m6A mRNA Methylation in Hematopoiesis: The Importance of Writing, Erasing, and Reading
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Biochemistry of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification
2. The Role of m6A RNA Methylation in Normal Hematopoiesis and Disease
2.1. HSCs and Endothelial-to-Hematopoietic Transition
2.2. HSC Self-Renewal and Maintenance
2.3. Erythropoiesis
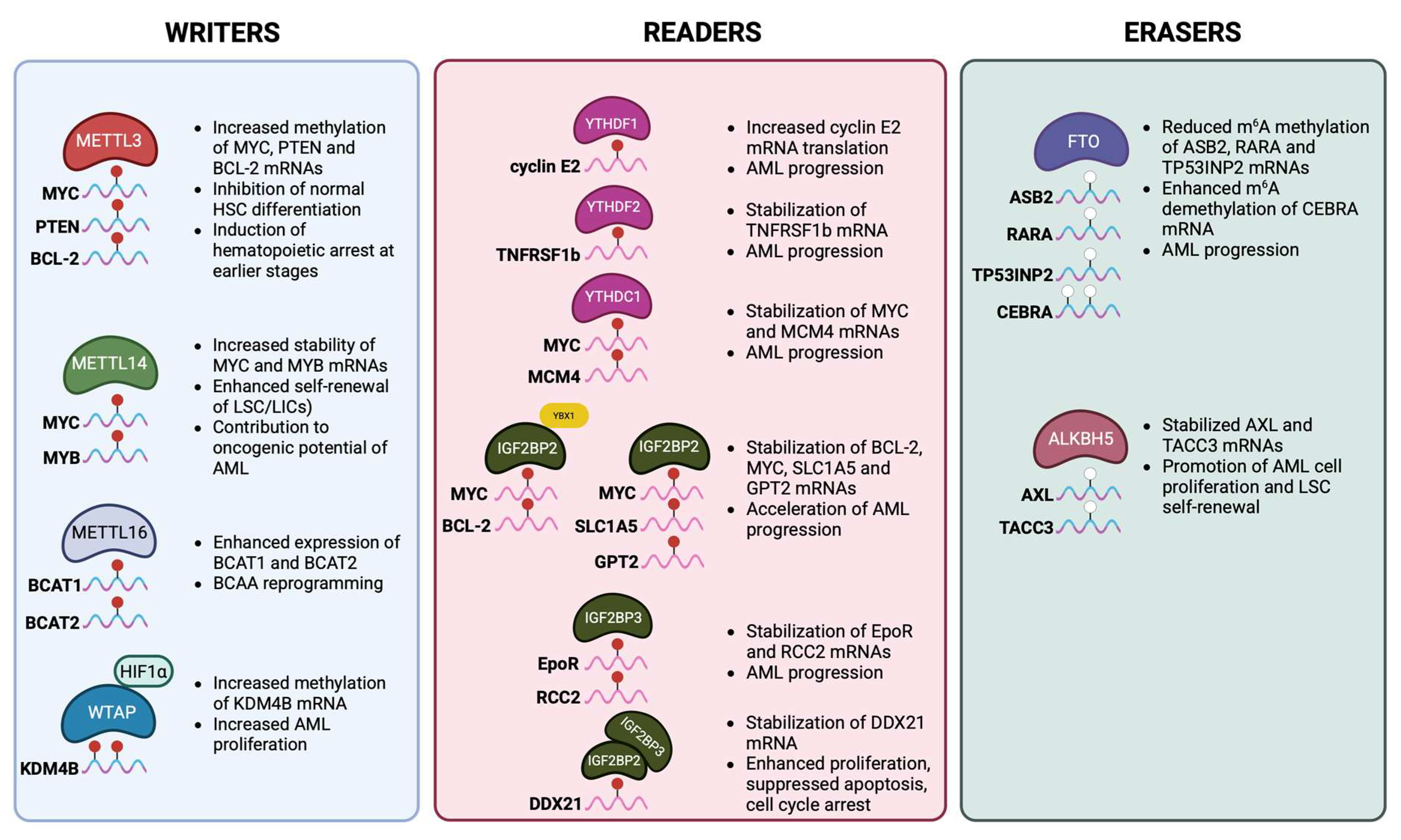
2.4. The Role of m6A Modification in Malignant Myeloid Hematopoiesis
| m6A Regulator | Type | Role in HSCs | Effect on Self-Renewal, Differentiation and Maintainance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| METTL3 | Writer (m6A methyltransferase) | Catalyzes m6A deposition with METTL14 | Essential for HSC self-renewal; loss leads to impaired HSC maintenance, defective differentiation, and bone marrow failure | [56,57] |
| METTL14 | Writer (METTL3 partner) | Stabilizes METTL3 and regulates target mRNAs | Required for HSC self-renewal; deletion causes loss of HSC quiescence and differentiation bias | [29,56] |
| WTAP | Writer complex component | Regulatory subunit for METTL3/METTL14 | Contributes to HSC survival and lineage commitment | [66] |
| FTO | Eraser (demethylase) | Removes m6A from target transcripts | Overexpression reduces differentiation, maintaining stemness; depletion promotes myeloid differentiation | [59] |
| ALKBH5 | Eraser (demethylase) | Regulates mRNA stability and splicing | Helps maintain stem cell pool under stress; linked to leukemogenesis | [58] |
| YTDHF1 | Reader (cytoplasmic) | Enhances translation of m6A-marked transcripts | Promotes lineage-specific differentiation by boosting translation of key regulators | [54] |
| YTDHF2 | Reader (cytoplasmic) | Mediates degradation of m6A-modified RNAs | Critical for HSC self-renewal; deletion leads to increased HSC numbers but reduced long-term function | [50,51,52] |
| YTHDF3 | Reader (cooperates with YTHDF1/2) | Balances translation vs decay | Coordinates with YTHDF1/2 in HSC maintenance | [54] |
| YTHDC1 | Reader (nuclear) | Controls mRNA splicing and export | Ensures proper transcript processing in HSC renewal; deletion causes impaired hematopoiesis | [53,55] |
| IGF2BP1/2/3 | Readers (stabilizers) | Bind and stabilize m6A-marked mRNAs | Enhance expression of stemness-associated genes, supporting HSC maintenance and survival | [31] |
| HNRNPC | Reader (nuclear) | Binds to m6A-switch structures | Controls transcript fate, influencing HSC homeostasis | [90] |
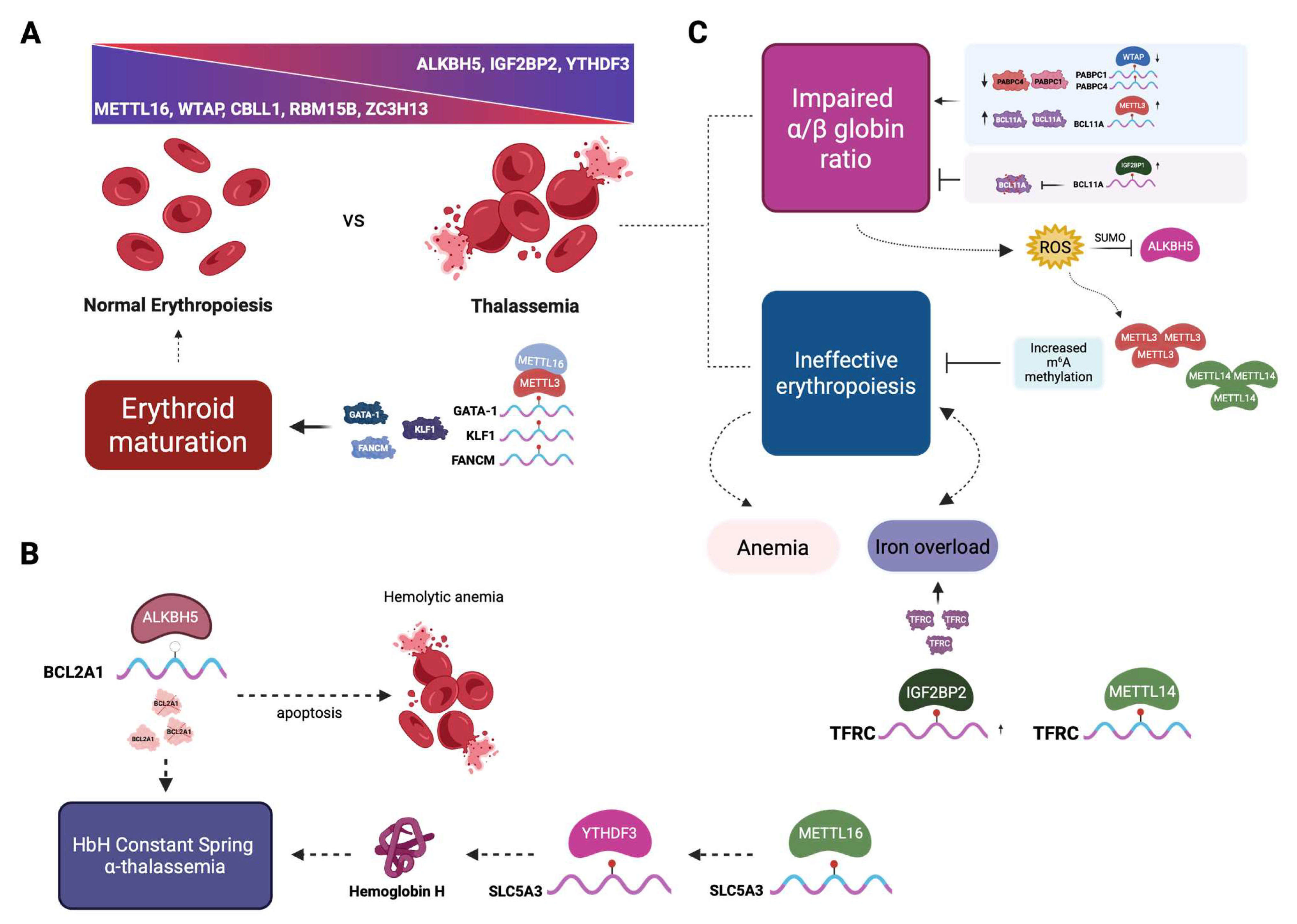
2.5. Ineffective Erythropoiesis and Apoptosis
2.6. The Role of m6A Modification in Thalassemia
3. Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, K.; Zang, C.; Roh, T.Y.; Schones, D.E.; Childs, R.W.; Peng, W.; Zhao, K. Chromatin Signatures in Multipotent Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells Indicate the Fate of Bivalent Genes during Differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.V.; Athans, B.; Iben, J.R.; Johnson, K.; Russanova, V.; Castranova, D.; Pham, V.N.; Butler, M.G.; Williams-Simons, L.; Nichols, J.T.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of hematopoiesis by DNA methylation. eLife 2016, 5, e11813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, H.; Izzo, F.; Pickering, B.F.; Nguyen, D.; Myers, R.; Schurer, A.; Gourkanti, S.; Brüning, J.C.; Vu, L.P.; et al. m6A RNA Methylation Maintains Hematopoietic Stem Cell Identity and Symmetric Commitment. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 1703–1716.