Kynurenic Acid Synthesis from D-Kynurenine in the Cerebellum: A Distinct Role of D-Amino Acid Oxidase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Human Brain Tissue
2.3. Animals
2.4. In Vitro Studies
2.4.1. KYNA Production from Pure D-AAO
2.4.2. KYNA Production from D-KYN in Tissue Homogenates from Human and Rat Brain
2.5. In Vivo Microdialysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
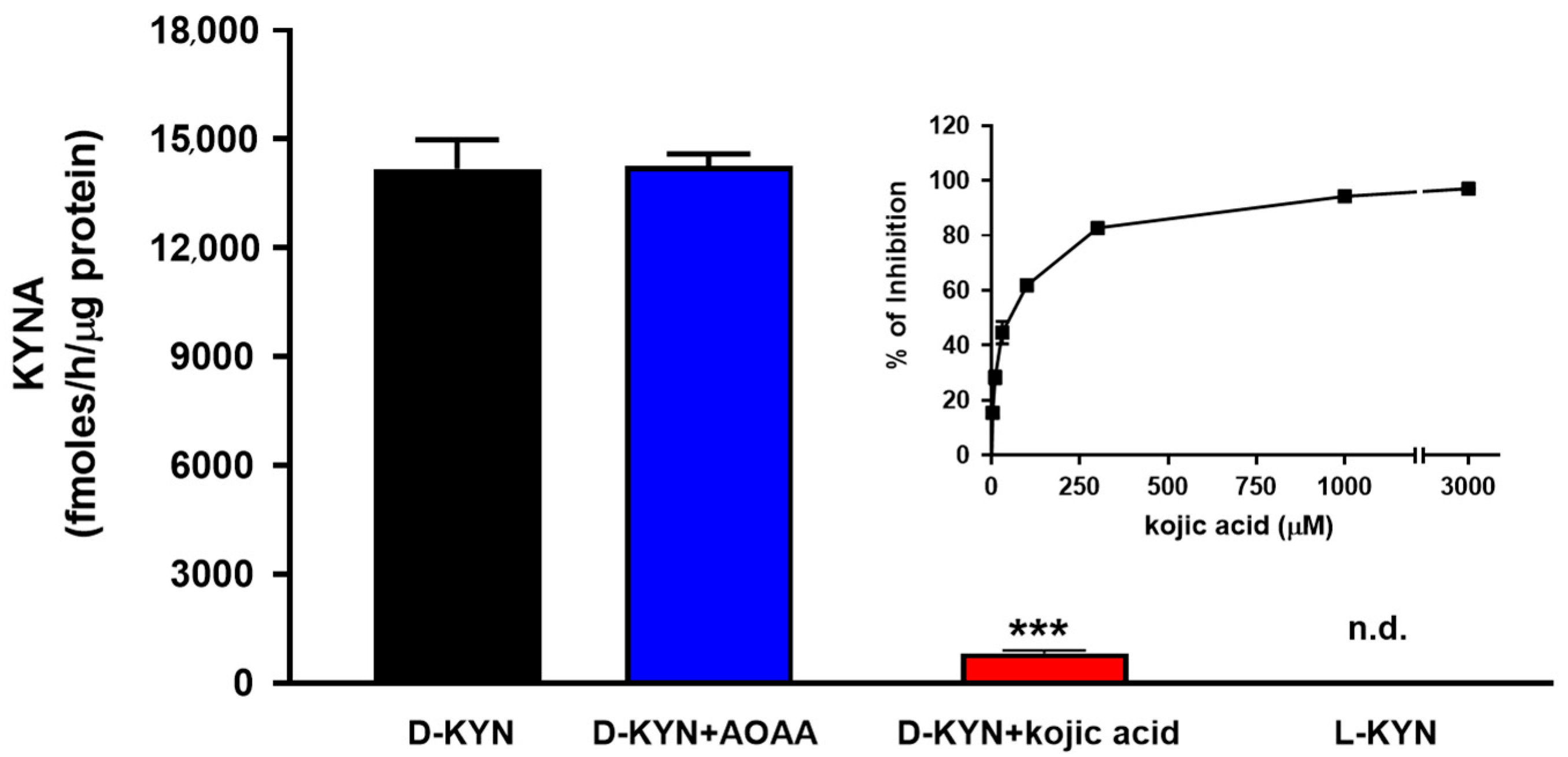
3.1. Pure D-AAO Produces KYNA from D-KYN
3.2. KYNA Production from D-KYN in Human Brain Tissue Homogenates In Vitro
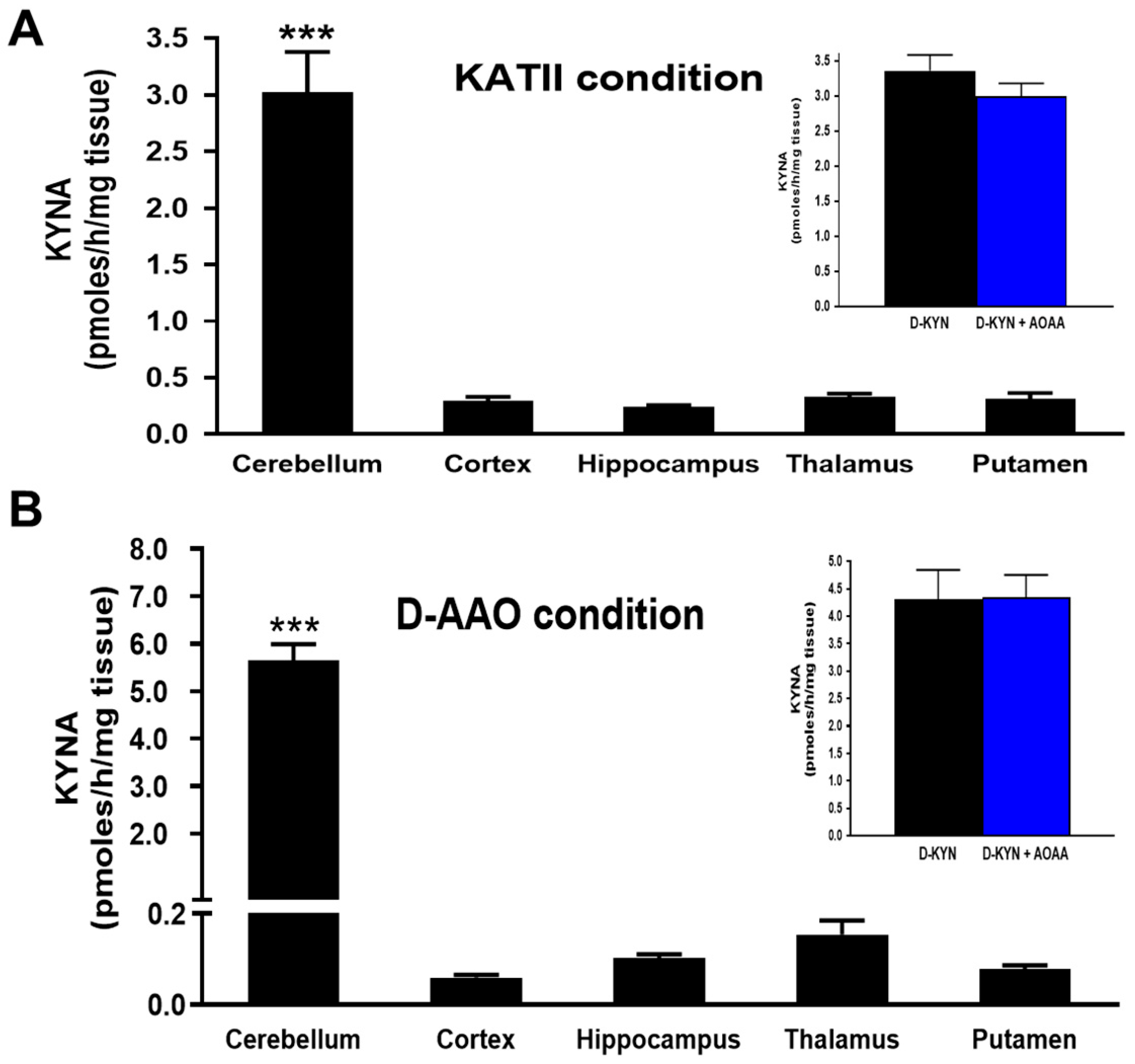
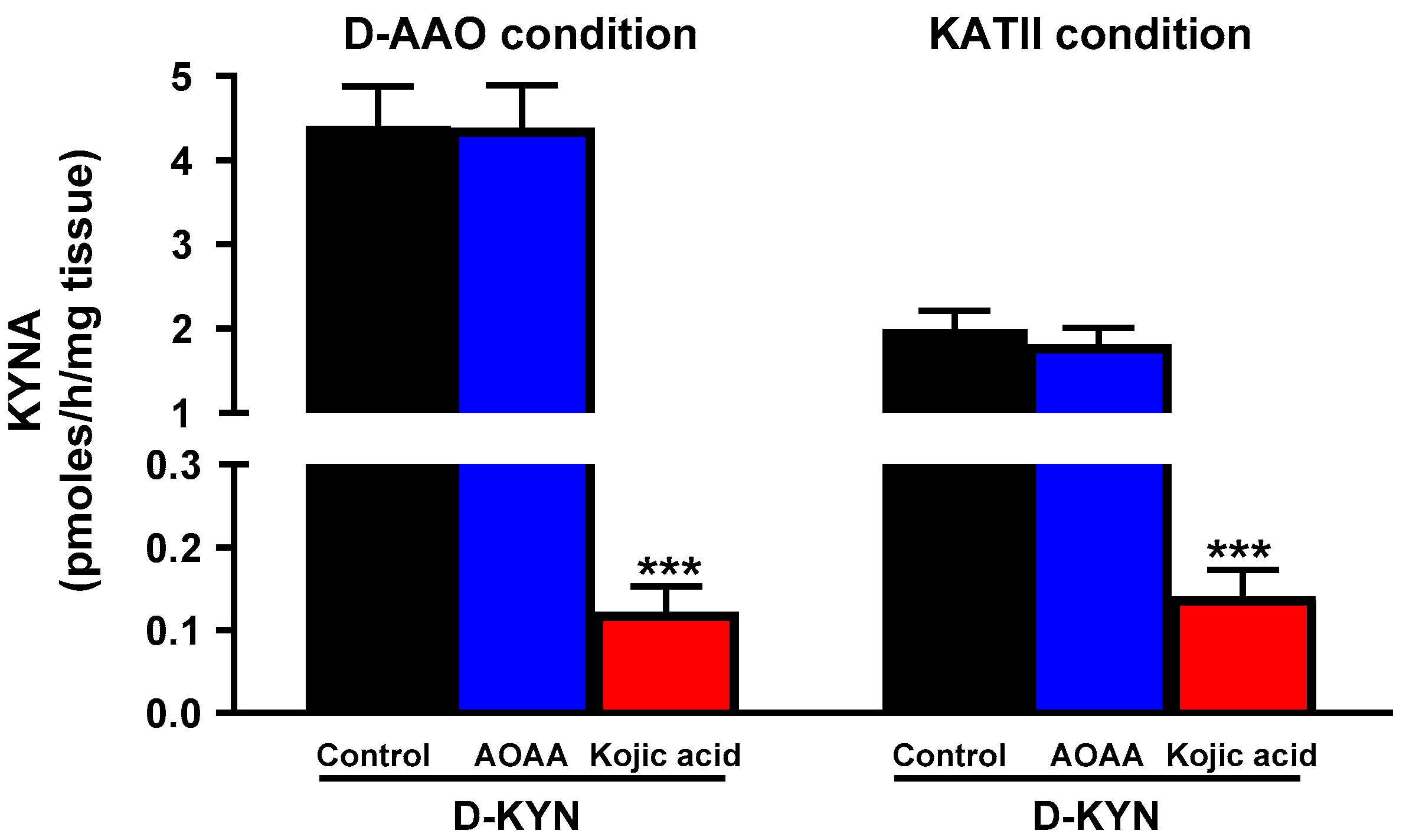
3.3. Roles of D-AAO and KATII in the Production of KYNA from D-KYN in the Rat Cerebellum In Vitro
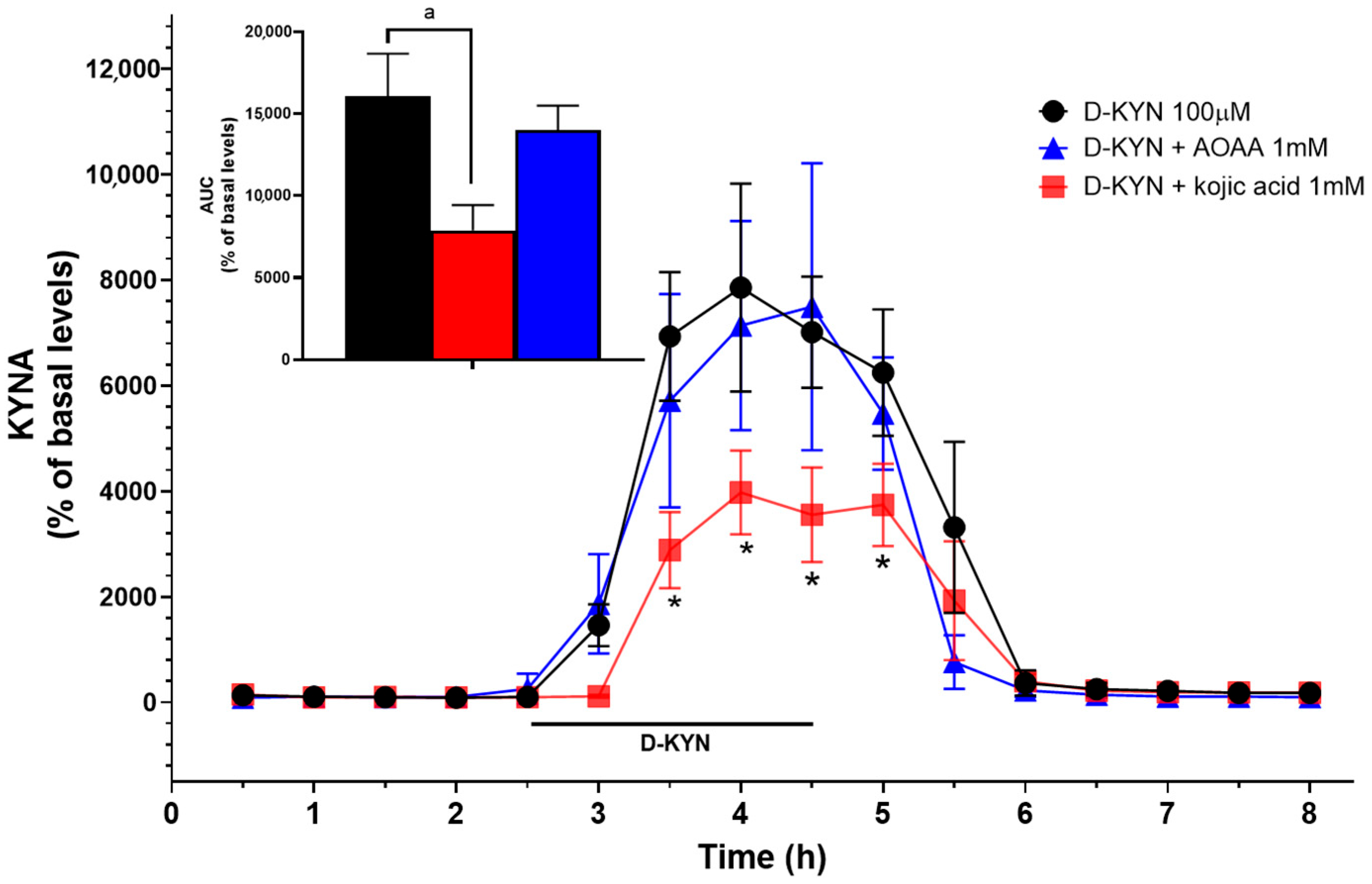
3.4. Roles of D-AAO and KATII in the Production of KYNA from D-KYN in Rat Cerebellum In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pocivavsek, A.; Schwarcz, R.; Erhardt, S. Neuroactive Kynurenines as Pharmacological Targets: New Experimental Tools and Exciting Therapeutic Opportunities. Pharmacol. Rev. 2024, 76, 978–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, P.J.; Grossman, C.J.; Hayes, A.G. Kynurenic acid antagonises responses to NMDA via an action at the strychnine-insensitive glycine receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 154, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, M.; Terramani, T.; Lynch, G.; Baudry, M. A glycine site associated with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors: Characterization and identification of a new class of antagonists. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmas, C.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rassoulpour, A.; Schwarcz, R.; Albuquerque, E.X. The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression: Physiopathological implications. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7463–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M.N.; Stone, T.W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982, 247, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic acid as a ligand for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Murray, I.A.; Schroeder, J.C.; Flaveny, C.A.; Lahoti, T.S.; Laurenzana, E.M.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Perdew, G.H. Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassoulpour, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Ferre, S.; Schwarcz, R. Nanomolar concentrations of kynurenic acid reduce extracellular dopamine levels in the striatum. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Rassoulpour, A.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenic acid leads, dopamine follows: A new case of volume transmission in the brain? J. Neural Transm. 2007, 114, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenedo, R.; Pittaluga, A.; Cozzi, A.; Attucci, S.; Galli, A.; Raiteri, M.; Moroni, F. Presynaptic kynurenate-sensitive receptors inhibit glutamate release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradsson-Geuken, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Gash, C.R.; Alexander, K.S.; Campbell, A.; Sozeri, Y.; Pellicciari, R.; Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P. Cortical kynurenic acid bi-directionally modulates prefrontal glutamate levels as assessed by microdialysis and rapid electrochemistry. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmarowski, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Brooks, J.M.; Potter, M.C.; Pellicciari, R.; Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P. Astrocyte-derived kynurenic acid modulates basal and evoked cortical acetylcholine release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggiato, S.; Tanganelli, S.; Fuxe, K.; Antonelli, T.; Schwarcz, R.; Ferraro, L. Endogenous kynurenic acid regulates extracellular GABA levels in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2014, 82, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenic acid as an antagonist of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain: Facts and challenges. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocivavsek, A.; Erhardt, S. Kynurenic acid: Translational perspectives of a therapeutically targetable gliotransmitter. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, O.A.; Levin, E.D. Glutamate and nicotinic receptor interactions in working memory: Importance for the cognitive impairment of schizophrenia. Neuroscience 2011, 195, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toth, F.; Polyak, H.; Szabo, A.; Mandi, Y.; Vecsei, L. Immune Influencers in Action: Metabolites and Enzymes of the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Guidetti, P.; Goodman, J.H.; Varasi, M.; Ceresoli-Borroni, G.; Speciale, C.; Scharfman, H.E.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenergic manipulations influence excitatory synaptic function and excitotoxic vulnerability in the rat hippocampus in vivo. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocivavsek, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Elmer, G.I.; Bruno, J.P.; Schwarcz, R. Pre- and postnatal exposure to kynurenine causes cognitive deficits in adulthood. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershing, M.L.; Bortz, D.M.; Pocivavsek, A.; Fredericks, P.J.; Jorgensen, C.V.; Vunck, S.A.; Leuner, B.; Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P. Elevated levels of kynurenic acid during gestation produce neurochemical, morphological, and cognitive deficits in adulthood: Implications for schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 2015, 90, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chess, A.C.; Simoni, M.K.; Alling, T.E.; Bucci, D.J. Elevations of endogenous kynurenic acid produce spatial working memory deficits. Schizophr. Bull. 2007, 33, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forcelli, P.A.; Palchik, G.; Leath, T.; DesJardin, J.T.; Gale, K.; Malkova, L. Memory loss in a nonnavigational spatial task after hippocampal inactivation in monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4315–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.C.; Elmer, G.I.; Bergeron, R.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Guidetti, P.; Wu, H.Q.; Schwarcz, R. Reduction of endogenous kynurenic acid formation enhances extracellular glutamate, hippocampal plasticity, and cognitive behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocivavsek, A.; Elmer, G.I.; Schwarcz, R. Inhibition of kynurenine aminotransferase II attenuates hippocampus-dependent memory deficit in adult rats treated prenatally with kynurenine. Hippocampus 2019, 29, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco Ayala, T.B.; Ramirez Ortega, D.R.; Ovalle Rodriguez, P.O.; Pineda, B.; Perez de la Cruz, G.P.; Gonzalez Esquivel, D.G.; Schwarcz, R.; Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Jimenez Anguiano, A.J.; Perez de la Cruz, V.P. Subchronic N-acetylcysteine Treatment Decreases Brain Kynurenic Acid Levels and Improves Cognitive Performance in Mice. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P.; Muchowski, P.J.; Wu, H.Q. Kynurenines in the mammalian brain: When physiology meets pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P.; Amori, L.; Sapko, M.T.; Okuno, E.; Schwarcz, R. Mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase: A third kynurenate-producing enzyme in the mammalian brain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Robinson, H.; Cai, T.; Tagle, D.A.; Li, J. Biochemical and structural properties of mouse kynurenine aminotransferase III. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-de la Cruz, V.; Amori, L.; Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Wang, X.D.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Wu, H.Q.; Schwarcz, R. Enzymatic transamination of D-kynurenine generates kynurenic acid in rat and human brain. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Wang, J.Z.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenic acid and 3-hydroxykynurenine production from D-kynurenine in mice. Brain Res. 2012, 1455, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Horning, K.J.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Schwarcz, R. A method for the determination of D-kynurenine in biological tissues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9747–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco Ayala, T.; Lugo Huitron, R.; Carmona Aparicio, L.; Ramirez Ortega, D.; Gonzalez Esquivel, D.; Pedraza Chaverri, J.; Perez de la Cruz, G.; Rios, C.; Schwarcz, R.; Perez de la Cruz, V. Alternative kynurenic acid synthesis routes studied in the rat cerebellum. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Chavez, L.A.; Lugo Huitron, R.; Gonzalez Esquivel, D.; Pineda, B.; Rios, C.; Silva-Adaya, D.; Sanchez-Chapul, L.; Roldan-Roldan, G.; Perez de la Cruz, V. Relevance of Alternative Routes of Kynurenic Acid Production in the Brain. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5272741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogaya, T.; Song, Z.; Ishii, K.; Fukushima, T. Changes in extracellular kynurenic acid concentrations in rat prefrontal cortex after D-kynurenine infusion: An in vivo microdialysis study. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozaki, A.; Iwasa, S.; Hosoda, S.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Ichiba, H.; Fukushima, T. Fluorimetric assay for D-amino acid oxidase activity in rat brain homogenate by using D-kynurenine as a substrate. Biosci. Trends 2012, 6, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Sone, Y.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Tomiya, M.; Toyo’oka, T. Alteration of kynurenic acid concentration in rat plasma following optically pure kynurenine administration: A comparative study between enantiomers. Chirality 2009, 21, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Ogaya, T.; Ishii, K.; Ichiba, H.; Iizuka, H.; Fukushima, T. Utilization of Kynurenic Acid Produced from D-kynurenine in an in Vitro Assay of D-Amino Acid Oxidase