Innate Immune Pairing: Eosinophils as Hidden Architects of T Cell Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Eosinophil Development and Tissue Heterogeneity
3. Aspects of Eosinophil Immunobiology That Equip for Immunomodulation
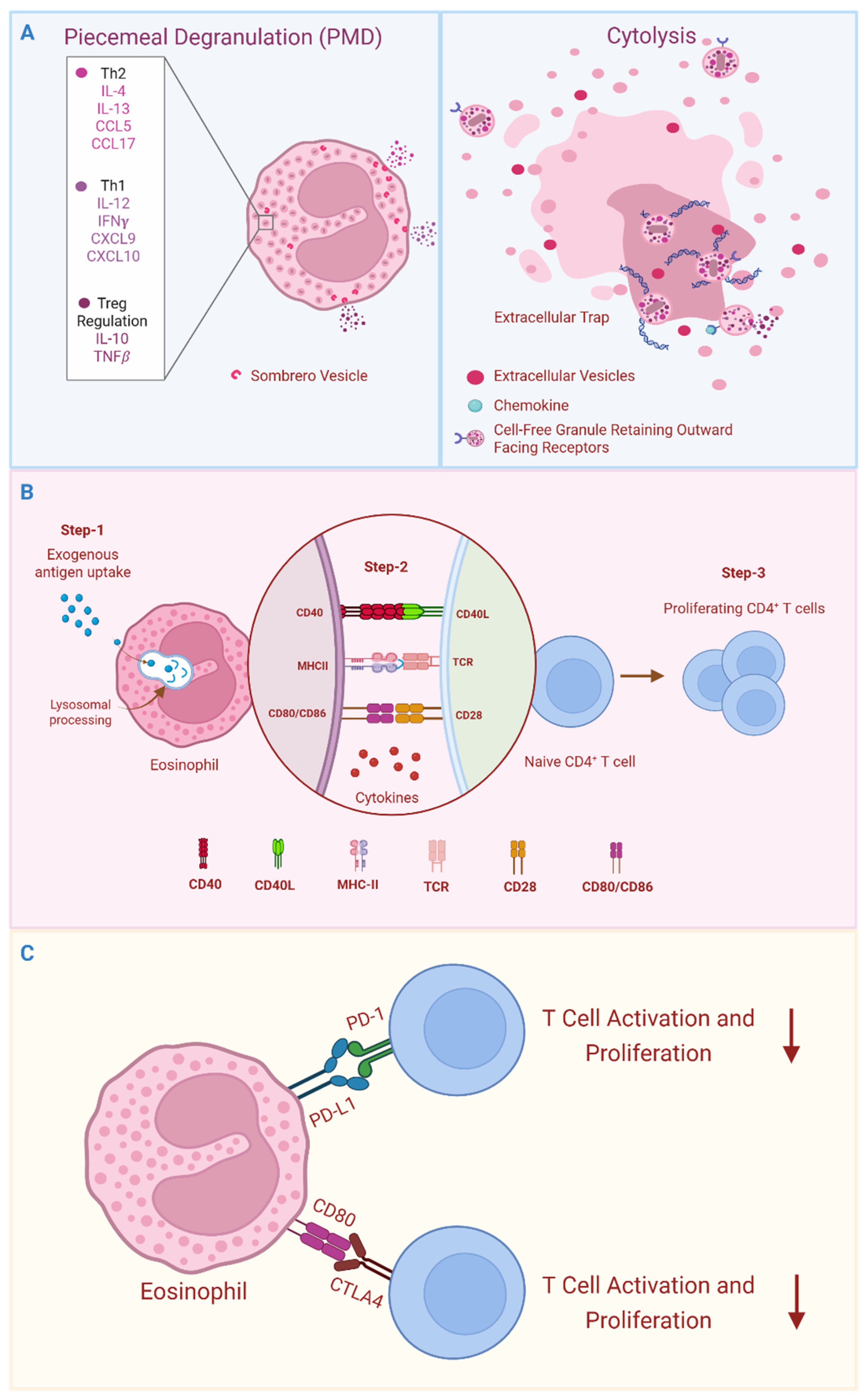
3.1. Secretion of Immunomodulatory Cytokines
3.2. Eosinophils as Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs)
3.3. Antigen Non-Specific Cellular Interactions
4. Steady-State Tissue Immune Homeostasis
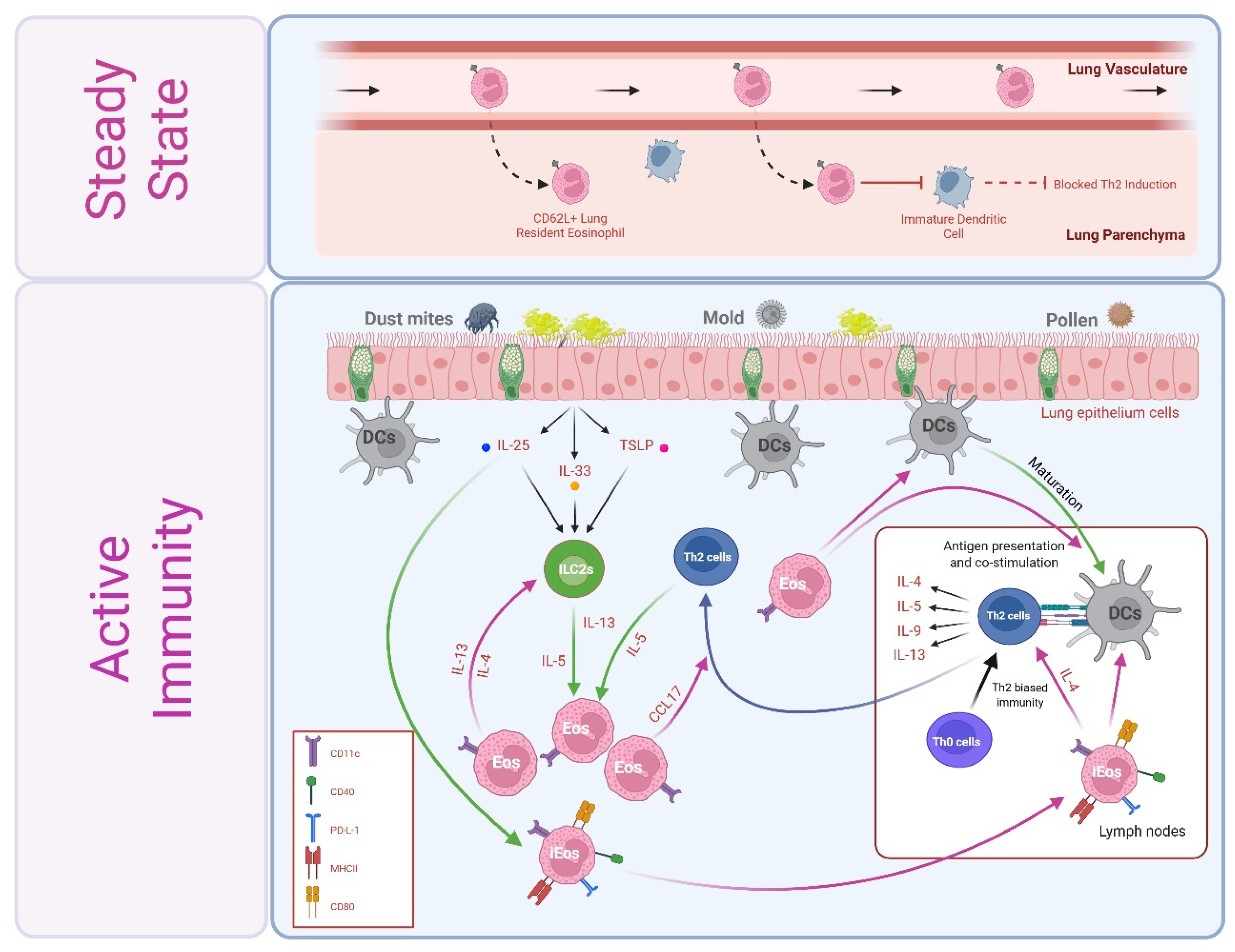
4.1. Steady-State Th2 Immunosuppression by Lung Resident Eosinophils
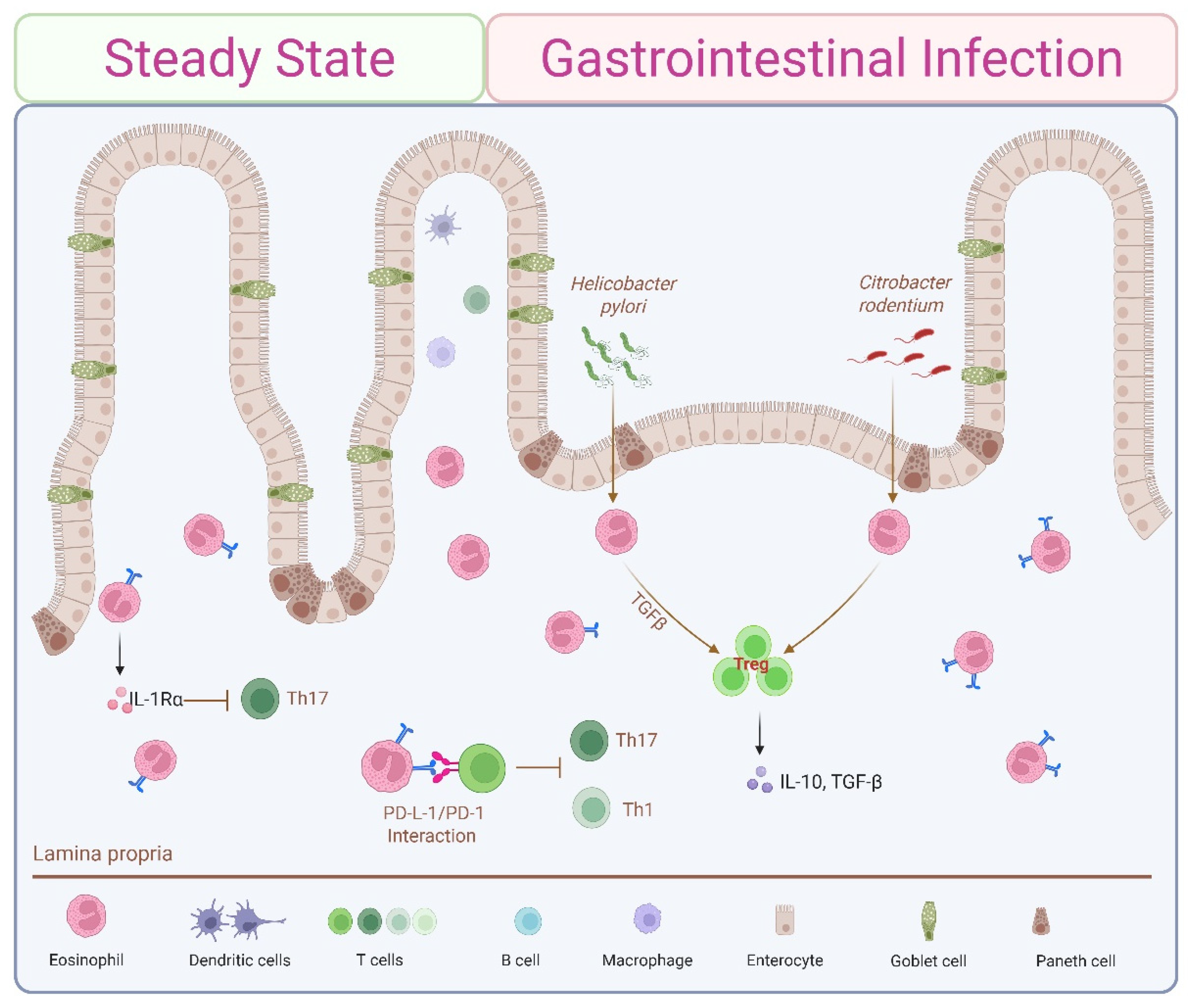
4.2. Steady-State Th1/Th17 Immunosuppression by Small Intestine-Resident Eosinophils
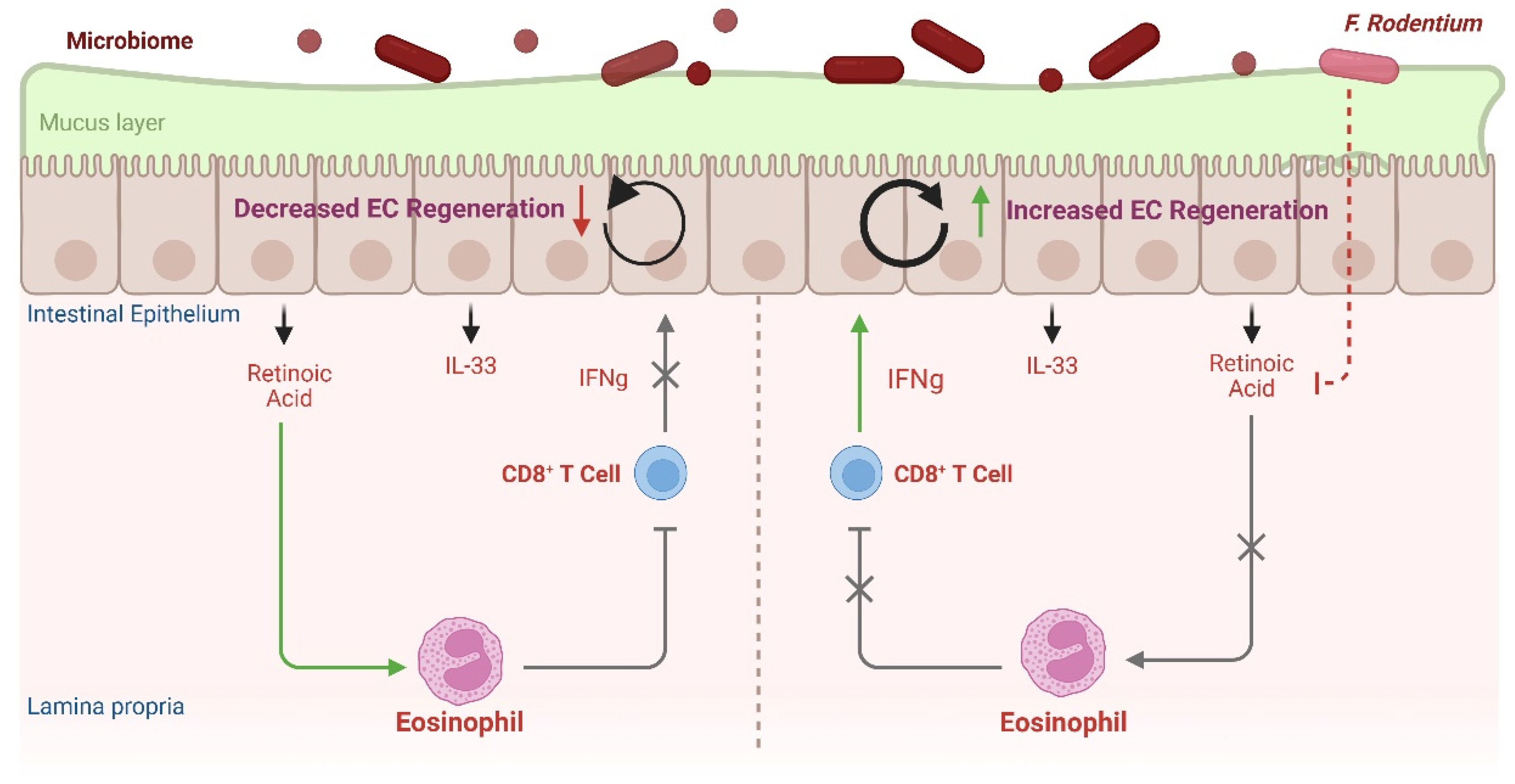
4.3. Eosinophil–CD8+ IEL Circuit Contributes to Intestinal Barrier Defense
5. Eosinophil Contributions to Immunomodulation in Active Immunity
5.1. Allergic Airways
5.2. Lung Microbial and Fungal Infections
5.3. Gut Microbial Infections
5.4. Oral Tolerance
5.5. Systemic Microbial Infection
5.6. Parasitic Helminths
5.7. Non-Infectious Immune Responses
5.7.1. Transplantation
5.7.2. Cancer
6. Thymic Eosinophils
6.1. Shaping the Peripheral T Cell Pool
6.2. Thymic Regeneration
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| ILC2 | Innate lymphoid cell type 2 |
| IL-5 | Interleukin 5 |
| MBP | Major basic protein |
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| EETs | Eosinophil extracellular traps |
| EoSVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| iEos | Inflammatory eosinophils |
| PMD | Piecemeal degranulation |
| IELs | Intraepithelial lymphocytes |
| RA | Retinoic acid |
| iBALTs | Inducible bronchus-associated lymphoid tissues |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
References
- Weller, P.F.; Spencer, L.A. Functions of tissue-resident eosinophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, A.; Borrelli, C.; Gonzalez-Perez, I.; Bach, K.; Acar, I.E.; Núñez, N.G.; Crepaz, D.; Handler, K.; Vu, V.P.; Lafzi, A.; et al. Active eosinophils regulate host defence and immune responses in colitis. Nature 2022, 615, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, I.C.; Munitz, A. Spatial adaptation of eosinophils and their emerging roles in homeostasis, infection and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masterson, J.C.; Menard-Katcher, C.; Larsen, L.D.; Furuta, G.T.; Spencer, L.A. Heterogeneity of Intestinal Tissue Eosinophils: Potential Considerations for Next-Generation Eosinophil-Targeting Strategies. Cells 2021, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigon, L.; Fettrelet, T.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, D.; Simon, H. Eosinophils from A to Z. Allergy 2023, 78, 1810–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, F.; Klion, A.D. Biologic Therapies Targeting Eosinophils: Current Status and Future Prospects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, L.K.; Hsu, C.-L.; Krier-Burris, R.A.; Chhiba, K.D.; Chien, K.B.; McKenzie, A.; Berdnikovs, S.; Bryce, P.J. IL-33 Precedes IL-5 in Regulating Eosinophil Commitment and Is Required for Eosinophil Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.K.; Bryce, P.J. Understanding Interleukin 33 and Its Roles in Eosinophil Development. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, E.A.; Pear, W.S. Transcription factor and cytokine regulation of eosinophil lineage commitment. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2020, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, R.; Shimizu, R.; Takahashi, S.; Osawa, M.; Takayanagi, S.; Kato, Y.; Onodera, M.; Minegishi, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Fukao, K.; et al. Essential and Instructive Roles of GATA Factors in Eosinophil Development. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfurth, E.; Schuster, M.; Kulessa, H.; Crispino, J.D.; Döderlein, G.; Orkin, S.H.; Graf, T.; Nerlov, C. Antagonism between C/EBPβ and FOG in eosinophil lineage commitment of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Ackerman, S.J.; Minegishi, N.; Takiguchi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Suda, T. Mechanisms of transcription in eosinophils: GATA-1, but not GATA-2, transactivates the promoter of the eosinophil granule major basic protein gene. Blood 1998, 91, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanovic, M.; Terszowski, G.; Struck, D.; Liesenfeld, O.; Carstanjen, D. IFN Consensus Sequence Binding Protein (Icsbp) Is Critical for Eosinophil Development. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5045–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Cantor, A.B.; Yang, H.; Browne, C.; Wells, R.A.; Fujiwara, Y.; Orkin, S.H. Targeted Deletion of a High-Affinity GATA-binding Site in the GATA-1 Promoter Leads to Selective Loss of the Eosinophil Lineage In Vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettigole, S.E.; Lis, R.; Adoro, S.; Lee, A.-H.; Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F.; Glimcher, L.H. The transcription factor XBP1 is selectively required for eosinophil differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochkur, S.I.; Doyle, A.D.; Jacobsen, E.A.; LeSuer, W.E.; Li, W.; Protheroe, C.A.; Zellner, K.R.; Colbert, D.; Shen, H.H.; Irvin, C.G.; et al. Frontline Science: Eosinophil-deficient MBP-1 and EPX double-knockout mice link pulmonary remodeling and airway dysfunction with type 2 inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.O.; Malik, A.; Reichman, H.; Munitz, A.; Barski, A.; Fulkerson, P.C. Reuse of public, genome-wide, murine eosinophil expression data for hypotheses development. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diny, N.L.; Schonfeldova, B.; Shapiro, M.; Winder, M.L.; Varsani-Brown, S.; Stockinger, B. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor contributes to tissue adaptation of intestinal eosinophils in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20210970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hulst, G.; Bureau, F.; Desmet, C.J. Eosinophils as Drivers of Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: Endotypes or Plasticity? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoine, F.; Lacy, P. Eosinophil Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors: Emerging Roles in Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, L.A.; Szela, C.T.; Perez, S.A.C.; Kirchhoffer, C.L.; Neves, J.S.; Radke, A.L.; Weller, P.F. Human eosinophils constitutively express multiple Th1, Th2, and immunoregulatory cytokines that are secreted rapidly and differentially. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 85, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Bates, M.E.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Bertics, P.J.; Kelly, E.A.B. Generation of Th1 and Th2 Chemokines by Human Eosinophils: Evidence for a Critical Role of TNF-α. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4840–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.A.; Doyle, A.D.; Colbert, D.C.; Zellner, K.R.; Protheroe, C.A.; LeSuer, W.E.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J. Differential activation of airway eosinophils inducesIL-13-mediated allergic Th2 pulmonary responses in mice. Allergy 2015, 70, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolitzky, A.; Shapira, G.; Grisaru-Tal, S.; Hazut, I.; Avlas, S.; Gordon, Y.; Itan, M.; Shomron, N.; Munitz, A. Transcriptional Profiling of Mouse Eosinophils Identifies Distinct Gene Signatures Following Cellular Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 802839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, R.C.; Perez, S.A.; Spencer, L.A.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Intragranular Vesiculotubular Compartments are Involved in Piecemeal Degranulation by Activated Human Eosinophils. Traffic 2005, 6, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, L.A.; Melo, R.C.N.; Perez, S.A.C.; Bafford, S.P.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Cytokine receptor-mediated trafficking of preformed IL-4 in eosinophils identifies an innate immune mechanism of cytokine secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3333–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Gold, J.A.; Andina, N.; Lee, J.J.; Kelly, A.M.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Straumann, A.; Reichenbach, J.; Gleich, G.; et al. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Miyabe, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fukuchi, M.; Hirokawa, M.; Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F. Charcot-Leyden Crystals in Eosinophilic Inflammation: Active Cytolysis Leads to Crystal Formation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Tokunaga, T.; Fujieda, S.; Honda, K.; Hirokawa, M.; Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophil ETosis and DNA Traps: A New Look at Eosinophilic Inflammation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, I.C.; Artola-Borán, M.; de Lara, P.T.; Kyburz, A.; Taube, C.; Ottemann, K.; Broek, M.v.D.