Role of Nucleotide P2 Receptors in the Immune System: Focus on Effector T Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. P2 Receptor Expression in the Immune System
3. Role of P2 Receptors in T Cell Activation and Chemotaxis
4. Role of P2 Receptors in Effector T Cells
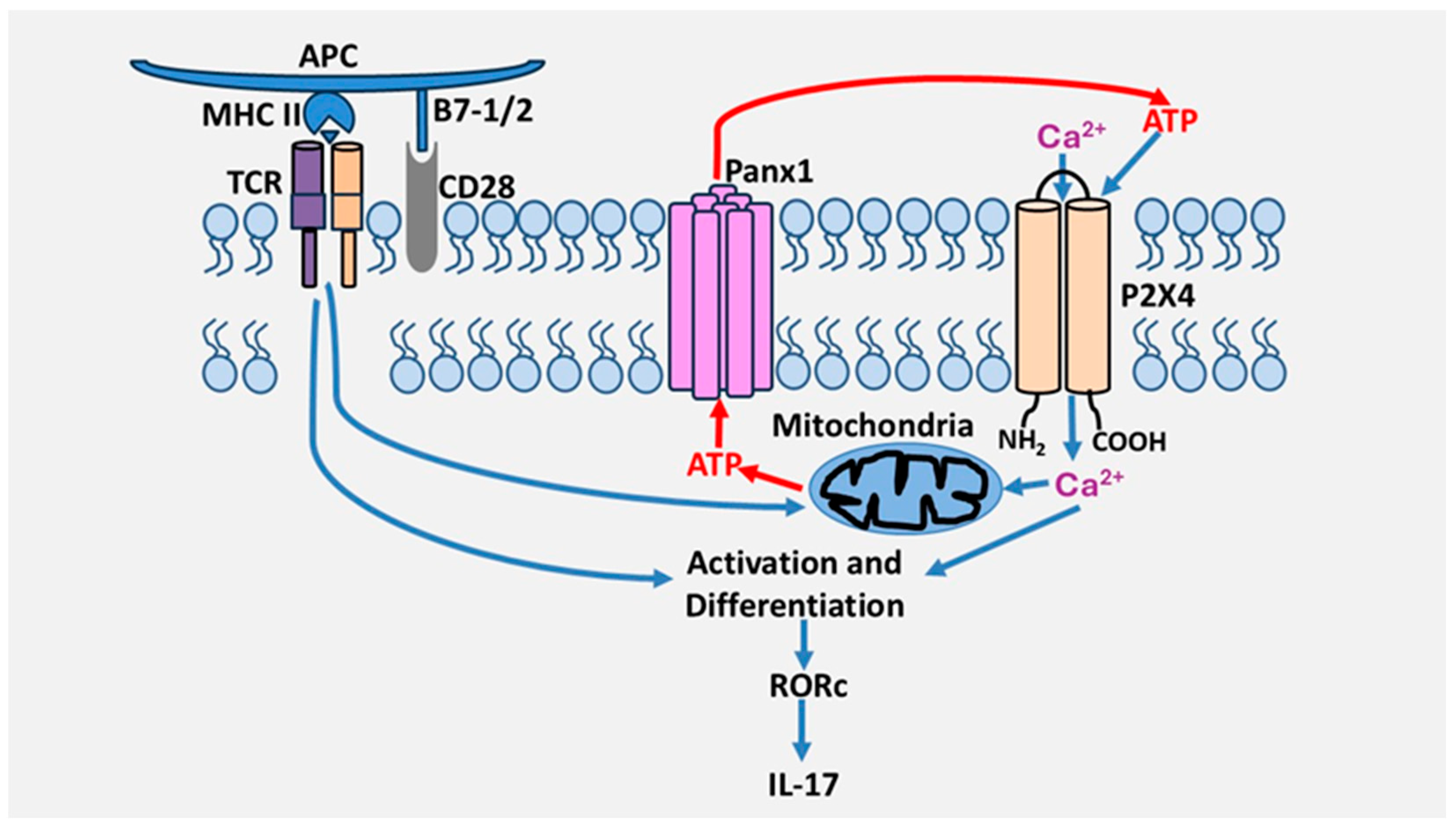
4.1. Role of P2 Receptors in Th17 Cells Differentiation and Activation
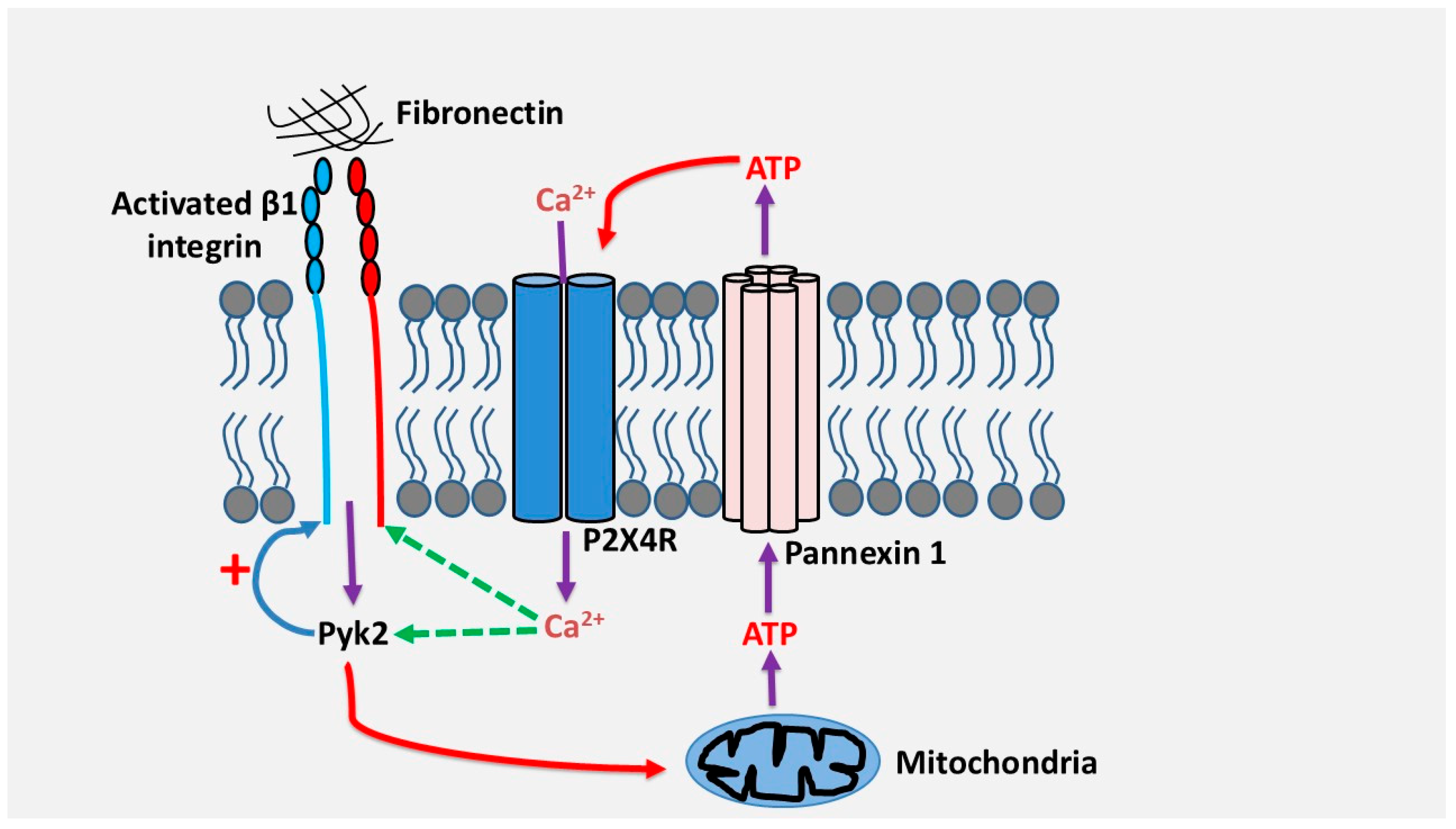
4.2. Role of P2 Receptors in Th17 Cell Migration
5. P2 Receptors in Effector T Cells and Autoimmune Diseases
5.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5.3. Multiple Sclerosis
5.4. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD)
5.5. Liver Autoimmunity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giuliani, A.L.; Sarti, A.C.; Di Virgilio, F. Extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides as signalling molecules. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vultaggio-Poma, V.; Falzoni, S.; Salvi, G.; Giuliani, A.L.; Di Virgilio, F. Signalling by extracellular nucleotides in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H. Extracellular ATP and other nucleotides-ubiquitous triggers of intercellular messenger release. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 12, 25–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Campbell, G.; Satchell, D.; Smythe, A. Evidence that adenosine triphosphate or a related nucleotide is the transmitter substance released by non-adrenergic inhibitory nerves in the gut. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1970, 40, 668–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, C.; Junger, W.G. Mitochondria Synergize with P2 Receptors to Regulate Human T Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 549889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.J.; Derkach, V.; Surprenant, A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature 1992, 357, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H. ATP and acetylcholine, equal brethren. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Signalling: Therapeutic Developments. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C. The P2Y/P2X divide: How it began. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 187, 114408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Delicado, E.G.; Gachet, C.; Kennedy, C.; Von Kugelgen, I.; Li, B.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Novak, I.; Schoneberg, T.; Perez-Sen, R.; et al. Update of P2Y receptor pharmacology: IUPHAR Review 27. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2413–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Kugelgen, I. Molecular pharmacology of P2Y receptor subtypes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 187, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, L.; Bidula, S.; Bibic, L.; Allum, E. To Inhibit or Enhance? Is There a Benefit to Positive Allosteric Modulation of P2X Receptors? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, D.; Hattori, M. Recent progress in the structural biology of P2X receptors. Proteins 2022, 90, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junger, W.G. Immune cell regulation by autocrine purinergic signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Pacher, P.; Vizi, E.S.; Hasko, G. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Longhi, M.S.; Robson, S.C.; Stagg, J. The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73, Novel checkpoint inhibitor targets. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G. The Purinergic System as a Pharmacological Target for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 345–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, A.K.N.; Montes, G.C.; Barreiro, E.J.; Sudo, R.T.; Zapata-Sudo, G. Adenosine Receptors As Drug Targets for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G. Adenosine signaling and the immune system: When a lot could be too much. