect on markers of bone formation and resorption or bone mineral density in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus on metformin. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.I.; Blau, J.E.; Rother, K.I. Possible adverse effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on bone. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Youssef, M.E.; Yahya, G.; Popoviciu, M.S.; Cavalu, S.; Abd-Eldayem, M.A.; Saber, S. Unlocking the Full Potential of SGLT2 Inhibitors: Expanding Applications beyond Glycemic Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frias, J.; Páll, D.; Charbonnel, B.; Pascu, R.; Saur, D.; Darekar, A.; Huyck, S.; Shi, H.; Lauring, B.; et al. Effect of ertugliflozin on glucose control, body weight, blood pressure and bone density in type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy (VERTIS MET). Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2017, 20, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Duan, J.; Bi, S.; Swe, K.N.C.; Xi, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, X.; Liu, W. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and fracture risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11, 2040622320961599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jardine, M.; Perkovic, V.; Matthews, D.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Desai, M.; Oh, R.; Simpson, R.; et al. Canagliflozin and fracture risk in individuals with type 2 diabetes: Results from the CANVAS Program. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1854–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lupsa, B.C.; Inzucchi, S.E. Use of SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: Weighing the risks and benefits. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on fractures, BMD, and bone metabolism markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2023, 34, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armandi, A.; Bugianesi, E. Dietary and pharmacological treatment in patients with metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 122, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillon, N.J.; Loos, R.J.F.; Marshall, S.M.; Zierath, J.R. Metabolic consequences of obesity and type 2 diabetes: Balancing genes and environment for personalized care. Cell 2021, 184, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Procyk, G.; Jaworski, J.; Gąsecka, A.; Filipiak, K.J.; Borovac, J.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease—A new indication for sodium-glucose Co-transporter-2 inhibitors. Adv. Med. Sci. 2024, 69, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, H.; Malek, M.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Zamani, F.; Sohrabi, M.; Babaei, M.R.; Khamseh, M.E. Effect of empagliflozin on liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 4697–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.L.; Vethakkan, S.R.; Nik Mustapha, N.R.; Mahadeva, S.; Chan, W.K. Empagliflozin for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuta, N.; Kawamura, Y.; Fujiyama, S.; Saito, S.; Muraishi, N.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Arase, Y.; et al. Favorable impact of long-term SGLT2 inhibitor for NAFLD complicated by diabetes mellitus: A 5-year follow-up study. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2286–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Hayashi, A.; Taguchi, T.; Arai, R.; Sasaki, S.; Takano, K.; Inoue, Y.; Shichiri, M. Effects of canagliflozin on body composition and hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 10, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Agrawal, P.K.; Doneria, J.; Nigam, A. Effects of canagliflozin on abnormal liver function tests in patients of type 2 diabetes with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Assoc. Phys. India 2018, 66, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.Y.; Nakamura, A.; Omori, K.; Takase, T.; Miya, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Nomoto, H.; Kameda, H.; Taneda, S.; Kurihara, Y.; et al. Favorable effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease compared with pioglitazone. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, T.; Shimoda, M.; Nakashima, K.; Fushimi, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Tanabe, A.; Tatsumi, F.; Hirukawa, H.; Sanada, J.; Kohara, K.; et al. Comparison of the effects of three kinds of glucose-lowering drugs on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, open-label, three-arm, active control study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aso, Y.; Kato, K.; Sakurai, S.; Kishi, H.; Shimizu, M.; Jojima, T.; Iijima, T.; Maejima, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Usui, I. Impact of dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, on serum levels of soluble dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 73, e13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.H.; Aby, E.S.; Vock, D.; Farley, J.F. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on major liver outcomes in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 5116–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Fujishima, Y.; Wakasugi, D.; Io, F.; Sato, Y.; Uchida, S.; Kitajima, Y. