Purinergic Signaling in Swallowing Reflex Initiation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Purinergic Receptors in Peripheral Swallowing-Related Regions
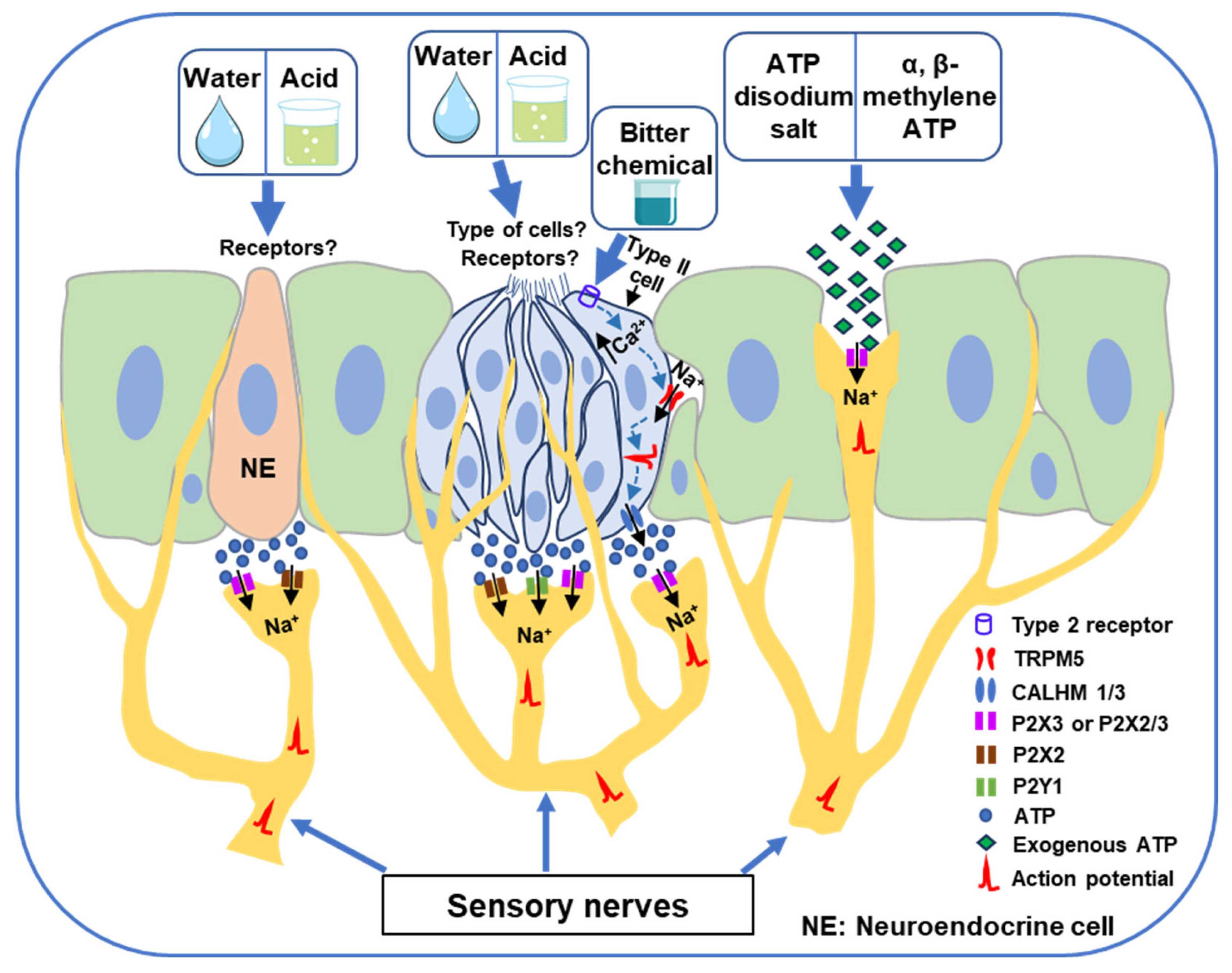
3. Involvement of Purinergic Signaling in Water and Acid-Induced Swallowing Reflex
4. Involvement of Purinergic Signaling in Bitter Chemical Substance-Induced Swallowing Reflex
5. Exogenous ATP Application to the Swallowing-Related Regions Triggers Swallowing Reflexes
6. Clinical Implications of Purinergic Signaling in Triggering the Swallowing Reflex
7. Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ascl1 | Achaete-scute family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1 |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| CALHM1/3 | Calcium homeostasis modulator 1/3 |
| NE | Neuroendocrine |
| NPJc | Nodose–petrosal–jugular ganglionic complex |
| NTS | Nucleus of the solitary tract |
| P1 | Purinergic receptor type 1 |
| P2 | Purinergic receptor type 2 |
| P2X | Purinergic receptor type 2X |
| P2X1 | Purinergic receptor type 2X1 |
| P2X2 | Purinergic receptor type 2X2 |
| P2X3 | Purinergic receptor type 2X3 |
| P2X2/3 | Heteromeric purinergic receptor composed of P2X2 and P2X3 subunits |
| P2X7 | Purinergic receptor type 2X7 |
| P2Y | Purinergic receptor type 2Y |
| P2Y1 | Purinergic receptor type 2Y1 |
| P2Y2 | Purinergic receptor type 2Y2 |
| P2Y4 | Purinergic receptor type 2Y4 |
| P2Y6 | Purinergic receptor type 2Y6 |
| P2Y11 | Purinergic receptor type 2Y11 |
| P2Y14 | Purinergic receptor type 2Y14 |
| Pou2f3 | POU class 2 homeobox factor 3 |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
| SLN | Superior laryngeal nerve |
| sCPG | Swallowing central pattern generator |
| T2Rs | Type 2 taste receptors |
| TRP | Transient receptor potential |
| TRPA1 | Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 |
| TRPM5 | Transient receptor potential melastatin 5 |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 |
References
- Goyal, R.K.; Mashimo, H. Physiology of Oral, Pharyngeal, and Esophageal Motility. GI Motil. Online 2006, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J. Deglutition. Physiol. Rev. 1982, 62, 129–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, K.; Kitagawa, J.; Kurose, M.; Sugino, S.; Takatsuji, H.; Md Mostafeezur, R.; Md Zakir, H.; Yamada, Y. Neural mechanisms of swallowing and effects of taste and other stimuli on swallow initiation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, A. Brain stem control of swallowing: Neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 929–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Kitagawa, J. Targeting chemosensory ion channels in peripheral swallowing-related regions for the management of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T. The swallowing reflex and its significance as an airway defensive reflex. Front. Physiol. 2013, 3, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingai, T.; Shimada, K. Reflex swallowing elicited by water and chemical substances applied in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx of the rabbit. Jpn. J. Physiol. 1976, 26, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingai, T.; Miyaoka, Y.; Ikarashi, R.; Shimada, K. Swallowing reflex elicited by water and taste solutions in humans. Am. J. Physiol.—Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1989, 256, R822–R826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, Y.; Yahagi, R.; Okuda-Akabane, K. Effect of stimulation of the laryngopharynx with water and salt solutions on voluntary swallowing in humans: Characteristics of water receptors in the laryngopharyngeal mucosa. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.I.; Shingai, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamada, Y. Pharyngeal branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a major role in reflex swallowing from the pharynx. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R1342–R1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Kitagawa, J. TRPA1s act as chemosensors but not as cold sensors or mechanosensors to trigger the swallowing reflex in rats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, T.; Ueha, R.; Yoshihara, M.; Takei, E.; Nagoya, K.; Shiraishi, N.; Magara, J.; Inoue, M. Involvement of the epithelial sodium channel in initiation of mechanically evoked swallows in anaesthetized rats. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2949–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theurer, J.A.; Czachorowski, K.A.; Martin, L.P.; Martin, R.E. Effects of oropharyngeal air-pulse stimulation on swallowing in healthy older adults. Dysphagia 2009, 24, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theurer, J.A.; Bihari, F.; Barr, A.M.; Martin, R.E. Oropharyngeal stimulation with air-pulse trains increases swallowing frequency in healthy adults. Dysphagia 2005, 20, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajii, Y.; Shingai, T.; Kitagawa, J.I.; Takahashi, Y.; Taguchi, Y.; Noda, T.; Yamada, Y. Sour taste stimulation facilitates reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 77, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Kitagawa, J. Functional involvement of acid-sensing ion channel 3 in the swallowing reflex in rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Roy, R.R.; Kitagawa, J. Pharmacological activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 promotes triggering of the swallowing reflex in rats. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1149793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafeezur, R.M.; Zakir, H.M.; Takatsuji, H.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Kitagawa, J. Cannabinoids Facilitate the Swallowing Reflex Elicited by the Superior Laryngeal Nerve Stimulation in Rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Shingai, T.; Saito, I.; Yamamura, K.; Yamada, Y.; Kitagawa, J. Facilitation of the swallowing reflex with bilateral afferent input from the superior laryngeal nerve. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 562, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeishi, R.; Magara, J.; Watanabe, M.; Tsujimura, T.; Hayashi, H.; Hori, K.; Inoue, M. Effects of pharyngeal electrical stimulation on swallowing performance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, T.; Udemgba, C.; Inoue, M.; Canning, B.J. Laryngeal and tracheal afferent nerve stimulation evokes swallowing in anaesthetized guinea pigs. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuji, H.; Zakir, H.M.; Mostafeezur, R.M.; Saito, I.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Kitagawa, J. Induction of the swallowing reflex by electrical stimulation of the posterior oropharyngeal region in awake humans. Dysphagia 2012, 27, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavé, P.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Almirall, J.; Cabré, M.; Campins, L.; García-Peris, P.; Speyer, R. Diagnosis and management of oropharyngeal dysphagia and its nutritional and respiratory complications in the elderly. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 818979. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, S. Neurological disorders affecting oral, pharyngeal swallowing. GI Motil. Online 2006, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.R.d.S.; Costa, A.G.d.S.; Morais, H.C.C.; Cavalcante, T.F.; Lopes, M.V.d.O.; de Araujo, T.L. Clinical factors predicting risk for aspiration and respiratory aspiration among patients with Stroke. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2015, 23, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Dziewas, R.; Beck, A.M.; Clavé, P.; Hamdy, S.; Heppner, H.J.; Langmore, S.; Leischker, A.H.; Martino, R.; Pluschinski, P.; et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons—From pathophysiology to adequate intervention: A review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, O.; Cabre, M.; Clave, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Aetiology and effects of ageing. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 3, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Val, C.; Martín-Martínez, A.; Graupera, M.; Arias, O.; Elvira, A.; Cabré, M.; Palomera, E.; Bolívar-Prados, M.; Clavé, P.; Ortega, O. Prevalence, risk factors, and complications of oropharyngeal dysphagia in older patients with dementia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Vaezi, M.F. Dysphagia in the elderly. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Nozal, J.; Martos, J.; Masiero, S. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia as a Geriatric Syndrome. In A Multidisciplinary Approach to Managing Swallowing Dysfunction in Older People; Elsevier: London, UK, 2024; pp. 7–23. ISBN 9780323916868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, S.; Lauretani, F.; Pelá, G.; Meschi, T.; Maggio, M. The risk of dysphagia is associated with malnutrition and poor functional outcomes in a large population of outpatient older individuals. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2684–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, S.; Cabré, M.; Monteis, R.; Roca, M.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Rofes, L.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a prevalent risk factor for malnutrition in a cohort of older patients admitted with an acute disease to a general hospital. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabre, M.; Serra-Prat, M.; Palomera, E.; Almirall, J.; Pallares, R.; Clavé, P. Prevalence and prognostic implications of dysphagia in elderly patients with pneumonia. Age Ageing 2009, 39, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, S.; Sekiya, H.; Miyagi, M.; Ebihara, T.; Okazaki, T. Dysphagia, dystussia, and aspiration pneumonia in elderly people. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Kitagawa, J. Transient receptor potential channels as an emerging therapeutic target for oropharyngeal dysphagia. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2023, 59, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vultaggio-Poma, V.; Falzoni, S.; Salvi, G.; Giuliani, A.L.; Di Virgilio, F. Signalling by extracellular nucleotides in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xie, N.; Illes, P.; Di Virgilio, F.; Ulrich, H.; Semyanov, A.; Verkhratsky, A.; Sperlagh, B.; Yu, S.G.; Huang, C.; et al. From purines to purinergic signalling: Molecular functions and human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 659–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Qi, Y.; Tang, S.; Tang, J.; Chen, N. Purine and purinergic receptors in health and disease. MedComm 2023, 4, e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, S.L.; Umans, B.D.; Williams, E.K.; Brust, R.D.; Liberles, S.D. An Airway Protection Program Revealed by Sweeping Genetic Control of Vagal Afferents. Cell 2020, 181, 574–589.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeholzer, L.F.; Julius, D. Neuroendocrine cells initiate protective upper airway reflexes. Science 2024, 384, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, S.; Hayatsu, N.; Nomura, K.; Sherwood, M.W.; Murakami, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Suematsu, N.; Aoki, T.; Yamada, Y.; Asayama, M.; et al. Channel synapse mediates neurotransmission of airway protective chemoreflexes. Cell 2025, 188, 2687–2704.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Roy, R.R.; Kitagawa, J. Topical ATP Application in the Peripheral Swallowing-Related Regions Facilitates Triggering of the Swallowing Reflex Involving P2X3 Receptors. Function 2025, 6, zqaf010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Nakamuta, N.; Yamamoto, Y. Morphology of P2X3-immunoreactive nerve endings in the rat laryngeal mucosa. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 145, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, Y.; Yamamoto, Y. Morphology and chemical characteristics of subepithelial laminar nerve endings in the rat epiglottic mucosa. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 138, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamuta, N. Morphology of P2X3-immunoreactive nerve endings in the rat tracheal mucosa. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Neuhuber, W.L. Intraganglionic laminar endings in the rat esophagus contain purinergic P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactivity. Anat. Embryol. 2003, 207, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, T.E.; Danilova, V.; Barrows, J.; Bartel, D.L.; Vigers, A.J.; Stone, L.; Hellekant, G.; Kinnamon, S.C. ATP Signaling Is Crucial for Communication from Taste Buds to Gustatory Nerves. Science 2005, 310, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, B.; Jetté, M.E.; Li, M.; Ramakrishnan, V.R.; Clary, M.; Prager, J.; Draf, J.; Hummel, T.; Finger, T.E. Variability in P2X receptor composition in human taste nerves: Implications for treatment of chronic cough. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00007-2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, S.; Toyono, T.; Seta, Y.; Toyoshima, K. Expression of ATP-gated P2X3 receptors in rat gustatory papillae and taste buds. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 2006, 69, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, X.; Alavi, A.; Xiang, Z.; Oglesby, I.; Ford, A.; Burnstock, G. Localization of ATP-gated P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactive nerves in rat taste buds. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Montoya, A.; Bond, A.; Walton, J.; Kinnamon, J.C. Immunocytochemical analysis of P2X2 in rat circumvallate taste buds. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, M.; Linnoila, R.I.; Van De Velde, H.J.K.; Chen, H.; Nelkin, B.D.; Mabry, M.; Baylin, S.B.; Ball, D.W. An achaete-scute homologue essential for neuroendocrine differentiation in the lung. Nature 1997, 386, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.T.; Barden, J.A.; Lawrence, A.J. On the immunohistochemical distribution of ionotropic P2X receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat. Neuroscience 2001, 108, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn-Smith, I.J.; Burnstock, G. Ultrastructural localization of P2X3 receptors in rat sensory neurons. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.H.; Bailey, T.W.; Li, B.Y.; Schild, J.H.; Andresen, M.C. Purinergic and vanilloid receptor activation releases glutamate from separate cranial afferent terminals in nucleus tractus solitarius. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4709–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, F.; Shigetomi, E. Distinct modulation of evoked and spontaneous EPSCs by purinoceptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat. J. Physiol. 2001, 530, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigetomi, E.; Kato, F. Action Potential-Independent Release of Glutamate by Ca2+ Entry through Presynaptic P2X Receptors Elicits Postsynaptic Firing in the Brainstem Autonomic Network. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieger, D. Central nervous system control mechanisms of swallowing: A neuropharmacological perspective. Dysphagia 1993, 8, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, P.; De Kraa, M.; Arreola, V.; Girvent, M.; Farré, R.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, R.; Vilardell, N.; Clavé, P.; Speyer, R. Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia 2016, 31, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabib, C.; Ortega, O.; Kumru, H.; Palomeras, E.; Vilardell, N.; Alvarez-Berdugo, D.; Muriana, D.; Rofes, L.; Terré, R.; Mearin, F.; et al. Neurorehabilitation strategies for poststroke oropharyngeal dysphagia: From compensation to the recovery of swallowing function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1380, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, O.; Martín, A.; Clavé, P. Diagnosis and Management of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Among Older Persons, State of the Art. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, R.; McCulloch, T. Therapeutic intervention in oropharyngeal dysphagia. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmore, S.E.; Pisegna, J.M. Efficacy of exercises to rehabilitate dysphagia: A critique of the literature. Int. J. Speech. Lang. Pathol. 2015, 17, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyer, R.; Baijens, L.; Heijnen, M.; Zwijnenberg, I. Effects of therapy in oropharyngeal dysphagia by speech and language therapists: A systematic review. Dysphagia 2010, 25, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Shutoh, N.; Tonai, M.; Ogata, N. The Effect of Capsaicin-Containing Food on the Swallowing Response. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakato, R.; Manabe, N.; Shimizu, S.; Hanayama, K.; Shiotani, A.; Hata, J.; Haruma, K. Effects of Capsaicin on Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Digestion 2017, 95, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Berdugo, D.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Martin, A.; Molina, L.; Clavé, P. A comparative study on the therapeutic effect of TRPV1, TRPA1, and TRPM8 agonists on swallowing dysfunction associated with aging and neurological diseases. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsen, N.; Ortega, O.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Martin, A.; Mundet, L.; Clavé, P. Acute and subacute effects of oropharyngeal sensory stimulation with TRPV1 agonists in older patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: A biomechanical and neurophysiological randomized pilot study. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 175628481984204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomsen, N.; Alvarez-Berdugo, D.; Rofes, L.; Ortega, O.; Arreola, V.; Nascimento, W.; Martin, A.; Cabib, C.; Bolivar-Prados, M.; Mundet, L.; et al. A randomized clinical trial on the acute therapeutic effect of TRPA1 and TRPM8 agonists in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, I.; Sasegbon, A.; Hamdy, S. Effects of pharmacological agents for neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 34, e14220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavé, P.; Ortega, O.; Rofes, L.; Alvarez-Berdugo, D.; Tomsen, N. Brain and Pharyngeal Responses Associated with Pharmacological Treatments for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older Patients. Dysphagia 2023, 38, 1449–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Dziewas, R. Dysphagia and pharmacotherapy in older adults. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zou, Y.; Huang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, L.D.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, F. Gustatory stimulus interventions for older adults with dysphagia: A scoping review. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Masuda, Y.; Kitagawa, J. Activation of TRPV1 and TRPM8 channels in the larynx and associated laryngopharyngeal regions facilitates the swallowing reflex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Martin, A.; Clavé, P. Effect of oral piperine on the swallow response of patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Martin, A.; Clavé, P. Natural capsaicinoids improve swallow response in older patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gut 2013, 62, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, O.; Rofes, L.; Martin, A.; Arreola, V.; López, I.; Clavé, P. A Comparative Study Between Two Sensory Stimulation Strategies After Two Weeks Treatment on Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonte, R.; Di Luciano, C.; Chiaramonte, I.; Serra, A.; Bonfiglio, M. Multi-disciplinary clinical protocol for the diagnosis of bulbar amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2019, 70, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjaden, K. Speech and swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 2008, 24, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, R.; Rumbach, A.; Farrell, A.; Hutchinson, N.; Verner-Wren, S.; Henderson, R.; McCombe, P. Living with Dysphagia and Dysarthria: A Qualitative Exploration of the Perspectives of People with Motor Neuron Disease and Their Caregivers. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, C.; Gray, L.T.; Anderson, A.; Dibiase, L.; Wymer, J.P.; Plowman, E.K. Profiles of Dysarthria and Dysphagia in Individuals With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2023, 66, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślak, M.; Roszek, K.; Wujak, M. Purinergic implication in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—From pathological mechanisms to therapeutic perspectives. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, M.; Komoszyński, M.; Wojtczak, A. Adenosine A2A receptors in Parkinson’s disease treatment. Purinergic Signal. 2008, 4, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandelman, M.; Peluffo, H.; Beckman, J.S.; Cassina, P.; Barbeito, L. Extracellular ATP and the P2X7receptor in astrocyte-mediated motor neuron death: Implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosi, N.; Finocchi, P.; Apolloni, S.; Cozzolino, M.; Ferri, A.; Padovano, V.; Pietrini, G.; Carrì, M.T.; Volonté, C. The Proinflammatory Action of Microglial P2 Receptors Is Enhanced in SOD1 Models for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4648–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volonté, C.; Amadio, S. Rethinking purinergic concepts and updating the emerging role of P2X7 and P2X4 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropharmacology 2022, 221, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, L.; Woods, L.T.; Khalafalla, M.G.; Weisman, G.A. Purinergic signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 151, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Antal, Z.; Bereczki, D.; Sperlágh, B. Purinergic Signalling in Parkinson’s Disease: A Multi-target System to Combat Neurodegeneration. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Giacomelli, Á.; Naaldijk, Y.; Sardá-Arroyo, L.; Gonçalves, M.C.B.; Corrêa-Velloso, J.; Pillat, M.M.; de Souza, H.D.N.; Ulrich, H. Purinergic receptors in neurological diseases with motor symptoms: Targets for therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, Y.; Pitman, M.J.; de Nooij, J.C. Airway Protection—A Role for Vagal P2RY1 Receptors. Cell 2020, 181, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, X. Sentinels of the airways. Science 2024, 384, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, Y.S.; Tang, Y. Commentary: Vagal P2RY1 Receptors: A Novel Target for Airway Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 574–589. [Google Scholar]
- Zocchi, D.; Wennemuth, G.; Oka, Y. The cellular mechanism for water detection in the mammalian taste system. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuri, T.; Horio, N.; Stratford, J.M.; Finger, T.E.; Ninomiya, Y. Residual chemoresponsiveness to acids in the superior laryngeal nerve in “taste-blind” (p2x2/p2x3 double-ko) mice. Chem. Senses 2012, 37, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, T.; Sakai, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ujihara, I.; Tsuji, K.; Magara, J.; Canning, B.J.; Inoue, M. Central inhibition of initiation of swallowing by systemic administration of diazepam and baclofen in anaesthetized rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G498–G507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, M.; Tsujimura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Nagoya, K.; Shiraishi, N.; Magara, J.; Miho Terunuma, X.; Makoto Inoue, X. Sustained laryngeal transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 activation inhibits mechanically induced swallowing in anesthetized rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G412–G419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Sasaki, H. Capsaicin and swallowing reflex. Lancet 1993, 341, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Muhle, P.; Kampe, I.; Egidi, P.; Ruck, T.; Lenze, F.; Jungheim, M.; Gminski, R.; Labeit, B.; Claus, I.; et al. Effect of Capsaicinoids on Neurophysiological, Biochemical, and Mechanical Parameters of Swallowing Function. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, W.; Tomsen, N.; Acedo, S.; Campos-Alcantara, C.; Cabib, C.; Alvarez-Larruy, M.; Clavé, P. Effect of aging, gender and sensory stimulation of trpv1 receptors with capsaicin on spontaneous swallowing frequency in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: A proof-of-concept study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Purinergic Receptors | Regions | Localization | Species | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2X3 | Larynx (epiglottis, arytenoid, glottic and subglottic regions) | Intraepithelial ramified nerve fibers Nerve fibers associated with chemosensory cells and neuroendocrine cells Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Rats | [45] |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Mice | [50] | |
| Larynx (epiglottis) | Intraepithelial nerve fibers | Rats | [46] | |
| Trachea | Intraepithelial and subepithelial nerve fibers | Rats | [47] | |
| Pharynx | Intraepithelial nerve fibers | Rats | [48] | |
| Laryngopharynx and associated laryngeal regions | Intraepithelial and subepithelial nerve fibers Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Rats | [44] | |
| Hypopharynx | Nerve fibers contacting Pou2f3+ (POU class 2 homeobox factor 3) chemosensory cells | Mice | [43] | |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers contacting Pou2f3+ chemosensory cells | Mice | [43] | |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Humans | [51] | |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Monkeys | [51] | |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Mice | [51] | |
| Back of the tongue | Nerve fibers associated with circumvallate taste buds | Rats | [52,53] | |
| P2X2 | Larynx (epiglottis, arytenoid region, glottic and subglottic regions) | Intraepithelial ramified nerve fibers Nerve fibers associated with chemosensory cells and neuroendocrine cells Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Rats | [45] |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Mice | [50] | |
| Trachea | Intraepithelial and subepithelial nerve fibers | Rats | [47] | |
| Hypopharynx | Nerve fibers contacting Pou2f3+ chemosensory cells | Mice | [43] | |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers contacting Pou2f3+ chemosensory cells | Mice | [43] | |
| Larynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Mice | [51] | |
| Back of the tongue | Nerve fibers associated with circumvallate taste buds | Rats | [53,54] | |
| P2Y1 | Larynx | Nerve fibers innervating the epithelium Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Mice | [41] |
| Pharynx | Nerve fibers associated with taste buds | Mice | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Roy, R.R.; Kitagawa, J. Purinergic Signaling in Swallowing Reflex Initiation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia—A Narrative Review. Cells 2025, 14, 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221795
Qi J, Hossain MZ, Ando H, Roy RR, Kitagawa J. Purinergic Signaling in Swallowing Reflex Initiation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia—A Narrative Review. Cells. 2025; 14(22):1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221795
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Junrong, Mohammad Zakir Hossain, Hiroshi Ando, Rita Rani Roy, and Junichi Kitagawa. 2025. "Purinergic Signaling in Swallowing Reflex Initiation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia—A Narrative Review" Cells 14, no. 22: 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221795
APA StyleQi, J., Hossain, M. Z., Ando, H., Roy, R. R., & Kitagawa, J. (2025). Purinergic Signaling in Swallowing Reflex Initiation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia—A Narrative Review. Cells, 14(22), 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221795








