A Bispecific Antibody Blocking Both TSLP and IL-4Rα for the Treatment of Allergic Inflammatory Diseases
Highlights
- A bispecific antibody targeting both TSLP and IL-4Rα was generated to block TSLP, IL-4, and IL-13 signaling.
- Dual blockade of both the initiator and effectors of type 2 inflammation showed a more comprehensive control of allergic inflammation.
- The bispecific antibody could be developed as a promising therapeutic drug for allergic and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibody Expression and Purification
2.2. BsAb Generation by Controlled Fab Arm Exchange
2.3. ELISA Binding Assay
2.4. Blocking TSLP Binding to Its Cell Surface Receptor Complex
2.5. TSLP-Mediated Reporter Gene Assay
2.6. TSLP-Driven Proliferation of Activated Human CD4+ T Cell Assay
2.7. IL-4/IL-13-Mediated HEK-Blue Reporter Gene Assay
2.8. IL-4/IL-13-Mediated TF-1 Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9. Der p Stimulated IL-5/CCL26 Release from PBMC, MRC-5, and A549 Cell Co-Culture Assay
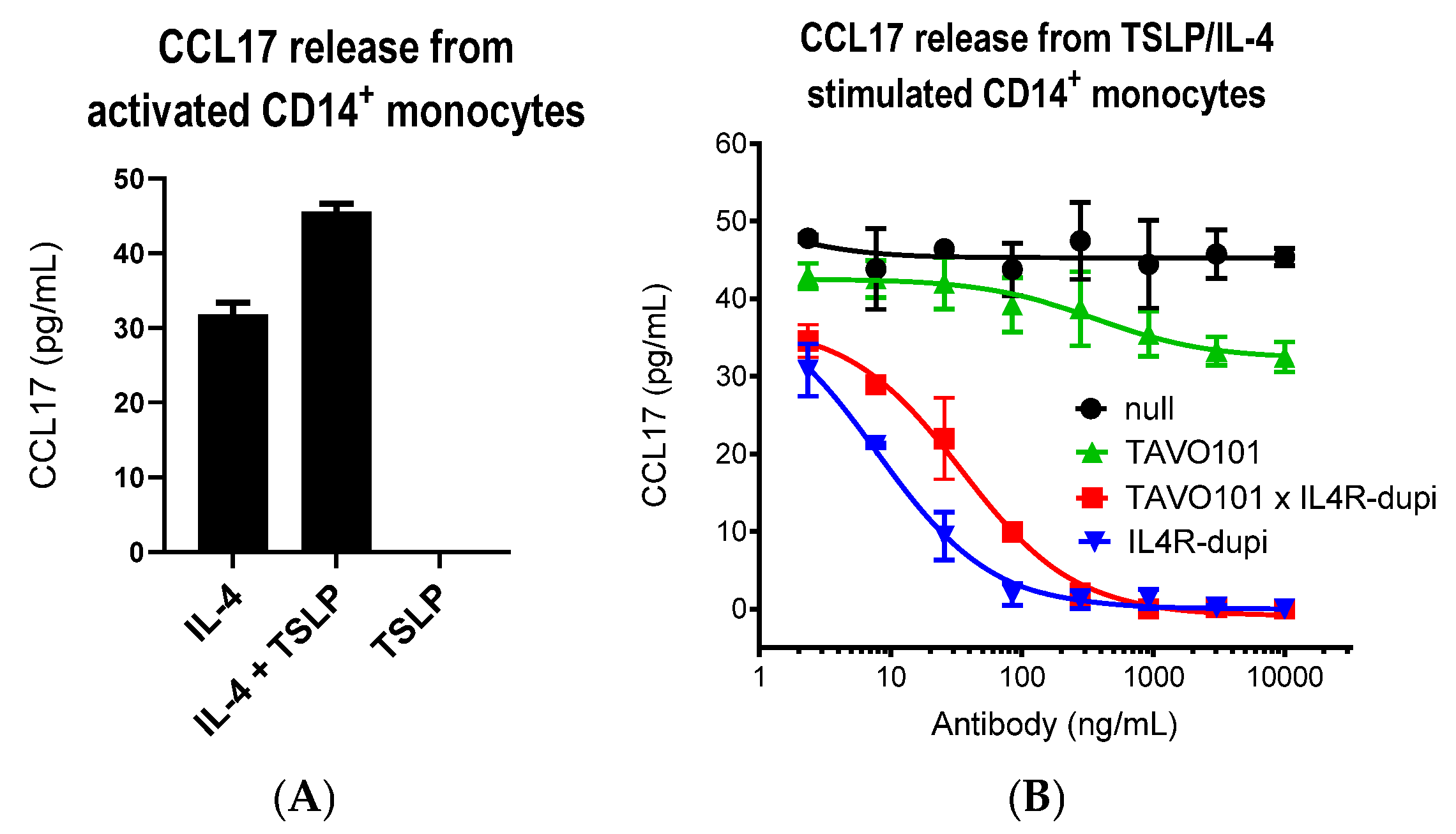
2.10. TSLP/IL-4-Mediated CCL17 Release from Activated Monocyte Assay
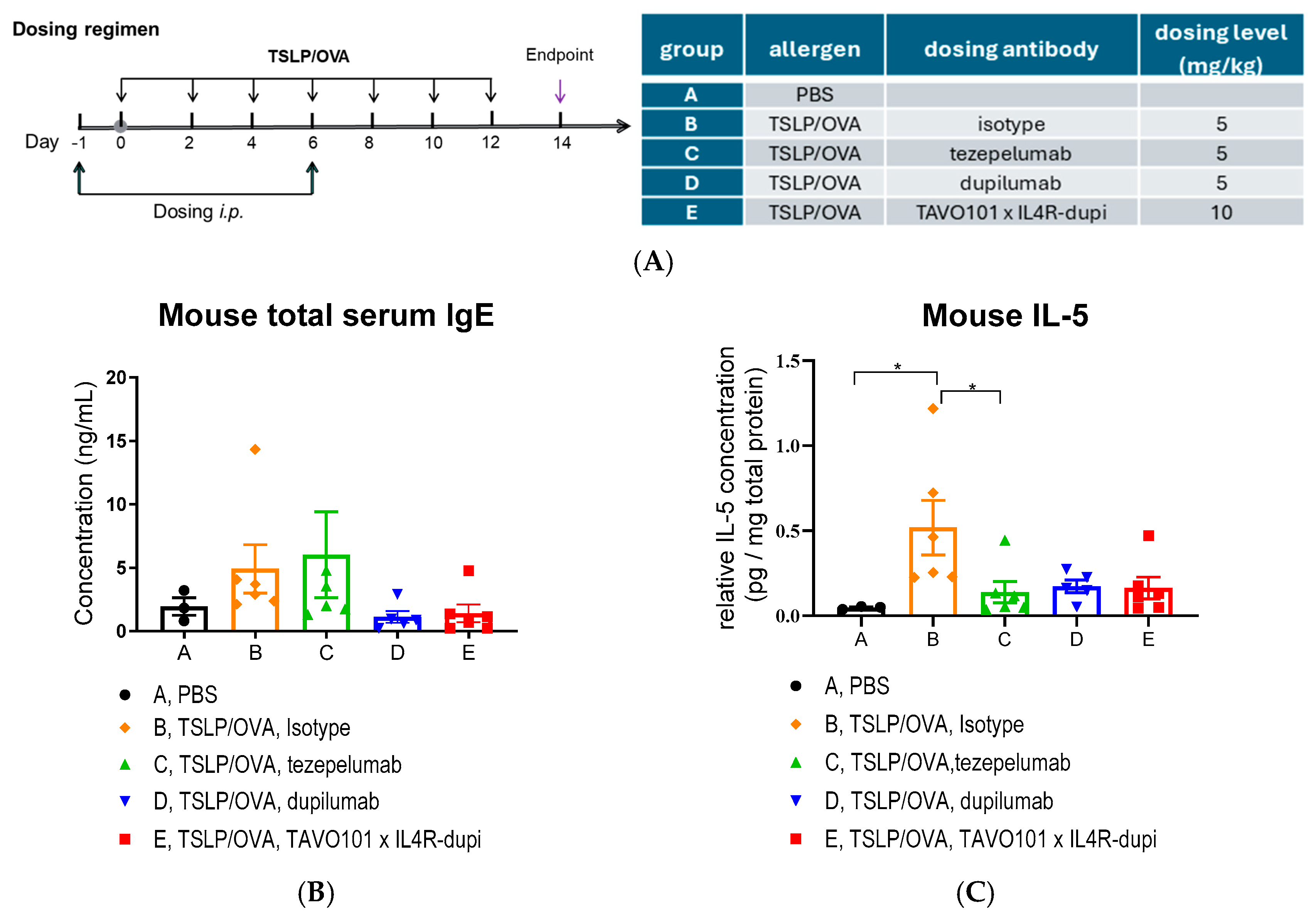
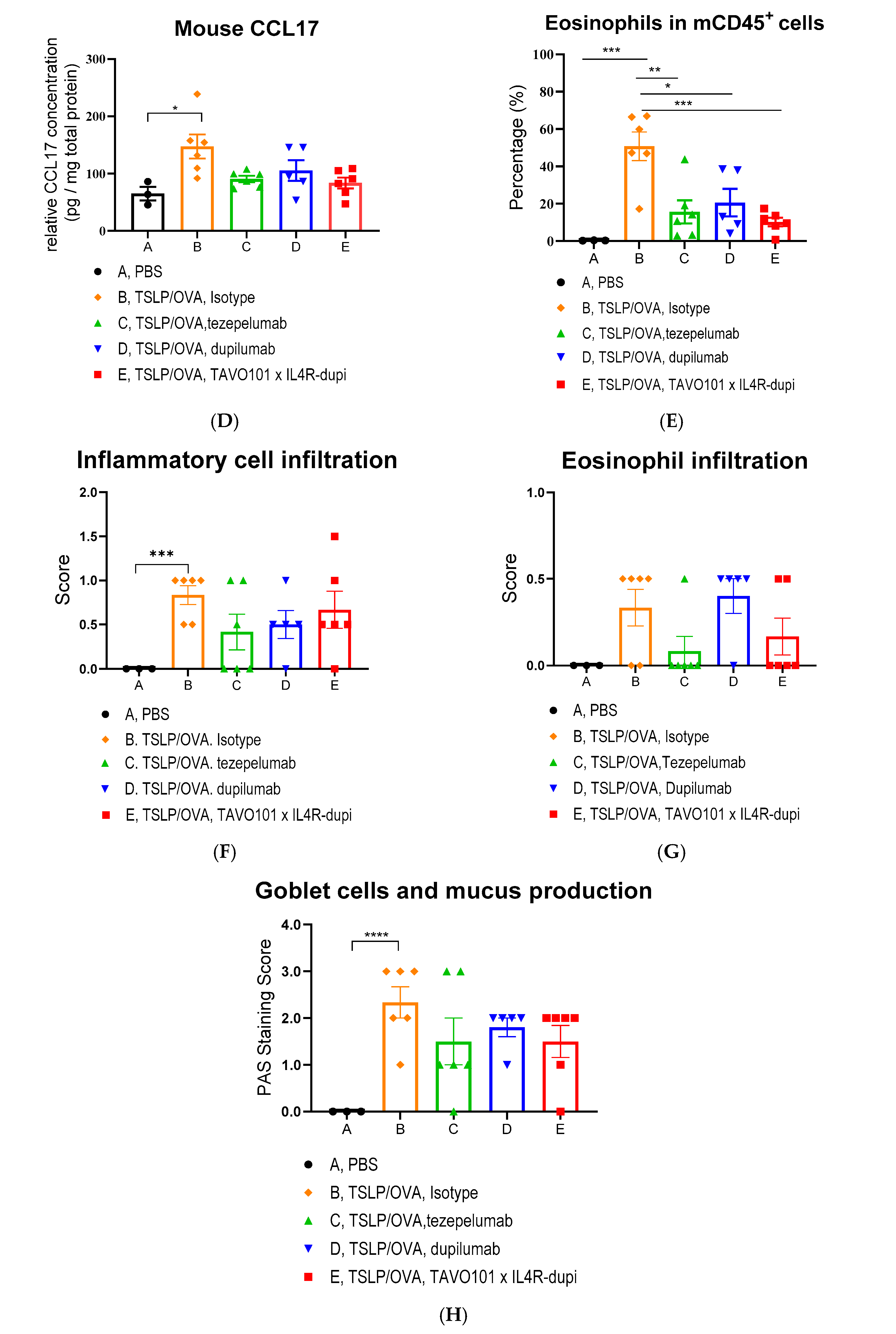
2.11. TSLP/OVA-Induced Asthma Model Using Humanized Mice
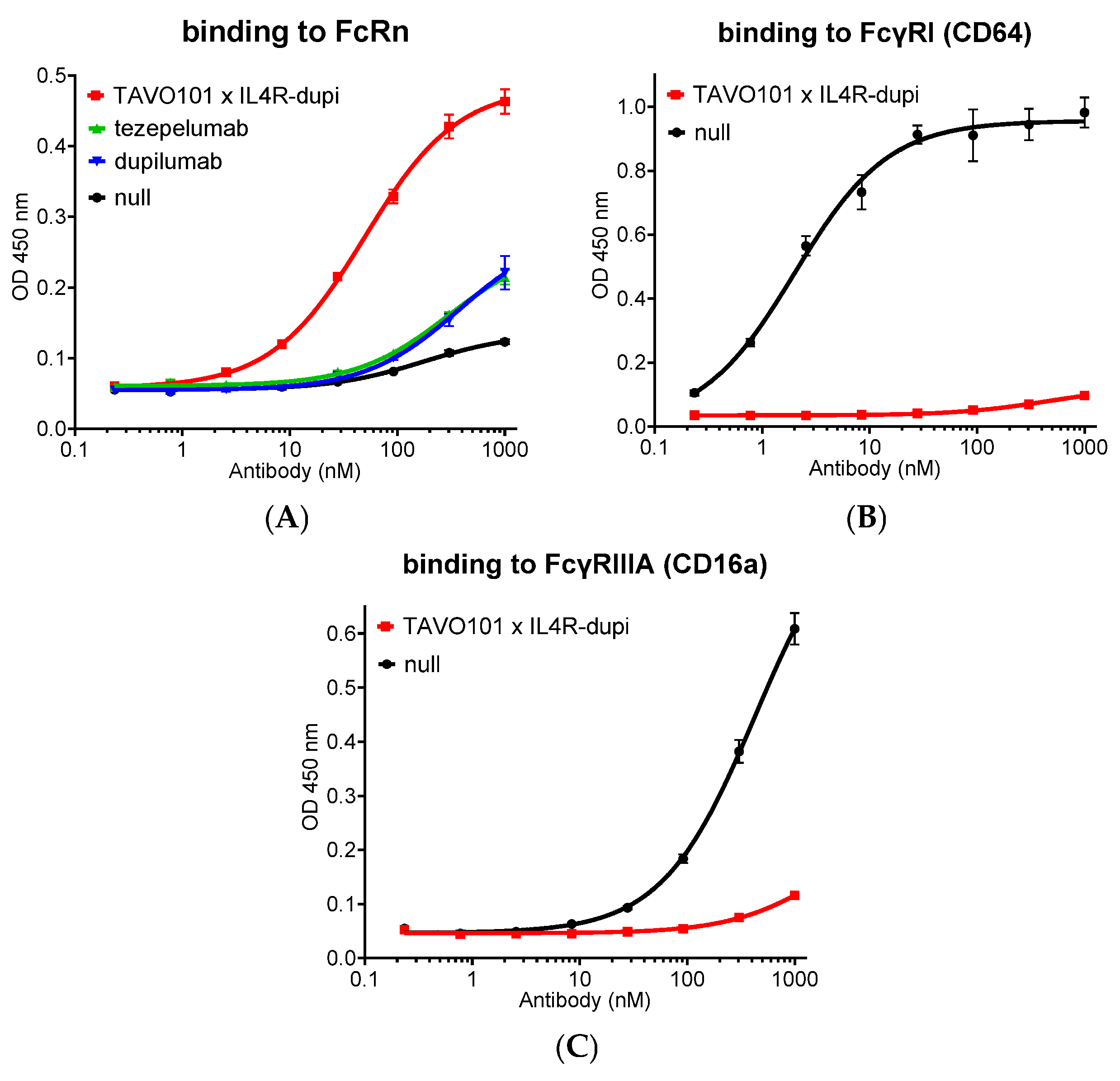
2.12. FcRn Binding Assay
2.13. FcγRI (CD64) and FcγRIIIA (CD16a) Binding Assay
3. Results
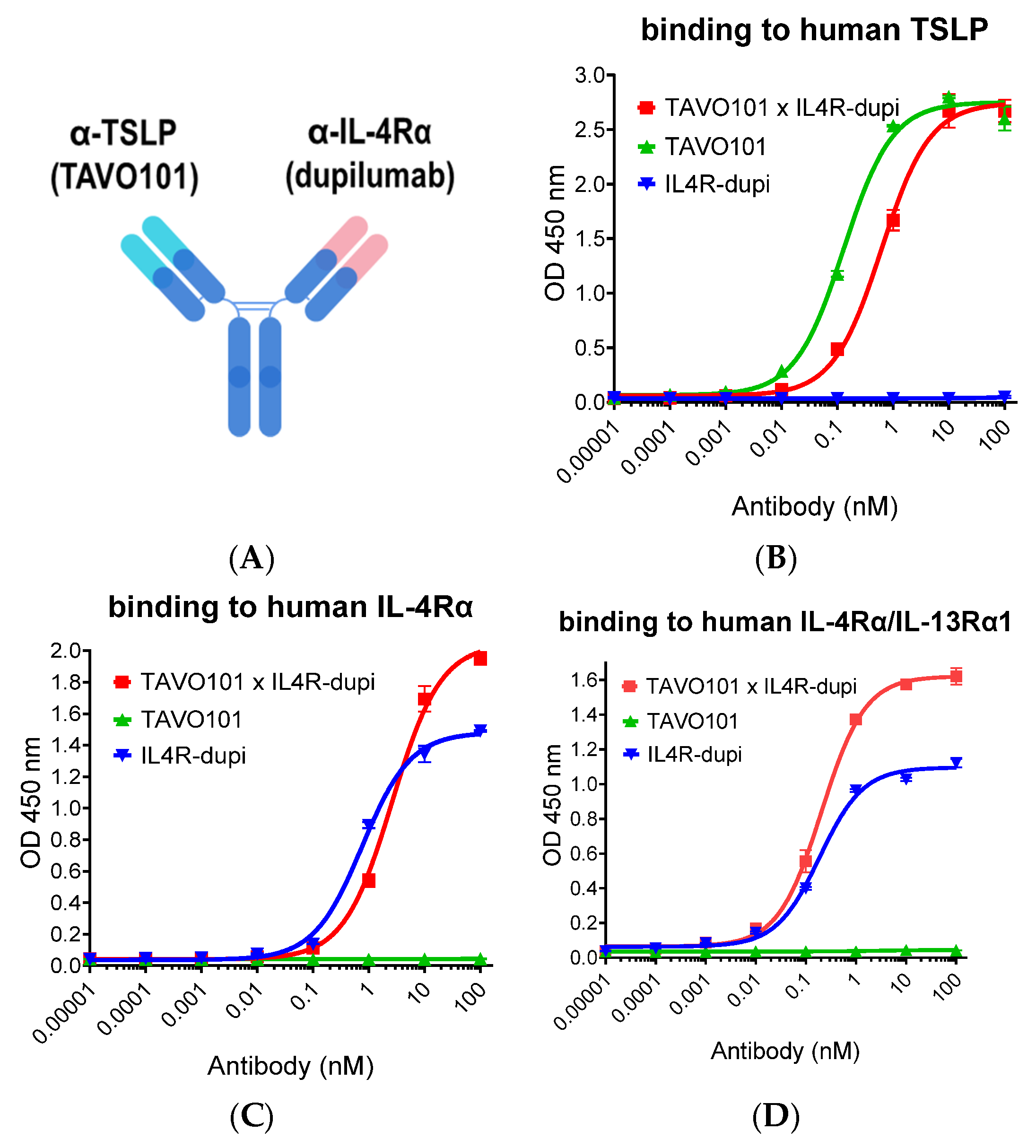
3.1. Generation of a Bispecific Antibody Binding to Both TSLP and IL-4Rα
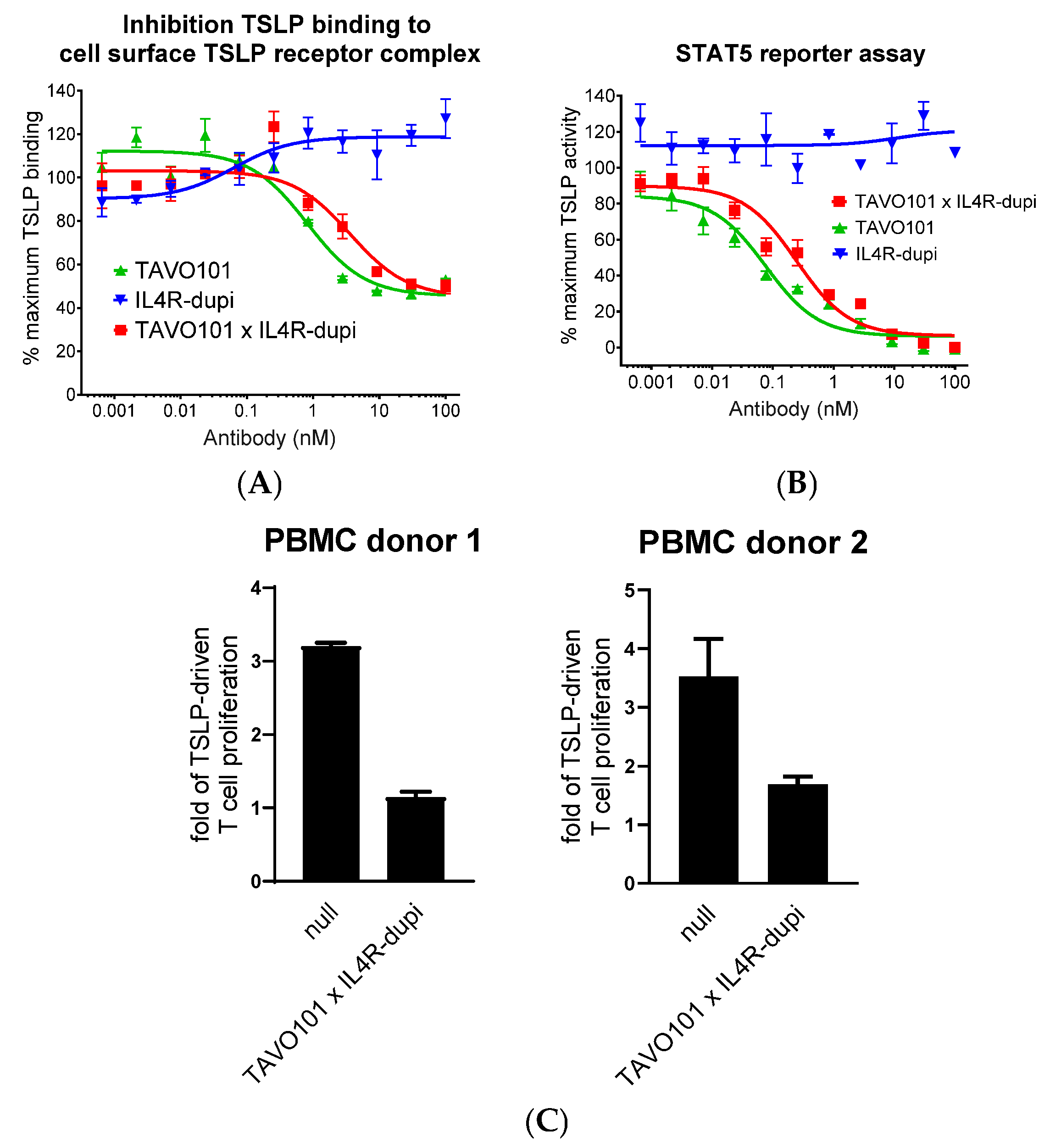
3.2. Neutralization of TSLP Activity by the Bispecific Antibody TAVO101 × IL4R-dupi
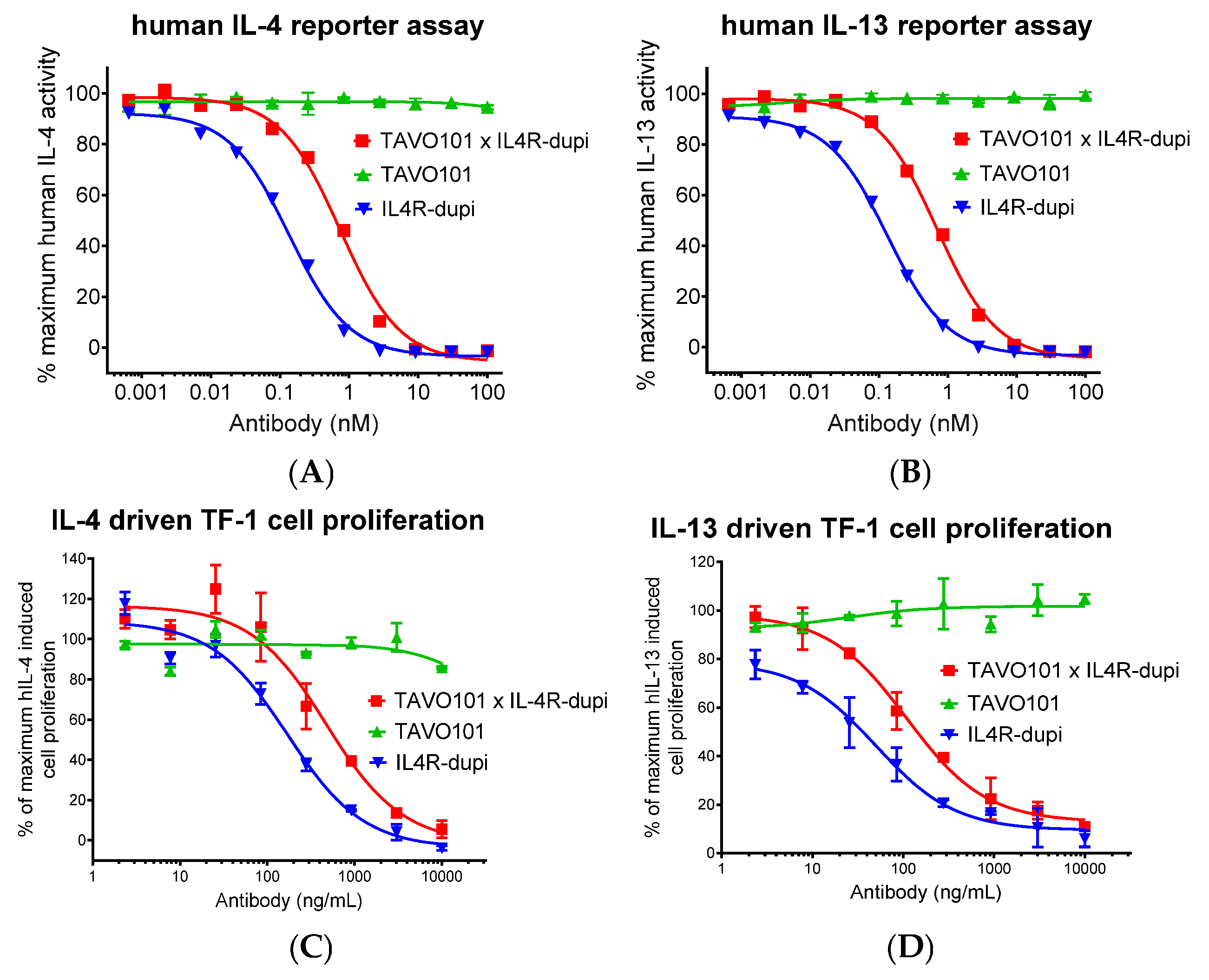
3.3. Neutralization of IL-4/IL-13 Activities by the Bispecific Antibody TAVO101 × IL4R-dupi
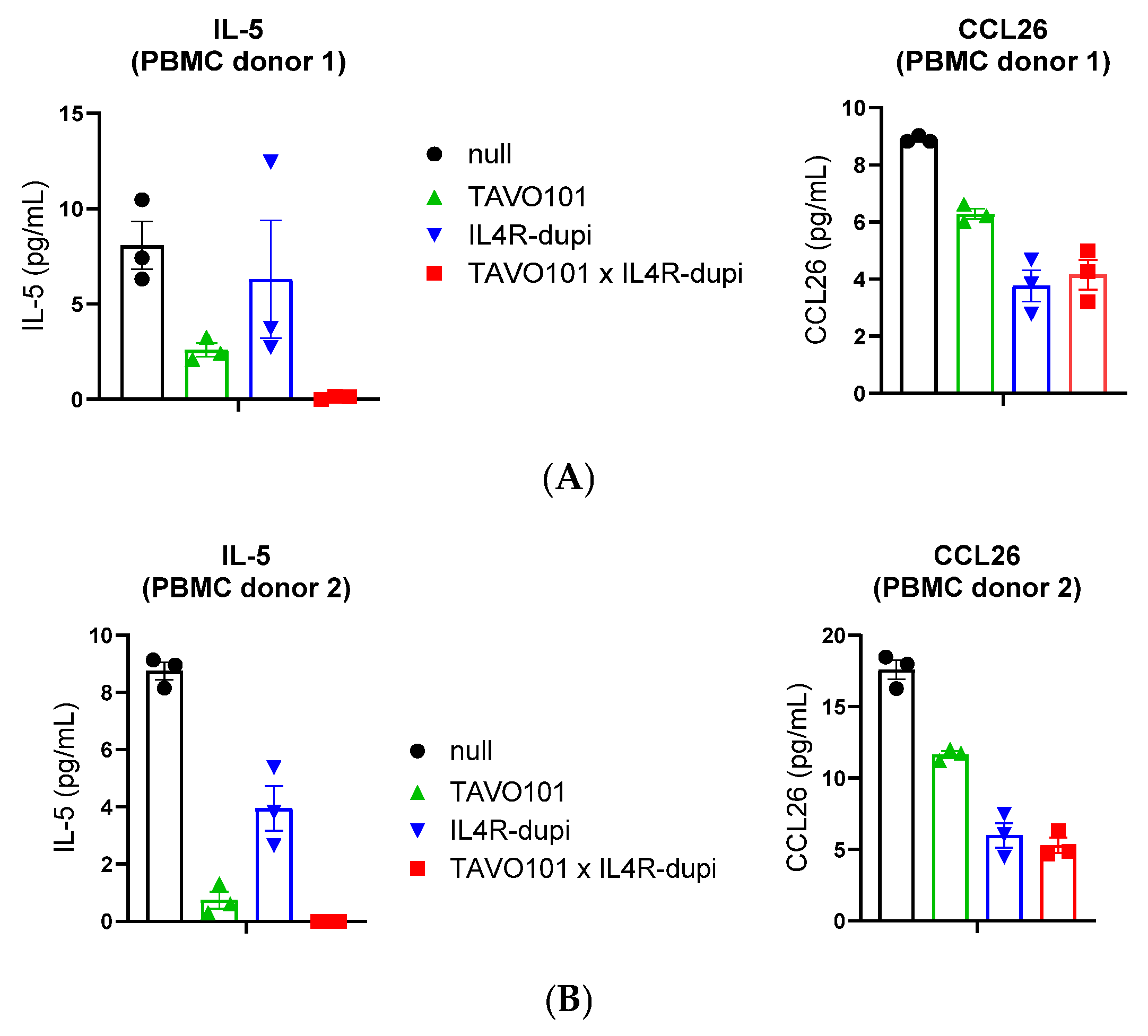
3.4. Neutralization of TSLP/IL-4/IL-13 Activities by BsAb TAVO101 × IL4R-dupi
3.5. Efficacy of BsAb TAVO101 × IL4R-dupi in a TSLP/OVA-Induced Asthma Model
3.6. Fc Engineering of TAVO101 × IL4R-dupi BsAb for Half-Life Extension and Reduced Effector Functions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ebina-Shibuya, R.; Leonard, W.J. Role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergy and beyond. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell 2021, 184, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, Y.; Dienger-Stambaugh, K.; Richgels, P.K.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Kartashov, A.V.; Barski, A.; Khurana Hershey, G.K.; Leonard, W.J.; Singh, H. TSLP signaling in CD4+ T cells programs a pathogenic T helper 2 cell state. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaam8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.F.; Roan, F.; Bell, B.D.; Stoklasek, T.A.; Kitajima, M.; Han, H. The biology of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). Adv. Pharmacol. 2013, 66, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Soumelis, V.; Watanabe, N.; Ito, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Malefyt Rde, W.; Omori, M.; Zhou, B.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP: An epithelial cell cytokine that regulates T cell differentiation by conditioning dendritic cell maturation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, Y.; Leonard, W.J. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: A new cytokine in asthma. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, C.L.; Barton, G.M.; Farr, A.G.; Medzhitov, R. A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, I.; Savvides, S.N. Modulation of Signaling Mediated by TSLP and IL-7 in Inflammation, Autoimmune Diseases, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, K.; van Schie, L.; Vyncke, L.; Bloch, Y.; Tavernier, J.; Pauwels, E.; Peelman, F.; Savvides, S.N. Structural basis of the proinflammatory signaling complex mediated by TSLP. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Sharma, J.; Raju, R.; Palapetta, S.M.; Prasad, T.S.; Huang, T.C.; Yoda, A.; Tyner, J.W.; van Bodegom, D.; Weinstock, D.M.; et al. TSLP signaling pathway map: A platform for analysis of TSLP-mediated signaling. Database 2014, 2014, bau007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlmann, A.; Sebastian, K.; Borowski, A.; Krause, S.; Friedrich, K. Signal transduction by the atopy-associated human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) receptor depends on Janus kinase function. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, Y.; Kashyap, M.; Robinson, G.W.; Sakamoto, K.; Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Wagner, K.U.; Leonard, W.J. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated STAT5 phosphorylation via kinases JAK1 and JAK2 reveals a key difference from IL-7-induced signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19455–19460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumelis, V.; Reche, P.A.; Kanzler, H.; Yuan, W.; Edward, G.; Homey, B.; Gilliet, M.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Lauerma, A.; et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.F. