FSH-Induced Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO1 Mediated by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Granulosa Cells Is Associated with Follicle Selection and Growth of the Hen Ovary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Animal and Granulosa Cell Culture and Treatment with Reagents
2.3. Construction of Recombinant Plasmids and Cell Transfection
2.4. Transfection of siRNA
2.5. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.6. Western Blotting Assay
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.8. Flow Cytometry Assay
2.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
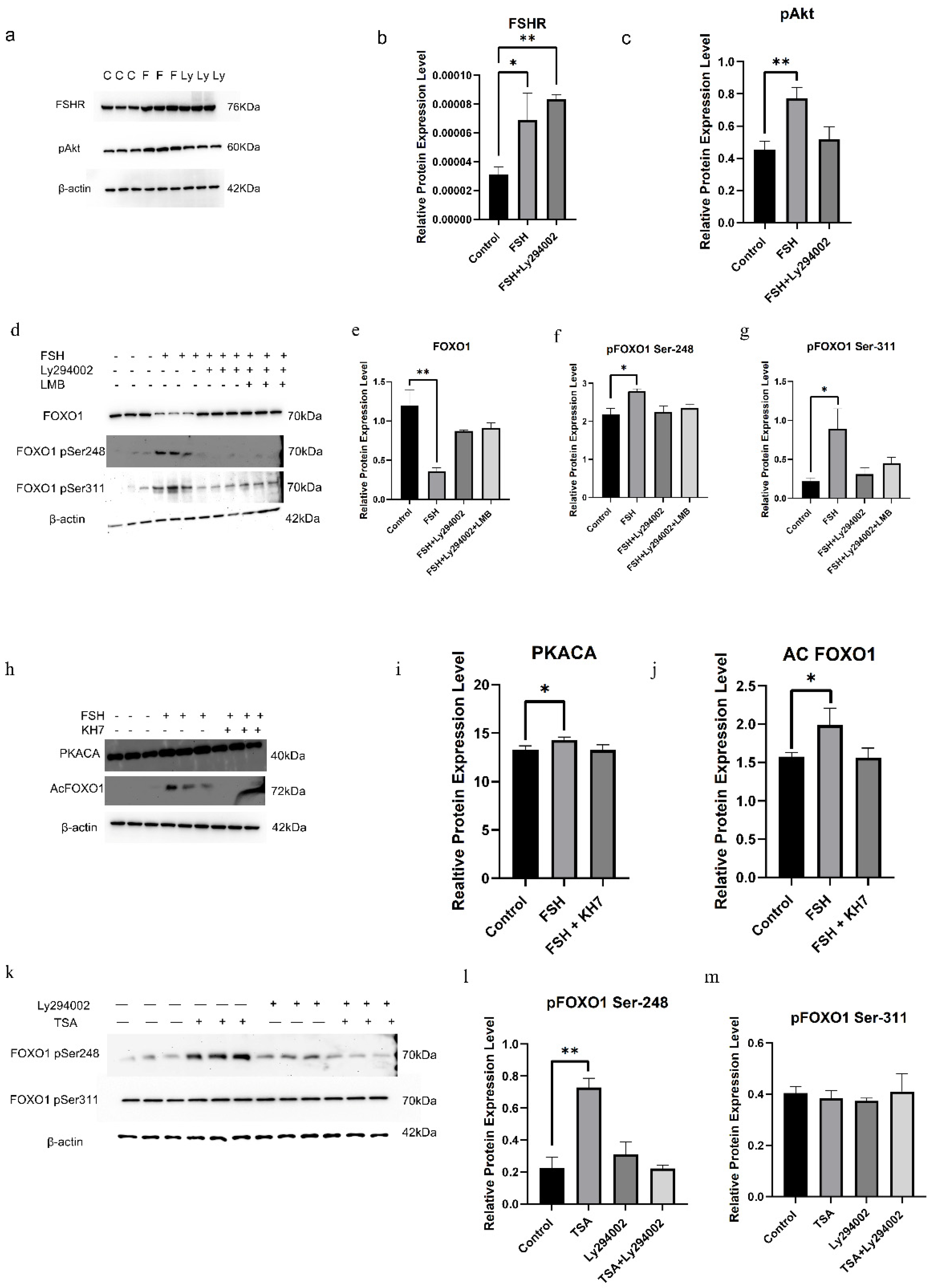
3.1. Influence of FSH on Phosphorylation of FOXO1 in Hen Ovarian GCs
3.2. FSH-Induced FOXO1 Phosphorylation Mediated by FSHR/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
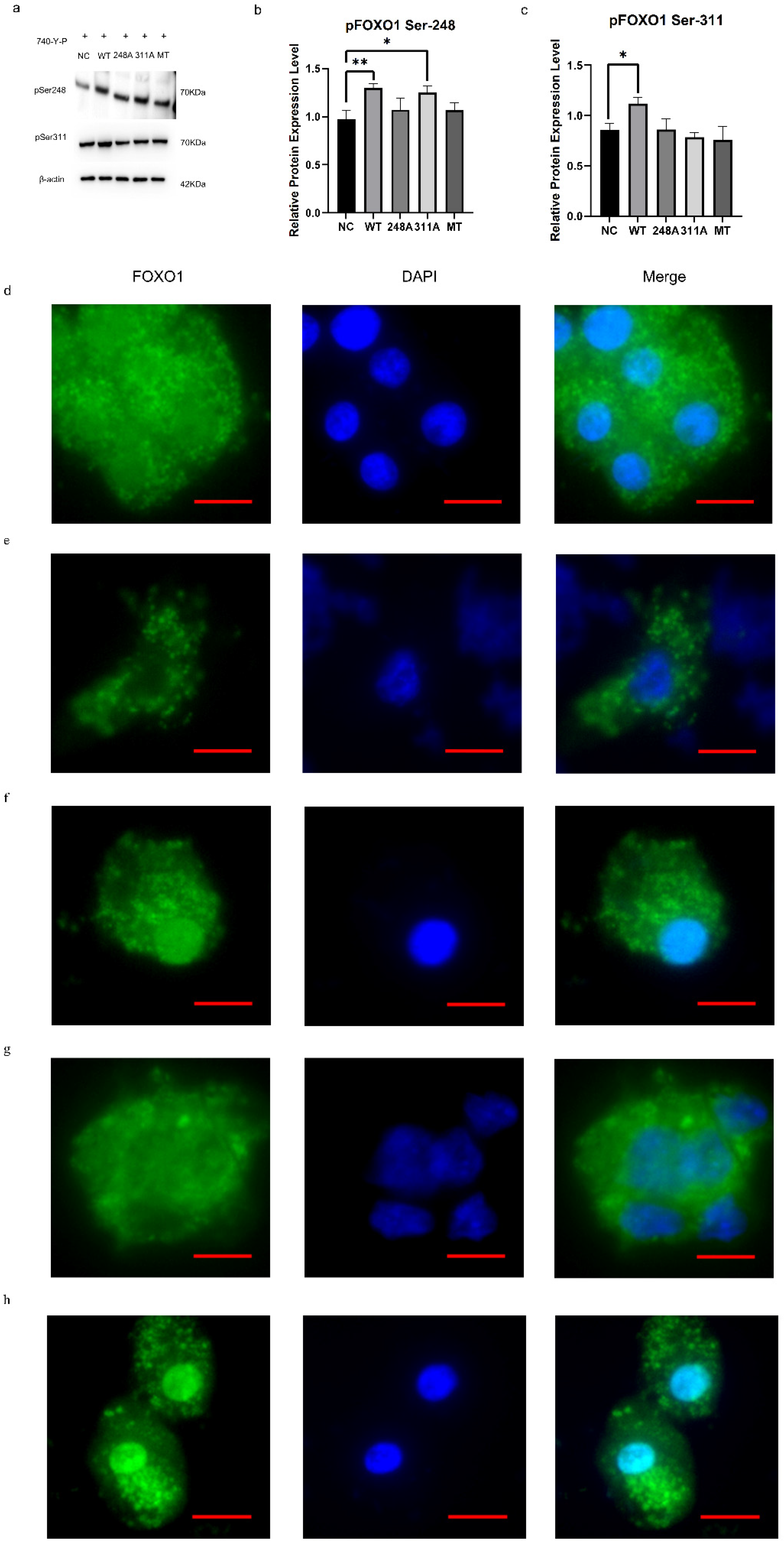
3.3. Roles of the FOXO1 Phosphorylation Sites in Regulating Its Nuclear Exclusion
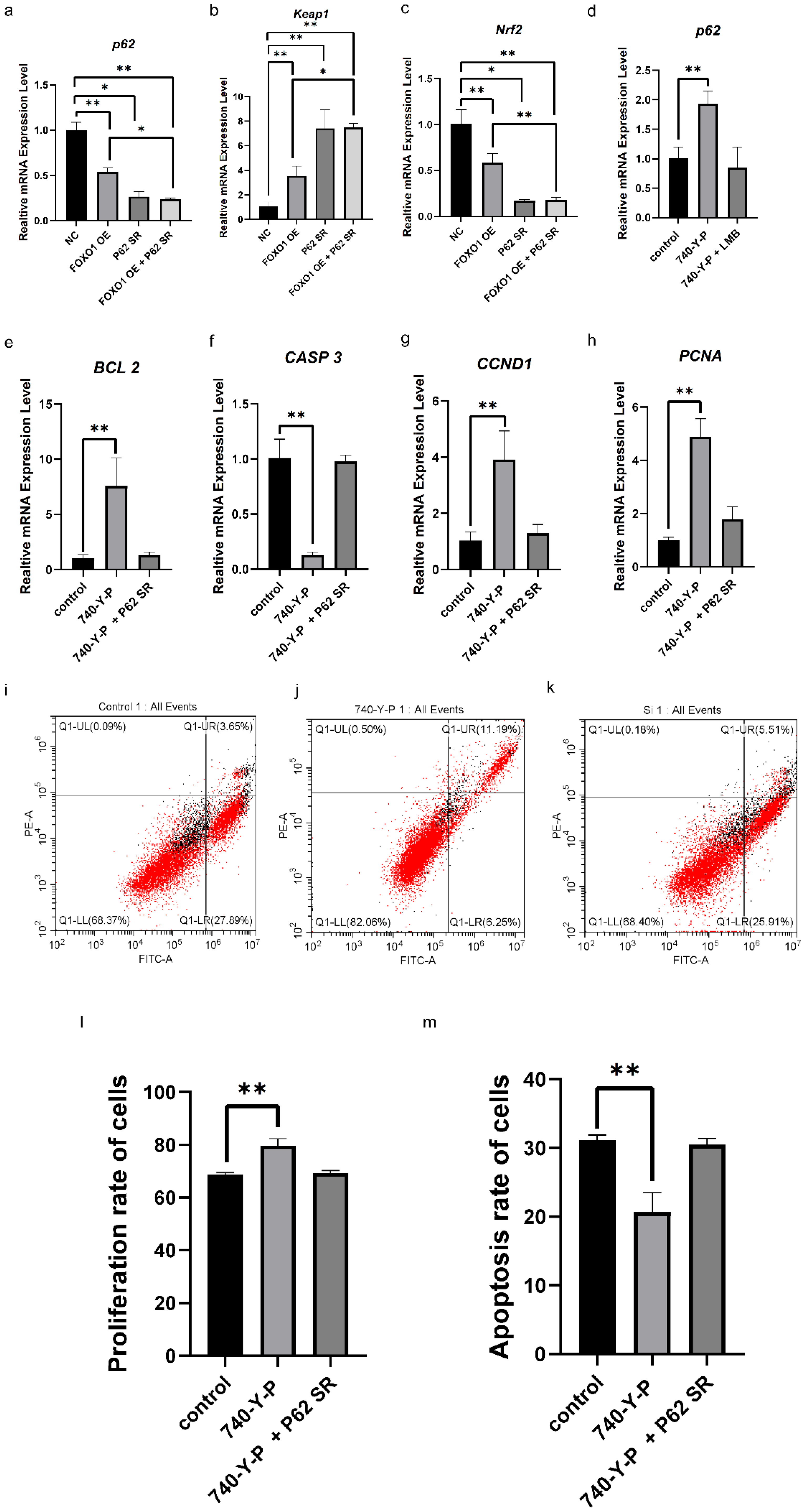
3.4. Effects of FSH-Induced FOXO1 Nuclear Exclusion on Ovarian Follicle Growth and Selection Mediated by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
3.5. Crosstalk Between the PI3K/Akt and P62/Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in Ovarian Follicle Growth and Selection Mediated by FOXO1 Factor
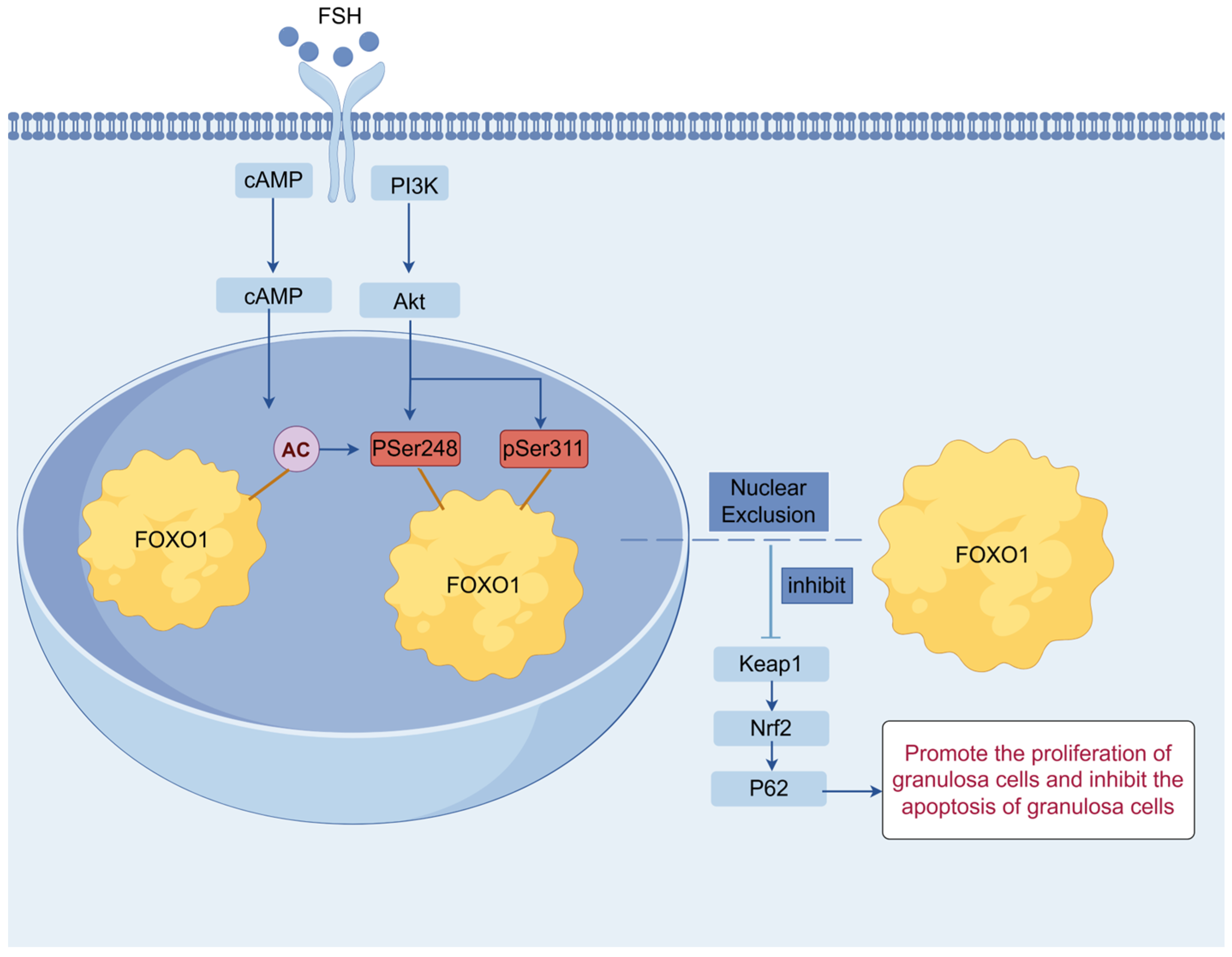
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FSH | follicle-stimulating hormone |
| FSHR | follicle-stimulating hormone receptor |
| FOXO | Forkhead box O transcription factor |
| FOXO1 | forkhead box O1 |
| p-FOXO1 | Phosphorylated FOXO1 |
| GC | granulosa cell |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| Akt | Protein kinase B (PKB) |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| PKB | protein kinase B |
| CRM1 | chromosome region maintenance 1 |
| LMB | Leptomycin B |
| TSA | Trichostatin A |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| RIPA | radio immunoprecipitation assay |
| PKACA | PKA catalytic (Cα) subunit |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| P62 | Sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) |
| BCA | bicinchoninic acid |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PBS | phosphate buffer saline |
| ECL | enhanced chemiluminescence |
| HRP | horseradish peroxidase |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| qRT-PCR | real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR |
| OE | overexpression |
| NC | negative control |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| SR | siRNA |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| CASP3 | caspase 3 |
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
| CCND1 | cyclin D1 |
| EDTA | ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| IGF-1 | insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-beta |
| Erα | estrogen receptor alpha |
| SQSTM1 | sequestosome 1 |
References
