An Ex Vivo Intervertebral Disc Slice Culture Model for Studying Disc Degeneration and Immune Cell Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Lumbar Disc Isolation and Disc Slicing
2.2. IL-1β Treatment of Disc Slices
2.3. Live Dead Assay to Assess Disc Cell Viability
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM) Imaging and Analysis
2.6. TUNEL Assay for Cell Apoptosis
2.7. Biochemical Assays
2.8. Macrophages and Disc Slice Co-Culture
2.9. Macrophage Overlay Experiment
2.10. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
2.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Establishment of a New Disc Slice Culture Model
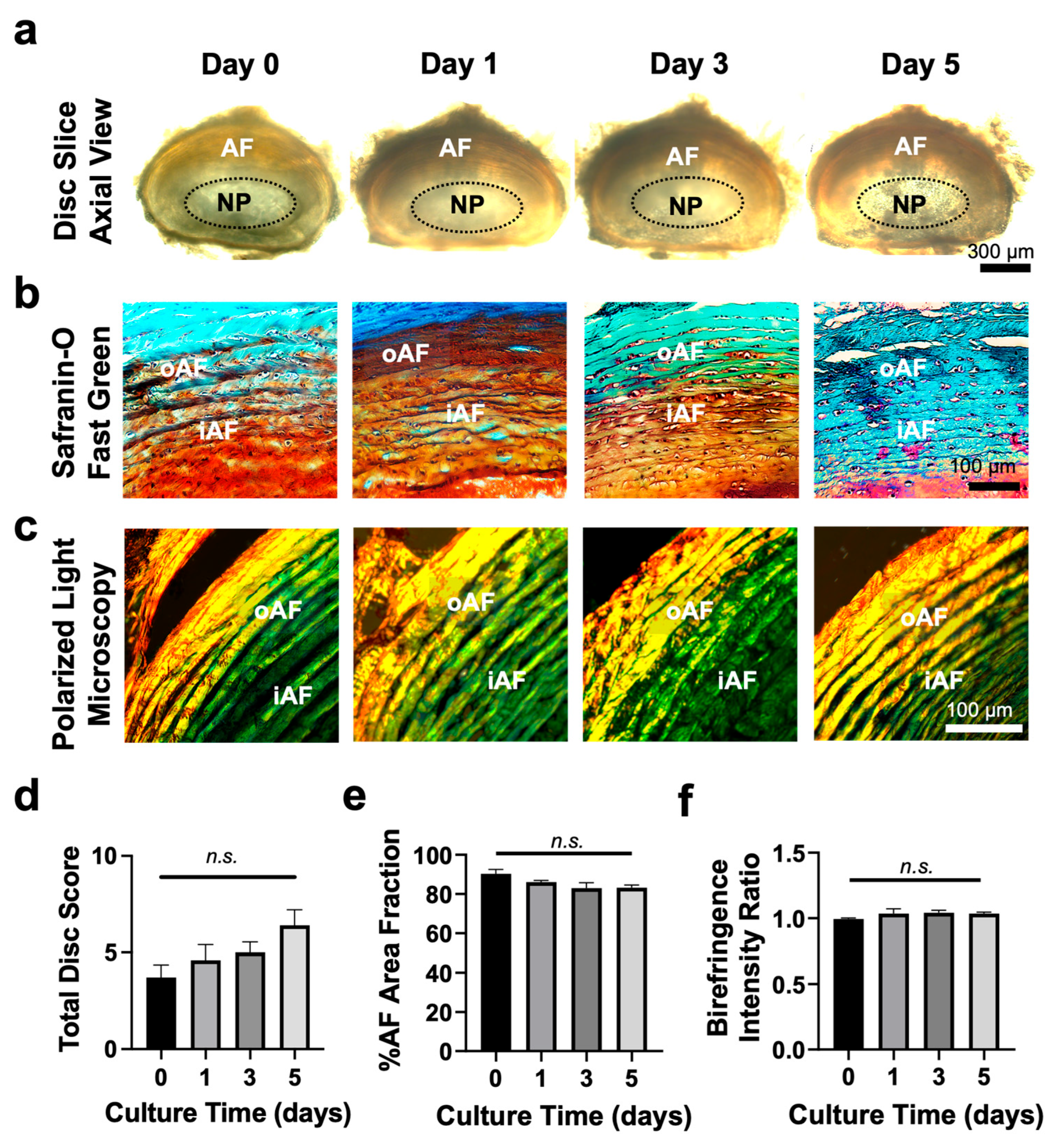
3.2. Tissue Slice Culture Maintains Disc Structure for up to 5 Days
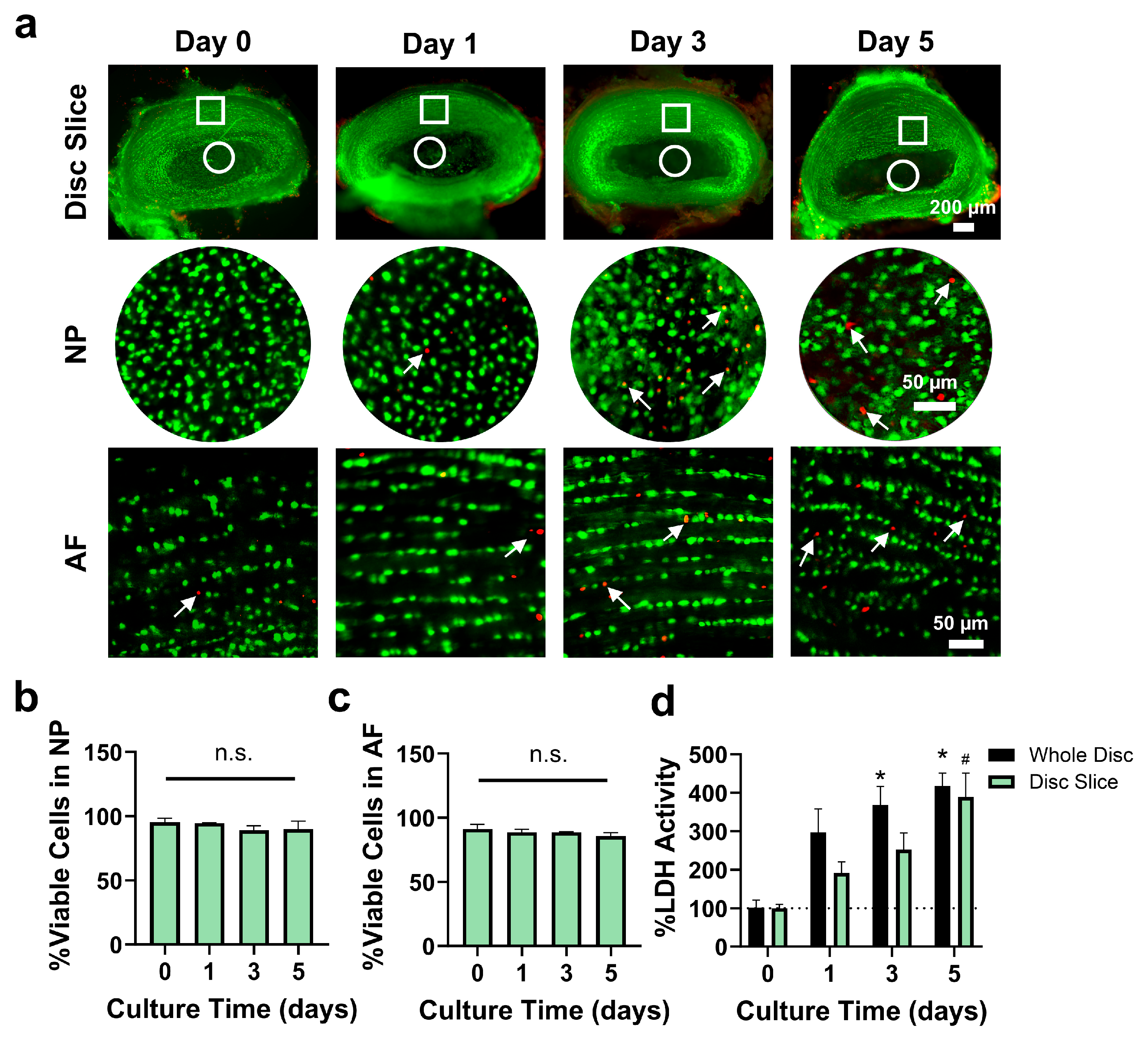
3.3. Disc Slice Culture Maintained Disc Cell Viability for up to Day 5
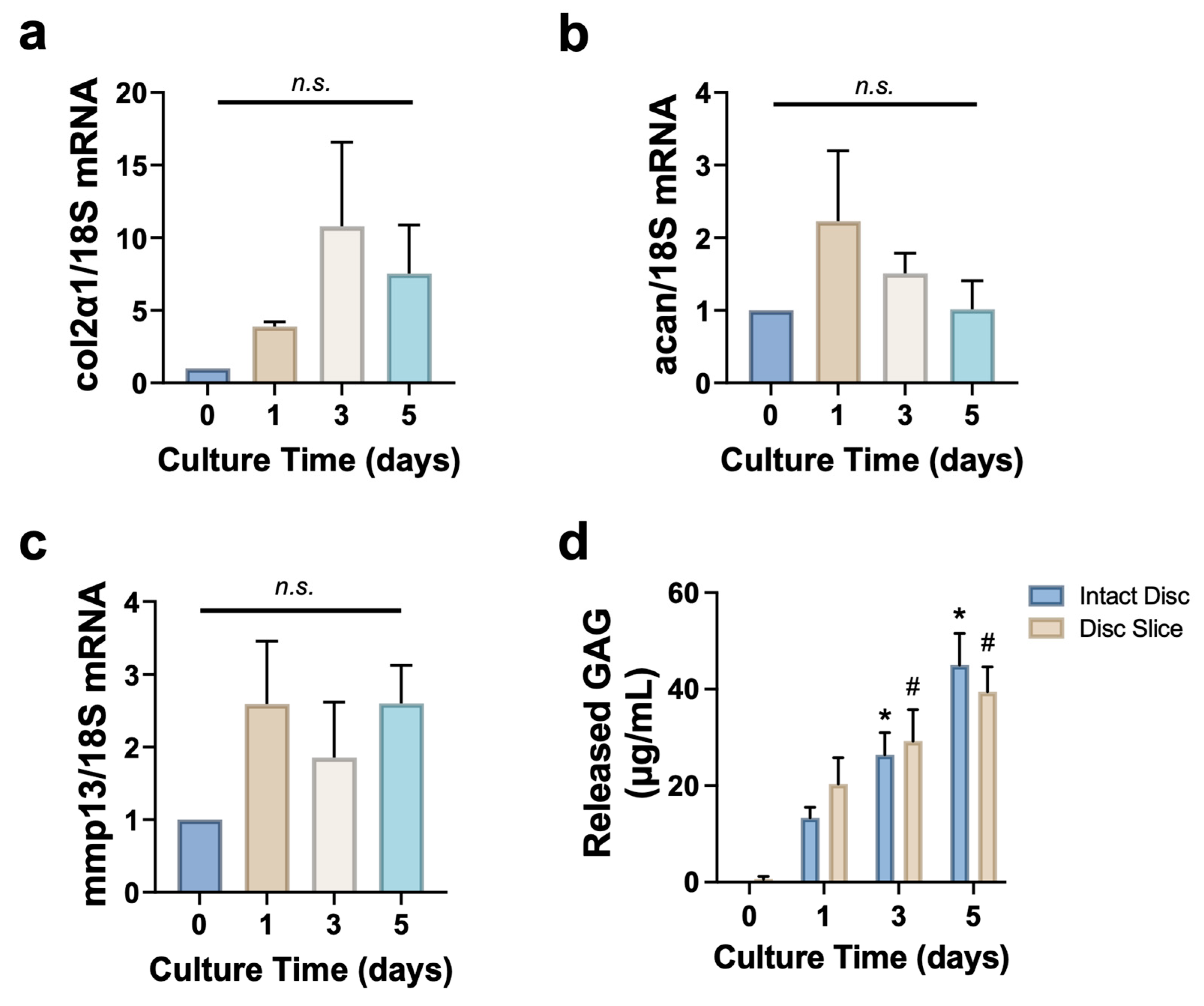
3.4. Disc Slice Culture Preserves Matrix Proteins
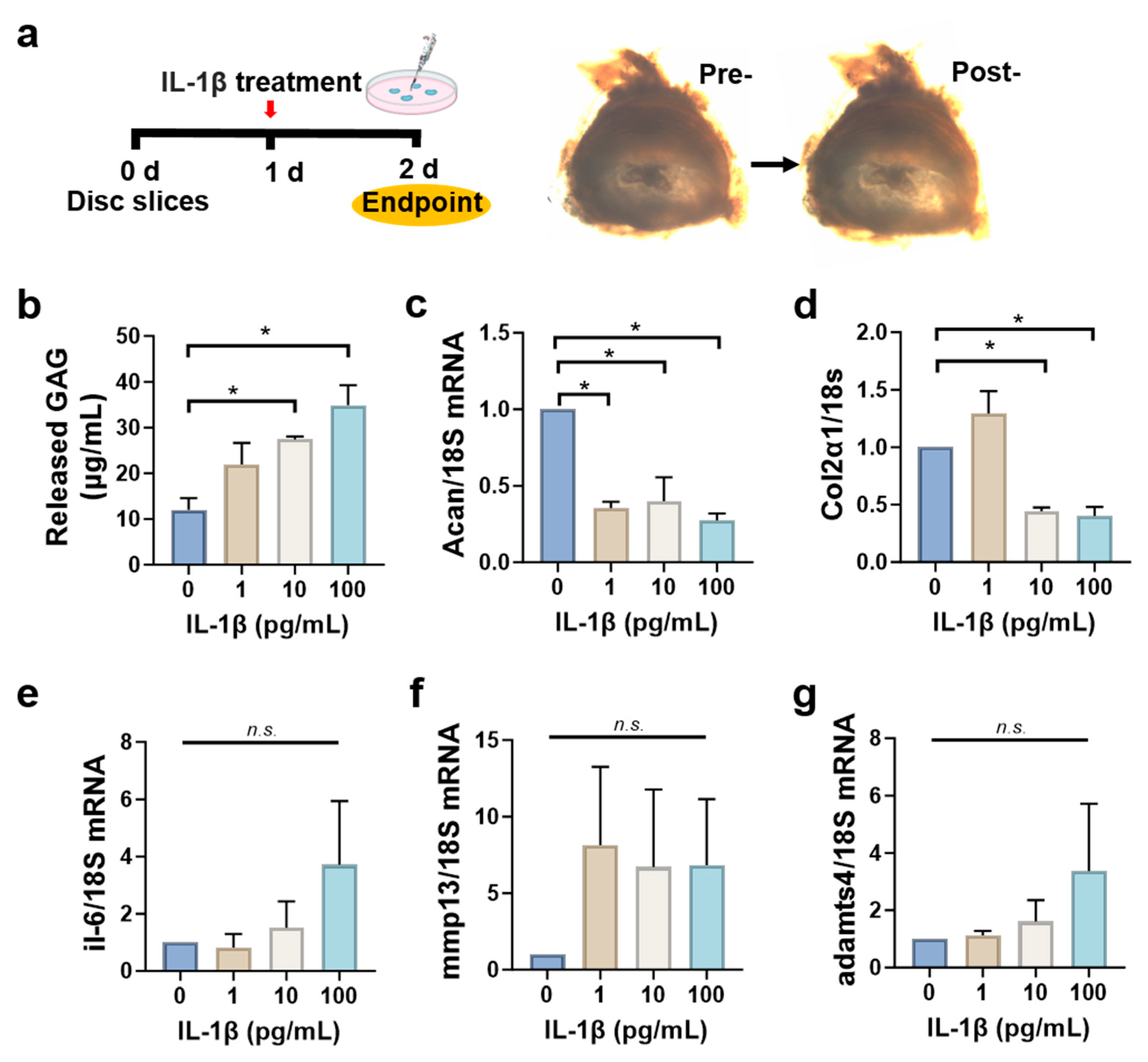
3.5. Disc Slices Respond to Inflammatory Cytokine IL-1β Stimulation
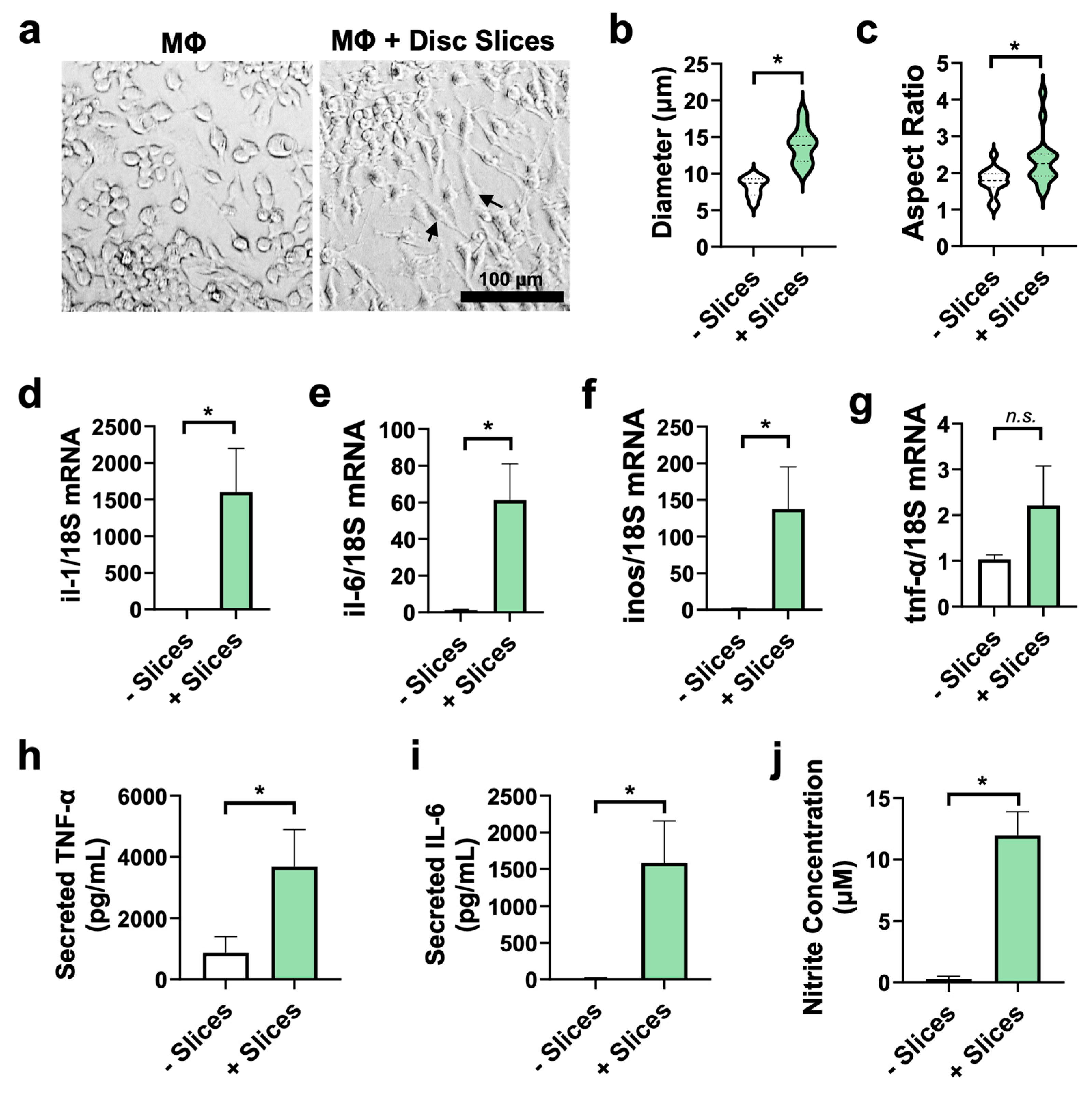
3.6. Disc Slices Activate Macrophages Toward Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype
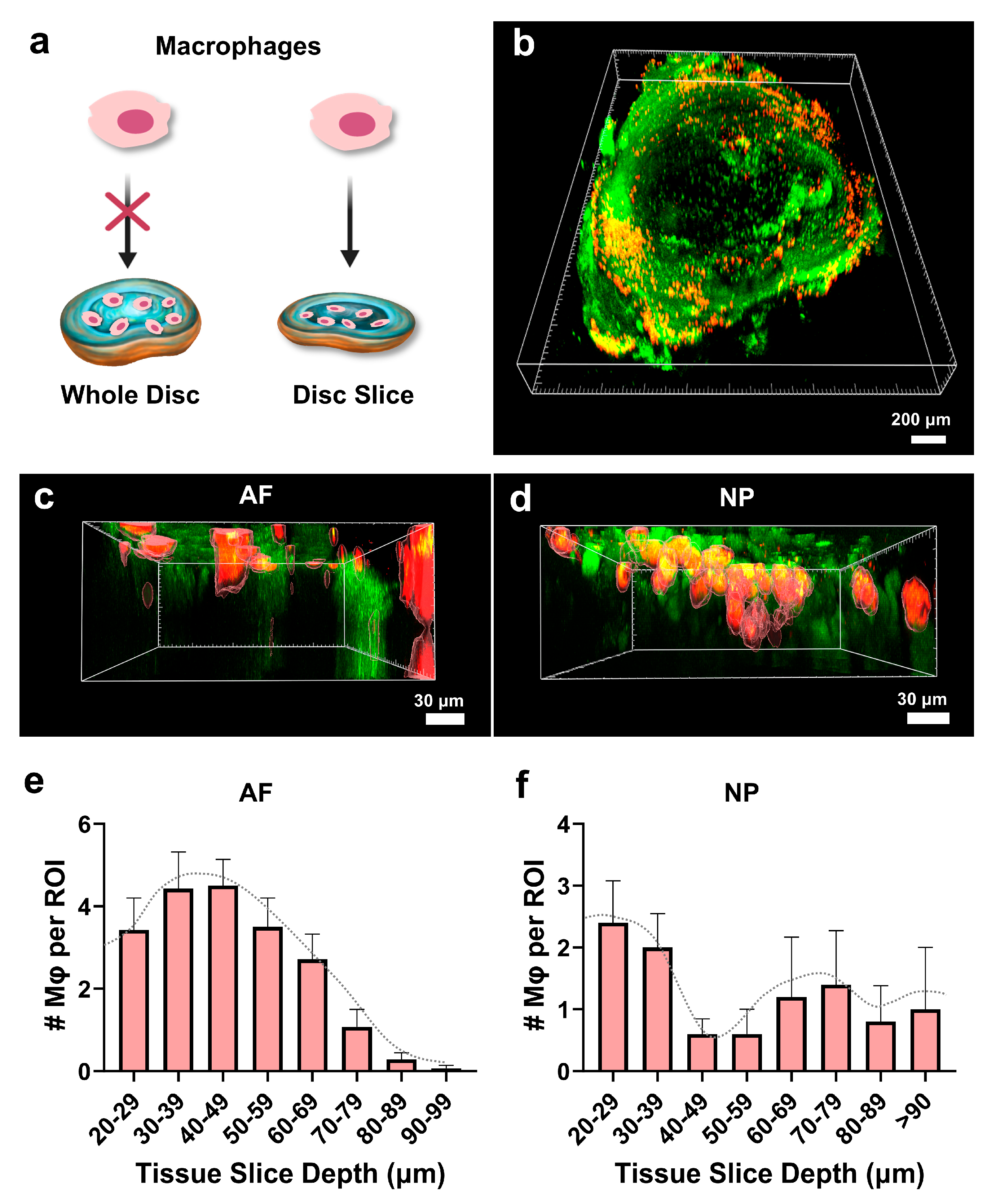
3.7. Macrophages Infiltrate the Disc Tissue Slices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IVD | Intervertebral disc |
| AF | Annulus Fibrosus |
| NP | Nucleus Pulposus |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| GAG | Glycosaminoglycans |
| POD | Postoperative Day |
| DMEM/F12 | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12 |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered Saline |
| Anti-Anti | Antibiotic–Antimycotic solution |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| DMMB | Dimethyl methylene blue |
| inos | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| ADAMTS4 | A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs 4 |
