Fibroblast Growth Factors in Lung Development and Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
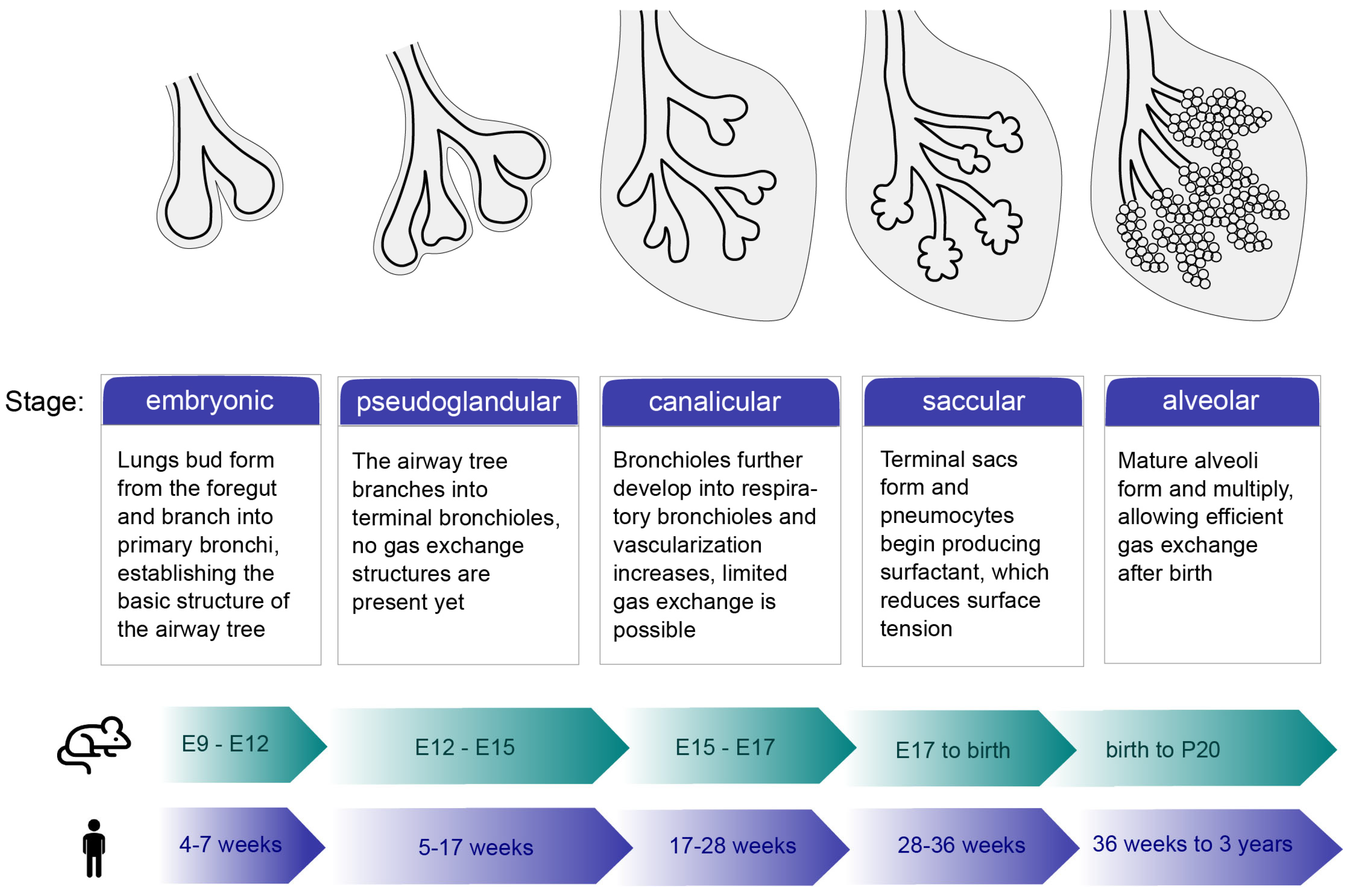
1. An Overview of the Morphological Development of Lungs
1.1. Stages of Lung Development
1.2. Progenitor Cells
1.3. Transcription Factors
2. Fibroblast Growth Factors in Lung Development
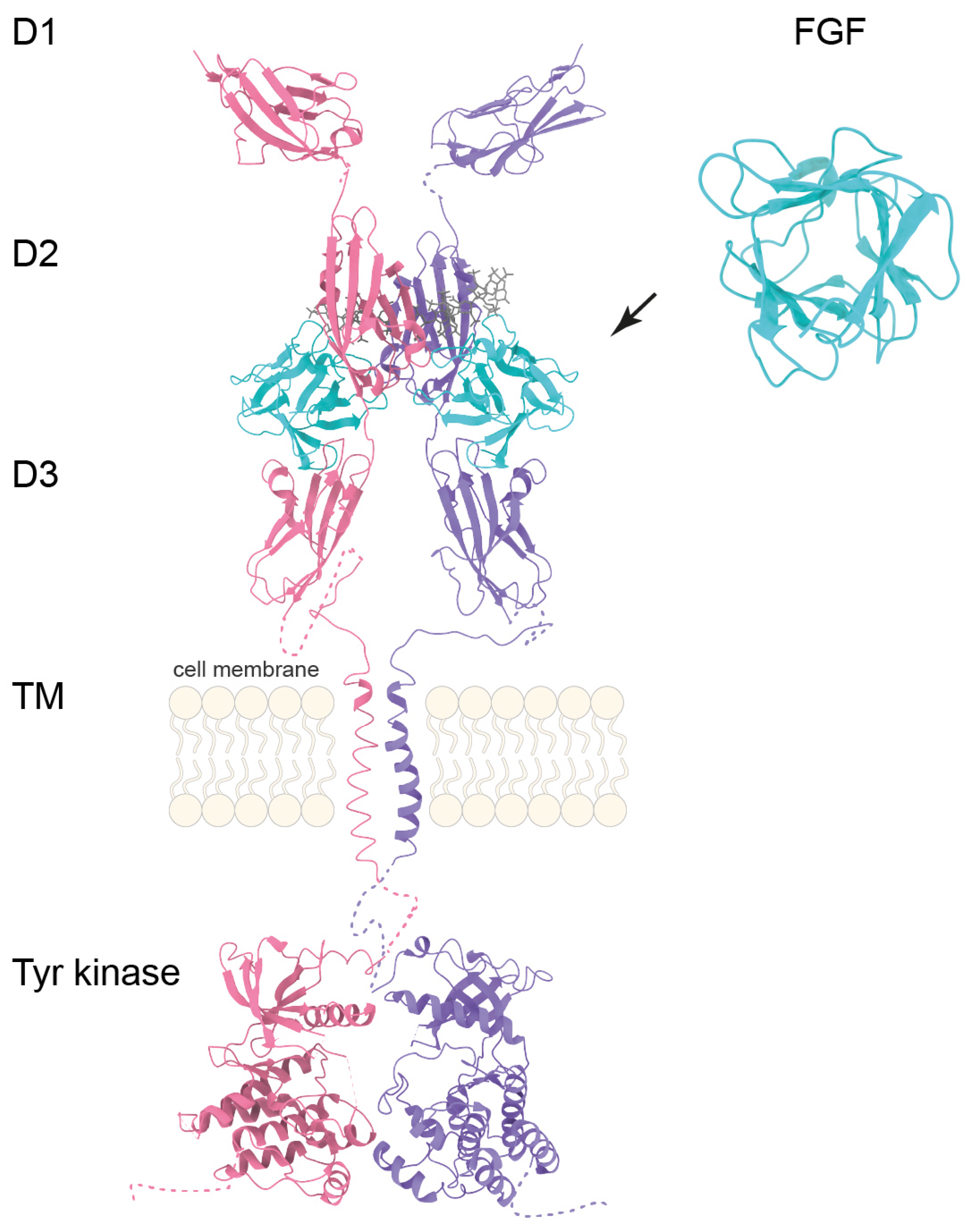
2.1. FGF-FGFR Signaling
2.2. FGFs and Their Receptors in Lung Formation
2.3. FGFRs Expression in Lung Development
2.4. FGF1 and FGF2
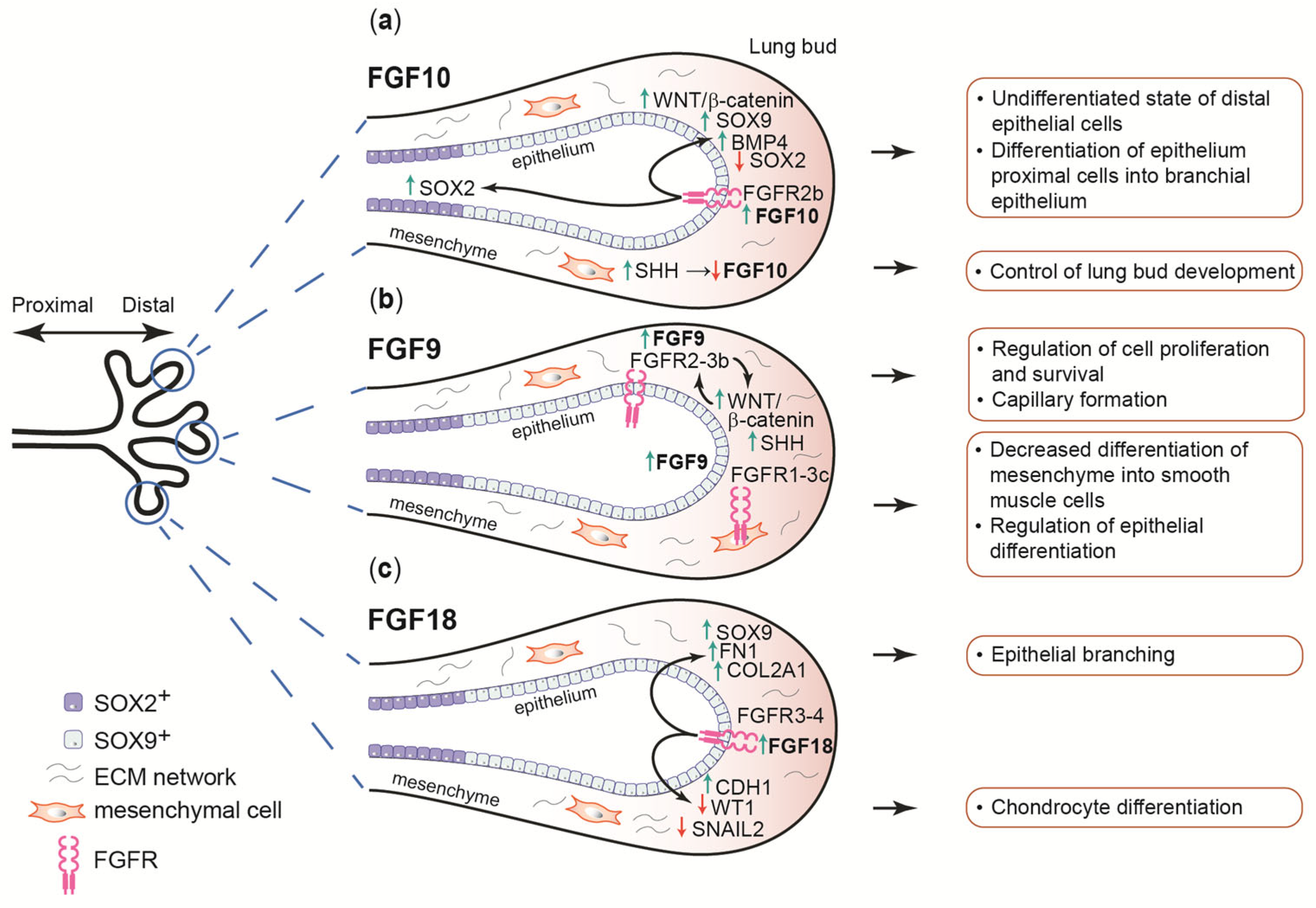
2.5. FGF7 and FGF10
2.6. FGF9
2.7. FGF8 and FGF18
3. The Role of FGF-FGFR Signaling in the Regeneration of Lungs
3.1. Adult Stem Cell Niche Maintenance
3.2. Basal Stem Cells Maintenance
3.3. Alveolar Stem Cells Maintenance
3.4. FGFR Signaling in the Regeneration of Mature Alveoli
3.5. FGF10-Dependent Regeneration of Adult Airways of the Lungs
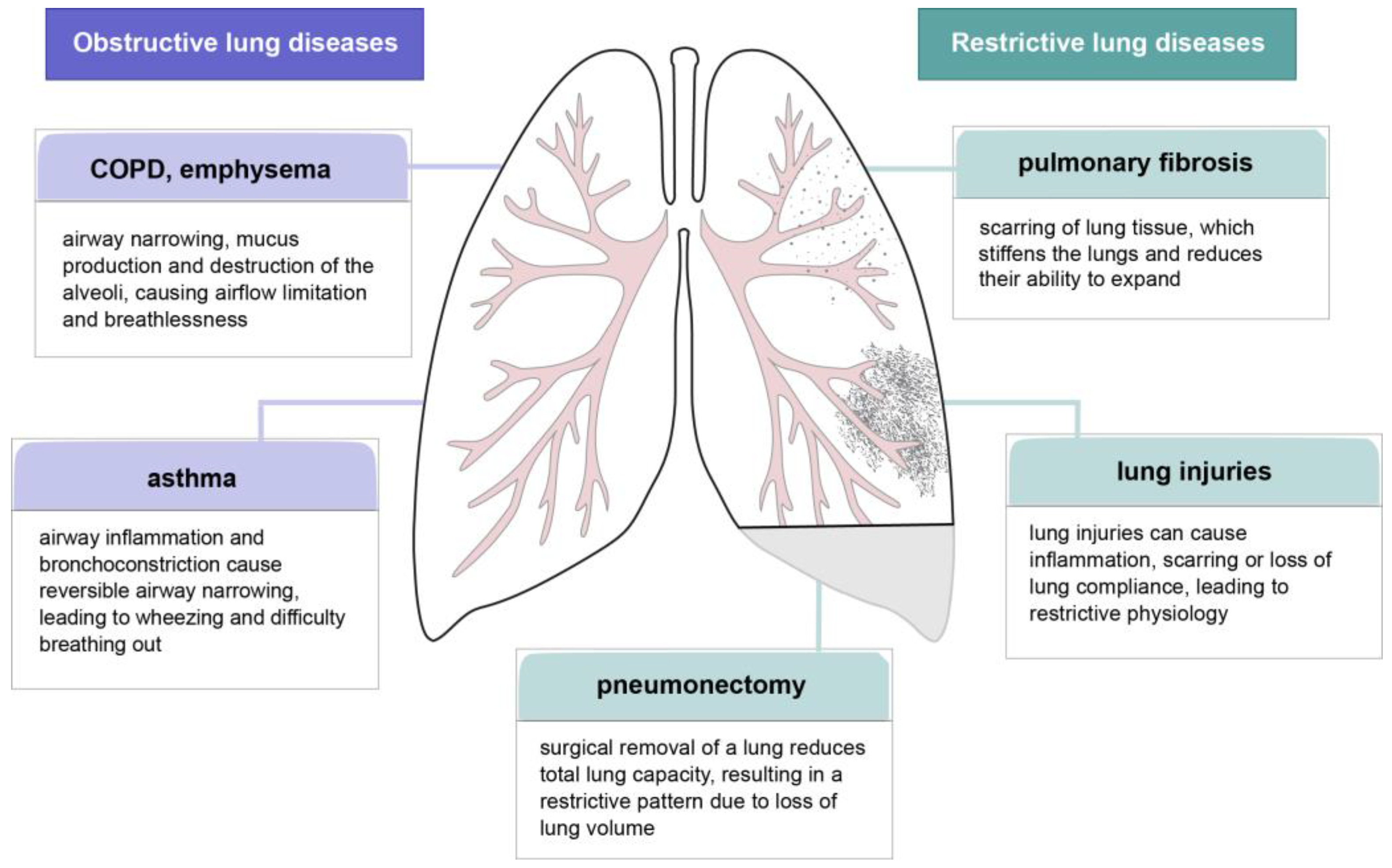
4. Lung Dysfunctions and the Potential of FGF-Related Treatments
4.1. Pulmonary Fibrosis
4.2. Lung Injuries
4.3. COVID-19 Infections
4.4. COPD and Emphysema
4.5. Pneumonectomy
4.6. Asthma
5. Potential Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the FGF-FGFR Pathway for the Treatment of Lung Dysfunctions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-SMA | smooth muscle actin alpha |
| AEP | alveolar epithelial progenitor |
| ALI | acute lung injury |
| AT1 | alveolar type I |
| AT2 | alveolar type II |
| BASCs | bronchioalveolar stem cells |
| BMP | bone morphogenetic protein |
| COL2A1 | collagen type II alpha 1 chain |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| FGFR | fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| FN1 | fibronectin |
| IAV | influenza A virus |
| ICS | inhaled corticosteroids |
| LMSC | lung mesenchymal stromal cell |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K/AKT | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase—protein kinase B |
| PLCγ | phospholipase C gamma |
| PNX | pneumonectomy |
| PSMCs | parabronchial smooth muscle cell progenitors |
| SHH | sonic hedgehog |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TGF-α/β | transforming growth factor alpha/beta |
| TM | transmembrane domain |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WNT | wingless-type mouse mammary tumor virus integration site |
References
- Rao Tata, P.; Rajagopal, J. Plasticity in the Lung: Making and Breaking Cell Identity. Development 2017, 144, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, M.Z.; Sun, D.; Rawlins, E.L. Human Lung Development: Recent Progress and New Challenges. Development 2018, 145, dev163485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, J.C. Development of the Lung. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Kalin, T.V.; Xu, Y.; Kalinichenko, V.V. Building and Regenerating the Lung Cell by Cell. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 513–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, D.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Huang, X. FGF/FGFR Signaling: From Lung Development to Respiratory Diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 62, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Lingampally, A.; Wu, J.; Sedighi, J.; Ahmadvand, N.; Wilhelm, J.; Vazquez-Armendariz, A.I.; Herold, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.S.; et al. Evidence for Overlapping and Distinct Biological Activities and Transcriptional Targets Triggered by Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2b Signaling between Mid- and Early Pseudoglandular Stages of Mouse Lung Development. Cells 2020, 9, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdowska, J.; Cousens, C.; Finlayson, J.; Collie, D.; Dagleish, M.P. Structural Development, Cellular Differentiation and Proliferation of the Respiratory Epithelium in the Bovine Fetal Lung. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 154, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, J.R.; Onaitis, M.W.; Rawlins, E.L.; Lu, Y.; Clark, C.P.; Xue, Y.; Randell, S.H.; Hogan, B.L.M. Basal Cells as Stem Cells of the Mouse Trachea and Human Airway Epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12771–12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, A.K.T.; Wert, S.E.; Nagy, A.; Lobe, C.G.; Whitsett, J.A. Early Restriction of Peripheral and Proximal Cell Lineages during Formation of the Lung. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10482–10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, M.J.; Putney, L.F.; Wyatt, G.; Finkbeiner, W.E.; Hyde, D.M. Growth of Alveoli during Postnatal Development in Humans Based on Stereological Estimation. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, J.R.; Hogan, B.L.M. Epithelial Progenitor Cells in Lung Development, Maintenance, Repair, and Disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alysandratos, K.D.; Herriges, M.J.; Kotton, D.N. Epithelial Stem and Progenitor Cells in Lung Repair and Regeneration. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, J.R.; Gao, X.; Xue, Y.; Randell, S.H.; Kong, Y.Y.; Hogan, B.L.M. Notch-Dependent Differentiation of Adult Airway Basal Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkauskas, C.E.; Cronce, M.J.; Rackley, C.R.; Bowie, E.J.; Keene, D.R.; Stripp, B.R.; Randell, S.H.; Noble, P.W.; Hogan, B.L.M. Type 2 Alveolar Cells Are Stem Cells in Adult Lung. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Tang, N. Stem Cells in Pulmonary Alveolar Regeneration. Development 2021, 148, dev193458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Jones, M.R.; Olmer, R.; Ulrich, S.; Danopoulos, S.; Shen, C.; Chen, C.; Wilhelm, J.; Martin, U.; Chen, C.; et al. Fgf10 Signaling-Based Evidence for the Existence of an Embryonic Stage Distinct from the Pseudoglandular Stage During Mouse Lung Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 576604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, S.; Cao, Y.; Tagne, J.