- Johnson, A.L. Ovarian follicle selection and granulosa cell differentiation. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, X.; Lv, Z.; Wei, M.; Jing, Y.; Mu, F.; Xu, R.F. Association of novel polymorphisms of forkhead box L2 and growth differentiation factor-9 genes with egg production traits in local Chinese Dagu hens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Niu, X.; Qin, N.; Shan, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, C.; Xu, R.; Mishra, B. Novel insights into the regulation of LATS2 kinase in prehierarchical follicle development via the Hippo pathway in hen ovary. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.K. Encyclopedia of Reproduction; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.; Woods, D.C. Dynamics of avian ovarian follicle development: Cellular mechanisms of granulosa cell differentiation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 163, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Qin, N.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J. Inhibitory effect of SLIT2 on granulosa cell proliferation mediated by the CDC42-PAKs-ERK1/2 MAPK pathway in the prehierarchical follicles of the chicken ovary. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Z.; Qin, N.; Tyasi, T.L.; Zhu, H.; Liu, D.; Yuan, S.; Xu, R. The Hippo/MST pathway member SAV1 plays a suppressive role in development of the prehierarchical follicles in hen ovary. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liswaniso, S.; Shan, X.; Zhao, J.; Chimbaka, I.M.; Xu, R. Qin NJT: The opposite effects of VGLL1 and VGLL4 genes on granulosa cell proliferation and apoptosis of hen ovarian prehierarchical follicles. Theriogenology 2022, 181, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, E.D.; Agarwal, E.; Leiphrakpam, P.D.; Haferbier, K.L.; Brattain, M.G.; Chowdhury, S. Differential PKA activation and AKAP association determines cell fate in cancer cells. J. Mol. Signal. 2013, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskén, K.; Aandahl, E.M. Localized effects of cAMP mediated by distinct routes of protein kinase A. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 137–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.C.; Johnson, A.L. Regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone-receptor messenger RNA in hen granulosa cells relative to follicle selection. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.; Han, D.; Yang, X.; Cai, G.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Deng, X. Endothelin-3 Suppresses Luteinizing Hormone Receptor Expression by Regulating the cAMP-PKA Pathway in Hen Granulosa Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 7832–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Sun, S.-C.; Liu, H. Involvement of FoxO1 in the effects of follicle-stimulating hormone on inhibition of apoptosis in mouse granulosa cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, J.; Reverchon, M.; Cloix, L.; Froment, P.; Ramé, C. Involvement of adipokines, AMPK, PI3K and the PPAR signaling pathways in ovarian follicle development and cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 56, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, W.; Das, M.; Shalom-Paz, E.; Holzer, H. Mechanisms of follicle selection and development. Minerva Ginecol. 