C-Kit Is Essential for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch In Vitro and In Vivo After Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Model and Right Carotid Artery Ligation
2.2. Isolation of Primary Murine Aortic SMCs and Maintenance in Culture
2.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. 5-Bromo-2′-Deoxyuridine (BrdU) Incorporation Assay
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. BAC c-Kit Vector Generation and Transfection in c-kitw/+ CSCs
2.9. Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation
2.10. PDGF-BB Cell Treatment
2.11. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Analysis
2.12. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
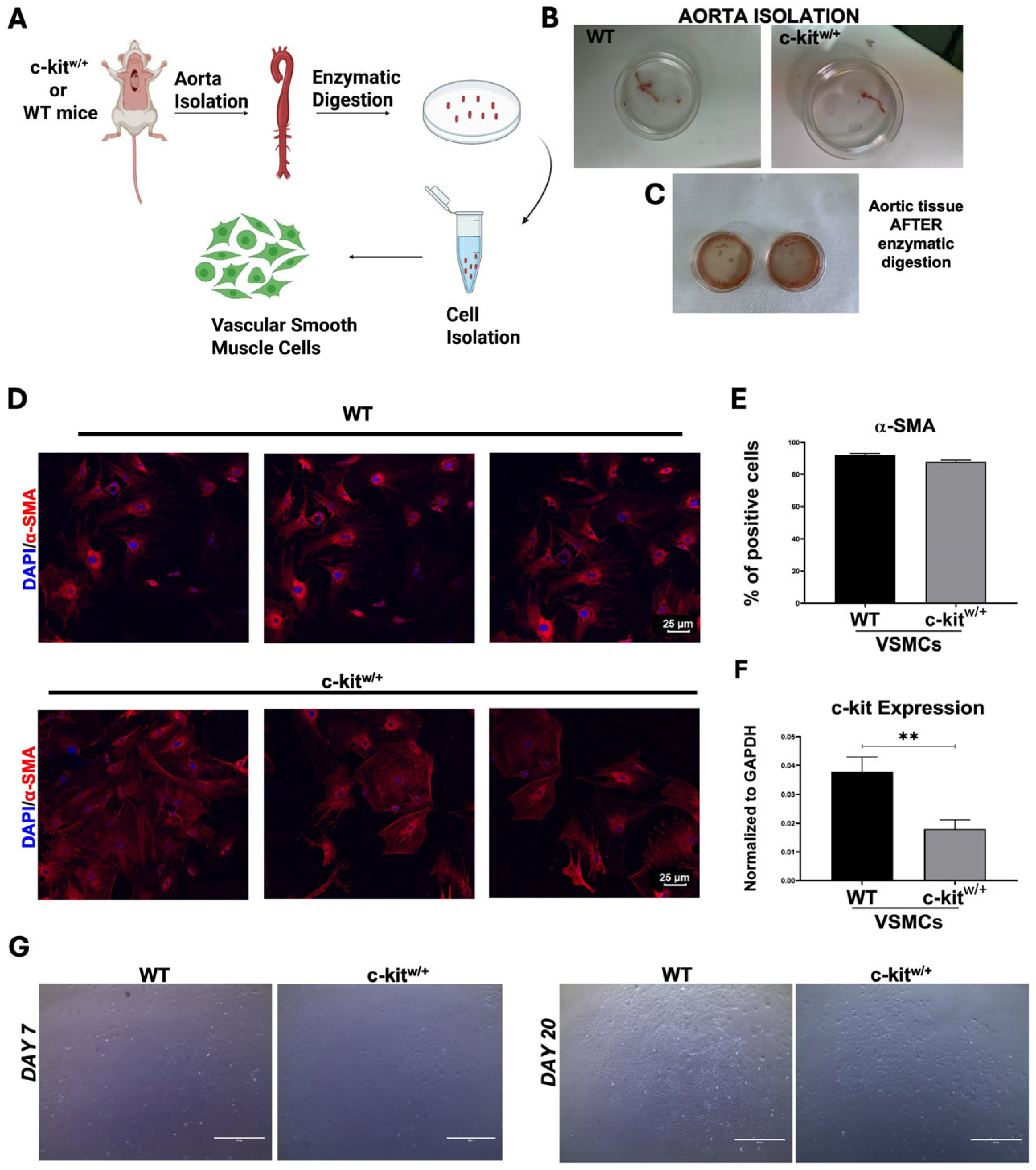
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Mouse Aortic SMCs
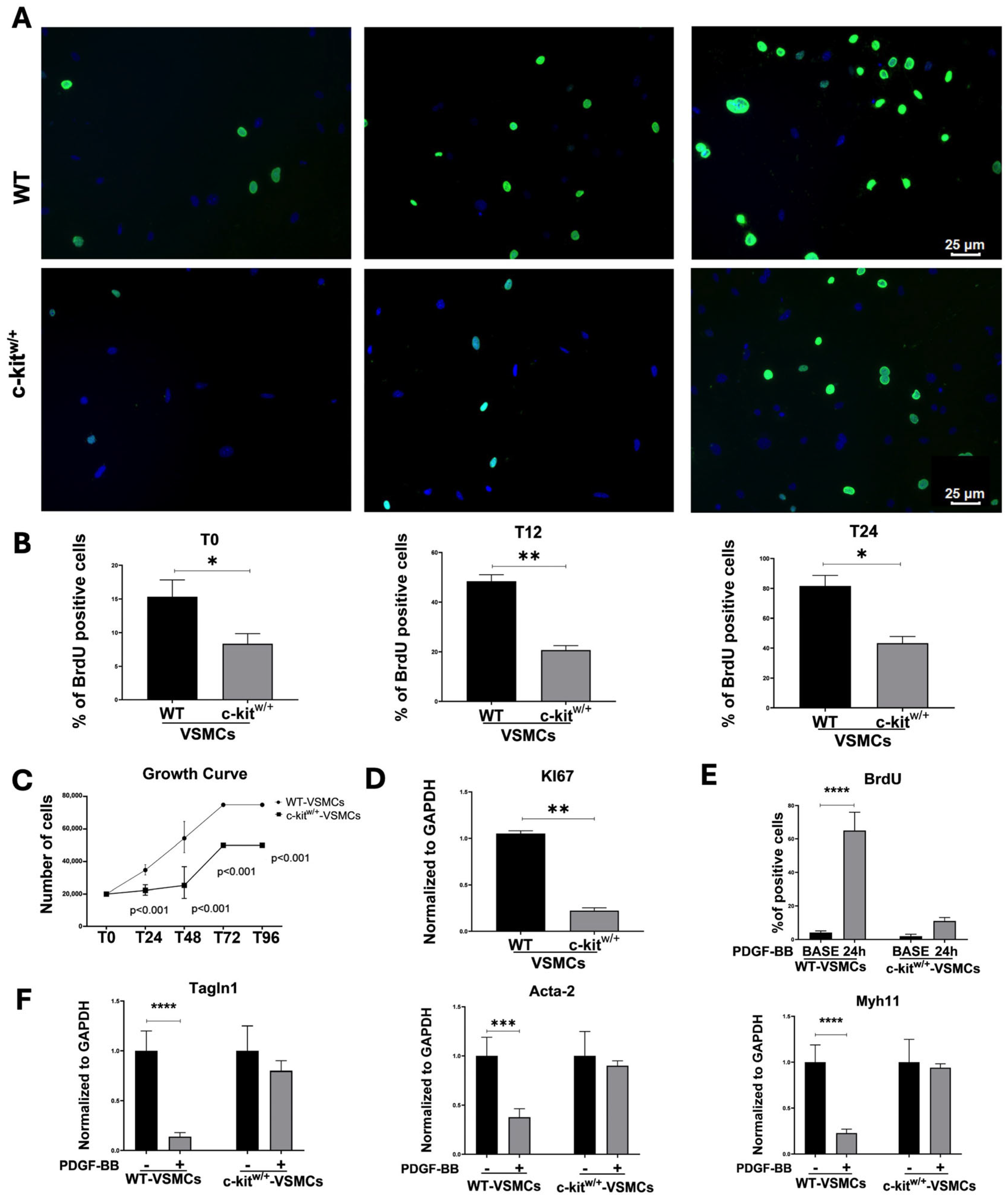
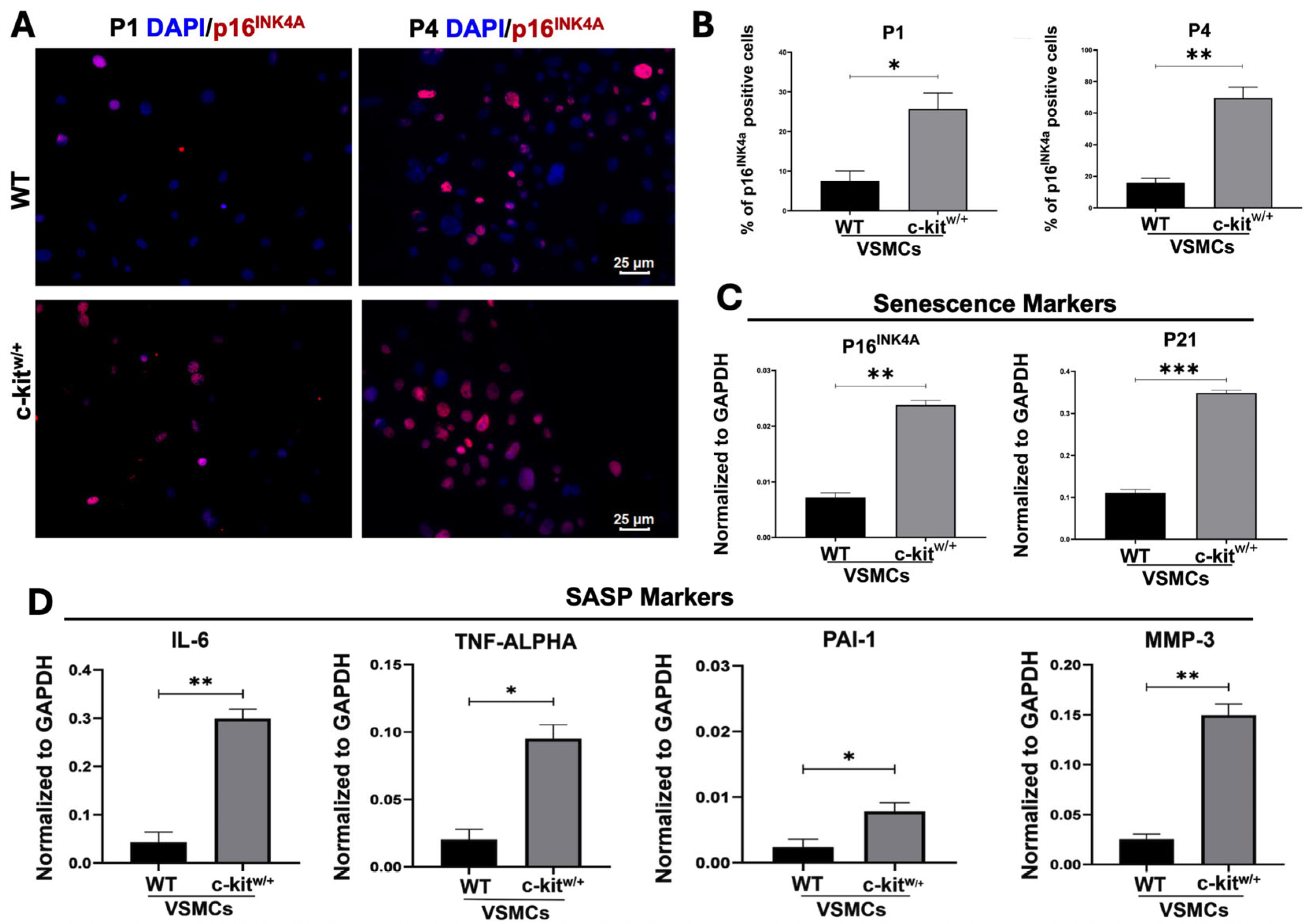
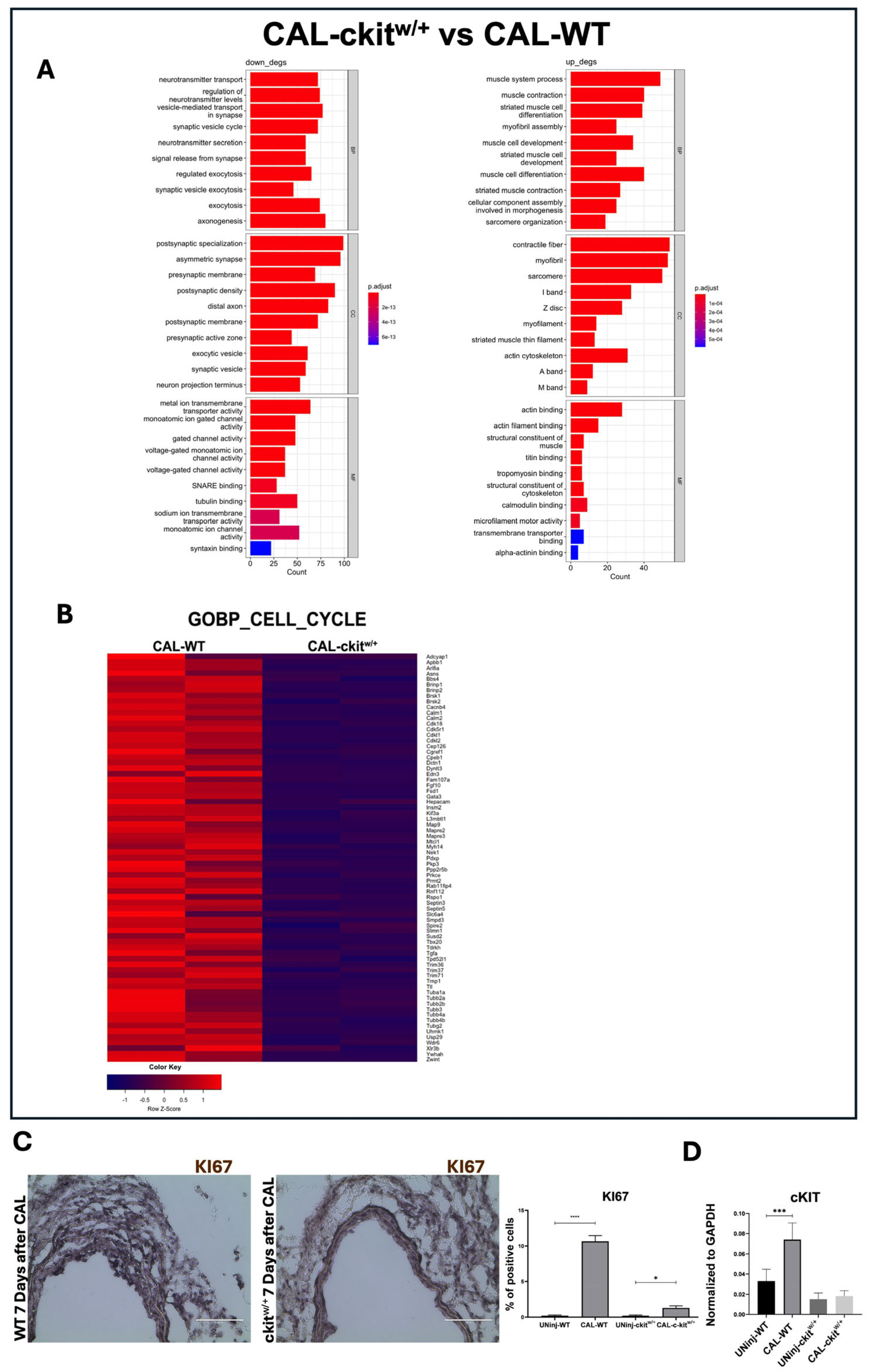
3.2. c-Kit Haploinsufficiency Affects Mouse Aortic VSMC Proliferation Inducing Cellular Senescence and SASP In Vitro
3.3. c-Kit Haploinsufficiency Affects VSMC Differentiation In Vitro
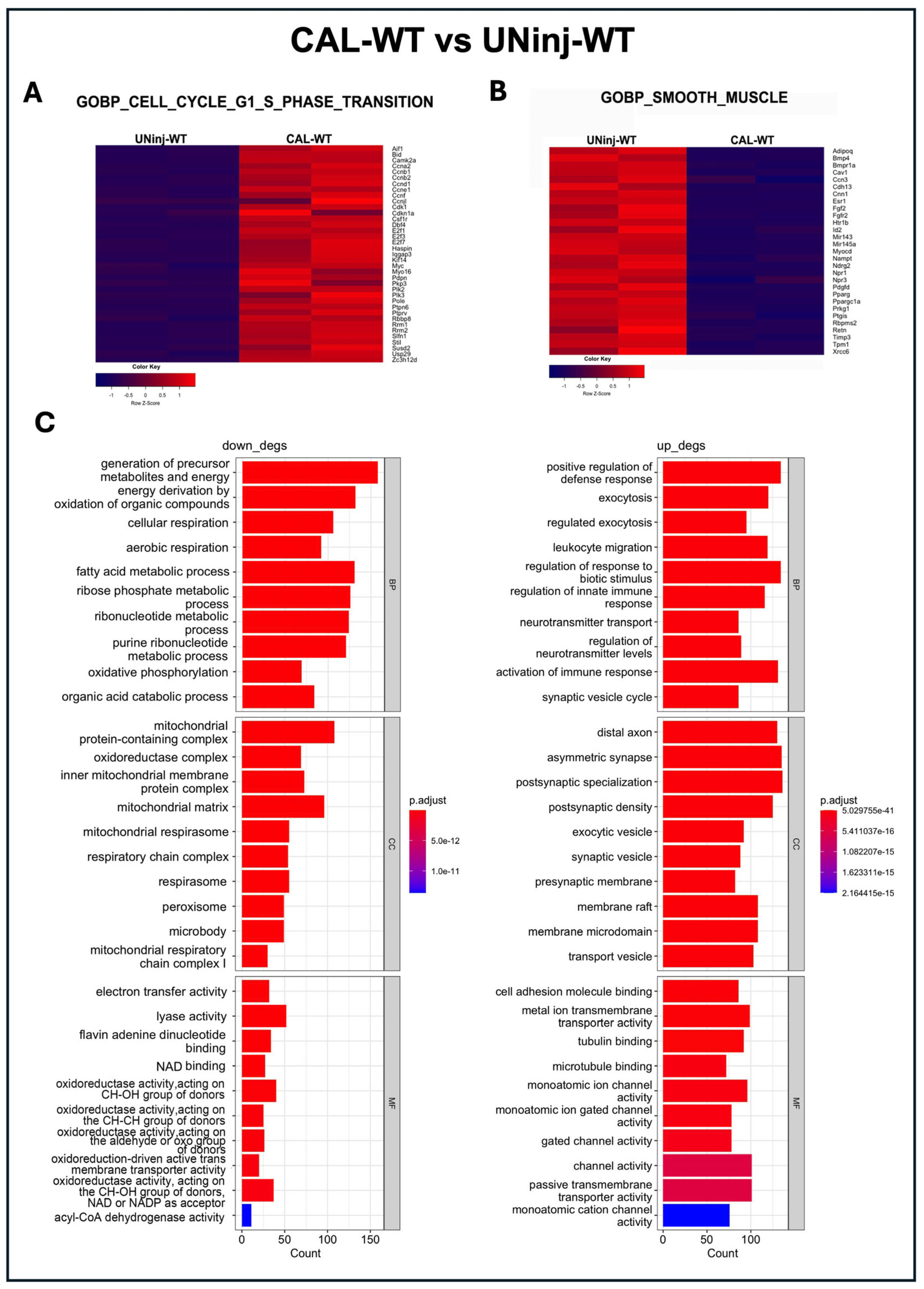
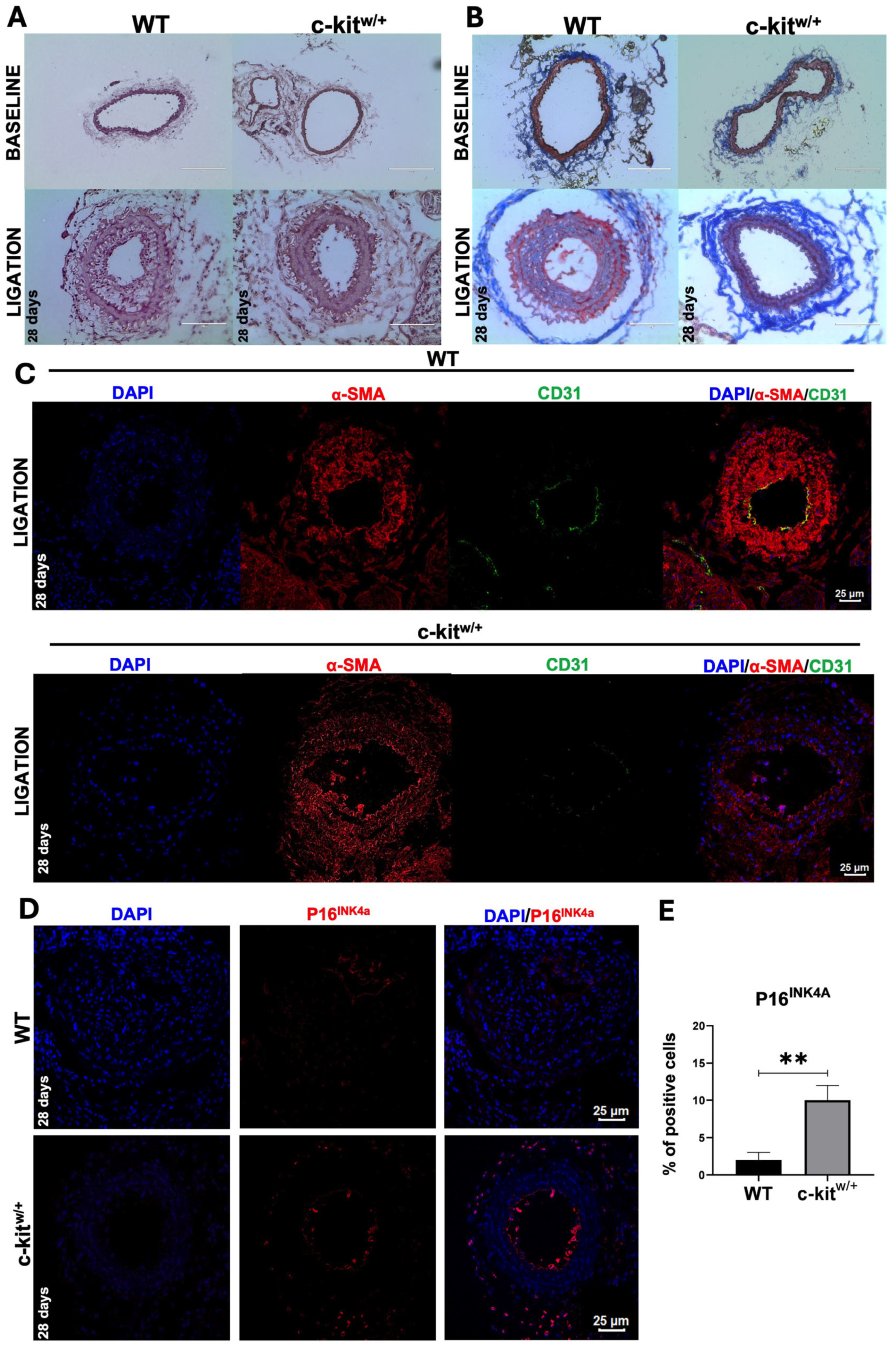
3.4. c-Kit Haploinsufficient Mice Display a Lower Proliferative Activity and an Increased SMC Senescence after Injury
3.5. c-Kit Haploinsufficient Mice Display a Reduced Neointima Formation In Vivo in a Mouse Model of Carotid Ligation
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1958–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, G.D.; Nayak, M.K. A Brief Review of Cardiovascular Diseases, Associated Risk Factors and Current Treatment Regimes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 4063–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, R.P.; Patterson, J.L.; Wilson, E. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Isolation, Culture, and Characterization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 843, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frismantiene, A.; Philippova, M.; Erne, P.; Resink, T.J. Smooth Muscle Cell-Driven Vascular Diseases and Molecular Mechanisms of VSMC Plasticity. Cell Signal 2018, 52, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.K. Regulation of Differentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Physiol. Rev. 1995, 75, 487–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Tkachenko, S.; Gomez, D.; Tripathi, R.; Owens, G.K.; Cherepanova, O.A. Smooth Muscle Cells-Specific Loss of OCT4 Accelerates Neointima Formation after Acute Vascular Injury. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1276945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.R.; Owens, G.K. Epigenetic Control of Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation and Phenotypic Switching in Vascular Development and Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2012, 74, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.K.; Kumar, M.S.; Wamhoff, B.R. Molecular Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation in Development and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 767–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, A.; Di Lascio, A.; Francesconi, A.; Scioli, M.G.; Arcuri, G.; Ferlosio, A.; Spagnoli, L.G. Stem Cell Marker Expression and Proliferation and Apoptosis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clowes, A.W.; Schwartz, S.M. Significance of Quiescent Smooth Muscle Migration in the Injured Rat Carotid Artery. Circ. Res. 1985, 56, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissberg, P.L.; Cary, N.R.; Shanahan, C.M. Gene Expression and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype. Blood Press. Suppl. 