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. m6A-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2013, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.M.; Moss, B. Nucleotide Sequences at the N6-Methyladenosine Sites of HeLa Cell Messenger Ribonucleic Acid. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrosiers, R.; Friderici, K.; Rottman, F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Luo, G.Z.; Liu, N.; Han, D.; Dominissini, D.; Dai, Q.; Pan, T.; et al. High-resolution N6-methyladenosine (m6A) map using photo-crosslinking-assisted m6A sequencing. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, H.; Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Wu, L. YTHDF2 destabilizes m6A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4–NOT deadenylase complex. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.D.; Patil, D.P.; Zhou, J.; Zinoviev, A.; Skabkin, M.A.; Elemento, O.; Pestova, T.V.; Qian, S.B.; Jaffrey, S.R. 5′ UTR m6A Promotes Cap-Independent Translation. Cell 2015, 163, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, F.; Yan, J.; Hou, M.; Sun, M.; Zhang, D.; Gong, Z.; Dong, X.; Tang, C.; Yin, P. WTAP–VIRMA counteracts dsDNA binding of the m6A writer METTL3–METTL14 complex and maintains N 6-adenosine methylation activity. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Yu, M.; Lu, Z.; Deng, X.; et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 10, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Cao, J.; Luo, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Gao, M.; Shu, X.; et al. VIRMA mediates preferential m6A mRNA methylation in 3′UTR and near stop codon and associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.P.; Chen, C.K.; Pickering, B.F.; Chow, A.; Jackson, C.; Guttman, M.; Jaffrey, S.R. M6 A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 2016, 537, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Lv, R.; Ma, H.; Shen, H.; He, C.; Wang, J.; Jiao, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, P.; Tan, L.; et al. Zc3h13 Regulates Nuclear RNA m6A Methylation and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 1028–1038.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, F.; Huang, S.; Su, S.; Tan, X.; Zhong, L.; Deng, L.; Pang, L. METTL16 participates in haemoglobin H disease through m6A modification. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; He, P.C.; Liu, W.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, L.; Han, L.; et al. METTL16 exerts an m6A-independent function to facilitate translation and tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine in Nuclear RNA is a Major Substrate of the Obesity-Associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887, Erratum in Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.M.; Li, C.J.; Vågbø, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Song, S.H.; et al. ALKBH5 Is a Mammalian RNA Demethylase that Impacts RNA Metabolism and Mouse Fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Song, B.; Xu, H.; Tang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Meng, J. m6A Reader: Epitranscriptome Target Prediction and Functional Characterization of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) Readers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P.J.; Liu, C.; He, C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Adhikari, S.; Dahal, U.; Chen, Y.S.; Hao, Y.J.; Sun, B.F.; Sun, H.Y.; Li, A.; Ping, X.L.; Lai, W.Y.; et al. Nuclear m6A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Jiao, R.; Xu, P.; Sun, Y.; Li, X. m6A Topological Transition Coupled to Developmental Regulation of Gene Expression During Mammalian Tissue Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 916423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fustin, J.M.; Doi, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Hida, H.; Nishimura, S.; Yoshida, M.; Isagawa, T.; Morioka, M.S.; Kakeya, H.; Manabe, I.; et al. RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed of the circadian clock. Cell 2013, 155, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Z.