Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticle Treatment Enhances Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cells
2.3. Apoptosis and Cell Death Analysis
2.4. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
2.5. Preparation of PLGA Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.6. Preparation of Doxorubicin-Loaded NPs
2.7. In Vivo DLBCL Subcutaneous Xenograft Model
2.8. Immune Activation Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
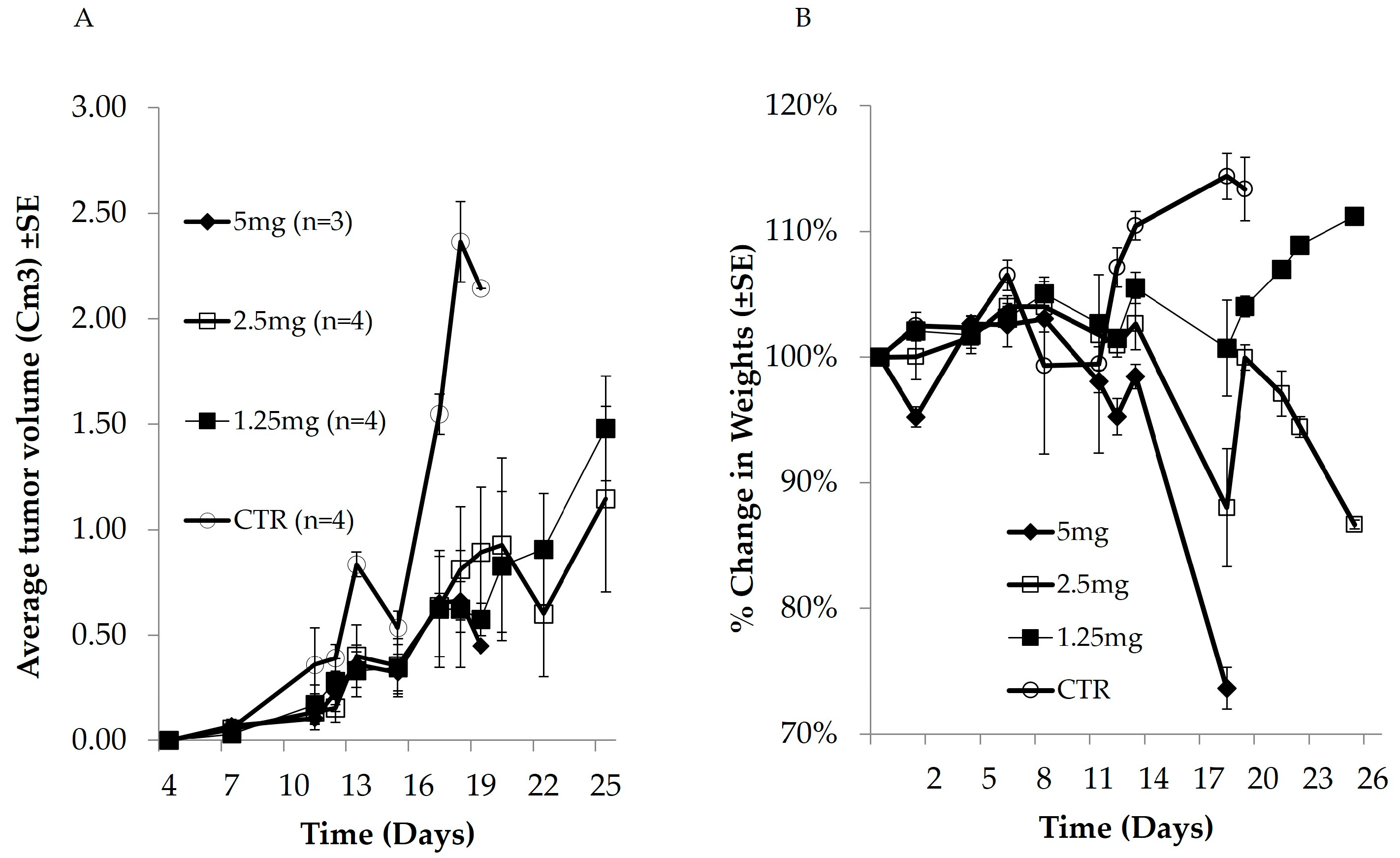
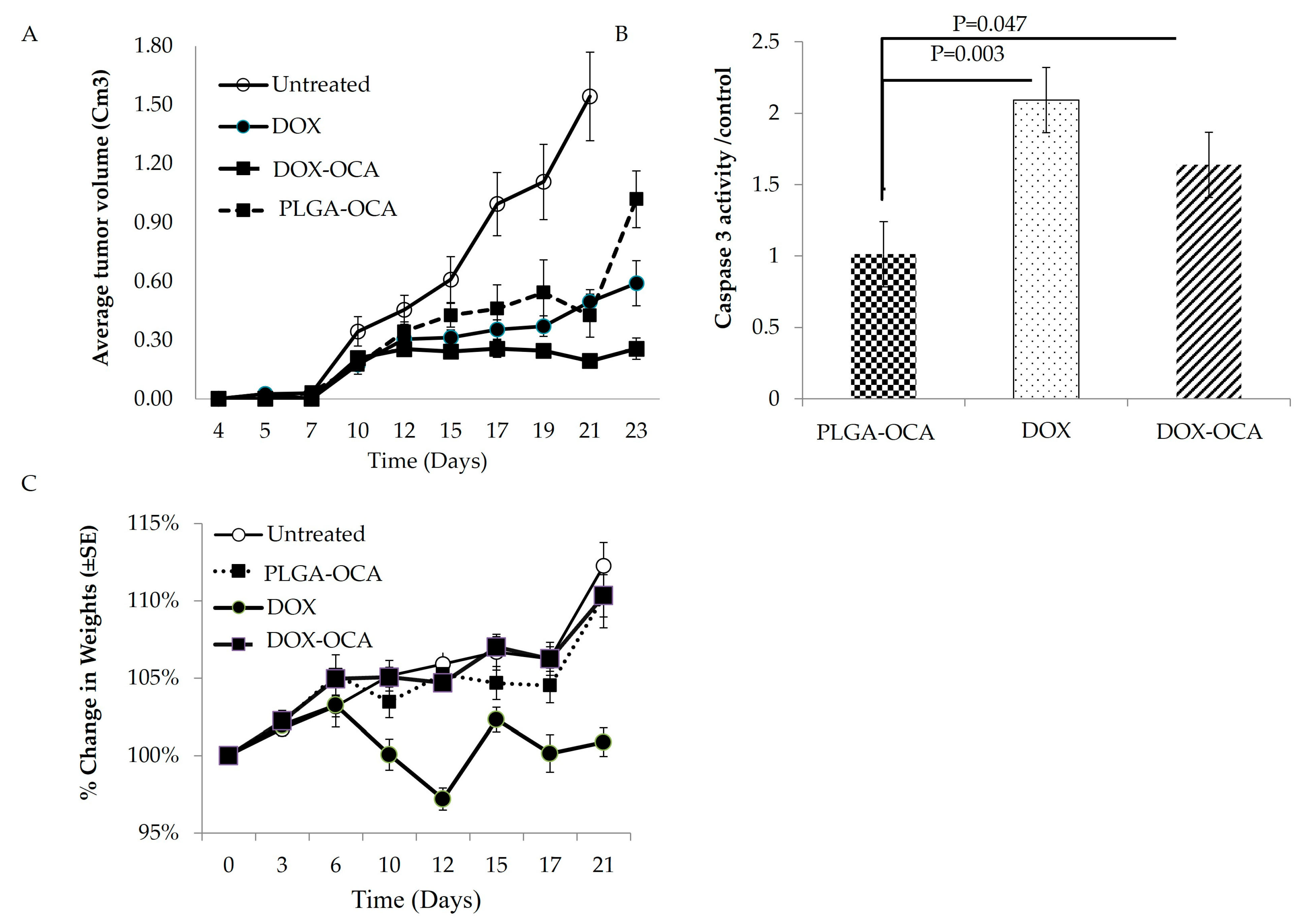
3.1. In Vivo Anticancer Activity and Cytotoxic Effect of Dox
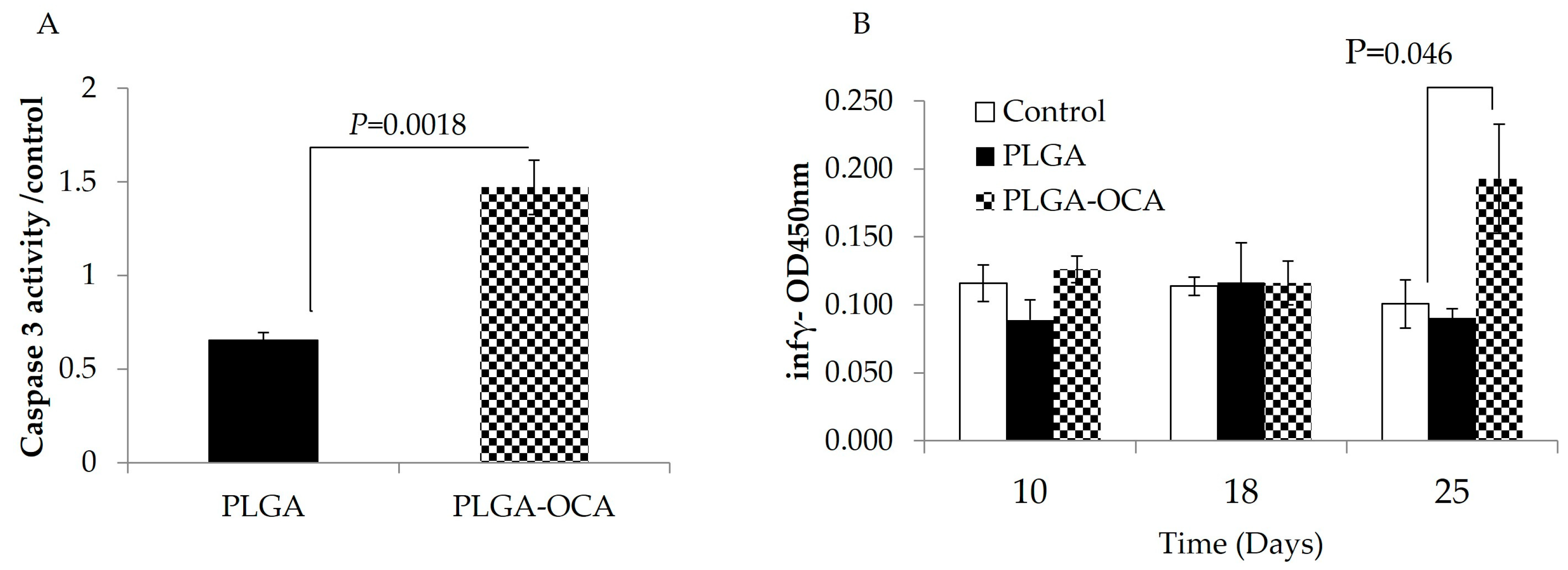
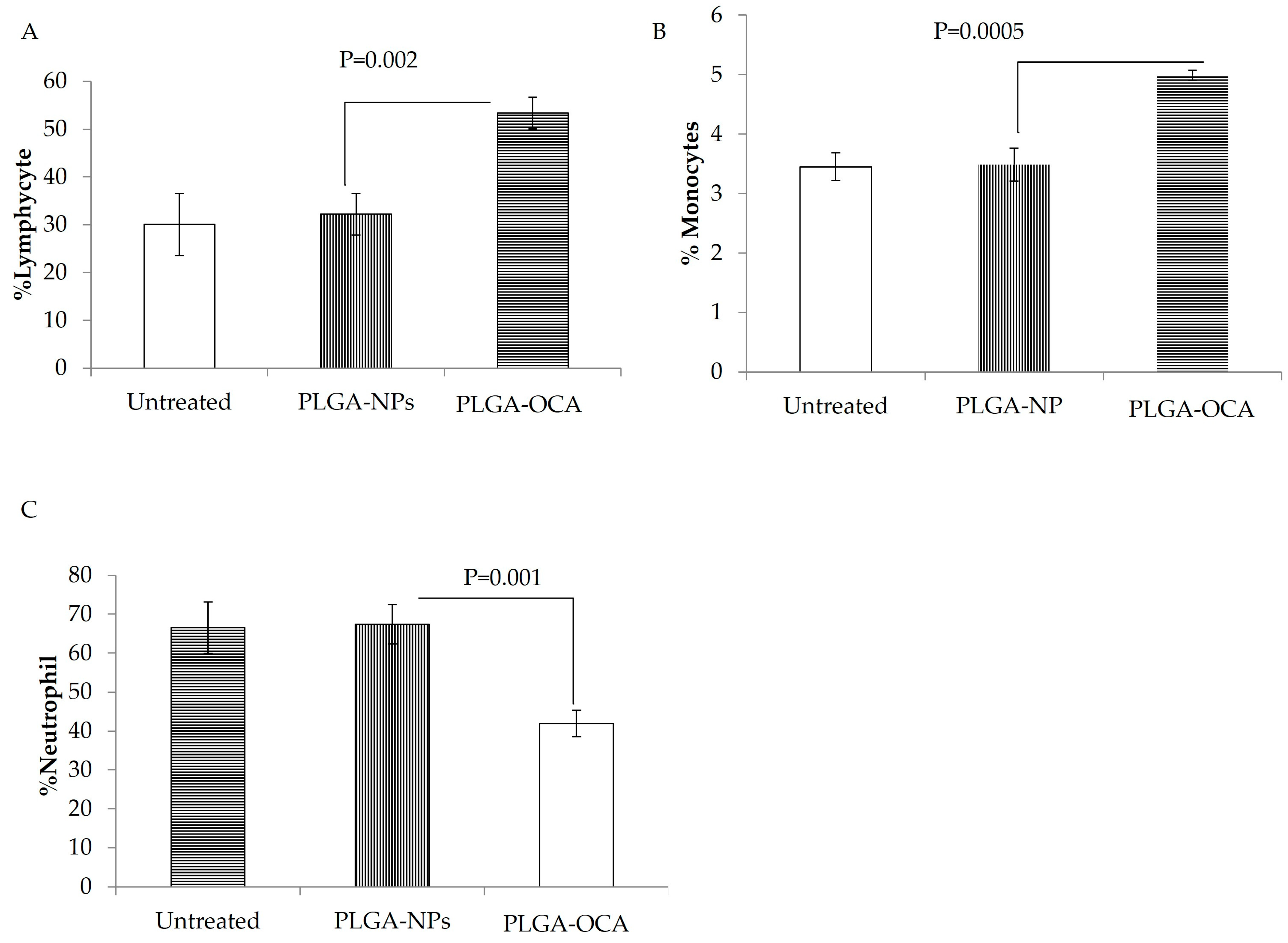
3.2. PLGA–OCA May Augment Immune Responses and Contribute to Tumor-Cell Death
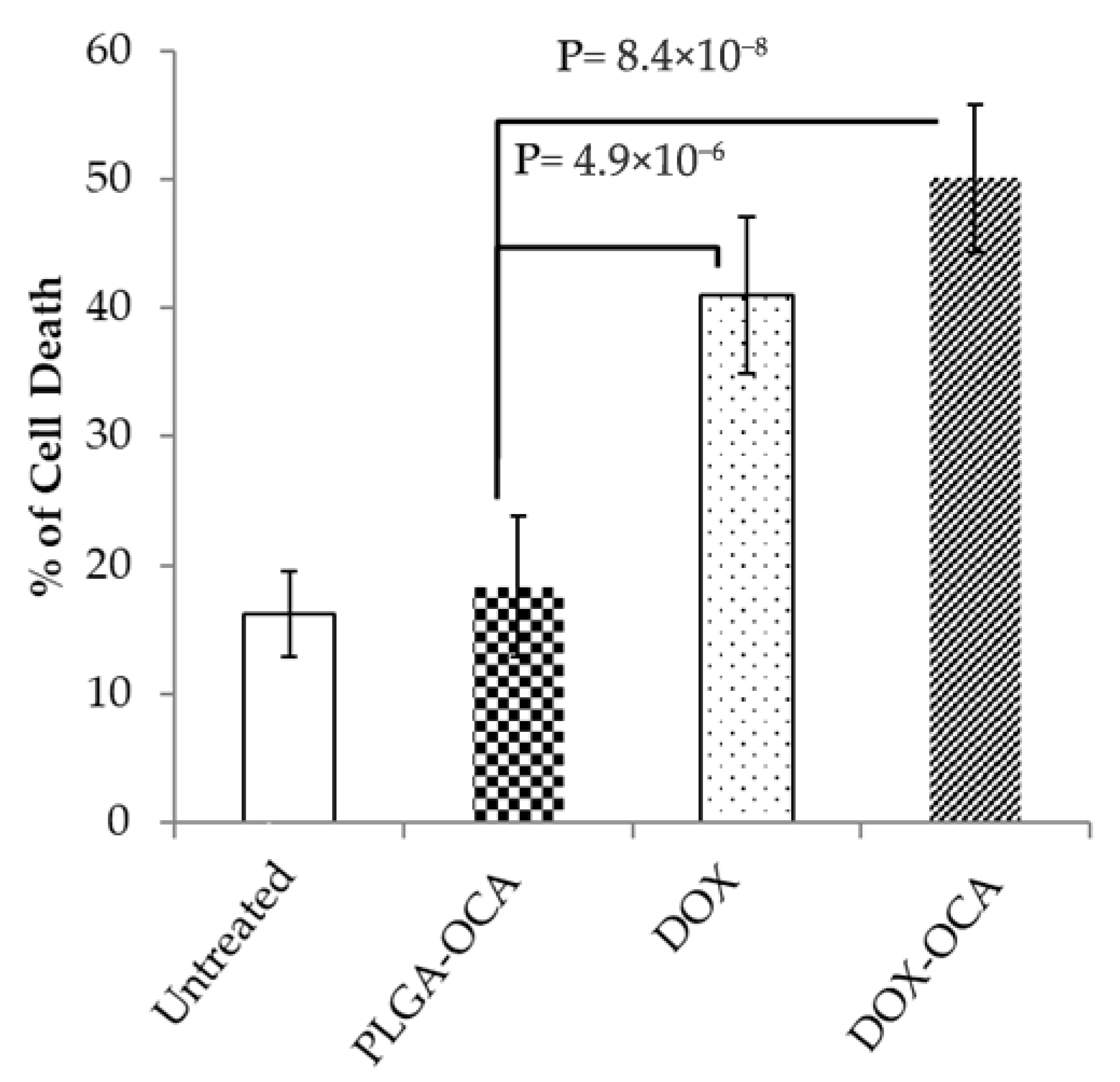
3.3. DOX-OCA Induces Cell Death In Vitro and In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foo, J.; Michor, F. Evolution of acquired resistance to anti-cancer therapy. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 355, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, M.R.; Marais, R. Deja Vu: EGF receptors drive resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanibar-Adaniya, S.; Barta, S.K. 2021 Update on Diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A review of current data and potential applications on risk stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Sarkozy, C. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure-what to do? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2016, 2016, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.C.; Bachmeier, C.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A. CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell lymphomas: Clinical trial results of available products. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10, 2040620719841581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Zhang, J.; Honbo, N.; Karliner, J.S. Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Cardiology 2010, 115, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denard, B.; Lee, C.; Ye, J. Doxorubicin blocks proliferation of cancer cells through proteolytic activation of CREB3L1. eLife 2012, 1, e00090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denard, B.; Pavia-Jimenez, A.; Chen, W.; Williams, N.S.; Naina, H.; Collins, R.; Brugarolas, J.; Ye, J. Identification of CREB3L1 as a Biomarker Predicting Doxorubicin Treatment Outcome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüpertz, R.; Wätjen, W.; Kahl, R.; Chovolou, Y. Dose- and time-dependent effects of doxorubicin on cytotoxicity, cell cycle and apoptotic cell death in human colon cancer cells. Toxicology 2010, 271, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, P.K.; Iliskovic, N. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Santos, R.X.; Cardoso, S.; Correia, S.; Oliveira, P.J.; Santos, M.S.; Moreira, P.I. Doxorubicin: The good, the bad and the ugly effect. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3267–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiyath, S.M.; Rasul, M.; Lee, B.; Wei, G.; Lamba, G.; Liu, D. Comparison of safety and toxicity of liposomal doxorubicin vs. conventional anthracyclines: A meta-analysis. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, S.C. Micro and nano-fabrication of biodegradable polymers for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: The key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 2001, 41, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, D.; Trad, M.; Hanke, N.T.; Larmonier, C.B.; Janikashvili, N.; Bonnotte, B.; Katsanis, E.; Larmonier, N. Doxorubicin eliminates myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances the efficacy of adoptive T-cell transfer in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, O.; Paul, S.; Das, S.; Rakshit, S.; Shanmugam, G.; George, M.; Sarkar, K. Doxorubicin induced epigenetic regulation of dendritic cell maturation in association with T cell activation facilitates tumor protective immune response in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Pathol. Res. Pr. 2024, 253, 155004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xiong, Z.A.; Qin, Q.; Yao, C.G.; Zhao, X.Z. Picosecond pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in a cervical cancer xenograft. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer deposition following solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, N.; Nassar, T.; Ripin, A.N.; Schwob, O.; Borlak, J.; Benita, S. Antibody conjugated PLGA nanoparticles for targeted delivery of paclitaxel palmitate: Efficacy and biofate in a lung cancer mouse model. Small 2013, 9, 4221–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacz, M.; Kusowska, A.; Winiarska, M.; Bobrowicz, M. In Vitro Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Line Models as Tools to Investigate Novel Immunotherapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2022, 15, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Wu, S.; Cai, D.Y.; Hong, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.Q.; Hua, H.Y.; Wu, X.H. Prognostic significance of serum aspartic transaminase