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U.; Müller, A. Eosinophils suppress Th1 responses and restrict bacterially induced gastrointestinal inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2055–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D.; Radonjic-Hösli, S.; Straumann, A.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U. Active eosinophilic esophagitis is characterized by epithelial barrier defects and eosinophil extracellular trap formation. Allergy 2015, 70, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, S.; Tokunaga, T.; Melo, R.C.N.; Saito, H.; Honda, K.; Fukuchi, M.; Konno, Y.; Takeda, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirokawa, M.; et al. Charcot-Leyden crystal formation is closely associated with eosinophil extracellular trap cell death. Blood 2018, 132, 2183–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, V.S.; Baptista-Dos-Reis, R.; Benjamim, C.F.; Mata-Santos, H.A.; Pyrrho, A.S.; Strauch, M.A.; Melo, P.A.; Vicentino, A.R.R.; Silva-Paiva, J.; Bandeira-Melo, C.; et al. Purinergic P2Y12 Receptor Activation in Eosinophils and the Schistosomal Host Response. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.S.; Perez, S.A.C.; Spencer, L.A.; Melo, R.; Reynolds, L.; Ghiran, I.; Mahmudi-Azer, S.; Odemuyiwa, S.O.; Dvorak, A.M.; Moqbel, R.; et al. Eosinophil granules function extracellularly as receptor-mediated secretory organelles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18478–18483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.S.; Radke, A.L.; Weller, P.F. Cysteinyl leukotrienes acting via granule membrane-expressed receptors elicit secretion from within cell-free human eosinophil granules. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, D.R.; Nicholson-Weller, A.; Weller, P.F. Mature human eosinophils have the capacity to express HLA-DR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, T.T.; Braunstein, J.B.; Walker, C.; Blaser, K.; Bruijnzeel, P.L.B.; Virchow, J.; Virchow, C. Sputum eosinophils from asthmatics express ICAM-1 and HLA-DR. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 86, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, J.B.; Calhoun, W.J.; Vrtis, R.F.; Bates, M.E.; McAllister, P.K.; Busse, W.W. Comparison of airway and blood eosinophil function after in vivo antigen challenge. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 3710–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beninati, W.; Derdak, S.; Dixon, P.; Grider, D.; Strollo, D.; Hensley, R.; Lucey, D. Pulmonary eosinophils express HLA-DR in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 92, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Vrtis, R.F.; Busse, W.W. The Effect of Transendothelial Migration on Eosinophil Function. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawhorter, S.D.; Pearlman, E.; Kazura, J.W.; Boom, W.H. Class II major histocompatibility complex molecule expression on murine eosinophils activated in vivo by Brugia malayi. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 5410–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padigel, U.M.; Lee, J.J.; Nolan, T.J.; Schad, G.A.; Abraham, D. Eosinophils Can Function as Antigen-Presenting Cells to Induce Primary and Secondary Immune Responses to Strongyloides stercoralis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3232–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, P.; Wang, H.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophils as antigen-presenting cells in allergic upper airway disease. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenakis, J.J.; Howard, E.D.; Smith, K.M.; Olbrich, C.L.; Huang, Y.; Anketell, D.; Maldonado, S.; Cornwell, E.W.; Spencer, L.A. Resident intestinal eosinophils constitutively express antigen presentation markers and include two phenotypically distinct subsets of eosinophils. Immunology 2017, 154, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawhorter, S.D.; Kazura, J.W.; Boom, W.H. Human eosinophils as antigen-presenting cells: Relative efficiency for superantigen- and antigen-induced CD4+ T-cell proliferation. Immunology 1994, 81, 584–591. [Google Scholar]