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, D.E.; Baumann, H.; Zhou, B.; Nivollet, S.; Farr, A.G.; Levin, S.D.; Ziegler, S.F. Uncoupling of proliferation and Stat5 activation in thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated signal transduction. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Luyimbazi, J.; Xu, X.; Schofield, B.; Neben, T.Y.; Karp, C.L.; Donaldson, D.D. Interleukin-13: Central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Type 2 cytokines: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, K.; Keegan, A.D.; Zamorano, J.; Ryan, J.J.; Paul, W.E. The IL-4 receptor: Signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 701–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, A.L.; Nasir, T.; Bucchieri, F.; Holloway, J.W.; Holgate, S.T.; Davies, D.E. IL-13 receptor alpha 2: A regulator of IL-13 and IL-4 signal transduction in primary human fibroblasts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPorte, S.L.; Juo, Z.S.; Vaclavikova, J.; Colf, L.A.; Qi, X.; Heller, N.M.; Keegan, A.D.; Garcia, K.C. Molecular and structural basis of cytokine receptor pleiotropy in the interleukin-4/13 system. Cell 2008, 132, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonte, M.G.; Donaldson, D.D.; Cheever, A.W.; Wynn, T.A. An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.H.; Schindler, U.; Smiley, S.T.; Grusby, M.J. Stat6 is required for mediating responses to IL-4 and for development of Th2 cells. Immunity 1996, 4, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Tanaka, T.; Shi, W.; Matsumoto, M.; Minami, M.; Kashiwamura, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature 1996, 380, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, N.M.; Qi, X.; Junttila, I.S.; Shirey, K.A.; Vogel, S.N.; Paul, W.E.; Keegan, A.D. Type I IL-4Rs selectively activate IRS-2 to induce target gene expression in macrophages. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.L.; Kraft, M. IL-13 in asthma and allergic disease: Asthma phenotypes and targeted therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 829–842, quiz 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, W.E. History of interleukin-4. Cytokine 2015, 75, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, N.; Wills-Karp, M. IL-4 and IL-13 signaling in allergic airway disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Homer, R.J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Geba, G.P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Elias, J.A. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnes, J.R.; Molfino, N.A.; Colice, G.; Martin, U.; Corren, J.; Menzies-Gow, A. Targeting TSLP in Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, A.A.; Dimond, C.; Choy, D.F.; Pappu, R.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Mohan, D.; Chung, K.F. Targeting interleukin-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin pathways for novel pulmonary therapeutics in asthma and COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2023, 32, 220144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Deng, F.; Chang, B.; Zhou, J.; Sun, L. The Role of TSLP in Atopic Dermatitis: From Pathogenetic Molecule to Therapeutical Target. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 7697699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corren, J.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP: From allergy to cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, E.B.; Ruff, B.P.; Filuta, A.L.; Chang, W.C.; Shik, D.; Khurana Hershey, G.K. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin rather than IL-33 drives food allergy after epicutaneous sensitization to food allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1660–1666.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jeong, D.Y.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Eisenhut, M.; Shin, J.I. Insight into the role of TSLP in inflammatory bowel diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, E.; Pattarini, L.; Martinez-Cingolani, C.; Meller, S.; Donnadieu, M.H.; Bogiatzi, S.I.; Fernandez, M.I.; Touzot, M.; Bichet, J.C.; Reyal, F.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin links keratinocytes and dendritic cell-derived IL-23 in patients with psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwarsa, O.; Dharmadji, H.P.; Sutedja, E.; Herlina, L.; Sori, P.R.; Hindritiani, R.; Dwiyana, R.F.; Gunawan, H. Skin tissue expression and serum level of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Dermatol. Rep. 2019, 11, 8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Ozawa, T.; Hatsushika, K.; Ando, T.; Takano, S.; Wako, M.; Suenaga, F.; Ohnuma, Y.; Ohba, T.; Katoh, R.; et al. A possible role for TSLP in inflammatory arthritis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret, F.M.; Hack, C.E.; van der Wurff-Jacobs, K.M.; Radstake, T.R.; Lafeber, F.P.; van Roon, J.A. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, a novel proinflammatory mediator in rheumatoid arthritis that potently activates CD1c+ myeloid dendritic cells to attract and stimulate T cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protti, M.P.; De Monte, L. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Cancer: Th2-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.M.; Zhao, C.N.; Leng, J.; Leng, R.X.; Ye, D.Q.; Zheng, S.G.; Pan, H.F. Interleukin-13: A promising therapeutic target for autoimmune disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 45, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaszko, M.; Bialy, S.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Significance of Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 in Inflammatory Arthritis. Cells 2021, 10, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; O'Byrne, P.M.; Boulet, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Cockcroft, D.; Bigler, J.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Boedigheimer, M.; Davis, B.E.; Dias, C.; et al. Effects of an anti-TSLP antibody on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Ford, L.; Pearlman, D.; Spector, S.; Sher, L.; Skobieranda, F.; Wang, L.; Kirkesseli, S.; Rocklin, R.; Bock, B.; et al. Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Gooderham, M.; Cather, J.C.; Weisman, J.; Pariser, D.; Simpson, E.L.; Papp, K.A.; Hong, H.C.; Rubel, D.; et al. Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids (LIBERTY AD CHRONOS): A 1-year, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2287–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Blauvelt, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Worm, M.; Lynde, C.; Lacour, J.P.; Spelman, L.; Katoh, N.; Saeki, H.; Poulin, Y.; et al. Tralokinumab for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from two 52-week, randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase III trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2). Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Toth, D.; Bieber, T.; Alexis, A.F.; Elewski, B.E.; Pink, A.E.; Hijnen, D.; Jensen, T.N.; Bang, B.; Olsen, C.K.; et al. Tralokinumab plus topical corticosteroids for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from the double-blind, randomized, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase III ECZTRA 3 trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Thyssen, J.P.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bieber, T.; Serra-Baldrich, E.; Simpson, E.; Rosmarin, D.; Elmaraghy, H.; Meskimen, E.; Natalie, C.R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of lebrikizumab in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: 52-week results of two randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled phase III trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Parnes, J.R.; She, D.; Crouch, S.; Rees, W.; Mo, M.; van der Merwe, R. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bult, L.; Thelen, J.C.; Rauh, S.P.; Veen, J.; Braunstahl, G.J. Dupilumab responder types and predicting factors in patients with type 2 severe asthma: A real-world cohort study. Respir. Med. 2024, 231, 107720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Sjobring, U.; Peterffy, A.; Wessman, P.; Bowen, K.; Piper, E.; Colice, G.; Brightling, C.E. Tralokinumab for severe, uncontrolled asthma (STRATOS 1 and STRATOS 2): Two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, E.; Brightling, C.; Niven, R.; Oh, C.; Faggioni, R.; Poon, K.; She, D.; Kell, C.; May, R.D.; Geba, G.P.; et al. A phase II placebo-controlled study of tralokinumab in moderate-to-severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiteren, A.; Bontinck, L.; Conickx, G.; Vigan, M.; Dervaux, N.; Gassiot, M.; Bas, S.; Suratt, B.; Staudinger, H.; Krupka, E. A first-in-human, single and multiple dose study of lunsekimig, a novel anti-TSLP/anti-IL-13 NANOBODY(R) compound, in healthy volunteers. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Floc'h, A.; Allinne, J.; Nagashima, K.; Scott, G.; Birchard, D.; Asrat, S.; Bai, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Martin, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Ralpha antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.R.; Kosloski, M.P.; Xu, C.; Davis, J.D.; Kamal, M.A. Dupilumab: Mechanism of action, clinical, and translational science. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kong, Y.; Qiu, T.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, J. Development of a novel humanized anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody, QX008N, and exploration of combination therapy of anti-TSLP antibody and anti-IL-4R antibody. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Meesters, J.I.; de Goeij, B.E.; van den Bremer, E.T.; Neijssen, J.; van Kampen, M.D.; Strumane, K.; Verploegen, S.; Kundu, A.; Gramer, M.J.; et al. Efficient generation of stable bispecific IgG1 by controlled Fab-arm exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5145–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Yu, M.