Podocyte A20/TNFAIP3 Controls Glomerulonephritis Severity via the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses and Effects on the Cytoskeleton
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
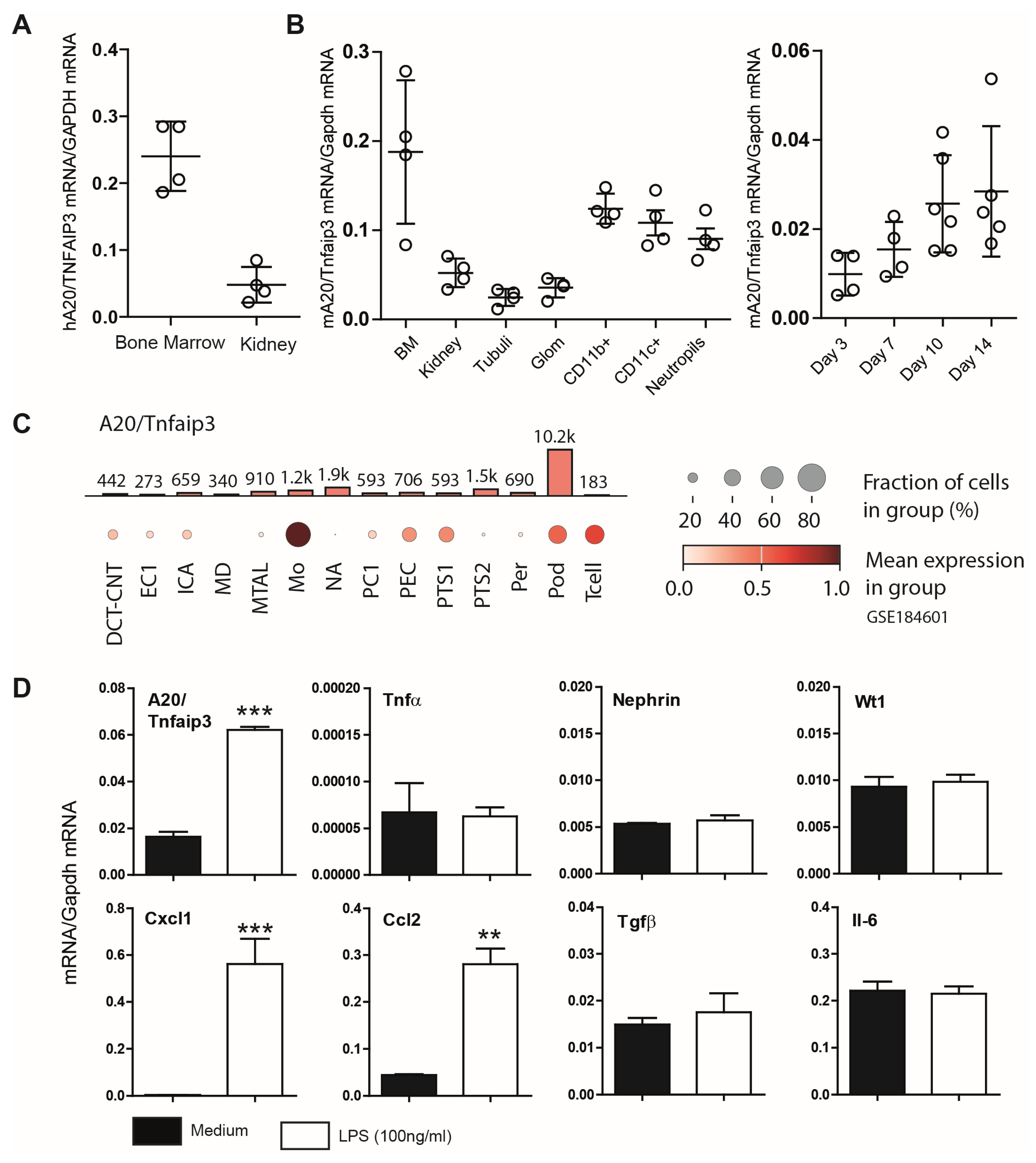
3.1. Characterization of A20 Expression in Mouse Podocytes
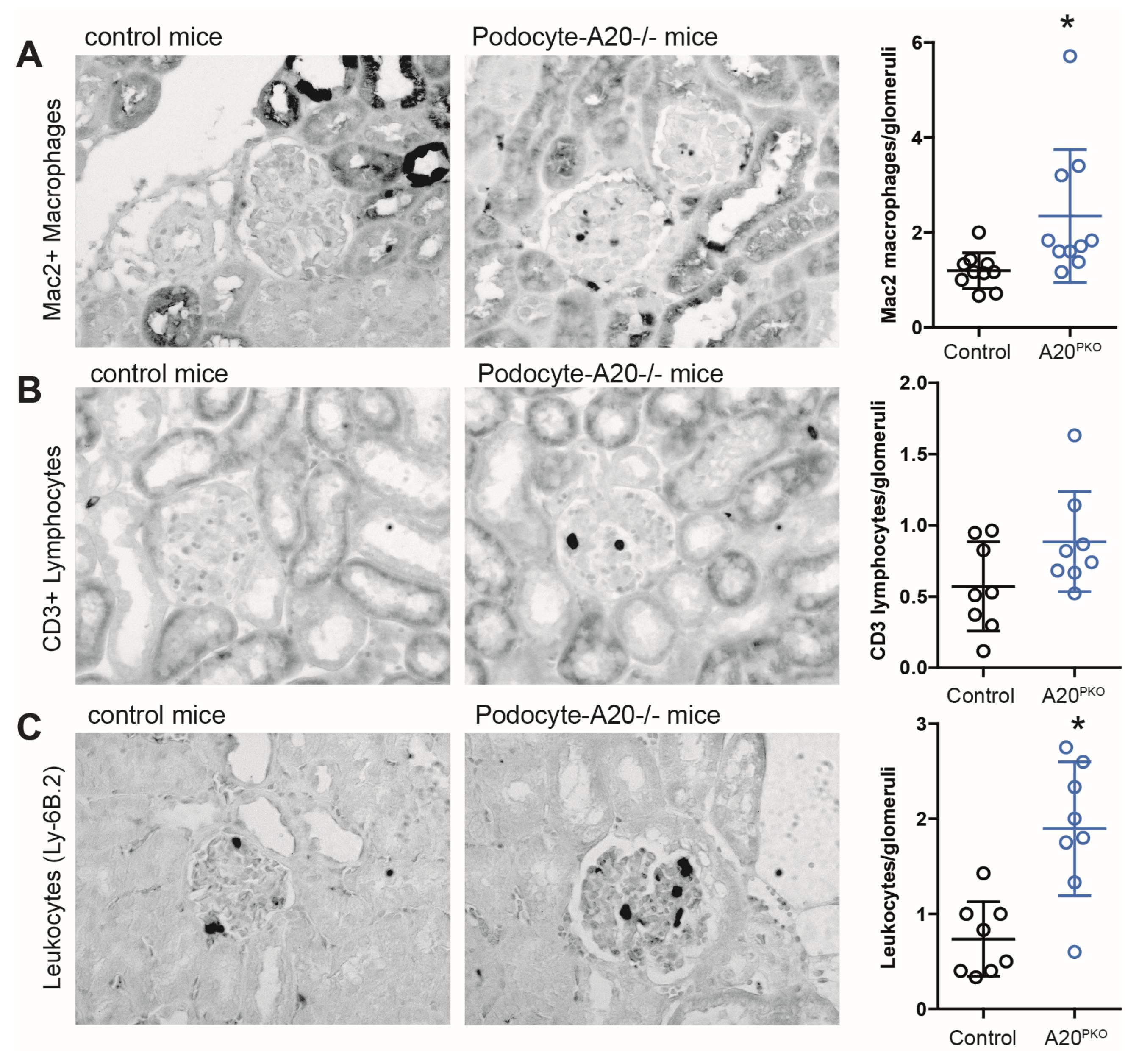
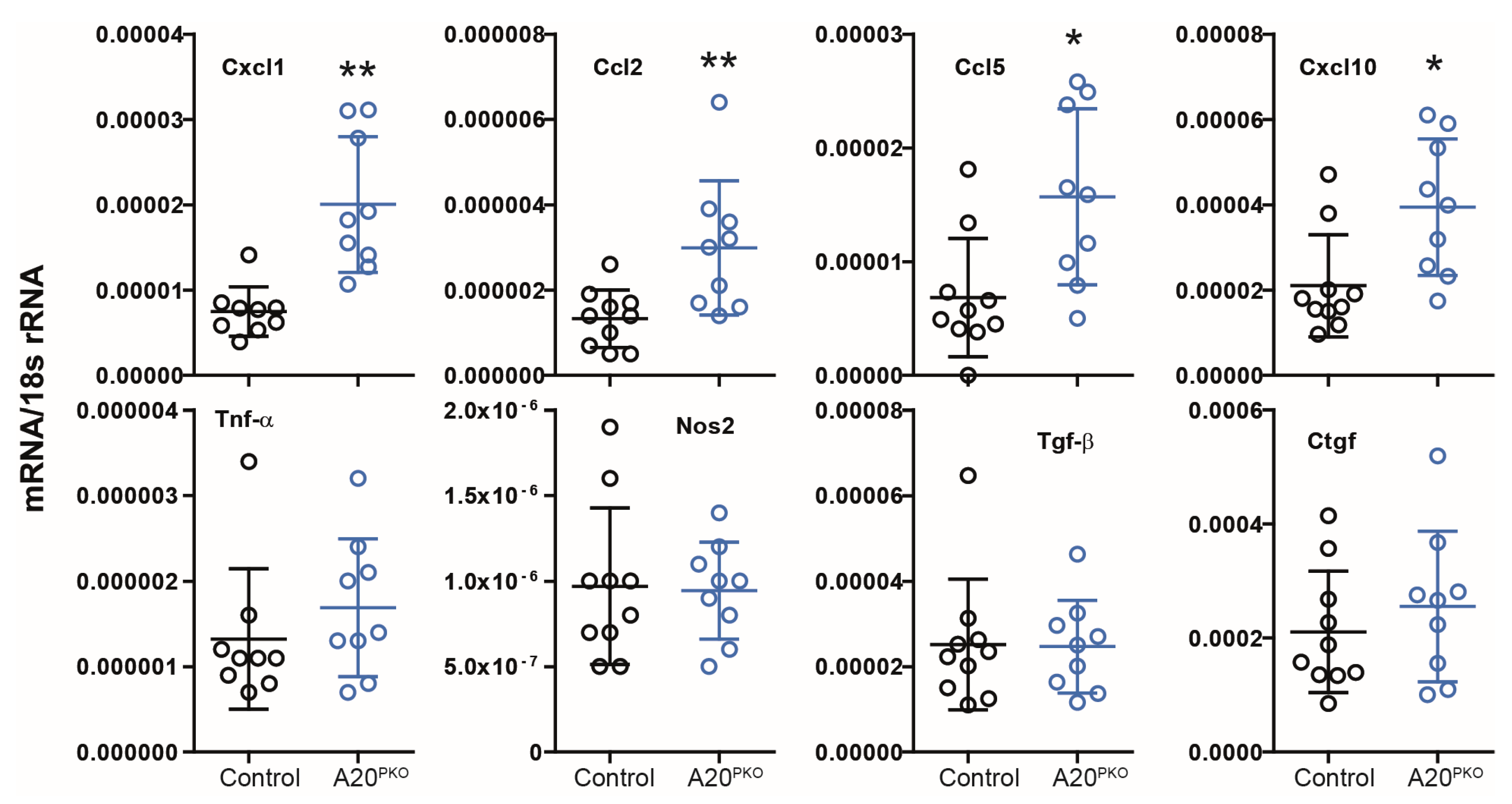
3.2. A20Δpodocyte Mice Exhibit Enhanced Glomerular Inflammation
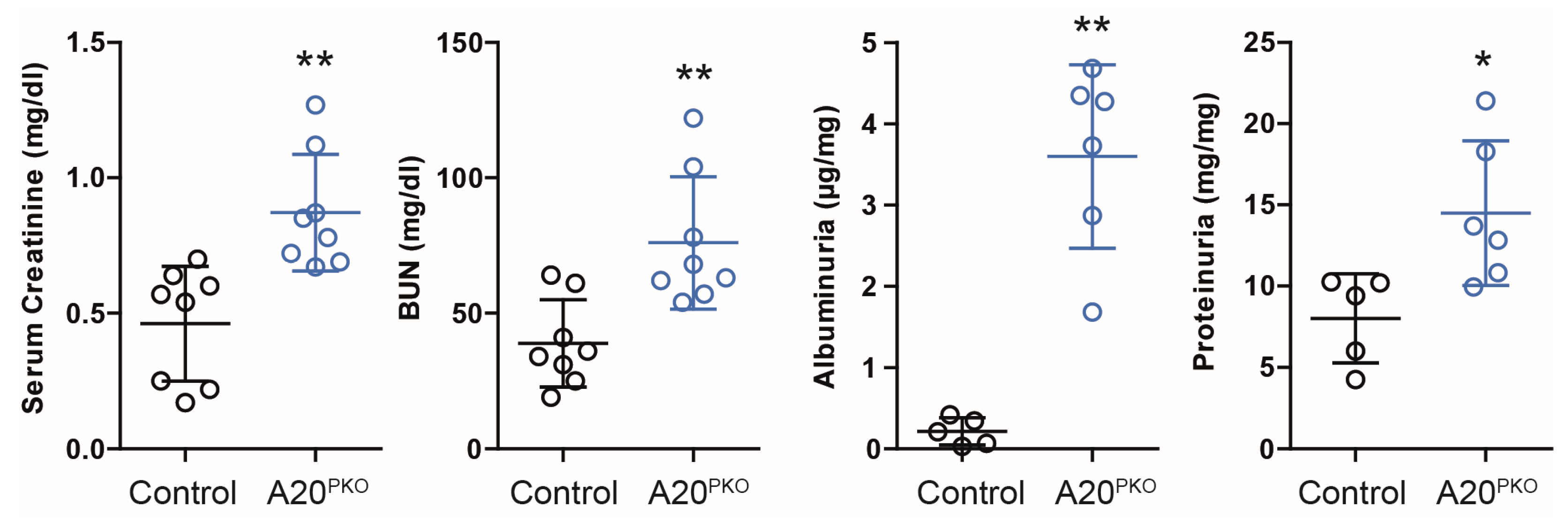
3.3. A20Δpodocyte Mice Exhibit Increased Glomerular Injury
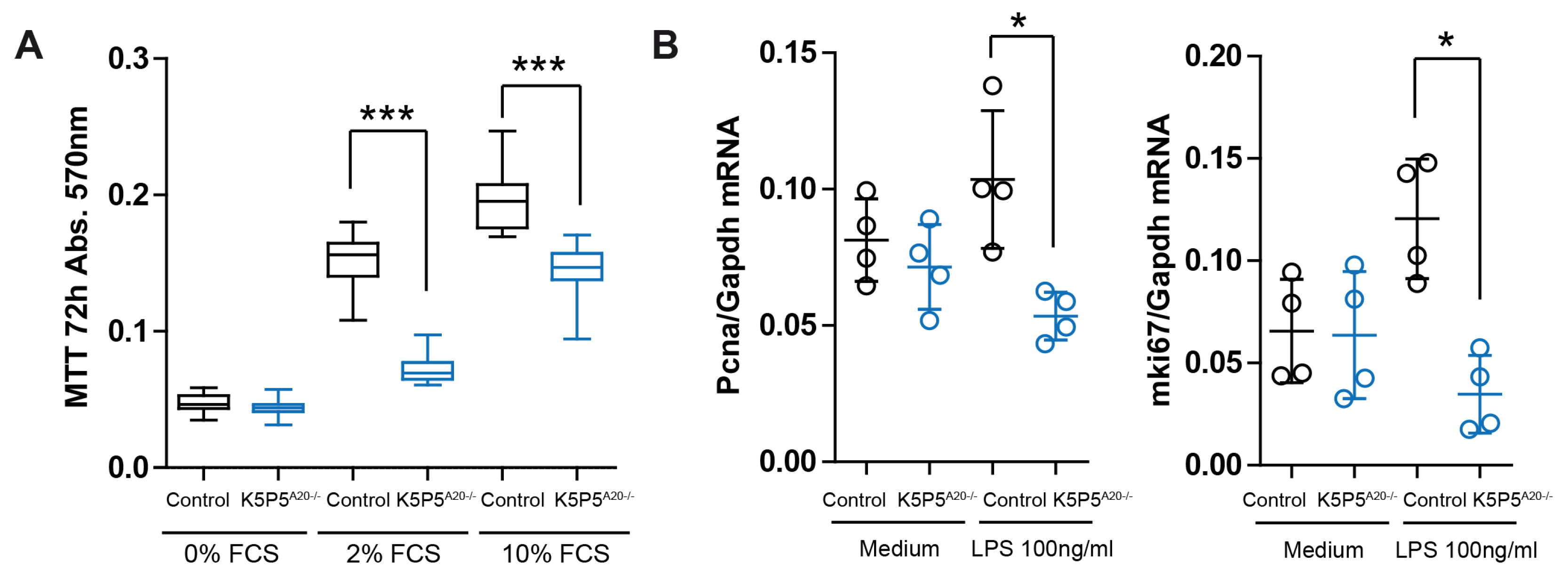
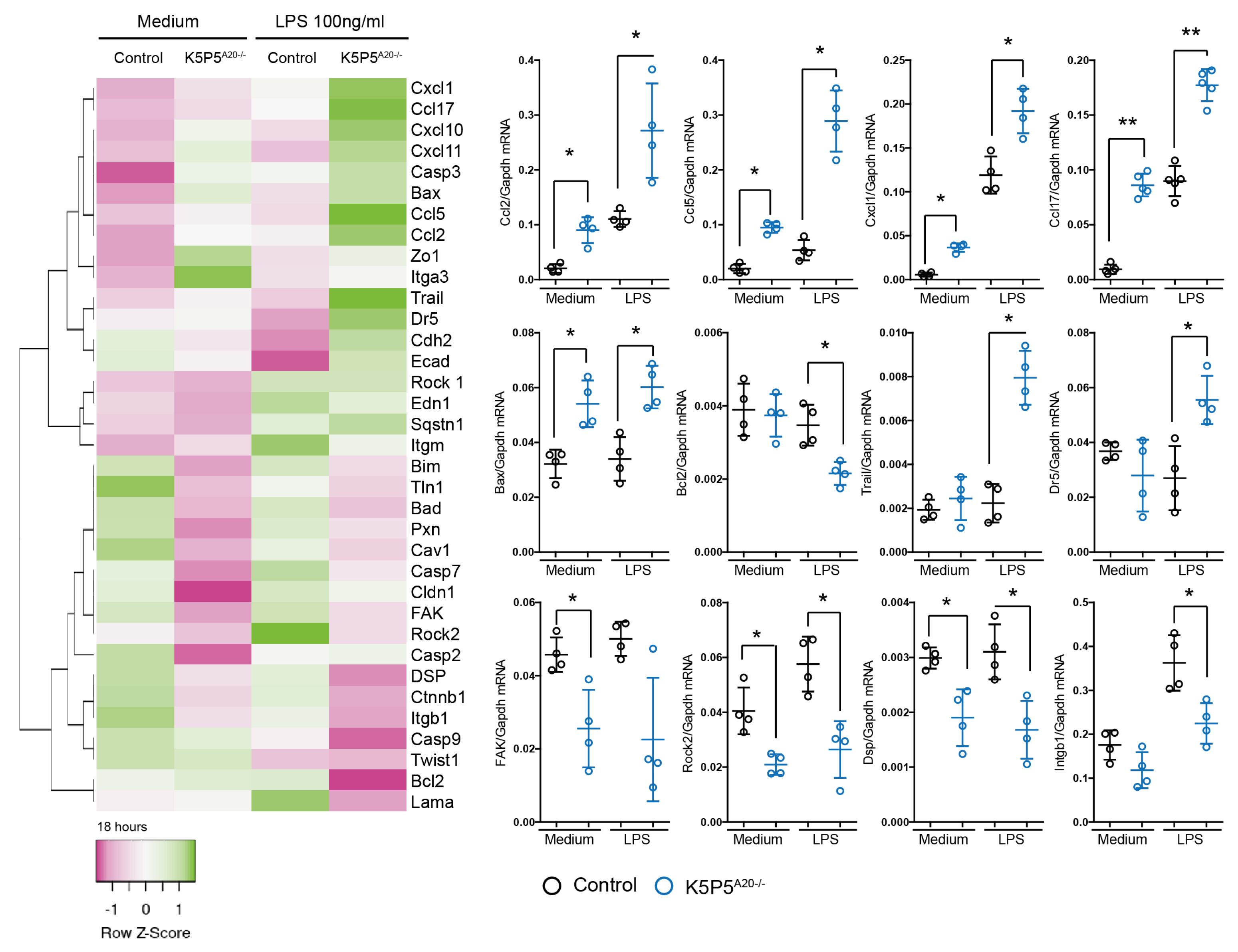
3.4. Loss of A20 in Cultured Podocytes Results in Increased Cell Death and the Production of Chemotactic Mediators
3.5. A20-Knockout K5P5A20−/− Podocytes Are More Susceptible to Cytoskeleton Rearrangements and Show a Reduction in Integrin b1 Expression
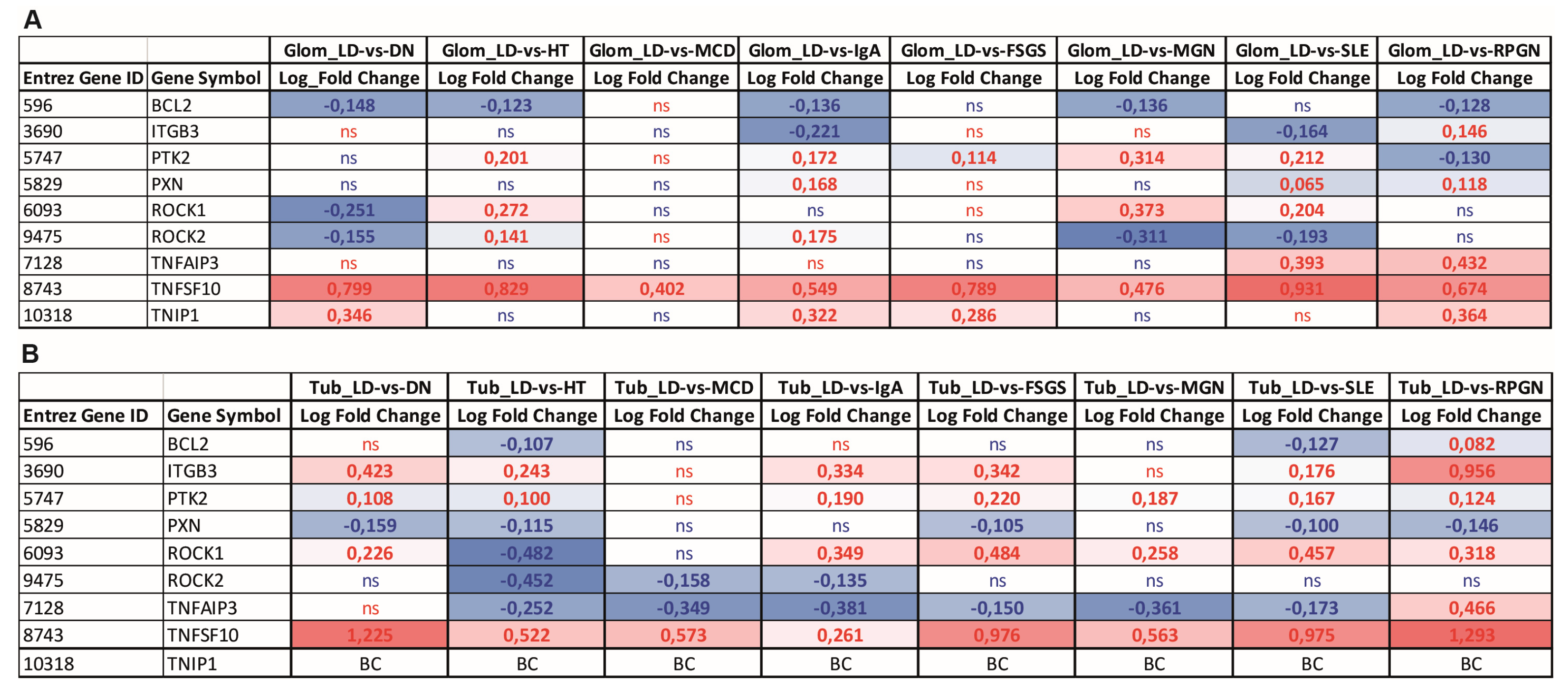
3.6. Gene Expression Analysis of TNFAIP3 and Selected Genes Involved in Anoikis, NF-κB Regulation, and Cell Attachment in Biopsies of Patients with Various Kidney Diseases
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Q.; Tang, B.; Zhang, C. Signaling pathways of chronic kidney diseases, implications for therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, M. Podocyte injury and its consequences. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiser, J.; von Gersdorff, G.; Loos, M.; Oh, J.; Asanuma, K.; Giardino, L.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Calvaresi, N.; Watanabe, H.; Schwarz, K.; et al. Induction of B7-1 in podocytes is associated with nephrotic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Bao, W.; Shi, S. Innate Immune Activity in Glomerular Podocytes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Bock, F.; Al-Dabet, M.M.; Gadi, I.; Kohli, S.; Nazir, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ranjan, S.; Wang, H.; Madhusudhan, T.; et al. Caspase-1, but Not Caspase-3, Promotes Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2270–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Millward, C.A.; Inoshita, H.; Saikia, P.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C.; Emancipator, S.N. Antiviral innate immunity disturbs podocyte cell function. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banas, M.C.; Banas, B.; Hudkins, K.L.; Wietecha, T.A.; Iyoda, M.; Bock, E.; Hauser, P.; Pippin, J.W.; Shankland, S.J.; Smith, K.D.; et al. TLR4 links podocytes with the innate immune system to mediate glomerular injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, K.M.; Ford, S.L.; Longano, A.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R. Intrarenal Toll-like receptor 4 and Toll-like receptor 2 expression correlates with injury in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1283–F1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. Overexpression of toll-like receptor 2 in glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes in septic acute kidney injury mouse model. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, M.A.; Ichii, O.; Hosny Ali Elewa, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Otani, Y.; Hosotani, M.; Kon, Y. Overexpression of toll-like receptor 9 correlates with podocyte injury in a murine model of autoimmune membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Autoimmunity 2018, 51, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, J.; Ichii, O.; Miyazono, K.; Nakamura, T.; Horino, T.; Otsuka-Kanazawa, S.; Kon, Y. Overexpression of Toll-like receptor 8 correlates with the progression of podocyte injury in murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, G.W., 3rd; Mitrofanova, A.; Fontanella, A.; Ciancio, G.; Roth, D.; Ruiz, P.; Abitbol, C.; Chandar, J.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. The podocyte: Glomerular sentinel at the crossroads of innate and adaptive immunity. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1201619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Shang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Xu, C.; Yuan, W. DC-SIGN expression on podocytes and its role in inflammatory immune response of lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 183, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, H.S.; Abou-Samra, E.; Scur, M.; Gutsol, A.; Hall, C.W.; Dasgupta, B.; Gharibeh, L.; Abujamel, T.; Medina-Luna, D.; Gamage, G.S.; et al. Clr-f expression regulates kidney immune and metabolic homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Guo, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Jin, O.; Hu, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, B.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.; et al. Podocyte Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes Contributes to the Development of Proteinuria in Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunte, S.C.; Marschner, J.A.; Klaus, M.; Honda, T.; Li, C.; Motrapu, M.; Walz, C.; Angelotti, M.L.; Antonelli, G.; Melica, M.E.; et al. No NLRP3 inflammasome activity in kidney epithelial cells, not even when the NLRP3-A350V Muckle-Wells variant is expressed in podocytes of diabetic mice. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1230050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coers, W.; Brouwer, E.; Vos, J.T.; Chand, A.; Huitema, S.; Heeringa, P.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Weening, J.J. Podocyte expression of MHC class I and II and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in experimental pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 98, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akilesh, S.; Huber, T.B.; Wu, H.; Wang, G.; Hartleben, B.; Kopp, J.B.; Miner, J.H.; Roopenian, D.C.; Unanue, E.R.; Shaw, A.S. Podocytes use FcRn to clear IgG from the glomerular basement membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldwich, A.; Burkard, M.; Olke, M.; Daniel, C.; Amann, K.; Hugo, C.; Kurts, C.; Steinkasserer, A.; Gessner, A. Podocytes are nonhematopoietic professional antigen-presenting cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matmati, M.; Jacques, P.; Maelfait, J.; Verheugen, E.; Kool, M.; Sze, M.; Geboes, L.; Louagie, E.; Mc Guire, C.; Vereecke, L.; et al. A20 (TNFAIP3) deficiency in myeloid cells triggers erosive polyarthritis resembling rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; et al. Infantile Onset Intractable Inflammatory Bowel Disease Due to Novel Heterozygous Mutations in TNFAIP3 (A20). Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, D.; Huynh, H.Q.; Carroll, M.W.; Baksh, S.; Wine, E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (A20) is dysregulated in pediatric Crohn disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Chen, Z.; Hendriks, R.W.; Kool, M. A20/Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha-Induced Protein 3 in Immune Cells Controls Development of Autoinflammation and Autoimmunity: Lessons from Mouse Models. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storz, P.; Doppler, H.; Ferran, C.; Grey, S.T.; Toker, A. Functional dichotomy of A20 in apoptotic and necrotic cell death. Biochem. J. 2005, 387, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, M.J.; Sanden, S.K.; Soofi, A.; Wiggins, R.C.; Holzman, L.B. Podocyte-specific expression of cre recombinase in transgenic mice. Genesis 2003, 35, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecke, L.; Sze, M.; Mc Guire, C.; Rogiers, B.; Chu, Y.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; Pasparakis, M.; Beyaert, R.; van Loo, G. Enterocyte-specific A20 deficiency sensitizes to tumor necrosis factor-induced toxicity and experimental colitis. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanos-Miranda, A.; Marquez-Acosta, J.; Romero-Arauz, F.; Cardenas-Mondragon, G.M.; Rivera-Leanos, R.; Isordia-Salas, I.; Ulloa-Aguirre, A. Protein:creatinine ratio in random urine samples is a reliable marker of increased 24-hour protein excretion in hospitalized women with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saleem, M.A.; O’Hare, M.J.; Reiser, J.; Coward, R.J.; Inward, C.D.; Farren, T.; Xing, C.Y.; Ni, L.; Mathieson, P.W.; Mundel, P. A conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating nephrin and podocin expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, A.P.; Mansotra, K.; Yadav, S.K.; Kumar, V. An overview of designing and selection of sgRNAs for precise genome editing by the CRISPR-Cas9 system in plants. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shved, N.; Warsow, G.; Eichinger, F.; Hoogewijs, D.; Brandt, S.; Wild, P.; Kretzler, M.; Cohen, C.D.; Lindenmeyer, M.T. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals renal cell type-specific dysregulation of hypoxia-associated transcripts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, C.D.; Klingenhoff, A.; Boucherot, A.; Nitsche, A.; Henger, A.; Brunner, B.; Schmid, H.; Merkle, M.; Saleem, M.A.; Koller, K.P.; et al. Comparative promoter analysis allows de novo identification of specialized cell junction-associated proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5682–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, M.; Ettou, S.; Jung, Y.L.; Lenz, M.O.; Taglienti, M.E.; Park, P.J.; Schermer, B.; Benzing, T.; Kreidberg, J.A. Genome-Wide Analysis of Wilms’ Tumor 1-Controlled Gene Expression in Podocytes Reveals Key Regulatory Mechanisms. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Nie, H.; Deng, J.; Liang, S.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Gong, S.; Wang, G.; Zuo, W.; Hou, F.; et al. WT1(+) glomerular parietal epithelial progenitors promote renal proximal tubule regeneration after severe acute kidney injury. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.; Ding, G. Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury. Metabolism 2024, 150, 155718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.D.; Beresford, M.W. Podocytes contribute, and respond, to the inflammatory environment in lupus nephritis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1683–F1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoud, A.; Burian, A.; Borowska-Wykret, D.; Uyttewaal, M.; Wrzalik, R.; Kwiatkowska, D.; Hamant, O. FibrilTool, an ImageJ plug-in to quantify fibrillar structures in raw microscopy images. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, G.I.; Saleem, M.A. The podocyte cytoskeleton--key to a functioning glomerulus in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, C.; Huber, T.B. The Evolving Complexity of the Podocyte Cytoskeleton. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Yang, C.; Su, Q.; Huang, L.; Fu, K.; An, S.; Xie, F.; To, K.K.W.; et al. A20 promotes colorectal cancer immune evasion by upregulating STC1 expression to block “eat-me” signal. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pora, A.; Yoon, S.; Dreissen, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Merkel, R.; Windoffer, R.; Leube, R.E. Regulation of keratin network dynamics by the mechanical properties of the environment in migrating cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura-Yoshida, C.; Mochida, K.; Nakaya, M.A.; Mizutani, T.; Matsuo, I. Cytoplasmic localization of GRHL3 upon epidermal differentiation triggers cell shape change for epithelial morphogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Zhou, M.; Lu, D.; Li, J.; Tang, Q.; Xiong, C.; Liang, F.; Chen, R. The mechanism of ITGB4 in tumor migration and invasion. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1421902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamilov, R.; Aneskievich, B.J. TNIP1 in Autoimmune Diseases: Regulation of Toll-like Receptor Signaling. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3491269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Fu, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Lin, L.; Stolz, D.B.; Liu, Y. Sonic hedgehog connects podocyte injury to mesangial activation and glomerulosclerosis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e130515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Niu, J.; Min, W.; Ai, J.; Lin, X.; Miao, J.