Exploring the Correlation Between NLRP3 Activation and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the Heart of a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Heart Tissue Collection from Mice
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Histological Staining
2.4.1. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.4.2. Masson’s Trichrome Staining
2.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Microscopy and Image Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
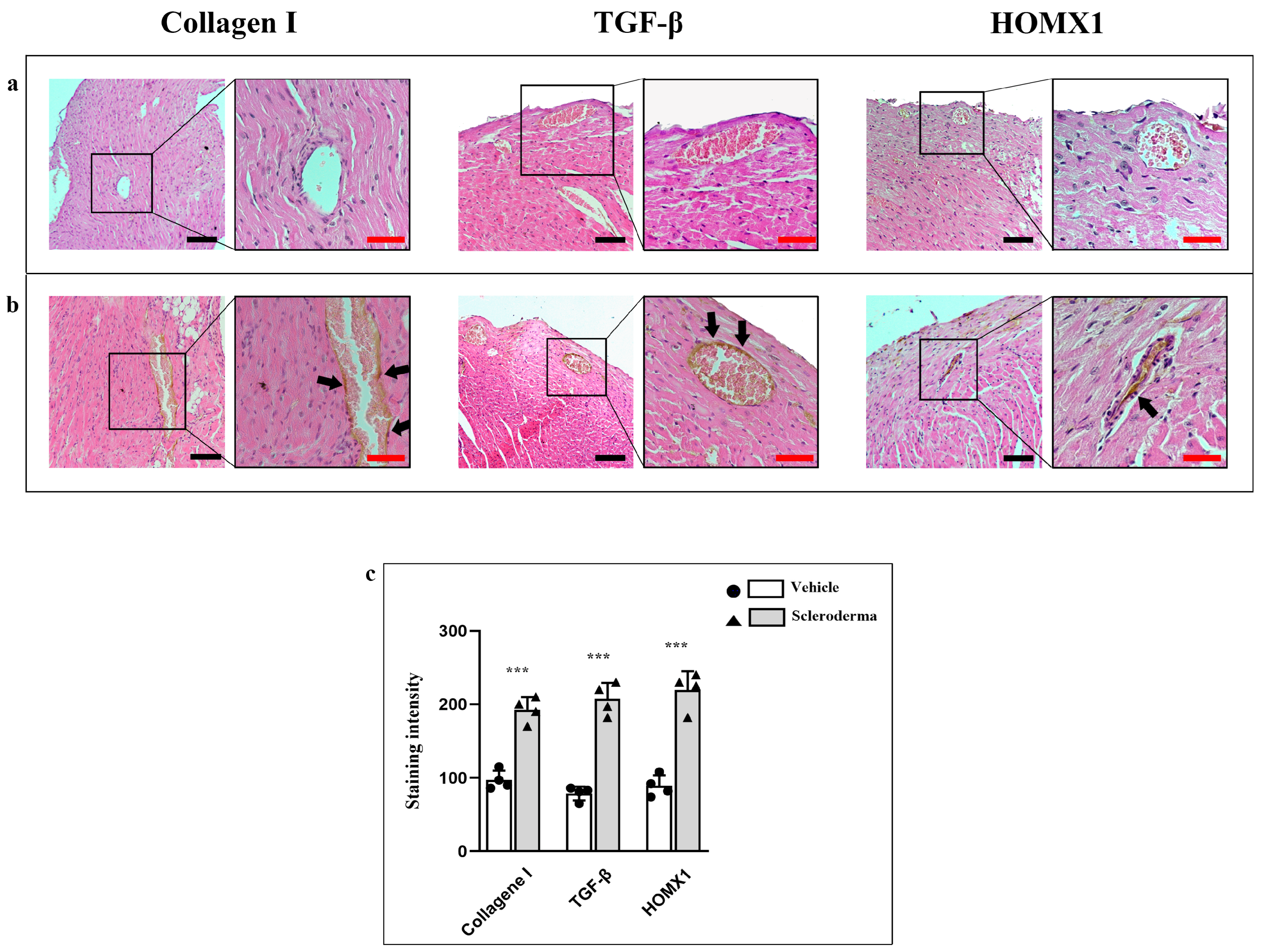
3.1. Heart Structure Evaluation
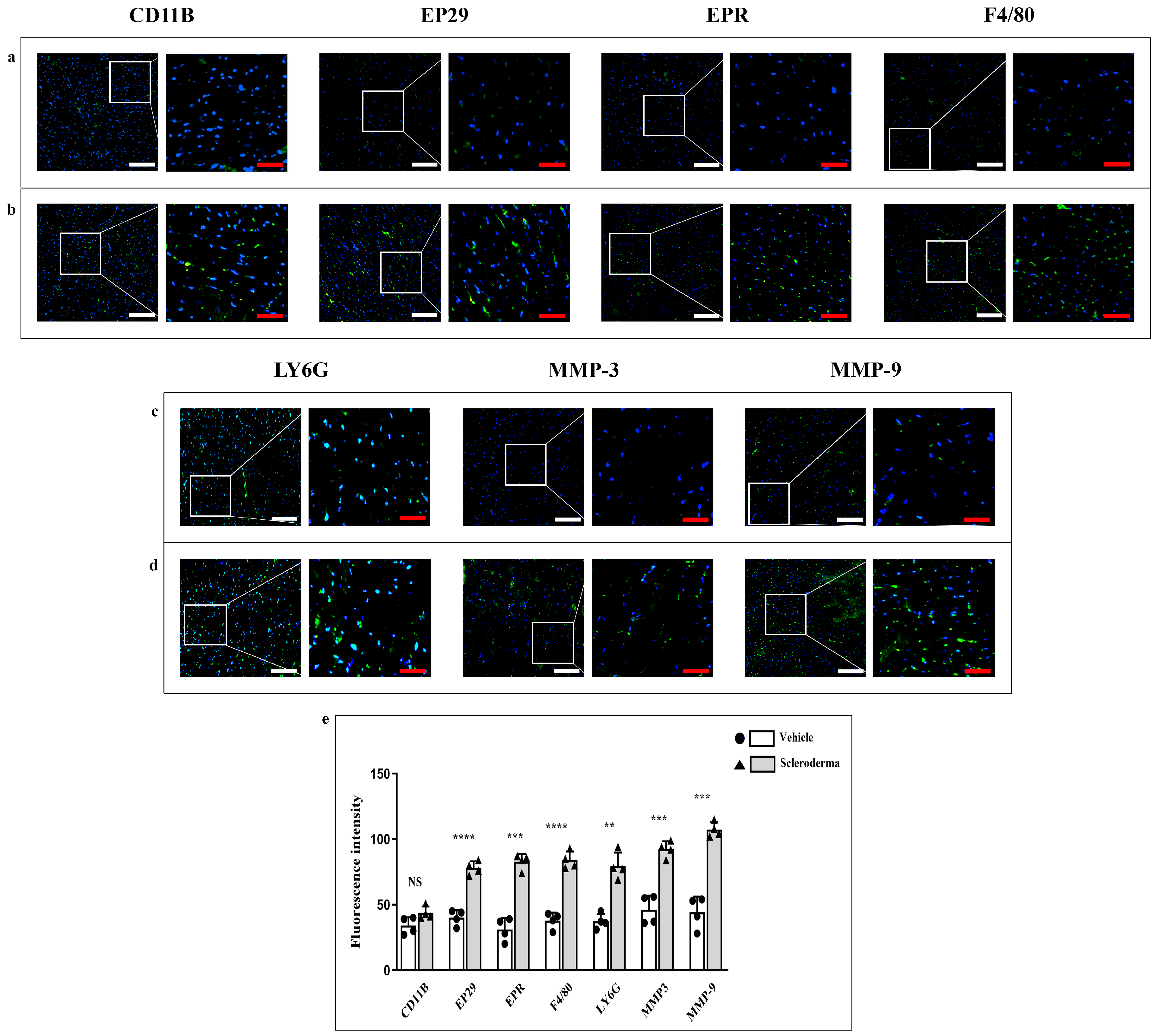
3.2. Immunofluorescence Analysis of Structural Proteins and Inflammatory/Pro-Fibrotic Markers
3.3. Immunoenzymatic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, I.; Faria, R.; Vita, P.; Vasconcelos, C. Systemic Sclerosis Refractory Disease: From the Skin to the Heart. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Jinnin, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kuwana, M.; Goto, D.; Sato, S.; Takehara, K.; Hatano, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Mugii, N.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria, Severity Classification and Guidelines of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 633–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis: An Understanding Based on a Common Pathologic Cascade across Multiple Organs and Additional Organ-Specific Pathologies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecasteele, E.H.; De Pauw, M.; Brusselle, G.; Decuman, S.; Piette, Y.; De Keyser, F.; Smith, V. The Heart and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis. Acta Clin. Belg. 2016, 71, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaci, M.; Schinocca, C.; Bosco, Y.D.; Ronsivalle, G.; Guggino, G.; de Andres, I.; Russo, A.A.; Sambataro, D.; Sambataro, G.; Malatino, L. Heart Valve Abnormalities in Systemic Sclerosis Patients: A Multicenter Cohort Study and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Rheumatol. Pract. Rep. Rheum. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 28, e95–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Mavrogeni, S.I. Diagnosis and Management of Primary Heart Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2024, 36, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, K.A.L.; Mueller, I.I.; Eppler, D.; Zuern, C.S.; Seizer, P.; Kramer, U.; Koetter, I.; Roecken, M.; Kandolf, R.; Gawaz, M.; et al. Clinical and Histopathological Features of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Undergoing Endomyocardial Biopsy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogeni, S.; Pepe, A.; Gargani, L.; Bruni, C.; Quaia, E.; Kitas, G.D.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Cardiac Inflammation and Fibrosis Patterns in Systemic Sclerosis, Evaluated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Update. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 58, 152126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.D.; Nauffal, V.; Ambale-Venkatesh, B.; Vasconcellos, H.D.; Wu, C.; Bahrami, H.; Tracy, R.P.; Cushman, M.; Bluemke, D.A.; Lima, J.A.C. Association Between Inflammatory Markers and Myocardial Fibrosis. Hypertension 2018, 72, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuruchi, M.; Mannino, F.; Imbesi, C.; Pallio, G.; Vermiglio, G.; Bagnato, G.; Minutoli, L.; Bitto, A.; Squadrito, F.; Irrera, N. Biglycan Involvement in Heart Fibrosis: Modulation of Adenosine 2A Receptor Improves Damage in Immortalized Cardiac Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uccello, G.; Bonacchi, G.; Rossi, V.A.; Montrasio, G.; Beltrami, M. Myocarditis and Chronic Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy, from Acute Inflammation to Chronic Inflammatory Damage: An Update on Pathophysiology and Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, A.; Toldo, S.; Marchetti, C.; Kron, J.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and the Inflammasome as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1260–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Escames, G.; Lei, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Jing, T.; Yao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: Contributions to Inflammation-Related Diseases. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrand, J.; Soyfoo, M.S. Involvement of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H.Y.; Migliarino, S.; Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Guzik, T.J. Hypertension: Focus on Autoimmunity and Oxidative Stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, S.A.; Ashour, N.A.; Marawan, M.E.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Fibrosis: Types, Effects, Markers, Mechanisms for Disease Progression, and Its Relation with Oxidative Stress, Immunity, and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Yazdi, A.S.; Menu, P.; Tschopp, J. A Role for Mitochondria in NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Nature 2011, 469, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal Research: Reporting in Vivo Experiments: The ARRIVE Guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servettaz, A.; Goulvestre, C.; Kavian, N.; Nicco, C.; Guilpain, P.; Chéreau, C.; Vuiblet, V.; Guillevin, L.; Mouthon, L.; Weill, B.; et al. Selective Oxidation of DNA Topoisomerase 1 Induces Systemic Sclerosis in the Mouse. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5855–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, P.A.; Khalid, N.; Carnahan, K.E.; Westfall, M.V.; Stegemann, J.P. Substrate Stiffness Affects Sarcomere and Costamere Structure and Electrophysiological Function of Isolated Adult Cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Pathol. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2013, 22, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambova, S. Cardiac Manifestations in Systemic Sclerosis. World J. Cardiol. 2014, 6, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, X.M.; Bottini, N.; Boin, F.; Marbán, E. Cardiac Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Critical Review of Knowledge Gaps and Opportunities. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2025, 10, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, S.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, H.J.; Park, E.-J.; Kim, I.S.; Jo, E.-K. Updated Insights into the Molecular Networks for NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 563–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, K.; Gong, X.; Huang, R.; Zhou, C.; Mao, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Enhanced Oxidative Stress Aggravates BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Promoting Cellular Senescence through Enhancing NLRP3 Activation. Life Sci. 2024, 358, 123128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra-Torres, J.S.; Pinzón-Fernández, M.V.; Ocampo-Posada, M.; Nati-Castillo, H.A.; Jiménez Hincapie, L.A.; Cadrazo-Gil, E.J.; Arias-Intriago, M.; Rojas-Cadena, M.; Tello-De-la-Torre, A.; Osejos, W.; et al. Inflammasomes and Signaling Pathways: Key Mechanisms in the Pathophysiology of Sepsis. Cells 2025, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piera-Velazquez, S.; Li, Z.; Jimenez, S.A. Role of Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EndoMT) in the Pathogenesis of Fibrotic Disorders. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, D.M.; Pioli, P.A. Macrophages in Systemic Sclerosis: Novel Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, S.; Agarwal, S.K. Macrophages and Cadherins in Fibrosis and Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwi, Y.; Westra, J.; van Goor, H.; Burgess, J.K.; Denton, C.P.; Mulder, D.J. Macrophages as Determinants and Regulators of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetti, M.; Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; De Paulis, A.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction and Dermal Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talotta, R.; Atzeni, F.; Ditto, M.C.; Gerardi, M.C.; Batticciotto, A.; Bongiovanni, S.; Puttini, P.S. Certainties and Uncertainties Concerning the Contribution of Pericytes to the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, P.; Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Capece, D.; Zazzeroni, F.; Liakouli, V.; Pantano, I.; Berardicurti, O.; Carubbi, F.; Pecetti, G.; et al. The Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Systemic Sclerosis Is Induced by Endothelin-1 and Transforming Growth Factor-β and May Be Blocked by Macitentan, a Dual Endothelin-1 Receptor Antagonist. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostin, S.; Hein, S.; Arnon, E.; Scholz, D.; Schaper, J. The Cytoskeleton and Related Proteins in the Human Failing Heart. Heart Fail. Rev. 2000, 5, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centofanti, A.; Vermiglio, G.; Cutroneo, G.; Favaloro, A.; Picciolo, G.; Festa, F.; Anastasi, G.P. Dystrophin-Glycoprotein Complex Behavior in Sternocleidomastoid Muscle of High- and Low-Ranking Baboons: A Possible Phylogenetic Arrangement. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutroneo, G.; Centofanti, A.; Speciale, F.; Rizzo, G.; Favaloro, A.; Santoro, G.; Bruschetta, D.; Milardi, D.; Micali, A.; Di Mauro, D.; et al. Sarcoglycan Complex in Masseter and Sternocleidomastoid Muscles of Baboons: An Immunohistochemical Study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2015, 59, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Kharkwal, G.; Mishra, R.; Singh, G. Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Signaling in Heavy Metals-Induced Oxidative Stress. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Wu, C.; Tang, L.; Bian, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Targeting Epigenetic and Post-Translational Modifications of NRF2: Key Regulatory Factors in Disease Treatment. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, V.; Sorrenti, V.; Grosso, S.; Vanella, L. Heme Oxygenase-1 Signaling and Redox Homeostasis in Physiopathological Conditions. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, S.W. Heme Oxygenase-1: An Anti-Inflammatory Effector in Cardiovascular, Lung, and Related Metabolic Disorders. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardali, E.; Sanchez-Duffhues, G.; Gomez-Puerto, M.C.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-β-Induced Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Fibrotic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caja, L.; Dituri, F.; Mancarella, S.; Caballero-Diaz, D.; Moustakas, A.; Giannelli, G.; Fabregat, I. TGF-β and the Tissue Microenvironment: Relevance in Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Antibody | Species | Dilution | Catalog#/Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-sarcoglycan | mouse | 1:150 | SC-390647 (SantaCruzBiotecnology, Dallas, TX, USA) |
| γ-sarcoglycan | mouse | 1:150 | SC-515628 (SantaCruzBiotecnology) |
| Dystrophin | mouse | 1:50 | NCLDYS2 (Novocatsra, Wetzlar, Germany) |
| β-Dystroglycan | mouse | 1:250 | SC-33702 (SantaCruzBiotecnology) |
| Talin | mouse | 1:500 | T3287 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) |
| Vinculin | mouse | 1:500 | V9131 (Sigma-Aldrich) |
| CD11B | rat | 1:250 | AB8878 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) |
| EP29 | rabbit | 1:250 | AB75853 (Abcam) |