- Weller, P.F.; Rand, T.H.; Barrett, T.; Elovic, A.; Wong, D.T.; Finberg, R.W. Accessory cell function of human eosinophils. HLA-DR-dependent, MHC-restricted antigen-presentation and IL-1 alpha expression. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 2554–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, P.; Melo, R.C.N.; Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F. MHC Class II and CD9 in Human Eosinophils Localize to Detergent-Resistant Membrane Microdomains. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.-Z.; Humbles, A.; Gerard, C.; Jin, Z.; Weller, P.F. Lymph node trafficking and antigen presentation by endobronchial eosinophils. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xiao, C.; Li, C.; Mo, X.; Yang, Q.; Leng, J.; Chen, Y. Endobronchial eosinophils preferentially stimulate T helper cell type 2 responses. Allergy 2004, 59, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duez, C.; Dakhama, A.; Tomkinson, A.; Marquillies, P.; Balhorn, A.; Tonnel, A.-B.; Bratton, D.L.; Gelfand, E.W. Migration and accumulation of eosinophils toward regional lymph nodes after airway allergen challenge. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijt, L.S.; Vos, N.; Hijdra, D.; de Vries, V.C.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N. Airway eosinophils accumulate in the mediastinal lymph nodes but lack antigen-presenting potential for naive T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3372–3378. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-B.; Ghiran, I.; Matthaei, K.; Weller, P.F. Airway Eosinophils: Allergic Inflammation Recruited Professional Antigen-Presenting Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7585–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padigel, U.M.; Hess, J.A.; Lee, J.J.; Lok, J.B.; Nolan, T.J.; Schad, G.A.; Abraham, D. Eosinophils Act as Antigen-Presenting Cells to Induce Immunity to Strongyloides stercoralis in Mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1844–1851. [Google Scholar]
- Hansel, T.T.; De Vries, I.J.; Carballido, J.M.; Braun, R.K.; Carballido-Perrig, N.; Rihs, S.; Blaser, K.; Walker, C. Induction and function of eosinophil intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and HLA-DR. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo, V.; de Andrés, B.; Martín, E.; Cárdaba, B.; Fernández, J.C.; Gallardo, S.; Tramón, P.; Palomino, P.; Lahoz, C.; Leyva-Cobian, F. Eosinophil as antigen-presenting cell: Activation of T cell clones and T cell hybridoma by eosinophils after antigen processing. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.M.; Rahman, R.S.; Spencer, L.A. Humoral Immunity Provides Resident Intestinal Eosinophils Access to Luminal Antigen via Eosinophil-Expressed Low-Affinity Fcγ Receptors. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 3716–3724. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Kinet, J.-P.; Weller, P.F. Humanized FcεRI Expressed on Mouse Eosinophils Mediates IgE-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation. Cells 2025, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.D.; Kian, A.; Falta, N.A.; Fox, B.; Spencer, L.A. Unsupervised Clustering Reveals Intestine-Adapted Eosinophil Subsets Shaped by Local Inflammation. Allergy 2025, 80, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Sun, L.; Zhang, M.; Yan, H.; Shi, G.; Xia, Z.; Dai, R.; Tang, W. Role of IL-25 on Eosinophils in the Initiation of Th2 Responses in Allergic Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 842500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, A.; Wojcik, K.; Petri, B.; Aulakh, G.; Jacobsen, E.A.; LeSuer, W.E.; Colarusso, P.; Patel, K.D. Intravital imaging allows real-time characterization of tissue resident eosinophils. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaikhly, T.; Murphy, R.C.; Parker, A.; Lai, Y.; Altman, M.C.; Larmore, M.; Altemeier, W.A.; Frevert, C.W.; Debley, J.S.; Piliponsky, A.M.; et al. Location of eosinophils in the airway wall is critical for specific features of airway hyperresponsiveness and T2 inflammation in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnil, C.; Raulier, S.; Paulissen, G.; Xiao, X.; Birrell, M.A.; Pirottin, D.; Janss, T.; Starkl, P.; Ramery, E.; Henket, M.; et al. Lung-resident eosinophils represent a distinct regulatory eosinophil subset. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3279–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willetts, L.; Parker, K.; Wesselius, L.J.; Protheroe, C.A.; Jaben, E.; Graziano, P.; Moqbel, R.; Leslie, K.O.