Inflammatory Factors: A Key Contributor to Stress-Induced Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of Depressive Disorder
3. Impact of Stress on Depression
3.1. Sex-Specific Effects on Depression During Stress
3.2. Expression Changes in Stress-Related Inflammatory Factors in MDD
3.3. Effects of Stress on the Nervous System
4. Association of Stress-Mediated Inflammation with Depression
4.1. Relationship Between Stress and Inflammation
4.2. Association of Stress with Signaling Pathways
4.2.1. Relationship Between NF-κB and Major Depressive Disorder
4.2.2. NF-κB Pathway
4.2.3. NF-κB Pathway and Major Depressive Disorder
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benazzi, F. Is there a continuity between bipolar and depressive disorders? Psychother. Psychosom. 2007, 76, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; D’Alessio, A.; Airoldi, C.; Scotti, L.; Demirtas, C.O.; Gennari, A.; Cortellini, A.; Pinato, D.J. Comparative efficacy of novel combination strategies for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network metanalysis of phase III trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 174, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, T.R.; Cuthbert, B.N. Brain disorders? Precisely. Science 2015, 348, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labaka, A.; Goñi-Balentziaga, O.; Lebeña, A.; Pérez-Tejada, J. Biological Sex Differences in Depression: A Systematic Review. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2018, 20, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micek, A.; Jurek, J.; Owczarek, M.; Guerrera, I.; Torrisi, S.A.; Castellano, S.; Grosso, G.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Godos, J. Polyphenol-Rich Beverages and Mental Health Outcomes. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, K.M.; Van Assche, E.; Andlauer, T.F.M.; Choi, K.W.; Luykx, J.J.; Schulte, E.C.; Lu, Y. The genetic basis of major depression. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 2217–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Thompson, M.; An, U.; Krebs, M.; Appadurai, V.; Border, R.; Bacanu, S.A.; Werge, T.; Flint, J.; Schork, A.J.; et al. Phenotype integration improves power and preserves specificity in biobank-based genetic studies of major depressive disorder. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Scott, L.; Song, P.; Burmeister, M.; Sen, S. Genomic prediction of depression risk and resilience under stress. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.; Cars, T.; Lampa, E.; Ekholm Selling, K.; Leval, A.; Gannedahl, A.; Själin, M.; Björkholm, C.; Hellner, C. Determinants and Outcomes of Suicidal Behavior Among Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corponi, F.; Fabbri, C.; Bitter, I.; Montgomery, S.; Vieta, E.; Kasper, S.; Pallanti, S.; Serretti, A. Cognitive dysfunction: An important feature of major depressive disorder. J. Neurons Neurol. Disord. 