Na+/H+ Exchanger 1 Inhibition Overcomes Venetoclax Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Leukemia Cell Lines and Treatment
2.3. Annexin-V FITC/Propidium Iodide (PI) Apoptosis Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. siRNA Transfection
2.6. Cytosol and Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
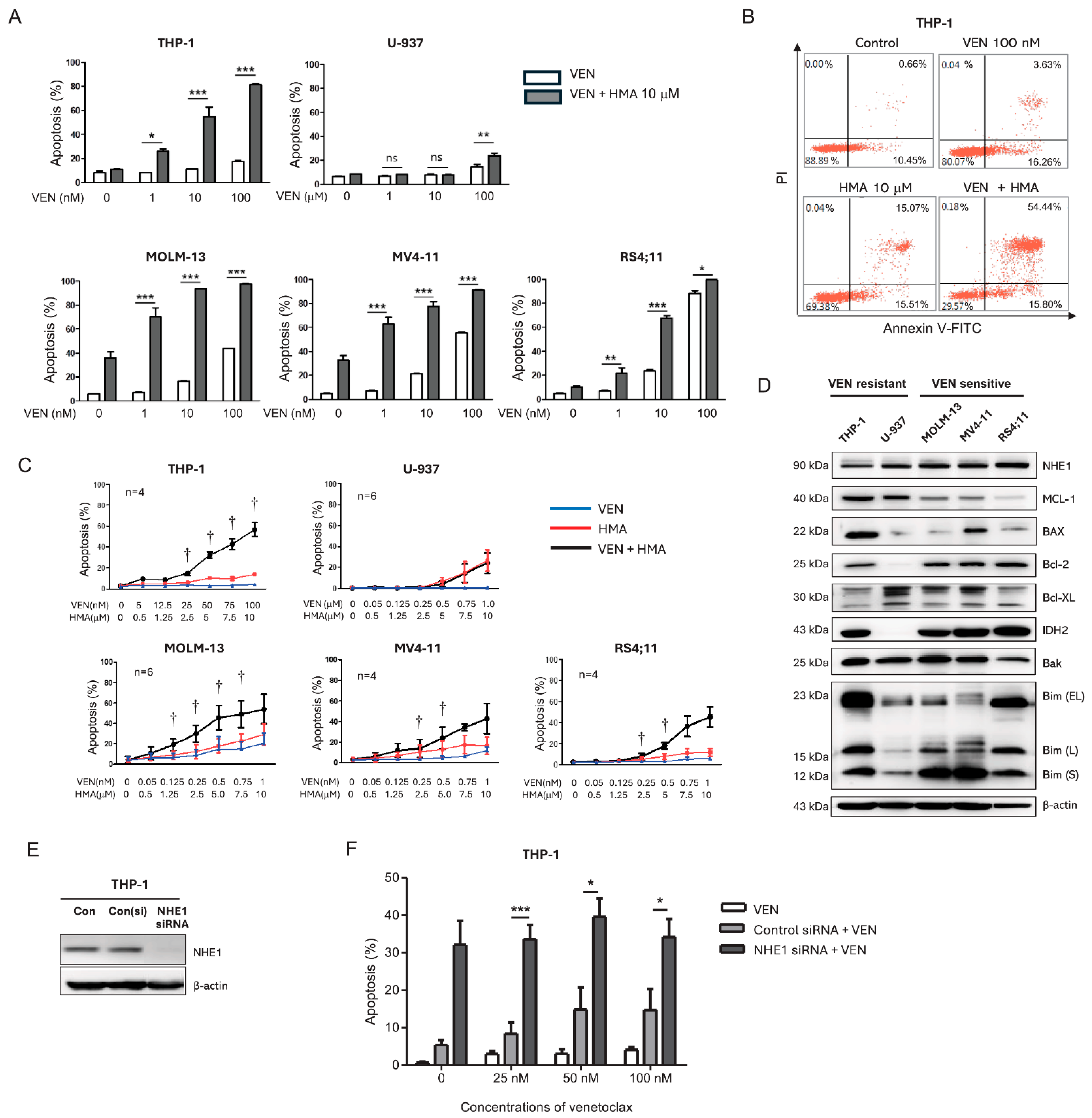
3.1. NHE1 Inhibition with Venetoclax Synergistically Enhances Apoptosis in Venetoclax-Sensitive and -Resistant Leukemic Cell Lines
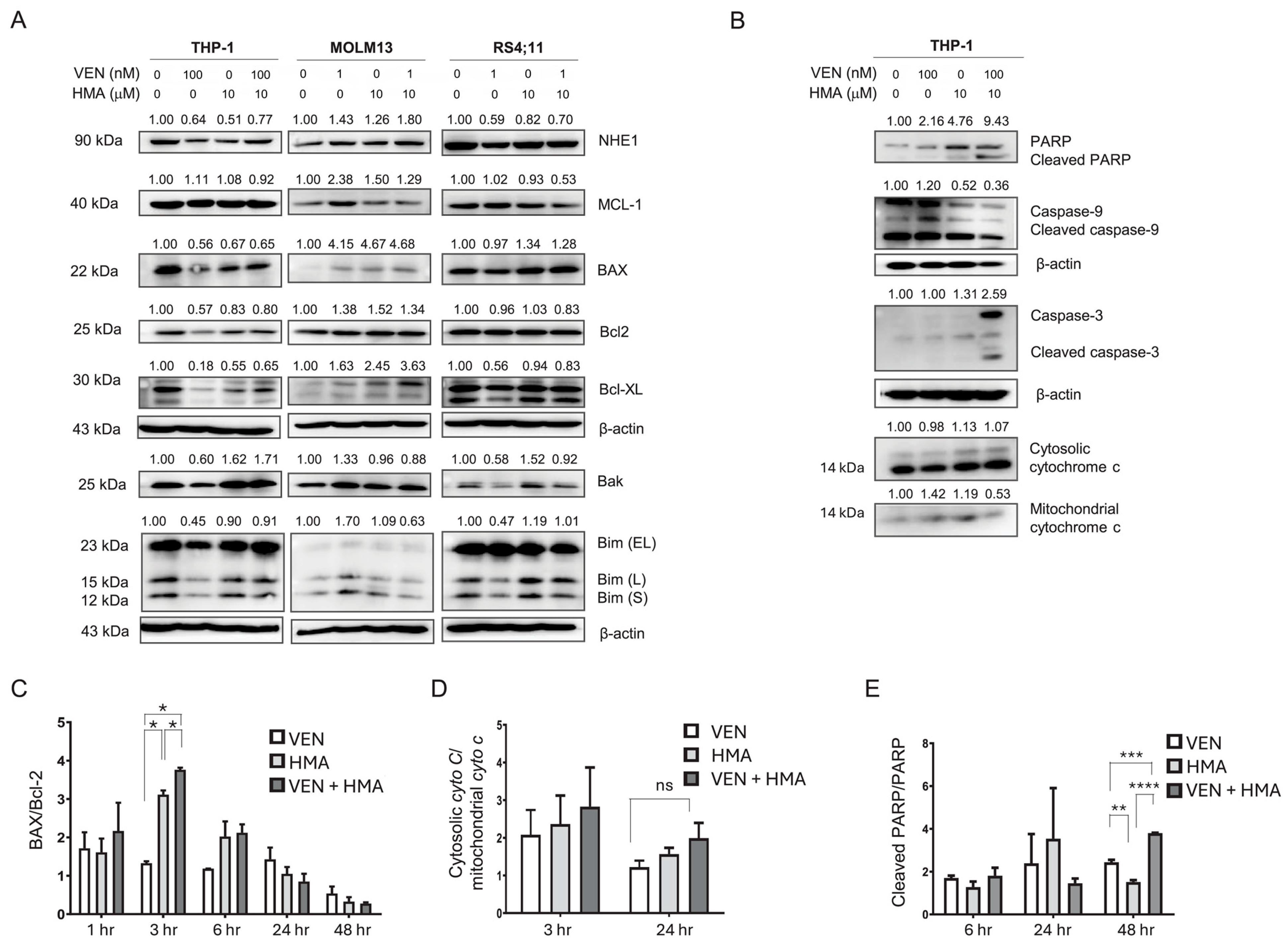
3.2. MCL-1 Downregulation Contributes to Synergistic Apoptosis Induced by Venetoclax and HMA
3.3. Activation of Intrinsic Apoptosis via Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Caspase Signaling Also Contributes to the Synergistically Induced Apoptosis by Venetoclax and HMA
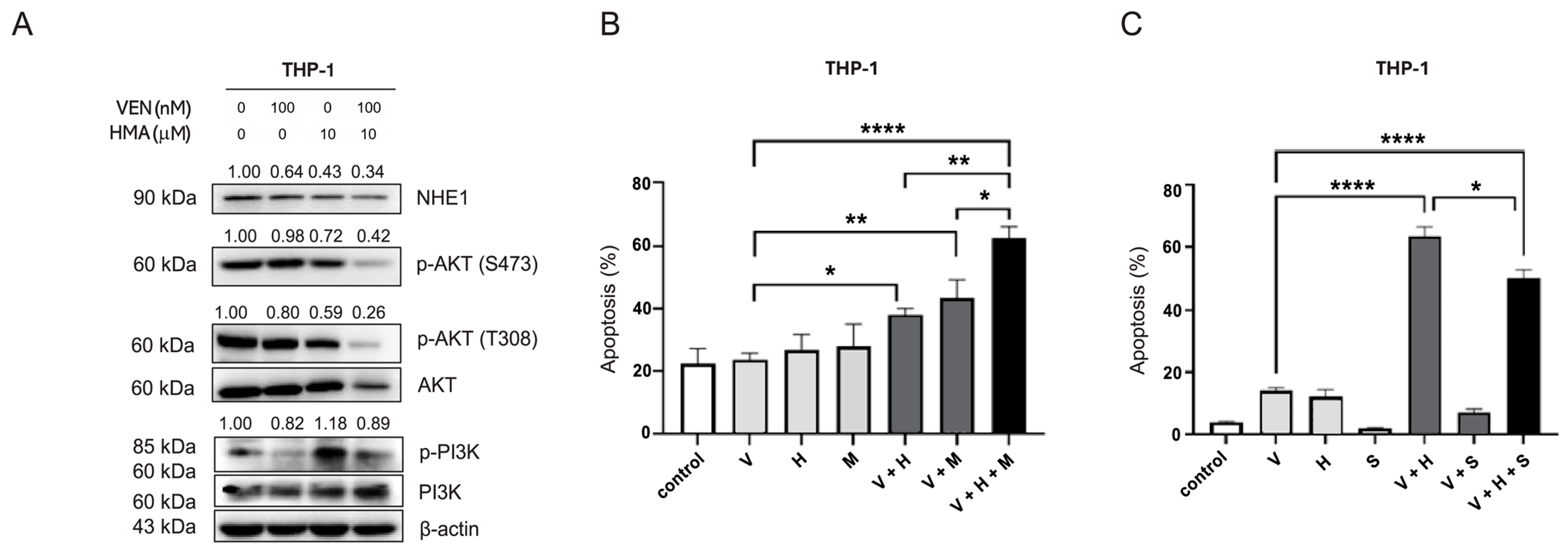
3.4. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt Pathway Mediates Reversal of Venetoclax Resistance by NHE1 Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| BCL-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| H+ | Proton (Hydrogen ion) |
| IC50 | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| IDH | Isocitrate Dehydrogenase |
| MCL-1 | Myeloid Cell Leukemia 1 |
| Na+ | Sodium ion |
| NHE1 | Na+/H+ Exchanger 1 |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute (medium) |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| WB | Western Blot |
References
- Lachowiez, C.A.; DiNardo, C.D.; Loghavi, S. Molecularly targeted therapy in acute myeloid leukemia: Current treatment landscape and mechanisms of response and resistance. Cancers 2023, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhansali, R.S.; Pratz, K.W.; Lai, C. Recent advances in targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thol, F.; Döhner, H.; Ganser, A. How I treat refractory and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2024, 143, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepkov, E.R.; Rainey, J.K.; Sykes, B.D.; Fliegel, L. Structural and functional analysis of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem. J. 2007, 401, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Feng, F.; Yang, H.; Xu, W. Increased NHE1 expression is targeted by specific inhibitor cariporide to sensitize resistant breast cancer cells to doxorubicin in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebillard, A.; Tekpli, X.; Meurette, O.; Sergent, O.; LeMoigne-Muller, G.; Vernhet, L.; Gorria, M.; Chevanne, M.; Christmann, M.; Kaina, B.; et al. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis involves membrane fluidification via inhibition of NHE1 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7865–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.Y.; Na, E.J.; Jang, J.E.; Chung, H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kong, J.H.; Shim, K.Y.; Lee, J.I.; Min, Y.H.; et al. Induction of apoptosis and differentiation by Na/H exchanger 1 modulation in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Huang, K.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, L.; Liu, F.; Huang, R.; Du, J.; Zeng, H. Hexamethylene amiloride synergizes with venetoclax to induce lysosome-dependent cell death in acute myeloid leukemia. iScience 2024, 27, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.H.; Zeng, X.; Lam, W.; Ng, T.C.C.; Kwok, T.H.; Dang, K.C.C.; Leung, T.W.Y.; Ng, N.K.L.; Lam, S.S.Y.; Cher, C.Y.; et al. Regulation of proton partitioning in kinase-activating acute myeloid leukemia and its therapeutic implication. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.H.; Lam, S.S.Y.; Sun, M.K.H.; Chow, H.C.H.; Gill, H.; Kwong, Y.L.; Leung, A.Y.H. A novel tescalcin-sodium/hydrogen exchange axis underlying sorafenib resistance in FLT3-ITD+ AML. Blood 2014, 123, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Hogdal, L.J.; Benito, J.M.; Bucci, D.; Han, L.; Borthakur, G.; Cortes, J.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Debose, L.; Mu, H.; et al. Selective BCL-2 inhibition by ABT-199 causes on-target cell death in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Boghaert, E.R.; Ackler, S.L.; Catron, N.D.; Chen, J.; Dayton, B.D.; Ding, H.; Enschede, S.H.; Fairbrother, W.J.; et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Kuang, P.; Liu, T. Venetoclax