Polo-like Kinase 4: A Molecular Culprit in Skin Cancer Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
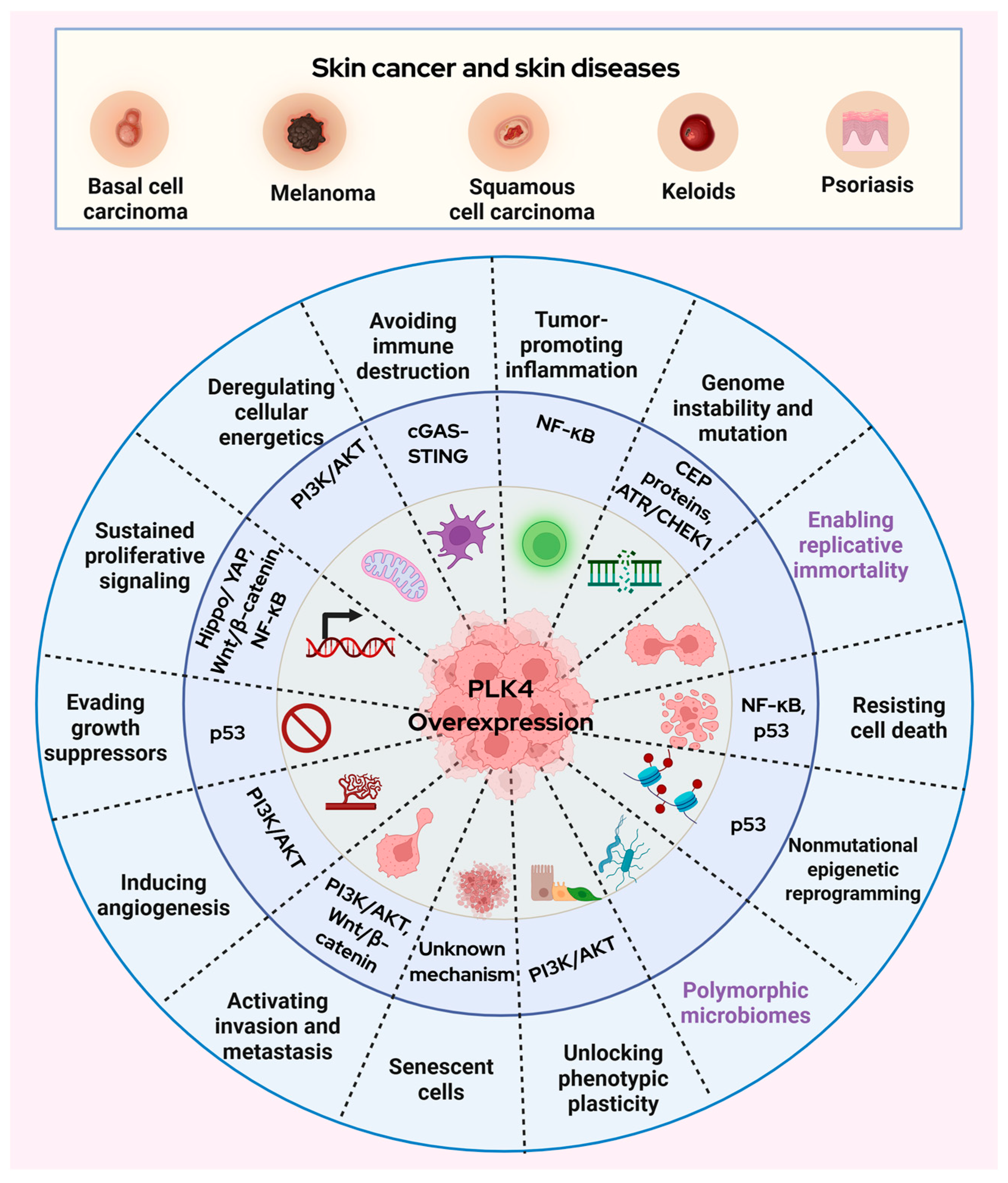
2. Polo-like Kinase 4 in Skin Diseases and Skin Cancer
3. Prospective Roles of PLK4 in Skin Cancer
3.1. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
3.2. p53 Signaling
3.3. PI3K/AKT Signaling
3.4. Hippo/YAP Signaling
3.5. cGAS-STING Signaling
3.6. NF-κB Signaling
3.7. ATR/CHEK1 Signaling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLK4 | Polo-like kinase 4 |
| cSCC | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma |
| DDR | DNA damage repair |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| ATR | Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| CA | Centrosome amplification |
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zompit, M.D.M.; Stucki, M. Mechanisms of genome stability maintenance during cell division. DNA Repair 2021, 108, 103215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cárcer, G.; Manning, G.; Malumbres, M. From Plk1 to Plk5: Functional evolution of polo-like kinases. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Soung, N.-K.; Johmura, Y.; Kang, Y.H.; Liao, C.; Park, C.H.; Nicklaus, M.C.; Lee, K.S. Polo-box domain: A versatile mediator of polo-like kinase function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1957–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slevin, L.K.; Nye, J.; Pinkerton, D.C.; Buster, D.W.; Rogers, G.C.; Slep, K.C. The Structure of the Plk4 Cryptic Polo Box Reveals Two Tandem Polo Boxes Required for Centriole Duplication. Structure 2012, 20, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Yu, Q.; Yang, N.; Xiao, Z.; Song, C.; Zhang, R.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Deng, H. Therapeutic potential of targeting polo-like kinase 4. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 265, 116115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; et al. YLZ-F5, a novel polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor, inhibits human ovarian cancer cell growth by inducing apoptosis and mitotic defects. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, F.; Casás-Selves, M.; Bubenik, M.; Duplessis, M.; Sow, B.; Suarez, C.; Sangiorgi, B.; Li, L.; Hyer, M.; Papp, R.; et al. Discovery of RP-1664: A First-in-Class Orally Bioavailable, Selective PLK4 Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 10631–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, B.A.; Yee, K.; Koller, P.B.; Brandwein, J.; Mims, A.S.; Michelson, G.C.; Nguyen, L.; Bray, M.R.; Roberts-Thomson, E.L.; Borthakur, G. Preliminary Results from a Phase 2 Open-Label, Multicenter, Dose Optimization Clinical Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetic (PK) and Pharmacodynamic (PD) Profiles of Cfi-400945 As a Single Agent or in Combination with Azacitidine or Decitabine in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Myelodysplastic Syndrome or Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (TWT-202). Blood 2022, 140, 9076–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denu, R.A.; Shabbir, M.; Nihal, M.; Singh, C.K.; Longley, B.J.; Burkard, M.E.; Ahmad, N. Centriole Overduplication is the Predominant Mechanism Leading to Centrosome Amplification in Melanoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Han, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Miao, G.; Niu, L. Polo-Like Kinase 4 Correlates with Aggressive Tumor Characteristics, Shortened Disease-Free Survival and Overall Survival in Patients with Cutaneous Melanoma who Undergo Surgical Resection. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2024, 262, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.A.; Bury, L.; Shahbazi, M.N.; Liakath-Ali, K.; Tate, P.H.; Wormald, S.; Hindley, C.J.; Huch, M.; Archer, J.; Skarnes, W.C.; et al. Over-expression of Plk4 induces centrosome amplification, loss of primary cilia and associated tissue hyperplasia in the mouse. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 150209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulukian, A.; Holland, A.J.; Vitre, B.; Naik, S.; Cleveland, D.W.; Fuchs, E. Epidermal development, growth control, and homeostasis in the face of centrosome amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6311–E6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serçin, Ö.; Larsimont, J.-C.; Karambelas, A.E.; Marthiens, V.; Moers, V.; Boeckx, B.; Le Mercier, M.; Lambrechts, D.; Basto, R.; Blanpain, C. Transient PLK4 overexpression accelerates tumorigenesis in p53-deficient epidermis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 18, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitre, B.; Holland, A.J.; Kulukian, A.; Shoshani, O.; Hirai, M.; Wang, Y.; Maldonado, M.; Cho, T.; Boubaker, J.; Swing, D.A.; et al. Chronic centrosome amplification without tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6321–E6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, T.; Muntaqua, D.; Chhabra, G.; Ahmad, N. Polo-like kinases and UV -induced skin car-cinogenesis: What we know and what’s next. Photochem. Photobiol. 2025. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandarian, F.; Razi, F.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Arjmand, B.; Sherafat, S.J.; Nejad, M.R. Assessment of Recovery Time Effects on Human Primary Neonatal Dermal Fibroblasts After Exposure to Solar-Simulated Ultraviolet Radiation. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2024, 15, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, M.A.; Garvey, D.R.; Chhabra, G.; Singh, C.K.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. PLK4 is a potential therapeutic target in nonmelanoma skin cancers: Evidence from molecular and in vivo studies. Photochem. Photobiol. 2025. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Miller, H.D.; He, L.; Ge, D.; Wang, A.R.; You, Z. Defect of IL17 Signaling, but Not Centrinone, Inhibits the Development of Psoriasis and Skin Papilloma in Mouse Models. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, C.; Fu, R.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q. Downregulation of PLK4 expression induces apoptosis and G0/G1-phase cell cycle arrest in keloid fibroblasts. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, C.; Liang, H.; Han, L. Polo-Like Kinase 4’s Critical Role in Cancer Development and Strategies for Plk4-Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 587554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, M.; Pang, R. PLK4 Reflects Extrathyroidal Invasion, High Tumor Stage And Poor Prognosis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients. Biomarkers Med. 2024, 18, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fan, P.; Huang, Q.; Dong, K.; Qi, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, L.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; et al. High PLK4 expression promotes tumor progression and induces epithelial mesenchymal transition by regulating the Wnt/β catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, H.; Ma, W.; Wu, K.; Peng, G.; Ou, T.; Wu, S. Down-regulation of Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) induces G1 arrest via activation of the p38/p53/p21 signaling pathway in bladder cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 2631–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.-S.; Wei, C.; Yu, R.-Z.; Du, X.-Z.; He, Y.-J.; Ren, Y.; Zhen, Y.-W.; Han, L. Polo-like kinase 4 promotes tumorigenesis and glucose metabolism in glioma by activating AKT1 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2024, 585, 216665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, J.; Xu, D.; Ran, Q. PLK4 inhibitor plus bortezomib exhibits a synergistic effect on treating multiple myeloma via inactivating PI3K/AKT signaling. Ir. J. Med. Sci. (1971) 2022, 192, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y.; Han, Y.; Hu, S.; Ren, S.