| HMGB1 | High Mobility Group Box 1 |
| OCT | Optimal Cutting Temperature Compound |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PLM | Polarized Light Microscopy |
References
- Kos, N.; Gradisnik, L.; Velnar, T. A brief review of the degenerative intervertebral disc disease. Med. Arch. 2019, 73, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Lui, A.; Matsoyan, A.; Safaee, M.M.; Aryan, H.; Ames, C. Comparative review of the socioeconomic burden of lower back pain in the United States and globally. Neurospine 2024, 21, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sono, T.; Shima, K.; Shimizu, T.; Murata, K.; Matsuda, S.; Otsuki, B. Regenerative therapies for lumbar degenerative disc diseases: A literature review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1417600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dou, Q.; Kong, Q. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2016, 26, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Risbud, M.V.; Shapiro, I.M. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroth, J.; Buko, E.O.; Abbott, R.; Johnson, C.P.; Ogle, B.M.; Stone, L.S.; Ellingson, A.M.; Bradley, E.W. Macrophages and intervertebral disc degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Xiao, L.; Manley, B.J.; Oh, E.G.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, J.; Shi, W.; Kerrigan, J.R.; Sung, S.-S.J.; et al. CCR2 monocytes as therapeutic targets for acute disc herniation and radiculopathy in mouse models. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 32, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Matharoo, J.; Chi, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, M.; Manley, B.; Xu, P.; Shi, W.; Felder, R.; Sung, S.-S.; et al. Transient depletion of macrophages alters local inflammatory response at the site of disc herniation in a transgenic mouse model. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chordia, M.; Pan, D.; Shimer, A.; Shen, F.; Glover, D.; Jin, L.; Li, X. A novel modality for functional imaging in acute intervertebral disk herniation via tracking leukocyte infiltration. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Che, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhu, L.; Gao, J.; Vo, N.V. Immune exposure: How macrophages interact with the nucleus pulposus. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1155746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakawaki, M.; Uchida, K.; Miyagi, M.; Inoue, G.; Kawakubo, A.; Satoh, M.; Takaso, M. Changes in nerve growth factor expression and macrophage phenotype following intervertebral disc injury in mice. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, A.; Uchida, K.; Miyagi, M.; Nakawaki, M.; Satoh, M.; Sekiguchi, H.; Yokozeki, Y.; Inoue, G.; Takaso, M. Investigation of resident and recruited macrophages following disc injury in mice. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Zeng, B.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Huang, Y.; et al. Single-cell rna-seq analysis reveals macrophage involved in the progression of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 833420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, K.R.; Walter, B.A.; Laudier, D.M.; Krishnamoorthy, D.; Mosley, G.E.; Spiller, K.L.; Iatridis, J.C. Accumulation and localization of macrophage phenotypes with human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2018, 18, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, N.; Lafeber, G.; Li, W.; van Duinen, S.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C. Exploring macrophage differentiation and its relation to Modic changes in human herniated disc tissue. Brain Spine 2022, 2, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, K.G.; Kim, M.K.M.; Viola, D.C.; Abraham, A.C.; Chahine, N.O. Nuclear factor κB overactivation in the intervertebral disc leads to macrophage recruitment and severe disc degeneration. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Studer, R.K.; Sowa, G.A.; Vo, N.V.; Kang, J.D. Activated macrophage-like THP-1 cells modulate anulus fibrosus cell production of inflammatory mediators in response to cytokines. Spine 2008, 33, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-C.; Luo, S.-J.; Fan, W.; Zhou, T.-L.; Tan, D.-Q.; Tan, R.-X.; Xian, Q.-Z.; Li, J.; Huang, C.-M.; Wang, M.-S. Macrophage polarization regulates intervertebral disc degeneration by modulating cell proliferation, inflammation mediator secretion, and extracellular matrix metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 922173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, K.; Yao, D.; Chen, E.; Wang, P.; et al. HMGB1-mediated macrophage regulation of NF-κB activation and MMP3 upregulation in nucleus pulposus cells: A critical mechanism in the vicious cycle of intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell. Signal. 2025, 127, 111628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Deng, C. Recent advances in organotypic tissue slice cultures for anticancer drug development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5885–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Velicky, P.; Hollergschwandtner, E.; Itakura, M.; Fukazawa, Y.; Danzl, J.G.; Shigemoto, R. Advantages of acute brain slices prepared at physiological temperature in the characterization of synaptic functions. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humpel, C. Neuroscience forefront review Organotypic brain slice cultures: A review. Neuroscience 2015, 305, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speier, S.; Rupnik, M. A novel approach to in situ characterization of pancreatic β-cells. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2003, 446, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewyse, L.; De Smet, V.; Verhulst, S.; Eysackers, N.; Kunda, R.; Messaoudi, N.; Reynaert, H.; van Grunsven, L.A. Improved precision-cut liver slice cultures for testing drug-induced liver fibrosis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 862185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Chan, M.; Shin, J.S.; Nishida-Aoki, N.; Kenerson, H.L.; Elemento, O.; Beltran, H.; Yeung, R.; Gujral, T.S. Organotypic tumor slice cultures provide a versatile platform for immuno-oncology and drug discovery. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1670019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, M.C.; Ball, A.G.; Catterton, M.A.; Kinman, A.W.; Anbaei, P.; Groff, B.D.; Melchor, S.J.; Lukens, J.R.; Ross, A.E.; Pompano, R.R. Acute lymph node slices are a functional model system to study immunity ex vivo. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, L.; Li, J.; Cao, R.; He, Y.; Fang, H.; Periasamy, A.; Oberhozler, J.; Jin, L.; et al. Microfluidic disc-on-a-chip device for mouse intervertebral disc—Pitching a next-generation research platform to study disc degeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ding, M.; Fernandez, A.; Zhao, P.; Jin, L.; Li, X. Curcumin alleviates lumbar radiculopathy by reducing neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and nociceptive factors. Eur. Cells Mater. 2017, 33, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.E.; de Medeiros, V.P.; Wajchenberg, M.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Lima, M.; Reginato, R.D.; Nader, H.B.; Puertas, E.B.; Faloppa, F.; Smith, L.J. Changes in human intervertebral disc biochemical composition and bony end plates between middle and old age. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, T.-J. Differences in collagen fibres in the capsule walls of parakeratinized and orthokeratinized odontogenic cysts. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Ding, M.; Saadoon, O.; Vess, E.; Fernandez, A.; Zhao, P.; Jin, L.; Li, X. A novel culture platform for fast proliferation of human annulus fibrosus cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 367, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, A.; Rane, A.; Xiao, L.; Honrado, C.