in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.M.; Bhatt, S.; Patricelli, M.P.; Nomanbhoy, T.K.; Jiang, X.; Natkunam, Y.; Gentles, A.J.; Martinez, E.; Zhu, D.; Chapman, J.R.; et al. Pathophysiological significance and therapeutic targeting of germinal center kinase in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elrahman, I.; Nassar, T.; Khairi, N.; Perlman, R.; Benita, S.; Ben Yehuda, D. Novel targeted mtLivin nanoparticles treatment for disseminated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston, W.J.; Hope, D.E.; Nowak, A.K.; Robinson, B.W.; Lake, R.A.; Lesterhuis, W.J. A systematic investigation of the maximum tolerated dose of cytotoxic chemotherapy with and without supportive care in mice. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asnani, A.; Moslehi, J.J.; Adhikari, B.B.; Baik, A.H.; Beyer, A.M.; de Boer, R.A.; Ghigo, A.; Grumbach, I.M.; Jain, S.; Zhu, H. Preclinical Models of Cancer Therapy-Associated Cardiovascular Toxicity: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, e21–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, M.; Manning, N.; Sexton, C.; Sabulski, A.; Byerly, L.; O’Brien, E.; Perentesis, J.P.; Mizukawa, B.; Mulloy, J.C. Improved chemotherapy modeling with RAG-based immune deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harush-Frenkel, O.; Bivas-Benita, M.; Nassar, T.; Springer, C.; Sherman, Y.; Avital, A.; Altschuler, Y.; Borlak, J.; Benita, S. A safety and tolerability study of differently-charged nanoparticles for local pulmonary drug delivery. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 246, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno, B.M.; Garbow, J.R.; Kolar, G.R.; Jackson, E.N.; Engelbach, J.A.; Becker-Hapak, M.; Carayannopoulos, L.N.