Progress in Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Swertiamarin: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Plant Sources | Part | Pharmacological Effects | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swertia mussotii Franch | Whole plants | Hepatoprotective effects | [17,18] |
| Swertia pseudochinensis Hara | Whole plants | Anti-cholestasis effects | [19] |
| Enicostemmalittorale Blume | Whole plants | Anti-diabetic effects | [20] |
| Lomatogonium rotatum | Whole plants | Anti-diabetic effects | [21] |
| Enicostemma axillare | Whole plants | Antioxidant effects | [22] |
| Enicostemmalittorale Blume | Whole plants | Anti-hyperlipidemic effect | [23] |
| Enicostemma axillare | Whole plants | Antinociceptive activity | [24] |
| Gentiana straminea | Roots | Antioxidant effects | [25] |
| Gentiana kurroo | Roots | Anti-cancer effects | [26] |
| Swertia japonica Makino | Whole plants | Stimulate the gastric emptying effect | [27] |
| Centaurium pulchellum | Aerial parts and roots | Antibacterial and antifungal effects | [28] |
2. Pharmacokinetic Properties
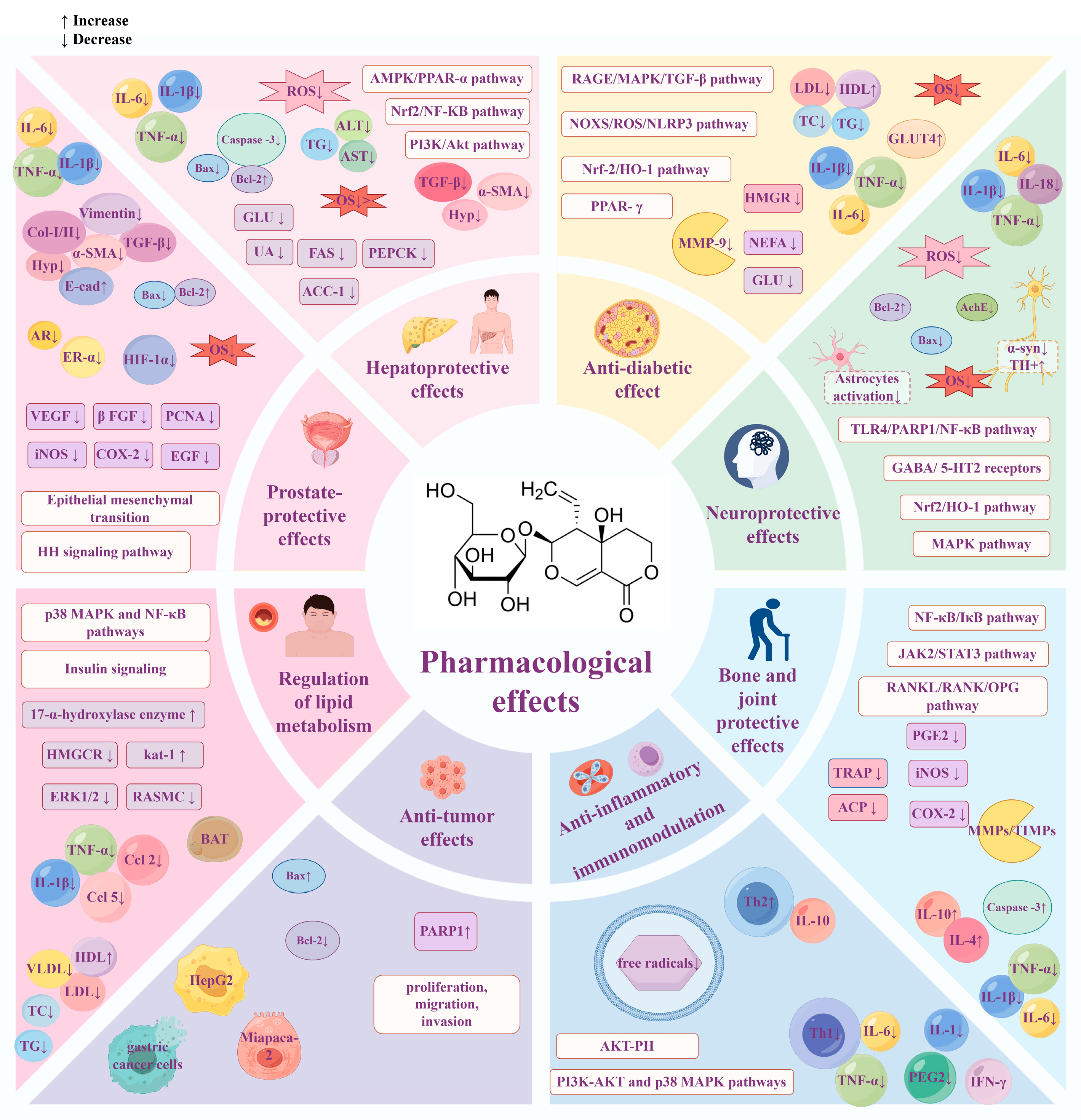
3. Pharmacological Effects
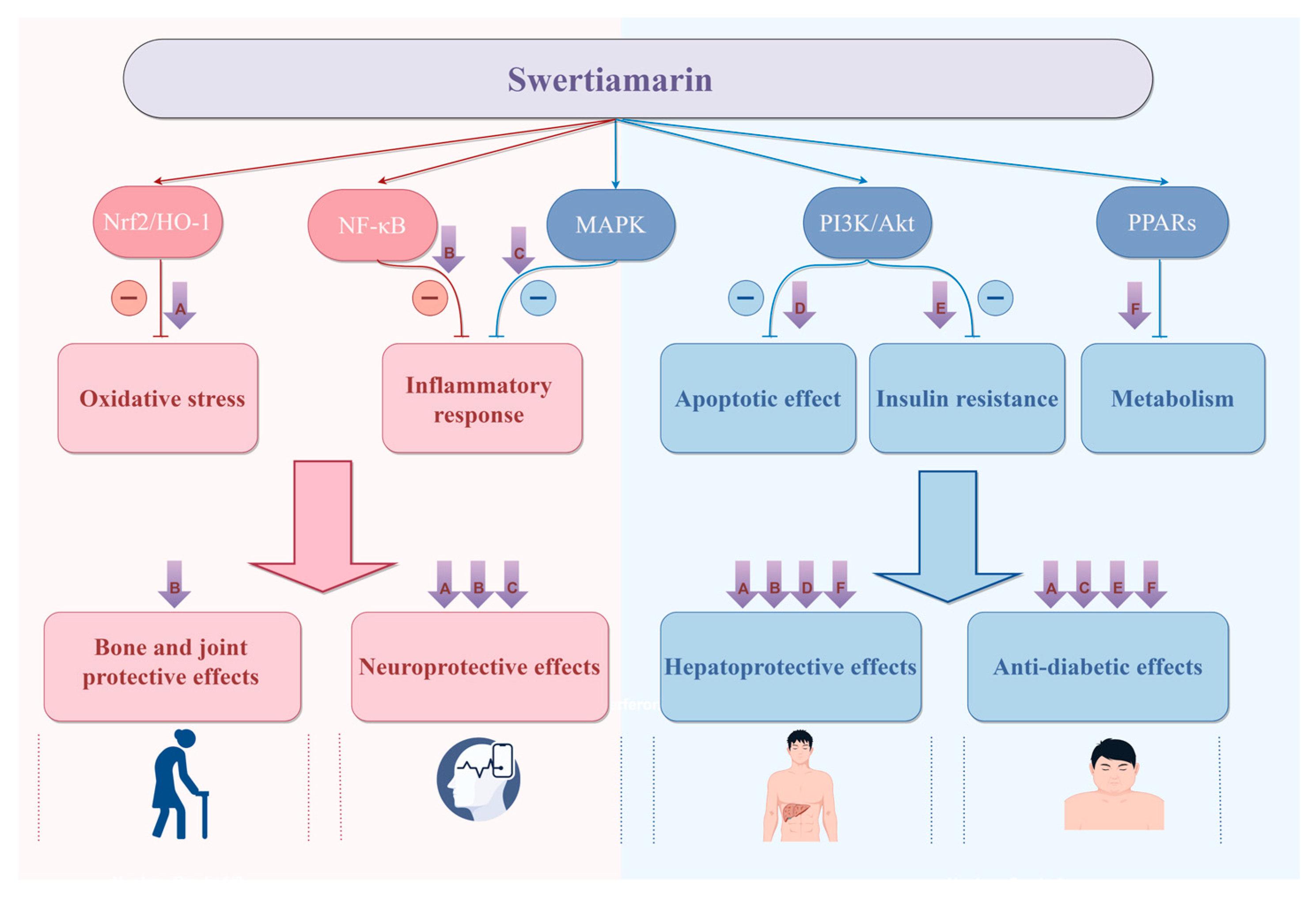
3.1. Hepatoprotective Effects
3.2. Anti-Diabetic Effects
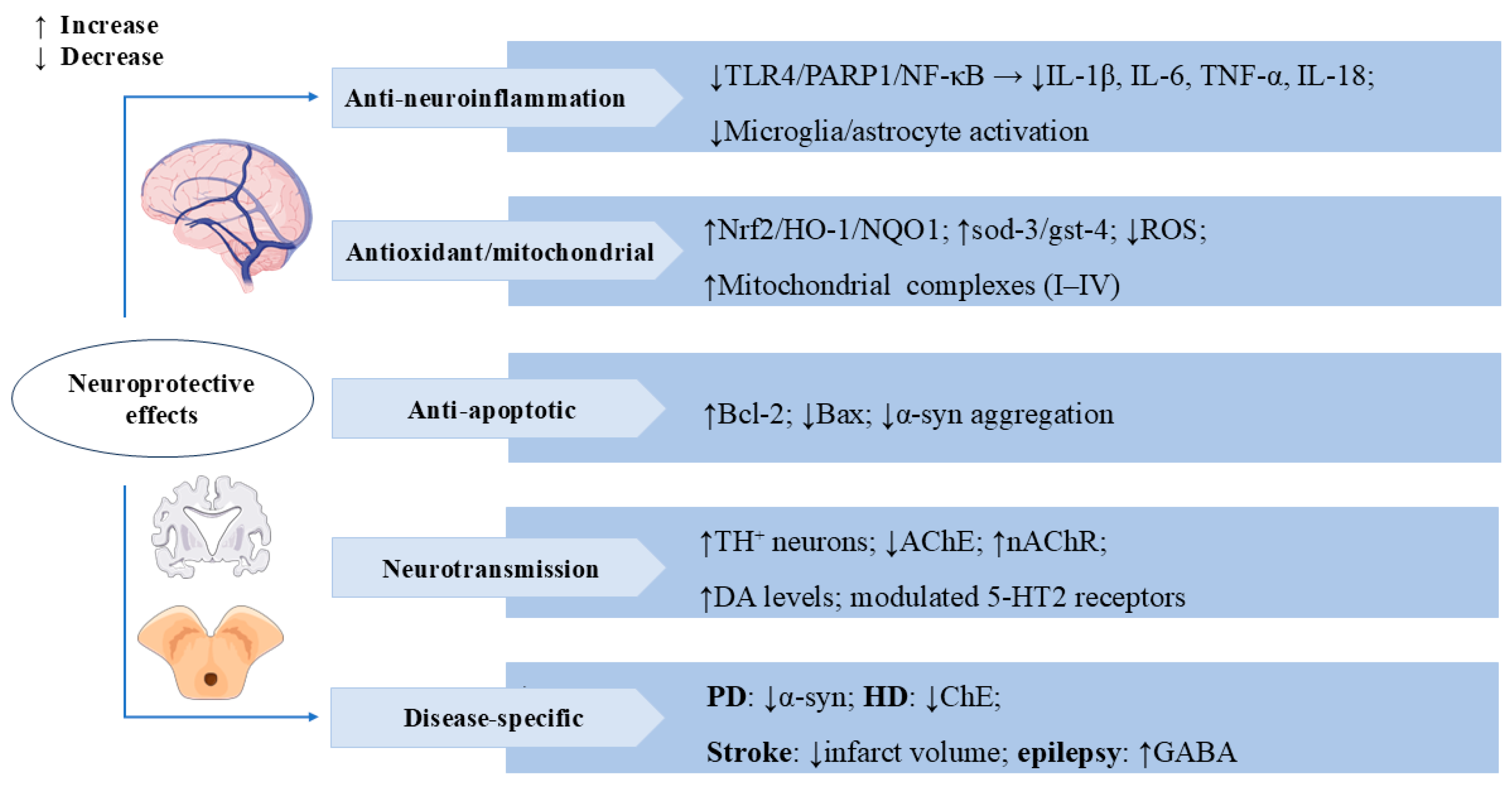
3.3. Neuroprotective Effects
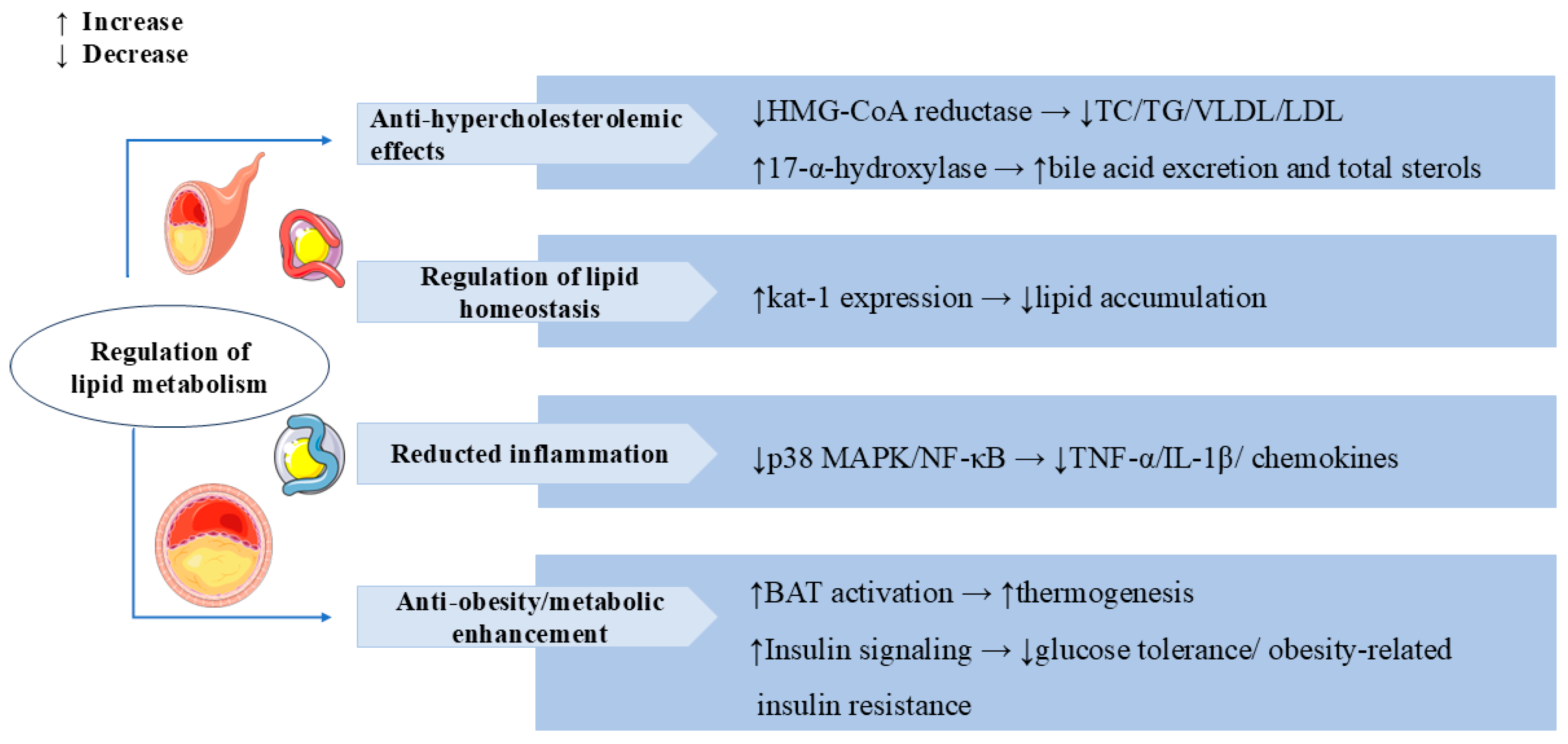
3.4. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
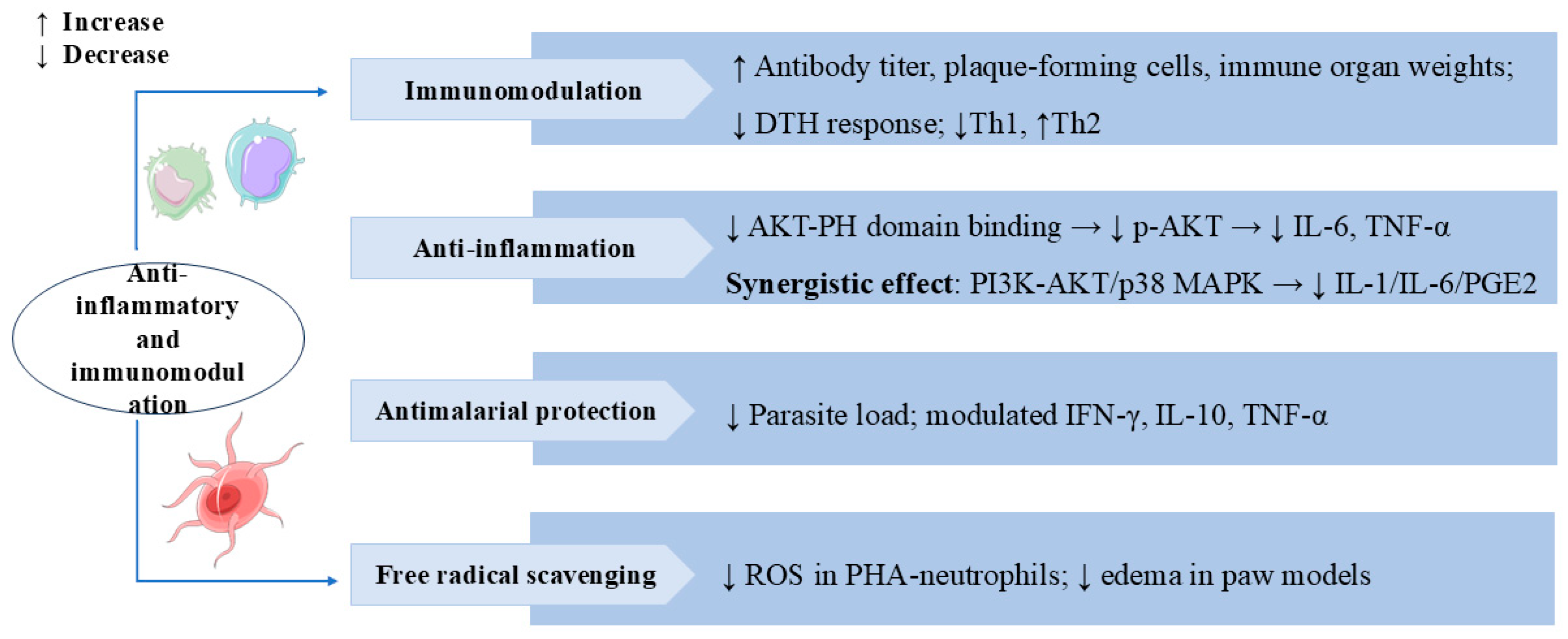
3.5. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulation
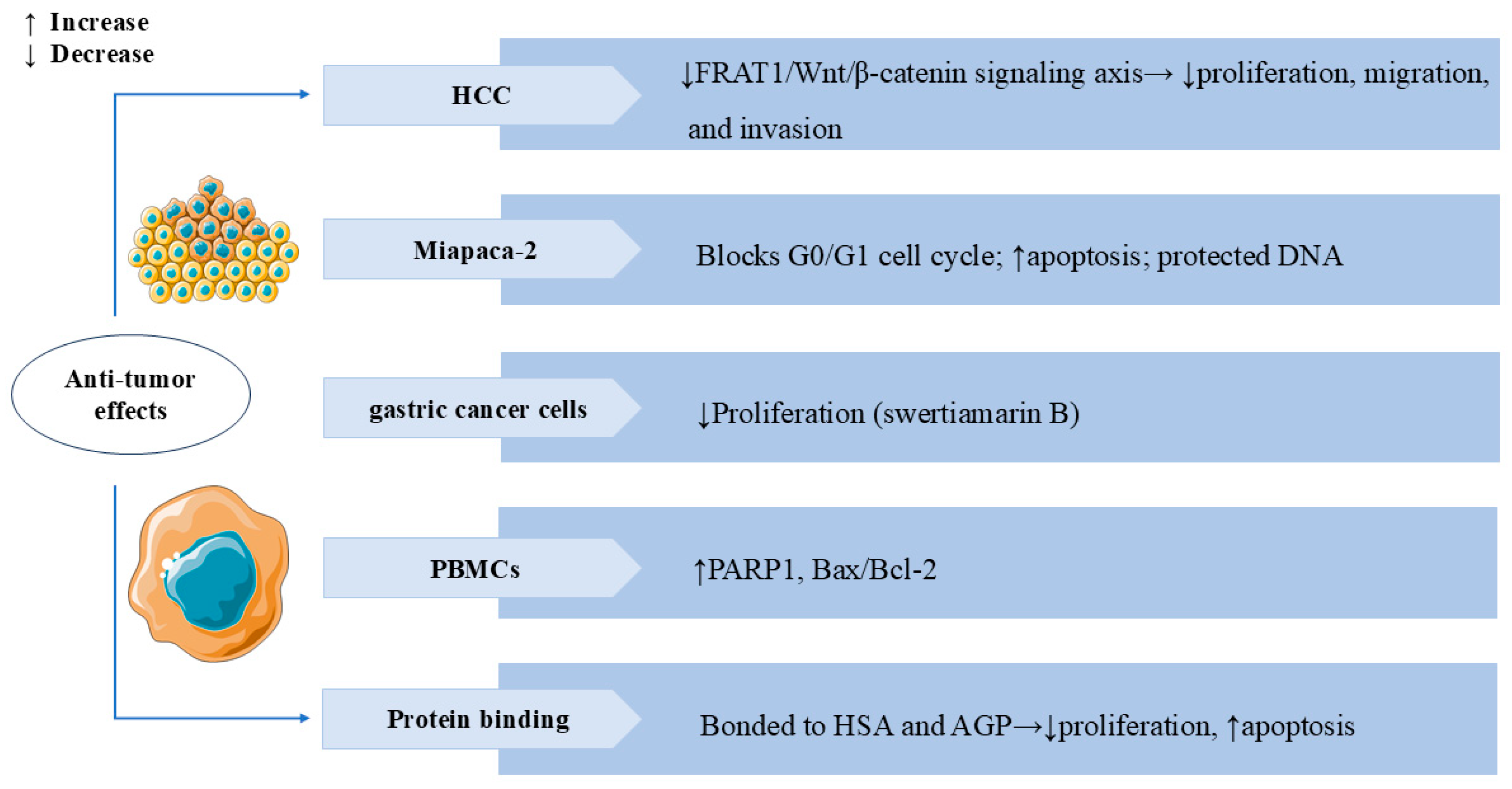
3.6. Anti-Tumor Effects
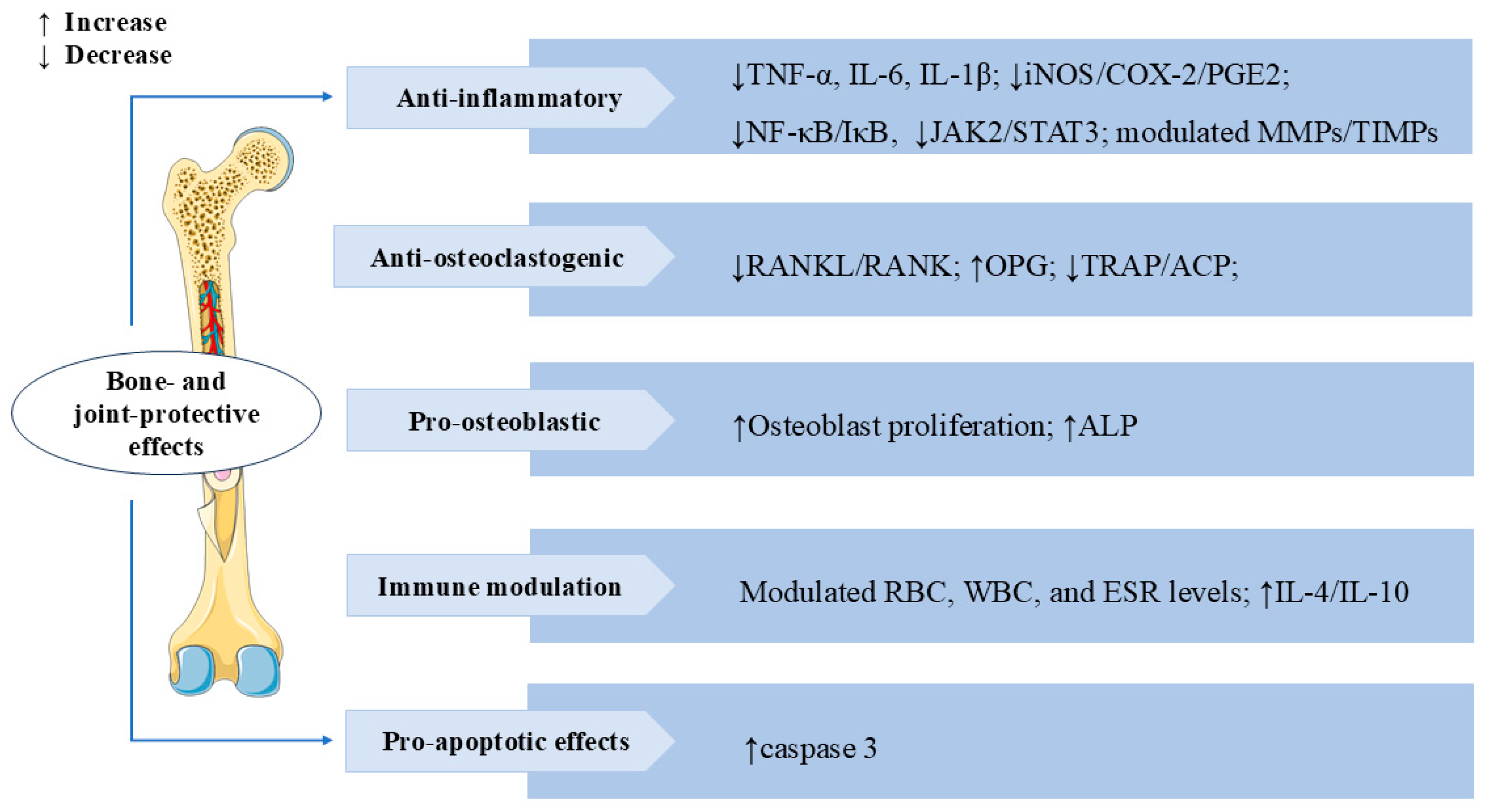
3.7. Bone and Joint Protective Effects
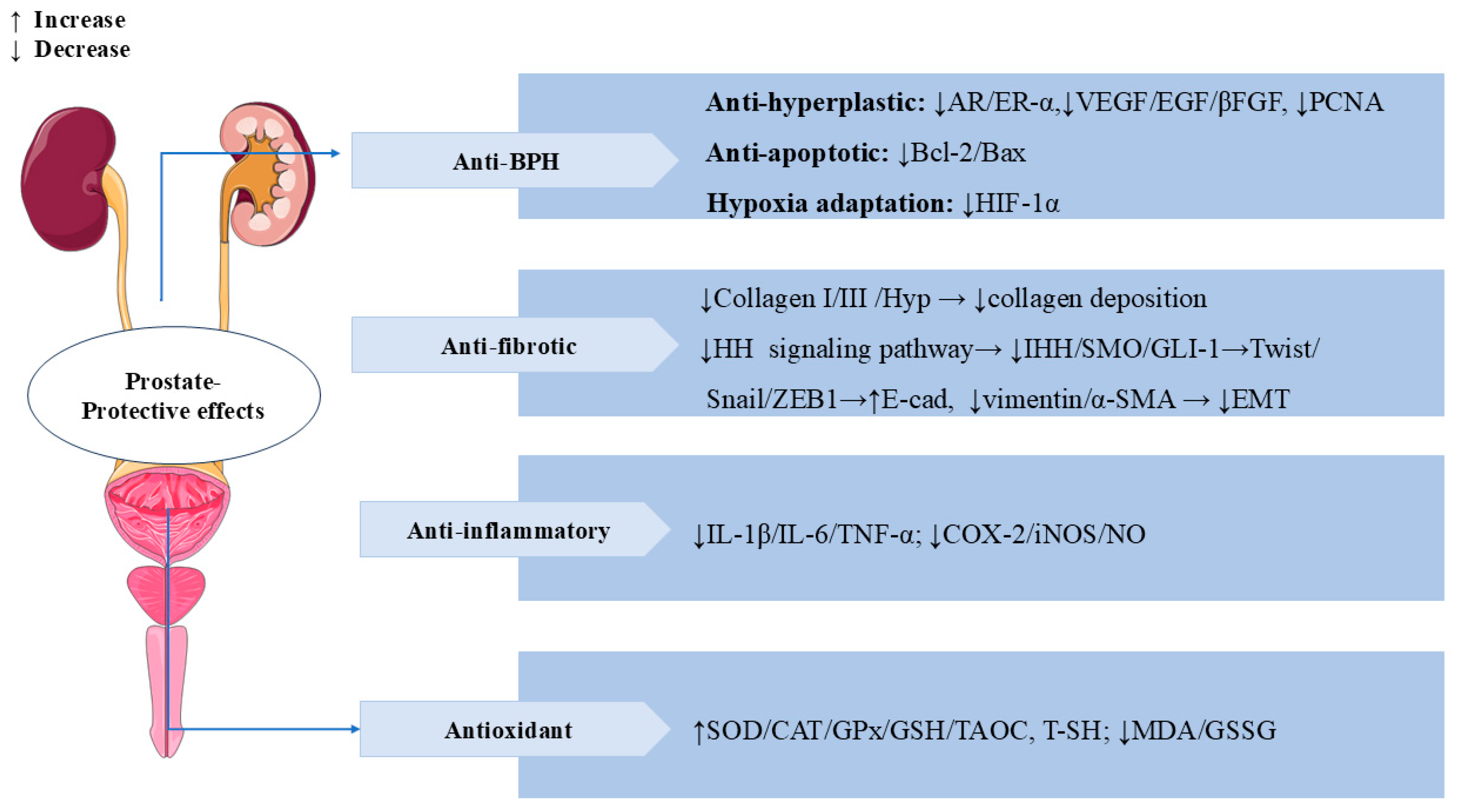
3.8. Prostate-Protective Effects
3.9. Other Therapeutic Effects
4. Toxicology
5. Traditional Medical Background and Application of Swertiamarin
5.1. Applications in Ayurvedic Medicine
5.2. Applications in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Other Traditional Medicine
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, X.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Q.; Xing, R.; Chen, S. A Review on the Ethnomedicinal Usage, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Properties of Gentianeae (Gentianaceae) in Tibetan Medicine. Plants 2021, 10, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Gadimli, A.I.; Isaev, J.I.; Kashchenko, N.I.; Prokopyev, A.S.; Kataeva, T.N.; Chirikova, N.K.; Vennos, C. Caucasian Gentiana Species: Untargeted LC-MS Metabolic Profiling, Antioxidant and Digestive Enzyme Inhibiting Activity of Six Plants. Metabolites 2019, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Su, H.; Yang, Q.; Wulu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Z. Comparative analysis of phytochemical profile and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of four Gentiana species from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 326, 117926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoboo, S.; Pinto Mda, S.; Barbosa, A.C.; Sarkar, D.; Bhowmik, P.C.; Jha, P.K.; Shetty, K. Phenolic-linked biochemical rationale for the anti-diabetic properties of Swertia chirayita (Roxb. ex Flem.) Karst. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.B.; Mishra, S.H. Hypoglycemic activity of C-glycosyl flavonoid from Enicostemma hyssopifolium. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lad, H.; Bhatnagar, D. Amelioration of oxidative and inflammatory changes by Swertia chirayita leaves in experimental arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecová, A.; Kusznierewicz, B.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Magdolenová, Z.; Hasplová, K.; Rinna, A.; Fjellsbø, L.M.; Kruszewski, M.; Lankoff, A.; Sandberg, W.J.; et al. Silver nanoparticles induce premutagenic DNA oxidation that can be prevented by phytochemicals from Gentiana asclepiadea. Mutagenesis 2012, 27, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Yi, X.J.; Huang, X.J.; Muhammad, A.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Yang, G.Z.; Gao, Y. Hepatoprotective activity of iridoids, seco-iridoids and analog glycosides from Gentianaceae on HepG2 cells via CYP3A4 induction and mitochondrial pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, V.; Katanić, J.; Mišić, D.; Stanković, V.; Mihailović, M.; Uskoković, A.; Arambašić, J.; Solujić, S.; Mladenović, M.; Stanković, N. Hepatoprotective effects of secoiridoid-rich extracts from Gentiana cruciata L. against carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in rats. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Tyagi, R.K.; Tandel, N.; Garg, N.K.; Soni, N. The Molecular Targets of Swertiamarin and its Derivatives Confer Anti-Diabetic and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Effects. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Sashidhara, K.V. Lipid lowering agents of natural origin: An account of some promising chemotypes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, X.Y.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Pandey, M.; Ramamurthy, S. A systematic review of the protective role of swertiamarin in cardiac and metabolic diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad Fadzil, N.S.; Sekar, M.; Gan, S.H.; Bonam, S.R.; Wu, Y.S.; Vaijanathappa, J.; Ravi, S.; Lum, P.T.; Dhadde, S.B. Chemistry, Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potential of Swertiamarin—A Promising Natural Lead for New Drug Discovery and Development. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 2721–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Wang, X.J.; Sun, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, C.M. Determination of novel nitrogen-containing metabolite after oral administration of swertiamarin to rats. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.D.; Ma, X.X.; Du, S.N.; Qi, P.X.; He, F.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Tan, W.H.; Khan, A.; Zhou, Z.H.; Liu, L. Sweritranslactone D, a hepatoprotective novel secoiridoid dimer with tetracyclic lactone skeleton from heat-transformed swertiamarin. Fitoterapia 2021, 151, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Lv, J.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Iridoid compounds from the aerial parts of Swertia mussotii Franch. with cytotoxic activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Du, X.; Chen, S.; Feng, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, M.; Chen, L.; et al. Swertianlarin, an Herbal Agent Derived from Swertia mussotii Franch, Attenuates Liver Injury, Inflammation, and Cholestasis in Common Bile Duct-Ligated Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 948376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Shan, Q.; Jiang, L. The hepatoprotective effect and chemical constituents of total iridoids and xanthones extracted from Swertia mussotii Franch. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Tang, J.; Zhang, T.; Han, H. Swertiamarin, an active iridoid glycoside from Swertia pseudochinensis H. Hara, protects against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis by activating the farnesoid X receptor and bile acid excretion pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, R.D.; Vishwakarma, S.L.; Lakshmi, S.; Rajani, M.; Padh, H.; Goyal, R.K. Amelioration of STZ-induced type 1 diabetic nephropathy by aqueous extract of Enicostemma littorale Blume and swertiamarin in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 340, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.L.; Cho, S.B.; Li, H.F.; A, L.S.; Ji, X.P.; Pan, S.; Bao, M.L.; Bai, L.; Ba, G.N.; Fu, M.H. Lomatogonium rotatum extract alleviates diabetes mellitus induced by a high-fat, high-sugar diet and streptozotocin in rats. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaijanathappa, J.; Badami, S. Antiedematogenic and free radical scavenging activity of swertiamarin isolated from Enicostemma axillare. Planta Medica 2009, 75, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, H.; Rajani, M.; Sudarsanam, V.; Padh, H.; Goyal, R. Swertiamarin: A lead from Enicostemma littorale Blume. for anti-hyperlipidaemic effect. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 617, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishree, V.; Badami, S.; Rupesh Kumar, M.; Tamizhmani, T. Antinociceptive activity of swertiamarin isolated from Enicostemma axillare. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Chen, G.; He, W.; Chi, H.; Abe, H.; Yamashita, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Kodama, H. Inhibitory effects of secoiridoids from the roots of Gentiana straminea on stimulus-induced superoxide generation, phosphorylation and translocation of cytosolic compounds to plasma membrane in human neutrophils. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, B.A.; Ramamoorthy, D.; Rather, M.A.; Arumugam, N.; Qazi, A.K.; Majeed, R.; Hamid, A.; Ganie, S.A.; Ganai, B.A.; Anand, R.; et al. Induction of apoptosis in human pancreatic MiaPaCa-2 cells through the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) by Gentiana kurroo root extract and LC-ESI-MS analysis of its principal constituents. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Sumiyoshi, M. Effects of Swertia japonica extract and its main compound swertiamarin on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal motility in mice. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siler, B.; Misić, D.; Nestorović, J.; Banjanac, T.; Glamoclija, J.; Soković, M.; Cirić, A. Antibacterial and antifungal screening of Centaurium pulchellum crude extracts and main secoiridoid compounds. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Peng, X.J.; He, J.C.; Feng, E.F.; Xu, G.L.; Rao, G.X. Development and validation of a LC-ESI-MS/MS method for the determination of swertiamarin in rat plasma and its application in pharmacokinetics. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; He, J.C.; Bai, M.; Song, Q.Y.; Feng, E.F.; Rao, G.X.; Xu, G.L. Determination of the plasma pharmacokinetic and tissue distributions of swertiamarin in rats by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Arzneimittelforschung 2012, 62, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.M.; Lin, L.C.; Tsai, T.H. Determination and pharmacokinetic study of gentiopicroside, geniposide, baicalin, and swertiamarin in Chinese herbal formulae after oral administration in rats by LC-MS/MS. Molecules 2014, 19, 21560–21578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.L.; Li, H.L.; He, J.C.; Feng, E.F.; Shi, P.P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, C.X. Comparative pharmacokinetics of swertiamarin in rats after oral administration of swertiamarin alone, Qing Ye Dan tablets and co-administration of swertiamarin and oleanolic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ai, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, W.; Bian, Q.; Lee, D.Y.; Dai, R. Simultaneous determination of four secoiridoid and iridoid glycosides in rat plasma by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, T.; Han, H. Metabolite Profiling of Swertia cincta Extract in Rats and Pharmacokinetics Study of Three Bioactive Compounds Using UHPLC-MS/MS. Planta Medica 2023, 89, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Zhu, H.; Guan, J.; Zhao, L.; Gu, J.; Yin, L.; Fawcett, J.P.; Liu, W. A rapid and sensitive UFLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of gentiopicroside and swertiamarin in rat plasma and its application in pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, N.; Zhi, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Pharmacokinetic and excretion study of three secoiridoid glycosides and three flavonoid glycosides in rat by LC-MS/MS after oral administration of the Swertia pseudochinensis extract. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 967, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, H.; Goyal, R.K.; Cheema, S.K. Anti-diabetic activity of swertiamarin is due to an active metabolite, gentianine, that upregulates PPAR-γ gene expression in 3T3-L1 cells. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Liu, C.; Han, Z.Z.; Han, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.T. Microbial Biotransformation of Iridoid Glycosides from Gentiana rigescens by Penicillium brasilianum. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Highly sensitive determination of new metabolite in rat plasma after oral administration of swertiamarin by liquid chromatography/time of flight mass spectrometry following picolinoyl derivatization. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hattori, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. New analytical method for the study of metabolism of swertiamarin in rats after oral administration by UPLC-TOF-MS following DNPH derivatization. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Xiong, K.; Zhang, T.; Han, H. Pharmacokinetics and metabolic profiles of swertiamarin in rats by liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Lou, T.; Wang, T.