Claudin 5 Across the Vascular Landscape: From Blood–Tissue Barrier Regulation to Disease Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physiology of Cldn5: Structure, Expression Regulation, Function, and Interactions
2.1. Structural Features and Protein Interactions
2.2. Regulation of Cldn5 Expression
2.3. Cell-Type and Organ-Specific Expression
3. Cldn5 in Endothelial-Barrier Regulation
4. Cldn5 and BBB Permeability Modulation in Health and Disease
5. Cldn5 in Retinal Vascular Pathophysiology
5.1. Diabetic Retinopathy
5.2. Diabetic Macular Edema
5.3. Retinopathy of Prematurity
5.4. Stressors and Cytokine-Mediated Disruption of Cldn5 and Retinal Barrier Integrity
6. Cldn5 in Peripheral Nerves and Cranial Nerve Barriers
7. Cldn5 in Cardiovascular Diseases and Organ Injuries
7.1. Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy
7.2. Lung-Air Barrier Dysfunction
7.3. Liver Physiology and Pathology
7.4. Gut Health and Disease
7.5. Renal and Urinary Tract Barrier Function and Disease
7.6. Skin Barrier Integrity and Dermatological Disorders
8. Targeting Cldn5 to Restore Barrier Integrity in Diseases
8.1. Therapeutic Modulation of Cldn5 to Enhance Drug Delivery
8.2. Modulation of Cldn5 Expression as a Therapeutic Strategy in DR
8.3. Potential Utility of Cldn5 as a Functional Reporter and a Screening Target
8.4. Targeting Cldn5 to Restore Barrier Integrity in Cancers and Other Diseases
9. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| BRB | Blood–Retinal Barrier |
| iBRB | Inner Blood–Retinal Barrier |
| oBRB | Outer Blood–Retinal Barrier |
| Cldn5 | Claudin-5 |
| TJs | Tight Junctions |
| ECs | Endothelial Cells |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| ZO-1 | Zonula Occludens-1 |
| GDNF | Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| Akt | Protein Kinase B |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead Box O1 |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| EAE | Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation (e.g., CD4+ T cells) |
| HG | High Glucose |
| AGE | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| TEER | Transendothelial/Transepithelial Electrical Resistance |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| OCD | Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IR | Insulin Receptor |
| VEC | Vascular Endothelial Cadherin |
| VDR | Vitamin D Receptor |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| DKD | Diabetic Kidney Disease |
| DN | Diabetic Nephropathy |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| cSCC | Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| EpV | Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MMP3 | Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 |
| JAM-A | Junctional Adhesion Molecule-A |
| VE-cadherin | Vascular Endothelial Cadherin |
| SH-SY5Y | Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line |
| U251 | Human Glioblastoma Astrocytoma Cell Line |
| hCMEC/D3 | Human Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells (immortalized line) |
References
- Garcia, M.A.; Nelson, W.J.; Chavez, N. Cell-Cell Junctions Organize Structural and Signaling Networks. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.R.; Felgueiras, J.; Fardilha, M. Signaling pathways in anchoring junctions of epithelial cells: Cell-to-cell and cell-to-extracellular matrix interactions. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2015, 35, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittler, H.J. Structural and functional aspects of intercellular junctions in vascular endothelium. Basic Res. Cardiol. 1998, 93 (Suppl. S3), 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Girardello, R.; Dittmar, G.; Ludwig, A. New insights into the organization and regulation of the apical polarity network in mammalian epithelial cells. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 7073–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.S.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Cell-cell junctions: Structure and regulation in physiology and pathology. Tissue Barriers 2021, 9, 1848212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, P.; Goodenough, D.A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from “tight” and “leaky” epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 58, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, M.G.; Palade, G.E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 375–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeberger, E.E.; Lynch, R.D. Structure, function, and regulation of cellular tight junctions. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, L647–L661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.W. Barrier function of epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 241, G275–G288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbiner, B.M. Breaking through the tight junction barrier. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Doi, Y.; Itoh, M.; Fujimoto, T.; Furuse, M.; Takano, H.; Noda, T.; Tsukita, S. Occludin-deficient embryonic stem cells can differentiate into polarized epithelial cells bearing tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineta, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Tada, Y.; Saito, K.; Tamura, A.; Igarashi, M.; Endo, T.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Tani, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Tamura, A.; Ishitani, R.; Dohmae, N.; Tsukita, S.; Nureki, O.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Crystal structure of a claudin provides insight into the architecture of tight junctions. Science 2014, 344, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Itoh, M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukita, S.; Tanaka, H.; Tamura, A. The Claudins: From Tight Junctions to Biological Systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, S.; Anwer, S.; Szászi, K. Claudin-2: Roles beyond Permeability Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, G.; Winkler, L.; Mueller, S.L.; Haseloff, R.F.; Piontek, J.; Blasig, I.E. Structure and function of claudins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Greene, C.; Munnich, A.; Campbell, M. The CLDN5 gene at the blood-brain barrier in health and disease. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlingmann, B.; Molina, S.A.; Koval, M. Claudins: Gatekeepers of lung epithelial function. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 42, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunzel, D.; Yu, A.S. Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enck, A.H.; Berger, U.V.; Yu, A.S. Claudin-2 is selectively expressed in proximal nephron in mouse kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2001, 281, F966–F974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi-Saishin, Y.; Gotoh, S.; Furuse, M.; Takasuga, A.; Tano, Y.; Tsukita, S. Differential expression patterns of claudins, tight junction membrane proteins, in mouse nephron segments. