Molecular Effect of Variants in Serotonin Transporter Gene in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health and Treatment of Substance Use Disorders; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, A.; Humphreys, K. Governmental Standard Drink Definitions and Low-Risk Alcohol Consumption Guidelines in 37 Countries. Addict. Abingdon Engl. 2016, 111, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1.
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Singla, R.; Maheshwari, O.; Fontaine, C.J.; Gil-Mohapel, J. Alcohol Use Disorder: Neurobiology and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.-H. Dopamine Signaling in Reward-Related Behaviors. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.O.; Battagello, D.S.; Cardoso, A.R.; Hauser, D.N.; Bittencourt, J.C.; Correa, R.G. Dopamine: Functions, Signaling, and Association with Neurological Diseases. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhamzeh, M.; Moravej, F.G.; Arabi, M.; Shahriari, E.; Mehrabi, S.; Ward, R.; Ahadi, R.; Joghataei, M.T. The Roles of Serotonin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.Z.; Cheer, J.F.; Tonini, R. Modulating the Neuromodulators: Dopamine, Serotonin, and the Endocannabinoid System. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, L.; di Porzio, U.; Viggiano, D.; de Donato, A.; Volpicelli, F. Dopamine: The Neuromodulator of Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity, Reward and Movement Control. Cells 2021, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasmari, F.; Goodwani, S.; McCullumsmith, R.E.; Sari, Y. Role of Glutamatergic System and Mesocorticolimbic Circuits in Alcohol Dependence. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 171, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Verma, H.K.; Bhaskar, L. Alcohol and Alcoholism Associated Neurological Disorders: Current Updates in a Global Perspective and Recent Recommendations. World J. Exp. Med. 2025, 15, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoch, M.-A.; Gorodetsky, E.; Hodgkinson, C.; Roy, A.; Goldman, D. Functional Genetic Variants That Increase Synaptic Serotonin and 5-HT3 Receptor Sensitivity Predict Alcohol and Drug Dependence. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengeliene, V.; Bilbao, A.; Molander, A.; Spanagel, R. Neuropharmacology of Alcohol Addiction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkiewcz, C.A. Serotonergic Systems in the Pathophysiology of Ethanol Dependence: Relevance to Clinical Alcoholism. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloninger, C.R. Neurogenetic Adaptive Mechanisms in Alcoholism. Science 1987, 236, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccaro, E.F.; Siever, L.J.; Owen, K.R.; Davis, K.L. Serotonin in Mood and Personality Disorders. Am. Psychiatr. Assoc. 1990, 20, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Glennon, R.; Dukat, M. Serotonin Receptors and Drugs Affecting Serotonergic Neurotransmission. Foye’s Princ. Med. Chem. 2002, 11, 365–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer, D.; Hannon, J.P.; Martin, G.R. Molecular, Pharmacological and Functional Diversity of 5-HT Receptors. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 71, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormfelde, S.V.; Hoell, I.; Tzvetkov, M.; Jamrozinski, K.; Sehrt, D.; Brockmöller, J.; Leibing, E. Anxiety- and Novelty Seeking-Related Personality Traits and Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphisms. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2006, 40, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heils, A.; Teufel, A.; Petri, S.; Seemann, M.; Bengel, D.; Balling, U.; Riederer, P.; Lesch, K.-P. Functional Promoter and Polyadenylation Site Mapping of the Human Serotonin (5-HT) Transporter Gene. J. Neural Transm. 1995, 102, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, A.; Goldman, D.; Gallinat, J.; Schumann, G.; Puls, I. Pharmacogenetic Insights to Monoaminergic Dysfunction in Alcohol Dependence. Psychopharmacology 2004, 174, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinckers, A.S.; Laucht, M.; Schmidt, M.H.; Mann, K.F.; Schumann, G.; Schuckit, M.A.; Heinz, A. Low Level of Response to Alcohol as Associated with Serotonin Transporter Genotype and High Alcohol Intake in Adolescents. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Das, S.K.; Vaidyanathan, K.; Vasudevan, D.M. Consequences of Alcohol Consumption on Neurotransmitters -an Overview. