Let-7 Family microRNAs Regulate the Expression of the Urokinase-Receptor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. In Vitro Transfection
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Luciferase Assay
2.6. Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
2.7. MS2-Tagged RNA Affinity Purification
2.8. Cell Adhesion Assay
2.9. Cell Migration Assay
2.10. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
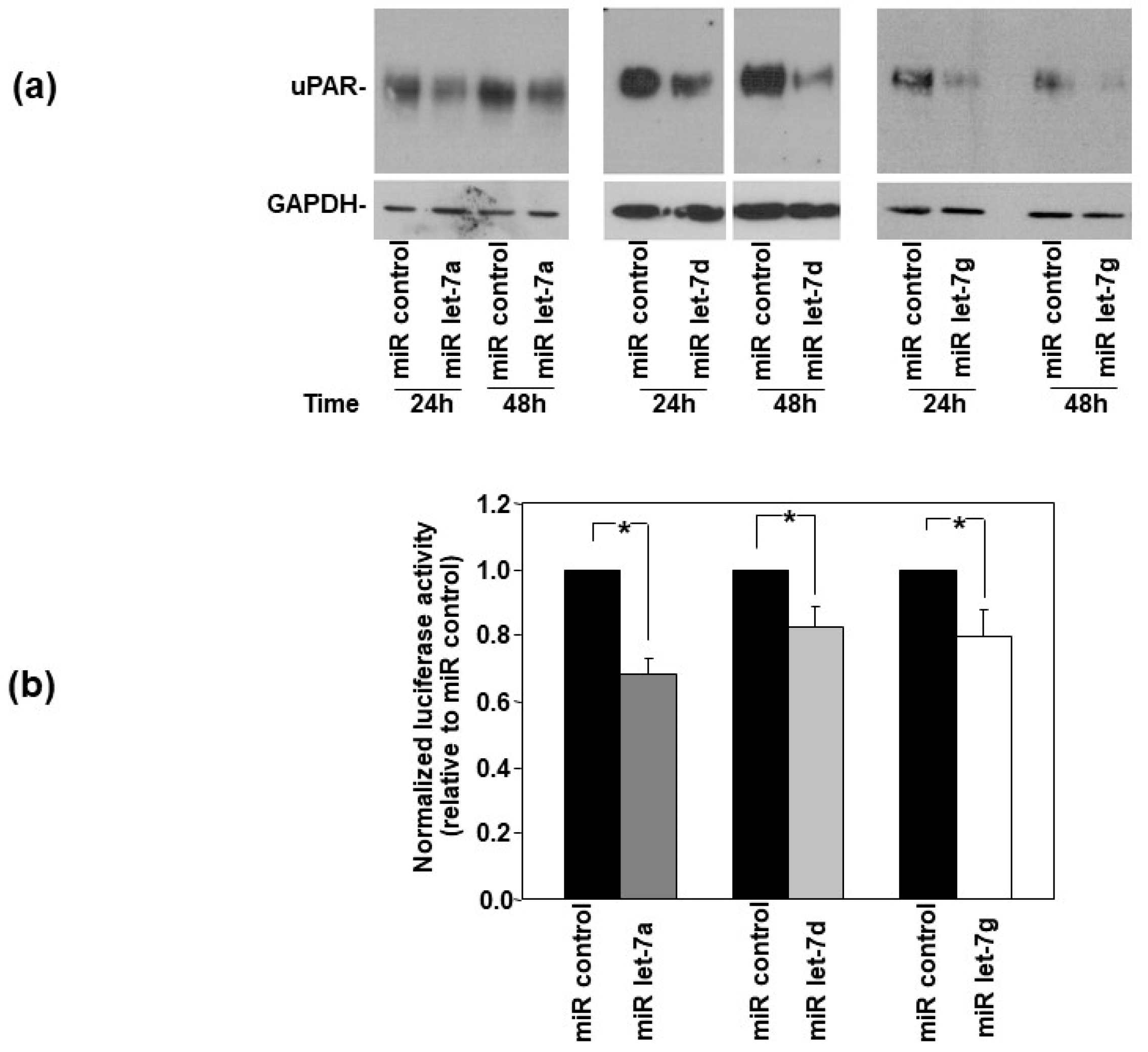