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Swami, N.S. Single-cell assessment of the modulation of macrophage activation by ex vivo intervertebral discs using impedance cytometry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, V.; Chan, W.C.; Leung, V.Y.; Cheah, K.S.; Cheung, K.M.; Sakai, D.; McCann, M.R.; Bedore, J.; Séguin, C.A.; Chan, D. Histological and reference system for the analysis of mouse intervertebral disc. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 36, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-T.; Wang, Y.-X.; Feng, X.-M.; Feng, M.; Sun, H.-H. Update on the roles of macrophages in the degeneration and repair process of intervertebral discs. Jt. Bone Spine 2023, 90, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinjikji, W.; Luetmer, P.; Comstock, B.; Bresnahan, B.; Chen, L.; Deyo, R.; Halabi, S.; Turner, J.; Avins, A.; James, K.; et al. Systematic literature review of imaging features of spinal degeneration in asymptomatic populations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraguchi, M.; Yoshimura, N.; Hashizume, H.; Muraki, S.; Yamada, H.; Minamide, A.; Oka, H.; Ishimoto, Y.; Nagata, K.; Kagotani, R.; et al. Prevalence and distribution of intervertebral disc degeneration over the entire spine in a population-based cohort: The Wakayama Spine Study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Leaker, B.; Qiao, G.; Sojoodi, M.; Eissa, I.R.; Epstein, E.T.; Eddy, J.; Dimowo, O.; Lauer, G.M.; Qadan, M.; et al. Precision-cut liver slices as an ex vivo model to evaluate antifibrotic therapies for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenerson, H.L.; Sullivan, K.M.; Seo, Y.D.; Stadeli, K.M.; Ussakli, C.; Yan, X.; Lausted, C.