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Comprehensive metabolism study of swertiamarin in rats using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with Quadrupole-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Xenobiotica 2021, 51, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishree, V.; Badami, S. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of swertiamarin from Enicostemma axillare against D-galactosamine induced acute liver damage in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Song, H. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect of Swertiamarin on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, S.; Dai, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ali, M.; Ataya, F.S.; Sahar, I.; Iqbal, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analysis and the remedial effects of Swertiamarin on hepatic injuries caused by CCl(4). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, K.; Wu, T.; Song, H. Swertiamarin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic apoptosis via blocking the PI3K/Akt pathway in rats. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 23, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolure, R.; Vinaitheerthan, N.; Thakur, S.; Godela, R.; Doli, S.B.; Santhepete Nanjundaiah, M. Protective effect of Enicostemma axillare—Swertiamarin on oxidative stress against nicotine-induced liver damage in SD rats. Ann. Pharm. Françaises 2024, 84, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, G.L.; Ma, X.X.; Khan, A.; Tan, W.H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhou, Z.H. Sweritranslactones A-C: Unusual Skeleton Secoiridoid Dimers via [4 + 2] Cycloaddition from Swertiamarin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 13263–13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, R.; Zhang, P.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Khan, A.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, W.; Liu, L. Swertiamarin or heat-transformed products alleviated APAP-induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of apoptotic and Nrf-2/NF-κB pathways. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Liu, C. Swertiamarin Attenuates Experimental Rat Hepatic Fibrosis by Suppressing Angiotensin II-Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 359, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, T.G.; Rinella, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease 2020: The State of the Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1851–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, C.; He, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Qiao, B.; He, J. Amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by swertiamarin in fructose-fed mice. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.P.; Rawal, K.; Soni, S.; Gupta, S. Swertiamarin ameliorates oleic acid induced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress by attenuating gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis in hepatic steatosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, C.; Ziani, S.; Nelson, L.J.; Ávila, M.A.; Nevzorova, Y.A.; Cubero, F.J. Fibrotic Events in the Progression of Cholestatic Liver Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padda, M.S.; Sanchez, M.; Akhtar, A.J.; Boyer, J.L. Drug-induced cholestasis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; Khunti, K.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, R.D.; Deore, V.B.; Patil, S.D.; Patil, C.R.; Surana, S.J.; Goyal, R.K. Role of 5-HT2 receptors in diabetes: Swertiamarin seco-iridoid glycoside might be a possible 5-HT2 receptor modulator. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 144, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishree, V.; Narsimha, S. Swertiamarin and quercetin combination ameliorates hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.P.; Soni, S.; Parikh, P.; Gosai, J.; Chruvattil, R.; Gupta, S. Swertiamarin: An Active Lead from Enicostemma littorale Regulates Hepatic and Adipose Tissue Gene Expression by Targeting PPAR-γ and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Experimental NIDDM Rat Model. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 358673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Long, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D. Uncovering the key pharmacodynamic material basis and possible molecular mechanism of Xiaoke formulation improve insulin resistant through a comprehensive investigation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 323, 117752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanavathy, G. Immunohistochemistry, histopathology, and biomarker studies of swertiamarin, a secoiridoid glycoside, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced β-cell damage in Wistar rat pancreas. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parwani, K.; Patel, F.; Bhagwat, P.; Dilip, H.; Patel, D.; Thiruvenkatam, V.; Mandal, P. Swertiamarin mitigates nephropathy in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 130, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, H.; Prajapati, A.; Rajani, M.; Sudarsanam, V.; Padh, H.; Goyal, R.K. Beneficial effects of swertiamarin on dyslipidaemia in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1259–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parwani, K.; Patel, F.; Patel, D.; Mandal, P. Protective Effects of Swertiamarin against Methylglyoxal-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Improving Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney Epithelial (NRK-52E) Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.W.; Chen, Y.G.; Xing, N.; Lin, H.B.; Zhou, P.; Yu, X.P. Progress in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajah, D.; Kar, D.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J.; Scott, A.R.; Walker, J.; Tesfaye, S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Advances in diagnosis and strategies for screening and early intervention. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, J.; Yao, X.; Lao, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Lu, Y. Swertiamarin alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats by suppressing NOXS/ROS/NLRP3 signal pathway. J. South. Med. Univ. 2021, 41, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, H.; Giri, S.; Jain, M.; Goyal, R. Decrease in serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-3 levels in Zucker fa/fa obese rats after treatment with swertiamarin. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2012, 17, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Malim, F.M.; Goswami, A.; Sharma, N.; Juvvalapalli, S.S.; Chatterjee, S.; Kate, A.S.; Khairnar, A. Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamarin in a Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Role of Neuroinflammation and Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, S.F.; Elbadry, A.M.M.; Elbokhomy, A.S.; Salama, G.A.; Salama, R.M. The dual face of microglia (M1/M2) as a potential target in the protective effect of nutraceuticals against neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Aging 2023, 4, 1231706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Smita, S.S.; Mishra, A.; Sammi, S.R.; Pandey, R. Swertiamarin, a secoiridoid glycoside modulates nAChR and AChE activity. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 138, 111010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ss, S. To Study the Effect of Swertiamarin in Animal Model of Huntington’s Disease. Open Access J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 2, 000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Quan, J.; Su, N.; Li, P.; Yu, Q. Proteomic Analysis of Swertiamarin-treated BV-2 Cells and Possible Implications in Neuroinflammation. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Wu, T.; Liu, L.; Song, H. Swertiamarin protects neuronal cells from oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation via TLR4/PARP1/NF-κB pathway. Die Pharm. 2019, 74, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Shukla, A.; Trivedi, M.; Khan, F.; Pandey, R. Swertiamarin from Enicostemma littorale, counteracts PD associated neurotoxicity via enhancement α-synuclein suppressive genes and SKN-1/NRF-2 activation through MAPK pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Q.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Gan, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Pharmacological therapy to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Focus on saponins. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 133696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Lan, X.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, T.; Peng, X.; Zhuang, C.; Yu, J. Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamain on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing the Nrf2 Protective Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2276–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, P.S.; Ma, L.; Niu, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhou, R.; Yu, J.Q. Anticonvulsant Effect of Swertiamarin Against Pilocarpine-Induced Seizures in Adult Male Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaijanathappa, J.; Puttaswamygowda, J.; Bevanhalli, R.; Dixit, S.; Prabhakaran, P. Molecular docking, antiproliferative and anticonvulsant activities of swertiamarin isolated from Enicostemma axillare. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jiang, M.; Ma, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; et al. Anthelmintics nitazoxanide protects against experimental hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in hamsters and mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1322–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, J. Mechanisms of Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, H.; Rajani, M.; Sudarsanam, V.; Padh, H.; Goyal, R. Antihyperlipidaemic activity of swertiamarin, a secoiridoid glycoside in poloxamer-407-induced hyperlipidaemic rats. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 63, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, J. Swertiamarin decreases lipid accumulation dependent on 3-ketoacyl-coA thiolase. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, S.; Liang, X.; Tang, Y.; Jin, S.; Ding, C. Swertiamarin supplementation prevents obesity-related chronic inflammation and insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, O.; Cai, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Jin, S.; Ding, C.; et al. Swertiamarin ameliorates diet-induced obesity by promoting adipose tissue browning and oxidative metabolism in preexisting obese mice. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2022, 55, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Pandikumar, P.; Prakash Babu, N.; Hairul Islam, V.I.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Gabriel Paulraj, M.; Balakrishna, K.; Ignacimuthu, S. In vivo and in vitro immunomodulatory potential of swertiamarin isolated from Enicostema axillare (Lam.) A. Raynal that acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. Inflammation 2014, 37, 1374–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Hou, Y.; Bai, G. A natural AKT inhibitor swertiamarin targets AKT-PH domain, inhibits downstream signaling, and alleviates inflammation. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1816–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Zinzuvadia, A.; Prajapati, M.; Tyagi, R.K.; Dalai, S. Swertiamarin-mediated immune modulation/adaptation confers protection against Plasmodium berghei. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitlani, D.; Choudhary, R.; Pandey, D.P.; Bodakhe, S.H. Ameliorative antimalarial effects of the combination of rutin and swertiamarin on malarial parasites. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2016, 6, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, L.; Han, Y.; Ma, X.; Hou, Y.; Bai, G. Mechanism Assay of Honeysuckle for Heat-Clearing Based on Metabolites and Metabolomics. Metabolites 2022, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Ke, Y.; Ren, Z.; Lei, X.; Xiao, S.; Bao, T.; Shi, Z.; Zou, R.; Wu, T.; Zhou, J.; et al. Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed genes in hepatocellular carcinoma cells exposed to Swertiamarin. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6526–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Tang, H.; Bai, Y.; Zou, R.; Ren, Z.; Wu, X.; Shi, Z.; Lan, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, T.; et al. Swertiamarin suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via negative regulation of FRAT1. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta Šobot, A.; Drakulić, D.; Todorović, A.; Janić, M.; Božović, A.; Todorović, L.; Filipović Tričković, J. Gentiopicroside and swertiamarin induce non-selective oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxic effects in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2024, 398, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Kallubai, M.; Subramanyam, R. Comparative binding of Swertiamarin with human serum albumin and α-1 glycoprotein and its cytotoxicity against neuroblastoma cells. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 5266–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Islam, V.I.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Pazhanivel, N.; Raghuraman, N.; Paulraj, M.G.; Ignacimuthu, S. Swertiamarin ameliorates inflammation and osteoclastogenesis intermediates in IL-1β induced rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, N.; Takayanagi, H. Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis—Immune cell-fibroblast-bone interactions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairul-Islam, M.I.; Saravanan, S.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Chellappandian, M.; Simon Durai Raj, C.; Karikalan, K.; Gabriel Paulraj, M.; Ignacimuthu, S. Swertiamarin, a natural steroid, prevent bone erosion by modulating RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 53, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, S.; Islam, V.I.; Babu, N.P.; Pandikumar, P.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Chellappandian, M.; Raj, C.S.; Paulraj, M.G.; Ignacimuthu, S. Swertiamarin attenuates inflammation mediators via modulating NF-κB/I κB and JAK2/STAT3 transcription factors in adjuvant induced arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 56, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedtke, V.; Stöckle, M.; Junker, K.; Roggenbuck, D. Benign prostatic hyperplasia—A novel autoimmune disease with a potential therapy consequence? Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, L. The anti-hyperplasia, anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of Qing Ye Dan and swertiamarin in testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 265, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, M. The anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative and anti-fibrosis properties of swertiamarin in cigarette smoke exposure-induced prostate dysfunction in rats. Aging 2019, 11, 10409–10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Tian, S.; Jin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H. Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury: Injury Mechanism and Potential Treatment Strategies. Toxics 2023, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Gong, L.; Tang, C.; Peng, H.; Qiu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; et al. Swertiamarin relieves radiation-induced intestinal injury by limiting DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 480, 2277–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabane, S.; Boudjelal, A.; Bouaziz-Terrachet, S.; Spinozzi, E.; Maggi, F.; Petrelli, R.; Tail, G. Analgesic effect of Centaurium erythraea and molecular docking investigation of the major component swertiamarin. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 38, 4511–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, Y.; Nahar, L.; Cox, P.J.; Jaspars, M.; Sarker, S.D. Bioactivity of secoiridoid glycosides from Centaurium erythraea. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Gopal Samy, M.; Subramanian, D. In vitro and in silico screening of novel typhoid drugs from endangered herb (Enicostema axillare). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Samy, M.G.; Subramanian, D. Effect of novel therapeutic medicine swertiamarin from Enicostema axillare in zebrafish infected with Salmonella typhi. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belani, M.A.; Shah, P.; Banker, M.; Gupta, S.S. Investigating the potential role of swertiamarin on insulin resistant and non-insulin resistant granulosa cells of poly cystic ovarian syndrome patients. J. Ovarian Res. 2023, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Zou, S.; Xu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, D. Screening of Inhibitors against Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Few-shot Machine Learning and Molecule Docking based Drug Repurposing. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 2024, 20, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Zou, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, D. Identification and validation of targets of swertiamarin on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through bioinformatics and molecular docking-based approach. Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Ibrahim, I.A.A.; Fan, L. Cardioprotective Role of Swertiamarin, a Plant Glycoside Against Experimentally Induced Myocardial Infarction via Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Functions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 5394–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanavathy, G.; Jayakumar, S. Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies of Swertiamarin A lead Compound Isolated from Enicostemma littorale blume in wistar rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2017, 14, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Gopal Samy, M.V.; Subramanian, D. Developmental toxicity, antioxidant, and marker enzyme assessment of swertiamarin in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.N.; Bhutani, K.K. Ayurveda and gynecological disorders. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, N.; Ankita, G.; Chaitali, M.; Rakesh, D.; Sandip, M.; Manish Kumar, G. Exploring Herbal Approaches for Type II Diabetes Management: A Focus on Swertia chirayita. Curr. Tradit. Med. 2025, 11, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Srivastava, S.; Yadav, B.; Rai, A.K.; Jameela, S.; Muralidharan, S.; Mohan, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Singhal, R.; Rana, R.; et al. AYUSH-64 as an adjunct to standard care in mild to moderate COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled trial in Chandigarh, India. Complement. Ther. Med. 2022, 66, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.D.; Wu, M.; Cheng, X.Z.; Ma, Z.H.; Zheng, Y.G.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Song, Y.X.; Ma, D. Swertia mussotii prevents high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by inhibiting expression the TLR4/MyD88 and the phosphorylation of NF-κB. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1960–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Feng, B.; Chen, J.; Tan, Q.R.; Chen, Z.X.; Chen, W.S.; Wang, P.R.; Zhang, Z.J. Herbal medicine for hospitalized patients with severe depressive episode: A retrospective controlled study. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 170, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Coyle, M.E.; Mansu, S.; Zhang, A.L.; Xue, C.C. Gentiana scabra Bunge. Formula for Herpes Zoster: Biological Actions of Key Herbs and Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Niguram, P.; Jairaj, V.; Chauhan, N.; Jinagal, S.; Sagar, S.; Sindhu, R.K.; Chandra, A. Exploring the potential of semi-synthetic Swertiamarin analogues for GLUT facilitation and insulin secretion in NIT-1 cell lines: A molecular docking and in-vitro study. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Niguram, P.; Bhat, V.; Jinagal, S.; Jairaj, V.; Chauhan, N. Synthesis, molecular docking and ADMET prediction of novel Swertiamarin analogues for the restoration of type-2 diabetes: An enzyme inhibition assay. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.X.; Geng, C.A.; Huang, X.Y.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, R.P.; Chen, J.J. Five new secoiridoid glycosides and one unusual lactonic enol ketone with anti-HBV activity from Swertia cincta. Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
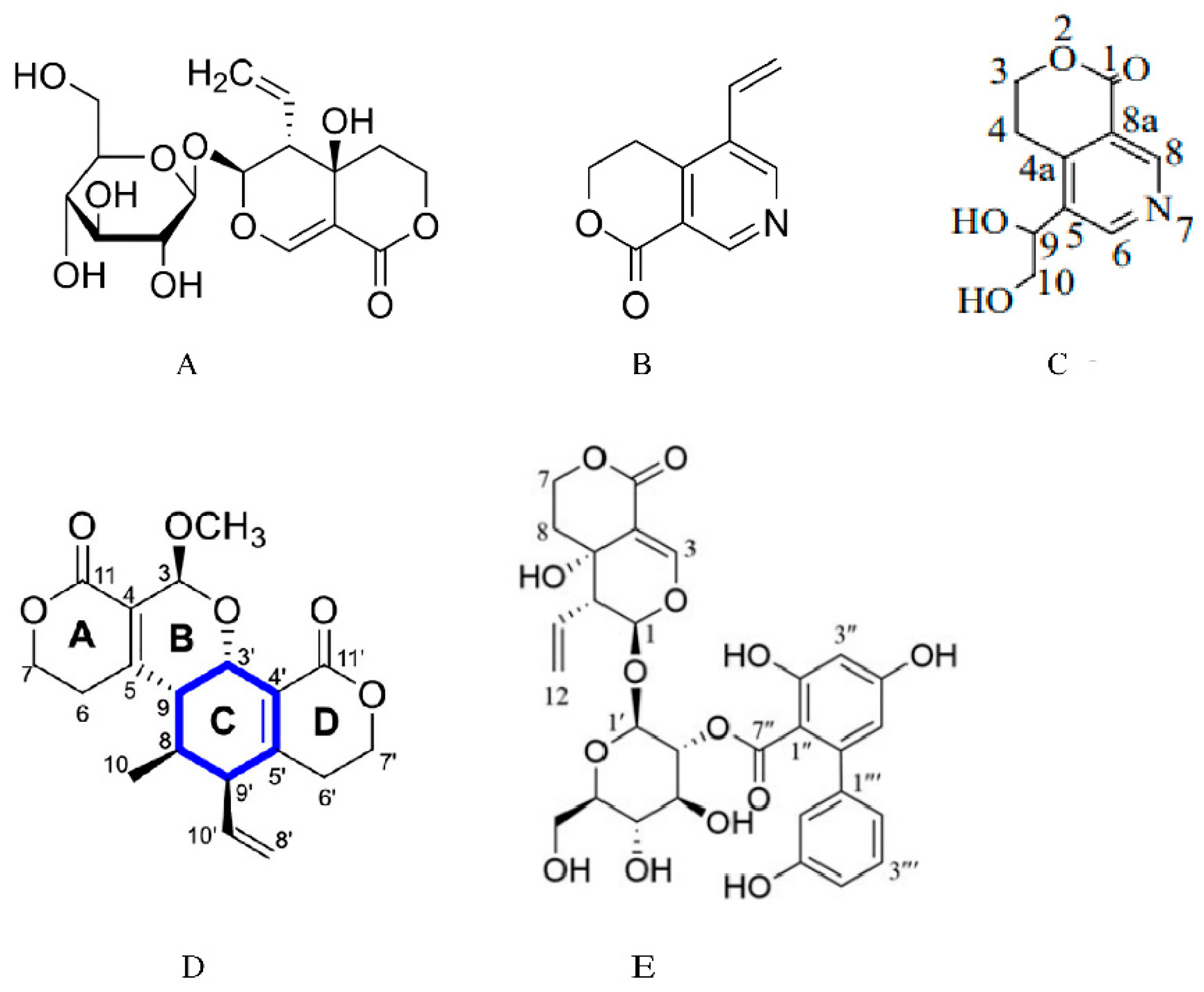
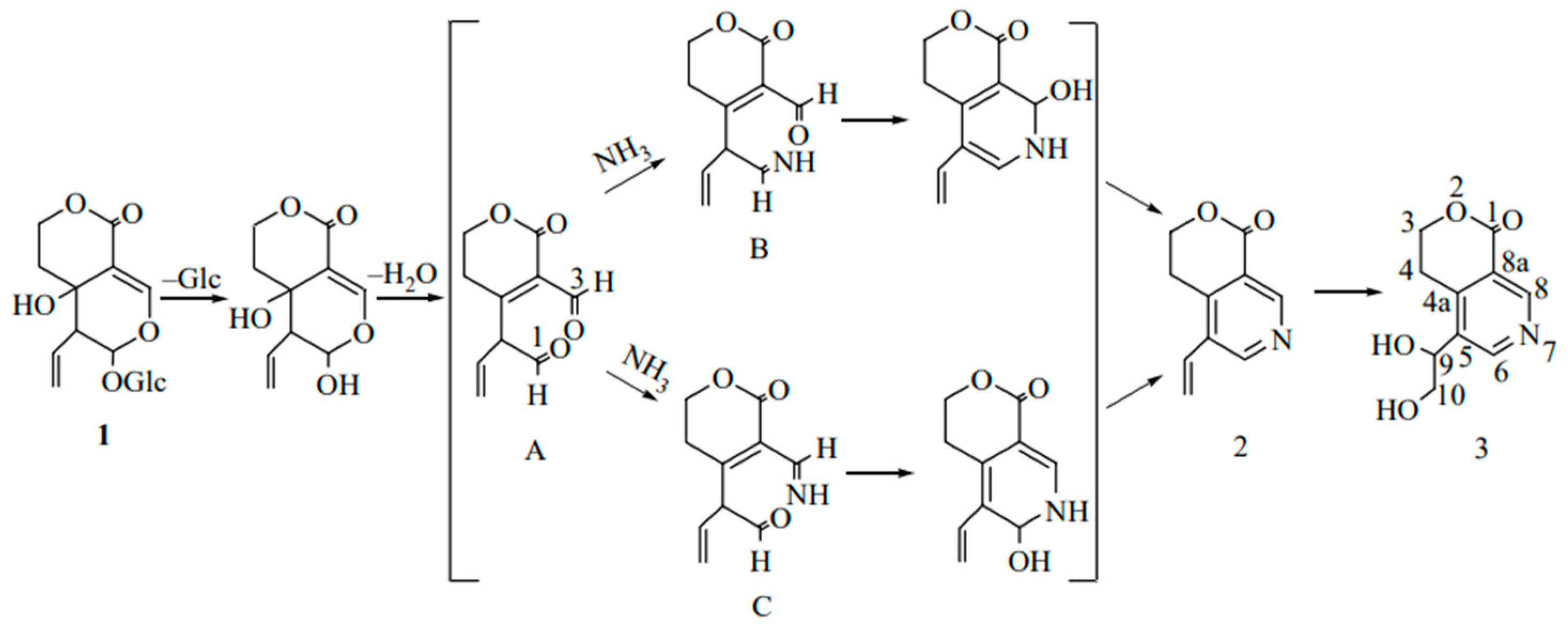
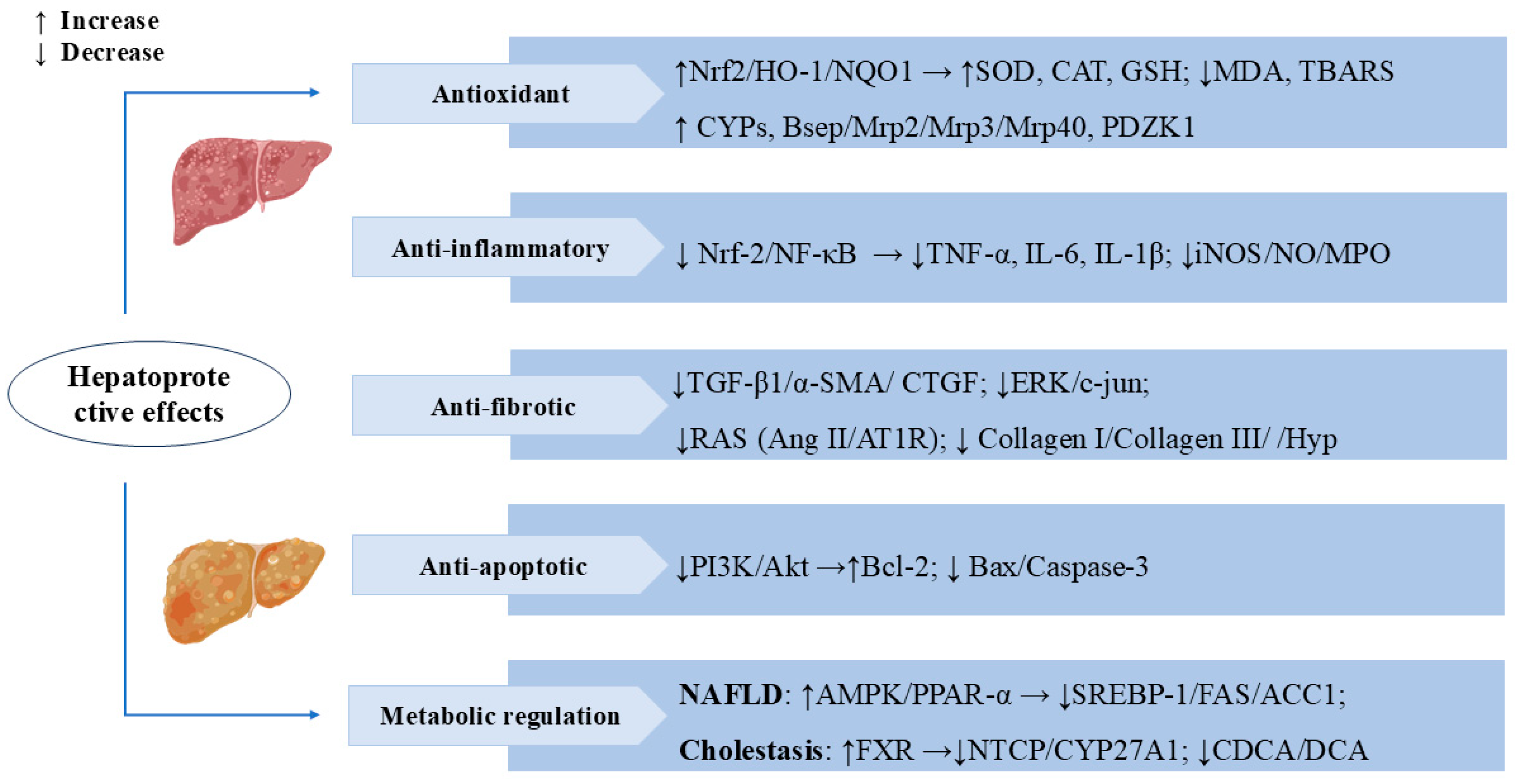
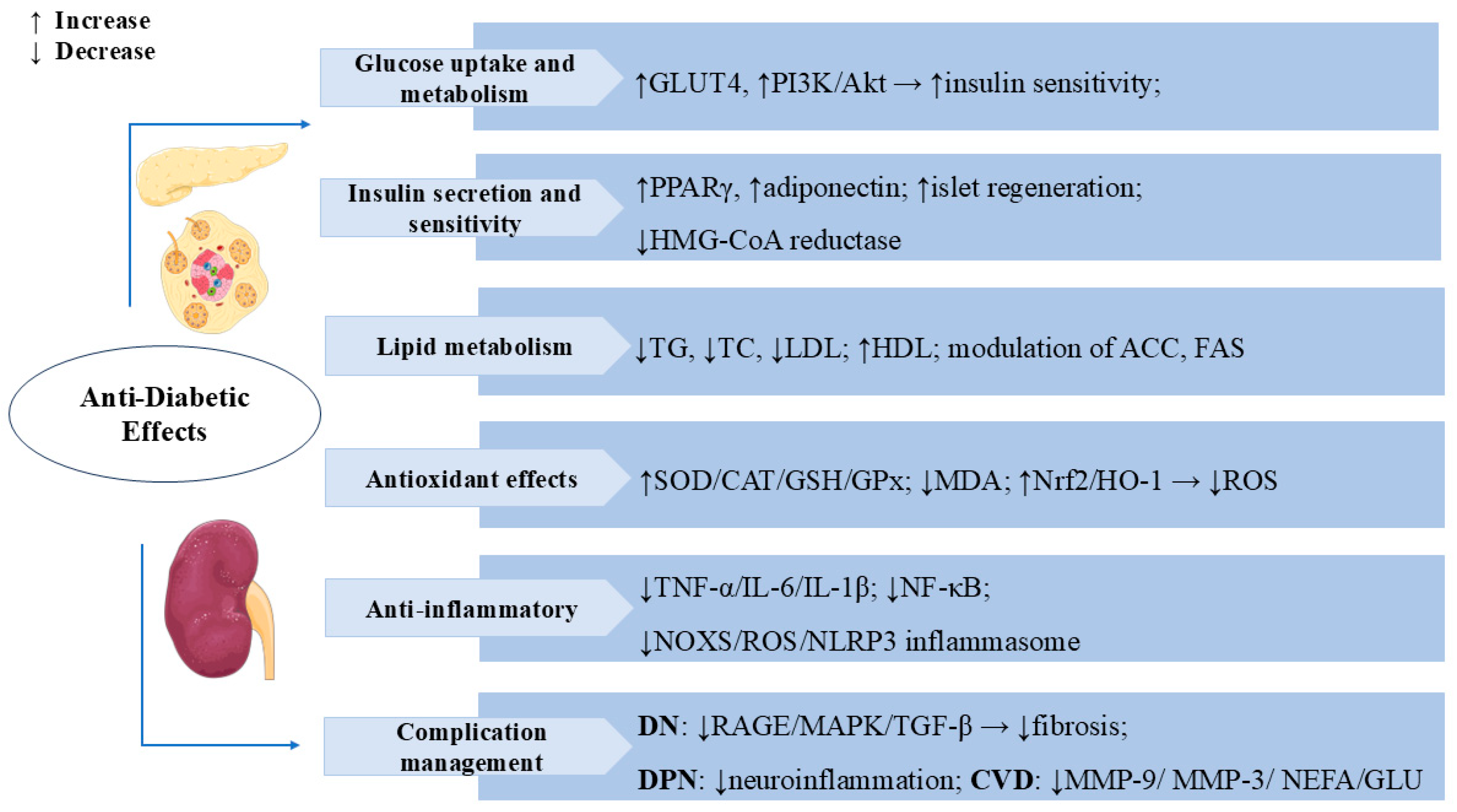
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.-X.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Liang, R.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X. Progress in Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Swertiamarin: A Comprehensive Review. Cells 2025, 14, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151173
Yang H-X, Hu Y-Y, Liang R, Zheng H, Zhang X. Progress in Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Swertiamarin: A Comprehensive Review. Cells. 2025; 14(15):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151173
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hao-Xin, Ying-Yue Hu, Rui Liang, Hong Zheng, and Xuan Zhang. 2025. "Progress in Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Swertiamarin: A Comprehensive Review" Cells 14, no. 15: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151173
APA StyleYang, H.-X., Hu, Y.-Y., Liang, R., Zheng, H., & Zhang, X. (2025). Progress in Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Swertiamarin: A Comprehensive Review. Cells, 14(15), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151173