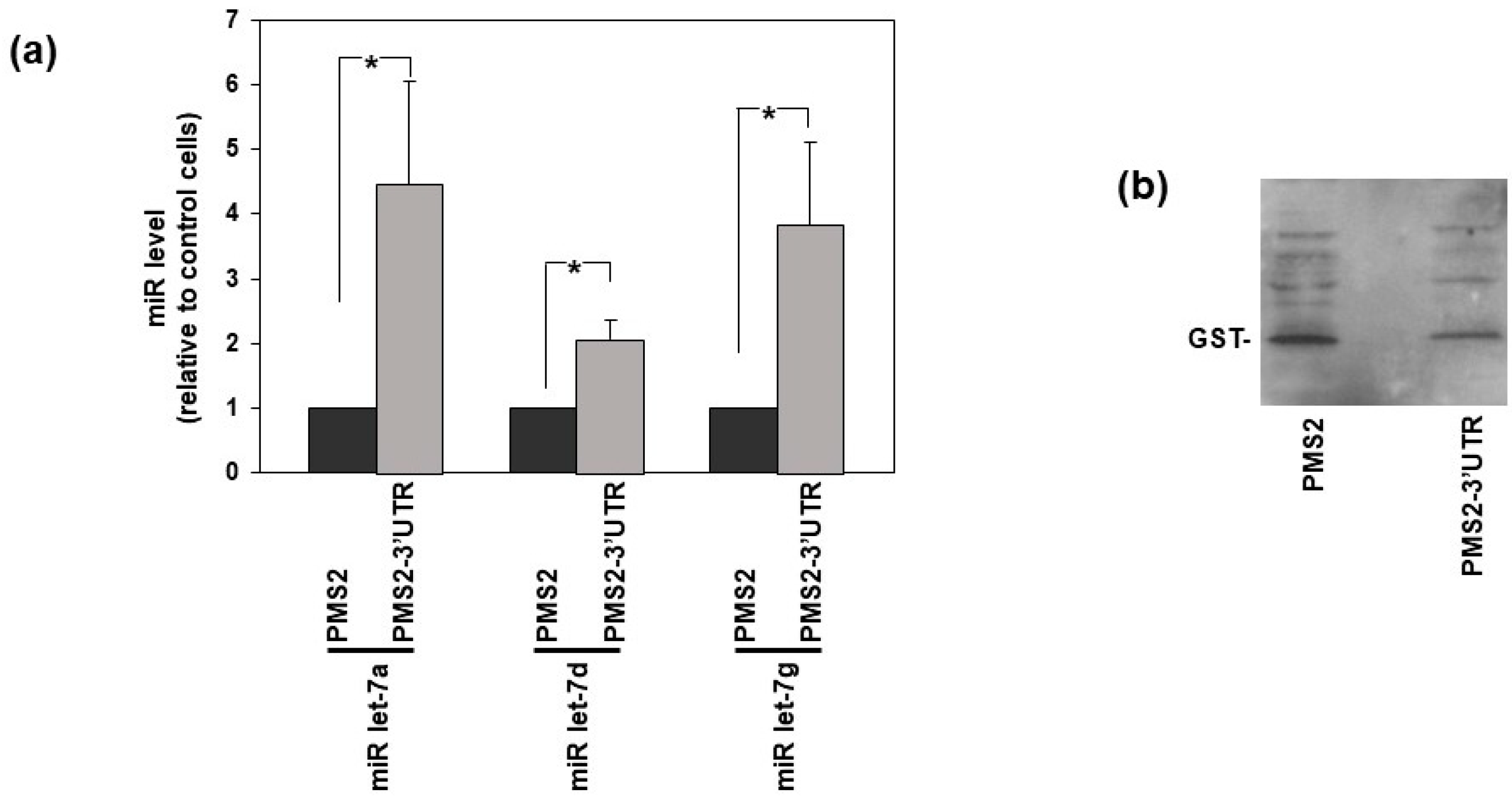
3.1. uPAR Is a Direct Target of Let-7 miRNAs in HeLa Cells
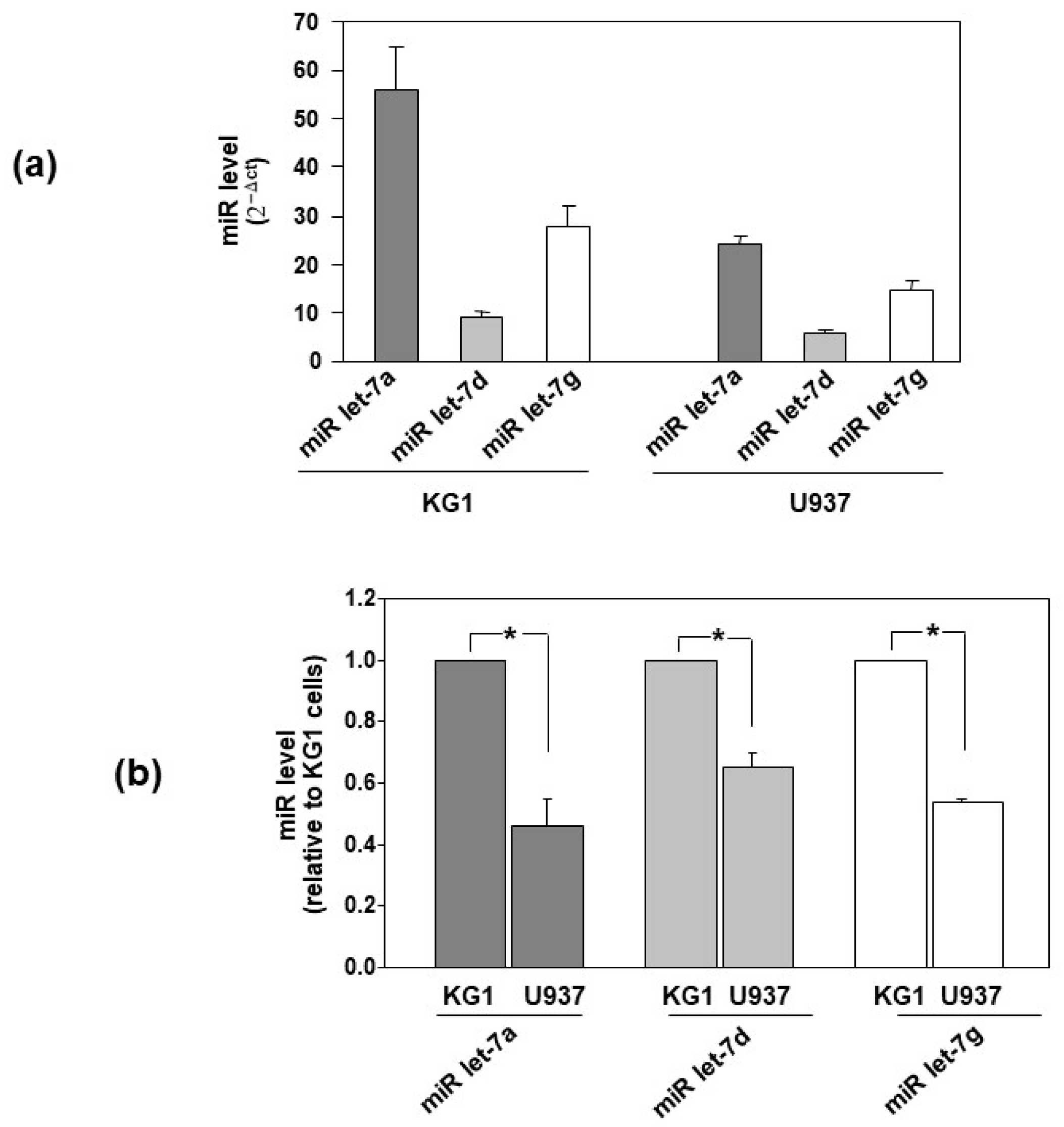
3.2. Let-7 miRNAs Are Differently Expressed in AML Cells