1995, 2, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lindner, V.; Giachelli, C.M.; Schwartz, S.M.; Reidy, M.A. A Subpopulation of Smooth Muscle Cells in Injured Rat Arteries Expresses Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-B Chain mRNA. Circ. Res. 1995, 76, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackers-Johnson, M.; Talasila, A.; Sage, A.P.; Long, X.; Bot, I.; Morrell, N.W.; Bennett, M.R.; Miano, J.M.; Sinha, S. Myocardin Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Inflammatory Activation and Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majesky, M.W. Adventitia and Perivascular Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, e31–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majesky, M.W.; Horita, H.; Ostriker, A.; Lu, S.; Regan, J.N.; Bagchi, A.; Dong, X.R.; Poczobutt, J.; Nemenoff, R.A.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.M. Differentiated Smooth Muscle Cells Generate a Subpopulation of Resident Vascular Progenitor Cells in the Adventitia Regulated by Klf4. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déglise, S.; Bechelli, C.; Allagnat, F. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Intimal Hyperplasia, an Update. Front. Physiol. 2023, 13, 1081881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.R.; Rojas, M.G.; Martinez, L.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Zigmond, Z.M.; Vazquez-Padron, R.I.; Lassance-Soares, R.M. C-Kit Deficiency Impairs Nitric Oxide Signaling in Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-H.; Verma, S.; Hsieh, I.-C.; Hung, A.; Cheng, T.-T.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Stanford, W.L.; Weisel, R.D.; Li, R.-K.; et al. Stem Cell Factor Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Apoptosis and Increases Intimal Hyperplasia after Vascular Injury. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.; Deng, J.; Potter, C.M.F.; Nowak, W.N.; Gu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, T.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, B.; et al. Recipient C-Kit Lineage Cells Repopulate Smooth Muscle Cells of Transplant Arteriosclerosis in Mouse Models—PubMed. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 223–241. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31079549/ (accessed on 1 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Schlessinger, J.; Kong, X.P. Crystal Structure of Human Stem Cell Factor: Implication for Stem Cell Factor Receptor Dimerization and Activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7732–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besmer, P.; Manova, K.; Duttlinger, R.; Huang, E.J.; Packer, A.; Gyssler, C.; Bachvarova, R.F. The Kit-Ligand (Steel Factor) and Its Receptor c-Kit/W: Pleiotropic Roles in Gametogenesis and Melanogenesis. Dev. Suppl. 1993, 119, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Siena, S.; Gimmelli, R.; Nori, S.L.; Barbagallo, F.; Campolo, F.; Dolci, S.; Rossi, P.; Venneri, M.A.; Giannetta, E.; Gianfrilli, D.; et al. Activated C-Kit Receptor in the Heart Promotes Cardiac Repair and Regeneration after Injury. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, E.; De Angelis, L.; Frati, G.; Morrone, S.; Chimenti, S.; Fiordaliso, F.; Salio, M.; Battaglia, M.; Latronico, M.V.; Coletta, M.; et al. Isolation and expansion of adult cardiac stem cells from human and murine heart. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicinanza, C.; Aquila, I.; Scalise, M.; Cristiano, F.; Marino, F.; Cianflone, E.; Mancuso, T.; Marotta, P.; Sacco, W.; Lewis, F.C.; et al. Adult Cardiac Stem Cells Are Multipotent and Robustly Myogenic: C-Kit Expression Is Necessary but Not Sufficient for Their Identification. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 2101–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicinanza, C.; Aquila, I.; Cianflone, E.; Scalise, M.; Marino, F.; Mancuso, T.; Fumagalli, F.; Giovannone, E.D.; Cristiano, F.; Iaccino, E.; et al. Kitcre Knock-in Mice Fail to Fate-Map Cardiac Stem Cells. Nature 2018, 555, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.; Hirota, S.; Nishida, T. A Loss-of-Function Mutation of c-Kit Results in Depletion of Mast Cells and Interstitial Cells of Cajal, While Its Gain-of-Function Mutation Results in Their Oncogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2001, 477, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Martinez, L.; Zigmond, Z.M.; Hernandez, D.R.; Lassance-Soares, R.M.; Selman, G.; Vazquez-Padron, R.I. C-Kit Modifies the Inflammatory Status of Smooth Muscle Cells. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigmond, Z.M.; Song, L.; Martinez, L.; Lassance-Soares, R.M.; Velazquez, O.C.; Vazquez-Padron, R.I. C-Kit Expression in Smooth Muscle Cells Reduces Atherosclerosis Burden in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Atherosclerosis 2021, 324, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquila, I.; Cianflone, E.; Scalise, M.; Marino, F.; Mancuso, T.; Filardo, A.; Smith, A.J.; Cappetta, D.; De Angelis, A.; Urbanek, K.; et al. Correction: C-Kit Haploinsufficiency Impairs Adult Cardiac Stem Cell Growth, Myogenicity and Myocardial Regener-ation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 436, Erratum in Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berlo, J.