2011, 63, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hillier, S.J.M. Gonadotropic control of ovarian follicular growth and development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 179, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arden, K.C.; Biggs Iii, W.H.J. Regulation of the FoxO family of transcription factors by phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-activated signaling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 403, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Wang, H.; Little, P.J.; Quirion, R.; Zheng, W. Forkhead family transcription factor FoxO and neural differentiation. Neurogenetics 2012, 13, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, F.M.; Van der Heide, L.P.; Wijchers, P.J.; Burbach, J.P.H.; Hoekman, M.F.; Smidt, M.P. FoxO6, a novel member of the FoxO class of transcription factors with distinct shuttling dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35959–35967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs Iii, W.H.; CaveneeKaren, C.W.K. Identification and characterization of members of the FKHR (FOX O) subclass of winged-helix transcription factors in the mouse. Mamm. Genome 2001, 12, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M.; Candau, R.B.; Bernardi, H.J.C. FoxO transcription factors: Their roles in the maintenance of skeletal muscle homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Castrillon, D.H.; Zhou, W.; Richards, J.S. FOXO1/3 depletion in granulosa cells alters follicle growth, death and regulation of pituitary FSH. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisarska, M.D.; Kuo, F.-T.; Tang, D.; Zarrini, P.; Khan, S.; Ketefian, A. sterility: Expression of forkhead transcription factors in human granulosa cells. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 1392–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; LaPolt, P.S. Relationship between FoxO1 protein levels and follicular development, atresia, and luteinization in the rat ovary. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 179, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, S.C. Protective mechanism of FSH against oxidative damage in mouse ovarian granulosa cells by repressing autophagy. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1364–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Rudd, M.D.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, I.; Gonzalez-Robayna, I.; Fan, H.-Y.; Zeleznik, A.J.; Richards, J.S. FSH and FOXO1 regulate genes in the sterol/steroid and lipid biosynthetic pathways in granulosa cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Maizels, E.T.; Feiger, Z.J.; Alam, H.; Peters, C.A.; Woodruff, T.K.; Unterman, T.G.; Lee, E.J.; Jameson, J.L.; HunzickerDunn, M. Induction of cyclin D2 in rat granulosa cells requires FSH-dependent relief from FOXO1 repression coupled with positive signals from Smad. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9135–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, M.K.; Law, N.C.; Donaubauer, E.M.; Kyriss, B.; Hunzicker-Dunn, M. Forkhead box O member FOXO1 regulates the majority of follicle-stimulating hormone responsive genes in ovarian granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 434, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Lin, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, W.-K.; Liu, H. Involvement of the up-regulated FoxO1 expression in follicular granulosa cell apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 287, 25727–25740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-Y.; O’Connor, A.; Shitanaka, M.; Shimada, M.; Liu, Z.; Richards, J.S. β-Catenin (CTNNB1) promotes preovulatory follicular development but represses LH-mediated ovulation and luteinization. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.C.; Tanabe, K.; Cras-Méneur, C.; Abumrad, N.A.