3.3. Let-7 miRNAs Regulate uPAR Expression in AML Cells
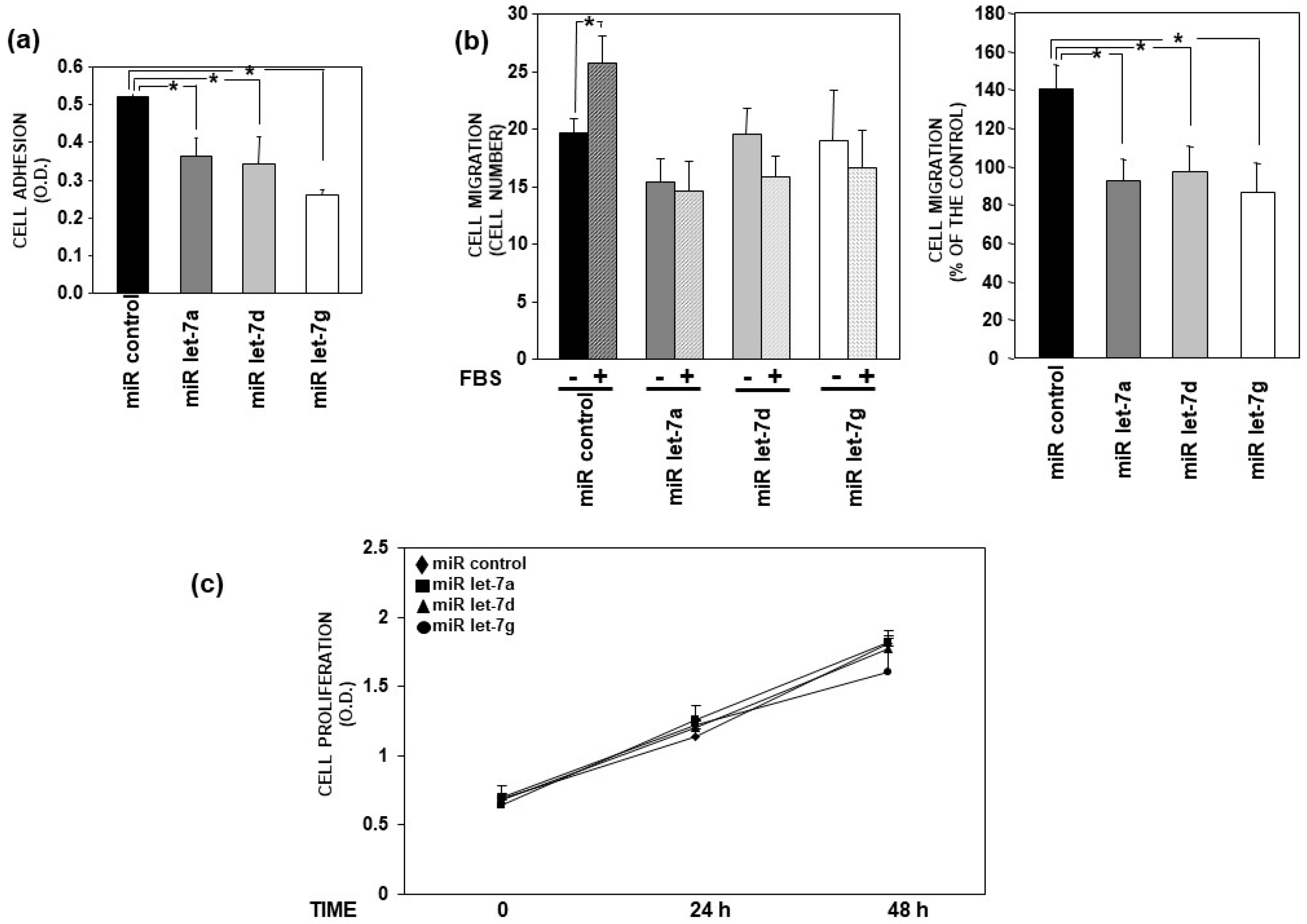
3.4. Let-7 miRNAs Impair Adhesion and Migration of AML Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , PRIN-PNRR call 2022, Prot. P2022HB33K.
