Homocysteine-Mediated Neuronal Pyroptosis Contributes to Brain Injury in Heatstroke Rats by Activating the m6A-YTHDF2-NLRP3 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rat HS Model
2.2. Vitamin B-Complex Treatment
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Cell Culture and Intervention
2.9. m6A Dot Blot Assay
2.10. Methylated RNA Immunoprecipitation (MeRIP) qPCR Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
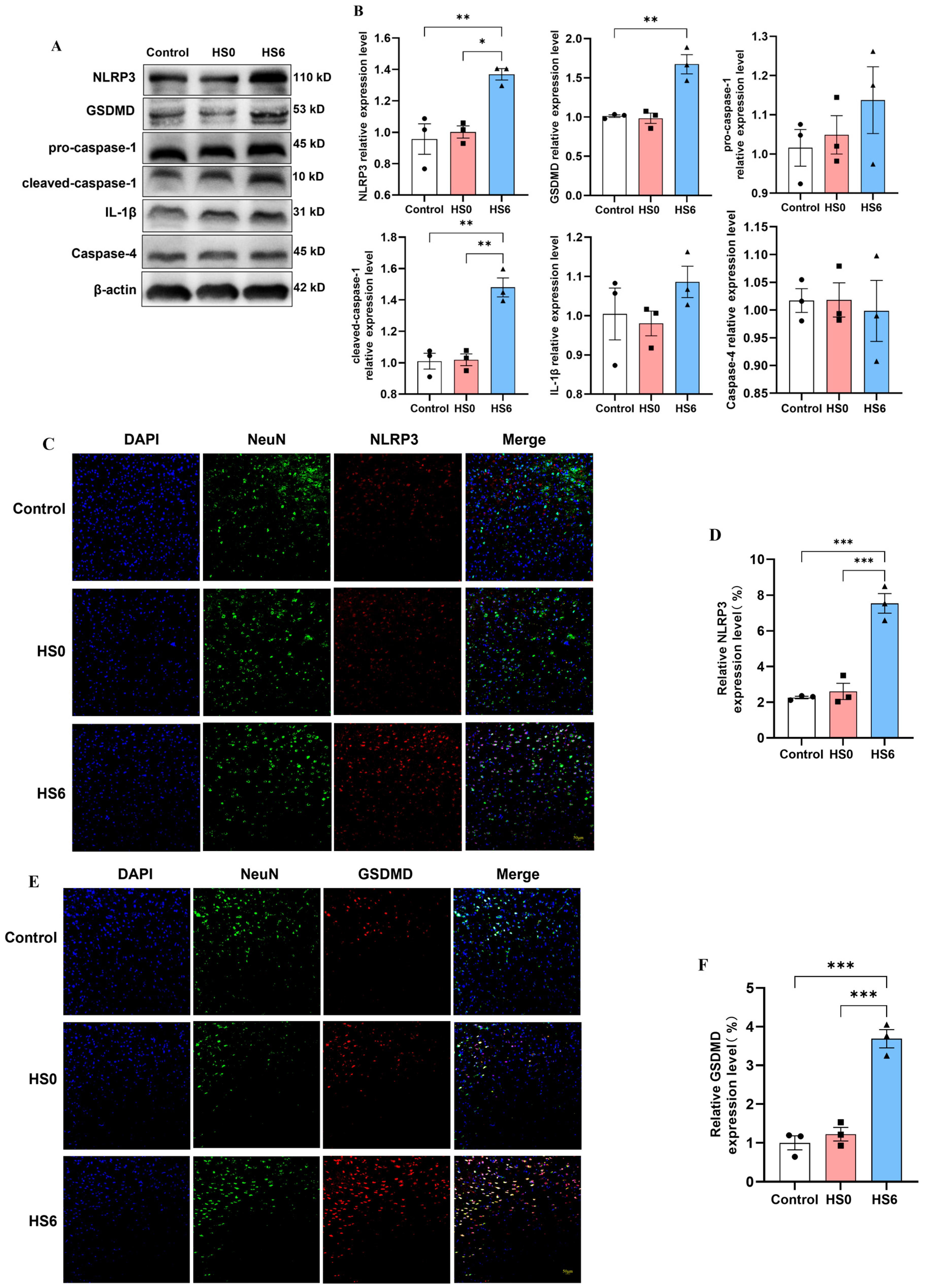
3.1. Increased Neuronal Pyroptosis in Prefrontal Cortex of HS Rats
3.2. Pyroptosis in Prefrontal Cortical Neurons of HS Rats Primarily Occurs Through the Classical Pathway
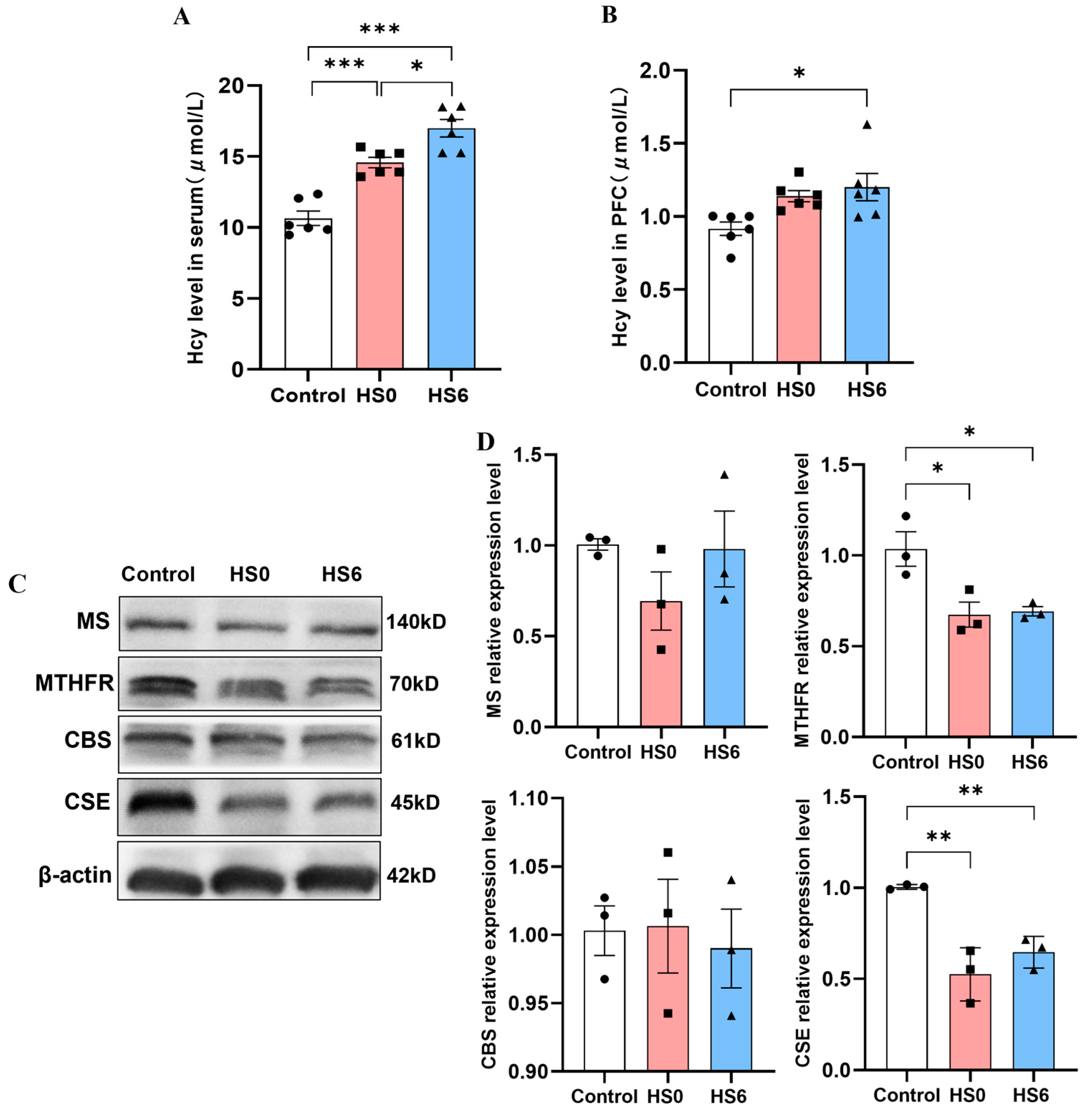
3.3. Hcy Metabolism Disorder in the Prefrontal Cortex of HS Rats
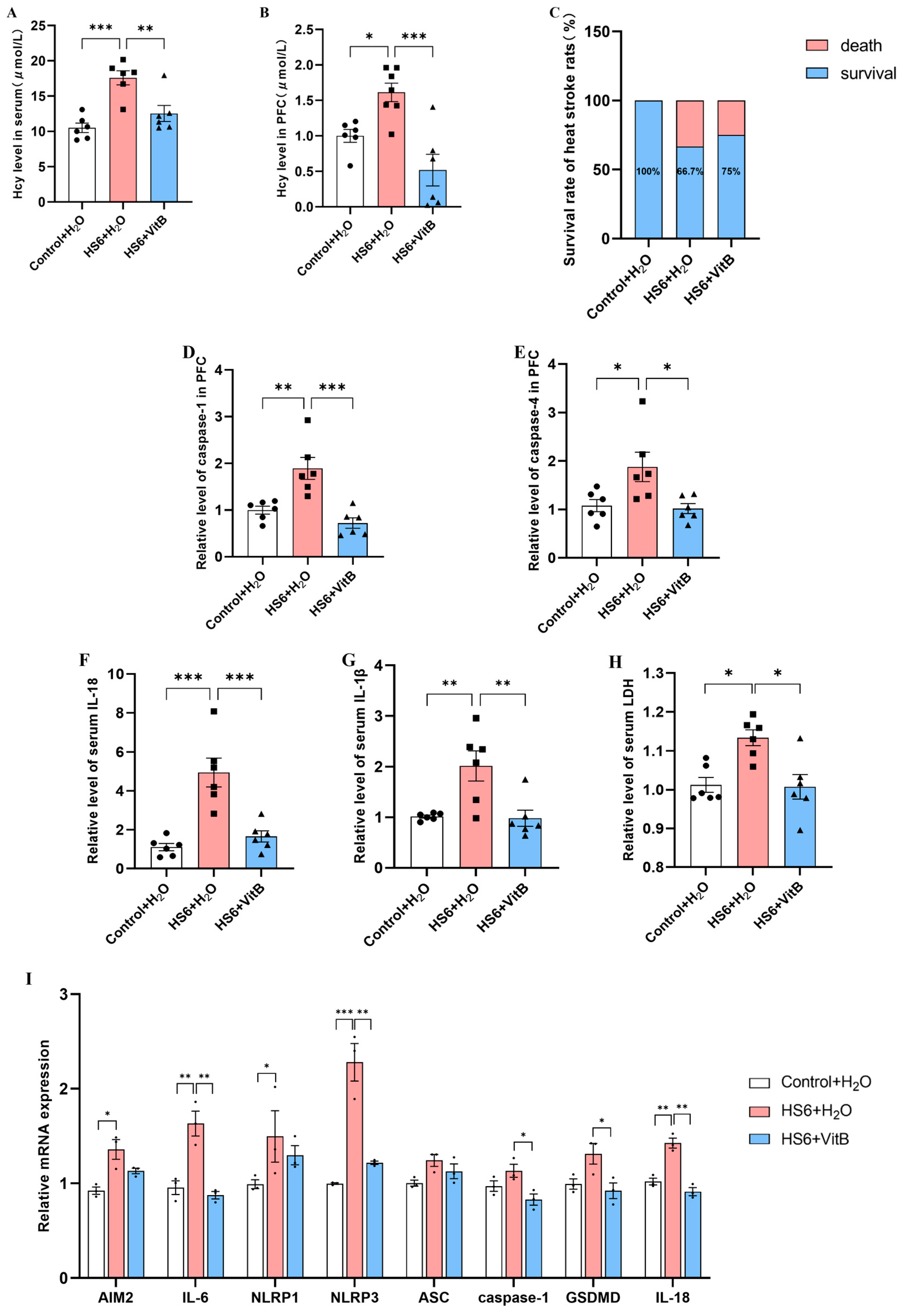
3.4. Hcy Mediates Pyroptosis of Neurons in the Prefrontal Cortex of HS Rats
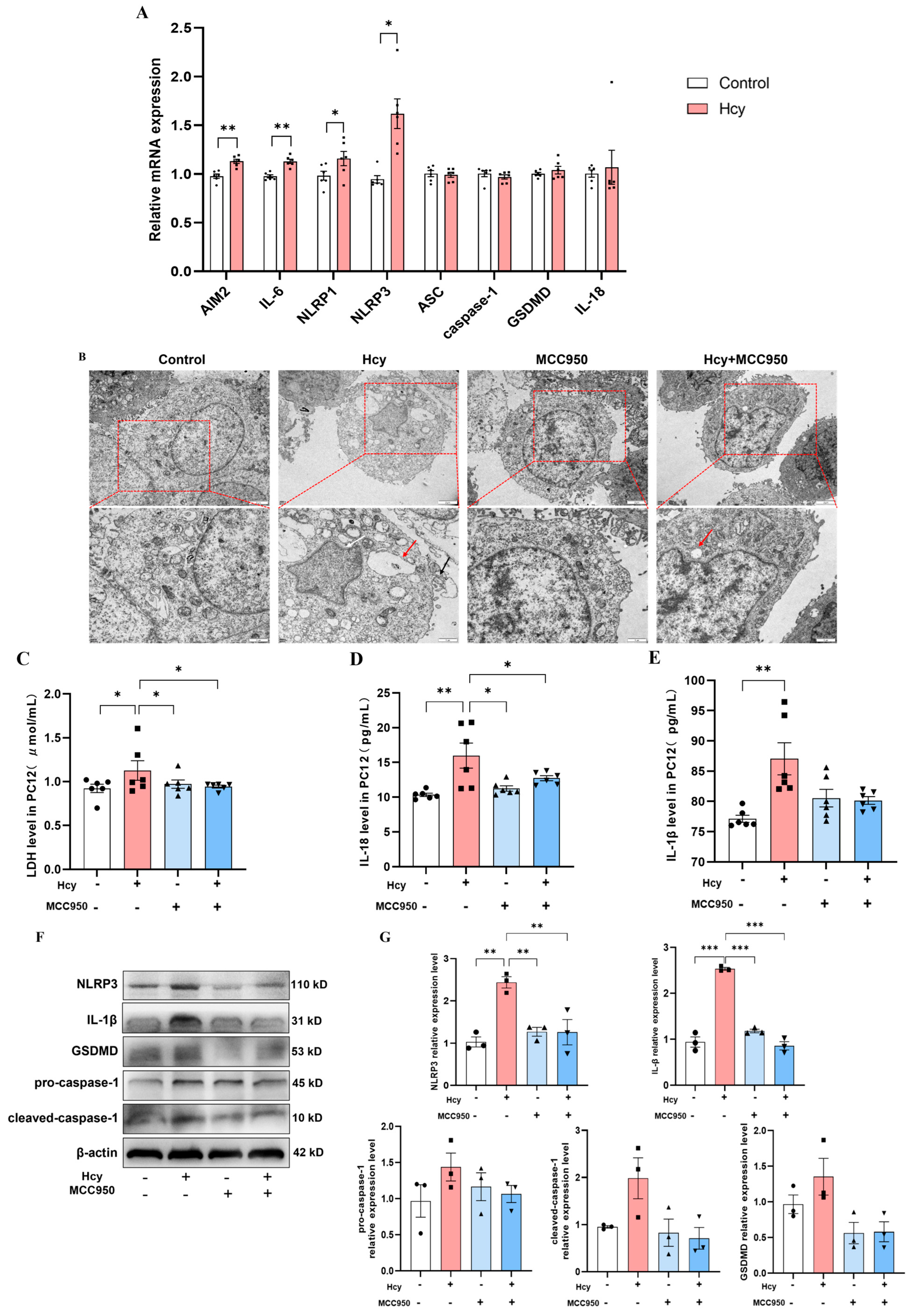
3.5. NLRP3 Inhibition Attenuates Hcy-Induced Pyroptosis in PC12 Cells
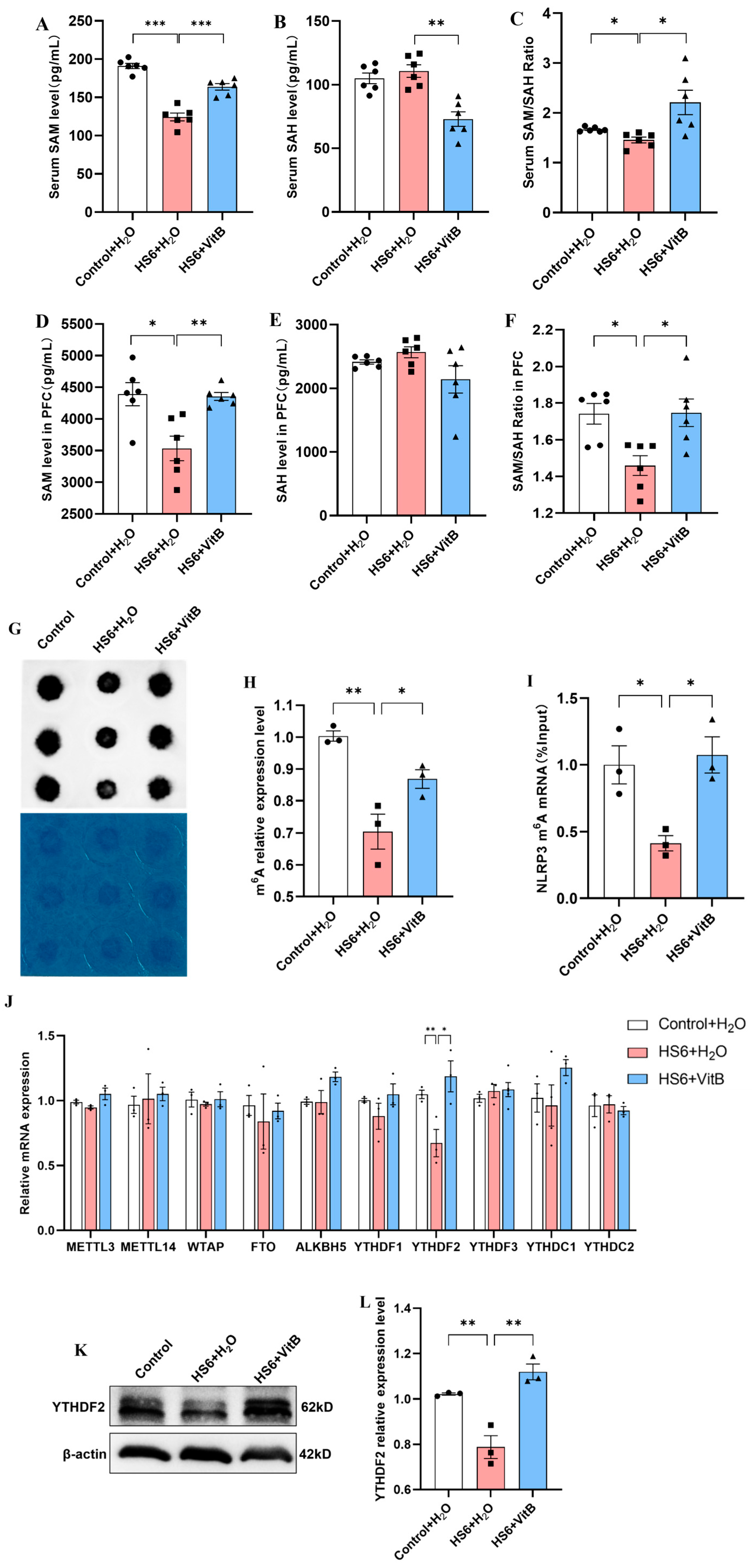
3.6. Hcy Mediates NLRP3 m6A Modification and YTHDF2 Expression in the Prefrontal Cortex of HS Rats
3.7. Hcy Impairs m6A Modification and YTHDF2 Expression in PC12 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchama, A.; Knochel, J.P. Heat stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yin, B.; Fang, Z.; Tian, M.; Ke, L.; Ma, X.; Di, Q. Heat stroke-induced cerebral cortex nerve injury by mitochondrial dysfunction: A comprehensive multi-omics profiling analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubel, S.; Edelstein, C.L. Caspases as drug targets in ischemic organ injury. Curr. Drug Targets Immune Endocr. Metabol. Disord. 2005, 5, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.H.; Tseng, Y.S.; Kuo, N.C.; Kung, C.W.; Amin, S.; Lam, K.K.; Lee, Y.M. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Protects Cardiomyocytes against Heat Stroke-Induced Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses Associated with the Induction of Hsp70 and Activation of Autophagy. Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 8187529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Rong, Y. Extracellular histones exacerbate heat stroke-induced liver injury by triggering hepatocyte pyroptosis and liver injury via the TLR9-NLRP3 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 126, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Berghe, T.V.; Vandenabeele, P.; Kroemer, G. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Chang, H.; Sang, T. Neuronal Cell Death Mechanisms in Major Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, H. Homocysteine Editing, Thioester Chemistry, Coenzyme A, and the Origin of Coded Peptide Synthesis. Life 2017, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, R.; Herrmann, W. Mechanisms of homocysteine neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases with special reference to dementia. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2994–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.S.; Kumar, T.; Dar, T.A.; Singh, L.R. Protein N-homocysteinylation: From cellular toxicity to neurodegeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Peng, L.M.; Ou, Y.J.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Z.Y. The relationship between serum cystatin C, homocysteine, and febrile seizures in children and subsequent epileptic seizures. Chin. J. Eugen. Genet. 2023, 31, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Kose, E.; Besci, O.; Gudeloglu, E.; Suncak, S.; Oymak, Y.; Ozen, S.; Isguder, R. Transcobalamin II deficiency in twins with a novel variant in the TCN2 gene: Case report and review of literature. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Luo, X.; Weng, X.; Qi, J.; Bai, X.; Zhao, C.; Zeng, M.; Bao, X.; Dai, X.; et al. Homocysteine promotes atherosclerosis through macrophage pyroptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and calcium disorder. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Chen, T.; Fang, K.; Zeng, Z.; Ye, H.; Chen, Y. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferases: Functions, regulation, and clinical potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Doxtader, K.A.; Nam, Y. Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Mao, L.; Zhang, L. Crosstalk among N6-methyladenosine modification and RNAs in central nervous system injuries. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1013450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Zeng, R.; Liu, R.; Wang, P.; Jin, X.; Zhao, Y. Epitranscriptomic profiling of N6-methyladenosine-related RNA methylation in rat cerebral cortex following traumatic brain injury. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Mo, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, Q.; Wang, L.; Lin, F.; Kong, C.; Balelang, M.F.; Zhang, A.; Chen, S.; et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylases Alkbh5/Fto regulate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11, 1754207800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, G.; Zheng, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, R. YTHDC1 mitigates ischemic stroke by promoting Akt phosphorylation through destabilizing PTEN mRNA. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Castillo, D.; Ramos-Molina, B.; Cardona, F.; Queipo-Ortuno, M.I. Epigenetic regulation of white adipose tissue in the onset of obesity and metabolic diseases. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhong, K.Y.; Huang, W.G.; Huang, Z.H.; He, T.T.; Yang, M.T.; Wusiman, M.; Zhou, D.D.; Chen, S.; et al. Betaine alleviates cognitive impairment induced by homocysteine through attenuating NLRP3-mediated microglial pyroptosis in an m(6)A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, K.; Gao, R.; Cao, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, S.; Rong, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Inhibition of ALKBH5 attenuates I/R-induced renal injury in male mice by promoting Ccl28 m6A modification and increasing Treg recruitment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa, D.J.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Anderson, S.A.; Courson, R.W.; Heck, J.F.; Jimenez, C.C.; McDermott, B.P.; Miller, M.G.; Stearns, R.L.; Swartz, E.E.; et al. National athletic trainers’ association position statement: Preventing sudden death in sports. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, J.; Pipatti, R.; Hashimoto, S.; Diaz, C.; Mareckova, K.; Diaz, L.; Kjeldsen, P.; Monni, S.; Faaij, A.; Gao, Q.; et al. Mitigation of global greenhouse gas emissions from waste: Conclusions and strategies from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report. Working Group III (Mitigation). Waste Manag. Res. 2008, 26, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Yin, T.; Hu, X.; Mao, Z.; Xiao, J.; et al. Outcome and risk factors associated with extent of central nervous system injury due to exertional heat stroke. Medicine 2017, 96, e8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dematte, J.E.; O’Mara, K.; Buescher, J.; Whitney, C.G.; Forsythe, S.; McNamee, T.; Adiga, R.B.; Ndukwu, I.M. Near-fatal heat stroke during the 1995 heat wave in Chicago. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.S.; Kumar, S.; Agarwal, R.; Gupta, P.K. Acute Vertebrobasilar Territory Infarcts due to Heat Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, e135–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Moon, M.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, T.H.; Oh, M.S. Heat stress-induced memory impairment is associated with neuroinflammation in mice. J Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C.; Benitez-Temino, B.; Blesa, F.J.; Guridi, J.; Marin, C.; Rodriguez, M. Functional organization of the basal ganglia: Therapeutic implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23 (Suppl. S3), S548–S559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.J. Regional brain responses in humans during body heating and cooling. Temperature 2016, 3, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Shen, J.; Ye, Z.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Microglia polarization in heat-induced early neural injury. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hu, C.; Tsai, C.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J. Heat stroke induces autophagy as a protection mechanism against neurodegeneration in the brain. Shock 2010, 34, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.M.