Knockout of Perilipin-2 in Microglia Alters Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Response to Alzheimer’s Disease Stimuli
Highlights
- Knockout of Plin2 in microglia reduces lipid droplet burden, while enhancing phagocytic clearance capacity.
- Transcriptomic, bioenergetic, and lipidomic analyses reveal that loss of Plin2 reprograms microglial metabolism toward reduced TAG storage and improved mitochondrial resilience.
- Plin2 serves as a key regulator of microglial lipid droplet stability, metabolic flexibility, and immune function under Alzheimer’s-relevant stressors.
- Targeting Plin2 may represent a therapeutic strategy to alleviate lipid droplet-driven dysfunction and restore microglial performance in aging and neurodegeneration.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BV2 Cell Culture
2.2. Mouse Model
2.3. Mouse Tissue Staining
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Lipid Droplet Staining
2.6. LD Time Course Experiment
2.7. Phagocytosis Assay
2.8. Image Analysis
2.9. Lipidomics
2.10. Transcriptomics
2.11. Co-Expression Network Construction
2.12. Seahorse Extracellular Flux Assay
2.13. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Plin2 KO Lowers LD Accumulation and Size in BV2 Cells After Oleic Acid Stimulation
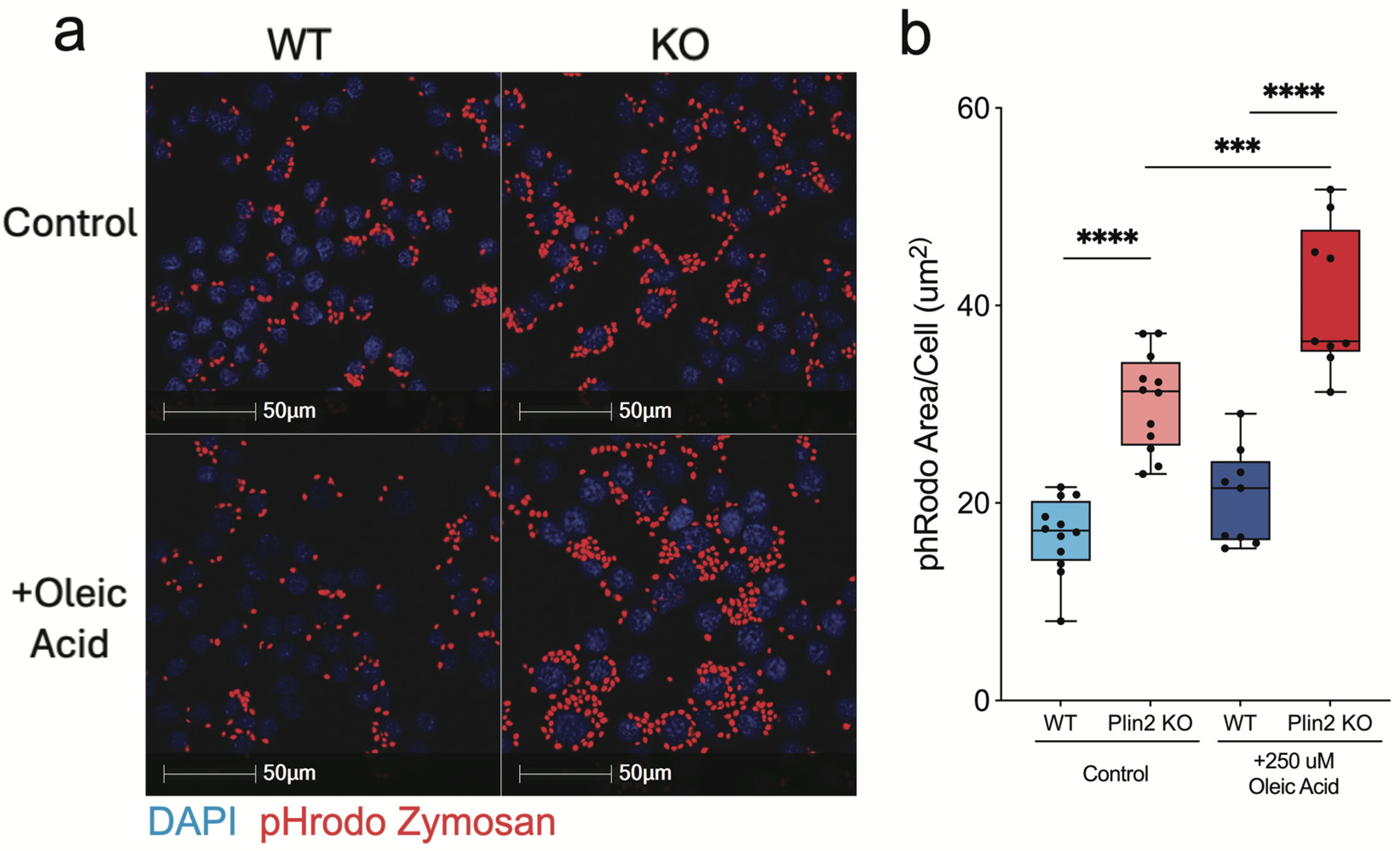
3.2. Phagocytosis of Zymosan Particles Is Enhanced in Plin2 KO Cells
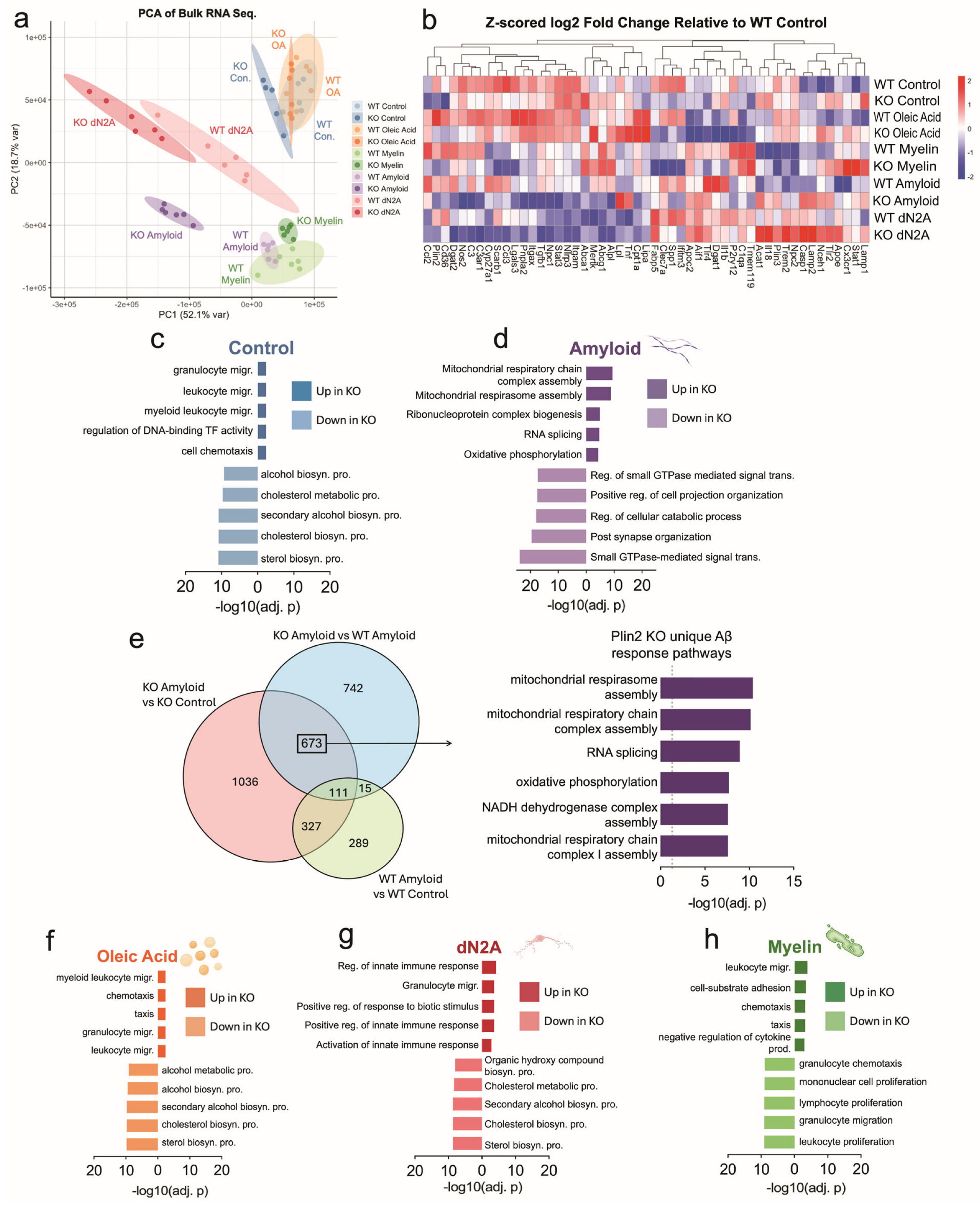
3.3. Bulk RNA-Sequencing Shows Plin2 Alters BV2 Response Profiles to AD-Relevant Stimuli
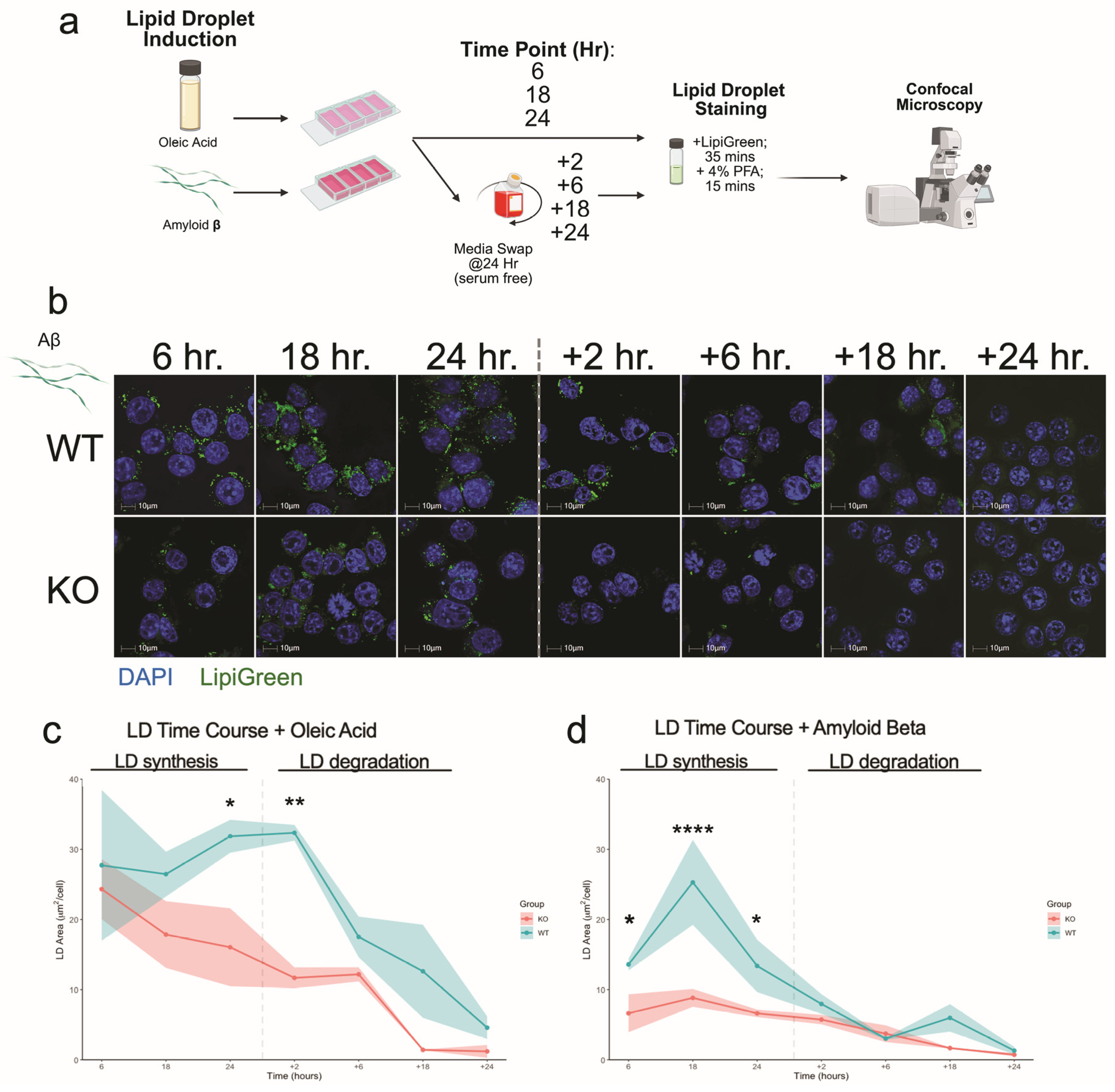
3.4. Plin2 Regulates Lipid Droplet Dynamics in Response to Oleic Acid and Amyloid-β
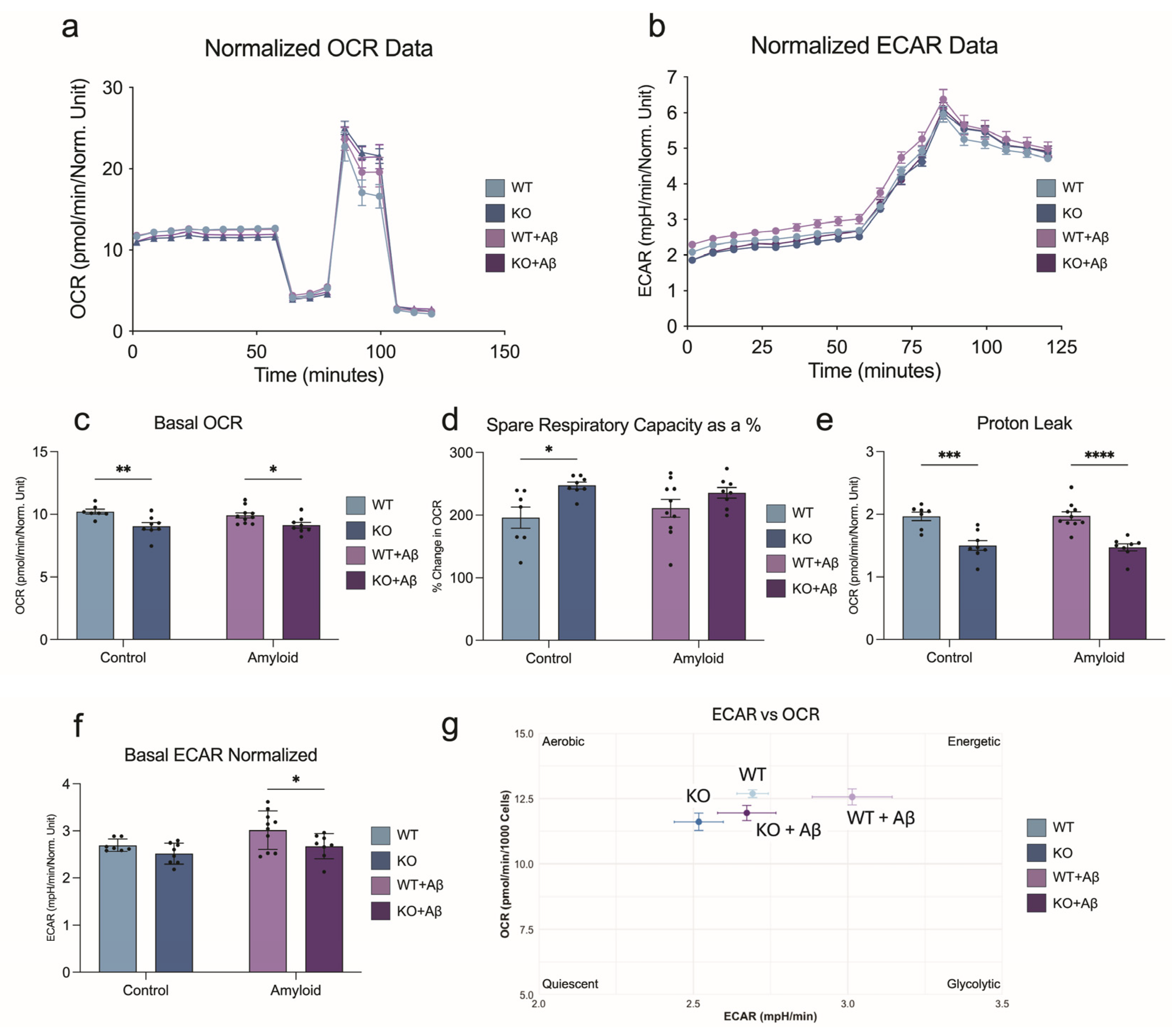
3.5. Mitochondrial Respiration in BV2 Microglia Under Basal and Amyloid-β Challenge
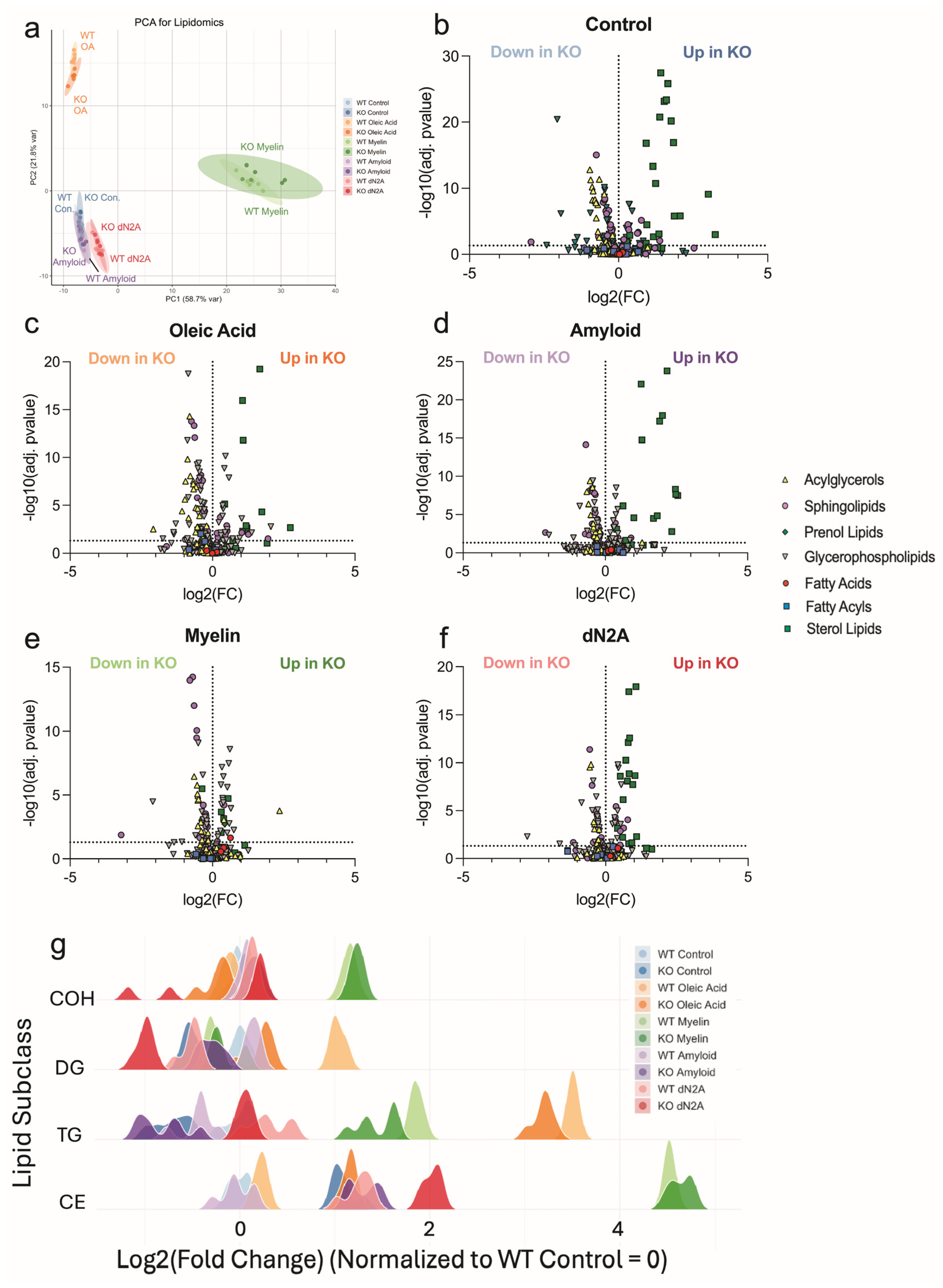
3.6. Plin2 KO Significantly Alters the Microglia Lipidome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid-β |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| BV2 | BV2 microglial cell line |