, PRIN-PNRR call 2022, Prot. P2022HB33K.Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shabalina, S.A.; Spiridonov, N.A. The Mammalian Transcriptome and the Function of Non-Coding DNA Sequences. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. Non-Coding RNAs: Classification, Biology and Functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Alfieri, M.; Meo, L.; Ragno, P. Posttranscriptional Regulation of the Plasminogen Activation System by Non-Coding RNA in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, F.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell 2019, 179, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, D.; Gorrasi, A.; Li Santi, A.; Ricci, P.; Montuori, N.; Selleri, C.; Ragno, P. Urokinase receptor and CXCR4 are regulated by common microRNAs in leukaemia cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Huang, M. Does the urokinase receptor exist in a latent form? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, N.; Cosimato, V.; Rinaldi, L.; Rea, V.E.; Alfano, D.; Ragno, P. uPAR regulates pericellular proteolysis through a mechanism involving integrins and fMLF-receptors. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Waltz, D.A.; Rao, N.; Drummond, R.J.; Rosenberg, S.; Chapman, H.A. Identification of the urokinase receptor as an adhesion receptor for vitronectin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 32380–32388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, C.D.; Sidenius, N. The interaction between urokinase receptor and vitronectin in cell adhesion and signalling. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, D.; Franco, P.; Stoppelli, M.P. Modulation of Cellular Function by the Urokinase Receptor Signalling: A Mechanistic View. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 818616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrasi, A.; Petrone, A.M.; Li Santi, A.; Alfieri, M.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P. New Pieces in the Puzzle of uPAR Role in Cell Migration Mechanisms. Cells 2020, 9, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Santi, A.; Napolitano, F.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P. The Urokinase Receptor: A Multifunctional Receptor in Cancer Cell Biology. Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selleri, C.; Montuori, N.; Ricci, P.; Visconte, V.; Baiano, A.; Carriero, M.V.; Rotoli, B.; Rossi, G.; Ragno, P. In vivo activity of the cleaved form of soluble urokinase receptor: A new hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell mobilizer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10885–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleri, C.; Montuori, N.; Salvati, A.; Serio, B.; Pesapane, A.; Ricci, P.; Gorrasi, A.; Li Santi, A.; Hoyer-Hansen, G.; Ragno, P. Involvement of urokinase receptor in the cross-talk between human hematopoietic stem cells and bone marrow microenvironment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60206–60217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Labbaye, C. miR-146 and miR-155: Two Key Modulators of Immune Response and Tumor Development. Noncoding RNA 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanek, J. Role of microRNA dysregulation in childhood acute leukemias: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics: A comprehensive review. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 348–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yin, J.; He, R.; Chao, R.; Zhu, S. Circ_KCNQ5 participates in the progression of childhood acute myeloid leukemia by enhancing the expression of RAB10 via binding to miR-622. Hematology 2022, 27, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Hongcheng, L.; Yonghang, T.; Yuchen, W.; Wei, W.; Lifan, Z.; Jie, C. The Development and Controversy of Competitive Endogenous RNA Hypothesis in Non-Coding Genes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Santi, A.; Gorrasi, A.; Alfieri, M.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P. A novel oncogenic role for urokinase receptor in leukemia cells: Molecular sponge for oncosuppressor microRNAs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27823–27834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, M.; Li Santi, A.; Meo, L.; Giudice, V.; Selleri, C.; Ragno, P. Identification of uPAR Variants Acting as ceRNAs in Leukaemia Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirshev, E.; Oberg, K.C.; Ioffe, Y.J.; Unternaehrer, J. Let-7 as biomarker, prognostic indicator, and therapy for precision medicine in cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Luo, M. The Roles of the Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness. Cells. 2021, 10, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazarlou, F.; Kadkhoda, S.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Emerging role of let-7 family in the pathogenesis of hematological malignancies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, G.; Augugliaro, L.; Salemi, D.; Agueli, C.; La Rosa, M.; Dagnino, L.; Civiletto, G.; Messana, F.; Marfia, A.; Bica, M.G.; et al. Differential expression of specific microRNA and their targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Garofalo, M.; Martelli, M.P.; Briesewitz, R.; Wang, L.