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. m6A mRNA methylation controls autophagy and adipogenesis by targeting Atg5 and Atg7. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Lin, T.; Chen, G.; Shangguan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W. METTL3 Affects Spinal Cord Neuronal Apoptosis by Regulating Bcl-2 m6A Modifications After Spinal Cord Injury. Neurospine 2023, 20, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhuo, L.; Zhai, B.; Sui, X.; Hu, X.; Xie, T. The emerging molecular mechanism of m6A modulators in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, G.-C.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wen, R.; Liu, W.; et al. The RNA m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes hematopoietic malignancy by maintaining oncogenic translation. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Bao, S.; Qian, Y.; Geula, S.; Leslie, J.; Zhang, C.; Hanna, J.H.; Ding, L. Stage-specific requirement for Mettl3-dependent m6A mRNA methylation during haematopoietic stem cell differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Vasic, R.; Tebaldi, T.; Song, Y.; Teng, R.; Joshi, P.; Viero, G.; Xiao, A.; Batista, P.; Li, H.; et al. Mettl3 Mediated m6A Modification Is Essential in Fetal Hematopoiesis. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. S1), 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Han, G.; Chai, J.; Feng, M.; Wang, P.; et al. Differential m6A RNA landscapes across hematopoiesis reveal a role for IGF2BP2 in preserving hematopoietic stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 149–159.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, M.A.; Schroeder, T. Hematopoiesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.H. Embryonic origins of mammalian hematopoiesis. Exp. Hematol. 2003, 31, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekas, C.; Rhodes, K.E.; van Handel, B.; Chhabra, A.; Ueno, M.; Mikkola, H.K.A. Hematopoietic stem cell development in the placenta. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2010, 54, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Li, Y.; De Obaldia, M.E.; Yang, Q.; Yzaguirre, A.D.; Yamada-Inagawa, T.; Vink, C.S.; Bhandoola, A.; Dzierzak, E.; Speck, N.A. Erythroid/myeloid progenitors and hematopoietic stem cells originate from distinct populations of endothelial cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 541–552, Erratum in Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiers, G.; Baumann, C.; O’Rourke, J.; Giannoulatou, E.; Taylor, S.; Joshi, A.; Moignard, V.; Pina, C.; Bee, T.; Kokkaliaris, K.D.; et al. Early dynamic fate changes in haemogenic endothelium characterized at the single-cell level. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissa, K.; Herbomel, P. Blood stem cells emerge from aortic endothelium by a novel type of cell transition. Nature 2010, 464, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottersbach, K. Endothelial-to-haematopoietic transition: An update on the process of making blood. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Yokomizo, T.; Zeigler, B.M.; Dzierzak, E.; Speck, N.A. Runx1 is required for the endothelial to hematopoietic cell transition but not thereafter. Nature 2009, 457, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, Y.K.; Reddy, E.P. Conditional c-myb knockout in adult hematopoietic stem cells leads to loss of self-renewal due to impaired proliferation and accelerated differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21689–21694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Mesquitta, W.T.; Jung, H.S.; Moskvin, O.V.; Thomson, J.A.; Slukvin, I.I. GATA2 Is Dispensable for Specification of Hemogenic Endothelium but Promotes Endothelial-to-Hematopoietic Transition. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.; Lv, J.; Heng, J.; Ding, Y.; Xue, Y.; et al. m6A modulates haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification. Nature 2017, 549, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.G.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, F. Endothelial-specific m6A modulates mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell development via Notch signaling. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.M.; Wang, M.; Han, W.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, L.; et al. m6A RNA Methylation Is Regulated by MicroRNAs and Promotes Reprogramming to Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 289–301, Erratum in Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M.; Nolan, D.J.; Vertes, E.L.; Varnum-Finney, B.; Kobayashi, H.; Hooper, A.T.; Seandel, M.; Shido, K.; White, I.A.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Endothelial Cells Are Essential for the Self-Renewal and Repopulation of Notch-Dependent Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reya, T.; Duncan, A.W.; Ailles, L.; Domen, J.; Scherer, D.C.; Willert, K.; Hintz, L.; Nusse, R.; Weissman, I.L. A role for Wnt signalling in self-renewal of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 2003, 423, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, G.; Blank, U.; Moody, J.L.; Ehinger, M.; Singbrant, S.; Deng, C.-X.; Karlsson, S. Smad4 is critical for self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, G.; Blank, U.; Moody, J.L.; Ehinger, M.; Singbrant, S.; Deng, C.X.; Karlsson, S. Sonic hedgehog induces the proliferation of primitive human hematopoietic cells via BMP regulation. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zon, L.I. Intrinsic and extrinsic control of haematopoietic stem-cell self-renewal. Nature 2008, 453, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zuo, H.; Liu, J.; Wen, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Xiao, F.; Wang, W.; Huang, G.; et al. Loss of YTHDF2-mediated m6A-dependent mRNA clearance facilitates hematopoietic stem cell regeneration. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapperley, C.; van de Lagemaat, L.N.; Lawson, H.; Tavosanis, A.; Paris, J.; Campos, J.; Wotherspoon, D.; Durko, J.; Sarapuu, A.; Choe, J.; et al. The mRNA m6A reader YTHDF2 suppresses proinflammatory pathways and sustains hematopoietic stem cell function. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20200829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qian, P.; Shao, W.; Shi, H.; He, X.C.; Gogol, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, M.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Suppression of m6A reader Ythdf2 promotes hematopoietic stem cell expansion. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 904–917, Erratum in Cell Res. 2018, 28, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Wei, J.; Yu, F.; Xu, H.; Yu, C.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, X.L.; Gu, X.; et al. A critical role of nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 in leukemogenesis by regulating MCM complex–mediated DNA replication. Blood 2021, 138, 2838–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cong, T.; Wei, L.; Zhong, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.M.