Activity. J. Health Sci. 2010, 56, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.; Oh, D.C.; Cava, F.; Takacs, C.N.; Clardy, J.; de Pedro, M.A.; Waldor, M.K. D-amino acids govern stationary phase cell wall remodeling in bacteria. Science 2009, 325, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Ogaya, T.; Song, Z.; Iizuka, H.; Fukushima, T. Changes in the plasma concentrations of D-kynurenine and kynurenic acid in rats after intraperitoneal administration of tryptophan enantiomers. Chirality 2010, 22, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilone, M.S. D-Amino acid oxidase: New findings. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 1732–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldinelli, L.; Molla, G.; Sacchi, S.; Pilone, M.S.; Pollegioni, L. Relevance of weak flavin binding in human D-amino acid oxidase. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrall, L.; Burnet, P.W.; Betts, J.F.; Harrison, P.J. The neurobiology of D-amino acid oxidase and its involvement in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollegioni, L.; Sacchi, S.; Murtas, G. Human D-Amino Acid Oxidase: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, I.N.O.; Roychaudhuri, R.; de Belleroche, J.; Mothet, J.P. d-Amino acids: New clinical pathways for brain diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckler, J.M.; Lewis, S.J. Advances in D-Amino Acids in Neurological Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, H.; Ishii, K.; Hirasa, Y.; Kubo, K.; Fukushima, T. Fluorescence determination of D- and L-tryptophan concentrations in rat plasma following administration of tryptophan enantiomers using HPLC with pre-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, F.M.; Wang, X.D.; Horning, K.J.; Schwarcz, R. Role of d-amino acid oxidase in the production of kynurenine pathway metabolites from d-tryptophan in mice. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrall, L.; Walker, M.; Rawlings, N.; Benzel, I.; Kew, J.N.; Harrison, P.J.; Burnet, P.W. d-Amino acid oxidase and serine racemase in human brain: Normal distribution and altered expression in schizophrenia. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, C.; Freitas, M.E.; Vargas-Lopes, C.; Wolosker, H.; Panizzutti, R. Increased brain D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) activity in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 101, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Lim, K.S.; Cheng, A.; Garrick, T.; Kapoor, V. Preliminary evidence