2023, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hannibal, K.E.; Bishop, M.D. Chronic stress, cortisol dysfunction, and pain: A psychoneuroendocrine rationale for stress management in pain rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentsch, M.C.; Burger, H.; Meddens, M.B.M.; Beijers, L.; van den Heuvel, E.R.; Meddens, M.J.M.; Schoevers, R.A. Gender Differences in Developing Biomarker-Based Major Depressive Disorder Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, K.M.; Newhouse, P.A. Estrogen, Stress, and Depression: Cognitive and Biological Interactions. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2019, 15, 399–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Halldorsdottir, T.; Zhu, H.; Bertone-Johnson, E.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.A.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D. Premenstrual disorders and gender differences in adolescent mental health. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 340, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Hu, N.; Lu, L.; Tan, L.; Li, P. Gender differences in major depressive disorder at different ages: A REST-meta-MDD project-based study. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion-Albert, L.; Cadoret, A.; Doney, E.; Kaufmann, F.N.; Dudek, K.A.; Daigle, B.; Parise, L.F.; Cathomas, F.; Samba, N.; Hudson, N. Vascular and blood-brain barrier-related changes underlie stress responses and resilience in female mice and depression in human tissue. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xia, M.; Li, B. Major depressive disorder: Hypothesis, mechanism, prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.; Pessoni, A.M.; Marroquín-Rivera, A.; Parise, E.M.; Tamminga, C.A.; Turecki, G.; Nestler, E.J.; Chen, T.H.; Labonté, B. Transcriptional dissection of symptomatic profiles across the brain of men and women with depression. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, C.; Feng, B.; Lu, W.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhou, W.; Jing, H.; Yang, J. Mendelian randomization integrating GWAS and eQTL data revealed genes pleiotropically associated with major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, R.J. Genes, stress, and depression. Metabolism 2005, 54 (Suppl. S1), 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Abdellaoui, A.; Verweij, K.J.H.; van Wingen, G.A. Gene Expression has Distinct Associations with Brain Structure and Function in Major Depressive Disorder. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2205486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.; Penninx, B.W.; Madar, V.; Xia, K.; Milaneschi, Y.; Hottenga, J.J.; Hammerschlag, A.R.; Beekman, A.; van der Wee, N.; Smit, J.H.; et al. Gene expression in major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, P.; Li, F.; Huang, J.; Fan, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, F.; Gao, Y. An association study of clock genes with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 341, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, K.; Pain, O.; Tosto, M.G.; Du Rietz, E.; Carboni, L.; Schalkwyk, L.C. Identification of genes and gene pathways associated with major depressive disorder by integrative brain analysis of rat and human prefrontal cortex transcriptomes. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, J. Cortisol and depression: Three questions for psychiatry. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolak, S.; Suwannarat, P.; Lipsky, R.H. Epigenetics of depression. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 128, 103–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, K.A.; Dion-Albert, L.; Lebel, M.; LeClair, K.; Labrecque, S.; Tuck, E.; Ferrer Perez, C.; Golden, S.A.; Tamminga, C.; Turecki, G.; et al. Molecular adaptations of the blood-brain barrier promote stress resilience vs. depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3326–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.; Pfau, M.L.; Hodes, G.E.; Kana, V.; Wang, V.X.; Bouchard, S.; Takahashi, A.; Flanigan, M.E.; Aleyasin, H.; LeClair, K.B.; et al. Social stress induces neurovascular pathology promoting depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, G.J.; Vallender, E.J.; Garrett, M.R.; Challagundla, L.; Overholser, J.C.; Jurjus, G.; Dieter, L.; Syed, M.; Romero, D.G.; Benghuzzi, H.; et al. Altered neuro-inflammatory gene expression in hippocampus in major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 82, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, S.P.; Nerurkar, L.; Krishnadas, R.; Johnman, C.; Graham, G.J.; Cavanagh, J. Chemokines in depression in health and in inflammatory illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, S.A.; Beurel, E.; Loewenstein, D.A.; Lowell, J.A.; Craighead, W.E.; Dunlop, B.W.; Mayberg, H.S.; Dhabhar, F.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W.; et al. Defective Inflammatory Pathways in Never-Treated Depressed Patients Are Associated with Poor Treatment Response. Neuron 2018, 99, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiraly, D.D.; Horn, S.R.; Van Dam, N.T.; Costi, S.; Schwartz, J.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Patel, M.; Hodes, G.E.; Russo, S.J.; Merad, M.; et al. Altered peripheral immune profiles in treatment-resistant depression: Response to ketamine and prediction of treatment outcome. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umamaheswaran, S.; Dasari, S.K.; Yang, P.