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, H.; et al. YTHDF3 modulates hematopoietic stem cells by recognizing RNA m6A modification on Ccnd1. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2381–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, B.; Sheng, Y.; Ju, Z.; Wang, H. YTHDC1-mediated microRNA maturation is essential for hematopoietic stem cells maintenance. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.J.; Sang, L.; Lin, M.; Yin, X.; Dong, W.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, B.O. Mettl3–Mettl14 methyltransferase complex regulates the quiescence of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Vasic, R.; Song, Y.; Teng, R.; Liu, C.; Gbyli, R.; Biancon, G.; Nelakanti, R.; Lobben, K.; Kudo, E.; et al. m6A Modification Prevents Formation of Endogenous Double-Stranded RNAs and Deleterious Innate Immune Responses during Hematopoietic Development. Immunity 2020, 52, 1007–1021.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zimmer, J.T.; Vasic, R.; Liu, C.; Gbyli, R.; Zheng, S.J.; Patel, A.; Liu, W.; Qi, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. ALKBH5 modulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell energy metabolism through m6A modification-mediated RNA stability control. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasala, A.R.; Hassan, T.; Pineault, N.; Maganti, H. Fat Mass Obesity-Associated (FTO) Driven Gene Regulatory Networks Control Hematopoietic Stem Cell Expansion and Homing. Blood 2024, 14 (Suppl. S1), 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierzak, E.; Philipsen, S. Erythropoiesis: Development and Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, K.; Traver, D.; Miyamoto, T.; Weissman, I.L. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature 2000, 404, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfsson, J.; Månsson, R.; Buza-Vidas, N.; Hultquist, A.; Liuba, K.; Jensen, C.T.; Bryder, D.; Yang, L.; Borge, O.J.; Thoren, L.A.M.; et al. Identification of Flt3+ lympho-myeloid stem cells lacking erythro-megakaryocytic potential: A revised road map for adult blood lineage commitment. Cell 2005, 121, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, C.N.; Olson, M.C.; Barton, K.P.; Leiden, J.M. Transcription factor GATA-3 is required for development of the T-cell lineage. Nature 1996, 384, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Bigby, M.; Wang, J.H.; Molnar, A.; Wu, P.; Winandy, S.; Sharpe, A. The ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 1994, 79, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.W.; Simon, M.C.; Anastasi, J.; Singh, H. Requirement of Transcription Factor PU.1 in the Development of Multiple Hematopoietic Lineages. Science 1994, 265, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppers, D.A.; Arora, S.; Lim, Y.; Lim, A.R.; Carter, L.M.; Corrin, P.D.; Plaisier, C.L.; Basom, R.; Delrow, J.J.; Wang, S.; et al. N6-methyladenosine mRNA marking promotes selective translation of regulons required for human erythropoiesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Mettl3-Mediated m6a Modification Is Essential for the Maintenance of Genomic Stability of Erythroid Cells. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, M.; Han, K.; Morgens, D.W.; Horii, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Tsuruyama, T.; Hia, F.; Yasukura, S.; Kajiya, A.; Cai, T.; et al. The N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL16 enables erythropoiesis through safeguarding genome integrity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarani, G.; Fugazza, C.; Strouboulis, J.; Ronchi, A.E. The pleiotropic effects of GATA1 and KLF1 in physiological erythropoiesis and in dyserythropoietic disorders. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallack, M.R.; Perkins, A.C. KLF1 directly coordinates almost all aspects of terminal erythroid differentiation. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithanatudom, P.; Leecharoenkiat, A.; Wannatung, T.; Svasti, S.; Fucharoen, S.; Smith, D.R. A mechanism of ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia/Hb E disease. Haematologica 2010, 95, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, J.N.; Sivasudhan, E.; Tegowski, M.; Xing, Z.; McGinnis, M.M.; Hunter, O.V.; Featherston, K.M.; Sethia, K.; Tu, B.P.; Meyer, K.D.; et al. The catalytic efficiency of METTL16 affects cellular processes by governing the intracellular S-adenosylmethionine setpoint. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayavelu, A.K.; Schnöder, T.M.; Perner, F.; Herzog, C.; Meiler, A.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Huber, N.; Mohr, J.; Edelmann-Stephan, B.; Austin, R.; et al. Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms. Nature 2020, 588, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.P.; Pickering, B.F.; Cheng, Y.; Zaccara, S.; Nguyen, D.; Minuesa, G.; Chou, T.; Chow, A.; Saletore, Y.; Mackay, M.; et al. The N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shao, F.; Guo, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Gao, Y.; He, J.; Lu, Z. WNT/β-catenin-suppressed FTO expression increases m6A of c-Myc mRNA to promote tumor cell glycolysis and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lou, S.; Deng, J. The m6A reader IGF2BP3 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression by enhancing RCC2 stability. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B.S.; Mesquita, A.; Liu, C.; Yuan, C.L.; et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP Proteins Enhances mRNA Stability and Translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, H.; Huang, H.; Wu, H.; Qin, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Dong, L.; Shi, H.; Skibbe, J.; Shen, C.; Hu, C.; et al. METTL14 Inhibits Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Differentiation and Promotes Leukemogenesis via mRNA m6A Modification. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 191–205.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.; Morgan, M.; Campos, J.; Spencer, G.J.; Shmakova, A.; Ivanova, I.; Mapperley, C.; Lawson, H.; Wotherspoon, D.A.; Sepulveda, C.; et al. Targeting the RNA m6A Reader YTHDF2 Selectively Compromises Cancer Stem Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 137–148.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, G.D.; Mercher, T.; Shigematsu, H.; Williams, I.R.; Cullen, D.E.; Akashi, K.; Bernard, O.A.; Gilliland, D.G. Ott1(Rbm15) has pleiotropic roles in hematopoietic development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6001–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, J.; Breslin, P.; Onciu, M.; Ma, Z.; Morris, S.W. c-Myc is a target of RNA-binding motif protein 15 in the regulation of adult hematopoietic stem cell and megakaryocyte development. Blood 2009, 114, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, A.C.; Robinson, S.; Jiang, X.; Dong, L.; Chen, H.; Su, R.; Yin, Z.; Li, W.; et al. RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 Selectively Promotes Tumorigenesis and Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 64–80.