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P.; Mu, G.; Tam, S.H.; Cho, M.; Tornetta, M.; Han, C.; Fung, M.C.; et al. A novel monoclonal antibody against human thymic stromal lymphopoietin for the treatment of TSLP-mediated diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1442588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, I.; Watanabe, N.; Arima, K.; Liu, Y.J.; Leonard, W.J. Cutting edge: Direct action of thymic stromal lymphopoietin on activated human CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6720–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Takaku, F.; Miyajima, A. IL-1 up-regulates the expression of cytokine receptors on a factor-dependent human hemopoietic cell line, TF-1. Int. Immunol. 1991, 3, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommelaere, H.; Brigé, A.; Cornelis, S.; Dombrecht, B.; Lorent, E.; Rieger, M.; Soos, T.; Park, J.; Weigle, B.; Erb, K. Polypeptides Comprising Immunoglobulin Single Variable Domains Targeting Il-13 And TSLP. WO 2021/116182 A1, 9 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Borriello, F.; Iannone, R.; Di Somma, S.; Vastolo, V.; Petrosino, G.; Visconte, F.; Raia, M.; Scalia, G.; Loffredo, S.; Varricchi, G.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Elicited TSLPR Expression Enriches a Functionally Discrete Subset of Human CD14+ CD1c+ Monocytes. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3426–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, B.J.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Narayan, K.; Wollacott, A.M.; Babcock, G.J.; Shriver, Z.; Viswanathan, K. Extending human IgG half-life using structure-guided design. mAbs 2018, 10, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezareh, M.; Hessell, A.J.; Jensen, R.C.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Parren, P.W. Effector function activities of a panel of mutants of a broadly neutralizing antibody against human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 12161–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Fung, I.; Zhang, D.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P.; Tam, S.; Chiu, M.L.; Fung, M.C. Phase 1 Safety and Pharmacokinetics Study of TAVO101, an Anti-Human Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Antibody for the Treatment of Allergic Inflammatory Conditions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 65, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.E.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Bando, J.K.; Sullivan, B.M.; Ho, I.C.; Locksley, R.M. Divergent expression patterns of IL-4 and IL-13 define unique functions in allergic immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 13, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akenroye, A.; Boyce, J.A.; Kita, H. Targeting alarmins in asthma: From bench to clinic. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 155, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Reinhardt, R.L. The differential expression of IL-4 and IL-13 and its impact on type-2 immunity. Cytokine 2015, 75, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, G.J.; Fallon, P.G.; Emson, C.L.; Grencis, R.K.; McKenzie, A.N. Simultaneous disruption of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 defines individual roles in T helper cell type 2-mediated responses. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Ruddy, M.K.; Pavord, I.D.; Israel, E.; Rabe, K.F.; Ford, L.B.; Maspero, J.F.; Abdulai, R.M.; Hu, C.C.; Martincova, R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Itepekimab in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1656–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, P.; DiCioccio, A.T.; Davis, J.D.; Li, M.; Ardeleanu, M.; Graham, N.; Soltys, R. Exploratory Population PK Analysis of Dupilumab, a Fully Human Monoclonal Antibody Against IL-4Ralpha, in Atopic Dermatitis Patients and Normal Volunteers. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2016, 5, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.; Chen, P.; Jin, Y.; Huang, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, F.; Chiu, M.L.; Zhang, D. A Bispecific Antibody Blocking Both TSLP and IL-4Rα for the Treatment of Allergic Inflammatory Diseases. Cells 2025, 14, 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221747
Yu M, Chen P, Jin Y, Huang S, Jiang H, Zhou F, Chiu ML, Zhang D. A Bispecific Antibody Blocking Both TSLP and IL-4Rα for the Treatment of Allergic Inflammatory Diseases. Cells. 2025; 14(22):1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221747
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Mingcan, Peng Chen, Ying Jin, Sheng Huang, Hao Jiang, Fulai Zhou, Mark L. Chiu, and Di Zhang. 2025. "A Bispecific Antibody Blocking Both TSLP and IL-4Rα for the Treatment of Allergic Inflammatory Diseases" Cells 14, no. 22: 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221747
APA StyleYu, M., Chen, P., Jin, Y., Huang, S., Jiang, H., Zhou, F., Chiu, M. L., & Zhang, D. (2025). A Bispecific Antibody Blocking Both TSLP and IL-4Rα for the Treatment of Allergic Inflammatory Diseases. Cells, 14(22), 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221747