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the onset of esophageal varices and extrahepatic cancer in type 2 diabetic patients with suspected MASLD: A nationwide database study in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Camilli, M.; Viscovo, M.; Maggio, L.; Bonanni, A.; Torre, I.; Pellegrino, C.; Lamendola, P.; Tinti, L.; Teofili, L.; Hohaus, S.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and the cancer patient: From diabetes to cardioprotection and beyond. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2024, 120, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simela, C.; Walker, J.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Chen, D.H. SGLT2 inhibitors for prevention and management of cancer treatment-related cardiovascular toxicity: A review of potential mechanisms and clinical insights. Cardio-Oncology 2025, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Osataphan, N.; Abdel-Qadir, H.; Zebrowska, A.M.; Borowiec, A. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors During Cancer Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Ongoing Clinical Trials. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2024, 26, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W. Advances in sodium-glucose transporter protein 2 inhibitors and tumors. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1522059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y. Unveiling the anticancer effects of SGLT-2i: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1369352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Benedetti, R.; Benincasa, G.; Glass, K.; Chianese, U.; Vietri, M.T.; Congi, R.; Altucci, L.; Napoli, C. Effects of novel SGLT2 inhibitors on cancer incidence in hyperglycemic patients: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, D.; Gamez, D.; Deb, S. SGLT2 Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Flausino, L.E.; Carrasco, A.G.M.; Furuya, T.K.; Tuan, W.J.; Chammas, R. Impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on survival in gastrointestinal cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy: A real-world data retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chiang, C.H.; Chiang, C.H.; Hsia, Y.P.; Jaroenlapnopparat, A.; Horng, C.S.; Wong, K.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, B.S.; Luan, Y.Z.; et al. The impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on outcome of patients with diabetes mellitus and colorectal cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendryx, M.; Dong, Y.; Ndeke, J.M.; Luo, J. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor initiation and hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, J.; Hendryx, M.; Dong, Y. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and non-small cell lung cancer survival. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chung, C.T.; Lakhani, I.; Chou, O.H.I.; Lee, T.T.L.; Dee, E.C.; Ng, K.; Wong, W.T.; Liu, T.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors on new-onset overall cancer in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based study. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 12299–12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chou, O.H.I.; Lu, L.; Chung, C.T.; Chan, J.S.K.; Chan, R.N.C.; Lee, A.Y.H.; Dee, E.C.; Ng, K.; Pui, H.H.H.; Lee, S.; et al. Comparisons of the risks of new-onset prostate cancer in type 2 diabetes mellitus between SGLT2I and DPP4I users: A population-based cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 51, 101571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, C.H. New users of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are at low risk of incident pancreatic cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2025, 51, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafoglio, C.R.; Villegas, B.; Abdelhady, G.; Bailey, S.T.; Liu, J.; Shirali, A.S.; Wallace, W.D.; Magyar, C.E.; Grogan, T.R.; Elashoff, D.; et al. Sodium-glucose transporter 2 is a diagnostic and therapeutic target for early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Makaro, A.; Świerczyński, M.; Pokora, K.; Sarniak, B.; Kordek, R.; Fichna, J.; Salaga, M. Empagliflozin attenuates intestinal inflammation through suppression of nitric oxide synthesis and myeloperoxidase activity in in vitro and in vivo models of colitis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 32, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Althagafy, H.S.; Ali, F.E.; Hassanein, E.H.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; El-Sayed, M.I.K.; Atwa, A.M.; Sayed, A.M.; Soubh, A.A. Canagliflozin ameliorates ulcerative colitis via regulation of TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB and Nrf2/PPAR-γ/SIRT1 signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 960, 176166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Saad, M.A. Activation of autophagy and suppression of apoptosis by dapagliflozin attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats: Targeting AMPK/mTOR, HMGB1/RAGE and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Chem. Interactions 2021, 335, 109368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Jeong, H.J.; Ah, Y.M.; Yu, Y.M. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and their potential role in dementia onset and cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neuroendocr. 