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J. Immunodetection of occult eosinophils in lung tissue biopsies may help predict survival in acute lung injury. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.A.; Zellner, K.R.; Colbert, D.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J. Eosinophils Regulate Dendritic Cells and Th2 Pulmonary Immune Responses following Allergen Provocation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.A.; LeSuer, W.E.; Willetts, L.; Zellner, K.R.; Mazzolini, K.; Antonios, N.; Beck, B.; Protheroe, C.; Ochkur, S.I.; Colbert, D.; et al. Eosinophil activities modulate the immune/inflammatory character of allergic respiratory responses in mice. Allergy 2013, 69, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, R.; Lee, E.-J.; Jang, M.S.; Jeun, E.-J.; Hong, C.-P.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, A.; Yun, C.H.; Hong, S.-W.; Kim, Y.-M.; et al. Small intestinal eosinophils regulate Th17 cells by producing IL-1 receptor antagonist. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Wen, T.; Mingler, M.K.; Caldwell, J.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Chaplin, D.D.; Lee, E.H.; Jang, M.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Seoh, J.Y.; et al. IL-1β in eosinophil-mediated small intestinal homeostasis and IgA production. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailer, R.K.W.; Joly, A.-L.; Liu, S.; Elias, S.; Tegner, J.; Andersson, J. IL-1β promotes Th17 differentiation by inducing alternative splicing of FOXP3. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, I.; Arnold, I.C. Intestinal eosinophils, homeostasis and response to bacterial intrusion. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, V.T.; Beller, A.; Rausch, S.; Strandmark, J.; Zänker, M.; Arbach, O.; Kruglov, A.; Berek, C. Eosinophils Promote Generation and Maintenance of Immunoglobulin-A-Expressing Plasma Cells and Contribute to Gut Immune Homeostasis. Immunity 2014, 40, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Brass, A.; Knight, C.G.; Cruickshank, S.M. Gut eosinophils and their impact on the mucus-resident microbiota. Immunology 2019, 158, 194–205. [Google Scholar]
- Ignacio, A.; Shah, K.; Bernier-Latmani, J.; Köller, Y.; Coakley, G.; Moyat, M.; Hamelin, R.; Armand, F.; Wong, N.C.; Ramay, H.; et al. Small intestinal resident eosinophils maintain gut homeostasis following microbial colonization. Immunity 2022, 55, 1250–1267.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.F.; Costanzo, A.; Gareau, M.G.; Armando, A.M.; Quehenberger, O.; Jameson, J.M.; Olefsky, J.M. High Fat Diet Causes Depletion of Intestinal Eosinophils Associated with Intestinal Permeability. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.G.; Bae, S.; Villarreal, J.; Moy, M.; Chun, E.; Michaud, M.; Lang, J.K.; Glickman, J.N.; Lobel, L.; Garrett, W.S. Faecalibaculum rodentium remodels retinoic acid signaling to govern eosinophil-dependent intestinal epithelial homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1295–1310.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Yamauchi, Y.; Konno, Y.; Tamaki, M.; Itoga, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takeda, M.; Moritoki, Y.; Ito, W.; et al. Retinoic acids up-regulate functional eosinophil-driving receptor CCR3. Allergy 2013, 68, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kutyavin, V.I.; Korn, L.L.; Medzhitov, R. Nutrient-derived signals regulate eosinophil adaptation to the small intestine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2316446121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Fukuchi, M.; Konno, Y.; Takeda, M.; Moritoki, Y.; Chihara, J.; Omokawa, A.; Saga, T.; Hirokawa, M. ICAM-1 upregulation is not required for retinoic acid-induced human eosinophil survival. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 196, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeSuer, W.E.; Kienzl, M.; Ochkur, S.I.; Schicho, R.; Doyle, A.D.; Wright, B.L.; Rank, M.A.; Krupnick, A.S.; Kita, H.; Jacobsen, E.A. Eosinophils promote effector functions of lung group 2 innate lymphoid cells in allergic airway inflammation in mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 469–485.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Smith, S.G.; Beaudin, S.; Dua, B.; Howie, K.; Gauvreau, G.; O’Byrne, P.M. IL-25 and IL-25 Receptor Expression on Eosinophils from Subjects with Allergic Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 163, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Smith, S.G.; Salter, B.; Oliveria, J.P.; Mitchell, P.; Nusca, G.M.; Howie, K.