-B.; Lakshminarayanan, M.; Li, J.; Friedman, T.B.; Morell, R.J.; Warburton, D.; Kotton, D.N.; Ramirez, M.I. The Transcription Factors Grainyhead-like 2 and NK2-Homeobox 1 Form a Regulatory Loop That Coordinates Lung Epithelial Cell Morphogenesis and Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37282–37295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, S.; Shiosaki, J.; Al Alam, D. FGF Signaling in Lung Development and Disease: Human versus Mouse. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, S.; Alonso, I.; Thornton, M.E.; Grubbs, B.H.; Bellusci, S.; Warburton, D.; Al Alam, D. Human Lung Branching Morphogenesis Is Orchestrated by the Spatiotemporal Distribution of ACTA2, SOX2, and SOX9. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L144–L149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulley, D.; Wienhold, M.; Sun, X. The Pulmonary Mesenchyme Directs Lung Development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 32, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, B.L. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: Multifunctional Regulators of Vertebrate Development. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1580–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, B.A.; McMahon, A.P. Wnt Genes and Vertebrate Development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1994, 4, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmidt, M.; Brook, A.; McMahon, A.P. The World According to bedgebog. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. New Developments in the Biology of Fibroblast Growth Factors. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2022, 14, e1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, A.N.; Hubbard, S.R.; Schlessinger, J.; Mohammadi, M. Crystal Structures of Two FGF-FGFR Complexes Reveal the Determinants of Ligand-Receptor Specificity. Cell 2000, 101, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswarakumar, V.P.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Cellular Signaling by Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenken, A.; Mohammadi, M. The FGF Family: Biology, Pathophysiology and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Su, N.; Yang, J.; Tan, Q.; Huang, S.; Jin, M.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Luo, F.; et al. FGF/FGFR Signaling in Health and Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, R.; Borea, R.; Coelho, A.; Khan, S.; Araújo, A.; Reclusa, P.; Franchina, T.; Van Der Steen, N.; Van Dam, P.; Ferri, J.; et al. FGFR a Promising Druggable Target in Cancer: Molecular Biology and New Drugs. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babina, I.S.; Turner, N.C. Advances and Challenges in Targeting FGFR Signalling in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.; Bellusci, S.; De Langhe, S.; Del Moral, P.M.; Fleury, V.; Mailleux, A.; Tefft, D.; Unbekandt, M.; Wang, K.; Shi, W.W.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Early Lung Specification and Branching Morphogenesis. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 26R–37R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeche, D.; Malpel, S.; Cardoso, W.V. Fibroblast Growth Factor Interactions in the Developing Lung. Mech. Dev. 1999, 86, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, E.; Haffner-Krausz, R.; Gorivodsky, M.; Lonai, P. Fgfr2 Is Required for Limb Outgrowth and Lung-Branching Morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11895–11899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danopoulos, S.; Thornton, M.E.; Grubbs, B.H.; Frey, M.R.; Warburton, D.; Bellusci, S.; Al Alam, D. Discordant Roles for FGF Ligands in Lung Branching Morphogenesis between Human and Mouse. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolobaric, A.; Vukojevic, K.; Brekalo, S.; Misković, J.; Ries, M.; Lasic Arapovic, L.; Soljic, V. Expression and Localization of FGFR1, FGFR2 and CTGF during Normal Human Lung Development. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Klinkhammer, K.; Lyu, H.; Gao, S.; Yuan, J.; Hopkins, S.; Zhang, J.S.; De Langhe, S.P. Temporospatial Expression of Fgfr1 and 2 During Lung Development, Homeostasis, and Regeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Agha, E.; Herold, S.; Al Alam, D.; Quantius, J.; MacKenzie, B.A.; Carraro, G.; Moiseenko, A.; Chao, C.M.; Minoo, P.; Seeger, W.; et al. Fgf10-Positive Cells Represent a Progenitor Cell Population during Lung Development and Postnatally. Development 2014, 141, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Herriges, J.C.; Chen, L.; Mecham, R.P.; Sun, X. FGF Receptors Control Alveolar Elastogenesis. Development 2017, 144, 4563–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuma, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Simon, D.M.; Solleti, S.K.; Tyagi, S.; Starcher, B.; Mariani, T.J. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors Control Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions Necessary for Alveolar Elastogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Agha, E.; Seeger, W.; Bellusci, S. Therapeutic and Pathological Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factors in Pulmonary Diseases. Dev. Dyn. 2017, 246, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, W.V.; Itoh, A.; Nogawa, H.; Mason, I.; Brody, J.S. FGF-1 and FGF-7 Induce Distinct Patterns of Growth and Differentiation in Embryonic Lung Epithelium. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 1997, 208, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J.; Klagsbrun, M. Angiogenic Factors. Science 1987, 235, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.N.; Liu, J.; Tanswell, A.K.; Post, M. Expression of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor and Receptor: Immunolocalization Studies in Developing Rat Fetal Lung. Pediatr. Res. 1992, 31, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padela, S.; Yi, M.; Cabacungan, J.; Shek, S.; Belcastro, R.; Masood, A.; Jankov, R.P.; Tanswell, A.K. A Critical Role for Fibroblast Growth Factor-7 during Early Alveolar Formation in the Neonatal Rat. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, M.; Oshika, E.; Ung, L.P.; Singh, G.; Shinozuka, H.; Warburton, D.; Michalopoulos, G.; Katyal, S.L. Keratinocyte Growth Factor and Embryonic Rat Lung Morphogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 15, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, D.; Butler, R.; Rawlins, E.L. RTK Signalling Promotes Epithelial Columnar Cell Shape and Apical Junction Maintenance in Human Lung Progenitor Cells. Development 2023, 150, dev201284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, H.; Yoneda, A.; Puri, P. Gene Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factors 10 and 7 Is Downregulated in the Lung of Nitrofen-Induced Diaphragmatic Hernia in Rats. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003, 38, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D.; El-Hashash, A.; Carraro, G.; Tiozzo, C.; Sala, F.; Rogers, O.; De Langhe, S.; Kemp, P.J.; Riccardi, D.; Torday, J.; et al. Chapter Three—Lung Organogenesis. In Organogenesis in Development; Koopman, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 90, pp. 73–158. ISBN 0070-2153. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.R.; Chong, L.; Bellusci, S. Fgf10/Fgfr2b Signaling Orchestrates the Symphony of Molecular, Cellular, and Physical Processes Required for Harmonious Airway Branching Morphogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 620667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Ornitz, D.M. FGF9 and FGF10 Activate Distinct Signaling Pathways to Direct Lung Epithelial Specification and Branching. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Volckaert, T.; Chanda, D.; Thannickal, V.J.; De Langhe, S.P. Fgf10 Signaling in Lung Development, Homeostasis, Disease, and Repair After Injury. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abler, L.L.; Mansour, S.L.; Sun, X. Conditional Gene Inactivation Reveals Roles for Fgf10 and Fgfr2 in Establishing a Normal Pattern of Epithelial Branching in the Mouse Lung. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, K.; Ohuchi, H.; Fujiwara, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Yoshizawa, T.; Sato, T.; Yagishita, N.; Matsui, D.; Koga, Y.; Itoh, N.; et al. Fgf10 Is Essential for Limb and Lung Formation. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moerlooze, L.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Revest, J.M.; Hajihosseini, M.; Rosewell, I.; Dickson, C. An Important Role for the IIIb Isoform of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 (FGFR2) in Mesenchymal-Epithelial Signalling during Mouse Organogenesis. Development 2000, 127, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyrek, A.A.; Baran, K.; Hruba, E.; Horackova, A.; Bosakova, V.; Chudzian, J.; Fafilek, B.; Laskova, V.; Stepankova, V.; Bednar, D.; et al. Increased Thermal Stability of FGF10 Leads to Ectopic Signaling during Development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2025, 82, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volckaert, T.; Campbell, A.; Dill, E.; Li, C.; Minoo, P.; De Langhe, S. Localized Fgf10 Expression Is Not Required for Lung Branching Morphogenesis but Prevents Differentiation of Epithelial Progenitors. Development 2013, 140, 3731–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, J.; Zhao, S.; Rong, Z.; Lin, Y. SOX9 Inactivation Affects the Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Lung Organoids. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.; Bellusci, S.; Del Moral, P.-M.; Kaartinen, V.; Lee, M.; Tefft, D.; Shi, W. Growth Factor Signaling in Lung Morphogenetic Centers: Automaticity, Stereotypy and Symmetry. Respir. Res. 2003, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, P.-T.; Kawcak, T.; McMahon, A.P. Feedback Control of Mammalian Hedgehog Signaling by the Hedgehog-Binding Protein, Hip1, Modulates Fgf Signaling during Branching Morphogenesis of the Lung. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, F.; Ornitz, D.M. Mesothelial- and Epithelial-Derived FGF9 Have Distinct Functions in the Regulation of Lung Development. Development 2011, 138, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Domyan, E.T.; Lewandoski, M.; Sun, X. Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 Signaling Inhibits Airway Smooth Muscle Differentiation in Mouse Lung. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2009, 238, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Moral, P.-M.; De Langhe, S.P.; Sala, F.G.; Veltmaat, J.M.; Tefft, D.; Wang, K.; Warburton, D.; Bellusci, S. Differential Role of FGF9 on Epithelium and Mesenchyme in Mouse Embryonic Lung. Dev. Biol. 2006, 293, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.C.; Xu, J.; Yin, Y.; Smith, C.; Schmid, G.; Ornitz, D.M. FGF9 and SHH Signaling Coordinate Lung Growth and Development through Regulation of Distinct Mesenchymal Domains. Development 2006, 133, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, J.S.; White, A.C.; Pratt, S.J.; Ornitz, D.M. Lung Hypoplasia and Neonatal Death in Fgf9-Null Mice Identify This Gene as an Essential Regulator of Lung Mesenchyme. Development 2001, 2106, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.C.; Lavine, K.J.; Ornitz, D.M. FGF9 and SHH Regulate Mesenchymal Vegfa Expression and Development of the Pulmonary Capillary Network. Development 2007, 134, 3743–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Poe, B.; Schwarz, M.; Elliot, S.A.; Albertine, K.H.; Fenton, S.; Garg, V.; Moon, A.M. Fetal and Postnatal Lung Defects Reveal a Novel and Required Role for Fgf8 in Lung Development. Dev. Biol. 2010, 347, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.U.; Fotheringham, L.K.; Brewer, J.A.; Muglia, L.J.; Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Capecchi, M.R.; Moon, A.M. An Fgf8 Mouse Mutant Phenocopies Human 22q11 Deletion Syndrome. Development 2002, 129, 4591–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Montoya, M.