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2008, 5, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Report on Trends in Prevalence of Tobacco Use 2000–2025, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, M.; Howes, S.; Bebbington, P.; Brugha, T.; Jenkins, R.; Lewis, G.; Marsden, J.; Taylor, C.; Meltzer, H. Nicotine, Alcohol and Drug Dependence and Psychiatric Comorbidity: Results of a National Household Survey. Br. J. Psychiatry 2001, 179, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolka, M.N.; Reimold, M.; Kobiella, A.; Reischl, G.; Rietschel, M.; Heinz, A. Smoking Moderates Association of 5-HTTLPR and in vivo Availability of Serotonin Transporters. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloninger, C.R. Inheritance of Alcohol Abuse: Cross-Fostering Analysis of Adopted Men. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1981, 38, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloninger, C.R. Etiologic Factors in Substance Abuse: An Adoption Study Perspective. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1988, 89, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heath, A.C. Genetic Influences on Alcoholism Risk: A Review of Adoption and Twin Studies. Alcohol Health Res. World 1995, 19, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Verhulst, B.; Neale, M.C.; Kendler, K.S. The Heritability of Alcohol Use Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Twin and Adoption Studies. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierut, L.J. Genetic Vulnerability and Susceptibility to Substance Dependence. Neuron 2011, 69, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, T.V.; Goldman, D.; Mackay, T.F.; Anholt, R.R. The Genetic Basis of Alcoholism: Multiple Phenotypes, Many Genes, Complex Networks. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, W.R.; Xian, H.; Scherrer, J.F.; Madden, P.A.F.; Bucholz, K.K.; Heath, A.C.; Eisen, S.A.; Lyons, M.J.; Goldberg, J.; Tsuang, M. Common Genetic Vulnerability for Nicotine and Alcohol Dependence in Men. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1999, 56, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sealock, J.M.; Sanchez-Roige, S.; Clarke, T.-K.; Levey, D.F.; Cheng, Z.; Li, B.; Polimanti, R.; Kember, R.L.; Smith, R.V.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Problematic Alcohol Use in 435,563 Individuals Yields Insights into Biology and Relationships with Other Traits. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, P.B.; Dick, D.M. The Genetics of Externalizing Problems. In Recent Advances in Research on Impulsivity and Impulsive Behaviors; Wit, H.D., Jentsch, J.D., Eds.; Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 47, pp. 93–112. ISBN 978-3-030-60510-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, D.M.; Agrawal, A. The Genetics of Alcohol and Other Drug Dependence. Alcohol Res. Health J. Natl. Inst. Alcohol Abuse Alcohol. 2008, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, B.M.; Krueger, R.F.; Iacono, W.G.; McGue, M.; Patrick, C.J. Family Transmission and Heritability of Externalizing Disorders: A Twin-Family Study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S.; Prescott, C.A.; Myers, J.; Neale, M.C. The Structure of Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors for Common Psychiatric and Substance Use Disorders in Men and Women. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heils, A.; Teufel, A.; Petri, S.; Stöber, G.; Riederer, P.; Bengel, D.; Lesch, K.P. Allelic Variation of Human Serotonin Transporter Gene Expression. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Balling, U.; Gross, J.; Strauss, K.; Wolozin, B.L.; Murphy, D.L.; Riederer, P. Organization of the Human Serotonin Transporter Gene. J. Neural Transm. 1994, 95, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Ueno, S.; Sano, A.; Tanabe, H. The Human Serotonin Transporter Gene Linked Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) Shows Ten Novel Allelic Variants. Mol. Psychiatry 2000, 5, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Bengel, D.; Heils, A.; Sabol, S.Z.; Greenberg, B.D.; Petri, S.; Benjamin, J.; Müller, C.R.; Hamer, D.H.; Murphy, D.L. Association of Anxiety-Related Traits with a Polymorphism in the Serotonin Transporter Gene Regulatory Region. Science 1996, 274, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, R.K.; Hofmann, S.G.; Asnaani, A.; Sawyer, A.T.; Otto, M.W. The Serotonin Transporter Gene and Risk for Alcohol Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010, 108, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinn, R.; Nellissery, M.; Kranzler, H.R. Meta-analysis of the Association of a Functional Serotonin Transporter Promoter Polymorphism with Alcohol Dependence. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2005, 133B, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, Y.S.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, K.-U.; Pae, C.U. Association of the Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism with Korean Male Alcoholics. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2005, 39, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pombo, S.; de Quinhones Levy, P.; Bicho, M.; Barbosa, A.; Ismail, F.; Cardoso, N. Association of the functional serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) with externalizing and internalizing aggressivity and alcohol abuse. Acta Med. Port. 2008, 21, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gokturk, C.; Schultze, S.; Nilsson, K.W.; Knorring, L.V.; Oreland, L.; Hallman, J. Serotonin Transporter (5-HTTLPR) and Monoamine Oxidase (MAOA) Promoter Polymorphisms in Women with Severe Alcoholism. Arch. Womens Ment. Health 2008, 11, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronek, M.H.; Laucht, M.; Hohm, E.; Becker, K.; Schmidt, M.H. Interaction between the Dopamine D4 Receptor and the Serotonin Transporter Promoter Polymorphisms in Alcohol and Tobacco Use Among 15-Year-Olds. Neurogenetics 2006, 7, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Mazzanti, C.; Smith, T.L.; Ahmed, U.; Radel, M.; Iwata, N.; Goldman, D. Selective Genotyping for the Role of 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and GABAα6 Receptors and the Serotonin Transporter in the Level of Response to Alcohol: A Pilot Study. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, K.; Attonito, J.; Mendy, A.; Devieux, J.G.; Gasana, J.; Dorak, T.M. A Meta-Analysis of the Associations Between the SLC6A4 Promoter Polymorphism (5HTTLPR) and the Risk for Alcohol Dependence. Psychiatr. Genet. 2015, 25, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhnke, M.D.; Kolb, W.; Lutz, U.; Maurer, S.; Batra, A. The Serotonin Transporter Promotor Polymorphism 5-HTTLPR Is Not Associated with Alcoholism or Severe Forms of Alcohol Withdrawal in a German Sample. Psychiatr. Genet. 2006, 16, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, P.A.; Garcia-Portilla, M.P.; Florez, G.; Arango, C.; Corcoran, P.; Morales, B.; Bascaran, M.-T.; Alvarez, C.; Narciso, G.S.; Carreño, E.; et al. Differential Role of Serotonergic Polymorphisms in Alcohol and Heroin Dependence. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, H.; Bagger, Y.; Tanko, L.B.; Christiansen, C.; Werge, T. Lack of Association of the Serotonin Transporter Gene Promoter Region Polymorphism, 5-HTTLPR, Including Rs25531 with Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 150B, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltenberg, S.F.; Twitchell, G.R.; Hanna, G.L.; Cook, E.H.; Fitzgerald, H.E.; Zucker, R.A.; Little, K.Y. Serotonin Transporter Promoter Polymorphism, Peripheral Indexes of Serotonin Function, and Personality Measures in Families with Alcoholism. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 114, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrae, R.R.; Costa, P.T. NEO Inventories: Professional Manual; PAR: Lutz, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McCrae, R.R.; John, O.P. An Introduction to the Five-Factor Model and Its Applications. J. Pers. 1992, 60, 175–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, L.R. An Alternative “Description of Personality”: The Big-Five Factor Structure. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1990, 59, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruyt, F.D.; Bolle, M.D.; McCrae, R.R.; Terracciano, A.; Costa, P.T. Assessing the Universal Structure of Personality in Early Adolescence: The NEO-PI-R and NEO-PI-3 in 24 Cultures. Assessment 2009, 16, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedvadjiev, V.; van de Vijver, F.J.R. Universality of the Five-Factor Model of Personality. Int. Encycl. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 9, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, D.M. How Can Evolutionary Psychology Successfully Explain Personality and Individual Differences? Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 4, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrae, R.R.; Costa, P.T., Jr.; Pilar, G.H.D.; Rolland, J.-P.; Parker, W.D. Cross-Cultural Assessment of the Five-Factor Model: The Revised NEO Personality Inventory. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 1998, 29, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.T., Jr.; McCrae, R.R. Domains and Facets: Hierarchical Personality Assessment Using the Revised NEO Personality Inventory. J. Pers. Assess. 1995, 64, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, B.; First, M.B. Application of the ICD-11 Classification of Personality Disorders. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiger, T.A. Bruno Klopfer Award Address: Five-Factor Model Personality Disorder Scales. J. Pers. Assess. 2020, 102, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics. 11th revision. ICD-11; WHO: Geneve, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Delić, M.; Kajdiž, K.; Pregelj, P. Association of the Five-Factor Model Personality Traits and Opioid Addiction Treatment Outcome. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017, 29, 289–291. [Google Scholar]
- Kotov, R.; Gamez, W.; Schmidt, F.; Watson, D. Linking “Big” Personality Traits to Anxiety, Depressive, and Substance Use Disorders: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 136, 768–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raketic, D.; Barisic, J.V.; Svetozarevic, S.M.; Gazibara, T.; Tepavcevic, D.K.; Milovanovic, S.D. Five-Factor Model Personality Profiles: The Differences Between Alcohol and Opiate Addiction Among Females. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017, 29, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, E.; Erga, A.H.; Hagen, K.P.; Nesvåg, S.M.; McKay, J.R.; Lundervold, A.J.; Walderhaug, E. Assessment of Executive Function in Patients with Substance Use Disorder: A Comparison of Inventory- and Performance-Based Assessment. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2016, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogg, T.; Roberts, B.W. Duel or Diversion? Conscientiousness and Executive Function in the Prediction of Health and Longevity. Ann. Behav. Med. 2013, 45, 400–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, K.; Cloitre, M.; Tardiff, K.; Marzuk, P.M.; Portera, L.; Leon, A.C. Childhood Trauma as a Correlate of Lifetime Opiate Use in Psychiatric Patients. Addict. Behav. 2000, 25, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodl, T. Comorbidity of ADHD and Substance Use Disorder (SUD): A Neuroimaging Perspective. J. Atten. Disord. 2010, 14, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielberger, C.; Gorsuch, R.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.; Jacobs, G. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (Form Y1–Y2); Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983; Volume IV. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, B.F.; Goldstein, R.B.; Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Jung, J.; Zhang, H.; Pickering, R.P.; Ruan, W.J.; Smith, S.M.; Huang, B.; et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 Alcohol Use Disorder: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, M.G.; Abrams, K.; Thuras, P.; Hanson, K.L.; Brekke, M.; Sletten, S. Follow-up Study of Anxiety Disorder and Alcohol Dependence in Comorbid Alcoholism Treatment Patients. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennin, D.S.; Heimberg, R.G.; Turk, C.L.; Fresco, D.M. Preliminary Evidence for an Emotion Dysregulation Model of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Behav. Res. Ther. 2005, 43, 1281–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroń, A.; Suchanecka, A.; Chmielowiec, K.; Chmielowiec, J.; Lachowicz, M.; Strońska-Pluta, A.; Trybek, G.; Wach, T.; Domenech, P.J.G.; Grzywacz, A. Association Study of Serotonin 1A Receptor Gene, Personality, and Anxiety in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, K.A.; Olatunji, B.O. Specificity of Trait Anxiety in Anxiety and Depression: Meta-Analysis of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 82, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neda-Stepan, O.; Giurgi-Oncu, C.; Sălcudean, A.; Bernad, E.; Bernad, B.-C.; Enătescu, V.R. The Influence of Personality Traits on Postpartum Depression: A Systematic Review Based on the NEO-FFI Scale. Diseases 2024, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oreland, L.; Lagravinese, G.; Toffoletto, S.; Nilsson, K.W.; Harro, J.; Cloninger, C.R.; Comasco, E. Personality as an Intermediate Phenotype for Genetic Dissection of Alcohol Use Disorder. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaingankar, J.A.; Subramaniam, M.; Chong, S.A.; He, V.Y.F.; Abdin, E.; Picco, L.; Lim, W.Y.; Chia, S.E. Prevalence of Chronic Mental and Physical Disorders, Impact on Work Productivity and Correlates of Alcohol Use Disorders and Nicotine Dependence across Occupations. Ann. Acad. Med. Singapore 2015, 44, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, P.; Kaloiya, G.S. Quality of Life in Alcohol Use Disorder: Exploration of Predictive Factors in a Cross-Sectional Study. Psychiatry Int. 2024, 5, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, V.; Gomez, B.; Guo, S.; Low, Y.D.; Koh, P.K.; Wong, K.E. An Exploration of Quality of Life and Its Predictors in Patients with Addictive Disorders: Gambling, Alcohol and Drugs. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.M.; Rodríguez-Míguez, E. Using the SF-6D to Measure the Impact of Alcohol Dependence on Health-Related Quality of Life. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2015, 16, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmek, P.; Berlin, I.; Michel, L.; Berghout, C.; Meunier, N.; Aubin, H.-J. Determinants of Improvement in Quality of Life of Alcohol-Dependent Patients During an Inpatient Withdrawal Programme. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 6, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.Y.; Landron, F.; Lehert, P.; New European Alcoholism Treatment Study Group. Improvement in Quality of Life After Treatment for Alcohol Dependence with Acamprosate and Psychosocial Support. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, J.E.; Aggen, S.H.; Kendler, K.S. Role of Parental Divorce and Discord in the Intergenerational Transmission of Alcohol Use Disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022, 234, 109404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Johnson, E.C.; Colbert, S.; Pandey, G.; Chan, G.; Bauer, L.; Francis, M.W.; Hesselbrock, V.; Kamarajan, C.; Kramer, J.; et al. Evaluating Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder: Polygenic Risk Scores and Family History. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.; Steiner, M. Serotonin and Female Psychopathology. Womens Health 2013, 9, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciocha, F.; Suchanecka, A.; Chmielowiec, K.; Chmielowiec, J.; Ciechanowicz, A.; Boroń, A. Correlations of the CNR1 Gene with Personality Traits in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, M.L.; Martins, J.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gonçalves, J. Sex Differences in Tryptophan Metabolism: A Systematic Review Focused on Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savostyanov, A.N.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Lashin, S.А.; Tamozhnikov, S.S.; Saprygin, A.E.; Astakhova, T.N.; Kavai-Ool, U.N.; Borisova, N.V.; Karpova, A.G. Comprehensive Analysis of the 5-HTTLPR Allelic Polymorphism Effect on Behavioral and Neurophysiological Indicators of Executive Control in People from Different Ethnic Groups in Siberia. Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet. Sel. 2021, 25, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Mateu, F.; Escámez, T.; Koenen, K.C.; Alonso, J.; Sánchez-Meca, J. Meta-Analyses of the 5-HTTLPR Polymorphisms and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, N.; Glei, D.A.; Lin, Y.-H.; Weinstein, M. The Serotonin Transporter Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR): Allelic Variation and Links with Depressive Symptoms. Depress. Anxiety 2010, 27, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartter, M.A.; Ray, L.A. The Serotonin Transporter Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) and Alcohol Problems in Heavy Drinkers: Moderation by Depressive Symptoms. Front. Psychiatry 2011, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, D.; Ziółkowski, M.; Chodkiewicz, J.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Waszkiewicz, N.; Długosz, A.; Budzyński, J.; Junkiert-Czarnecka, A.; Kułak-Bejda, A. The Lack of Influence of Homozygous Long Allele of the 5-HTTLPR Gene on the Severity of Alcohol Craving During 6 Weeks of Rehab Hospitalisation in Comparison to Not Homozygous and Homozygous Short Alleles—Preliminary Report. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2023, 16, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, L.M.; Munier, E.C.; Trucco, E.M.; Hardee, J.E.; Burmeister, M.; Zucker, R.A.; Heitzeg, M.M. Effects of the Serotonin Transporter Gene, Sensitivity of Response to Alcohol, and Parental Monitoring on Risk for Problem Alcohol Use. Alcohol 2017, 59, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.I.; Conner, T.S.; Anton, R.F.; Gelernter, J.; Kranzler, H.R.; Covault, J. Variation in the Gene Encoding the Serotonin Transporter Is Associated with a Measure of Sociopathy in Alcoholics: Serotonin Transporter and Alcoholic Sociopathy. Addict. Biol. 2011, 16, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ferraguti, G.; Francati, S.; Codazzo, C.; Blaconà, G.; Testino, G.; Angeloni, A.; Fiore, M.; Ceccanti, M.; Lucarelli, M. DNA Sequence Variations Affecting Serotonin Transporter Transcriptional Regulation and Activity: Do They Impact Alcohol Addiction? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, A.; Jones, D.W.; Mazzanti, C.; Goldman, D.; Ragan, P.; Hommer, D.; Linnoila, M.; Weinberger, D.R. A Relationship between Serotonin Transporter Genotype and in vivo Protein Expression and Alcohol Neurotoxicity. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covault, J.; Armeli, S.; Tennen, H. The Moderating Effect of FKBP5 and 5-HTTLPR Polymorphisms on the Day-Level Association Between Drinking to Cope Motivation and Negative Affect. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 284, 112756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderrama, J.; Miranda, R. Early Life Stress Predicts Negative Urgency through Brooding, Depending on 5-HTTLPR Genotype: A Pilot Study with 6-Month Follow-up Examining Suicide Ideation. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 258, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talati, A.; Odgerel, Z.; Wickramaratne, P.J.; Norcini-Pala, A.; Skipper, J.L.; Gingrich, J.A.; Weissman, M.M. Associations between Serotonin Transporter and Behavioral Traits and Diagnoses Related to Anxiety. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 253, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A.V.; Swann, A.C.; Graham, D.P.; Patriquin, M.A.; Salas, R.; Nielsen, D.A.; Kosten, T.R. Emotional Self-Regulation, Impulsivity, 5-HTTLPR and Tobacco Use Behavior Among Psychiatric Inpatients. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 311, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukam, P.T.; Müller, D.K.; Deza-Lougovski, Y.I.; Pooseh, S.; Witt, S.H.; Rietschel, M.; Smolka, M.N. Connection Failure: Differences in White Matter Microstructure Are Associated with 5-HTTLPR but Not with Risk Seeking for Losses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordquist, N.; Oreland, L. Serotonin, Genetic Variability, Behaviour, and Psychiatric Disorders—A Review. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 115, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, M.R.; Brown, S.M.; Hariri, A.R. Serotonin Transporter (5-HTTLPR) Genotype and Amygdala Activation: A Meta-Analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, A.M.; Volkow, N.D.; Moeller, F.G.; Ferré, S. Personality Traits and Vulnerability or Resilience to Substance Use Disorders. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2014, 18, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, G.; Serretti, A. The Influence of the Serotonin Transporter Gene 5-HTTLPR Polymorphism on Suicidal Behaviors: A Meta-Analysis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 88, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, X.; Fountoulakis, K.N.; Juhasz, G.; Rihmer, Z.; Lazary, J.; Laszik, A.; Akiskal, H.S.; Bagdy, G. Association of the s Allele of the 5-HTTLPR with Neuroticism-Related Traits and Temperaments in a Psychiatrically Healthy Population. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 259, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Q.; Chen, H.; Hou, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhu, X.; Yi, J.; et al. Interaction Between a Serotonin Transporter Gene Promoter Region Polymorphism and Stress Predicts Depressive Symptoms in Chinese Adolescents: A Multi-Wave Longitudinal Study. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karg, K.; Burmeister, M.; Shedden, K.; Sen, S. The Serotonin Transporter Promoter Variant (5-HTTLPR), Stress, and Depression Meta-Analysis Revisited: Evidence of Genetic Moderation. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenness, J.L.; Hankin, B.L.; Young, J.F.; Smolen, A. Stressful Life Events Moderate the Relationship Between Genes and Biased Attention to Emotional Faces in Youth. Clin. Psychol. Sci. J. Assoc. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 4, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, C.R.; De Raedt, R. Differential Effects of 5-HTTLPR Genotypes on Inhibition of Negative Emotional Information Following Acute Stress Exposure and Tryptophan Challenge. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, L.R.; Hammen, C.; Brennan, P.A.; Najman, J.M. Relational Security Moderates the Effect of Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) on Stress Generation and Depression among Adolescents. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2013, 41, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, J.R.; Haas, G.L.; Goldstein, G.; Hanusa, B.; Walker, J.D.; Fox, L.J.; Ferrell, J. The “S” Allele of the Serotonin Transporter Is Not Associated with Major Depression in a Sample of Veterans. Adv. Genet. Res. 2014, 12, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Yao, S. The Involvement of Genes in Adolescent Depression: A Systematic Review. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummett, B.H.; Boyle, S.H.; Siegler, I.C.; Kuhn, C.M.; Ashley-Koch, A.; Jonassaint, C.R.; Züchner, S.; Collins, A.; Williams, R.B. Effects of Environmental Stress and Gender on Associations Among Symptoms of Depression and the Serotonin Transporter Gene Linked Polymorphic Region (5-HTTLPR). Behav. Genet. 2008, 38, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-A.; Fang, W.-H.; Liu, Y.-P.; Tzeng, N.-S.; Shyu, J.-F.; Wan, F.-J.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Chang, C.-C. Sex-Specific Pathways Among Tri-Allelic Serotonin Transporter Polymorphism, Trait Neuroticism and Generalized Anxiety Disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2020, 45, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, B.D.; Li, Q.; Lucas, F.R.; Hu, S.; Sirota, L.A.; Benjamin, J.; Lesch, K.-P.; Hamer, D.; Murphy, D.L. Association between the Serotonin Transporter Promoter Polymorphism and Personality Traits in a Primarily Female Population Sample. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 96, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-T.; Ham, B.-J. Serotonergic Genes and Amygdala Activity in Response to Negative Affective Facial Stimuli in Korean Women. Genes Brain Behav. 2008, 7, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingnell, M.; Comasco, E.; Oreland, L.; Fredrikson, M.; Sundström-Poromaa, I. Neuroticism-Related Personality Traits Are Related to Symptom Severity in Patients with Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder and to the Serotonin Transporter Gene-Linked Polymorphism 5-HTTPLPR. Arch. Womens Ment. Health 2010, 13, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochans, E.; Jurczak, A.; Szkup, M.; Samochowiec, A.; Włoszczak-Szubzda, A.; Karakiewicz, B.; Grzywacz, A.; Brodowska, A.; Samochowiec, J. Evaluation of the Relationship Between 5-HTT and MAO Gene Polymorphisms, Mood and Level of Anxiety among Postmenopausal Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2014, 12, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium, Including Analysis for Ascertainment Bias | Observed (Expected) | Allele Freq | χ2 (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUD n = 101 | L/S | 37 (30.5) | p (L) = 0.55 q (S) = 0.45 | 6.831 (0.0089) |
| S/S | 27 (20.5) | |||
| L/L | 37 (50.0) | |||
| Control n = 112 | L/S | 43 (48.5) | p (L) = 0.68 q (S) = 0.32 | 1.438 (0.230) |
| S/S | 14 (11.3) | |||
| L/L | 55 (52.3) | |||
| Genotypes | Alleles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/S | S/S | L/L | L | S | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| AUD | 37 | 27 | 37 | 111 | 91 |
| n = 101 | (36.63%) | (26.73%) | (36.63%) | (54.95%) | (45.05%) |
| Control | 43 | 14 | 55 | 153 | 71 |
| n = 112 | (38.39%) | (12.50%) | (49.11%) | (68.30%) | (31.70%) |
| χ2 | 7.545 | 8.036 | |||
| (p-value) | (0.0230) | (0.0046) | |||
| STAI NEO-FFI | Group | 5HTT (SLC6A4) | ANOVA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/S n = 80 M ± SD | S/S n = 92 M ± SD | L/L n = 41 M ± SD | Factor | F (p-Value) | ɳ2 | Power (alpha = 0.05) | ||
| STAI trait scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 7.24 ± 2.28 | 7.93 ± 2.02 | 7.43 ± 2.25 | Intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 1432.82 (p < 0.0001) *# F1,207 = 50.50 (p < 0.0001) *# F2,207 = 2.52 (p = 0.0833) F2,207 = 1.56 (p = 0.2121) | 0.874 0.196 0.024 0.015 | 1.000 1.000 0.500 0.329 |