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’BYrne, P.M.; Sehmi, R. Allergen-Induced Increases in Interleukin-25 and Interleukin-25 Receptor Expression in Mature Eosinophils from Atopic Asthmatics. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 170, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.K.; Jimenez-Saiz, R.; Verschoor, C.P.; Walker, T.D.; Goncharova, S.; Llop-Guevara, A.; Shen, P.; Gordon, M.E.; Barra, N.G.; Bassett, J.D.; et al. Indigenous enteric eosinophils control DCs to initiate a primary Th2 immune response in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1657–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfi, R.; Lotze, M.T. Eosinophils induce DC maturation, regulating immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 83, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, E.A.; Ochkur, S.I.; Pero, R.S.; Taranova, A.G.; Protheroe, C.A.; Colbert, D.C.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J. Allergic pulmonary inflammation in mice is dependent on eosinophil-induced recruitment of effector T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 699–710. [Google Scholar]
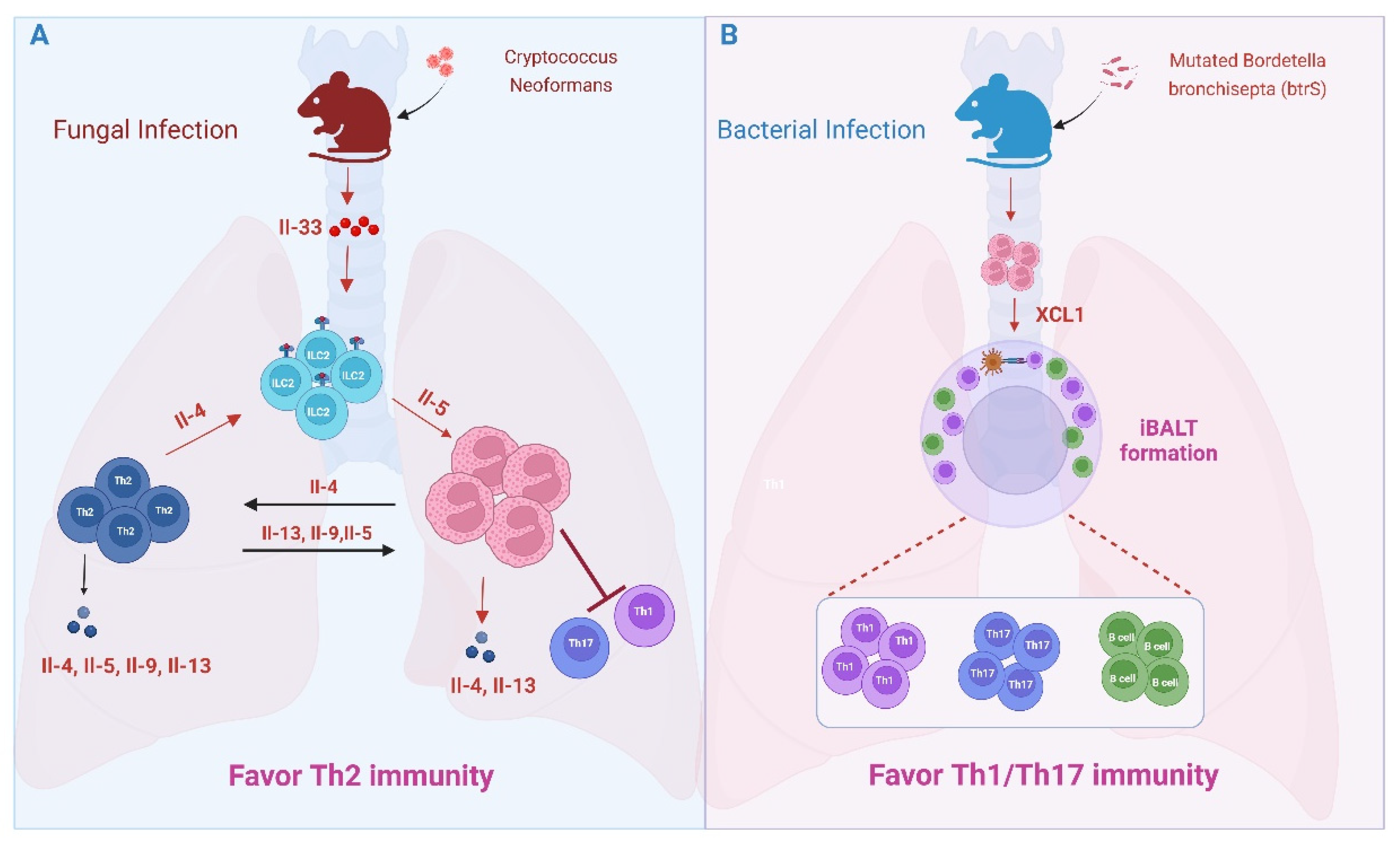
- Piehler, D.; Stenzel, W.; Grahnert, A.; Held, J.; Richter, L.; Köhler, G.; Richter, T.; Eschke, M.; Alber, G.; Müller, U. Eosinophils Contribute to IL-4 Production and Shape the T-Helper Cytokine Profile and Inflammatory Response in Pulmonary Cryptococcosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 733–744. [Google Scholar]
- Elsegeiny, W.; Marr, K.A.; Williamson, P.R. Immunology of Cryptococcal Infections: Developing a Rational Approach to Patient Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 651. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, K.; Miyazaki, Y. Detrimental impact of the IL-33/ST2 axis in an animal infection model with Cryptococcus neoformans. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Bueter, C.; Rothenberg, M.; Deepe, G. Eosinophils subvert host resistance to an intracellular pathogen by instigating non-protective IL-4 in CCR2(−/−) mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindermann, M.; Knipfer, L.; Obermeyer, S.; Müller, U.; Alber, G.; Bogdan, C.; Schleicher, U.; Neurath, M.F.; Wirtz, S. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILC2) Suppress Beneficial Type 1 Immune Responses During Pulmonary Cryptococcosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Gestal, M.C.; Blas-Machado, U.; Johnson, H.M.; Rubin, L.N.; Dewan, K.K.; Bryant, C.; Tiemeyer, M.; Harvill, E.T. Disrupting Bordetella Immunosuppression Reveals a Role for Eosinophils in Coordinating the Adaptive Immune Response in the Respiratory Tract. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, N.J.; Parrish, K.M.; Martínez-Pérez, A.; González-Fernández, Á.; Bharrhan, S.; Woolard, M.; McLachlan, J.B.; Scott, R.S.; Wang, J.; Gestal, M.C. Bordetella spp. block eosinophil recruitment to suppress the generation of early mucosal protection. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallegger, A.; Priola, M.; Artola-Borán, M.; Núñez, N.G.; Wild, S.; Gurtner, A.; Becher, B.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U.; Arnold, I.C.; et al. TGF-β production by eosinophils drives the expansion of peripherally induced neuropilin− RORγt+ regulatory T-cells during bacterial and allergen challenge. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-H.; Sun, A.-H.; Ojcius, D.M.; Hu, W.-L.; Ge, Y.-M.; Lin, X.; Li, L.-J.; Pan, J.-P.; Yan, J. Eosinophils from Murine Lamina Propria Induce Differentiation of Naïve T Cells into Regulatory T Cells via TGF-β1 and Retinoic Acid. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Gadir, A.; Stephen-Victor, E.; Gerber, G.K.; Rivas, M.N.; Wang, S.; Harb, H.