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Agalliu, D.; Cahoy, J.D.; Kaushal, A.; Barres, B.A. The mouse blood-brain barrier transcriptome: A new resource for understanding the development and function of brain endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Coranguez, M.; Ramos, C.; Antonetti, D.A. The inner blood-retinal barrier: Cellular basis and development. Vis. Res. 2017, 139, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.; Hanley, N.; Campbell, M. Claudin-5: Gatekeeper of neurological function. Fluids Barriers CNS 2019, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Sasaki, H.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Endothelial Claudin: Claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmuntz, E.; Emanuel, B.S. Genetic disorders of cardiac morphogenesis: The DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes. Circ. Res. 1997, 80, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Jun, K.H.; Jung, J.H.; Chin, H.M.; Park, W.B. The expression of claudin-1, claudin-2, claudin-3, and claudin-4 in gastric cancer tissue. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 167, e185–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Imasato, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Watanabe, M.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; Hikita, H.; Tatsumi, T.; Takehara, T.; et al. Claudin 2 deficiency reduces bile flow and increases susceptibility to cholesterol gallstone disease in mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1134–1145.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumasu, R.; Yamaga, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Murota, H.; Suzuki, K.; Tamura, A.; Bando, K.; Furuta, Y.; Katayama, I.; Tsukita, S. Dose-dependent role of claudin-1 in vivo in orchestrating features of atopic dermatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4061–E4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornavaca, O.; Chia, M.; Dufton, N.; Almagro, L.O.; Conway, D.E.; Randi, A.M.; Schwartz, M.A.; Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artham, S.; Gao, F.; Verma, A.; Alwhaibi, A.; Sabbineni, H.; Hafez, S.; Ergul, A.; Somanath, P.R. Endothelial stromelysin1 regulation by the forkhead box-O transcription factors is crucial in the exudative phase of acute lung injury. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 141, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Sabbineni, H.; Artham, S.; Somanath, P.R. Modulation of long-term endothelial-barrier integrity is conditional to the cross-talk between Akt and Src signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Artham, S.; Sabbineni, H.; Al-Azayzih, A.; Peng, X.D.; Hay, N.; Adams, R.H.; Byzova, T.V.; Somanath, P.R. Akt1 promotes stimuli-induced endothelial-barrier protection through FoxO-mediated tight-junction protein turnover. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3917–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, A.; Giampietro, C.; Conti, A.; Orsenigo, F.; Breviario, F.; Pirazzoli, V.; Potente, M.; Daly, C.; Dimmeler, S.; Dejana, E. Endothelial adherens junctions control tight junctions by VE-cadherin-mediated upregulation of claudin-5. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y. Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability via ZO-1, occludin and claudin-5. J. Cell Physiol. 2014, 229, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, C.; Mao, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Song, Y. Role of post-translational modifications of Sp1 in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1453901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastfriend, B.D.; Nishihara, H.; Canfield, S.G.; Foreman, K.L.; Engelhardt, B.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Wnt signaling mediates acquisition of blood-brain barrier properties in naive endothelium derived from human pluripotent stem cells. eLife 2021, 10, e70992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, M.; O’Meara, M.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Meda Venkata, S.P.; Nguyen, H.; Minjares, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.M. MicroRNA-466 and microRNA-200 increase endothelial permeability in hyperglycemia by targeting Claudin-5. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harati, R.; Hammad, S.; Tlili, A.; Mahfood, M.; Mabondzo, A.; Hamoudi, R. miR-27a-3p regulates expression of intercellular junctions at the brain endothelium and controls the endothelial barrier permeability. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Kang, X.; Yi, Y.; Feng, S.; Ma, G.; Qu, H. CLDN5: From structure and regulation to roles in tumors and other diseases beyond CNS disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 200, 107075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Liu, F.; Ford, E.; Caldwell, R.B.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Triciribine attenuates pathological neovascularization and vascular permeability in a mouse model of proliferative retinopathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudraraju, M.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Regulation of blood-retinal barrier cell-junctions in diabetic retinopathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudraraju, M.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Distinct Mechanisms of Human Retinal Endothelial Barrier Modulation In Vitro by Mediators of Diabetes and Uveitis. Life 2021, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Somanath, P.R.; Razorenova, O.; Chen, W.S.; Hay, N.; Bornstein, P.; Byzova, T.V. Akt1 regulates pathological angiogenesis, vascular maturation and permeability in vivo. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsenigo, F.; Giampietro, C.; Ferrari, A.; Corada, M.; Galaup, A.; Sigismund, S.; Ristagno, G.; Maddaluno, L.; Koh, G.Y.; Franco, D.; et al. Phosphorylation of VE-cadherin is modulated by haemodynamic forces and contributes to the regulation of vascular permeability in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Alwhaibi, A.; Artham, S.; Verma, A.; Somanath, P.R. Endothelial Akt1 loss promotes prostate cancer metastasis via β-catenin-regulated tight-junction protein turnover. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, R.W.; Adil, M.S.; Newsome, A.S.; Somanath, P.R. Cisatracurium attenuates LPS-induced modulation of MMP3 and junctional protein expression in human microvascular endothelial cells. Biosci. Trends 2021, 15, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwhaibi, A.; Verma, A.; Adil, M.S.; Somanath, P.R. The unconventional role of Akt1 in the advanced cancers and in diabetes-promoted carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 145, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, T.N.; Almousawi, A.A.; Robinson, K.F.; Fogel, A.B.; Class, J.; Minshall, R.D.; Tai, L.M.; Richner, J.M.; Lutz, S.E. Caveolin-1 mediates blood-brain barrier permeability, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairment in SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Neuroimmunol. 2024, 388, 578309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, R.; Takahashi, J.; Shirakura, K.; Funatsu, R.; Kosugi, K.; Deguchi, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsunoda, Y.; Morita, M.; Muraoka, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 disrupts respiratory vascular barriers by suppressing Claudin-5 expression. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, A.H.; Chastain, D.B.; Rudraraju, M.; Parvathagiri, V.; Shan, S.; Lin, X.; Henao-Martinez, A.F.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. A multi-arm, parallel, preclinical study investigating the potential benefits of acetazolamide, candesartan, and triciribine in combination with fluconazole for the treatment of cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 960, 176177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakogiannos, N.; Ferrari, L.; Giampietro, C.; Scalise, A.A.; Maderna, C.; Rava, M.; Taddei, A.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Pisati, F.; Malinverno, M.; et al. JAM-A Acts via C/EBP-alpha to Promote Claudin-5 Expression and Enhance Endothelial Barrier Function. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, M.F.; Giampietro, C.; Corada, M.; Pisati, F.; Lavarone, E.; Cunha, S.I.; Conze, L.L.; O’Reilly, N.; Joshi, D.; Kjaer, S.; et al. VE-Cadherin-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation of Endothelial Gene Expression. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Liebanas, E.; Mocci, G.; Li, W.; Lavina, B.; Reddy, A.; O’Connor, C.; Hudson, N.; Elbeck, Z.; Nikoloudis, I.; Gaengel, K.; et al. Mosaic deletion of claudin-5 reveals rapid non-cell-autonomous consequences of blood-brain barrier leakage. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, A.; Tschernutter, M.; Bainbridge, J.W.; Balaggan, K.S.; Mowat, F.; West, E.L.; Munro, P.M.; Thrasher, A.J.; Matter, K.; Balda, M.S.; et al. The tight junction associated signalling proteins ZO-1 and ZONAB regulate retinal pigment epithelium homeostasis in mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Hata, M.; Gotoh, S.; Seo, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagne, A.; Barnes, S.R.; Sweeney, M.D.; Halliday, M.R.; Sagare, A.P.; Zhao, Z.; Toga, A.W.; Jacobs, R.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Amezcua, L.; et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human hippocampus. Neuron 2015, 85, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, J. Claudin-5a is essential for the functional formation of both zebrafish blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakel, L.; Claassen, K.; De Kort, A.M.; Jolink, W.M.T.; Vermeiren, Y.; Schreuder, F.; Kusters, B.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Verbeek, M.M. Decreased microvascular claudin-5 levels in cerebral amyloid angiopathy associated with intracerebral haemorrhage. Brain Pathol. 2024, 34, e13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, W.; Tripathi, D.; Ronaldson, P.T. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: Targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 315, C343–C356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, A.T.; Asp, L.; Zhang, J.; Navrazhina, K.; Pham, T.; Mariani, J.N.; Mahase, S.; Dutta, D.J.; Seto, J.; Kramer, E.G.; et al. Astrocyte-derived VEGF-A drives blood-brain barrier disruption in CNS inflammatory disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2454–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.; Hanley, N.; Reschke, C.R.; Reddy, A.; Mae, M.A.; Connolly, R.; Behan, C.; O’Keeffe, E.; Bolger, I.; Hudson, N.; et al. Microvascular stabilization via blood-brain barrier regulation prevents seizure activity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.C.; Li, Q.; Peng, J.Y.; Zhouwen, J.L.; Diao, J.F.; Niu, J.X.; Wang, X.; Guan, X.D.; Jia, W.; Jiang, W.G. Claudin-5 regulates blood-brain barrier permeability by modifying brain microvascular endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion to prevent lung cancer metastasis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, S.; Nele, V.; Campani, V.; De Rosa, G.; Cinti, S. A comprehensive guide to extract information from extracellular vesicles: A tutorial review towards novel analytical developments. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1302, 342473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Baena, V.; Ge, S.; Jiang, X.; Jellison, E.R.; Kiprono, T.; Agalliu, D.; Pachter, J.S. Appearance of claudin-5(+) leukocytes in the central nervous system during neuroinflammation: A novel role for endothelial-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewski, D.; Paul, D.; Ge, S.; Jellison, E.; Pachter, J.S. Appearance of claudin-5(+) leukocyte subtypes in the blood and CNS during progression of EAE. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, P.; Cioni, C.; Masi, G.; Tassi, M.; Marotta, G.; Severi, S. Fingolimod reduces circulating tight-junction protein levels and in vitro peripheral blood mononuclear cells migration in multiple sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, H.; Ibanez, B.; Contreras, M.; Troncoso, F.; Castro, F.O.; Caamano, D.; Mendez, L.; Escudero-Guevara, E.; Nualart, F.; Mistry, H.D.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Preeclampsia Disrupt the Blood-Brain Barrier by Reducing CLDN5. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2025, 45, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Heldt, N.A.; Gajghate, S.; Seliga, A.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Persidsky, Y. Hyperglycemia and advanced glycation end products disrupt BBB and promote occludin and claudin-5 protein secretion on extracellular microvesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, T.; Quan, X.; Han, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Comparative study of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells and brain endothelial cells attenuating blood-brain barrier permeability via regulating Caveolin-1-dependent ZO-1 and Claudin-5 endocytosis in acute ischemic stroke. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, L.; Jokar, S.; Fatahi, Y.; Samandari, H.; Hamzehalipour Almaki, J.; Hosseini, M.; Parviz, M. Targeting Caveolin-1 and Claudin-5 with AY9944, Improve Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability; Computational Simulation and Experimental Study. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, P.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, W.; Wu, S.; Huang, C.; Feng, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Autophagy alleviates hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury via regulation of CLDN5 (claudin 5). Autophagy 2021, 17, 3048–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, I.; Cohen-Kashi-Malina, K.; Teichberg, V.I. Claudin-5 expression in in vitro models of the blood-brain barrier. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 762, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, R.S., Jr.; Hoettels, B.A.; Meegan, J.E.; Wertz, T.S.; Cha, B.J.; Yang, X.; Oxford, J.T.; Wu, M.H.; Yuan, S.Y. AKT2 maintains brain endothelial claudin-5 expression and selective activation of IR/AKT2/FOXO1-signaling reverses barrier dysfunction. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maridaki, Z.; Syrros, G.; Gianna Delichatsiou, S.; Warsh, J.; Konstantinou, G.N. Claudin-5 and occludin levels in patients with psychiatric disorders—A systematic review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 123, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usta, A.; Kilic, F.; Demirdas, A.; Isik, U.; Doguc, D.K.; Bozkurt, M. Serum zonulin and claudin-5 levels in patients with schizophrenia. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin-Kinay, F.; Uzun, N.; Kilinc, I.; Kilic, A.O. Tight Junction Proteins and Blood-brain Barrier Integrity in Pediatric Obsessive-compulsive Disorder: A Study on Claudin-5, Claudin-12, Occludin, Tricellulin, and Angulin-1. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2025, 23, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Shinohara, M.; Yamazaki, A.; Murray, M.E.; Liesinger, A.M.; Heckman, M.G.; Lesser, E.R.; Parisi, J.E.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Selective loss of cortical endothelial tight junction proteins during Alzheimer’s disease progression. Brain 2019, 142, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Hirayama, R.; Sato, N.; Hattori, K.; Kato, T.; Takeda, H.; Kondoh, M. Association of Plasma Claudin-5 with Age and Alzheimer Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huls, A.; Robins, C.; Conneely, K.N.; Edgar, R.; De Jager, P.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Wingo, A.P.; Epstein, M.P.; Wingo, T.S. Brain DNA Methylation Patterns in CLDN5 Associated with Cognitive Decline. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Wei, M.; Yuan, L.; He, X.; Chen, C.; Ji, A.; Zhang, G. Claudin-5 relieves cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease mice through suppression of inhibitory GABAergic neurotransmission. Aging 2022, 14, 3554–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Kanekiyo, T. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction and the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, F.; Isik, U.; Kumbul Doguc, D. Serum Claudin-5, but not Zonulin, May Be Associated with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Psychiatr. Danub. 2022, 34, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, Z.; Torok, D.; Gonda, X.; Eszlari, N.; Anderson, I.M.; Deakin, B.; Juhasz, G.; Bagdy, G.; Petschner, P. Inflammation and Blood-Brain Barrier in Depression: Interaction of CLDN5 and IL6 Gene Variants in Stress-Induced Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023, 26, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, I.E.; Toborek, M. HIV-1-induced alterations of claudin-5 expression at the blood-brain barrier level. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 762, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, I.E.; Pu, H.; Tian, J.; Deli, M.A.; Nath, A.; Hennig, B.; Toborek, M. Signaling mechanisms of HIV-1 Tat-induced alterations of claudin-5 expression in brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Yang, B.; Gendelman, H.E.; Persidsky, Y.; Kanmogne, G.D. STAT1 signaling modulates HIV-1-induced inflammatory responses and leukocyte transmigration across the blood-brain barrier. Blood 2008, 111, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shirakura, K.; Okada, Y.; Hirayama, R.; Iwashita, Y.; Nishino, I.; Ago, Y.; Takeda, H.; Kuniyasu, H.; et al. Safety and efficacy of an anti-claudin-5 monoclonal antibody to increase blood-brain barrier permeability for drug delivery to the brain in a non-human primate. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, E.; Kuzu, T.; Tachibana, K.; Hirayama, R.; Okada, Y.; Kondoh, M. Modifying the blood-brain barrier by targeting claudin-5: Safety and risks. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1514, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cao, Y.; Chang, S. An inhibitor of claudin-5 interactions, M01, alleviates neuroinflammation and vasogenic edema after blood-spinal cord barrier dysfunction. Neuroreport 2023, 34, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, D.A.; Klein, R.; Gardner, T.W. Diabetic retinopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Airey, M.; Baxter, H.; Forrester, J.; Kennedy-Martin, T.; Girach, A. Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema: A systematic review. Eye 2004, 18, 963–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, R.; Hernandez, C. Advances in the medical treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branisteanu, D.C.; Bilha, A.; Moraru, A. Vitrectomy surgery of diabetic retinopathy complications. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 60, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Reichle, M.L. Complications of intravitreal steroid injections. Optometry 2005, 76, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Bernardes, R.; Lobo, C. Blood-retinal barrier. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 21 (Suppl. S6), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antcliff, R.J.; Marshall, J. The pathogenesis of edema in diabetic maculopathy. Semin. Ophthalmol. 1999, 14, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, N.; Murata, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Osanai, M.; Tobioka, H.; Kojima, T.; Chiba, H. Tight junctions and human diseases. Med. Electron Microsc. 2003, 36, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.; Celkova, L.; Hopkins, A.; Greene, C.; Storti, F.; Ozaki, E.; Fahey, E.; Theodoropoulou, S.; Kenna, P.F.; Humphries, M.M.; et al. Dysregulated claudin-5 cycling in the inner retina causes retinal pigment epithelial cell atrophy. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e130273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Rahner, C.; Peng, S.; Rizzolo, L.J. Claudin 5 is transiently expressed during the development of the retinal pigment epithelium. J. Membr. Biol. 2002, 186, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, S.; Stewart, E.A.; Browning, A.C.; Allen, C.L.; Amoaku, W.M. The effect of hyperglycaemia on permeability and the expression of junctional complex molecules in human retinal and choroidal endothelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 121, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, I.; Hughes, J.M.; Vogels, I.M.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Van Noorden, C.J.; Schlingemann, R.O. Altered expression of genes related to blood-retina barrier disruption in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kase, S.; Yokoi, M.; Saito, W.; Furudate, N.; Ohgami, K.; Kitamura, M.; Kitaichi, N.; Yoshida, K.; Kase, M.; Ohno, S.; et al. Increased osteopontin levels in the vitreous of patients with diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Res. 2007, 39, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, H.; Ito, M.; Nishio, Y.; Sato, T.; Harimoto, K.; Takeuchi, M. Osteopontin-induced vascular hyperpermeability through tight junction disruption in diabetic retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 220, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebel, S.J.; Menicucci, G.; McGuire, P.G.; Das, A. Matrix metalloproteinases in early diabetic retinopathy and their role in alteration of the blood-retinal barrier. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2005, 85, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, S.B.; Rybak, J.N.; Rosli, C.; Neri, D.; Elia, G. Modulation of gene expression by hypoxia in human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells: A transcriptomic and proteomic study. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1737–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koto, T.; Takubo, K.; Ishida, S.; Shinoda, H.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; Okada, Y.; Ikeda, E. Hypoxia disrupts the barrier function of neural blood vessels through changes in the expression of claudin-5 in endothelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Alanazi, A.H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Pro-Inflammatory Characteristics of Extracellular Vesicles in the Vitreous of Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Fisher, K.P.; Hammer, S.S.; Navitskaya, S.; Blanchard, G.J.; Busik, J.V. Plasma Exosomes Contribute to Microvascular Damage in Diabetic Retinopathy by Activating the Classical Complement Pathway. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Campbell, M.; Tachibana, K.; Okada, Y.; Kondoh, M. Claudin-5: A Pharmacological Target to Modify the Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorour, O.A.; Levine, E.S.; Baumal, C.R.; Elnahry, A.G.; Braun, P.; Girgis, J.; Waheed, N.K. Persistent diabetic macular edema: Definition, incidence, biomarkers, and treatment methods. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2023, 68, 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Gu, L.; Luo, D.; Qiu, Q. Diabetic Macular Edema: Current Understanding, Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2022, 11, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, L.P.; Avery, R.L.; Arrigg, P.G.; Keyt, B.A.; Jampel, H.D.; Shah, S.T.; Pasquale, L.R.; Thieme, H.; Iwamoto, M.A.; Park, J.E.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaum, T.; Xu, Q.; Joussen, A.M.; Clemens, M.W.; Qin, W.; Miyamoto, K.; Hassessian, H.; Wiegand, S.J.; Rudge, J.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; et al. VEGF-initiated blood-retinal barrier breakdown in early diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 2408–2413. [Google Scholar]
- Arima, M.; Nakao, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Feng, H.; Fujii, Y.; Shibata, K.; Wada, I.; Kaizu, Y.; Ahmadieh, H.; Ishibashi, T.; et al. Claudin-5 Redistribution Induced by Inflammation Leads to Anti-VEGF-Resistant Diabetic Macular Edema. Diabetes 2020, 69, 981–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Smith, L.E. Retinopathy of prematurity. Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, M.R.; Katoch, D.; Dogra, M. An Update on Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP). Indian J. Pediatr. 2017, 84, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, X.; Mao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Tang, S.; Rizzolo, L.J. Differential expression of claudins in retinas during normal development and the angiogenesis of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7556–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, A.; Ambrosio, A.F.; Fernandes, R. Regulation of claudins in blood-tissue barriers under physiological and pathological states. Tissue Barriers 2013, 1, e24782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhumaid, A.; Liu, F.; Shan, S.; Jafari, E.; Nourin, N.; Somanath, P.R.; Narayanan, S.P. Spermine oxidase inhibitor, MDL 72527, reduced neovascularization, vascular permeability, and acrolein-conjugated proteins in a mouse model of ischemic retinopathy. Tissue Barriers 2025, 13, 2347070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Stahl, A.; Krah, N.M.; Seaward, M.R.; Dennison, R.J.; Sapieha, P.; Hua, J.; Hatton, C.J.; Juan, A.M.; Aderman, C.M.; et al. Wnt signaling mediates pathological vascular growth in proliferative retinopathy. Circulation 2011, 124, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveleira, C.A.; Lin, C.M.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Ambrosio, A.F.; Antonetti, D.A. TNF-alpha signals through PKCzeta/NF-κB to alter the tight junction complex and increase retinal endothelial cell permeability. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2872–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.J.; Liao, P.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Cheng, Y.W.; Lin, F.L.; Ho, J.D.; Chen, C.Y.; Li, C.H. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles impair the inner blood-retinal barrier and retinal electrophysiology through rapid ADAM17 activation and claudin-5 degradation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letterio, J.J.; Roberts, A.B. Regulation of immune responses by TGF-β. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, S.; Chung, S.H.; Zhu, L.; Stayt, J.; Su, T.; Couraud, P.O.; Romero, I.A.; Weksler, B.; Gillies, M.C. Tyrosine phosphorylation of VE-cadherin and claudin-5 is associated with TGF-β1-induced permeability of centrally derived vascular endothelium. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.R.; Kim, R.K.; Pober, J.S.; Kluger, M.S. Tumor necrosis factor disrupts claudin-5 endothelial tight junction barriers in two distinct NF-κB-dependent phases. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudraraju, M.; Shan, S.; Liu, F.; Tyler, J.; Caldwell, R.B.; Somanath, P.R.; Narayanan, S.P. Pharmacological Modulation of β-Catenin Preserves Endothelial Barrier Integrity and Mitigates Retinal Vascular Permeability and Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Teramachi, M.; Yasuda, H.; Kamiya, T.; Hara, H. Contribution of p38 MAPK, NF-κB and glucocorticoid signaling pathways to ER stress-induced increase in retinal endothelial permeability. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 520, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Numata, Y.; Mizusawa, H. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: Decreased claudin-5 and relocated ZO-1. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwamura, Y.; Sano, Y.; Abe, M.; Shimizu, F.; Haruki, H.; Maeda, T.; Kawai, M.; Kanda, T. Hydrocortisone enhances the function of the blood-nerve barrier through the up-regulation of claudin-5. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Saito, K.; Abe, M.A.; Maeda, T.; Haruki, H.; Kanda, T. Pericyte-derived glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increase the expression of claudin-5 in the blood-brain barrier and the blood-nerve barrier. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Abdel-Latif, A.; Kitakaze, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chou, D.; Kim, J.K. A Novel Role of Claudin-5 in Prevention of Mitochondrial Fission Against Ischemic/Hypoxic Stress in Cardiomyocytes. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 1593–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.L.; Edwards, J.D.; Mays, T.A.; Gong, B.; Merriam, A.P.; Rafael-Fortney, J.A. Claudin-5 localizes to the lateral membranes of cardiomyocytes and is altered in utrophin/dystrophin-deficient cardiomyopathic mice. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2005, 38, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfin, D.A.; Xu, Y.; Schill, K.E.; Mays, T.A.; Canan, B.D.; Zang, K.E.; Barnum, J.A.; Janssen, P.M.; Rafael-Fortney, J.A. Sustaining cardiac claudin-5 levels prevents functional hallmarks of cardiomyopathy in a muscular dystrophy mouse model. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Hou, Y.; Lu, C.; Yang, W.; Ji, T.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jin, Z. Cardiac-specific overexpression of Claudin-5 exerts protection against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. A novel function of claudin-5 in maintaining the structural integrity of the heart and its implications in cardiac pathology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, T.A.; Binkley, P.F.; Lesinski, A.; Doshi, A.A.; Quaile, M.P.; Margulies, K.B.; Janssen, P.M.; Rafael-Fortney, J.A. Claudin-5 levels are reduced in human end-stage cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 45, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swager, S.A.; Delfin, D.A.; Rastogi, N.; Wang, H.; Canan, B.D.; Fedorov, V.V.; Mohler, P.J.; Kilic, A.; Higgins, R.S.D.; Ziolo, M.T.; et al. Claudin-5 levels are reduced from multiple cell types in human failing hearts and are associated with mislocalization of ephrin-B1. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarteenaho, R.; Merikallio, H.; Lehtonen, S.; Harju, T.; Soini, Y. Divergent expression of claudin -1, -3, -4, -5 and -7 in developing human lung. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, P.; Yu, F.; Tan, D.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Ling, B. Involvement of claudin-5 in H(2)S-induced acute lung injury. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Singh, S.; Potula, R.; Persidsky, Y.; Kanmogne, G.D. Dysregulation of claudin-5 in HIV-induced interstitial pneumonitis and lung vascular injury. Protective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba, N.; Ma, Y.; Gahan, S.A.; Joly-Amado, A.; Spence, S.; Yang, X.; Nash, K.R.; Yuan, S.Y. Lung infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizuki, R.; Shimobaba, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A. Claudin-5, -7, and -18 suppress proliferation mediated by inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt in human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sharma, R.; Rizzo, A.N.; Siegler, J.H.; Garcia, J.G.; Jacobson, J.R. Role of claudin-5 in the attenuation of murine acute lung injury by simvastatin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Daugherty, B.; Keise, L.L.; Wei, Z.; Foley, J.P.; Savani, R.C.; Koval, M. Heterogeneity of claudin expression by alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.H.; Selim, M.S.; Yendamuri, M.R.; Zhang, D.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. The impact of diabetes mellitus on blood-tissue barrier regulation and vascular complications: Is the lung different from other organs? Tissue Barriers 2024, 13, 2386183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.H.; Selim, M.S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Advanced glycation endproducts induce cytokine dysregulation and weaken lung epithelial and endothelial barrier integrity. Tissue Barriers 2025, 2521136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Suzuki, S.; Higashi, H.; Inaba, K.; Nakamura, S.; Baba, S.; Kato, T.; Konno, H. Expression of tight junction protein claudin-5 in tumor vessels and sinusoidal endothelium in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 147, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, T.; Sherman-Baust, C.A.; Poosala, S.; Mullin, J.M.; Morin, P.J. Age-related changes of claudin expression in mouse liver, kidney, and pancreas. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchagier, K.A.; Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Karavias, D.D.; Maroulis, I.; Tzelepi, V.; Kalofonos, H.; Karavias, D.D.; Kardamakis, D.; Scopa, C.D.; Tsamandas, A.C. Expression of claudins-1, -4, -5, -7 and occludin in hepatocellular carcinoma and their relation with classic clinicopathological features and patients’ survival. In Vivo 2014, 28, 315–326. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, J.P. IL-21 mediates microRNA-423-5p /claudin-5 signal pathway and intestinal barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease. Aging 2020, 12, 16099–16110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, S.; Rabinowitz, K.M.; Martin, A.P.; Berin, M.C.; Unkeless, J.C.; Mayer, L. Notch-1 signaling regulates intestinal epithelial barrier function, through interaction with CD4+ T cells, in mice and humans. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeissig, S.; Burgel, N.; Gunzel, D.; Richter, J.; Mankertz, J.; Wahnschaffe, U.; Kroesen, A.J.; Zeitz, M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn’s disease. Gut 2007, 56, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Han, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Claudin Family Participates in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Garrett, S.; Carroll, R.E.; Xia, Y.; Sun, J. Vitamin D receptor upregulates tight junction protein claudin-5 against colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, R.; Zhao, L.; Yaoita, E.; Yoshida, Y.; Tsukita, S.; Tamura, A.; Nameta, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fujinaka, H.; Magdeldin, S.; et al. Novel expression of claudin-5 in glomerular podocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, M.; Fan, B.; Liu, J.; Lin, N.; Wang, X.; et al. Loss of CLDN5 in podocytes deregulates WIF1 to activate WNT signaling and contributes to kidney disease. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, H.; Mandai, S.; Shiwaku, H.; Koide, T.; Takahashi, N.; Yanagi, T.; Inaba, S.; Ida, S.; Fujiki, T.; Mori, Y.; et al. Chronic kidney disease causes blood-brain barrier breakdown via urea-activated matrix metalloproteinase-2 and insolubility of tau protein. Aging 2023, 15, 10972–10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Nunes, A.C.F.; Vasilevko, V.; Floriolli, D.; Lertpanit, L.; Savoj, J.; Bangash, M.; Yao, Z.; Shah, K.; Naqvi, S.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease Increases Cerebral Microbleeds in Mouse and Man. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuyu, N.F.; Camlica, T.; Asci, H.; Milletsever, A.; Ulusoy, A.; Gonuler, F.M.; Altuntas, A. Fluvoxamine may reverse the decrease in filtering capacity that occurs in acute kidney injury by increasing IL-10 and ACE expressions and preserving AQ-2, AQ-4, CL-5, and ZO-1 expressions. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 9021–9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, W.J.; Lyu, L.C.; Tu, Y.; Gu, H.; Chen, X.F.; Chai, Y.J.; Man, M.Q.; He, L. MiRNA-224-5p regulates the defective permeability barrier in sensitive skin by targeting claudin-5. Skin Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misery, L.; Stander, S.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Reich, A.; Wallengren, J.; Evers, A.W.; Takamori, K.; Brenaut, E.