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Q.; et al. B7-1 mediates podocyte injury and glomerulosclerosis through communication with Hsp90ab1-LRP5-beta-catenin pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 2399–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.C.; Wang, G.H.; Lu, J.; Chen, P.P.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.B.; Ma, K.L. Role of Podocyte Injury in Glomerulosclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1165, 195–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shembade, N.; Ma, A.; Harhaj, E.W. Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 2010, 327, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyninck, K.; De Valck, D.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Van Criekinge, W.; Contreras, R.; Fiers, W.; Haegeman, G.; Beyaert, R. The zinc finger protein A20 inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by interfering with an RIP- or TRAF2-mediated transactivation signal and directly binds to a novel NF-kappaB-inhibiting protein ABIN. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyninck, K.; Beyaert, R. A20 inhibits NF-kappaB activation by dual ubiquitin-editing functions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, S.; Teupser, D.; Tan, M.; Chen, K.Y.; Breslow, J.L. The protective effect of A20 on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice is associated with reduced expression of NF-kappaB target genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18601–18606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Dong, S.; Yin, H.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, G. Regulatory effect of zinc finger protein A20 on rheumatoid arthritis through NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling axis mediating pyroptosis of HFLS- RA cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Qian, T.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Hao, F. Aberrant Low Expression of A20 in Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha-stimulated SLE Monocytes Mediates Sustained NF-kappaB Inflammatory Response. Immunol. Investig. 2015, 44, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalvazo, P.; Carriazo, S.; Rojas-Rivera, J.; Ramos, A.M.; Ortiz, A.; Perez-Gomez, M.V. Gain-of-function TLR7 and loss-of-function A20 gene variants identify a novel pathway for Mendelian lupus and lupus nephritis. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. The transfection of A20 gene prevents kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Yanagihara, T.; Takada, T.; Itoh, M.; Matsuno, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kihara, I. Urinary excretion of podocytes reflects disease activity in children with glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Nephrol. 1998, 18, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, H.; Canzonieri, R.; Schiel, A.; Politei, J.; Stern, A.; Andrews, J.; Paulero, M.; Rengel, T.; Araoz, A.; Forrester, M.; et al. Podocyturia is significantly elevated in untreated vs treated Fabry adult patients. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, J.B.; Anders, H.J.; Susztak, K.; Podesta, M.A.; Remuzzi, G.; Hildebrandt, F.; Romagnani, P. Podocytopathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.A.; Monteiro, M.; Araujo, L.S.; Urzedo, M.G.; Rocha, L.B.; Dos Reis, M.A.; Machado, J.R. In situ evaluation of podocytes in patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and minimal change disease. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykratis, A.; Martens, A.; Eren, R.O.; Shirasaki, Y.; Yamagishi, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Uemura, S.; Miura, M.; Holzmann, B.; Kollias, G.; et al. A20 prevents inflammasome-dependent arthritis by inhibiting macrophage necroptosis through its ZnF7 ubiquitin-binding domain. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catrysse, L.; Farhang Ghahremani, M.; Vereecke, L.; Youssef, S.A.; Mc Guire, C.; Sze, M.; Weber, A.; Heikenwalder, M.; de Bruin, A.; Beyaert, R.; et al. A20 prevents chronic liver inflammation and cancer by protecting hepatocytes from death. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priem, D.; Devos, M.; Druwe, S.; Martens, A.; Slowicka, K.; Ting, A.T.; Pasparakis, M.; Declercq, W.; Vandenabeele, P.; van Loo, G.; et al. A20 protects cells from TNF-induced apoptosis through linear ubiquitin-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Oshima, S.; Takahara, M.; Maeyashiki, C.; Nemoto, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Nibe, Y.; Nozaki, K.; Nagaishi, T.; Okamoto, R.; et al. TNFAIP3 promotes survival of CD4 T cells by restricting MTOR and promoting autophagy. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.M.; Zammit, N.; Nguyen-Ngo, D.; Souilmi, Y.; Minhas, N.; Meijles, D.N.; Self, E.; Walters, S.N.; Warren, J.; Cultrone, D.; et al. The impact of the cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase TNFAIP3 gene variation on transcription factor NF-kappaB activation in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoli, S.; Angelotti, M.L.; Antonelli, G.; Kumar Vr, S.; Mulay, S.R.; Desai, J.; Anguiano Gomez, L.; Thomasova, D.; Eulberg, D.; Klussmann, S.; et al. CXCL12 blockade preferentially regenerates lost podocytes in cortical nephrons by targeting an intrinsic podocyte-progenitor feedback mechanism. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, E.A.; Caster, D.J.; Barati, M.T.; Tan, M.; Zheng, S.; Berthier, C.C.; Brosius, F.C., 3rd; Vieyra, M.B.; Sheehan, R.M.; Kosiewicz, M.; et al. ABIN1 Determines Severity of Glomerulonephritis via Activation of Intrinsic Glomerular Inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2799–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, C.; Pacifico, F.; Lavorgna, A.; Mellone, S.; Iannetti, A.; Acquaviva, R.; Formisano, S.; Vito, P.; Leonardi, A. ABIN-1 binds to NEMO/IKKgamma and co-operates with A20 in inhibiting NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18482–18488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, S.M.; Francis, H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.J.; Yang, J.W.; Do, W.S.; Fogo, A.B. Pathogenesis