Age-Related Increases in PDE11A4 Protein Expression Trigger Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) of the Enzyme That Can Be Reversed by PDE11A4 Small Molecule Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. LLPS Prediction
2.2. Plasmid Generation
2.3. Compounds
2.4. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.5. PDE Activity Assay
2.6. Quantification of GFP-mPDE11A4 Versus BODIPY-568 Signals
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Quantification of mPDE11A4 Clustering into Punctate Spherical Droplets
2.9. In Vivo Study
2.10. Immunofluorescence (IF)
2.11. Counting Ghost Axons
2.12. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PDE11A4 Exhibits Sequence Features Associated with Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS)
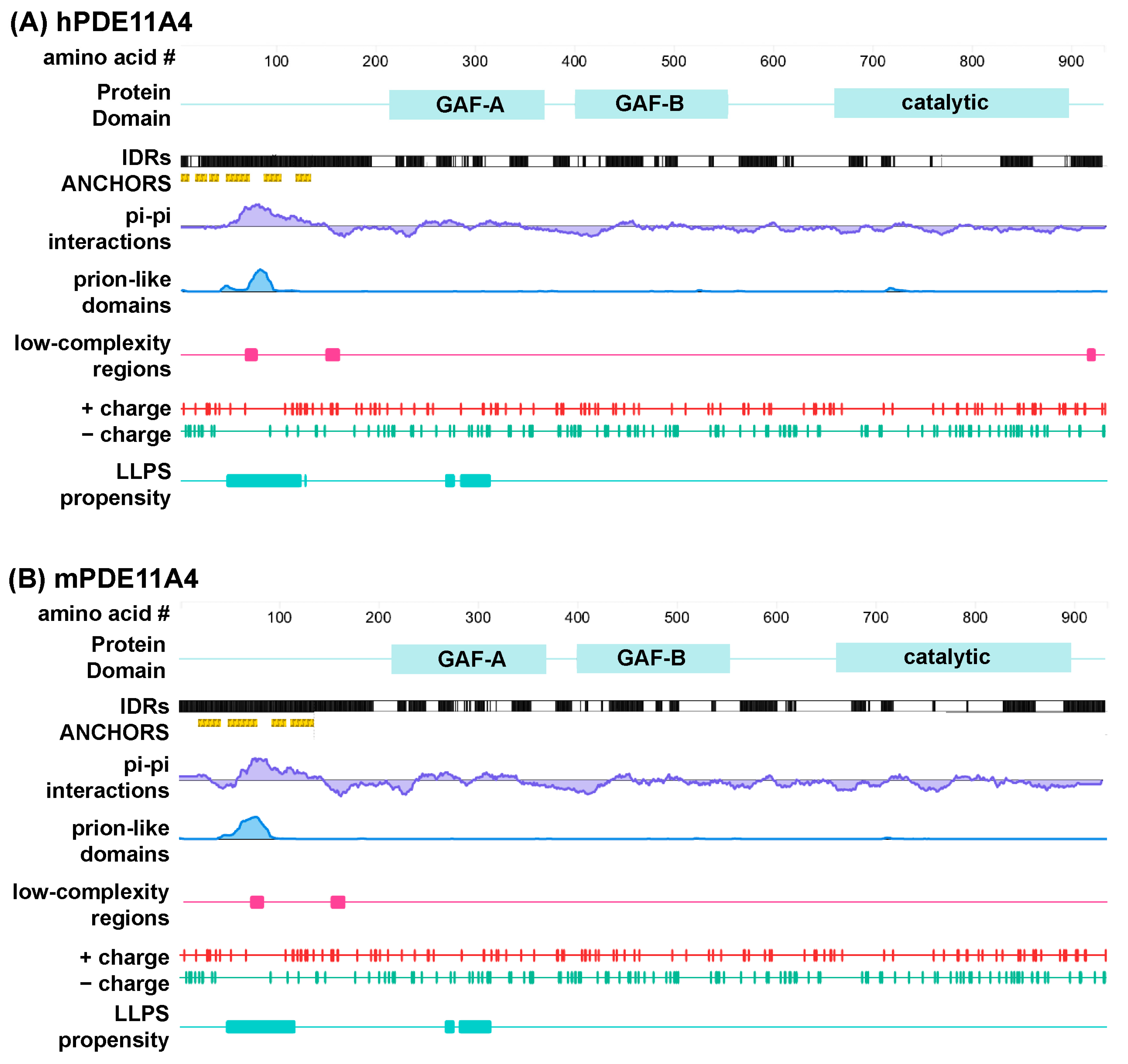
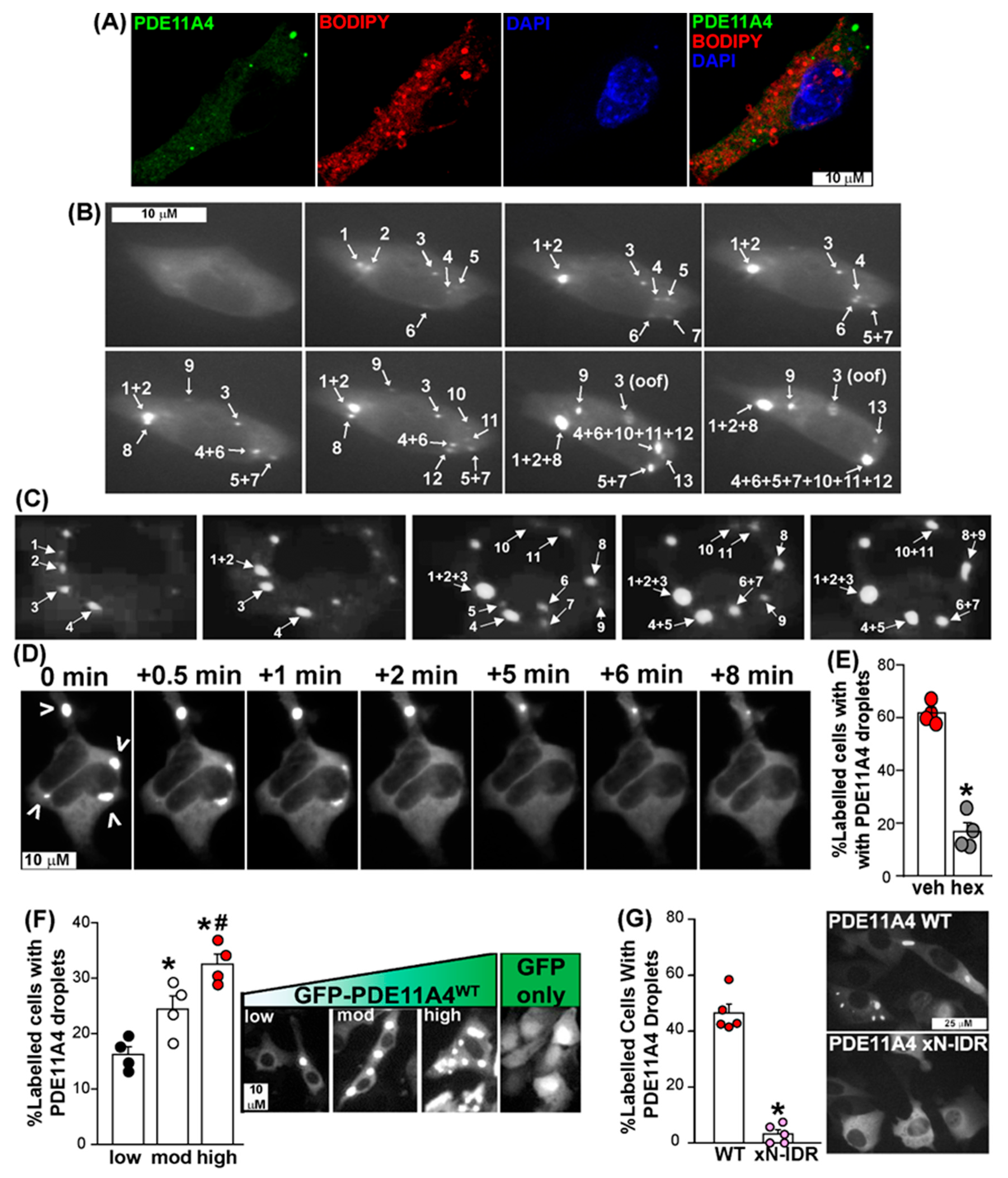
3.2. PDE11A4 Exhibits Physical Properties Associated with LLPS
3.3. PDE11A4’S N-Terminal Intrinsically Disordered Region Is Required for LLPS of the Enzyme
3.4. PDE11A Inhibitors (PDE11Ais) Inhibit GFP-mPDE11A4 Catalytic Activity in Mouse HT22 Hippocampal Neuronal Cells
3.5. PDE11Ais Reverse GFP-mPDE11A4 LLPS in Mouse HT22 Hippocampal Cells
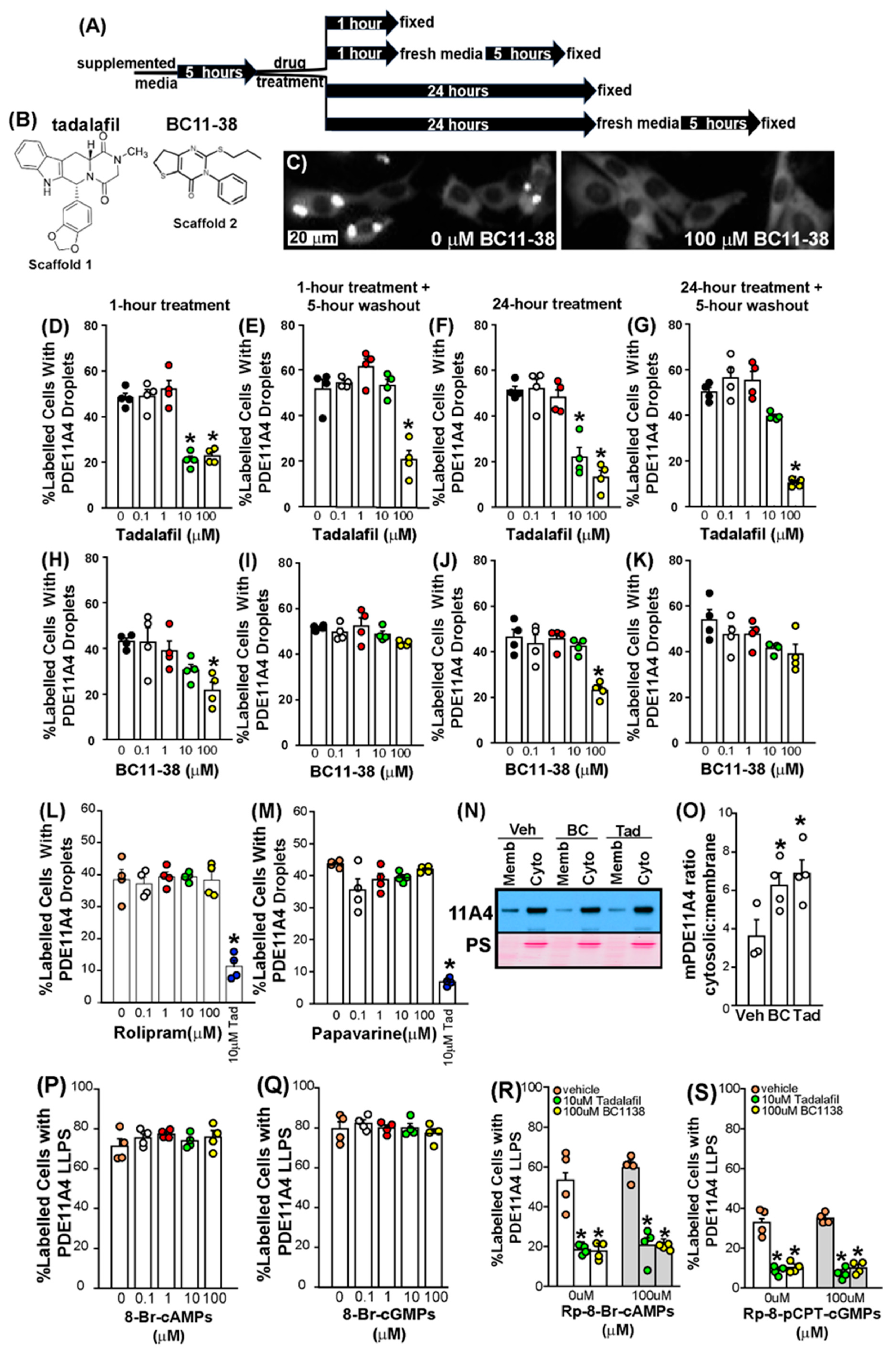
3.6. The Dispersal of PDE11A4 LLPS Is Not Regulated by Cyclic Nucleotide Levels
3.7. PDE11Ais Shift GFP-mPDE11A4 from the Membrane to the Cytosolic Fraction
3.8. Oral Dosing of Tadalafil to Old NIA C57BL6 Mice Reverses Age-Related Clustering of PDE11A4 in Ghost Axons
4. Discussion
4.1. Computational Analyses Identify Numerous LLPS-Promoting Features in Both mPDE11A4 and hPDE11A4 Enriched in the N-Terminal Regulatory Domain
4.2. PDE11A4 Clustering Meets the Minimum Physical Requirements for LLPS
4.3. PDE11Ai Small Molecule Inhibitors Reverse mPDE11A LLPS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, A. Cognition: The brain’s decline. Nature 2012, 492, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.P. A Role for Phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A) in the Formation of Social Memories and the Stabilization of Mood. Adv. Neurobiol. 2017, 17, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J. The age factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Plassman, B.L.; Langa, K.M.; Fisher, G.G.; Heeringa, S.G.; Weir, D.R.; Ofstedal, M.B.; Burke, J.R.; Hurd, M.D.; Potter, G.G.; Rodgers, W.L.; et al. Prevalence of cognitive impairment without dementia in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Wilson, S.P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.T. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of long-form phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D) enzyme reverses amyloid-beta42-induced memory deficits in mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2014, 38, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkale, W.L.; Cowburn, R.F.; Ohm, T.G.; Bogdanovic, N.; Fastbom, J. A quantitative autoradiographic study of [3H]cAMP binding to cytosolic and particulate protein kinase A in post-mortem brain staged for Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary changes and amyloid deposits. Brain Res. 1999, 818, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, D.J.; Furones, C.; Kang, Y.; Atkins, C.M. Age-dependent alterations in cAMP signaling contribute to synaptic plasticity deficits following traumatic brain injury. Neuroscience 2013, 231, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pilarzyk, K.; Capell, W.R.; Porcher, L.; Rips-Goodwin, A.; Kelly, M.P. Biologic that disrupts PDE11A4 homodimerization in hippocampus CA1 reverses age-related cognitive decline of social memories in mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2023, 131, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pilarzyk, K.; Porcher, L.; Capell, W.R.; Burbano, S.D.; Davis, J.; Fisher, J.L.; Gorny, N.; Petrolle, S.; Kelly, M.P. Conserved age-related increases in hippocampal PDE11A4 cause unexpected proteinopathies and cognitive decline of social associative memories. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kelly, M.P.; Adamowicz, W.; Bove, S.; Hartman, A.J.; Mariga, A.; Pathak, G.; Reinhart, V.; Romegialli, A.; Kleiman, R.J. Select 3’,5’-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases exhibit altered expression in the aged rodent brain. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houslay, M.D. Underpinning compartmentalised cAMP signalling through targeted cAMP breakdown. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkonen, K.; Kass, D.A. Nanodomain Regulation of Cardiac Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling by Phosphodiesterases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 455–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, G.S.; Tejeda, G.S.; Kelly, M.P. Therapeutic targeting of 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Inhibition and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 770–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alberti, S.; Gladfelter, A.; Mittag, T. Considerations and Challenges in Studying Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation and Biomolecular Condensates. Cell 2019, 176, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alberti, S.; Dormann, D. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Disease. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Longhi, S.; Grandori, R.; Brocca, S. Relevance of Electrostatic Charges in Compactness, Aggregation, and Phase Separation of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dual 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP and -GMP Phosphodiesterase 11A Isoform 4 [Homo Sapiens], Accession No. NP_058649.3 [Internet]. National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; [1988]. 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_058649.3 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Dual 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP and -GMP Phosphodiesterase 11A [Mus Musculus], Accession No. NP_001074502.1 [Internet]. National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; [1988]. 