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Permutt, M.A. Inhibition of Foxo1 protects pancreatic islet β-cells against fatty acid and endoplasmic reticulum stress–induced apoptosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 57, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Guo, S.; Cichy, S.C.; Unterman, T.G.; Cohen, P. Phosphorylation of the transcription factor forkhead family member FKHR by protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17179–17183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Gan, L.; Pan, H.; Kan, D.; Majeski, M.; Adam, S.A.; Unterman, T.G. Multiple elements regulate nuclear/cytoplasmic shuttling of FOXO1: Characterization of phosphorylation-and 14-3-3-dependent and-independent mechanisms. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Kanai, F.; Stehn, J.; Xu, J.; Sarbassova, D.; Frangioni, J.V.; Dalal, S.N.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Greenberg, M.E.; Yaffe, M.B. 14-3-3 transits to the nucleus and participates in dynamic nucleocytoplasmic transport. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownawell, A.M.; Kops, G.J.; Macara, I.G.; Burgering, B.M. Inhibition of nuclear import by protein kinase B (Akt) regulates the subcellular distribution and activity of the forkhead transcription factor AFX. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 3534–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornerod, M.; Ohno, M.; Yoshida, M.; Mattaj, I.W. CRM1 is an export receptor for leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Cell 1997, 90, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tan, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y. Omaveloxolone prevents polystyrene microplastic-induced ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis via the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; He, T.; Yang, H.; Dai, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Ma, J.; Yang, G.; Si, R.; Du, X.J.E.; et al. Activation of the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway protects against oxidative stress and excessive autophagy in ovarian granulosa cells to attenuate DEHP-induced ovarian impairment in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 265, 115534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Bao, S.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Hu, X.; Liang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yan, S. Xiaojianzhong decoction attenuates gastric mucosal injury by activating the p62/Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway to inhibit ferroptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liswaniso, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, X.; Yan, C.; Qin, N.; Xu, R. Regulation of Smad2/3 Nuclear Exclusion by Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) in Chicken Follicular Granulosa Cells and Its Effect on FOXO3/4. Genes 2025, 16, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, S.I.; Zvelebil, M.J.; Shuttleworth, S.J.; Hancox, T.; Saghir, N.; Timms, J.F.; Waterfield, M.D. Exploring the specificity of the PI3K family inhibitor LY294002. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Weng, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Curcumin Inhibits Hyperandrogen-Induced IRE1α-XBP1 Pathway Activation by Activating the PI3K/AKT Signaling in Ovarian Granulosa Cells of PCOS Model Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshana, C.; Tajima, A.; Ishikawa, N.; Asano, A. Membrane rafts regulate sperm acrosome reaction via cAMP-dependent pathway in chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Daitoku, H.; Hatta, M.; Aoyama, H.; Yoshimochi, K.; Fukamizu, A. Acetylation of Foxo1 alters its DNA-binding ability and sensitivity to phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigushin, D.M.; Coombes, R.C. Targeted histone deacetylase inhibition for cancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, F.; Leng, Y. Propofol ameliorates ox-LDL-induced endothelial damage through enhancing autophagy via PI3K/Akt/m-TOR pathway: A novel therapeutic strategy in atherosclerosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 695336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macara, I.G. Transport into and out of the Nucleus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 570–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.A. Follicle selection in the avian ovary. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihm, M.; Evans, A.C.O. Mechanisms for dominant follicle selection in monovulatory species: A comparison of morphological, endocrine and intraovarian events in cows, mares and women. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2008, 43, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Bridgham, J.T.; Foster, D.N.; Johnson, A.L. Characterization of the Chicken Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Receptor (cFSH-R) Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid, and Expression of cFSH-R Messenger Ribonucleic Acid in the Ovary. Biol. Reprod. 1996, 55, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tano, M.; Minegishi, T.; Kishi, H.; Kameda, T.; Abe, Y.; Miyamoto, K. The effect of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) on the expression of FSH receptor in cultured rat granulosa cells. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilly, J.L.; LaPolt, P.S.; Hsueh, A.J. Hormonal regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid levels in cultured rat granulosa cells. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.; Bachelot, A.; Cocca, M.; Vasseur, C.; Rodien, P.; Kuttenn, F.; Touraine, P.; Misrahi, M. Molecular pathology of the FSH receptor: New insights into FSH physiology. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 282, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Liswaniso, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, X.; Yan, C.; Qin, N.; Xu, R. The Effect of FSH-Induced Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO3/4 on Granulosa Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis of Hen Ovarian Follicles. Genes 2025, 16, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarlet, D.; Serbetci, I.; Lautner, M.; Kowalewski, M.P.; Bollwein, H. Exogenous FSH/LH modulates TGF beta signaling genes in granulosa cells of Simmental heifers without affecting IVP results. Theriogenology 2024, 227, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ao, C.; Li, M.; Deng, T.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, K.; Tu, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Lang, R.