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Sood, A.K. Stress, inflammation, and eicosanoids: An emerging perspective. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, J.; Godlewska, B.R.; Tirumalaraju, V.; Soares, J.C.; Cowen, P.J.; Selvaraj, S. Stress, inflammation and hippocampal subfields in depression: A 7 Tesla MRI Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantsoo, L.; Kornfield, S.; Anguera, M.C.; Epperson, C.N. Inflammation: A Proposed Intermediary Between Maternal Stress. and Offspring Neuropsychiatric Risk. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, B.R.; de Araujo Borba, L.; Borges de Souza, P.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Role of Inflammatory Mechanisms in Major. Depressive Disorder: From Etiology to Potential. Pharmacological Targets. Cells 2024, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanishi, K.; Doe, N.; Mukai, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Gamachi, N.; Hata, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamanishi, C.; Yagi, H.; Okamura, H.; et al. Acute stress induces severe neural inflammation and overactivation of glucocorticoid signaling in interleukin-18-deficient mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, B.K.; Munoz, D.P.; Khalid-Khan, S.; Brietzke, E.; Booij, L. Is subthreshold depression in adolescence clinically relevant? J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 309, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ruan, M.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y. Major Depressive Disorder: Advances in Neuroscience Research and Translational Applications. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, S.; Hanada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Watanabe, K.; Yonemochi, M.; Tomabechi, Y.; Shirouzu, M. The NF-kappaB regulator IkappaBbeta exhibits different molecular interactivity and phosphorylation status from IkappaBalpha in an IKK2-catalysed reaction. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 1532–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Zhuang, K.; Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, Y.; Chen, G.; Lin, H.; Hu, Y.; Wu, D.; Shi, M.; et al. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation. Neuron 2018, 100, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Bo, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, J. Bergapten alleviates depression-like behavior by inhibiting cyclooxygenase 2 activity and NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling pathway in microglia. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 365, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioz, B.I.; Tastan, B.; Tarakcioglu, E.; Tufekci, K.U.; Olcum, M.; Ersoy, N.; Bagriyanik, A.; Genc, K.; Genc, S. Melatonin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Depressive-Like Behaviors and MicroglialNLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Through the SIRT1/Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Sun, R.; Ji, Z.; Li, X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Perilla aldehyde attenuates CUMS-induced depressive-like behaviors via regulating TXNIP/TRX/NLRP3 pathway in rats. Life Sci. 2018, 206, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Ren, P.; Cui, L.Y.; Duan, J.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Zeng, Z.R.; Li, Y.F. Astrocyte-specific activation of sigma-1 receptors in mPFC mediates the faster onset antidepressant effect by inhibiting NF-kappaB-induced neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 120, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolino, M.; Vahedi, G. GR Extinguishes Inflamed Chromatin, and NF-kappaB Evacuates. Immunity 2017, 47, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, A.N.; Newton, R.; Sasse, S.K. Repression of transcription by the glucocorticoid receptor: A parsimonious model for the genomics era. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Song, S.; Yang, P.; Rao, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X. Aucubin improves chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive behavior in mice via the GR/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 123, 110677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, R.; Tian, L.; Anderson, M.A.; Flensburg, C.; Jarratt, A.; Garnham, A.L.; Jabbari, J.S.; Peng, H.; Lew, T.E.; Teh, C.E.; et al. Single-cell multiomics reveal the scale of multilayered adaptations enabling CLL relapse during venetoclax therapy. Blood 2022, 140, 2127–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: The enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, E.; Duckett, C.S. Dying for NF-kappaB? Control of cell death by transcriptional regulation of the apoptotic machinery. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.S.; Aw, R. The Commonalities in Bacterial Effector Inhibition of Apoptosis. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
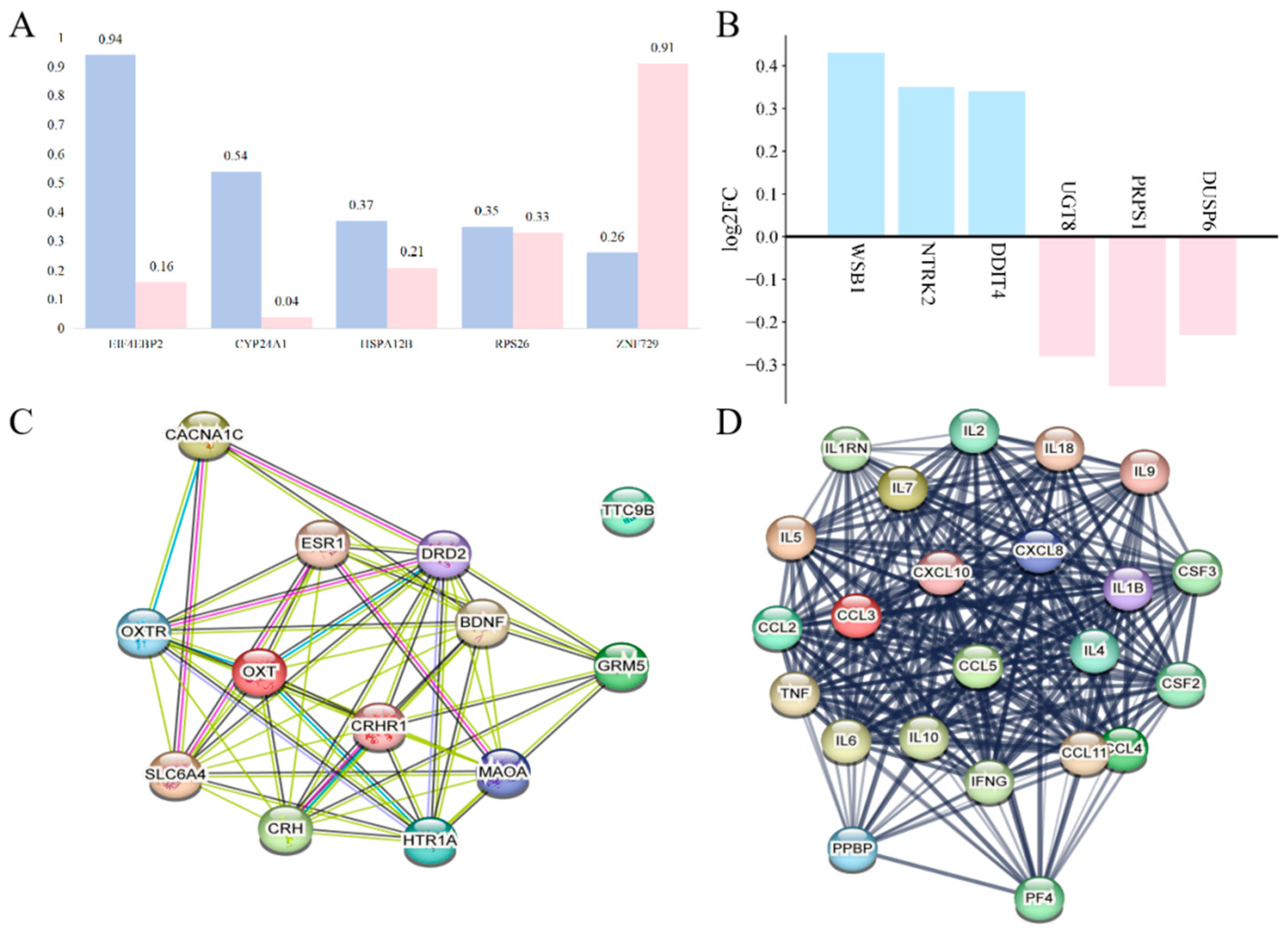
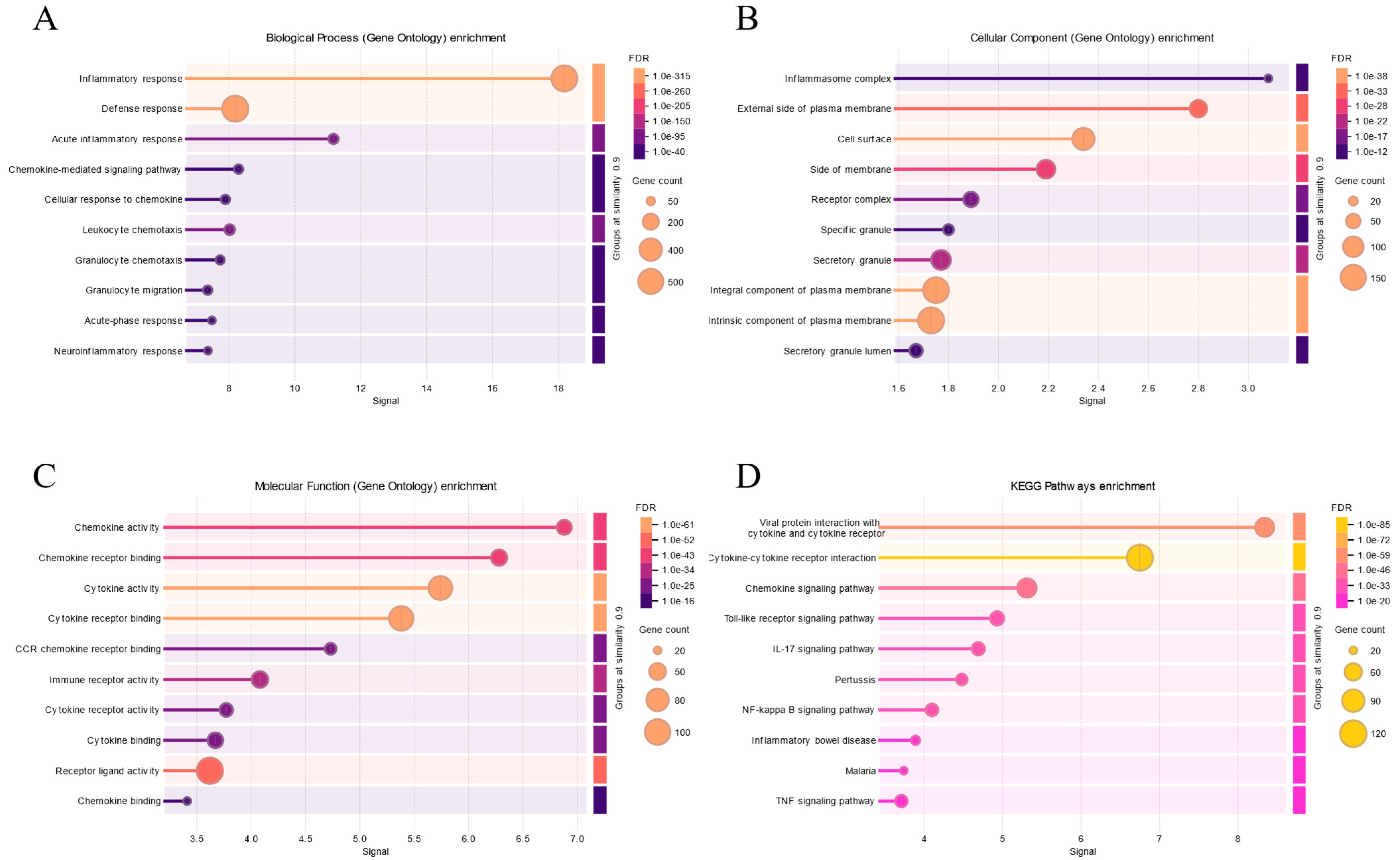



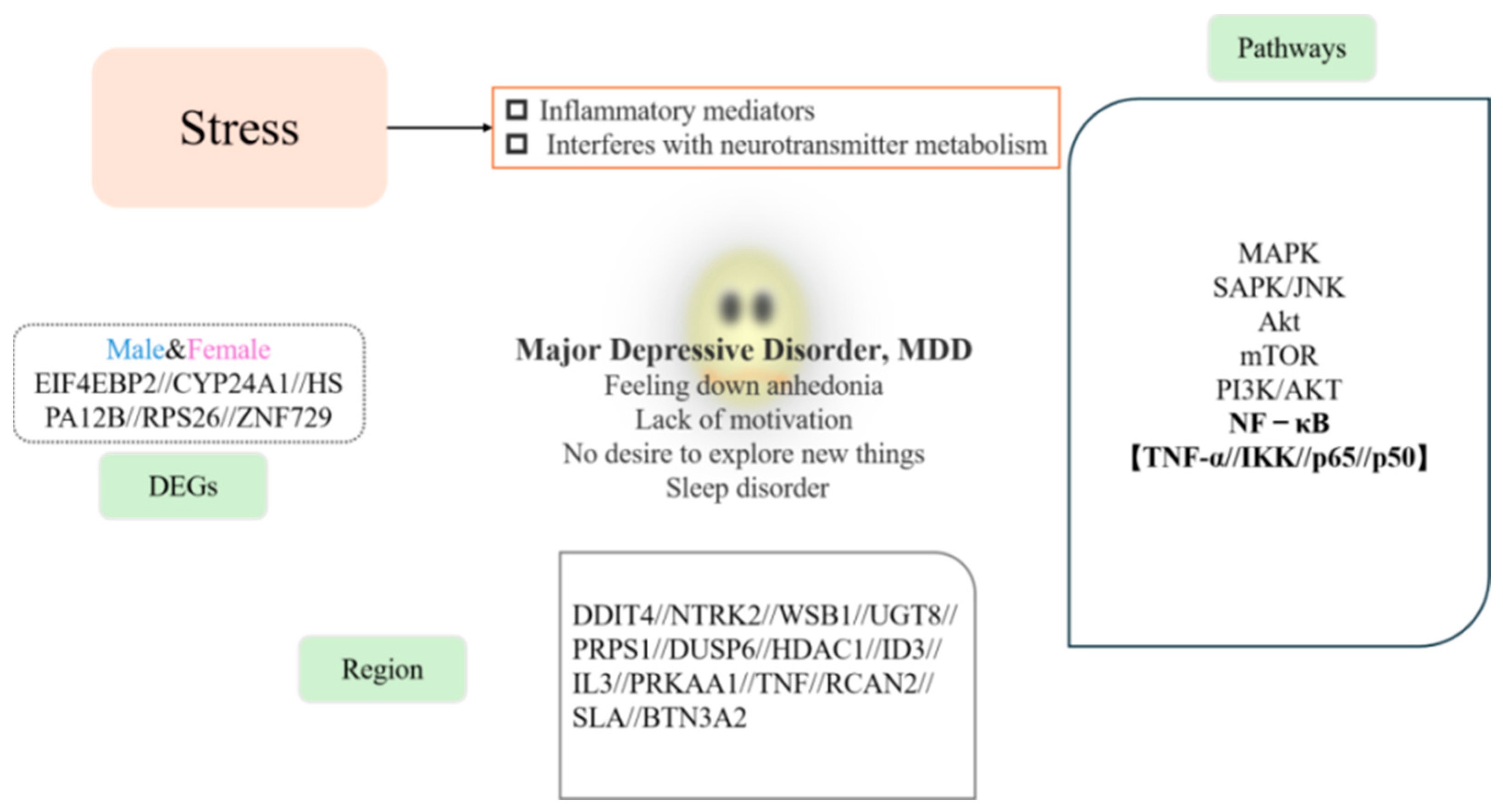
| Symbol | Gene Description | Express | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 | varies | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| CCL3 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 | up | Syed et al., 2018 [32]; Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| CCL4 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 | down | Syed et al., 2018 [32]; Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| CCL5 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 | up | Syed et al., 2018 [32]; |