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Schnittger, S.; Haferlach, T.; et al. Distinctive microRNA signature of acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3945–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Gorospe, M. Identification of mRNA-Interacting Factors by MS2-TRAP (MS2-Tagged RNA Affinity Purification). Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1421, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lundin, K.E.; Højland, T.; Hansen, B.R.; Persson, R.; Bramsen, J.B.; Kjems, J.; Koch, T.; Wengel, J.; Smith, C.I. Biological activity and biotechnological aspects of locked nucleic acids. Adv. Genet. 2013, 82, 47–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, M.T.; Minopoli, M.; Di Carluccio, G.; Motti, M.L.; Carriero, M.V. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Urokinase and Its Receptor in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassalli, J.D.; Baccino, D.; Belin, D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesner, T.; Ralfkiaer, E.; Wittrup, M.; Johnsen, H.; Pyke, C.; Pedersen, T.L.; Hansen, N.E.; Danø, K. Expression of the receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator in normal and neoplastic blood cells and hematopoietic tissue. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 102, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, F.; Castoldi, G.L.; Castagnari, B.; Todd, R.F., 3rd; Moretti, S.; Spisani, S.; Latorraca, A.; Focarile, E.; Roberti, M.G.; Traniello, S. Expression and functional role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor in normal and acute leukaemic cells. Br. J. Haematol. 1998, 103, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.; Reif, S.; Hecht, K.; Pelka-Fleischer, R.; Pfister, K.; Schmetzer, H. High expression of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (UPA-R) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is associated with worse prognosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 79, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherrer, A.; Wohlwend, A.; Kruithof, E.K.; Vassalli, J.D.; Sappino, A.P. Plasminogen activation in human acute leukaemias. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 105, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustjoki, S.; Alitalo, R.; Stephens, R.W.; Vaheri, A. Blast cell-surface and plasma soluble urokinase receptor in acute leukemia patients: Relationship to classification and response to therapy. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 81, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Mustjoki, S.; Sidenius, N.; Sier, C.F.; Blasi, F.; Elonen, E.; Alitalo, R.; Vaheri, A. Soluble urokinase receptor levels correlate with number of circulating tumor cells in acute myeloid leukemia and decrease rapidly during chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 7126–7132. [Google Scholar]
- Tjwa, M.; Sidenius, N.; Moura, R.; Jansen, S.; Theunissen, K.; Andolfo, A.; De Mol, M.; Dewerchin, M.; Moons, L.; Blasi, F.; et al. Membrane-anchored uPAR regulates the proliferation, marrow pool size, engraftment, and mobilization of mouse hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazitt, Y. Homing and mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoietic cancer cells are mirror image processes, utilizing similar signaling pathways and occurring concurrently: Circulating cancer cells constitute an ideal target for concurrent treatment with chemotherapy and antilineage-specific antibodies. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sevcikova, A.; Fridrichova, I.; Nikolaieva, N.; Kalinkova, L.; Omelka, R.; Martiniakova, M.; Ciernikova, S. Clinical Significance of microRNAs in Hematologic Malignancies and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2023, 15, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, S.M.; Ahmadi Afshar, N.; Almasi, P. Insight into microRNAs’ involvement in hematopoiesis: Current standing point of findings. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, C.; Ching, Y.Q.; Chooi, J.Y.; Lu, X.; Quah, J.Y.; Toh, S.H.; Chan, Z.L.; Tan, T.Z.; Chong, P.S.; et al. Inhibition of LIN28B impairs leukemia cell growth and metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jacamo, R.; Konopleva, M.; Garzon, R.; Croce, C.; Andreeff, M. CXCR4 downregulation of let-7a drives chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Muntean, A.G. Differential regulation of the c-Myc/Lin28 axis discriminates subclasses of rearranged MLL leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25208–25223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) of oncosuppressor let-7 miRNAs in AML allows for the expression (
) of oncosuppressor let-7 miRNAs in AML allows for the expression ( ) of their targets, thus promoting proliferation, survival, motility and stem-like phenotype.
) of their targets, thus promoting proliferation, survival, motility and stem-like phenotype.
 ) of oncosuppressor let-7 miRNAs in AML allows for the expression (
) of oncosuppressor let-7 miRNAs in AML allows for the expression ( ) of their targets, thus promoting proliferation, survival, motility and stem-like phenotype.