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Clusterin-carrying extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells restore the ovarian function of premature ovarian failure mice through activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tano, M.; Minegishi, T.; Nakamura, K.; Karino, S.; Ibuki, Y.; Miyamoto, K. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of FSH receptor in rat granulosa cells by cyclic AMP and activin. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 153, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, T.; Hirakawa, T.; Kishi, H.; Abe, K.; Abe, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Miyamoto, K. A Role of Insulin-Like Growth Factor I for Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Expression in Rat Granulosa Cells. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yao, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, S.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H. Interleukin-4 activates the PI3K/AKT signaling to promote apoptosis and inhibit the proliferation of granulosa cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 412, 113002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosbois, J.; Demeestere, I. Dynamics of PI3K and Hippo signaling pathways during in vitro human follicle activation. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Fang, Y.G. Research progress of acupuncture for the improvement of ovarian reserve by regulating different signal pathways. Acupunct. Res. 2022, 47, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, S.; Zhu, M.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Pu, L.; Lin, J.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y. Acupuncture reduces apoptosis of granulosa cells in rats with premature ovarian failure via restoring the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Nagaraju, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K. Functional roles of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) signaling in the mammalian ovary. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 356, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’SHaughnessy, P.; Dudley, K.; Rajapaksha, W. Expression of follicle stimulating hormone-receptor mRNA during gonadal development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 125, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, M.P.; Gromoll, J.; Behre, H.M.; Gassner, C.; Nieschlag, E.; Simoni, M. Ovarian response to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulation depends on the FSH receptor genotype. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 3365–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onagbesan, O.; Bruggeman, V.; Decuypere, E. Intra-ovarian growth factors regulating ovarian function in avian species: Areview. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 111, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, X.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Shen, J.Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Qi, Y. Phosphorylation of forkhead protein FoxO1 at S253 regulates glucose homeostasis in mice. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, H.; Weck, J.; Maizels, E.; Park, Y.; Lee, E.J.; Ashcroft, M.; Hunzicker-Dunn, M. Role of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and extracellular regulated kinase pathways in the induction of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 activity and the HIF-1 target vascular endothelial growth factor in ovarian granulosa cells in response to follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.