for a link between schizophrenia and NMDA-glycine site receptor ligand metabolic enzymes, d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) and kynurenine aminotransferase-1 (KAT-1). Brain Res. 2006, 1106, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bartolomeis, A.; Vellucci, L.; Austin, M.C.; De Simone, G.; Barone, A. Rational and Translational Implications of D-Amino Acids for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: From Neurobiology to the Clinics. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, M.; Baux, G.; Mothet, J.P. D-serine signalling in the brain: Friend and foe. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, M.; Hin, N.; Duvall, B.; Ferraris, D.V.; Berry, J.F.; Thomas, A.G.; Alt, J.; Rojas, C.; Slusher, B.S.; Tsukamoto, T. Synthesis of kojic acid derivatives as secondary binding site probes of D-amino acid oxidase. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3910–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.R. Inhibition of D-amino acid oxidase by aromatic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 205, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolosker, H.; Balu, D.T.; Coyle, J.T. The Rise and Fall of the d-Serine-Mediated Gliotransmission Hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploux, E.; Freret, T.; Billard, J.M. d-serine in physiological and pathological brain aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, M.; Berg, C.P. The metabolism of d- and l-tryptophan and d- and l-kynurenine by liver and kidney preparations. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.H.; Berg, C.P. Production of D-kynurenine and other metabolites from D-tryptophan by the intact rabbit and by rabbit tissue. J. Nutr. 1971, 101, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiike, K.; Tojo, H.; Arai, R.; Nozaki, M.; Maeda, T. D-amino-acid oxidase is confined to the lower brain stem and cerebellum in rat brain: Regional differentiation of astrocytes. Brain Res. 1994, 652, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, R.; Miyoshi, Y.; Sakaue, H.; Hamase, K.; Konno, R. Mouse d-Amino-Acid Oxidase: Distribution and Physiological Substrates. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasabe, J.; Suzuki, M.; Imanishi, N.; Aiso, S. Activity of D-amino acid oxidase is widespread in the human central nervous system. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2014, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskjær, A.B.; Roager, H.M.; Dragsted, L.O. D-Amino acids from foods and gut microbiota and their effects in health and disease. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 3196–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry, nutrition, and microbiology of D-amino acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3457–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradley, R.; Goetghebeur, P.; Miller, D.; Burley, R.; Almond, S.; Gruart, I.M.A.; Delgado Garcia, J.M.; Zhu, B.; Howley, E.; Neill, J.C.; et al. Luvadaxistat: A Novel Potent and Selective D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitor Improves Cognitive and Social Deficits in Rodent Models for Schizophrenia. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 3027–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, W.A.; Nakamura, M.; Todd, W.P.; Carpenter, B.K.; Whetsell, W.O., Jr.; Schwarcz, R. Identification and quantification of kynurenic acid in human brain tissue. Brain Res. 1988, 454, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habas, C. Functional Connectivity of the Cognitive Cerebellum. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; LeBel, A.; D’Mello, A.M. Ignoring the cerebellum is hindering progress in neuroscience. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2025, 29, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konarski, J.Z.; McIntyre, R.S.; Grupp, L.A.; Kennedy, S.H. Is the cerebellum relevant in the circuitry of neuropsychiatric disorders? J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005, 30, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Krienen, F.M.; Buckner, R.L. Segregated fronto-cerebellar circuits revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Stachowski, E.K.; Wonodi, I.; Roberts, R.C.; Rassoulpour, A.; McMahon, R.P.; Schwarcz, R. Impaired kynurenine pathway metabolism in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2011, 37, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, K.R.; Skogh, E.; Olsson, S.K.; Dahl, M.L.; Holtze, M.; Engberg, G.; Samuelsson, M.; Erhardt, S. Increased levels of kynurenine and kynurenic acid in the CSF of patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, H.; Jan Pietryja, M.; Kepplinger, B. Importance of Modulating Kynurenic Acid Metabolism-Approaches for the Treatment of Dementia. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, F.; Russi, P.; Carla, V.; Lombardi, G. Kynurenic acid is present in the rat brain and its content increases during development and aging processes. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 94, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramsbergen, J.B.; Schmidt, W.; Turski, W.A.; Schwarcz, R. Age-related changes in kynurenic acid production in rat brain. Brain Res. 1992, 588, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidetti, P.; Hoffman, G.E.; Melendez-Ferro, M.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Schwarcz, R. Astrocytic localization of kynurenine aminotransferase II in the rat brain visualized by immunocytochemistry. Glia 2007, 55, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakov, I.; Blumenfeld, M.; Guerassimenko, O.; Cavarec, L.; Palicio, M.; Abderrahim, H.; Bougueleret, L.; Barry, C.; Tanaka, H.; La Rosa, P.; et al. Genetic and physiological data implicating the new human gene G72 and the gene for D-amino acid oxidase in schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13675–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Tsukamoto, T. Evolution of D-amino acid oxidase inhibitors: From concept to clinic. Adv. Pharmacol. 2025, 102, 301–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez de la Cruz, V.; Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Wang, X.-D.; Blanco Ayala, T.; Beggiato, S.; González Esquivel, D.F.; Pineda, B.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenic Acid Synthesis from D-Kynurenine in the Cerebellum: A Distinct Role of D-Amino Acid Oxidase. Cells 2025, 14, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131030
Pérez de la Cruz V, Sathyasaikumar KV, Wang X-D, Blanco Ayala T, Beggiato S, González Esquivel DF, Pineda B, Schwarcz R. Kynurenic Acid Synthesis from D-Kynurenine in the Cerebellum: A Distinct Role of D-Amino Acid Oxidase. Cells. 2025; 14(13):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131030
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez de la Cruz, Verónica, Korrapati V. Sathyasaikumar, Xiao-Dan Wang, Tonali Blanco Ayala, Sarah Beggiato, Dinora F. González Esquivel, Benjamin Pineda, and Robert Schwarcz. 2025. "Kynurenic Acid Synthesis from D-Kynurenine in the Cerebellum: A Distinct Role of D-Amino Acid Oxidase" Cells 14, no. 13: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131030
APA StylePérez de la Cruz, V., Sathyasaikumar, K. V., Wang, X.-D., Blanco Ayala, T., Beggiato, S., González Esquivel, D. F., Pineda, B., & Schwarcz, R. (2025). Kynurenic Acid Synthesis from D-Kynurenine in the Cerebellum: A Distinct Role of D-Amino Acid Oxidase. Cells, 14(13), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131030