| CCL11 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 11 | up | Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| CXCL4 | platelet factor 4 | up | Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| CXCL7 | pro-platelet basic protein | up | Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| CXCL10 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 | Down | Syed et al., 2018 [32]; |
| G-CSF | colony stimulating factor 3 | up | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] Syed et al., 2018 [32]; |
| GM-CSF | colony stimulating factor 2 | up | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IFN-γ | interferon gamma | varies | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-1β | interleukin 1 beta | up | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-1RA | interleukin 1 receptor antagonist | varies | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-2 | interleukin 2 | up | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-4 | interleukin 4 | down | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-5 | interleukin 5 | up | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 | up | Kiraly et al., 2017 [33] |
| IL-7 | interleukin 7 | up | Syed et al., 2018 [32]; |
| IL-8/CXCL8 | interleukin 8 | varies | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; Leighton et al., 2018 [31] |
| IL-9 | interleukin 9 | up | Syed et al., 2018 [32]; |
| IL-10 | interleukin 10 | up | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; |
| IL-12 | interleukin 12 | up | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; |
| IL-18 | interleukin 18 | up | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor beta 1 | - | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; |
| sTNFR2 | TNF receptor superfamily member | up | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor | up | Köhler et al., 2017 [30]; |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Nie, B.; Cui, X.; Wang, W.; Duan, D. Inflammatory Factors: A Key Contributor to Stress-Induced Major Depressive Disorder. Cells 2025, 14, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090629
Liu Q, Nie B, Cui X, Wang W, Duan D. Inflammatory Factors: A Key Contributor to Stress-Induced Major Depressive Disorder. Cells. 2025; 14(9):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090629
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qian, Baowen Nie, Xuemin Cui, Wang Wang, and Dongxiao Duan. 2025. "Inflammatory Factors: A Key Contributor to Stress-Induced Major Depressive Disorder" Cells 14, no. 9: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090629
APA StyleLiu, Q., Nie, B., Cui, X., Wang, W., & Duan, D. (2025). Inflammatory Factors: A Key Contributor to Stress-Induced Major Depressive Disorder. Cells, 14(9), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090629