-C.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Han, L.-Y.; Hanover, J.A.; Rechler, M.M. Insulin inhibition of transcription stimulated by the forkhead protein Foxo1 is not solely due to nuclear exclusion. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 5615–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Lasick, K.; Jose, E.; Samayoa, A.M.; Shanks, L.; Pond, K.W.; A Thorne, C.; Paek, A.L. FOXO nuclear shuttling dynamics are stimulus-dependent and correspond with cell fate. Mol. Biol. Cell 2023, 34, ar21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.A.; Zhu, Q.; Unterman, T.G.; Hammond, J.M. Follicle-stimulating hormone promotes nuclear exclusion of the forkhead transcription factor FoxO1a via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in porcine granulosa cells. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 5585–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs III, W.H.; Meisenhelder, J.; Hunter, T.; Cavenee, W.K.; Arden, K.C. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steggerda, S.M.; Paschal, B.M. Regulation of nuclear import and export by the GTPase Ran. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 217, 41–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Heide, L.P.; Hoekman, M.F.M.; Smidt, M.P. The ins and outs of FoxO shuttling: Mechanisms of FoxO translocation and transcriptional regulation. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, T.; Güttler, T.; Neumann, P.; Dickmanns, A.; Görlich, D.; Ficner, R. Crystal structure of the nuclear export receptor CRM1 in complex with Snurportin1 and RanGTP. Science 2009, 324, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsilova, V.; Vecer, J.; Herman, P.; Pabianova, A.; Sulc, M.; Teisinger, J.; Boura, E.; Obsil, T. 14-3-3 Protein interacts with nuclear localization sequence of forkhead transcription factor FoxO4. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11608–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsil, T.; Ghirlando, R.; Anderson, D.E.; Hickman, A.B.; Dyda, F. Two 14-3-3 binding motifs are required for stable association of Forkhead transcription factor FOXO4 with 14-3-3 proteins and inhibition of DNA binding. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 15264–15272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; He, M.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, W.; Qin, S.; Gao, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Han, J.; et al. P62 promotes FSH-induced antral follicle formation by directing degradation of ubiquitinated WT1. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Antibody | Dilution | Manufacturer | Item Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| anti-β-actin antibody | 1:1000 | Bosterbio, Wuhan, China | MO1263-4 |
| rabbit anti-phospho-FOXO3a (Ser319) antibody | 1:1000 | Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA | AF3418 |
| rabbit anti-phospho-FOXO4 (Thr24) antibody | 1:1000 | Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA | bs-3145R |
| rabbit anti-phospho-FOXO4 (Ser256) antibody | 1:1000 | ZenBio Science, Cupertino, CA, USA | 310198 |
| rabbit anti-FOXO1 antibody | 1:1000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | 18592-1-AP |