of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, Y.; Koike, H.; Ikezumi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Oyanagi, A.; Gejyo, F.; Shimizu, F.; Kawachi, H. Podocyte injuries exacerbate mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 2192–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blaine, J.; Dylewski, J. Regulation of the Actin Cytoskeleton in Podocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, H.Y.; Roth, R.; Jain, S.; Heuser, J.E.; Shaw, A.S.; Miner, J.H. Injury-induced actin cytoskeleton reorganization in podocytes revealed by super-resolution microscopy. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e94137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Cho, N.J.; Heo, N.H.; Gil, H.W.; Lee, E.Y.; Moon, J.S.; Park, S. Severity of foot process effacement is associated with proteinuria in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 39, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Artomov, M.; Brahler, S.; Stander, M.C.; Shamsan, G.; Sampson, M.G.; White, J.M.; Kretzler, M.; Miner, J.H.; Jain, S.; et al. A role for genetic susceptibility in sporadic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, W.; Shirato, I.; Nagata, M.; LeHir, M.; Lemley, K.V. The podocyte’s response to stress: The enigma of foot process effacement. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F333–F347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, C.; Izquierdo-Lahuerta, A.; Vivas, Y.; Velasco, I.; Yeo, T.K.; Chen, S.; Medina-Gomez, G. Renal Lipotoxicity-Associated Inflammation and Insulin Resistance Affects Actin Cytoskeleton Organization in Podocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Saha, T.; Bose, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Dhar, S.; Khan, P.; Adhikary, A.; Das, T.; Sa, G. Integrin-EGFR interaction regulates anoikis resistance in colon cancer cells. Apoptosis 2019, 24, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinschek, R.; Hingerl, J.; Benge, A.; Zafiu, C.; Schuren, E.; Ehmoser, E.K.; Lossner, D.; Reuning, U. Constitutive activation of integrin alphavbeta3 contributes to anoikis resistance of ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, S.M.; Screaton, R.A. Anoikis mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Yu, J.; Guan, K.L. Cell detachment activates the Hippo pathway via cytoskeleton reorganization to induce anoikis. Genes. Dev. 2012, 26, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretland, A.J.; Lawry, J.; Sharrard, R.M. A study of death by anoikis in cultured epithelial cells. Cell Prolif. 