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Fluhr, J.; et al. Definition of Sensitive Skin: An Expert Position Paper from the Special Interest Group on Sensitive Skin of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cruz Silva, L.L.; de Oliveira, W.R.P.; Pereira, N.V.; Halpern, I.; Tanabe, C.K.D.; Mattos, M.S.G.; Sotto, M.N. Claudin expression profile in flat wart and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burek, M.; Arias-Loza, P.A.; Roewer, N.; Forster, C.Y. Claudin-5 as a novel estrogen target in vascular endothelium. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappi-Blanco, E.; Lehtonen, S.T.; Sormunen, R.; Merikallio, H.M.; Soini, Y.; Kaarteenaho, R.L. Divergence of tight and adherens junction factors in alveolar epithelium in pulmonary fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, S.M.; Wang, C.; Tigdi, J.; Si, X.; Dumpit, C.; Charles, S.; Gamage, A.; Moraes, T.J.; Lee, W.L. Influenza infects lung microvascular endothelium leading to microvascular leak: Role of apoptosis and claudin-5. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.Y.; Lee, P.H.; Kim, B.G.; Park, C.S.; Leikauf, G.D.; Jang, A.S. Claudin 5 in a murine model of allergic asthma: Its implication and response to steroid treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1694–1696.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artham, S.; Verma, A.; Alwhaibi, A.; Adil, M.S.; Manicassamy, S.; Munn, D.H.; Somanath, P.R. Delayed Akt suppression in the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury promotes resolution that is associated with enhanced effector regulatory T cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L750–L761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.H.; Selim, M.S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Pre-Existing Diabetes Alters Pulmonary Inflammatory Gene Expression Priming for Injury. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahner, C.; Mitic, L.L.; Anderson, J.M. Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the rat liver, pancreas, and gut. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Roca Suarez, A.A.; El Saghire, H.; Saviano, A.; Schuster, C.; Lupberger, J.; Baumert, T.F. Tight Junction Proteins and the Biology of Hepatobiliary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgalil, M.H.; Elhammamy, R.H.; Ragab, H.M.; Sheta, E.; Wahid, A. The hepatoprotective effect of 4-phenyltetrahydroquinolines on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in rats through autophagy inhibition. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.A.; Dion-Albert, L.; Lebel, M.; LeClair, K.; Labrecque, S.; Tuck, E.; Ferrer Perez, C.; Golden, S.A.; Tamminga, C.; Turecki, G.; et al. Molecular adaptations of the blood-brain barrier promote stress resilience vs. depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3326–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasheh, S.; Schmidt, T.; Mahn, M.; Florian, P.; Mankertz, J.; Tavalali, S.; Gitter, A.H.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 321, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, A.O.; Akin, F.; Yazar, A.; Metin Akcan, O.; Topcu, C.; Aydin, O. Zonulin and claudin-5 levels in multisystem inflammatory syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, R.A.; Al-Zahrani, M.H. Identification of key claudin genes associated with survival prognosis and diagnosis in colon cancer through integrated bioinformatic analysis. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1221815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaggin, S.E.; Kreidberg, J.A. Development of the renal glomerulus: Good neighbors and good fences. Development 2008, 135, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Sinomenine alleviates glomerular endothelial permeability by activating the C/EBP-alpha/claudin-5 signaling pathway. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, A.; Pan, Y.; Cao, S.; Terker, A.S.; Wang, S.; Fan, X.; Toth, C.L.; Ramirez Solano, M.A.; Michell, D.L.; et al. Profile of Podocyte Translatome During Development of Type 2 and Type 1 Diabetic Nephropathy Using Podocyte-Specific TRAP mRNA RNA-seq. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.T.; Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R.; Zuo, L. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1514, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, M.S.; Kassem, A.B.; El-Bassiouny, N.A.; Salahuddin, A.; Abu El-Ela, R.Y.; Hamza, M.S. Polymorphic renal transporters and cisplatin’s toxicity in urinary bladder cancer patients: Current perspectives and future directions. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, C.L.; Garthwaite, M.A.; Cross, W.; Hinley, J.; Trejdosiewicz, L.K.; Southgate, J. PPARgamma-regulated tight junction development during human urothelial cytodifferentiation. J. Cell Physiol. 2006, 208, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, A.; Dorokhov, N.; Ryerse, J.; Klumpp, D.J.; McHowat, J. Characterization of tight junction proteins in cultured human urothelial cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2008, 44, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.M. The skin: An indispensable barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, K.; Bergmann, S.; Heisig, M.; Naegel, A.; Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Brandner, J.M. The role of tight junctions in skin barrier function and dermal absorption. J. Control. Release 2016, 242, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, K.; Sasaki, H.; Furuse, K.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S.; Miyachi, Y. Expression of claudin-5 in dermal vascular endothelia. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, S.; Riehokainen, J.; Pummi, K.; Peltonen, J. Tight junction components occludin, ZO-1, and claudin-1, -4 and -5 in active and healing psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.; Nwadozi, E.; Pal, S.; Martinsson, P.; Kaakinen, M.; Gloger, M.; Sjoberg, E.; Koltowska, K.; Betsholtz, C.; Eklund, L.; et al. Claudin5 protects the peripheral endothelial barrier in an organ and vessel-type-specific manner. eLife 2022, 11, e78517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Kiang, A.S.; Tam, L.; Kenna, P.F.; Dhubhghaill, S.N.; Humphries, M.; Farrar, G.J.; Humphries, P. Reversible and size-selective opening of the inner Blood-Retina barrier: A novel therapeutic strategy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 664, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Cassidy, P.S.; O’Callaghan, J.; Crosbie, D.E.; Humphries, P. Manipulating ocular endothelial tight junctions: Applications in treatment of retinal disease pathology and ocular hypertension. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 62, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tischfield, M.; Williams, J.; Smallwood, P.M.; Rattner, A.; Taketo, M.M.; Nathans, J. Canonical WNT signaling components in vascular development and barrier formation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3825–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuercher, J.; Fritzsche, M.; Feil, S.; Mohn, L.; Berger, W. Norrin stimulates cell proliferation in the superficial retinal vascular plexus and is pivotal for the recruitment of mural cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 2619–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Coranguez, M.