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Park, J.O.; Riehle, K.J.; et al. Tumor slice culture as a biologic surrogate of human cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.Z.; Wagner, D.C.; Hörner, N.; Horst, D.; Lang, H.; Tagscherer, K.E.; Roth, W. Ex vivo tissue slice culture system to measure drug-response rates of hepatic metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckert, T.; Rassamegevanon, T.; Müller, J.; Dietrich, A.; Graja, A.; Reiche, M.; Löck, S.; Krause, M.; Beyreuther, E.; von Neubeck, C. Applying tissue slice culture in cancer research—Insights from preclinical proton radiotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziol-White, C.; Gebski, E.; Cao, G.; Panettieri, R.A. Precision cut lung slices: An integrated ex vivo model for studying lung physiology, pharmacology, disease pathogenesis and drug discovery. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, P.; Oh, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; He, Y.; Oh, E.G.; Cao, R.; et al. Intervertebral Disc-on-a-ChipMF: A new model for mouse disc culture via integrating mechanical loading and dynamic media flow. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfannkuche, J.J.; Guo, W.; Cui, S.; Ma, J.; Lang, G.; Peroglio, M.; Richards, R.G.; Alini, M.; Grad, S.; Li, Z. Intervertebral disc organ culture for the investigation of disc pathology and regeneration–benefits, limitations, and future directions of bioreactors. Connect. Tissue Res. 2020, 61, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.N.; Bonilla, A.F.; Chahine, N.O.; Colbath, A.C.; Easley, J.T.; Grad, S.; Haglund, L.; Le Maitre, C.L.; Leung, V.; McCoy, A.M.; et al. Controversies in spine research: Organ culture versus in vivo models for studies of the intervertebral disc. JOR SPINE 2022, 5, e1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ning, B.; Jia, T.; Gong, W.; Cong, M.; Chen, J.-F.; Yang, S.