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Kung, C.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, W.T.; Cheng, P.Y.; Shen, H.H.; Lee, Y.M. Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates heat stroke-induced multiple organ dysfunction and inflammatory responses by induction of stress proteins and activation of autophagy in rats. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2021, 38, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Geng, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, P.; Xue, S.; Xu, T.; Li, G. Inhibition of TLR4 Alleviates Heat Stroke-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Down-Regulating Inflammation and Ferroptosis. Molecules 2023, 28, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, S.; Bouadma, L.; Kermarrec, N.; Schortgen, F.; Regnier, B.; Wolff, M. Early organ dysfunction course, cooling time and outcome in classic heatstroke. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M.; Laursen, P.B. Treatment of hyperthermia: Is assessment of cooling efficiency enough? Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Xie, F.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L. Role of pyroptosis in inflammation and cancer. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 971–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, S.L.; Gerlic, M.; Metcalf, D.; Preston, S.; Pellegrini, M.; O’Donnell, J.A.; McArthur, K.; Baldwin, T.M.; Chevrier, S.; Nowell, C.J.; et al. NLRP1 inflammasome activation induces pyroptosis of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Immunity 2012, 37, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orning, P.; Weng, D.; Starheim, K.; Ratner, D.; Best, Z.; Lee, B.; Brooks, A.; Xia, S.; Wu, H.; Kelliher, M.A.; et al. Pathogen blockade of TAK1 triggers caspase-8-dependent cleavage of gasdermin D and cell death. Science 2018, 362, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayagaki, N.; Stowe, I.B.; Lee, B.L.; O’Rourke, K.; Anderson, K.; Warming, S.; Cuellar, T.; Haley, B.; Roose-Girma, M.; Phung, Q.T.; et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 