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Perez Novo, C.; Bachert, C.; Van Crombruggen, K. Purinergic signaling in inflammatory cells: P2 receptor expression, functional effects, and modulation of inflammatory responses. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Boeynaems, J.M. Purinergic signalling and immune cells. Purinergic Signal. 2014, 10, 529–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Huang, N.; Ma, H.H.; Huang, H.; Yu, H.G. Involvement of P2X7 receptor signaling on regulating the differentiation of Th17 cells and type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic, C.; Linden, J. Purinergic regulation of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. The role of nucleotides and purinergic signaling in apoptotic cell clearance—Implications for chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, C.; Liu, K.; Kondo, Y.; Slubowski, C.J.; Dertnig, T.; Denicolo, S.; Arbab, M.; Hubner, J.; Konrad, K.; Fakhari, M.; et al. Purinergic P2X4 receptors and mitochondrial ATP production regulate T cell migration. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3583–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledderose, C.; Bao, Y.; Lidicky, M.; Zipperle, J.; Li, L.; Strasser, K.; Shapiro, N.I.; Junger, W.G. Mitochondria are gate-keepers of T cell function by producing the ATP that drives purinergic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25936–25945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woehrle, T.; Ledderose, C.; Rink, J.; Slubowski, C.; Junger, W.G. Autocrine stimulation of P2Y1 receptors is part of the purinergic signaling mechanism that regulates T cell activation. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, U.; Westendorf, A.M.; Radaelli, E.; Casati, A.; Ferro, M.; Fumagalli, M.; Verderio, C.; Buer, J.; Scanziani, E.; Grassi, F. Purinergic control of T cell activation by ATP released through pannexin-1 hemichannels. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnstock, G.; Knight, G.E. Cellular distribution and functions of P2 receptor subtypes in different systems. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2004, 240, 31–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manohar, M.; Hirsh, M.I.; Chen, Y.; Woehrle, T.; Karande, A.A.; Junger, W.G. ATP release and autocrine signaling through P2X4 receptors regulate gammadelta T cell activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C. P2Y11 Receptors: Properties, Distribution and Functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1051, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Vuerich, M. Purinergic signaling in the immune system. Auton. Neurosci. 2015, 191, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woehrle, T.; Yip, L.; Elkhal, A.; Sumi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, Y.; Insel, P.A.; Junger, W.G. Pannexin-1 hemichannel-mediated ATP release together with P2X1 and P2X4 receptors regulate T-cell activation at the immune synapse. Blood 2010, 116, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, C.; Zhao, C.; Abderrazak, A.; Salem, M.; Fortin, P.R.; Sévigny, J.; Aoudjit, F. The Purinergic Receptor P2X4 Promotes Th17 Activation and the Development of Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotnis, S.; Bingham, B.; Vasilyev, D.V.; Miller, S.W.; Bai, Y.; Yeola, S.; Chanda, P.K.; Bowlby, M.R.; Kaftan, E.J.; Samad, T.A.; et al. Genetic and functional analysis of human P2X5 reveals a distinct pattern of exon 10 polymorphism with predominant expression of the nonfunctional receptor isoform. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, L.E.B.; De Andrade Mello, P.; Da Silva, C.G.; Coutinho-Silva, R. The P2X7 Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: Angel or Demon? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, C.; Bao, Y.; Ledderose, S.; Woehrle, T.; Heinisch, M.; Yip, L.; Zhang, J.; Robson, S.C.; Shapiro, N.I.; Junger, W.G. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Depleted Purinergic Signaling, and Defective T Cell Vigilance and Immune Defense. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswad, F.; Dennert, G. P2X7 receptor expression levels determine lethal effects of a purine based danger signal in T lymphocytes. Cell. Immunol. 2006, 243, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukimoto, M.; Maehata, M.; Harada, H.; Ikari, A.; Takagi, K.; Degawa, M. P2X7 receptor-dependent cell death is modulated during murine T cell maturation and mediated by dual signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2842–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledderose, C.; Bromberger, S.; Slubowski, C.J.; Sueyoshi, K.; Junger, W.G. Frontline Science: P2Y11 receptors support T cell activation by directing mitochondrial trafficking to the immune synapse. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreisig, K.; Kornum, B.R. A critical look at the function of the P2Y11 receptor. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 12, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreisig, K.; Sund, L.; Dommer, M.W.; Kristensen, N.P.; Boddum, K.; Viste, R.; Fredholm, S.; Odum, N.; Jaattela, M.; Skov, S.; et al. Human P2Y11 Expression Level Affects Human P2X7 Receptor-Mediated Cell Death. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, V.J.; Wolf, I.M.A.; Er-Lukowiak, M.; Lory, N.; Stahler, T.; Woelk, L.M.; Mittrucker, H.W.; Muller, C.E.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Rissiek, B.; et al. P2X4 and P2X7 are essential players in basal T cell activity and Ca2+ signaling milliseconds after T cell activation. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurvali, J.; Boudinot, P.; Kanellopoulos, J.; Ruutel Boudinot, S. P2X4, a fast and sensitive purinergic receptor. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, C.; Bromberger, S.; Slubowski, C.J.; Sueyoshi, K.; Aytan, D.; Shen, Y.; Junger, W.G. The purinergic receptor P2Y11 choreographs the polarization, mitochondrial metabolism, and migration of T lymphocytes. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaba3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Lv, L.; Li, B. Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Hirota, K. The pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov Ii Zhou, L.; Littman, D.R. Transcriptional regulation of Th17 cell differentiation. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake, S.; Yago, T.; Kobashigawa, T.; Nanke, Y. The Plasticity of Th17 Cells in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6, regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.G. Regulatory T cells vs Th17, differentiation of Th17 versus Treg, are the mutually exclusive? Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Su, X.; Huang, G.; Xin, X.F.; Cao, E.H.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y. Adenosine Triphosphate Promotes Allergen-Induced Airway Inflammation and Th17 Cell Polarization in Neutrophilic Asthma. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 5358647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Jiang, W. P2Y6 Deficiency Enhances Dendritic Cell-Mediated Th1/Th17 Differentiation and Aggravates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 387–397. [Google Scholar]