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.; Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Antonetti, D.A. Disheveled-1 Interacts with Claudin-5 and Contributes to Norrin-Induced Endothelial Barrier Restoration. Cells 2023, 12, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.M.; Yong, V.W. The many faces of EMMPRIN—Roles in neuroinflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, M.; Cui, D.; Kimura, T.; Sonoda, K.H.; Ishibashi, T.; Matsuda, S.; Ikeda, E. Basigin can be a therapeutic target to restore the retinal vascular barrier function in the mouse model of diabetic retinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudnicky, F.; Zhang, J.D.; Kim, B.K.; Pandya, N.J.; Lan, Y.; Sach-Peltason, L.; Ragelle, H.; Strassburger, P.; Gruener, S.; Lazendic, M.; et al. Inducers of the endothelial cell barrier identified through chemogenomic screening in genome-edited hPSC-endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19854–19865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yan, H. FTY720 Attenuates Retinal Inflammation and Protects Blood-Retinal Barrier in Diabetic Rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y. SIRT1 deacetylates KLF4 to activate Claudin-5 transcription in ovarian cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2418–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Al-Azayzih, A.; Somanath, P.R. Discrete functions of GSK3alpha and GSK3β isoforms in prostate tumor growth and micrometastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5947–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, S.H.; Fan, S.; Dykstra, H.; Rom, S.; Mercer, A.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Gofman, L.; Persidsky, Y. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes tight junction stability in brain endothelial cells by half-life extension of occludin and claudin-5. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
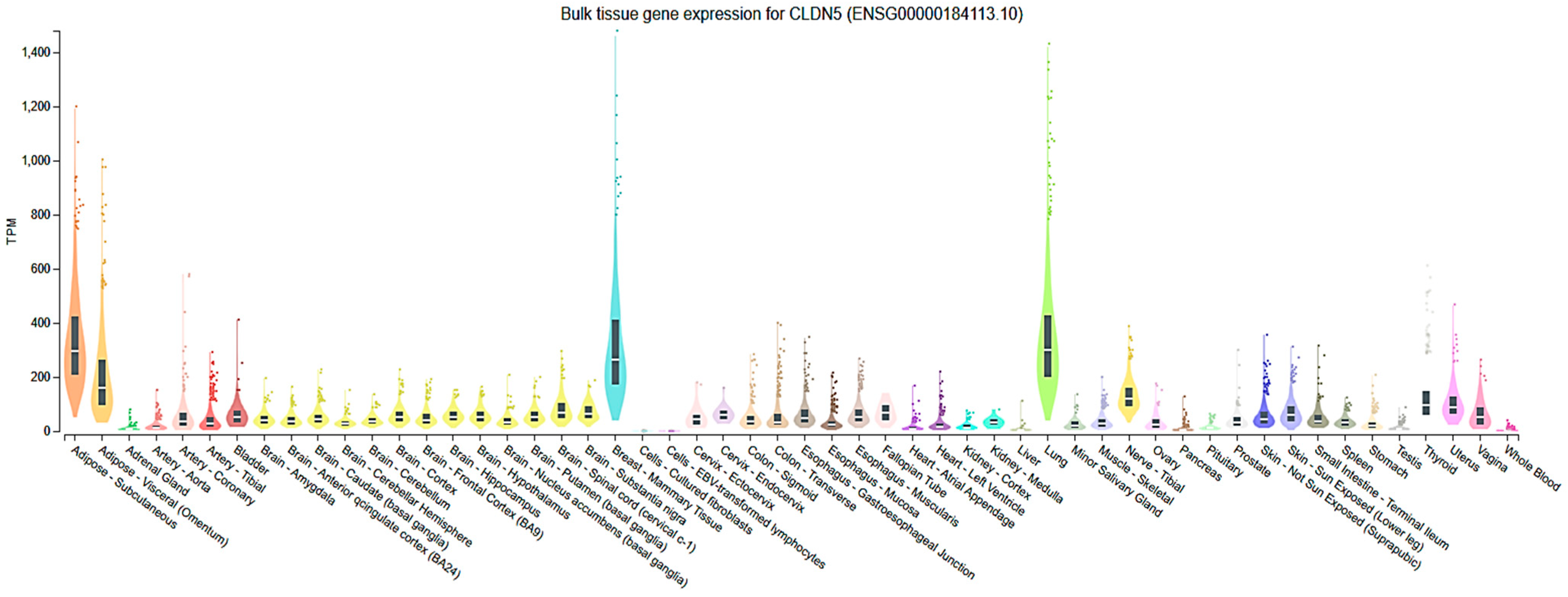
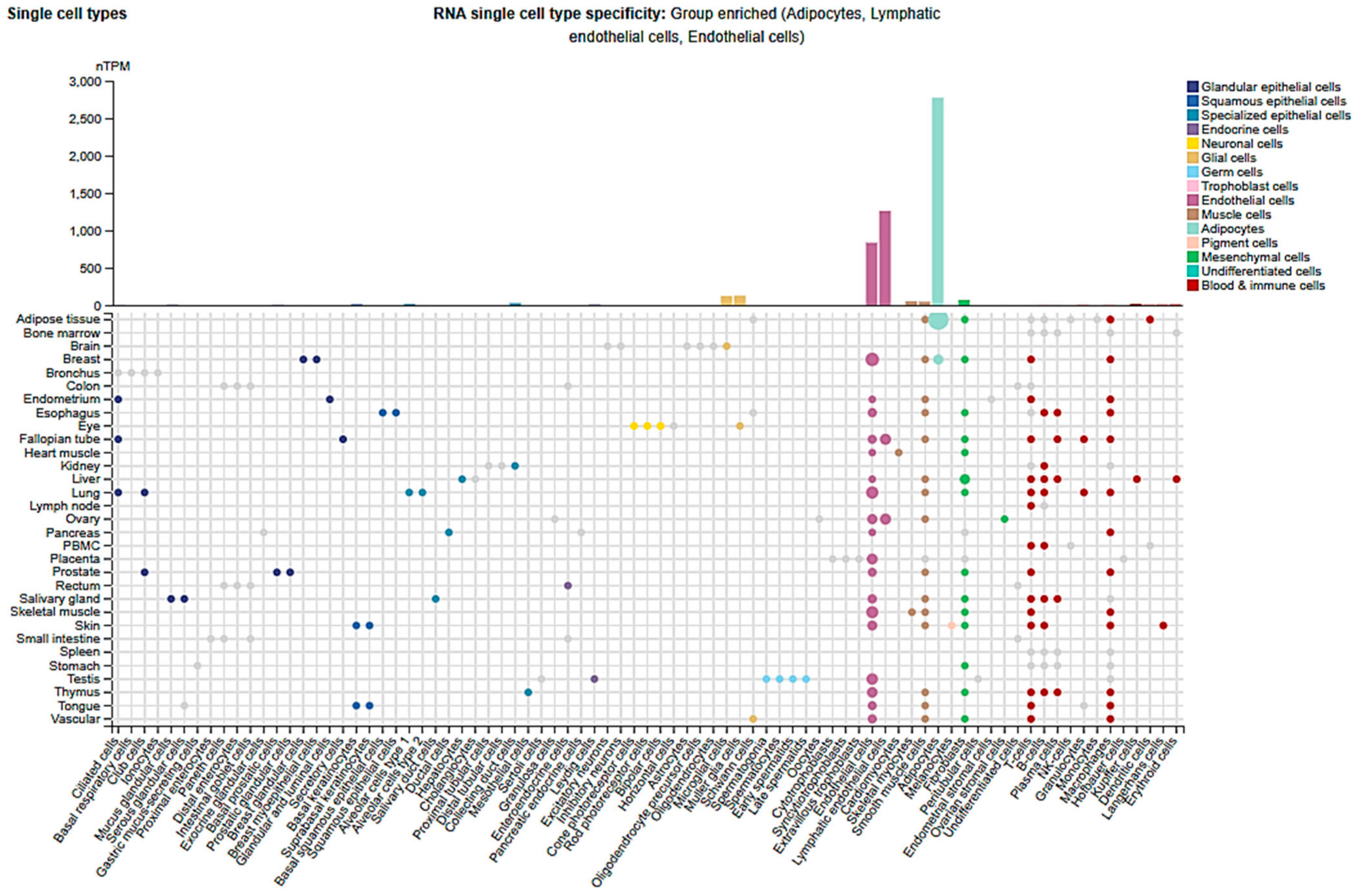
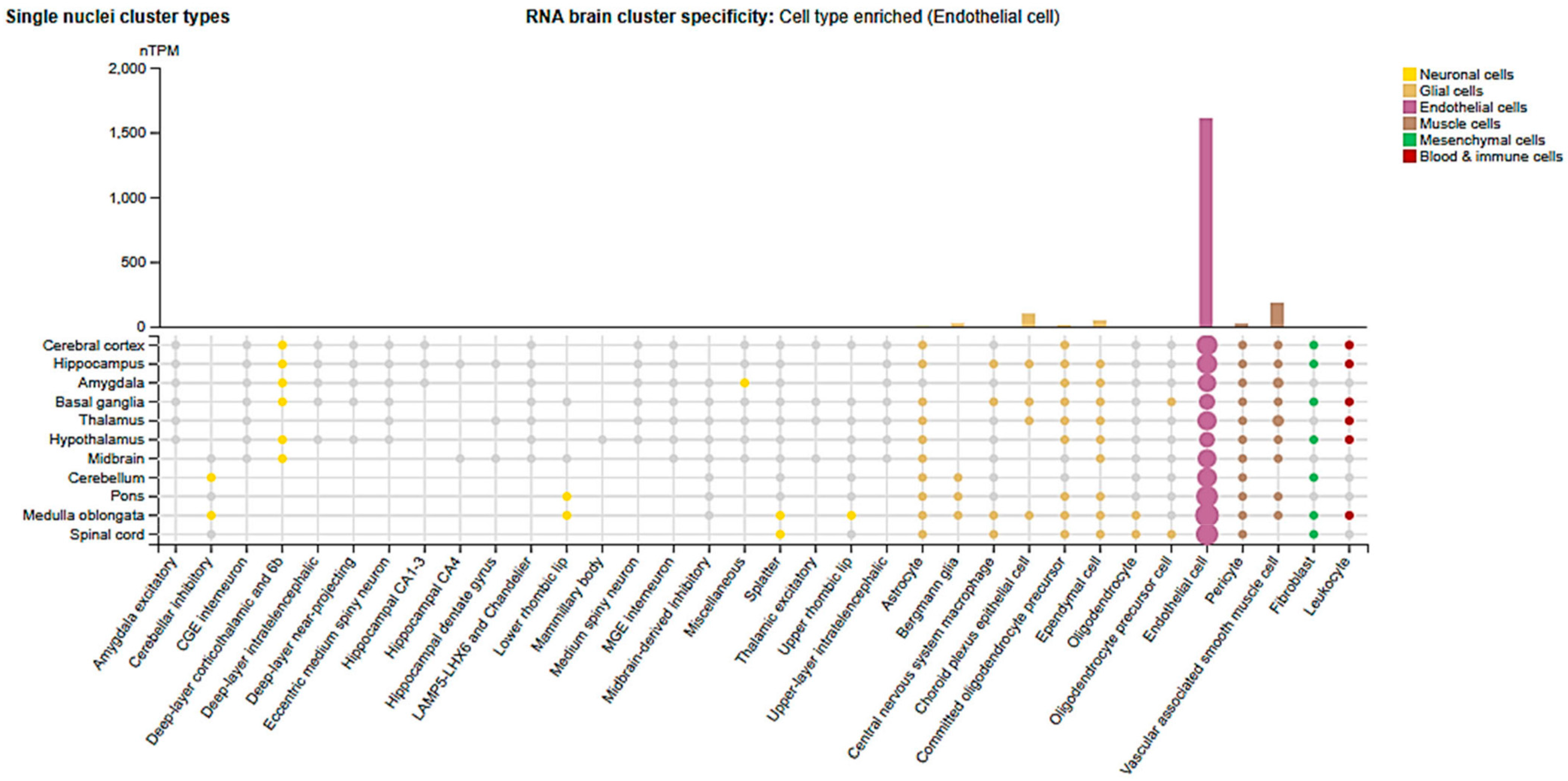
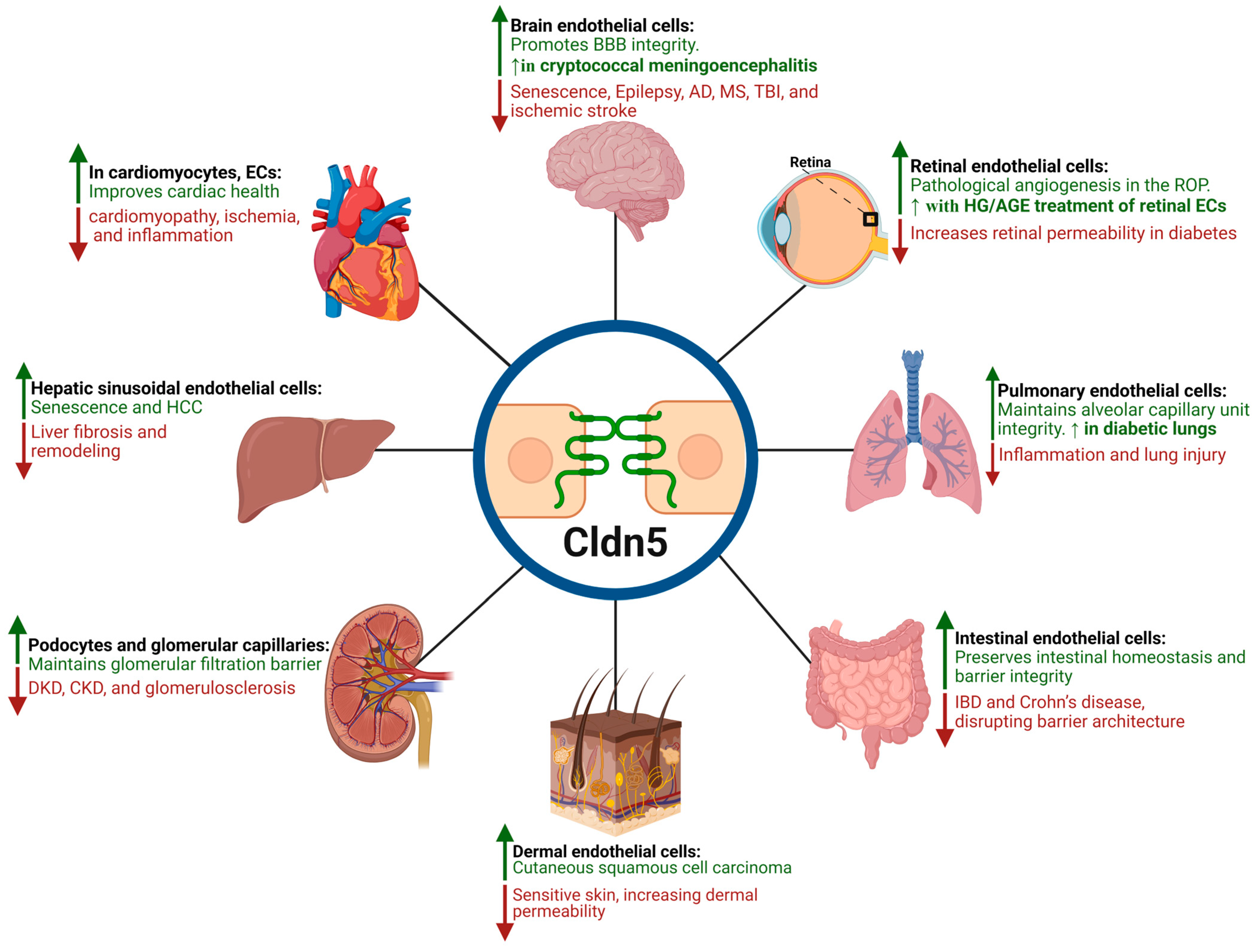
| Organ | Cell Type | Regulation | Mechanisms/Physiology/Pathology | Consequences | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain (BBB) | BMECs | Down |
| Size-selective BBB loosening precedes cognitive impairment and cerebral hemorrhage, facilitating neuroinflammation and immune cell infiltration into the CNS, exacerbating barrier breakdown through TJ disassembly and fragmented Cldn5 immunoreactivity, particularly in conditions like HIV. | [51,59,61,62,63,71,74,87,88,89] |
| Up |
| Restore BBB integrity by reinforcing TJs, promote EC proliferation, migration, and adhesion—mechanisms that impede cancer metastasis. | [53,63,65,72,73,75,76] | ||
| Retina (iBRB) | RECs; Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) | Down |
| Increased paracellular permeability, reduced TEER, increased retinal capillary permeability, and impaired barrier function | [103,107,109,117] |
| Up; Mis- localization |
| Impaired HREC barrier function, often due to mislocalization to cytosolic/ non-junctional regions), promoting pathological angiogenesis (OIR). | [43,45,106,120,122] | ||
| Peripheral Nerves (BNB) | Endoneurial ECs | Down |
| Compromises BNB, allowing immune cells and antibodies to infiltrate and attack peripheral nerve myelin. | [131] |
| Up |
| Tightens BNB, reduces permeability, restorative effect in neuropathies, helps maintain barrier integrity in nerves. | [132,133] | ||
| Cardiovascular System | Cardiomyocytes, ECs | Down |
| Contributes to cardiac injury, cardiac dysfunction associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (advanced stages), structural abnormalities and heart failure. | [134,135,136,137,138,139,140] |
| Up |
| Mitigates oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and cardiac dysfunction. Cardioprotective (inhibits cardiomyopathy hallmarks) and acts as a histological indicator of cardiac injury. | [136,137] | ||
| Lung (Alveolar-Capillary Barrier | Microvasculature; Alveolar Epithelium | Down |
| Induces acute lung injury, contributes to interstitial pneumonitis and vascular injury, perturbs the BBB (secondary to lung infection), and suppresses tumors upon overexpression. | [141,142,143,144,145] |
| Up |
| Enhances the endothelial barrier and paracellular barrier function. AGE disrupts epithelial barrier function and significantly reduces TEER. | [146,147,148,149] | ||
| Liver | Sinusoidal ECs; Arterial/Portal Veins | Down |
| Correlated with hepatic injury, fibrotic remodeling. | [150] |
| Up |
| Biomarker of hepatic vascular health and HCC progression. | [151,152] | ||
| Gut | Intestinal Epithelial Cells, ECs | Up |
| Promotes intestinal epithelium proliferation, differentiation, and maintains epithelial homeostasis. | [153,154] |
| Down |
| Compromises intestinal barrier integrity, disrupts TJ architecture, increases intestinal permeability, and higher incidence of colitis-associated tumors. | [153,155,156,157] | ||
| Kidney | Podocytes and glomerular capillaries | Down |
| Causes albuminuria, glomerulosclerosis, increased microhemorrhages, and barrier fragility. | [151,158,159,160,161] |
| Up |
| Protection from LPS-induced kidney injury. | [162] | ||
| Skin | Superficial layers, ECs | Down |
| Vascular leakage, increased permeability, and reduced TEER in sensitive skin. | [163,164] |
| Up |
| A marker of tumor progression. | [165] |
| Organ | Interventions | Approach/Physiology/Pathology | Consequences | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Therapeutic modulation |
|
| [90,92] |
| Restoration |
|
| [84] | |
| Retina | Restoration |
|
| [74,193,194,195,196,197,198] |
| Therapeutic modulation |
|
| [43,191,192] | |
| Gut | Restoration |
|
| [157] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selim, M.S.; Matani, B.R.; Henry-Ojo, H.O.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Claudin 5 Across the Vascular Landscape: From Blood–Tissue Barrier Regulation to Disease Mechanisms. Cells 2025, 14, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171346
Selim MS, Matani BR, Henry-Ojo HO, Narayanan SP, Somanath PR. Claudin 5 Across the Vascular Landscape: From Blood–Tissue Barrier Regulation to Disease Mechanisms. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171346
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelim, Mohamed S., Bayan R. Matani, Harry O. Henry-Ojo, S. Priya Narayanan, and Payaningal R. Somanath. 2025. "Claudin 5 Across the Vascular Landscape: From Blood–Tissue Barrier Regulation to Disease Mechanisms" Cells 14, no. 17: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171346
APA StyleSelim, M. S., Matani, B. R., Henry-Ojo, H. O., Narayanan, S. P., & Somanath, P. R. (2025). Claudin 5 Across the Vascular Landscape: From Blood–Tissue Barrier Regulation to Disease Mechanisms. Cells, 14(17), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171346