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001074502.1 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Owen, I.; Shewmaker, F. The Role of Post-Translational Modifications in the Phase Transitions of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pathak, G.; Agostino, M.J.; Bishara, K.; Capell, W.R.; Fisher, J.L.; Hegde, S.; Ibrahim, B.A.; Pilarzyk, K.; Sabin, C.; Tuczkewycz, T.; et al. PDE11A negatively regulates lithium responsivity. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, B.; Chen, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, T.; Shi, M.; Li, T. Computational Screening of Phase-separating Proteins. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pancsa, R.; Vranken, W.; Meszaros, B. Computational resources for identifying and describing proteins driving liquid-liquid phase separation. Brief Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jackson, R.J.; Howell, M.T.; Kaminski, A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, S.; Capell, W.R.; Ibrahim, B.A.; Klett, J.; Patel, N.S.; Sougiannis, A.T.; Kelly, M.P. Phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A), Enriched in Ventral Hippocampus Neurons, is Required for Consolidation of Social but not Nonsocial Memories in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2920–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kelly, M.P.; Logue, S.F.; Brennan, J.; Day, J.P.; Lakkaraju, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, X.; Tam, M.; Sukoff Rizzo, S.J.; Platt, B.J.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 11A in brain is enriched in ventral hippocampus and deletion causes psychiatric disease-related phenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8457–8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Lu, T.W.; Stolerman, L.M.; Tenner, B.; Yang, J.R.; Zhang, J.F.; Falcke, M.; Rangamani, P.; Taylor, S.S.; Mehta, S.; et al. Phase Separation of a PKA Regulatory Subunit Controls cAMP Compartmentation and Oncogenic Signaling. Cell 2020, 182, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mahmood, S.U.; Lozano Gonzalez, M.; Tummalapalli, S.; Eberhard, J.; Ly, J.; Hoffman, C.S.; Kelly, M.P.; Gordon, J.; Colussi, D.; Childers, W.; et al. First Optimization of Novel, Potent, Selective PDE11A4 Inhibitors for Age-Related Cognitive Decline. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 14597–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mahmood, S.U.; Eberhard, J.; Hoffman, C.S.; Colussi, D.; Gordon, J.; Childers, W.; Amurrio, E.; Patel, J.; Kelly, M.P.; Rotella, D.P. First Demonstration of In Vivo PDE11A4 Target Engagement for Potential Treatment of Age-Related Memory Disorders. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 17774–17784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybalkin, S.D.; Hinds, T.R.; Beavo, J.A. Enzyme assays for cGMP hydrolyzing phosphodiesterases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1020, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fosang, A.J.; Colbran, R.J. Transparency Is the Key to Quality. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29692–29694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patel, N.S.; Klett, J.; Pilarzyk, K.; Lee, D.I.; Kass, D.; Menniti, F.S.; Kelly, M.P. Identification of new PDE9A isoforms and how their expression and subcellular compartmentalization in the brain change across the life span. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 65, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porcher, L.; Bruckmeier, S.; Burbano, S.D.; Finnell, J.E.; Gorny, N.; Klett, J.; Wood, S.K.; Kelly, M.P. Aging triggers an upregulation of a multitude of cytokines in the male and especially the female rodent hippocampus but more discrete changes in other brain regions. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sbornova, I.; van der Sande, E.; Milosavljevic, S.; Amurrio, E.; Burbano, S.D.; Das, P.K.; Do, H.H.; Fisher, J.L.; Kargbo, P.; Patel, J.; et al. The Sleep Quality- and Myopia-Linked PDE11A-Y727C Variant Impacts Neural Physiology by Reducing Catalytic Activity and Altering Subcellular Compartmentalization of the Enzyme. Cells 2023, 12, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oates, M.E.; Romero, P.; Ishida, T.; Ghalwash, M.; Mizianty, M.J.; Xue, B.; Dosztanyi, Z.; Uversky, V.N.; Obradovic, Z.; Kurgan, L.; et al. D(2)P(2): Database of disordered protein predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D508–D516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dosztanyi, Z.; Meszaros, B.; Simon, I. ANCHOR: Web server for predicting protein binding regions in disordered proteins. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2745–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dosztanyi, Z.; Meszaros, B.; Simon, I. Bioinformatical approaches to characterize intrinsically disordered/unstructured proteins. Brief Bioinform. 2010, 11, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, R.M.; Chong, P.A.; Tsang, B.; Kim, T.H.; Bah, A.; Farber, P.; Lin, H.; Forman-Kay, J.D. Pi-Pi contacts are an overlooked protein feature relevant to phase separation. eLife 2018, 7, e31486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lancaster, A.K.; Nutter-Upham, A.; Lindquist, S.; King, O.D. PLAAC: A web and command-line application to identify proteins with prion-like amino acid composition. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2501–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wootton, J.C.; Federhen, S. Statistics of local complexity in amino acid sequences and sequence databases. Comput. Chem. 1993, 17, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hou, C.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Chen, T.; Shen, B.; Hou, Y.; Li, P.; Li, T. Screening membraneless organelle participants with machine-learning models that integrate multimodal features. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115369119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Holehouse, A.S.; Das, R.K.; Ahad, J.N.; Richardson, M.O.; Pappu, R.V. CIDER: Resources to Analyze Sequence-Ensemble Relationships of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bolognesi, B.; Lorenzo Gotor, N.; Dhar, R.; Cirillo, D.; Baldrighi, M.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Lehner, B. A Concentration-Dependent Liquid Phase Separation Can Cause Toxicity upon Increased Protein Expression. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chu, X.; Sun, T.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, L.; Pei, J. Prediction of liquid-liquid phase separating proteins using machine learning. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Welles, R.M.; Sojitra, K.A.; Garabedian, M.V.; Xia, B.; Wang, W.; Guan, M.; Regy, R.M.; Gallagher, E.R.; Hammer, D.A.; Mittal, J.; et al. Determinants of Disordered Protein Co-Assembly Into Discrete Condensed Phases. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kroschwald, S.; Maharana, S.; Simon, A.W. (Eds.) Hexanediol: A chemical probe to investigate the material properties of membrane-less compartments. Matters 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, J.L.; Zoraghi, R.; Beasley, A.; Sekhar, K.R.; Francis, S.H.; Corbin, J.D. High biochemical selectivity of tadalafil, sildenafil and vardenafil for human phosphodiesterase 5A1 (PDE5) over PDE11A4 suggests the absence of PDE11A4 cross-reaction in patients. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2005, 17, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.S.; Gary, B.D.; Tinsley, H.N.; Piazza, G.A.; Laufer, S.; Abadi, A.H. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship of functionalized tetrahydro-beta-carboline derivatives as novel PDE5 inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2011, 344, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ceyhan, O.; Birsoy, K.; Hoffman, C.S. Identification of Biologically Active PDE11-Selective Inhibitors Using a Yeast-Based High-Throughput Screen. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaqaman, K.; Ditlev, J.A. Biomolecular condensates in membrane receptor signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 69, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ditlev, J.A. Membrane-associated phase separation: Organization and function emerge from a two-dimensional milieu. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 13, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garcia-Barroso, C.; Ricobaraza, A.; Pascual-Lucas, M.; Unceta, N.; Rico, A.J.; Goicolea, M.A.; Salles, J.; Lanciego, J.L.; Oyarzabal, J.; Franco, R.; et al. Tadalafil crosses the blood-brain barrier and reverses cognitive dysfunction in a mouse model of AD. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Cao, X.; Liu, B. Effects of pH alterations on stress- and aging-induced protein phase separation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2022, 79, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farmer, R.; Burbano, S.D.; Patel, N.S.; Sarmiento, A.; Smith, A.J.; Kelly, M.P. Phosphodiesterases PDE2A and PDE10A both change mRNA expression in the human brain with age, but only PDE2A changes in a region-specific manner with psychiatric disease. Cell Signal. 2020, 70, 109592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kelly, M.P. Cyclic nucleotide signaling changes associated with normal aging and age-related diseases of the brain. Cell Signal. 2018, 42, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ainani, H.; Bouchmaa, N.; Ben Mrid, R.; El Fatimy, R. Liquid-liquid phase separation of protein tau: An emerging process in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 178, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Li, Y.; Ye, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, N.; Luo, S. The Regulatory Mechanism of Transthyretin Irreversible Aggregation through Liquid-to-Solid Phase Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, B.; Fan, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yu, H. Distinct Effects of Familial Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Mutations on alpha-Synuclein Phase Separation and Amyloid Aggregation. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qin, W.; Zhou, A.; Zuo, X.; Jia, L.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jin, H.; Cruchaga, C.; et al. Exome sequencing revealed PDE11A as a novel candidate gene for early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Filippatos, T.D.; Makri, A.; Elisaf, M.S.; Liamis, G. Hyponatremia in the elderly: Challenges and solutions. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohan, D.; Yap, K.H.; Reidpath, D.; Soh, Y.C.; McGrattan, A.; Stephan, B.C.M.; Robinson, L.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Siervo, M.; Pase, M. Link Between Dietary Sodium Intake, Cognitive Function, and Dementia Risk in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 76, 1347–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sakai, K.; Yamada, K.; Mori, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Nishimura, T. Age-dependent brain temperature decline assessed by diffusion-weighted imaging thermometry. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, Y.; Nemeth, E.; Schomburg, R.; Chemla, A.; Fulop, L.; Menger, M.D.; Liu, Y.; Fassbender, K. Decreased pH in the aging brain and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 101, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Ota, K.; Nardin, C.; Feldman, M.; Widman, A.; Wind, O.; Simon, A.; Reilly, M.; Levin, L.R.; Buck, J.; et al. Mammalian pigmentation is regulated by a distinct cAMP-dependent mechanism that controls melanosome pH. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaau7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Uhernik, A.L.; Li, L.; LaVoy, N.; Velasquez, M.J.; Smith, J.P. Regulation of monocarboxylic acid transporter-1 by cAMP dependent vesicular trafficking in brain microvascular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toyoda, H.; Saito, M.; Sato, H.; Dempo, Y.; Ohashi, A.; Hirai, T.; Maeda, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Kang, Y. cGMP activates a pH-sensitive leak K+ current in the presumed cholinergic neuron of basal forebrain. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Guo, Z.; Yao, Y. PDE5 inhibitor protects the mitochondrial function of hypoxic myocardial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Adderley, S.P.; Sprague, R.S.; Stephenson, A.H.; Hanson, M.S. Regulation of cAMP by phosphodiesterases in erythrocytes. Pharmacol. Rep. PR 2010, 62, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rocque, W.J.; Tian, G.; Wiseman, J.S.; Holmes, W.D.; Zajac-Thompson, I.; Willard, D.H.; Patel, I.R.; Wisely, G.B.; Clay, W.C.; Kadwell, S.H.; et al. Human recombinant phosphodiesterase 4B2B binds (R)-rolipram at a single site with two affinities. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 14250–14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.P. Pde11a. In Encyclopedia of Signaling Molecules; Choi, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Keseru, G.M.; Makara, G.M. The influence of lead discovery strategies on the properties of drug candidates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, R.A. Evaluation of enzyme inhibitors in drug discovery. A guide for medicinal chemists and pharmacologists. Methods Biochem. Anal. 2005, 46, 1–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Carter, G.T. Drug-like property concepts in pharmaceutical design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2184–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerns, E.H.; Di, L. Drug-Like Properties: Concepts, Structure Design and Methods: From ADME to Toxicity Optimization, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, A.T.; Beavo, J.A. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 488–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H. Biological assay challenges from compound solubility: Strategies for bioassay optimization. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.H.; Lee, S.W. Chronic low dosing of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor for erectile dysfunction. Korean J. Urol. 2012, 53, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Terry, R.; Cheung, Y.F.; Praestegaard, M.; Baillie, G.S.; Huston, E.; Gall, I.; Adams, D.R.; Houslay, M.D. Occupancy of the catalytic site of the PDE4A4 cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase by rolipram triggers the dynamic redistribution of this specific isoform in living cells through a cyclic AMP independent process. Cell Signal. 2003, 15, 955–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, F.; Anthony, D.F.; Vadrevu, S.; Riddell, T.; Day, J.P.; McLeod, R.; Adams, D.R.; Baillie, G.S.; Houslay, M.D. p62 (SQSTM1) and cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-4A4 (PDE4A4) locate to a novel, reversible protein aggregate with links to autophagy and proteasome degradation pathways. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1576–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houslay, M.D.; Christian, F. p62 (SQSTM1) forms part of a novel, reversible aggregate containing a specific conformer of the cAMP degrading phosphodiesterase, PDE4A4. Autophagy 2010, 6, 1198–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| GFP + 0 µM | m11A4 + 0 µM | m11A4 + 0.1 µM | m11A4 + 1 µM | m11A4 + 10 µM | m11A4 + 100 µM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cAMP-PDE | ||||||
| tadalafil * | 117.5 ± 23.9 | 3822.5 ± 97.3 | 3770.7 ± 460.0 | 3922.5 ± 182.0 | 2538.8 ± 137.8 | 574.5 ± 45.0 |
| BC11-38 | 155.0 ± 12.8 | 2720.9 ± 188.2 | 2961.0 ± 80.3 | 2908.8 ± 84.9 | 3129.6 ± 65.6 | 1882.5 ± 217.4 |
| cGMP-PDE | ||||||
| tadalafil * | 52.2 ± 15.5 | 3821.1 ± 175.5 | 3516.7 ± 441.8 | 3493.6 ± 239.3 | 2336.8 ± 239.4 | 536.6 ± 50.8 |
| BC11-38 | 54.8 ± 11.7 | 2665.8 ± 130.1 | 2855.5 ± 259.2 | 2956.7 ± 126.0 | 3017.7 ± 61.2 | 1894.3 ± 166.5 |
| PDE11A4 protein | ||||||
| tadalafil * | N/A | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.32 ± 0.28 | 1.21 ± 0.29 | 1.12 ± 0.17 | 0.94 ± 0.03 |
| BC11-38 | N/A | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 2.39 ± 0.94 | 1.41 ± 0.28 | 1.61 ± 0.38 | 2.45 ± 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amurrio, E.; Patel, J.H.; Danaher, M.; Goodwin, M.; Kargbo, P.; Klimentova, E.; Lin, S.; Kelly, M.P. Age-Related Increases in PDE11A4 Protein Expression Trigger Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) of the Enzyme That Can Be Reversed by PDE11A4 Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells 2025, 14, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120897
Amurrio E, Patel JH, Danaher M, Goodwin M, Kargbo P, Klimentova E, Lin S, Kelly MP. Age-Related Increases in PDE11A4 Protein Expression Trigger Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) of the Enzyme That Can Be Reversed by PDE11A4 Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells. 2025; 14(12):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120897
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmurrio, Elvis, Janvi H. Patel, Marie Danaher, Madison Goodwin, Porschderek Kargbo, Eliska Klimentova, Sonia Lin, and Michy P. Kelly. 2025. "Age-Related Increases in PDE11A4 Protein Expression Trigger Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) of the Enzyme That Can Be Reversed by PDE11A4 Small Molecule Inhibitors" Cells 14, no. 12: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120897
APA StyleAmurrio, E., Patel, J. H., Danaher, M., Goodwin, M., Kargbo, P., Klimentova, E., Lin, S., & Kelly, M. P. (2025). Age-Related Increases in PDE11A4 Protein Expression Trigger Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) of the Enzyme That Can Be Reversed by PDE11A4 Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells, 14(12), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120897