| CE | Cholesteryl ester |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline |
| ECAR | Extracellular acidification rate |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| KO | Knockout |
| kME | Module eigengene connectivity (WGCNA) |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| LD | Lipid droplet |
| OA | Oleic acid |
| OCR | Oxygen consumption rate |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PLL | Poly-L-lysine |
| PLIN2 | Perilipin-2 |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| TAG | Triacylglycerol (triglyceride; TG) |
| WGCNA | Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis |
| WT | Wild type |
| Zymosan | β-glucan yeast particle used for phagocytosis assays |
References
- Olzmann, J.A.; Carvalho, P. Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Goodman, J.M. The lipid droplet—A well-connected organelle. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambold, A.; Cohen, S.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Fatty Acid Trafficking in Starved Cells: Regulation by Lipid Droplet Lipolysis, Autophagy, and Mitochondrial Fusion Dynamics. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Sandoval, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Sanz, E.; Li, Z.; Hui, J.; Graham, B.H.; Quintana, A.; et al. Glial Lipid Droplets and ROS Induced by Mitochondrial Defects Promote Neurodegeneration. Cell 2015, 160, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, P.T.; Viola, J.P. Lipid droplets in inflammation and cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2010, 82, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avila, H.; Melo, R.C.N.; Parreira, G.G.; Werneck-Barroso, E.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Bozza, P.C.T. Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin induces TLR2-mediated formation of lipid bodies: Intracellular domains for eicosanoid synthesis in vivo. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, V.J.; Silver, D.L. The lipid droplet as a potential therapeutic target in NAFLD. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Chang, B.H.-J.; Li, L.; Yechoor, V.K.; Chan, L. Deficiency of Adipose Differentiation-Related Protein Impairs Foam Cell Formation and Protects Against Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liang, D.; Song, K.; Kong, X.; He, M.; Liao, X.; Huang, Z.; Kang, A.; Bai, R.; et al. Roles of lipid droplets and related proteins in metabolic diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, T.; Kozawa, J.; Fujita, Y.; Kawata, S.; Ozawa, H.; Ishibashi, C.; Yoneda, S.; Nammo, T.; Miyagawa, J.; Eguchi, H.; et al. Lipid droplet accumulation in β cells in patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with insulin resistance, hyperglycemia and β cell dysfunction involving decreased insulin granules. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 996716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschallinger, J.; Iram, T.; Zardeneta, M.; Lee, S.E.; Lehallier, B.; Haney, M.S.; Pluvinage, J.V.; Mathur, V.; Hahn, O.; Morgens, D.W.; et al. Lipid-droplet-accumulating microglia represent a dysfunctional and proinflammatory state in the aging brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ye, H.; Wang, M.J.; Ke, L.; Huang, T.; Lv, P.; et al. Lipid-accumulated reactive astrocytes promote disease progression in epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouna, G.; Klose, C.; Bosch-Queralt, M.; Liu, L.; Gokce, O.; Schifferer, M.; Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Simons, M. TREM2-dependent lipid droplet biogenesis in phagocytes is required for remyelination. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20210227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Medici, V.; Malagoli, D.; Chiariello, A.; Cirrincione, A.; Davin, A.; Chikhladze, M.; Vasuri, F.; Legname, G.; Ferrer, I.; et al. Expression pattern of perilipins in human brain during aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2022, 