-H.; Kanisicak, O.; Maillet, M.; Vagnozzi, R.J.; Karch, J.; Lin, S.C.; Middleton, R.C.; Marbán, E.; Molkentin, J.D. c-kit+ cells minimally contribute cardiomyocytes to the heart. Nature 2014, 509, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalise, M.; Marino, F.; Salerno, L.; Mancuso, T.; Cappetta, D.; Barone, A.; Parrotta, E.I.; Torella, A.; Palumbo, D.; Veltri, P.; et al. In Vitro CSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Exhibit the Typical microRNA-mRNA Blueprint of Endogenous Cardiomyocytes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquila, I.; Marino, F.; Cianflone, E.; Marotta, P.; Torella, M.; Mollace, V.; Indolfi, C.; Nadal-Ginard, B.; Torella, D. The Use and Abuse of Cre/Lox Recombination to Identify Adult Cardiomyocyte Renewal Rate and Origin. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 127, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotta, P.; Cianflone, E.; Aquila, I.; Vicinanza, C.; Scalise, M.; Marino, F.; Mancuso, T.; Torella, M.; Indolfi, C.; Torella, D. Combining Cell and Gene Therapy to Advance Cardiac Regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salabei, J.K.; Cummins, T.D.; Singh, M.; Jones, S.P.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hill, B.G. PDGF-Mediated Autophagy Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype and Resistance to Oxidative Stress. Biochem. J. 2013, 451, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dong, M.; Wen, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C.; Luan, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y. MiR-26a contributes to the PDGF-BB-induced phenotypic switch of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing Smad1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75844–75853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, S.; Xu, S.; Liu, A.