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Han, G.; Zhang, T.; Chang, J.; Yin, R.; Shan, Y.; Wen, J.; Xie, X.; et al. Leukemogenic Chromatin Alterations Promote AML Leukemia Stem Cells via a KDM4C-ALKBH5-AXL Signaling Axis. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 81–97.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Xie, X.; Han, G.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yin, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; et al. YBX1 is required for maintaining myeloid leukemia cell survival by regulating BCL2 stability in an m6A-dependent manner. Blood 2021, 138, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Dong, Z.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Liao, B.; Han, W.; et al. YTHDF1-enhanced iron metabolism depends on TFRC m6A methylation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 12072–12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ye, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Hu, X.; Su, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Lu, F.; et al. METTL3 mediates chemoresistance by enhancing AML homing and engraftment via ITGA4. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Dong, L.; Leung, K.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Chen, Z.; Xue, J.; Qing, Y.; Li, W.; et al. METTL16 drives leukemogenesis and leukemia stem cell self-renewal by reprogramming BCAA metabolism. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 52–68.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Zhou, H.S.; Liu, D.H.; Yu, L.; Lin, J.; Gao, X.N. HIF1α-mediated transactivation of WTAP promotes AML cell proliferation via m6A-dependent stabilization of KDM4B mRNA. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Weng, H.; Su, R.; Weng, X.; Zuo, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Nachtergaele, S.; Dong, L.; Hu, C.; et al. FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N6-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, V.; Meacham, A.; Katzell, L.M.; Winer, A.J.; Terrell, J.; Archibald, V.L.; Vaughn, L.T.; Drusbosky, L.; Thach, E.; Welmaker, G.; et al. Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein C is an Indispensable Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcheva, I.A.; Wood, T.; Chiarolanzio, K.; Chim, B.; Wong, M.; Singh, V.; Gowda, C.P.; Lu, Q.; Hafner, M.; Dovat, S.; et al. RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1 maintains leukemia stem cell properties by regulating HOXB4, MYB, and ALDH1A1. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, L.A.; Fisher, T.C.; Zeng, L.; Meiselman, H.J.; Weinberg, K.I.; Hiti, A.L.; Malik, P. Ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia major is due to apoptosis at the polychromatophilic normoblast stage. Exp. Hematol. 2000, 28, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichompoo, P.; Nithipongvanitch, R.; Kheansaard, W.; Tubsuwan, A.; Srinoun, K.; Vadolas, J.; Fucharoen, S.; Smith, D.R.; Winichagoon, P.; Svasti, S. Increased autophagy leads to decreased apoptosis during β-thalassaemic mouse and patient erythropoiesis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Fei, W.; Fang, X.; Hu, X. Epitranscriptomic m6A modification in the stem cell field and its effects on cell death and survival. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, X.; Gong, W.; Shao, X.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Shi, Y.; Shen, S.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Q.; et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of ATG7 regulates autophagy-GATA4 axis to promote cellular senescence and osteoarthritis progression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhuo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Yan, L.; Jin, T.; Pan, T.; Sui, X.; et al. METTL3 plays multiple functions in biological processes. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 1631–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, C.; Yin, H.; Gong, S.; Wu, N.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Y. RNA modifications act as regulators of cell death. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Tahir, M.; Zhang, F.; Ran, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Current insights into the implications of m6A RNA methylation and autophagy interaction in human diseases. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhuo, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Pan, T.; Yan, L.; et al. The mechanism of m6A methyltransferase METTL3-mediated autophagy in reversing gefitinib resistance in NSCLC cells by β-elemene. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Yang, F.; Deng, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Pang, L. Human m6A-mRNA and lncRNA epitranscriptomic microarray reveal function of RNA methylation in hemoglobin H-constant spring disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20478, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shuai, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, G. Small molecule inhibitors targeting m6A regulators. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.B.; Gross, J.; Pratt, K.; Guo, X.; Byrnes, C.; Lee, Y.T.; Lavelle, D.; Dean, A.; Miller, J.L.; Wilber, A. The mRNA-Binding Protein IGF2BP1 Restores Fetal Hemoglobin in Cultured Erythroid Cells from Patients with β-Hemoglobin Disorders. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, M.; Xu, L.; Huang, H. Regulation of N6-methyladenosine modification in erythropoiesis and thalassemia. Clin. Genet. 2024, 106, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Jaffrey, S.R. Hidden codes in mRNA: Control of gene expression by m6A. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2236–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Olarerin-George, A.O.; Liu, J.F.; Zaccara, S.; Hawley, B.; Jaffrey, S.R. m6A alters ribosome dynamics to initiate mRNA degradation. Cell 2025, 188, 3728–3743.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćorović, M.; Hoch-Kraft, P.; Zhou, Y.; Hallstein, S.; König, J.; Zarnack, K. m6A in the coding sequence: Linking deposition, translation, and decay. Trends Genet. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Sun, J.; Yao, M.; Miao, L.; Li, M. Biological roles of enhancer RNA m6A modification and its implications in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasilopoulou, A.-G.; Kalafati, E.; Drakopoulou, E.; Anagnou, N.P. m6A mRNA Methylation in Hematopoiesis: The Importance of Writing, Erasing, and Reading. Cells 2025, 14, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171388
Vasilopoulou A-G, Kalafati E, Drakopoulou E, Anagnou NP. m6A mRNA Methylation in Hematopoiesis: The Importance of Writing, Erasing, and Reading. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171388
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasilopoulou, Antonia-Gerasimina, Eleni Kalafati, Ekati Drakopoulou, and Nicholas P. Anagnou. 2025. "m6A mRNA Methylation in Hematopoiesis: The Importance of Writing, Erasing, and Reading" Cells 14, no. 17: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171388
APA StyleVasilopoulou, A.-G., Kalafati, E., Drakopoulou, E., & Anagnou, N. P. (2025). m6A mRNA Methylation in Hematopoiesis: The Importance of Writing, Erasing, and Reading. Cells, 14(17), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171388