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Crestani, E.; Spielman, S.; et al. Microbiota therapy acts via a regulatory T cell MyD88/RORγt pathway to suppress food allergy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedmi, R.; Najar, T.A.; Mesa, K.R.; Grayson, A.; Kroehling, L.; Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Pokrovskii, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; et al. A RORgammat(+) cell instructs gut microbiota-specific T(reg) cell differentiation. Nature 2022, 610, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kang, L.; Gaspal, F.; Zhou, W.; Goc, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Bank, J.L.C.; et al. ILC3s select microbiota-specific regulatory T cells to establish tolerance in the gut. Nature 2022, 610, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagbosu, B.; Tayyebi, Z.; Shibu, G.; Iza, Y.A.P.; Deep, D.; Parisotto, Y.F.; Fisher, L.; Pasolli, H.A.; Thevin, V.; Elmentaite, R.; et al. Novel antigen-presenting cell imparts Treg-dependent tolerance to gut microbiota. Nature 2022, 610, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, S.; Suzuki, K.; Yokota, M.; Ito, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Kikuchi, R.; Kageyama, T.; Meguro, K.; Tanaka, S.; Iwata, A.; et al. Eosinophils Contribute to Oral Tolerance via Induction of RORγt-Positive Antigen-Presenting Cells and RORγt-Positive Regulatory T Cells. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
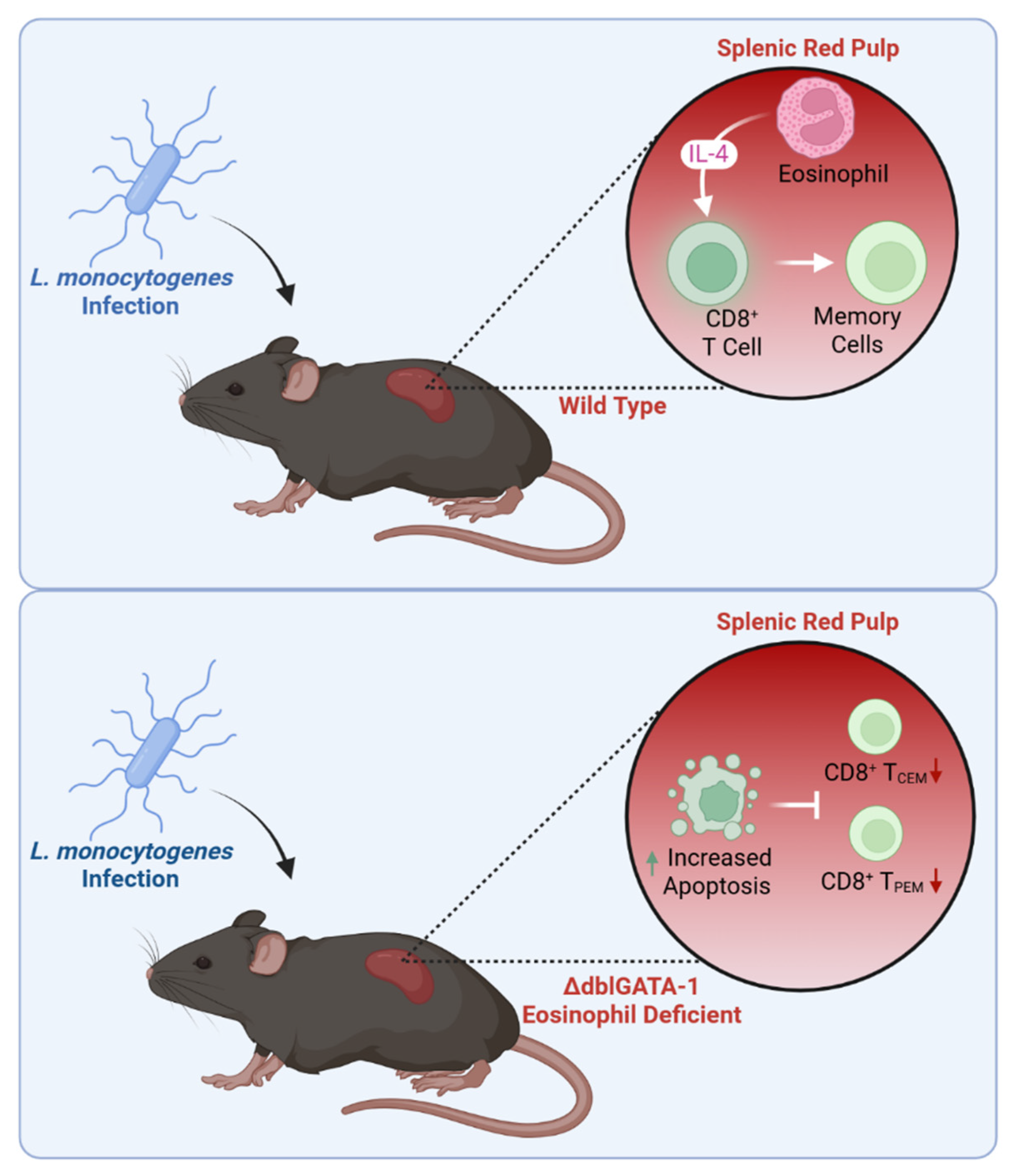
- Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Cao, X. Eosinophils promote CD8+ T cell memory generation to potentiate anti-bacterial immunity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, C.; Schumacher, P.P.; Vijayakumar, A.; Borgmann, H.; Balles, H.; Koschel, M.; Risch, F.; Lenz, B.; Hoerauf, A.; Hübnera, M.P.; et al. Eosinophils are an endogenous source of IL-4 during filarial infections and contribute to the development of an optimal T helper 2 response. J. Innate Immun. 2024, 16, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandmark, J.; Steinfelder, S.; Berek, C.; Kühl, A.; Rausch, S.; Hartmann, S. Eosinophils are required to suppress Th2 responses in Peyer’s patches during intestinal infection by nematodes. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyema, O.O.; Guo, Y.; Mahgoub, B.; Wang, Q.; Manafi, A.; Mei, Z.; Banerjee, A.; Li, D.; Stoler, M.H.; Zaidi, M.T.; et al. Eosinophils downregulate lung alloimmunity by decreasing TCR signal transduction. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 4, e2316446121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, T.; Sershen, C.L.; May, E. Investigating the Role of TNF-α and IFN-γ Activation on the Dynamics of iNOS Gene Expression in LPS Stimulated Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyema, O.O.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Stoler, M.H.; Lau, C.; Li, K.; Nazaroff, C.D.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Kreisel, D.; et al. Eosinophils promote inducible NOS–mediated lung allograft acceptance. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 2, e96455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaru-Tal, S.; Dulberg, S.; Beck, L.; Zhang, C.; Itan, M.; Hediyeh-Zadeh, S.; Caldwell, J.; Rozenberg, P.; Dolitzky, A.; Avlas, S.; et al. Metastasis-Entrained Eosinophils Enhance Lymphocyte-Mediated Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5555–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, I.C.; Artola-Boran, M.; Gurtner, A.; Bertram, K.; Bauer, M.; Frangez, Z.; Becher, B.; Kopf, M.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U.; et al. The GM-CSF–IRF5 signaling axis in eosinophils promotes antitumor immunity through activation of type 1 T cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, R.; Sektioglu, I.M.; Garbi, N.; Salgado, O.C.; Beckhove, P.; Hämmerling, G.J. Eosinophils orchestrate cancer rejection by normalizing tumor vessels and enhancing infiltration of CD8+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Qin, D.; He, F.; Xie, Q.; Ying, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, J.-N.; Zuo, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Peripheral eosinophil counts predict efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy against B-lineage non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, O.S.; Spagnuolo, L.; Garner, H.; Voorwerk, L.; Isaeva, O.I.; van Dyk, E.; Bakker, N.; Chalabi, M.; Klaver, C.; Duijst, M.; et al. IL-5-producing CD4+ T cells and eosinophils cooperate to enhance response to immune checkpoint blockade in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 41, 106–123.