combined with hypomethylating agents or low-dose cytarabine as induction chemotherapy for patients with untreated acute myeloid leukemia ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.H.; Montesinos, P.; Ivanov, V.; DiNardo, C.D.; Novak, J.; Laribi, K.; Kim, I.; Stevens, D.A.; Fiedler, W.; Pagoni, M.; et al. Venetoclax plus LDAC for newly diagnosed AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: A phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial. Blood 2020, 135, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Döhner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.; Pullarkat, V.; Jonas, B.A.; Arellano, M.; Becker, P.S.; Frankfurt, O.; Konopleva, M.; Wei, A.H.; Kantarjian, H.M.; et al. Venetoclax combined with decitabine or azacitidine in treatment-naive, elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, M.; Schmidt, C.; Bruch, P.M.; Blank, M.F.; Rohde, C.; Waclawiczek, A.; Heid, D.; Renders, S.; Göllner, S.; Vierbaum, L.; et al. Venetoclax synergizes with gilteritinib in FLT3 wild-type high-risk acute myeloid leukemia by suppressing MCL-1. Blood 2022, 140, 2594–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, D.A.; Niu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Edwards, H.; Chen, K.; Lin, H.; Taub, J.W.; Ge, Y. Inhibition of Mcl-1 enhances cell death induced by the Bcl-2-selective inhibitor ABT-199 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, J.; Xie, C.; Edwards, H.; Wang, G.; Caldwell, J.T.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chu, R.; et al. Binding of released Bim to Mcl-1 is a mechanism of intrinsic resistance to ABT-199 which can be overcome by combination with daunorubicin or cytarabine in AML cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4440–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Riley-Gillis, B.; Han, L.; Jia, Y.; Lodi, A.; Zhang, H.; Ganesan, S.; Pan, R.; Konoplev, S.N.; Sweeney, S.R.; et al. Activation of RAS/MAPK pathway confers MCL-1 mediated acquired resistance to BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax in acute myeloid leukemia. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hussain, Z.; Xie, Q.; Yan, X.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, G.; Cao, S. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to enhance the anti-leukemia efficacy of venetoclax. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 417, 113192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhatabi, H.A.; Zohny, S.F.; Shait Mohammed, M.R.; Choudhry, H.; Rehan, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, M.I. Venetoclax-resistant MV4-11 leukemic cells activate PI3K/AKT pathway for metabolic reprogramming and redox adaptation for survival. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, N.J.; Daver, N.; Dinardo, C.D.; Kadia, T.; Nasr, L.F.; Macaron, W.; Yilmaz, M.; Borthakur, G.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; et al. Azacitidine, venetoclax, and gilteritinib in newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Kantarjian, H.; Short, N.J.; Reville, P.; Konopleva, M.; Kadia, T.; DiNardo, C.; Borthakur, G.; Pemmaraju, N.; Maiti, A.; et al. Hypomethylating agent and venetoclax with FLT3 inhibitor “triplet” therapy in older/unfit patients with FLT3 mutated AML. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, H.E.; Fischer, M.A.; Lee, T.; Gorska, A.E.; Arrate, M.P.; Fuller, L.; Boyd, K.L.; Strickland, S.A.; Sensintaffar, J.; Hogdal, L.J.; et al. A novel MCL1 inhibitor combined with venetoclax rescues venetoclax-resistant acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1566–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Glytsou, C.; Zhou, H.; Narang, S.; Reyna, D.E.; Lopez, A.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Gong, Y.; Kloetgen, A.; Yap, Y.S.; et al. Targeting mitochondrial structure sensitizes acute myeloid leukemia to venetoclax treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 890–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting MCL-1 in cancer: Current status and perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolomsky, A.; Vogler, M.; Köse, M.C.; Heckman, C.A.; Ehx, G.; Ludwig, H.; Caers, J. MCL-1 inhibitors, fast-lane development of a new class of anti-cancer agents. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepstad, I.; Hatfield, K.J.; Grønningsæter, I.S.; Reikvam, H. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darici, S.; Alkhaldi, H.; Horne, G.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Marmiroli, S.; Huang, X. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR in AML: Rationale and clinical evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinner, S.; Platanias, L.C. Targeting the mTOR pathway in leukemia. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, J.; Heidari, N.; Mediani, L.; Capitani, S.; Shahjahani, M.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Saki, N. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Nkwocha, J.; Hawkins, E.; Pei, X.; Parker, R.E.; Kmieciak, M.; Leverson, J.D.; Sampath, D.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, A.; Grant, S. Cotargeting BCL-2 and PI3K induces BAX-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis in AML cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3075–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hyun, S.Y.; Na, E.J.; Kim, Y.R.; Min, Y.H.; Cheong, J.-W. Na+/H+ Exchanger 1 Inhibition Overcomes Venetoclax Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells 2025, 14, 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221759
Hyun SY, Na EJ, Kim YR, Min YH, Cheong J-W. Na+/H+ Exchanger 1 Inhibition Overcomes Venetoclax Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells. 2025; 14(22):1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221759
Chicago/Turabian StyleHyun, Shin Young, Eun Jung Na, Yu Ri Kim, Yoo Hong Min, and June-Won Cheong. 2025. "Na+/H+ Exchanger 1 Inhibition Overcomes Venetoclax Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Cells 14, no. 22: 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221759
APA StyleHyun, S. Y., Na, E. J., Kim, Y. R., Min, Y. H., & Cheong, J.-W. (2025). Na+/H+ Exchanger 1 Inhibition Overcomes Venetoclax Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells, 14(22), 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221759