2015, 526, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evavold, C.L.; Ruan, J.; Tan, Y.; Shiyu, X.; Hao, W.; Jonathan, C.K. The Pore-Forming Protein Gasdermin D Regulates Interleukin-1 Secretion from Living Macrophages. Immunity 2018, 48, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, R.J.; Buck, C.R.; Smith, A.M. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 1992, 116, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guieu, R.; Ruf, J.; Mottola, G. Hyperhomocysteinemia and cardiovascular diseases. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2022, 80, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, A.; Kamat, P.K.; Givvimani, S.; Brown, K.; Metreveli, N.; Tyagi, S.C.; Tyagi, N. Nutri-epigenetics ameliorates blood-brain barrier damage and neurodegeneration in hyperhomocysteinemia: Role of folic acid. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 52, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, J.A.; Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Caseley, E.; Lara-Reyna, S.; Poulter, J.A.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; Peckham, D.; McDermott, M.F. Neurodegenerative Disease and the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Gao, W.; Shao, F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.H.; Liu, X.D.; Jin, M.H.; Sun, H.N.; Kwon, T. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal pyroptosis and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 1839–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.; Guo, H.; David, C.N.; Brickey, W.J.; Jha, S.; Ting, J.P. NLR members NLRC4 and NLRP3 mediate sterile inflammasome activation in microglia and astrocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1351–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Abellan, A.; Angosto-Bazarra, D.; Martinez-Banaclocha, H.; de Torre-Minguela, C.; Ceron-Carrasco, J.P.; Perez-Sanchez, H.; Arostegui, J.I.; Pelegrin, P. MCC950 closes the active conformation of NLRP3 to an inactive state. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Zhao, M.; Xiong, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, F.