2024, 73, 101131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, V.; Mashkoor, Y.; Raj, N.; Rajak, K.; Jaiswal, A.; Fonarow, G.C. Association Between SGLT2 Inhibitors and Risk of Dementia and Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Med. 2024, 137, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Biessels, G.J.; Yu, M.H.; Hong, N.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.S.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, M. SGLT2 Inhibitor Use and Risk of Dementia and Parkinson Disease Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Neurology 2024, 103, e209805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Donahoo, W.T.; Svensson, M.; Shaaban, C.E.; Smith, G.; Jaffee, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Salloum, R.G.; et al. Heterogeneous treatment effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on risk of dementia in people with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 5528–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Iskander, C.; Wang, C.; Xiong, L.Y.; Shah, B.R.; Edwards, J.D.; Kapral, M.K.; Herrmann, N.; Lanctôt, K.L.; Masellis, M.; et al. Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors With Time to Dementia: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 46, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brikman, S.; Dori, G. Sodium glucose cotransporter2 inhibitor-possible treatment for patients with diabetes, pulmonary disease and CO2 retention. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 139, 109631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, M.; Goto, S. Possible Mechanism of Hematocrit Elevation by Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Associated Beneficial Renal and Cardiovascular Effects. Circulation 2019, 139, 1985–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahakos, V.; Marathias, K.; Lionaki, S.; Loukides, S.; Zakynthinos, S.; Vlahakos, D. The paradigm shift from polycythemia to anemia in COPD: The critical role of the renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2022, 16, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, M.E.; Qintar, M.; Windsor, S.L.; Jermyn, R.; Shavelle, D.M.; Tang, F.; Lamba, S.; Bhatt, K.; Brush, J.; Civitello, A.; et al. Empagliflozin Effects on Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Patients With Heart Failure: Results From the EMBRACE-HF Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Han, H.; Oh, E.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.W. Empagliflozin and Dulaglutide are Effective against Obesity-induced Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Fibrosis in A Murine Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, E.; Cho, W.; Rim, J.H.; Hwang, I.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity via ketones and insulin in diabetes with cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bonnet, F.; Scheen, A.J. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on systemic and tissue low-grade inflammation: The potential contribution to diabetes complications and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Metab. 2018, 44, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeland, I.J.; Eliasson, B.; Kasai, T.; Marx, N.; Zinman, B.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Wanner, C.; Zwiener, I.; Wojeck, B.S.; Yaggi, H.K.; et al. The Impact of Empagliflozin on Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes: An Exploratory Analysis of the EMPA REG OUTCOME Trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sawada, K.; Karashima, S.; Kometani, M.; Oka, R.; Takeda, Y.; Sawamura, T.; Fujimoto, A.; Demura, M.; Wakayama, A.; Usukura, M.; et al. Effect of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on obstructive sleep apnea in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Bai, X.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L.; Zhang, M. Effect of dapagliflozin on obstructive sleep apnea in patients with type 2 diabetes: A preliminary study. Nutr. Diabetes 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yin, D.G.; Qiu, M.; Duan, X.Y. Association Between SGLT2is and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Large Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 724405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pradhan, R.; Lu, S.; Yin, H.; Yu, O.H.Y.; Ernst, P.; Suissa, S.; Azoulay, L. Novel antihyperglycaemic drugs and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations among patients with type 2 diabetes: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2022, 379, e071380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Butt, J.H.; Lu, H.; Kondo, T.; Bachus, E.; de Boer, R.A.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Jhund, P.S.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.A.; et al. Heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction: Insights from DELIVER. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.S.Q.; Morton, J.I.; Wood, S.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J.; Ilomäki, J. SGLT-2 Inhibitor Use and Cause-Specific Hospitalization Rates: An Outcome-Wide Study to Identify Novel Associations of SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 115, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, P.C.M.; Tan, K.C.B.; Lam, D.C.L.; Cheung, B.M.Y.; Wong, I.C.K.; Kwok, W.C.; Sing, C.W.; Cheung, C.L. Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor vs Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use With Risk of Incident Obstructive Airway Disease and Exacerbation Events Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Hong Kong. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2251177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yen, F.S.; Wei, J.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Hsu, T.J.; Wang, S.T.; Hwu, C.M.; Hsu, C.C. SGLT-2 Inhibitors and the Risk of COPD Exacerbations and Mortality in COPD Patients. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2025, ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, P.; Docherty, K.F.; Bengtsson, O.; de Boer, R.A.; Desai, A.S.; Drozdz, J.; Hawkins, N.M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kitakaze, M.; Køber, L.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: An analysis of DAPA-HF. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 23, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anker, S.D.; Sander, L.-E.; Fitchett, D.H.; Zinman, B.; Ofstad, A.P.; Wanner, C.; Vedin, O.; Lauer, S.; Verma, S.; Yaggi, H.K.; et al. Empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 186, 109837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabchi, A.E.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Miles, J.M.; Fisher, J.N. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.J.; Gabb, G.; Jesudason, D. SGLT2 inhibitor-associated euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A South Australian clinical case series and Australian spontaneous adverse event notifications. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, e47–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvenkatarajan, V.; Meyer, E.J.; Nanjappa, N.; Van Wijk, R.M.; Jesudason, D. Perioperative diabetic ketoacidosis associated with sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors: A systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mechanism | Effect | Ref. No. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | Decrease in sodium reabsorption which results in reduction of intravascular volume [43] and the increase of sodium delivery to the macula densa that is followed by a re-activation of TGF. This effect is mediated by the vasoconstrictive adenosine and mitigates the renal hyperfiltration that is in turn responsible for deleterious long-term effects on the renal parenchyma [43]. Improve endothelial dysfunction and reduced oxidative stress and inflammation and decrease the renal resistive index (RI) [44]. | preserving eGFR decline over time | [37,38,39,40] |
| ↓ end-stage kidney disease, or death from renal or cardiovascular causes | [39,40,41] | ||
| ↓ 30% risk for dialysis for at least 30 days, transplantation, or a sustained eGFR of <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 for 30 days | [37,38,39,40] | ||
| Albuminuria | Improve the regulation of extracellular matrix deposition, by decreasing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by metalloproteinase [45,46]. Increased podocyte protection via mitochondrial membrane-mediated energy balancing [52]. | ↓ albuminuria | [37,38,39,40,41] |
| Na+ balance | Increased delivery of sodium to the macula densa and a fall in intraglomerular pressure [58]. | ↑ transient natriuresis with low risk of hyponatremia | [59] |
| K+ balance | small increase in potassium levels only with canagliflozin | [63] | |
| Mg+ balance | ↑ serum magnesium levels by approximately 0.08 to 0.2 mEq/L | [66] |
| Risk Factor | Direction (↑/↓) | Range/Δ (Units) | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI/body weight | ↓ | −1.9 → −4.6 kg (≈−0.66 → −1.6 kg m−2) | [76,77,78] |
| Blood pressure | ↓ | −1.3 → −5.7 mmHg (systolic) | [80,84] |
| LDL-cholesterol | ↑ | +0.07 → +0.12 mmol L−1 (+2.7 → 4.6 mg dL−1) | [93] |
| HDL-cholesterol | ↑ | +0.05 → +0.08 mmol L−1 (+1.9 → 3.1 mg dL−1) | [93] |
| Triglycerides | ↓ | −0.13 → −0.07 mmol L−1 (−11.5 → −6.2 mg dL−1) | [93] |
| Uric acid | ↓ | −0.53 → −1.54 mg dL−1 (−31 → −91 µmol L−1) | [73,74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuttone, A.; Cannavò, V.; Abdullah, R.M.S.; Fugazzotto, P.; Arena, G.; Brancati, S.; Muscarà, A.; Morace, C.; Quartarone, C.; Ruggeri, D.; et al. Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in T2D Patients Across Clinical Settings. Cells 2025, 14, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090668
Cuttone A, Cannavò V, Abdullah RMS, Fugazzotto P, Arena G, Brancati S, Muscarà A, Morace C, Quartarone C, Ruggeri D, et al. Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in T2D Patients Across Clinical Settings. Cells. 2025; 14(9):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090668
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuttone, Alessandro, Vittorio Cannavò, Raouf Mastan Sheik Abdullah, Pierluigi Fugazzotto, Giada Arena, Simona Brancati, Andrea Muscarà, Carmela Morace, Cristina Quartarone, Domenica Ruggeri, and et al. 2025. "Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in T2D Patients Across Clinical Settings" Cells 14, no. 9: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090668
APA StyleCuttone, A., Cannavò, V., Abdullah, R. M. S., Fugazzotto, P., Arena, G., Brancati, S., Muscarà, A., Morace, C., Quartarone, C., Ruggeri, D., Squadrito, G., & Russo, G. T. (2025). Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in T2D Patients Across Clinical Settings. Cells, 14(9), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090668