) of their targets, thus promoting proliferation, survival, motility and stem-like phenotype.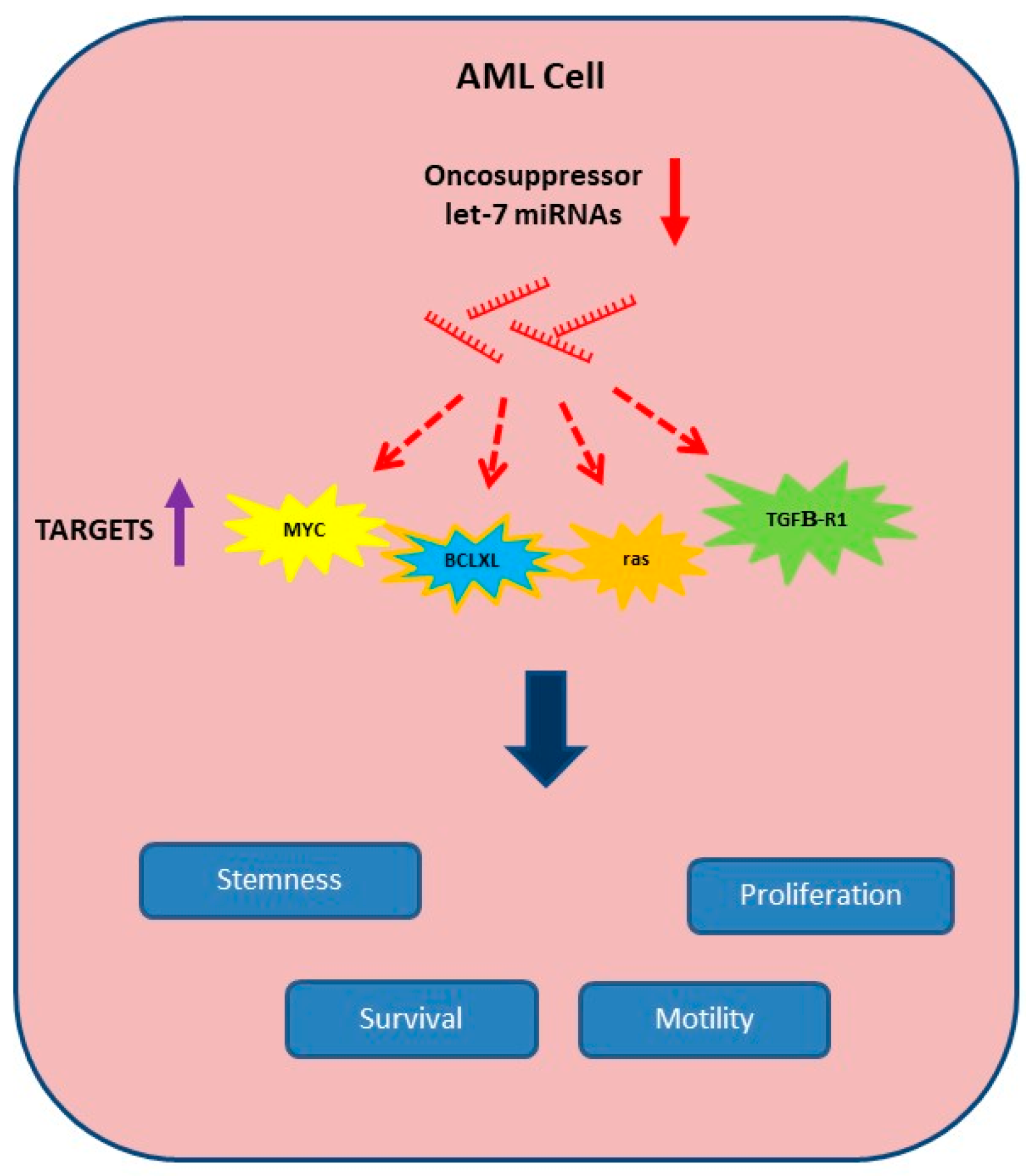

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li Santi, A.; Alfieri, M.; Meo, L.; Ragno, P. Let-7 Family microRNAs Regulate the Expression of the Urokinase-Receptor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090623
Li Santi A, Alfieri M, Meo L, Ragno P. Let-7 Family microRNAs Regulate the Expression of the Urokinase-Receptor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(9):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090623
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi Santi, Anna, Mariaevelina Alfieri, Luigia Meo, and Pia Ragno. 2025. "Let-7 Family microRNAs Regulate the Expression of the Urokinase-Receptor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells" Cells 14, no. 9: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090623
APA StyleLi Santi, A., Alfieri, M., Meo, L., & Ragno, P. (2025). Let-7 Family microRNAs Regulate the Expression of the Urokinase-Receptor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cells, 14(9), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090623