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent signalling in cancer progression and insights into cancer therapies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Qing, Y.; Horne, D.; Huang, H.; Chen, J. The roles and implications of RNA m(6)A modification in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, J.D. The metabolism of homocysteine: Pathways and regulation. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1998, 157 (Suppl. S2), S40–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selhub, J. Homocysteine metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1999, 19, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudill, M.A.; Wang, J.C.; Melnyk, S.; Pogribny, I.P.; Jernigan, S.; Collins, M.D.; Santos-Guzman, J.; Swendseid, M.E.; Cogger, E.A.; James, S.J. Intracellular S-adenosylhomocysteine concentrations predict global DNA hypomethylation in tissues of methyl-deficient cystathionine beta-synthase heterozygous mice. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R.; Marion, D.W.; Cornatzer, W.E.; Duerre, J.A. S-Adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocystein metabolism in isolated rat liver. Effects of L-methionine, L-homocystein, and adenosine. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 10822–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.J.; Melnyk, S.; Pogribna, M.; Pogribny, I.P.; Caudill, M.A. Elevation in S-adenosylhomocysteine and DNA hypomethylation: Potential epigenetic mechanism for homocysteine-related pathology. J. Nutr. 2002, 132 (Suppl. S8), 2361S–2366S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2014, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Primer Sequence (Forward) | Primer Sequence (Reverse) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CTTCCTGGGTATGGAATCCT | TCTTTACGGATGTCAACGTC |
| AIM2 | AAATGCTGTTGTTGACCGGC | CTCCGTCCTGTCTGCAATGT |
| IL-6 | ACAAGTCCGGAGAGGAGACT | TTCTGACAGTGCATCATCGC |
| NLRP1 | GACCCTATGTGAGGTCCCCT | GGTGGTCTGTGAGGTCAGTG |
| NLRP3 | TCTGTTCATTGGCTGCGGAT | TAGCCGCAAAGAACTCCTGG |