48, e12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Manchanda, P.; Paouri, E.; Bisht, K.; Sharma, K.; Rajpoot, J.; Wendt, V.; Hossain, A.; Wijewardhane, P.R.; Randolph, C.E.; et al. Amyloid-β induces lipid droplet-mediated microglial dysfunction via the enzyme DGAT2 in Alzheimer’s disease. Immunity 2025, 58, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatchadourian, A.; Bourque, S.D.; Richard, V.R.; Titorenko, V.I.; Maysinger, D. Dynamics and regulation of lipid droplet formation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated microglia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, C.; Danhash, E.P.; Hasselmann, J.; Chadarevian, J.P.; Shabestari, S.K.; England, W.E.; Lim, T.E.; Hidalgo, J.L.S.; Spitale, R.C.; Davtyan, H.; et al. Plaque-associated human microglia accumulate lipid droplets in a chimeric model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-H.; Chen, E.; Li, L.; Saha, P.; Lee, H.-J.; Huang, L.-S.; Shelness, G.S.; Chan, L.; Chang, B.H.-J. The constitutive lipid droplet protein PLIN2 regulates autophagy in liver. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztalryd, C.; Brasaemle, D.L. The perilipin family of lipid droplet proteins: Gatekeepers of intracellular lipolysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, G.M.; Antwi, D.A.; Dhir, R.; Yin, X.; Singhal, N.S.; Graham, M.J.; Crooke, R.M.; Ahima, R.S. Inhibition of ADRP prevents diet-induced insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G621–G628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najt, C.P.; Senthivinayagam, S.; Aljazi, M.B.; Fader, K.A.; Olenic, S.D.; Brock, J.R.L.; Lydic, T.A.; Jones, A.D.; Atshaves, B.P. Liver-specific loss of Perilipin 2 alleviates diet-induced hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G726–G738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlicky, D.J.; Libby, A.E.; Bales, E.S.; McMahan, R.H.; Monks, J.; Rosa, F.G.L.; McManaman, J.L. Perilipin-2 promotes obesity and progressive fatty liver disease in mice through mechanistically distinct hepatocyte and extra-hepatocyte actions. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 1565–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loix, M.; Wouters, E.; Vanherle, S.; Dehairs, J.; McManaman, J.L.; Kemps, H.; Swinnen, J.V.; Haidar, M.; Bogie, J.F.J.; Hendriks, J.J.A. Perilipin-2 limits remyelination by preventing lipid droplet degradation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.G.; Wisén, S.; Gestwicki, J.E. Heat Shock Proteins 70 and 90 Inhibit Early Stages of Amyloid β-(1–42) Aggregation in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33182–33191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, P.K.; Bowes, A.L.; Hall, J.C.E.; Burguillos, M.A.; Ip, T.H.R.; Baskerville, T.; Liu, Z.-H.; Mohamed, M.A.E.K.; Getachew, F.; Lindsay, A.D.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces microglia phagocytic activity via miR-124 and induces neuroprotection in rodent models of spinal cord contusion injury. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 2427–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantner, B.N.; Simmons, R.M.; Canavera, S.J.; Akira, S.; Underhill, D.M. Collaborative induction of inflammatory responses by dectin-1 and Toll-like receptor 2. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keaney, J.; Gasser, J.; Gillet, G.; Scholz, D.; Kadiu, I. Inhibition of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Modulates Microglial Phagocytosis: Therapeutic Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friday, C.M.; Stephens, I.O.; Smith, C.T.; Lee, S.; Satish, D.; Devanney, N.A.; Cohen, S.; Morganti, J.M.; Gordon, S.M.; Johnson, L.A. APOE4 reshapes the lipid droplet proteome and modulates microglial inflammatory responses. Neurobiol. Dis. 2025, 212, 106983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaizar-Rovirosa, M.; Pedragosa, J.; Lozano, J.J.; Casal, C.; Pol, A.; Gallizioli, M.; Planas, A.M. Aged lipid-laden microglia display impaired responses to stroke. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Dimitry, J.M.; Song, J.H.; Son, M.; Sheehan, P.W.; King, M.W.; Travis Tabor, G.; Goo, Y.A.; Lazar, M.A.; Petrucelli, L.; et al. Microglial REV-ERBα regulates inflammation and lipid droplet formation to drive tauopathy in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Munoz-Mayorga, D.; Nie, Y.; Kang, N.; Tao, Y.; Lagerwall, J.; Pernaci, C.; Curtin, G.; Coufal, N.G.; Mertens, J.; et al. Microglial lipid droplet accumulation in tauopathy brain is regulated by neuronal AMPK. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1351–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, A.E.; Bales, E.; Orlicky, D.J.; McManaman, J.L. Perilipin-2 Deletion Impairs Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Interfering with Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein (SREBP) Activation and Altering the Hepatic Lipidome. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24231–24246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManaman, J.L.; Bales, E.S.; Orlicky, D.J.; Jackman, M.; MacLean, P.S.; Cain, S.; Crunk, A.E.; Mansur, A.; Graham, C.E.; Bowman, T.A.; et al. Perilipin-2-null mice are protected against diet-induced obesity, adipose inflammation, and fatty liver disease. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Underhill, D.M.; Touret, N. Mechanisms of Fc Receptor and Dectin-1 Activation for Phagocytosis. Traffic 2012, 13, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najt, C.P.; Lwande, J.S.; McIntosh, A.L.; Senthivinayagam, S.; Gupta, S.; Kuhn, L.A.; Atshaves, B.P. Structural and Functional Assessment of Perilipin 2 Lipid Binding Domain(s). Biochemistry 2014, 53, 7051–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P.E.D.; Toledo, D.A.M.; Rodrigues, G.S.C.; D’Avila, H. Lipid Bodies as Sites of Prostaglandin E2 Synthesis During Chagas Disease: Impact in the Parasite Escape Mechanism. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, R.C.N.; Weller, P.F. Lipid droplets in leukocytes: Organelles linked to inflammatory responses. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 340, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mackenzie, K.R.; Putluri, N.; Maletić-Savatić, M.; Bellen, H.J. The Glia-Neuron Lactate Shuttle and Elevated ROS Promote Lipid Synthesis in Neurons and Lipid Droplet Accumulation in Glia via APOE/D. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, S.H.; Kang, S.; Lee, W.; Choi, H.; Chung, S.; Kim, J.-I.; Mook-Jung, I. A Breakdown in Metabolic Reprogramming Causes Microglia Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairley, L.H.; Wong, J.H.; Barron, A.M. Mitochondrial Regulation of Microglial Immunometabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 624538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Z.; Lund, J.; Li, Y.; Knabenes, I.K.; Bakke, S.S.; Kase, E.T.; Lee, Y.K.; Kimmel, A.R.; Thoresen, G.H.; Rustan, A.C.; et al. Loss of perilipin 2 in cultured myotubes enhances lipolysis and redirects the metabolic energy balance from glucose oxidation towards fatty acid oxidation. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2147–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, A.I.; Li, Y.; Khanal, P.; Hjorth, M.; Kolset, S.O.; Norheim, F.A.; Kimmel, A.R.; Dalen, K.T. Altered hepatic lipid droplet morphology and lipid metabolism in fasted Plin2 null mice. J. Lipid Res. 2023, 64, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.-H.; Goo, Y.-H.; Chang, B.H.; Paul, A. Perilipin 2 (PLIN2)-Deficiency Does Not Increase Cholesterol-Induced Toxicity in Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-H.; Goo, Y.-H.; Choi, M.; Saha, P.K.; Oka, K.; Chan, L.C.B.; Paul, A. Enhanced atheroprotection and lesion remodelling by targeting the foam cell and increasing plasma cholesterol acceptors. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 109, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.S.; Pálovics, R.; Munson, C.N.; Long, C.; Johansson, P.K.; Yip, O.; Dong, W.; Rawat, E.; West, E.