- Schenk, U.; Frascoli, M.; Proietti, M.; Geffers, R.; Traggiai, E.; Buer, J.; Ricordi, C.; Westendorf, A.M.; Grassi, F. ATP inhibits the generation and function of regulatory T cells through the activation of purinergic P2X receptors. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piconese, S.; Gri, G.; Tripodo, C.; Musio, S.; Gorzanelli, A.; Frossi, B.; Pedotti, R.; Pucillo, C.E.; Colombo, M.P. Mast cells counteract regulatory T-cell suppression through interleukin-6 and OX40/OX40L axis toward Th17-cell differentiation. Blood 2009, 114, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, A.N.; Noorbakhsh, S.M.; Hamedifar, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Yazdani, R.; Bautista, J.M.; Azizi, G. A role for Th1-like Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Chiricozzi, A. The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubberts, E. The IL-23-IL-17 axis in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azreq, M.A.; Arseneault, C.; Boisvert, M.; Page, N.; Allaeys, I.; Poubelle, P.E.; Tessier, P.A.; Aoudjit, F. Cooperation between IL-7 Receptor and Integrin alpha2beta1 (CD49b) Drives Th17-Mediated Bone Loss. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4198–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azreq, M.A.; Boisvert, M.; Cesaro, A.; Page, N.; Loubaki, L.; Allaeys, I.; Chakir, J.; Poubelle, P.E.; Tessier, P.A.; Aoudjit, F. alpha2beta1 integrin regulates Th17 cell activity and its neutralization decreases the severity of collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5941–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, C.; Muheidli, A.; Aoudjit, F. beta1 Integrin induces adhesion and migration of human Th17 cells via Pyk2-dependent activation of P2X4 receptor. Immunology 2023, 168, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bye, A.P.; Gibbins, J.M.; Mahaut-Smith, M.P. Ca2+ waves coordinate purinergic receptor-evoked integrin activation and polarization. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaav7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Lagos-Cabre, R.; Kong, M.; Cardenas, A.; Burgos-Bravo, F.; Schneider, P.; Quest, A.F.; Leyton, L. Integrin-mediated transactivation of P2X7R via hemichannel-dependent ATP release stimulates astrocyte migration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R. Cross Talk of Purinergic and Immune Signaling: Implication in Inflammatory and Pathogenic Diseases. In Purinergic System; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Liu, S.C.; Hu, S.Q.; Lu, J.F.; Wu, C.L.; Hu, D.X.; Zhang, W.J. ATP ion channel P2X purinergic receptors in inflammation response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Sarti, A.C.; Coutinho-Silva, R. Purinergic signaling, DAMPs, and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C832–C835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.L.G.; Passos, D.F.; Bernardes, V.M.; Leal, D.B.R. ATP and adenosine: Role in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 214, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Dal Ben, D.; Sarti, A.C.; Giuliani, A.L.; Falzoni, S. The P2X7 Receptor in Infection and Inflammation. Immunity 2017, 47, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portales-Cervantes, L.; Nino-Moreno, P.; Doniz-Padilla, L.; Baranda-Candido, L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Salgado-Bustamante, M.; Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Portales-Perez, D. Expression and function of the P2X7 purinergic receptor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portales-Cervantes, L.; Nino-Moreno, P.; Salgado-Bustamante, M.