-L.; Boucherat, O.; Thibault, C.; Chailley-Heu, B.; Incitti, R.; Delacourt, C.; Bourbon, J.R. Profiling Target Genes of FGF18 in the Postnatal Mouse Lung: Possible Relevance for Alveolar Development. Physiol. Genom. 2011, 43, 1226–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, S.E.; McCoy, D.M. Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling in Myofibroblasts Differs from Lipofibroblasts during Alveolar Septation in Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L463-74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailley-Heu, B.; Boucherat, O.; Barlier-Mur, A.-M.; Bourbon, J.R. FGF-18 Is Upregulated in the Postnatal Rat Lung and Enhances Elastogenesis in Myofibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 288, L43-51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Clark, J.C.; Picard, L.; Tichelaar, J.W.; Wert, S.E.; Itoh, N.; Perl, A.K.T.; Stahlman, M.T. Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 Influences Proximal Programming during Lung Morphogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22743–22749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, E.; Boucherat, O.; Franco-Montoya, M.-L.; Bourbon, J.R.; Delacourt, C.; Jarreau, P.-H. Nitric Oxide Donor Restores Lung Growth Factor and Receptor Expression in Hyperoxia-Exposed Rat Pups. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boucherat, O.; Benachi, A.; Barlier-Mur, A.-M.; Franco-Montoya, M.-L.; Martinovic, J.; Thébaud, B.; Chailley-Heu, B.; Bourbon, J.R. Decreased Lung Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 and Elastin in Human Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia and Animal Models. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, H.; Shibayama, M.; Ohbayashi, N.; Konishi, M.; Takada, S.; Itoh, N. Fgf18 Is Required for Embryonic Lung Alveolar Development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danopoulos, S.; Belgacemi, R.; Hein, R.F.C.; Miller, A.J.; Deutsch, G.H.; Glass, I.; Spence, J.R.; Al Alam, D. FGF18 Promotes Human Lung Branching Morphogenesis through Regulating Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2023, 324, L433–L444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo-Saganta, A.; Law, B.M.; Tata, P.R.; Villoria, J.; Saez, B.; Mou, H.; Zhao, R.; Rajagopal, J. Injury Induces Direct Lineage Segregation of Functionally Distinct Airway Basal Stem/Progenitor Cell Subpopulations. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 23, 237–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, K.R.; Nawroth, J.; Pai, A.; Busch, S.M.; Senger, C.N.; Ryan, A.L. Stem Cells and Lung Regeneration. Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C675–C693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlins, E.L.; Okubo, T.; Xue, Y.; Brass, D.M.; Auten, R.L.; Hasegawa, H.; Wang, F.; Hogan, B.L.M. The Role of Scgb1a1+ Clara Cells in the Long-Term Maintenance and Repair of Lung Airway, but Not Alveolar, Epithelium. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Limmon, G.V.; Yin, L.; Leung, N.H.N.; Yu, H.; Chow, V.T.K.; Chen, J. Regeneration of Alveolar Type I and II Cells from Scgb1a1-Expressing Cells Following Severe Pulmonary Damage Induced by Bleomycin and Influenza. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Chow, R.D.; Tran, J.; Desai, A.; Massri, A.J.; McCord, T.J.; Gunn, M.D.; Tata, P.R. Myoepithelial Cells of Submucosal Glands Can Function as Reserve Stem Cells to Regenerate Airways after Injury. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 668–683.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhang, T.; Wu, D.Z.A.; Guan, S.P.; Liew, A.A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Wang, X.; Lim, S.J.; Vincent, M.; Lessard, M.; et al. P63 + Krt5 + Distal Airway Stem Cells Are Essential for Lung Regeneration. Nature 2015, 517, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, A.; Deshpande, A.; Jain, A.; Sebastiani, P.; Cardoso, W.V. Uroplakin 3a+ Cells Are a Distinctive Population of Epithelial Progenitors That Contribute to Airway Maintenance and Post-Injury Repair. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwig, I.; Spitznagel, B.; Vazquez-Armendariz, A.I.; Khalooghi, K.; Guenther, S.; Herold, S.; Szibor, M.; Braun, T. Bronchioalveolar Stem Cells Are a Main Source for Regeneration of Distal Lung Epithelia In Vivo. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, M.C.; Katzen, J.; Engler, A.E.; Guo, M.; Herriges, M.J.; Kathiriya, J.J.; Windmueller, R.; Ysasi, A.B.; Zacharias, W.J.; Chapman, H.A.; et al. The Cellular and Physiological Basis for Lung Repair and Regeneration: Past, Present, and Future. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 482–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, W.J.; Frank, D.B.; Zepp, J.A.; Morley, M.P.; Alkhaleel, F.; Kong, J.; Zhou, S.; Cantu, E.; Edward, E. Regeneration of the Lung Alveolus by an Evolutionarily Conserved Epithelial Progenitor. Nature 2018, 555, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, Y. Roles of Airway Basal Stem Cells in Lung Homeostasis and Regenerative Medicine. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasooriya, G.I.; Johnson, J.A.; Basson, M.A.; Rawlins, E.L. An FGFR1-SPRY2 Signaling Axis Limits Basal Cell Proliferation in the Steady-State Airway Epithelium. Dev. Cell 2016, 37, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, G.I.; Goschorska, M.; Piddini, E.; Rawlins, E.L. FGFR2 Is Required for Airway Basal Cell Self-Renewal and Terminal Differentiation. Development 2017, 144, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volckaert, T.; Yuan, T.; Chao, C.M.; Bell, H.; Sitaula, A.; Szimmtenings, L.; El Agha, E.; Chanda, D.; Majka, S.; Bellusci, S.; et al. Fgf10-Hippo Epithelial-Mesenchymal Crosstalk Maintains and Recruits Lung Basal Stem Cells. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 48–59.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Volckaert, T.; Redente, E.F.; Hopkins, S.; Klinkhammer, K.; Wasnick, R.; Chao, C.M.