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Linette, G.P. Immunodeficient mouse strains display marked variability in growth of human melanoma lung metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3277–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorostkar, H.; Haghiralsadat, B.F.; Hemati, M.; Safari, F.; Hassanpour, A.; Naghib, S.M.; Roozbahani, M.H.; Mozafari, M.R.; Moradi, A. Reduction of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Co-Administration of Smart Liposomal Doxorubicin and Free Quercetin: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipani, M.; Rivolta, G.M.; Margiotta-Casaluci, G.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Al Essa, W.; Gaidano, G.; Bruna, R. New Frontiers in Monoclonal Antibodies for Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2023, 16, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Ye, Y.; Lei, Y.; Islam, R.; Tan, S.; Tong, R.; Miao, Y.B.; Cai, L. Smart nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, S.; Park, S.; Park, H.; Park, C.; Kim, W.C.; Thakur, D.; Won, Y.J.; Key, J. Clinical Trials for Oral, Inhaled and Intravenous Drug Delivery System for Lung Cancer and Emerging Nanomedicine-Based Approaches. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 7865–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehelgerdi, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Allela, O.Q.B.; Pecho, R.D.C.; Jayasankar, N.; Rao, D.P.; Thamaraikani, T.; Vasanthan, M.; Viktor, P.; Lakshmaiya, N.; et al. Progressing nanotechnology to improve targeted cancer treatment: Overcoming hurdles in its clinical implementation. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.W.; Emre, N.C.; Kohlhammer, H.; Dave, S.S.; Davis, R.E.; Carty, S.; Lam, L.T.; Shaffer, A.L.; Xiao, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13520–13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Svoboda, J.; Chong, E.A.; Nasta, S.D.; Mato, A.R.; Anak, Ö.; Brogdon, J.L.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Bhoj, V.; Landsburg, D.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehn, L.H.; Berry, B.; Chhanabhai, M.; Fitzgerald, C.; Gill, K.; Hoskins, P.; Klasa, R.; Savage, K.J.; Shenkier, T.; Sutherland, J.; et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 2007, 109, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd-Elrahman, I.; Khairi, N.; Nassar, T.; Perlman, R.; Ben Yehuda, D. Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticle Treatment Enhances Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Death. Cells 2025, 14, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171334
Abd-Elrahman I, Khairi N, Nassar T, Perlman R, Ben Yehuda D. Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticle Treatment Enhances Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Death. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171334
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd-Elrahman, Ihab, Noha Khairi, Taher Nassar, Riki Perlman, and Dina Ben Yehuda. 2025. "Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticle Treatment Enhances Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Death" Cells 14, no. 17: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171334
APA StyleAbd-Elrahman, I., Khairi, N., Nassar, T., Perlman, R., & Ben Yehuda, D. (2025). Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticle Treatment Enhances Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Death. Cells, 14(17), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171334