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.H.; Baranda-Candido, L.; Reynaga-Hernandez, E.; Barajas-Lopez, C.; Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Portales-Perez, D.P. The His155Tyr (489C>T) single nucleotide polymorphism of P2RX7 gene confers an enhanced function of P2X7 receptor in immune cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 276, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Theaker, J.; Pelegrin, P.; Clifton, A.D.; Braddock, M.; Surprenant, A. P2X7 receptor-mediated release of cathepsins from macrophages is a cytokine-independent mechanism potentially involved in joint diseases. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2611–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keystone, E.C.; Wang, M.M.; Layton, M.; Hollis, S.; Mcinnes, I.B.; Team, D.C.S. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of the P2X7 purinergic receptor antagonist AZD9056 on the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with active disease despite treatment with methotrexate or sulphasalazine. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, H.; Fujiwaki, T.; Tsukimoto, M.; Kawano, A.; Harada, H.; Kojima, S. P2X4 receptor regulates P2X7 receptor-dependent IL-1beta and IL-18 release in mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Pruneda, G.; Reyes, J.P.; Perez-Flores, G.; Perez-Cornejo, P.; Arreola, J. Functional interactions between P2X4 and P2X7 receptors from mouse salivary epithelia. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 2887–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Prudic, K.; Pippel, A.; Klapperstuck, M.; Braam, U.; Muller, C.E.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Interaction of Purinergic P2X4 and P2X7 Receptor Subunits. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Fornai, M.; Pacher, P.; Lee, H.T.; Hasko, G. P2X4 receptors, immunity, and sepsis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Luo, H.L.; Zhu, Z.M. The role of P2X4 receptors in chronic pain: A potential pharmacological target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, N.; Ma, Y.; Ning, B.; Wang, Y.; Kou, L. Inhibition of P2X4 suppresses joint inflammation and damage in collagen-induced arthritis. Inflammation 2014, 37, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Li, X. P2Y11 receptor antagonist NF340 ameliorates inflammation in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes: An implication in rheumatoid arthritis. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orriss, I.R.; Wang, N.; Burnstock, G.; Arnett, T.R.; Gartland, A.; Robaye, B.; Boeynaems, J.M. The P2Y6 receptor stimulates bone resorption by osteoclasts. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3706–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Floyd, D.H.; Hughes, A.; Xiang, J.; Schneider, J.G.; Uluckan, O.; Heller, E.; Deng, H.; Zou, W.; Craft, C.S.; et al. The ADP receptor P2RY12 regulates osteoclast function and pathologic bone remodeling. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3579–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewicz, N.; Komarova, S.V. Role of UDP-Sugar Receptor P2Y14 in Murine Osteoblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarowski, E.R.; Harden, T.K. UDP-Sugars as Extracellular Signaling Molecules: Cellular and Physiologic Consequences of P2Y14 Receptor Activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlenberg, J.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Smith, C.K.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular trap-associated protein activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is enhanced in lupus macrophages. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Giuliani, A.L. Purinergic signalling in autoimmunity: A role for the P2X7R in systemic lupus erythematosus? Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlenberg, J.M.; Thacker, S.G.; Berthier, C.C.; Cohen, C.D.; Kretzler, M.; Kaplan, M.J. Inflammasome activation of IL-18 results in endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6143–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Bao, C. Expressions of IL-18 and its binding protein in peripheral blood leukocytes and kidney tissues of lupus nephritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Drenker, M.; Eiz-Vesper, B.; Werfel, T.; Wittmann, M. Evidence for a pathogenetic role of interleukin-18 in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 3205–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Jia, L.; Peng, X.; Zhao, R. The Expression of P2X7 Receptor on Th1, Th17, and Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Correlations with Active Disease. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faliti, C.E.; Gualtierotti, R.; Rottoli, E.; Gerosa, M.; Perruzza, L.; Romagnani, A.; Pellegrini, G.; De Ponte Conti, B.; Rossi, R.L.; Idzko, M.; et al. P2X7 receptor restrains pathogenic Tfh cell generation in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyter, R. The P2X7 Receptor. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1051, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, M.; Hasanali, Z.S.; Zhao, Y.; Das, A.; Lavaert, M.; Roman, C.J.; Londregan, J.; Allman, D.; Bhandoola, A. Bone marrow plasma cells require P2RX4 to sense extracellular ATP. Nature 2024, 626, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovnick, A.D.; Gu, B.J.; Traboulsee, A.L.; Bernales, C.Q.; Encarnacion, M.; Yee, I.M.; Criscuoli, M.G.; Huang, X.; Ou, A.; Milligan, C.J.; et al. Purinergic receptors P2RX4 and P2RX7 in familial multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, A.; Vazquez-Villoldo, N.; Rissiek, B.; Gejo, J.; Martin, A.; Palomino, A.; Perez-Samartin, A.; Pulagam, K.R.; Lukowiak, M.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; et al. P2X4 receptor controls microglia activation and favors remyelination in autoimmune encephalitis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Lai, W.; Yang, C.; Cai, Y.; Chen, S.; Du, C. Critical Role of P2Y12 Receptor in Regulation of Th17 Differentiation and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Su, Q.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Ren, H.; Qian, M.; Liu, J.; Cui, S.; et al. Knockout of P2Y12 aggravates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice via increasing of IL-23 production and Th17 cell differentiation by dendritic cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Olst, L.; Rodriguez-Mogeda, C.; Picon, C.; Kiljan, S.; James, R.E.; Kamermans, A.; Van Der Pol, S.M.A.; Knoop, L.; Michailidou, I.; Drost, E.; et al. Meningeal inflammation in multiple sclerosis induces phenotypic changes in cortical microglia that differentially associate with neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, S.; Youssef, M.E.; Sharaf, H.; Amin, N.A.; El-Shedody, R.; Aboutouk, F.H.; El-Galeel, Y.A.; El-Hefnawy, A.; Shabaka, D.; Khalifa, A.; et al. BBG enhances OLT1177-induced NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation by targeting P2X7R/NLRP3 and MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling in DSS-induced colitis in rats. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 119123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.R.; Castelo-Branco, M.T.; Figliuolo, V.R.; Bernardazzi, C.; Buongusto, F.; Yoshimoto, A.; Nanini, H.F.; Coutinho, C.M.; Carneiro, A.J.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; et al. Overexpression of ATP-activated P2X7 receptors in the intestinal mucosa is implicated in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, Y.; Amiya, T.; Nochi, T.; Fujisawa, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Iba, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Sato, S.; Nakajima, S.; Iijima, H.; et al. Extracellular ATP mediates mast cell-dependent intestinal inflammation through P2X7 purinoceptors. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figliuolo, V.R.; Savio, L.E.B.; Safya, H.; Nanini, H.; Bernardazzi, C.; Abalo, A.; De Souza, H.S.P.; Kanellopoulos, J.; Bobe, P.; Coutinho, C.; et al. P2X7 receptor promotes intestinal inflammation in chemically induced colitis and triggers death of mucosal regulatory T cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grbic, D.M.; Degagne, E.; Langlois, C.; Dupuis, A.A.; Gendron, F.P. Intestinal inflammation increases the expression of the P2Y6 receptor on epithelial cells and the release of CXC chemokine ligand 8 by UDP. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placet, M.; Molle, C.M.; Arguin, G.; Geha, S.; Gendron, F.P. The expression of P2Y6 receptor promotes the quality of mucus in colitic mice. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 5459–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.; El Azreq, M.A.; Pelletier, J.; Robaye, B.; Aoudjit, F.; Sévigny, J. Exacerbated intestinal inflammation in P2Y6 deficient mice is associated with Th17 activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuerich, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Robson, S.C.; Longhi, M.S. Control of Gut Inflammation by Modulation of Purinergic Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubisic, V.; Perez-Medina, A.L.; Fried, D.E.; Sévigny, J.; Robson, S.C.; Galligan, J.J.; Gulbransen, B.D. NTPDase1 and -2 are expressed by distinct cellular compartments in the mouse colon and differentially impact colonic physiology and function after DSS colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G314–G332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshe, R.P.; Xie, A.; Vuerich, M.; Frank, L.A.; Gromova, B.; Zhang, H.; Robles, R.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Csizmadia, E.; Kokkotou, E.; et al. Endogenous antisense RNA curbs CD39 expression in Crohn’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettel, J.A.; Gandhi, R.; Kenison, J.E.; Yeste, A.; Murugaiyan, G.; Sambanthamoorthy, S.; Griffith, A.E.; Patel, B.; Shouval, D.S.; Weiner, H.L.; et al. AHR Activation Is Protective against Colitis Driven by T Cells in Humanized Mice. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, M.S.; Vuerich, M.; Kalbasi, A.; Kenison, J.E.; Yeste, A.; Csizmadia, E.; Vaughn, B.; Feldbrugge, L.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Wegiel, B.; et al. Bilirubin suppresses Th17 immunity in colitis by upregulating CD39. JCI Insight. 2017, 2, e92791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhage, T.; Dabritz, J.; Brockhausen, A.; Wirth, T.; Bruckner, M.; Belz, M.; Foell, D.; Varga, G. Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor-Activated CD39+/CD73+ Murine Monocytes Modulate Intestinal Inflammation via Induction of Regulatory T Cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 433–449.e431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, M.A.; Yeoman, A.D.; Verma, S.; Smith, A.D.; Longhi, M.S. Autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuerich, M.; Robson, S.C.; Longhi, M.S. Ectonucleotidases in Intestinal and Hepatic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, M.; Liu, W.; Feng, F.; Li, X.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Deficiency of purinergic P2X4 receptor alleviates experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 221, 116033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.R.; Liberal, R.; Holder, B.S.; Cardone, J.; Ma, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Longhi, M.S. Dysfunctional CD39(POS) regulatory T cells and aberrant control of T-helper type 17 cells in autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laketa, D.; Lavrnja, I. Extracellular Purine Metabolism-Potential Target in Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 8361–8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Kugelgen, I. Pharmacological characterization of P2Y receptor subtypes—An update. Purinergic Signal. 