2001, 34, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duxbury, M.S.; Ito, H.; Zinner, M.J.; Ashley, S.W.; Whang, E.E. Focal adhesion kinase gene silencing promotes anoikis and suppresses metastasis of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Surgery 2004, 135, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.R.; Noguchi, K.; Fukazawa, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Arai, H.; Uehara, Y. p38MAPK and Rho-dependent kinase are involved in anoikis induced by anicequol or 25-hydroxycholesterol in DLD-1 colon cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strater, J.; Wedding, U.; Barth, T.F.; Koretz, K.; Elsing, C.; Moller, P. Rapid onset of apoptosis in vitro follows disruption of beta 1-integrin/matrix interactions in human colonic crypt cells. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumigray, K.; Zhou, K.; Lechler, T. Cell-cell adhesions and cell contractility are upregulated upon desmosome disruption. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, M. The role of laminin in attachment, growth, and differentiation of cultured cells: A brief review. Cytotechnology 1992, 9, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, C. Cytoskeleton Rearrangement in Podocytopathies: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, S.M.; Yang, K.M.; Bae, E.; Ahn, S.G.; Park, J.S.; Seo, D.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.; Lee, J.; et al. A20 promotes metastasis of aggressive basal-like breast cancers through multi-monoubiquitylation of Snail1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, S.; Yi, X.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Gao, T.; Li, C.; Guo, W. A20 promotes melanoma progression via the activation of Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Köhler, P.; Ribeiro, A.; Honarpisheh, M.; von Rauchhaupt, E.; Lorenz, G.; Li, C.; Martin, L.; Steiger, S.; Lindenmeyer, M.; Schmaderer, C.; et al. Podocyte A20/TNFAIP3 Controls Glomerulonephritis Severity via the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses and Effects on the Cytoskeleton. Cells 2025, 14, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050381
Köhler P, Ribeiro A, Honarpisheh M, von Rauchhaupt E, Lorenz G, Li C, Martin L, Steiger S, Lindenmeyer M, Schmaderer C, et al. Podocyte A20/TNFAIP3 Controls Glomerulonephritis Severity via the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses and Effects on the Cytoskeleton. Cells. 2025; 14(5):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050381
Chicago/Turabian StyleKöhler, Paulina, Andrea Ribeiro, Mohsen Honarpisheh, Ekaterina von Rauchhaupt, Georg Lorenz, Chenyu Li, Lucas Martin, Stefanie Steiger, Maja Lindenmeyer, Christoph Schmaderer, and et al. 2025. "Podocyte A20/TNFAIP3 Controls Glomerulonephritis Severity via the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses and Effects on the Cytoskeleton" Cells 14, no. 5: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050381
APA StyleKöhler, P., Ribeiro, A., Honarpisheh, M., von Rauchhaupt, E., Lorenz, G., Li, C., Martin, L., Steiger, S., Lindenmeyer, M., Schmaderer, C., Anders, H.-J., Thomasova, D., & Lech, M. (2025). Podocyte A20/TNFAIP3 Controls Glomerulonephritis Severity via the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses and Effects on the Cytoskeleton. Cells, 14(5), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050381


.png)