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.S.; Yao, C.; et al. FGF10-FGFR2B Signaling Generates Basal Cells and Drives Alveolar Epithelial Regeneration by Bronchial Epithelial Stem Cells after Lung Injury. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberti, D.C.; Kremp, M.M.; Liberti, W.A.; Penkala, I.J.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Morrisey, E.E. Alveolar Epithelial Cell Fate Is Maintained in a Spatially Restricted Manner to Promote Lung Regeneration after Acute Injury. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorry, S.J.; Ansbro, B.O.; Ornitz, D.M.; Mutlu, G.M.; Guzy, R.D. FGFR2 Is Required for AEC2 Homeostasis and Survival after Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkala, I.J.; Liberti, D.C.; Pankin, J.; Sivakumar, A.; Kremp, M.M.; Jayachandran, S.; Katzen, J.; Leach, J.P.; Windmueller, R.; Stolz, K.; et al. Age-Dependent Alveolar Epithelial Plasticity Orchestrates Lung Homeostasis and Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1775–1789.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volckaert, T.; Dill, E.; Campbell, A.; Tiozzo, C.; Majka, S.; Bellusci, S.; De Langhe, S.P. Parabronchial Smooth Muscle Constitutes an Airway Epithelial Stem Cell Niche in the Mouse Lung after Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4409–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volckaert, T.; Campbell, A.; De Langhe, S. C-Myc Regulates Proliferation and Fgf10 Expression in Airway Smooth Muscle after Airway Epithelial Injury in Mouse. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQualter, J.L.; McCarty, R.C.; Van der Velden, J.; O’Donoghue, R.J.J.; Asselin-Labat, M.L.; Bozinovski, S.; Bertoncello, I. TGF-β Signaling in Stromal Cells Acts Upstream of FGF-10 to Regulate Epithelial Stem Cell Growth in the Adult Lung. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Zhou, J.; Rong, L.; Seeley, E.J.; Pan, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Qu, J.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor-10 (FGF-10) Mobilizes Lung-Resident Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Protects Against Acute Lung Injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marega, M.; Chen, C.; Bellusci, S. Cross-Talk Between Inflammation and Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 During Organogenesis and Pathogenesis: Lessons Learnt from the Lung and Other Organs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 656883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Song, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.S.; Dong, N.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 Alleviates Particulate Matter-Induced Lung Injury by Inhibiting the HMGB1-TLR4 Pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 1186–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, M.; Dunn, N.R.; Hogan, B.L. Bmp4 and Fgf10 Play Opposing Roles during Lung Bud Morphogenesis. Development 2000, 127, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellusci, S.; Grindley, J.; Emoto, H.; Itoh, N.; Hogan, B.L. Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 (FGF10) and Branching Morphogenesis in the Embryonic Mouse Lung. Development 1997, 124, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, L.B. Keratinocyte Growth Factor as an Epithelial Protective Agent: Where Do We Stand? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 1345–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.O.; Muyal, V.; John, G.; Müller, B.; Seifart, C.; Kasper, M.; Fehrenbach, H. Palifermin Induces Alveolar Maintenance Programs in Emphysematous Mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantier, L.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Antico Arciuch, V.G.; Boyer, L.; De Coster, C.; Marchal, J.; Bachoual, R.; Mailleux, A.; Boczkowski, J.; Crestani, B. Keratinocyte Growth Factor Protects against Elastase-Induced Pulmonary Emphysema in Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L1230-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzic, S.; Wu, C.-Y.; Gredic, M.; Pak, O.; Loku, E.; Kraut, S.; Kojonazarov, B.; Wilhelm, J.; Brosien, M.; Bednorz, M.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 Reverses Cigarette Smoke- and Elastase-Induced Emphysema and Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, 2201606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzy, R.D.; Li, L.; Smith, C.; Dorry, S.J.; Koo, H.Y.; Chen, L.; Ornitz, D.M. Pulmonary Fibrosis Requires Cell-Autonomous Mesenchymal Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10364–10378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Philp, A.M.; Corte, T.; Travis, M.A.; Schilter, H.; Hansbro, N.G.; Burns, C.J.; Eapen, M.S.; Sohal, S.S.; Burgess, J.K.; et al. Therapeutic Targets in Lung Tissue Remodelling and Fibrosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 225, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Zhu, H.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Nintedanib Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis, Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Oxidative Stress by Modulating PI3K/Akt/MTOR Pathway in Mice. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Racanelli, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Ding, B.; et al. Targeting Fibrosis, Mechanisms and Cilinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Zhao, M.-Y.; Su, X.-L.; Ye, T.-H.; Zhuang, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Yang, J.-L.; Chen, L.-J.; Long, C.-F.; et al. The Antifibrotic Effect and Mechanism of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, ZSP1603, in Preclinical Models of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Z.; He, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, J. Mutant Soluble Ectodomain of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-2 IIIc Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El Agha, E.; Schwind, F.; Ruppert, C.; Günther, A.; Bellusci, S.; Schermuly, R.T.; Kosanovic, D. Is the Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Pathway a Victim of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Pulmonary Parenchymal and Vascular Remodeling? Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L248–L252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jieming, G.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Mo, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Inhibitory Effects of MsFGFR2c on the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of AE2 Cells in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzy, R.D.; Stoilov, I.; Elton, T.J.; Mecham, R.P.; Ornitz, D.M. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Is Required for Epithelial Recovery, but Not for Pulmonary Fibrosis, in Response to Bleomycin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, G.A.; Thannickal, V.J.; Fanburg, B.L.; Paulson, K.E. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1-Induced Activation of the ERK Pathway/Activator Protein-1 in Human Lung Fibroblasts Requires the Autocrine Induction of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27650–27656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Zhihong, Y.; Zhiyou, Z.; Qin, H.; Dingding, W.; Li, S.; Baowei, Z.; Xing, W.; Ying, H.; An, H. Inhibition of α-SMA by the Ectodomain of FGFR2c Attenuates Lung Fibrosis. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joannes, A.; Brayer, S.; Besnard, V.; Marchal-Sommé, J.; Jaillet, M.; Mordant, P.; Mal, H.; Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Mailleux, A.A. FGF9 and FGF18 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Promote Survival and Migration and Inhibit Myofibroblast Differentiation of Human Lung Fibroblasts in Vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L615–L629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justet, A.; Ghanem, M.; Boghanim, T.; Hachem, M.; Vasarmidi, E.; Jaillet, M.; Vadel, A.; Joannes, A.; Mordant, P.; Bonniaud, P.; et al. FGF19 Is Downregulated in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Inhibits Lung Fibrosis in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, T.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Yin, J.; Ren, G.; et al. FGF21 Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrogenesis through Ameliorating Oxidative Stress In Vivo and In Vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, J.W.; Duncan, D.; Helton, S.; Hutcheson, S.; Kurundkar, D.; Logsdon, N.J.; Locy, M.; Garth, J.; Denson, R.; Farver, C.; et al. Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Klotho Cross Talk in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2019, 317, L141–L154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, C.J.; Doherty, P.C.; Thomas, P.G. Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Innate Immunity to Influenza Virus Infection. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lai, C.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Ni, B.; Bai, C.; Zhang, S.; Han, L.; Gu, H.; et al. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Protects against Influenza A Virus-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Recruiting Neutrophils. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 10, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, N.M.; Noel, J.G.; Pitstick, L.B.; Gardner, J.C.; Uehara, Y.; Wu, H.; Saito, A.; Lewnard, K.E.; Liu, H.; White, M.R.; et al. Mitogenic Stimulation Accelerates Influenza-Induced Mortality by Increasing Susceptibility of Alveolar Type II Cells to Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6613–E6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.; Devaux, Y.; Stolz, D.B.; Yarlagadda, M.; Watkins, S.C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.-F.; Ray, A. Inducible Expression of Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) in Mice Inhibits Lung Epithelial Cell Death Induced by Hyperoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6098–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichelaar, J.W.; Lu, W.; Whitsett, J.A. Conditional Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor-7 in the Developing and Mature Lung. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11858–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guery, B.P.; Mason, C.M.; Dobard, E.P.; Beaucaire, G.; Summer, W.R.; Nelson, S. Keratinocyte Growth Factor Increases Transalveolar Sodium Reabsorption in Normal and Injured Rat Lungs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaisdell, C.J.; Pellettieri, J.P.; Loughlin, C.E.; Chu, S.; Zeitlin, P.L. Keratinocyte Growth Factor Stimulates CLC-2 Expression in Primary Fetal Rat Distal Lung Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Folkesson, H.G.; Jayr, C.; Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. Alveolar Epithelial Fluid Transport Can Be Simultaneously Upregulated by Both KGF and Beta-Agonist Therapy. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Dai, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, H.; Shen, G.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L. FGF18 Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting the NF-ΚB Pathway. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, J.; Karatas, O.F.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Creighton, C.J.; Ittmann, M. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Plays a Key Role in Transformation Induced by the TMPRSS2/ERG Fusion Gene and Decreased PTEN. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14456–14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyan, Y.; Schultalbers, A.; Chernobrivaia, E.; Tkachuk, S.; Rong, S.; Shushakova, N.; Haller, H. Calcium Dobesilate Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Endothelial Cells by Inhibiting Virus Binding to Heparan Sulfate. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, P.; Manquillo, A.; Guillen, P.; GIménez-Gallego, G. Fibroblast Growth Factor: A Target for COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Med. Rev. Case Rep 2020, 4, 10–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meini, S.; Giani, T.; Tascini, C. Intussusceptive Angiogenesis in Covid-19: Hypothesis on the Significance and Focus on the Possible Role of FGF2. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 8301–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, H.; Avanoğlu Güler, A.; Özger, H.S.; Yıldız, P.A.; Erbaş, G.; Bozdayı, G.; Deveci Bulut, T.; Gülbahar, Ö.; Yapar, D.; Küçük, H.; et al. The Prognostic Value of Lung Injury and Fibrosis Markers, KL-6, TGF-Β1, FGF-2 in COVID-19 Patients. Biomark. Insights 2022, 17, 11772719221135444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Jayakumar, M.N.; Saleh, M.A.; Kannan, M.; Halwani, R.; Qaisar, R.; Ahmad, F. SARS-CoV-2 Infection- Induced Growth Factors Play Differential Roles in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Life Sci. 2022, 304, 120703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, A.D. Serum FGF-21 Levels During COVID-19 Infection Recovery Period. Med. Bull. Haseki 2024, 62, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global, Regional, and National Deaths, Prevalence, Disability-Adjusted Life Years, and Years Lived with Disability for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma, 1990-2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; Ren, C.; Lin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, H.; Yin, J.; Tan, L. Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 Attenuates Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Protecting against Glycocalyx Impairment and Endothelial Apoptosis. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenfeld, S.; Kuebler, W.M. Shedding First Light on the Alveolar Epithelial Glycocalyx. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 59, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, S.; Slaaf, D.W.; Vink, H.; van Zandvoort, M.A.M.J.; oude Egbrink, M.G.A. The Endothelial Glycocalyx: Composition, Functions, and Visualization. Pflugers Arch. 2007, 454, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, D.; Sciurba, F.C.; Gladwin, M.T. Endothelial Chronic Destructive Pulmonary Disease (E-CDPD): Is Endothelial Apoptosis a Subphenotype or Prequel to COPD? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, A.R.; Willems-Widyastuti, A.; Mooi, W.J.; Saxena, P.R.; Sterk, P.J.; de Boer, W.I.; Sharma, H.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Is Associated with Enhanced Bronchial Expression of FGF-1, FGF-2, and FGFR-1. J. Pathol. 2005, 206, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krick, S.; Grabner, A.; Baumlin, N.; Yanucil, C.; Helton, S.; Grosche, A.; Sailland, J.; Geraghty, P.; Viera, L.; Russell, D.W.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Klotho Contribute to Airway Inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Wells, J.M.; Urdaneta, G.P.; Balestrini, K.; Vital, I.; Tovar, K.; Barnes, J.W.; Bhatt, S.P.; Campos, M.; Krick, S. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Is Associated with a Frequent Exacerbator Phenotype in COPD: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Dai, J.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. The Early and Late Intervention Effects of Collagen-Binding FGF2 on Elastase-Induced Lung Injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawago, M.; Yoshimasu, T.; Tabata, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hirai, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Okamura, Y. Intrapleural Administration of Gelatin-Embedded, Sustained-Release Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor for the Regeneration of Emphysematous Lungs in Rats. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Hong, G.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, Y.-K.; Oh, Y.-M.; Jee, Y.-K. The Role of FGF-2 in Smoke-Induced Emphysema and the Therapeutic Potential of Recombinant FGF-2 in Patients with COPD. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morino, S.; Nakamura, T.; Toba, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kushibiki, T.; Tabata, Y.; Shimizu, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Induces Recovery of Pulmonary Blood Flow in Canine Emphysema Models. Chest 2005, 128, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kuang, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Feng, Y.; Su, Z. Association between Fibroblast Growth Factor 7 and the Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, J.; Niu, J.; Du, L.; Li, H.; Li, X. A Functional Variant Alters Binding of Activating Protein 1 Regulating Expression of FGF7 Gene Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokuto, I.; Perl, A.-K.T.; Whitsett, J.A. Prenatal, but Not Postnatal, Inhibition of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Causes Emphysema. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paisley, D.; Bevan, L.; Choy, K.J.; Gross, C. The Pneumonectomy Model of Compensatory Lung Growth: Insights into Lung Regeneration. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, J.S.; Burki, R.; Kaplan, N. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Lung Cells during Compensatory Lung Growth after Pneumonectomy. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 117, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Paxson, J.A.; Gruntman, A.; Parkin, C.D.; Mazan, M.R.; Davis, A.; Ingenito, E.P.; Hoffman, A.M. Age-Dependent Decline in Mouse Lung Regeneration with Loss of Lung Fibroblast Clonogenicity and Increased Myofibroblastic Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxson, J.A.; Gruntman, A.M.; Davis, A.M.; Parkin, C.M.; Ingenito, E.P.; Hoffman, A.M. Age Dependence of Lung Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Dynamics Following Pneumonectomy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; White, A.C.; Huh, S.