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. Inhibition of Polo-like kinase 4 induces mitotic defects and DNA damage in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Yuen, V.W.; Chiu, D.K.; Goh, C.; Thu, K.L.; Cescon, D.W.; Soria-Bretones, I.; Law, C.; Cheu, J.W.; Lee, D.; et al. Polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor CFI-400945 suppresses liver cancer through cell cycle perturbation and eliciting antitumor immunity. Hepatology 2023, 77, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, J.; et al. MiR-126 negatively regulates PLK-4 to impact the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via ATR/CHEK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, X.; Nusse, R. Wnt Signaling in Skin Development, Homeostasis, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 5, a008029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolomeo, L.; Vaccaro, F.; Irrera, N.; Borgia, F.; Pomi, F.L.; Squadrito, F.; Vaccaro, M. Wnt Signaling Pathways: From Inflammation to Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Czyz, M. WNT Signaling in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Xie, B. PLK4 inhibitor exhibits antitumor effect and synergizes sorafenib via arresting cell cycle and inactivating Wnt/β-catenin pathway in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2023, 24, 2223383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, C.; Ananthaswamy, H. p53 and the pathogenesis of skin cancer. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 224, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, J.B.; Raimundo, L.; Calheiros, J.; Carvalho, C.; Barcherini, V.; Lima, N.R.; Gomes, C.; Almeida, M.I.; Alves, M.G.; Costa, J.L.; et al. Targeting p53 for Melanoma Treatment: Counteracting Tumour Proliferation, Dissemination and Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Quaas, M.; Wintsche, A.; Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. Polo-like kinase 4 transcription is activated via CRE and NRF1 elements, repressed by DREAM through CDE/CHR sites and deregulated by HPV E7 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.; Hudson, J.W.; Rotter, V. p53-Dependent and Cell Specific Epigenetic Regulation of the Polo-like kinases under Oxidative Stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tan, M.; Li, L.; Pamarthy, D.; Lawrence, T.S.; Sun, Y. SAK, A New Polo-Like Kinase, Is Transcriptionally Repressed by p53 and Induces Apoptosis upon RNAi Silencing. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davies, M.A. The Role of the PI3K-AKT Pathway in Melanoma. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhou, D.; Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, B.; Cao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Polo-like kinase 4 mediates epithelial–mesenchymal transition in neuroblastoma via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, R.-Z.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhen, Y.-W.; Han, L. Polo-like kinase 4 accelerates glioma malignant progression and vasculogenic mimicry by phosphorylating EphA2. Cancer Lett. 2024, 611, 217397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Xu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Robichaud, P.; Betcher, S.; Calderone, K.; He, T.; Johnson, T.M.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Elevated YAP and its downstream targets CCN1 and CCN2 in basal cell carcinoma: Impact on keratinocyte pro-liferation and stromal cell activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Li, C.; Luo, S.; Liu-Smith, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Lai, B.; Lei, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Yes-Associated Protein Contributes to the Development of Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Activation of RAS. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Szeto, P.; Abali, G.K.; Zhang, Y.; Kulkarni, A.; Amarasinghe, K.; Li, J.; Vergara, I.A.; Molania, R.; et al. The Hippo pathway oncoprotein YAP promotes melanoma cell invasion and spontaneous metastasis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 5267–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jin, H.; Gao, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Ding, H.; Chen, A.; Tan, S.; Zhang, F.; Shao, J.; et al. A novel lncRNA PLK4 up-regulated by talazoparib represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by promoting YAP-mediated cell senescence. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5304–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Li, X.; Han, S.; Liang, Q.; Ma, X.; Rong, P.; Wang, W.; Li, W. The cGAS/STING Pathway: A Novel Target for Cancer Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 795401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falahat, R.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Mailloux, A.W.; Zhu, G.; Pilon-Thomas, S.; Barber, G.N.; Mulé, J.J. STING Signaling in Melanoma Cells Shapes Antigenicity and Can Promote Antitumor T-cell Activity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.-H.; Lam, W.; Dang, C.-C.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Zheng, L.-C.; Chan, N.N.-M.; Ng, K.-L.; Chan, K.-C.; Kwok, T.-H.; Ng, T.C.-C.; et al. Inhibition of PLK4 remodels histone methylation and activates the immune response via the cGAS-STING pathway in TP53-mutated AML. Blood 2023, 142, 2002–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Degitz, K.; Quirling, M.; Jilg, N.; Page, S.; Brand, K. Involvement of NF-κB signalling in skin physiology and disease. Cell Signal. 2003, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Pasparakis, M. Epidermal p65/NF-κB signalling is essential for skin carcinogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, Y.M.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Splittgerber, R.; Na, S.; Boyd, A.; Mosse, C.; Simons, C.; Richmond, A. NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK) modulates melanoma tumorigenesis by regulating expression of pro-survival factors through the β-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2011, 31, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, A.; Sellier, H.; Gillies, K.; Iannetti, A.; James, J.; Perkins, N. NFκB regulates expression of Polo-like kinase 4. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3052–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, K.; Wickett, R.R.; Zhang, Y. Dermal fibroblasts induce cell cycle arrest and block epithelial–mesenchymal transition to inhibit the early stage melanoma development. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hove, L.; Hoste, E. Activation of Fibroblasts in Skin Cancer. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Liang, H.; Zhang, A.; et al. PLK4 is a determinant of temozolomide sensitivity through phosphorylation of IKBKE in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, H.; Makinwa, Y.; Zou, Y. Novel Cellular Functions of ATR for Therapeutic Targeting: Embryogenesis to Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-F.; Ruiz-Vega, R.; Vasudeva, P.; Espitia, F.; Krasieva, T.B.; de Feraudy, S.; Tromberg, B.J.; Huang, S.; Garner, C.P.; Wu, J.; et al. ATR Mutations Promote the Growth of Melanoma Tumors by Modulating the Immune Microenvironment. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, R.A.; Appleman, L.J.; Bauman, J.E.; Sankunny, M.; Lewis, D.W.; Vlad, A.; Gollin, S.M. Upregulation of the ATR-CHEK1 pathway in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2013, 53, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Saito, H.; Takekawa, M. SAPK pathways and p53 cooperatively regulate PLK4 activity and centrosome integrity under stress. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. PLK4: A promising target for cancer therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaiswal, T.; Muntaqua, D.; Ahmad, N. Polo-like Kinase 4: A Molecular Culprit in Skin Cancer Pathogenesis. Cells 2025, 14, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171381
Jaiswal T, Muntaqua D, Ahmad N. Polo-like Kinase 4: A Molecular Culprit in Skin Cancer Pathogenesis. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171381
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaiswal, Tanya, Durdana Muntaqua, and Nihal Ahmad. 2025. "Polo-like Kinase 4: A Molecular Culprit in Skin Cancer Pathogenesis" Cells 14, no. 17: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171381
APA StyleJaiswal, T., Muntaqua, D., & Ahmad, N. (2025). Polo-like Kinase 4: A Molecular Culprit in Skin Cancer Pathogenesis. Cells, 14(17), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171381