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-N.; Luo, W.; Sun, C.; Jin, Z.; Zeng, X.; Alexander, P.B.; Gong, Z.; Xia, X.; Ding, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Radiation-induced eosinophils improve cytotoxic T lymphocyte recruitment and response to immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynagetdinov, R.; Sherrill, T.P.; Gleaves, L.A.; McLoed, A.G.; Saxon, J.A.; Habermann, A.C.; Connelly, L.; Dulek, D.; Peebles, R.S.; Fingleton, B.; et al. Interleukin-5 Facilitates Lung Metastasis by Modulating the Immune Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Yu, E.; Good, R.A.; Ikehara, S. Presence of eosinophilic precursors in the human thymus: Evidence for intra-thymic differentiation of cells in eosinophilic lineage. Pathol. Int. 1995, 45, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulic, M.K.; Reynolds, L.A. Thymic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive eosinophils in young children: Potential role in maturation of the naive immune system. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinsson, S.; Lingblom, C.; Lundqvist, C.; Telemo, E.; Ekwall, O.; Wennerås, C. Eosinophils interact with thymocytes and proliferate in the human thymus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, D.M.; Reynolds, L.A. Thymic eosinophils: What are you doing here? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, A.; Iguchi, T.; Nitta, S.; Muro, R.; Mino, N.; Tsukasaki, M.; Penninger, J.M.; Nitta, T.; Takayanagi, H. Synchronized development of thymic eosinophils and thymocytes. Int. Immunol. 2024, 36, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinsson, S.; Lingblom, C.; Lundqvist, C.; Hennings, V.; Telemo, E.; Ekwall, O.; Wennerås, C. Distinct populations of eosinophils in the human thymus with capacity to modulate thymocyte maturation. Immunology 2022, 169, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throsby, M.; Herbelin, A.; PléaU, J.-M.; Dardenne, M. CD11c+ Eosinophils in the Murine Thymus: Developmental Regulation and Recruitment upon MHC Class I-Restricted Thymocyte Deletion. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, D.M.; Gauthier, C.M.; Moeller, B.E.; FitzPatrick, R.D.; Kennedy, M.H.E.; Pluzhnikova, V.; Conway, K.M.E.; Smazynski, J.; Chow, R.L.; Reynolds, L.A. MHCII+CD80+ thymic eosinophils increase in abundance during neonatal development in mice and their accumulation is microbiota dependent. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, 114, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Alonzo, E.S.; Dorothee, G.; Pollard, J.W.; Sant’ANgelo, D.B. Selective Depletion of Eosinophils or Neutrophils in Mice Impacts the Efficiency of Apoptotic Cell Clearance in the Thymus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosway, E.J.; White, A.J.; Parnell, S.M.; Schweighoffer, E.; Jolin, H.E.; Bacon, A.; Rodewald, H.-R.; Tybulewicz, V.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Jenkinson, W.E.; et al. Eosinophils are an essential element of a type 2 immune axis that controls thymus regeneration. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabn3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, Y.P.S.; Henderson, N.C.; Heredia, J.E.; Red Eagle, A.; Odegaard, J.I.; Lehwald, N.; Nguyen, K.D.; Sheppard, D.; Mukundan, L.; Locksley, R.M.; et al. Eosinophils secrete IL-4 to facilitate liver regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9914–9919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, J.E.; Mukundan, L.; Chen, F.M.; Mueller, A.A.; Deo, R.C.; Locksley, R.M.; Rando, T.A.; Chawla, A. Type 2 Innate Signals Stimulate Fibro/Adipogenic Progenitors to Facilitate Muscle Regeneration. Cell 2013, 153, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shane, D.X.; Konovalova, D.M.; Rajendran, H.; Yuan, S.Y.; Ma, Y. Glucocorticoids impair T lymphopoiesis after myocardial infarction. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2024, 327, H533–H544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, K.; Falta, N.A.; Spencer, L.A. Innate Immune Pairing: Eosinophils as Hidden Architects of T Cell Immunity. Cells 2025, 14, 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221826
Gupta K, Falta NA, Spencer LA. Innate Immune Pairing: Eosinophils as Hidden Architects of T Cell Immunity. Cells. 2025; 14(22):1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221826
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Kriti, Natalie A. Falta, and Lisa A. Spencer. 2025. "Innate Immune Pairing: Eosinophils as Hidden Architects of T Cell Immunity" Cells 14, no. 22: 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221826
APA StyleGupta, K., Falta, N. A., & Spencer, L. A. (2025). Innate Immune Pairing: Eosinophils as Hidden Architects of T Cell Immunity. Cells, 14(22), 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221826