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Han, H.; Liu, Y. Elucidating VSMC Phenotypic Transition Mechanisms to Bridge Insights into Cardiovascular Disease Implications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1400780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-H.; Chen, C.-J.; Shih, C.-M.; Wang, M.-F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-H. Oxidative Stress-Induced Cellular Senescence Desensitizes Cell Growth and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through down-Regulation of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor-Beta. Aging 2019, 11, 8085–8102. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6814625/ (accessed on 26 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Uryga, A.K.; Grootaert, M.O.J.; Garrido, A.M.; Oc, S.; Foote, K.; Chappell, J.; Finigan, A.; Rossiello, F.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F.; Aravani, D.; et al. Telomere Damage Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Senescence and Immune Cell Recruitment after Vessel Injury. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, B.G.; Zhang, C.; Shuja, F.; Sturmlechner, I.; Trewartha, S.; Velasco, R.F.; Baker, D.J.; Li, H.; van Deursen, J.M. Senescent Cells Suppress Innate Smooth Muscle Cell Repair Functions in Atherosclerosis. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhu, X.; Pan, X. The Multifaceted Role of the SASP in Atherosclerosis: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbeck, S.T.; Sakakibara, K.; Faries, P.L.; Workhu, B.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. Stem Cell Factor and C-Kit Are Expressed by and May Affect Vascular SMCs through an Autocrine Pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2004, 120, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Cao, X.; Yu, B.; Qu, A. Vascular Stem/Progenitor Cells in Vessel Injury and Repair. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 845070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubner, A.M.; Lu, S.; Jolly, A.J.; Strand, K.A.; Mutryn, M.F.; Hinthorn, T.; Noble, T.; Nemenoff, R.A.; Moulton, K.S.; Majesky, M.W.; et al. Smooth Muscle-Derived Adventitial Progenitor Cells Direct Atherosclerotic Plaque Composition Complexity in a Klf4-Dependent Manner. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e174639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siracusa, C.; Canino, G.; Scalise, M.; Marino, F.; Pagano, L.; Santamaria, G.; Torella, A.; De Rosa, S.; Torella, D.; Cianflone, E. C-Kit Is Essential for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch In Vitro and In Vivo After Injury. Cells 2025, 14, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201641
Siracusa C, Canino G, Scalise M, Marino F, Pagano L, Santamaria G, Torella A, De Rosa S, Torella D, Cianflone E. C-Kit Is Essential for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch In Vitro and In Vivo After Injury. Cells. 2025; 14(20):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201641
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiracusa, Chiara, Giovanni Canino, Mariangela Scalise, Fabiola Marino, Loredana Pagano, Gianluca Santamaria, Annalaura Torella, Salvatore De Rosa, Daniele Torella, and Eleonora Cianflone. 2025. "C-Kit Is Essential for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch In Vitro and In Vivo After Injury" Cells 14, no. 20: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201641
APA StyleSiracusa, C., Canino, G., Scalise, M., Marino, F., Pagano, L., Santamaria, G., Torella, A., De Rosa, S., Torella, D., & Cianflone, E. (2025). C-Kit Is Essential for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch In Vitro and In Vivo After Injury. Cells, 14(20), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201641