-Y. Microcarrier bioreactor culture system promotes propagation of human intervertebral disc cells. Ir. J. Med. Sci. (1971-) 2010, 179, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Jeon, W.-J.; Ha, I.-H. IL-1β promotes disc degeneration and inflammation through direct injection of intervertebral disc in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. Spine J. 2021, 21, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Phillips, K.L.E.; Chiverton, N.; Haddock, G.; Bunning, R.A.; Cross, A.K.; Shapiro, I.M.; Le Maitre, C.L.; Risbud, M.V. Tumor necrosis factor α- and interleukin-1β-dependent induction of CCL3 expression by nucleus pulposus cells promotes macrophage migration through CCR1. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, E.G.; Xiao, L.; Xu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Anbaei, P.; Chi, J.A.; Jin, L.; Pompano, R.R.; Li, X. An Ex Vivo Intervertebral Disc Slice Culture Model for Studying Disc Degeneration and Immune Cell Interactions. Cells 2025, 14, 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161230
Oh EG, Xiao L, Xu Z, Xing Y, Zhang Y, Anbaei P, Chi JA, Jin L, Pompano RR, Li X. An Ex Vivo Intervertebral Disc Slice Culture Model for Studying Disc Degeneration and Immune Cell Interactions. Cells. 2025; 14(16):1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161230
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Eunha G., Li Xiao, Zhiwen Xu, Yuan Xing, Yi Zhang, Parastoo Anbaei, Jialun A. Chi, Li Jin, Rebecca R. Pompano, and Xudong Li. 2025. "An Ex Vivo Intervertebral Disc Slice Culture Model for Studying Disc Degeneration and Immune Cell Interactions" Cells 14, no. 16: 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161230
APA StyleOh, E. G., Xiao, L., Xu, Z., Xing, Y., Zhang, Y., Anbaei, P., Chi, J. A., Jin, L., Pompano, R. R., & Li, X. (2025). An Ex Vivo Intervertebral Disc Slice Culture Model for Studying Disc Degeneration and Immune Cell Interactions. Cells, 14(16), 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161230