2024, 20, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Su, K.; Yang, L.; Duan, H.; Tang, L.; Tang, M.; Zhao, M.; Ye, N.; Cai, X.; Jiang, X.; et al. Discovery of a Potent, Orally Active, and Long-Lasting P2X7 Receptor Antagonist as a Preclinical Candidate for Delaying the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 17472–17496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, K.; Baumann, S.; Gashaw, I.; Klein, S.; Rohde, B.; Zolk, O.; Fischer, O.M.; Friedrich, C. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Filapixant, a Highly Selective P2X3 Receptor Antagonist, in an Ascending-Single-Dose First-in-Human Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| P2 Receptor | Function | Autoimmune Disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2X4 | Pathogenic: Increased IL-17 production by effector/memory CD4+ T cells Activation and differentiation of Th17 cells | Rheumatoid Arthritis | [34] |
| Pathogenic: Promotion of Th17 activation and increased levels of IL-17 in arthritic joints | Collagen-induced Arthritis mouse model | [34] | |
| Pathogenic: Increased levels of serum of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-17 | Collagen-induced Arthritis mouse model | [78] | |
| Pathogenic: Increased Proteinuria (kidney disease) and autoantibody titers | NZB/W Mouse model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | [92] | |
| Pathogenic: Increased levels of serum inflammatory mediators IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17A, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. | Concanavalin-induced mouse model of Liver Autoimmunity | [113] | |
| Protective: Promotion of microglia remyelination | Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG35–55)-induced mouse model of EAE | [94] | |
| P2X7 | Pathogenic: Upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Myd88, NF-κB, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) production | DSS-induced rat colitis | [98] |
| Pathogenic: Promotion of Th17 differentiation and expression of Th17 polarizing cytokines (IL-1β, TGF-β1, IL-23p19, and IL-6) | Collagen-induced Arthritis mouse model | [22] | |
| P2Y6 | Protective: Reduction in Th1 and Th17 cells in the colon | DSS-induced mouse colitis | [104] |
| Protective: Promotes mucus quality | DSS-induced mouse colitis | [103] | |
| Protective: Inhibition of the production of Th1 and Th17 polarizing cytokines (IL-12 and IL-23) | MOG35–55-induced mouse model of EAE | [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babou Kammoe, R.B.; Hamoudi, C.; Aoudjit, F. Role of Nucleotide P2 Receptors in the Immune System: Focus on Effector T Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181467
Babou Kammoe RB, Hamoudi C, Aoudjit F. Role of Nucleotide P2 Receptors in the Immune System: Focus on Effector T Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(18):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181467
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabou Kammoe, Romuald Brice, Chakib Hamoudi, and Fawzi Aoudjit. 2025. "Role of Nucleotide P2 Receptors in the Immune System: Focus on Effector T Cells" Cells 14, no. 18: 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181467
APA StyleBabou Kammoe, R. B., Hamoudi, C., & Aoudjit, F. (2025). Role of Nucleotide P2 Receptors in the Immune System: Focus on Effector T Cells. Cells, 14(18), 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181467