| GSDMD | CGACTCTGGAGAACTGGTG | TGGGTTTCACTCAACCCAG |
| caspase-1 | GAAGATGATGGCATTAAGAAGG | CCAGGACACATTATCTGGTG |
| IL-18 | TATCTGTGAAGGATGGAAGGA | TTTCAGGTGGATTCATTTCCTC |
| ASC | CACAATGACTGTGCTTAGAGAC | CACAGCTCCAGACTCTTCC |
| METTL3 | ATGTGCAGCCCAACTGGATT | CTGTGCTTAAACCGGGCAAC |
| METTL14 | TCCGGGAACGGCAGAAGTTA | CACAGCACCAATGCTATCTGC |
| WTAP | AGCAGCAACAGCAGGAATCT | GGTGCACTCTTGCATCTCCT |
| FTO | GGAGCGGGAAGCTAAGAAACT | GACCTCTTTGTGCAGCTCCT |
| ALKBH5 | TGGCGCAAGTCCTATGAGTC | CTCATCTTCACCTTGCGGGT |
| YTHDF1 | GGGGACAAGTGGTTCTCAGG | GCCTTGTTGAGGGTGTCACT |
| YTHDF2 | AGTAGGGCAACAGACACAGC | AGTAGATCCAGAACCCGCCT |
| YTHDF3 | ACTTTCAAGCACACCACCTCA | TGGCTTCCTCCTCCTCTTGA |
| YTHDC1 | CAGCCGGGAGGAGAAAGATG | GAAGGCTTCTGTCGCTTGGT |
| YTHDC2 | GCTCATGCAATGATGACCTGT | CCCGCTTGTCTTGCTCATTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Xie, F.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Qian, L.; Zhao, Y. Homocysteine-Mediated Neuronal Pyroptosis Contributes to Brain Injury in Heatstroke Rats by Activating the m6A-YTHDF2-NLRP3 Pathway. Cells 2025, 14, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181437
Zhang S, Xie F, Wang X, Sun Z, Zhang L, Liu W, Chen X, Qian L, Zhao Y. Homocysteine-Mediated Neuronal Pyroptosis Contributes to Brain Injury in Heatstroke Rats by Activating the m6A-YTHDF2-NLRP3 Pathway. Cells. 2025; 14(18):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181437
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shijia, Fang Xie, Xue Wang, Zhaowei Sun, Ling Zhang, Weiwei Liu, Xiaobing Chen, Lingjia Qian, and Yun Zhao. 2025. "Homocysteine-Mediated Neuronal Pyroptosis Contributes to Brain Injury in Heatstroke Rats by Activating the m6A-YTHDF2-NLRP3 Pathway" Cells 14, no. 18: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181437
APA StyleZhang, S., Xie, F., Wang, X., Sun, Z., Zhang, L., Liu, W., Chen, X., Qian, L., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Homocysteine-Mediated Neuronal Pyroptosis Contributes to Brain Injury in Heatstroke Rats by Activating the m6A-YTHDF2-NLRP3 Pathway. Cells, 14(18), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181437