| EPR | rabbit | 1:250 | AB208670 (Abcam) |
| F4/80 | rat | 1:250 | AB6640 (Abcam) |
| LY6G | rat | 1:250 | AB210204 (Abcam) |
| MMP-3 | rabbit | 1:250 | AB52915 (Abcam) |
| MMP-9 | rabbit | 1:250 | AB283575 (Abcam) |
| Caspase-1 | rabbit | 1:100 | STJ92017 (St John’s, Anaheim, CA, USA) |
| IL-1β | mouse | 1:250 | SC-52012 (SantaCruzBiotecnology) |
| NLRP-3 | rabbit | 1:250 | AB263899 (Abcam) |
| α-SMA | mouse | 1:500 | SAB5700835 (Sigma-Aldrich) |
| CD31 | rabbit | 1:100 | AB222783 (Abcam) |
| Vimentin | rabbit | 1:1500 | 100619 (GeneTex, Irvine, CA, USA) |
| NOS | mouse | 1:200 | SC-7271 (SantaCruzBiotecnology) |
| NRF-2 | Rabbit | 1:100 | STJ97502 (St John’s) |
| HOMX1 | Rabbit | 1:150 | SC-390991 (SantaCruzBiotecnology) |
| TGF-β | mouse | 1:250 | SC-130348 (SantaCruzBiotecnology) |
| Collagen I | rabbit | 1:100 | PA1-26204 TermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| Antibody | Species | Dilution | Catalog#/Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescein anti-rat | goat | 1:100 | AP136F (Chemicon, Bangalore, India) |
| FITC anti-rabbit | goat | 1:100 | 111-096-045 (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA) |
| Alexa FluorTM | goat | 1:800 | A-11001 (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irrera, N.; De Filippis, L.; Labellarte, D.; Freni, J.; Santoro, G.; Favaloro, A.; Nicita, F.; Centofanti, A.; Vermiglio, G. Exploring the Correlation Between NLRP3 Activation and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the Heart of a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Cells 2025, 14, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211679
Irrera N, De Filippis L, Labellarte D, Freni J, Santoro G, Favaloro A, Nicita F, Centofanti A, Vermiglio G. Exploring the Correlation Between NLRP3 Activation and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the Heart of a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Cells. 2025; 14(21):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211679
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrrera, Natasha, Lidia De Filippis, Davide Labellarte, Josè Freni, Giuseppe Santoro, Angelo Favaloro, Fabiana Nicita, Antonio Centofanti, and Giovanna Vermiglio. 2025. "Exploring the Correlation Between NLRP3 Activation and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the Heart of a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis" Cells 14, no. 21: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211679
APA StyleIrrera, N., De Filippis, L., Labellarte, D., Freni, J., Santoro, G., Favaloro, A., Nicita, F., Centofanti, A., & Vermiglio, G. (2025). Exploring the Correlation Between NLRP3 Activation and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the Heart of a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Cells, 14(21), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211679