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; et al. APOE4/4 is linked to damaging lipid droplets in Alzheimer’s disease microglia. Nature 2024, 628, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, R.; Burm, S.M.; Bajramovic, J.J. An Overview of in vitro Methods to Study Microglia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, D.; Skola, D.; Coufal, N.G.; Holtman, I.R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Sajti, E.; Jaeger, B.N.; O’Connor, C.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Pasillas, M.P.; et al. An environment-dependent transcriptional network specifies human microglia identity. Science 2017, 356, eaal3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.R.; Dufort, C.; Dissing-Olesen, L.; Giera, S.; Young, A.; Wysoker, A.; Walker, A.J.; Gergits, F.; Segel, M.; Nemesh, J.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Microglia throughout the Mouse Lifespan and in the Injured Brain Reveals Complex Cell-State Changes. Immunity 2019, 50, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stephens, I.O.; Johnson, L.A. Knockout of Perilipin-2 in Microglia Alters Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Response to Alzheimer’s Disease Stimuli. Cells 2025, 14, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221783
Stephens IO, Johnson LA. Knockout of Perilipin-2 in Microglia Alters Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Response to Alzheimer’s Disease Stimuli. Cells. 2025; 14(22):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221783
Chicago/Turabian StyleStephens, Isaiah O., and Lance A. Johnson. 2025. "Knockout of Perilipin-2 in Microglia Alters Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Response to Alzheimer’s Disease Stimuli" Cells 14, no. 22: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221783
APA StyleStephens, I. O., & Johnson, L. A. (2025). Knockout of Perilipin-2 in Microglia Alters Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Response to Alzheimer’s Disease Stimuli. Cells, 14(22), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221783