| rabbit anti-FSHR antibody | 1:1000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | 10849-1-AP |
| rabbit anti-acetyl-FOXO1 antibody | 1:1000 | Immunoway, Suzhou, China | YK0110 |
| HRP-conjugated affinipure goat anti-Mouse | 1:2000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | SA00001-1 |
| HRP-conjugated affinipure Goat anti-rabbit | 1:2000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | SA00001-2 |
| rabbit anti-pAkt antibody | 1:1000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | P31749 |
| rabbit anti-PKACA antibody | 1:1000 | Bioss Antibodies, Beijing, China | bs-0520R |
| rabbit anti-CRM1 antibody | 1:1000 | Bioss Antibodies, Beijing, China | bs-3145R |
| rabbit anti-14-3-3 antibody | 1:1000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | 10849-1-AP |
| rabbit anti-RAN antibody | 1:1000 | Proteintech Group, Chicago, IL, USA | 10469-1-AP |
| Name | Primer | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Accession No. | Product Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| proFOXO1 | Forward | ACCCATCATCAGCCACCAAA | NM_204328.2 | 146 bp |
| Reverse | AGCAGATGACGACTGGGTTG | |||
| 18S rRNA | Forward | TAGTTGGTCGAGCGATTTGTCT | AF173612.1 | 169 bp |
| Reverse | CGGACATCTAAGGGCATCACA | |||
| Bcl2 | Forward | CCGCTACCAGAGGGACTT | NM_205339.3 | 155 bp |
| Reverse | ACATCACGCCGCCGAAC | |||
| Caspase3 | Forward | AAGAACTTCCACCGAGATACCG | XR_006936397.1 | 204 bp |
| Reverse | GCTTAGCAACACACAAACAAAA | |||
| CCND1 | Forward | ATAGTCGCCACTTGGATGCT | NM_205381.2 | 230 bp |
| Reverse | TCGGGTCTGATGGAGTTGTC | |||
| PCNA | Forward | CTGAGGCGTGCTGGG | NM_204170.3 | 133 bp |
| Reverse | ATGGCGATGTTGCGG | |||
| P62 | Forward | CCAGGAACACAGCGAGTCAA | 152 bp | |
| Reverse | CACCCTCATCAGAGAAGCCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, C.; Ou, Y.; Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Qin, N.; Xu, R. FSH-Induced Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO1 Mediated by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Granulosa Cells Is Associated with Follicle Selection and Growth of the Hen Ovary. Cells 2025, 14, 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231864
Yan C, Ou Y, Sun X, Sun Y, Zhao J, Qin N, Xu R. FSH-Induced Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO1 Mediated by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Granulosa Cells Is Associated with Follicle Selection and Growth of the Hen Ovary. Cells. 2025; 14(23):1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231864
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Chunchi, Yu Ou, Xue Sun, Yuhan Sun, Jinghua Zhao, Ning Qin, and Rifu Xu. 2025. "FSH-Induced Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO1 Mediated by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Granulosa Cells Is Associated with Follicle Selection and Growth of the Hen Ovary" Cells 14, no. 23: 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231864
APA StyleYan, C., Ou, Y., Sun, X., Sun, Y., Zhao, J., Qin, N., & Xu, R. (2025). FSH-Induced Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO1 Mediated by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Granulosa Cells Is Associated with Follicle Selection and Growth of the Hen Ovary. Cells, 14(23), 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231864