-H.; Hilton, M.J.; Kanazawa, H.; Long, F.; Ornitz, D.M. An FGF-WNT Gene Regulatory Network Controls Lung Mesenchyme Development. Dev. Biol. 2008, 319, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, C.; Flood, H.M.; Ren, X.; Jagannathan, S.; Barski, A.; Kalin, T.V.; Kalinichenko, V. V FOXF1 Transcription Factor Promotes Lung Regeneration after Partial Pneumonectomy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M. Syndromes of Telomere Shortening. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Vatrella, A.; Tinello, C.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Molecular Targets for Biological Therapies of Severe Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 603312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Wenzel, S.; Postma, D.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Renz, H.; Sly, P.D. Asthma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-Y.; Zhou, H.-Q.; Lin, Y.-J.; Yi, L.-T.; Chen, Z.-G.; Cao, Q.-D.; Guo, Y.-R.; Wang, Z.-N.; Chen, S.-D.; Li, Y.; et al. FGF2 Is Overexpressed in Asthma and Promotes Airway Inflammation through the FGFR/MAPK/NF-ΚB Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmagadda, S.R.; Spahn, J.D.; Leung, D.Y.; Szefler, S.J. Steroid-Resistant Asthma: Evaluation and Management. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996, 77, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, R.; Xu, D.; Choy, D.F.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Lee, W.P.; Modrusan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Marsters, S.; Ashkenazi, A.; Huynh, A.; et al. Steroid-Induced Fibroblast Growth Factors Drive an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Inflammatory Axis in Severe Asthma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabl8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L. Protective Effect of Keratinocyte Growth Factor against Lung Abnormalities Associated with Hyperoxia in Prematurely Born Rats. Neonatology 2003, 83, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, V.V.; Ramasamy, S.K.; Reddy, R.; Lee, J.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Guenther, A.; Warburton, D.; Driscoll, B.; Minoo, P.; et al. Overexpression of Fibroblast Growth Factor-10 during Both Inflammatory and Fibrotic Phases Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchtova, M.; Chaloupkova, R.; Zakrzewska, M.; Vesela, I.; Cela, P.; Barathova, J.; Gudernova, I.; Zajickova, R.; Trantirek, L.; Martin, J.; et al. Instability Restricts Signaling of Multiple Fibroblast Growth Factors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2445–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, M.; Krowarsch, D.; Wiedlocha, A.; Otlewski, J. Design of Fully Active FGF-1 Variants with Increased Stability. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, J.S.; Byron, P.R. Inhaling Medicines: Delivering Drugs to the Body through the Lungs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Sun, W.; Xiong, Z.F.; Liao, X.C.; Liu, M.Z.; Xu, B.; Guo, G.H. Effects of Aerosol Inhalation of Recombinant Human Keratinocyte Growth Factor 2 on the Lung Tissue of Rabbits with Severe Smoke Inhalation Injury. Chin. J. Burn. 2018, 34, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.M.; Jun, S.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Yeo, Y. Development of Inhalable Dry Powder Formulation of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yue, L.; Leng, Q.Q.; Chang, C.; Gan, C.; Ye, T.; Cao, D. Targeting FGFR for Cancer Therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulcaen, M.; Kortleven, P.; Liu, R.B.; Maule, G.; Dreano, E.; Kelly, M.; Ensinck, M.M.; Thierie, S.; Smits, M.; Ciciani, M.; et al. Prime Editing Functionally Corrects Cystic Fibrosis-Causing CFTR Mutations in Human Organoids and Airway Epithelial Cells. Cell Reports Med. 2024, 5, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Deng, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, X.L.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.D.; Fan, Y.J.; et al. Injectable Microgels with Hybrid Exosomes of Chondrocyte-Targeted FGF18 Gene-Editing. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2312559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cell Type | Differentiation Capability | Location | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airway stem cells niche | Basal stem/progenitor cells |
| Epithelium of the tracheobronchial tree | [10,77,78] |
| Club (secretory) cells |
| Epithelium of the tracheobronchial tree | [79,80] | |
| Myoepithelial cells |
| Submucosal gland | [81] | |
| Distal airway cell populations |
| Distal airways regions | [82,83,84,85] | |
| Alveolar stem cells niche | Alveolar type II cells |
| Lung alveolus | [14,86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baran, K.; Skrzynska, K.; Czyrek, A.A.; Wittek, A.; Krowarsch, D.; Szlachcic, A.; Zakrzewska, M.; Chudzian, J. Fibroblast Growth Factors in Lung Development and Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Cells 2025, 14, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161256
Baran K, Skrzynska K, Czyrek AA, Wittek A, Krowarsch D, Szlachcic A, Zakrzewska M, Chudzian J. Fibroblast Growth Factors in Lung Development and Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Cells. 2025; 14(16):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161256
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaran, Karolina, Kamila Skrzynska, Aleksandra A. Czyrek, Adrianna Wittek, Daniel Krowarsch, Anna Szlachcic, Malgorzata Zakrzewska, and Julia Chudzian. 2025. "Fibroblast Growth Factors in Lung Development and Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential" Cells 14, no. 16: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161256
APA StyleBaran, K., Skrzynska, K., Czyrek, A. A., Wittek, A., Krowarsch, D., Szlachcic, A., Zakrzewska, M., & Chudzian, J. (2025). Fibroblast Growth Factors in Lung Development and Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Cells, 14(16), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161256