| Control; n = 112 | 5.33 ± 2.33 | 5.79 ± 2.19 | 4.35 ± 2.20 | |||||
| STAI state scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 5.68 ± 2.48 | 6.37 ± 2.69 | 6.11 ± 2.41 | Intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 961.96 (p < 0.0001) * F1,207 = 14.35 (p = 0.0002) *# F2,207 = 1.17 (p = 0.3128) F2,207 = 2.00 (p = 0.1382) | 0.823 0.065 0.011 0.019 | 1.000 0.965 0.255 0.410 |
| Control; n = 112 | 5.02 ± 1.91 | 5.14 ± 1.83 | 4.04 ± 2.31 | |||||
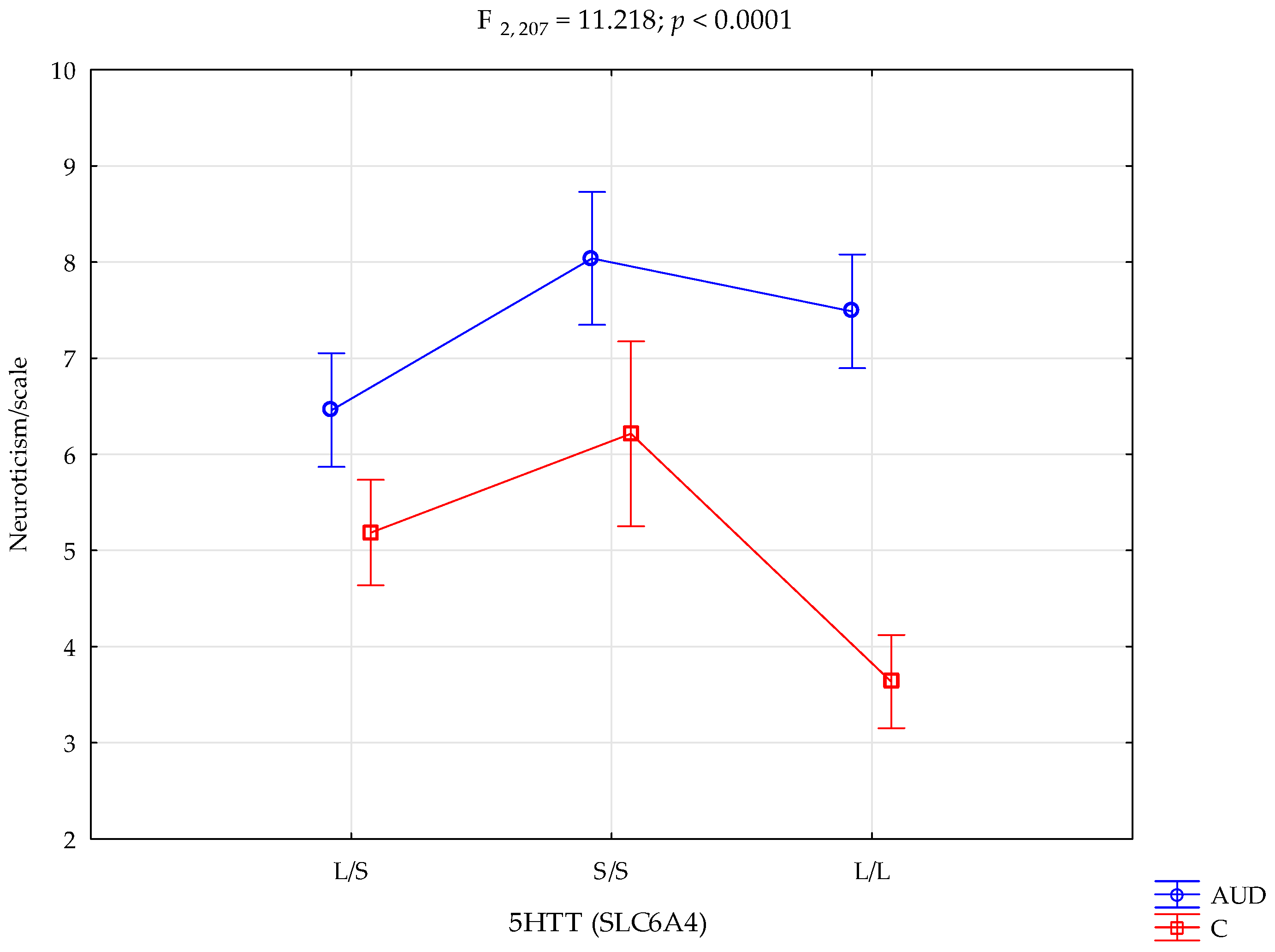
| Neuroticism scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 6.46 ± 1.61 | 8.04 ± 1.91 | 7.49 ± 1.79 | Intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 2024.63 (p < 0.0001) *# F1,207 = 71.28 (p < 0.0001) *# F2,207 = 9.88 (p = 0.0001) *# F2,207 = 11.22 (p < 0.0001) *# | 0.907 0.256 0.087 0.098 | 1.000 1.000 0.983 0.992 |
| Control; n = 112 | 5.19 ± 1.71 | 6.21 ± 2.08 | 3.64 ± 1.95 | |||||
| Extraversion scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 5.59 ± 2.07 | 4.00 ± 2.37 | 5.43 ± 2.09 | intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 1452.24 (p < 0.0001) *# F1,207 = 24.74 (p < 0.0001) *# F2,207 = 5.74 (p = 0.0037) *# F2,207 = 2.04 (p = 0.1328) | 0.875 0.107 0.053 0.019 | 1.000 0.999 0.863 0.417 |
| Control; n = 112 | 6.30 ± 1.67 | 6.00 ± 1.88 | 7.24 ± 1.99 | |||||
| Openness scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 4.81 ± 1.75 | 4.96 ± 2.41 | 5.51 ± 2.28 | intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 1104.62 (p < 0.0001) *# F1,207 = 5.09 (p = 0.0250) * F2,207 = 1.00 (p = 0.3689) F2,207 = 0.65 (p = 0.5259) | 0.842 0.024 0.009 0.006 | 1.000 0.613 0.223 0.157 |
| Control; n = 112 | 4.51 ± 1.72 | 4.29 ± 1.68 | 4.55 ± 1.63 | |||||
| Agreeability scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 3.89 ± 1.91 | 3.85 ± 2.03 | 3.78 ± 1.75 | intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 945.82 (p < 0.0001) *# F1,207 = 32.06 (p < 0.0001) *# F2,207 = 1.09 (p = 0.3365) F2,207 = 1.53 (p = 0.2184) | 0.820 0.134 0.010 0.015 | 1.000 0.999 0.241 0.324 |
| Control; n = 112 | 4.93 ± 1.93 | 6.00 ± 2.22 | 5.80 ± 2.30 | |||||
| Conscientiousness scale | Alcohol use disorder (AUD); n = 101 | 5.00 ± 2.43 | 4.81 ± 2.24 | 5.05 ± 2.37 | intercept AUD/control 5HTT (SLC6A4) AUD/control × 5HTT (SLC6A4) | F1,207 = 1275.86 (p < 0.0001) *# F1,207 = 27.98 (p < 0.0001) *# F2,207 = 1.48 (p = 0.2299) F2,207 = 0.75 (p = 0.4751) | 0.860 0.119 0.014 0.007 | 1.000 0.999 0.314 0.176 |
| Control; n = 112 | 6.60 ± 2.15 | 6.14 ± 1.66 | 7.29 ± 1.90 | |||||
| {1} | {2} | {3} | {4} | {5} | {6} | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M = 6.46 | M = 8.04 | M = 7.49 | M = 5.19 | M = 6.21 | M = 3.54 | |
| AUD L/S {1} | 0.0008 * | 0.0162 * | 0.0021 * | 0.6684 | 0.0000 * | |
| AUD S/S {2} | 0.2338 | 0.0000 * | 0.0027 * | 0.0000 * | ||
| AUD L/L {3} | 0.0000 * | 0.0271 * | 0.0000 * | |||
| Control L/S {4} | 0.0680 | 0.0000 * | ||||
| Control S/S {5} | 0.0000 * | |||||
| Control L/L {6} |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rychel, M.; Suchanecka, A.; Chmielowiec, J.; Chmielowiec, K.; Różański, J.; Masiak, J.; Grzywacz, A.; Boroń, A. Molecular Effect of Variants in Serotonin Transporter Gene in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder. Cells 2025, 14, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100699
Rychel M, Suchanecka A, Chmielowiec J, Chmielowiec K, Różański J, Masiak J, Grzywacz A, Boroń A. Molecular Effect of Variants in Serotonin Transporter Gene in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder. Cells. 2025; 14(10):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100699
Chicago/Turabian StyleRychel, Monika, Aleksandra Suchanecka, Jolanta Chmielowiec, Krzysztof Chmielowiec, Jacek Różański, Jolanta Masiak, Anna Grzywacz, and Agnieszka Boroń. 2025. "Molecular Effect of Variants in Serotonin Transporter Gene in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder" Cells 14, no. 10: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100699
APA StyleRychel, M., Suchanecka, A., Chmielowiec, J., Chmielowiec, K., Różański, J., Masiak, J., Grzywacz, A., & Boroń, A. (2025). Molecular Effect of Variants in Serotonin Transporter Gene in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder. Cells, 14(10), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100699








