Genome Instability and Senescence Are Markers of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Treatments
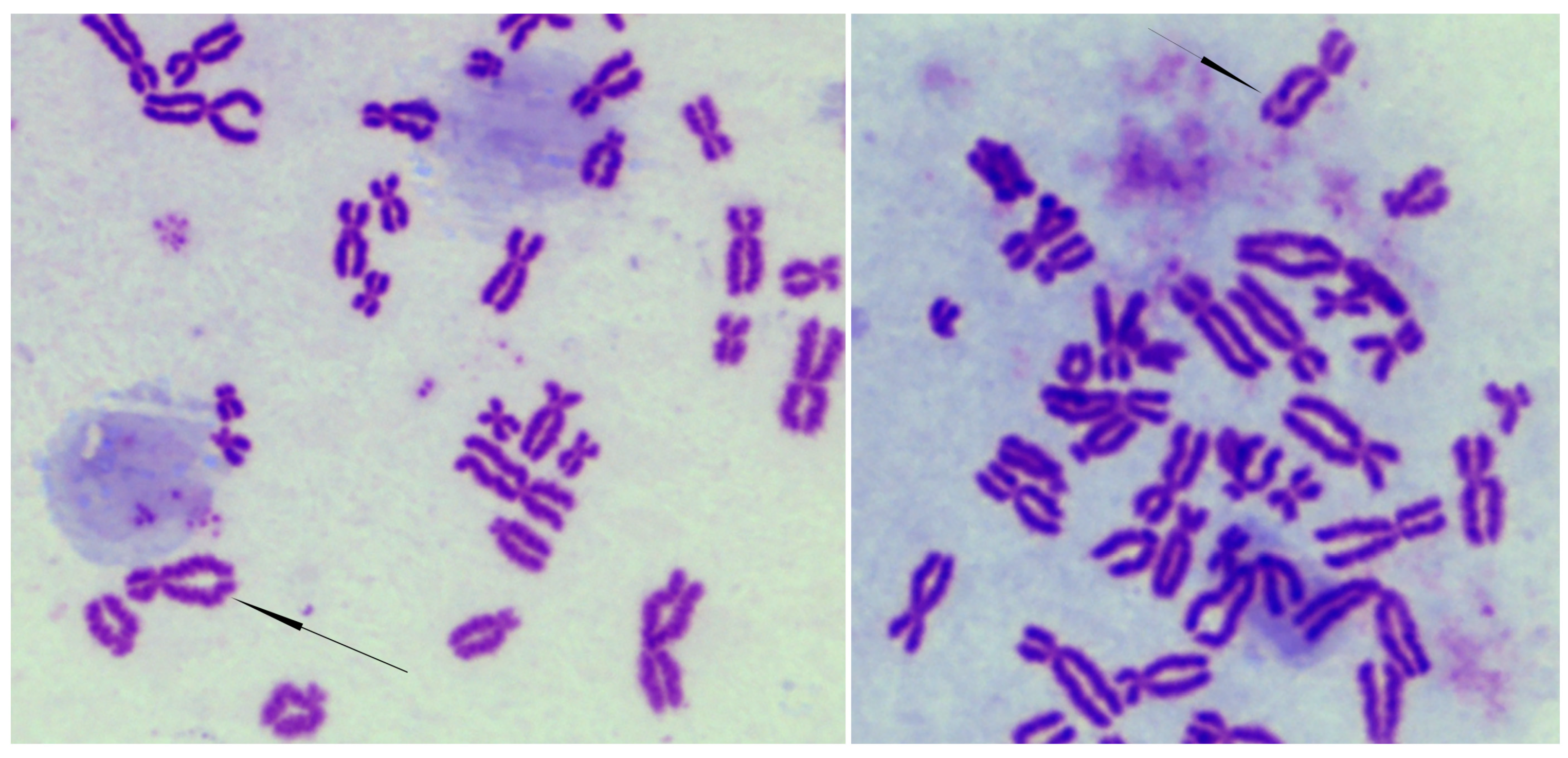
2.4. Cytogenetic Analysis
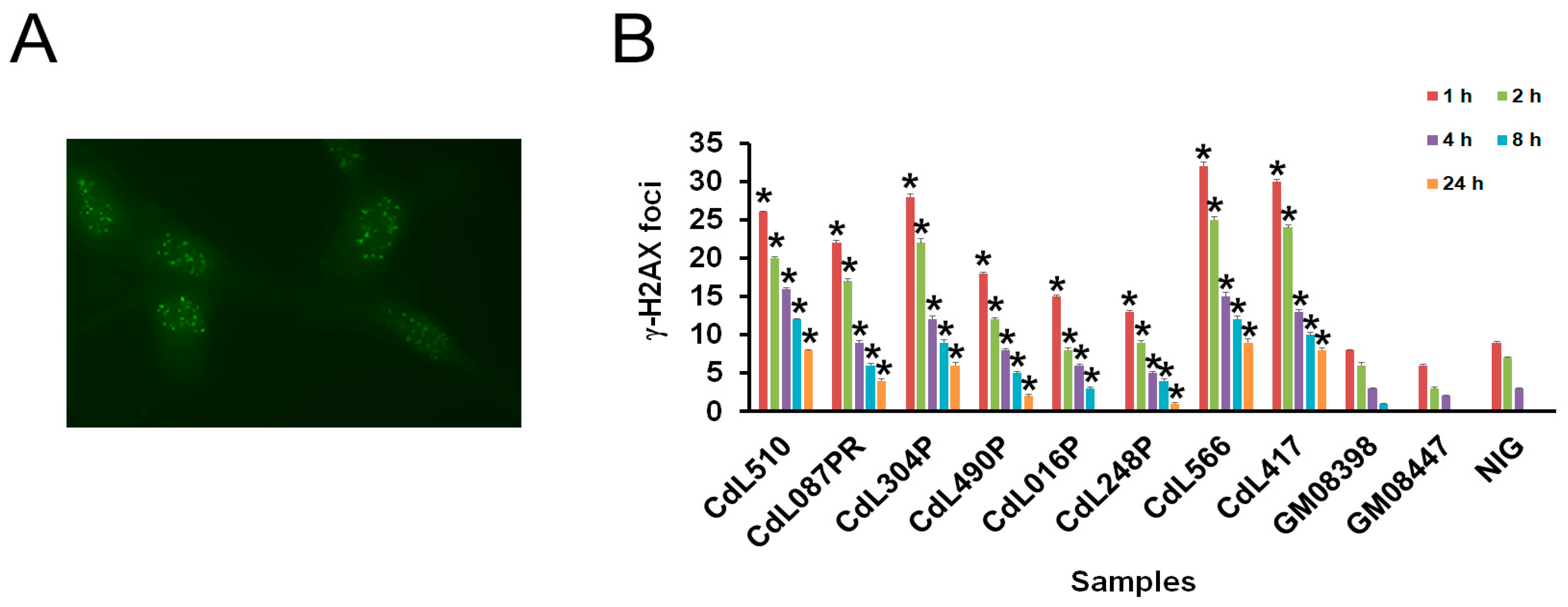
2.5. Immunofluorescence Labeling and Microscopy
2.6. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase (SA-β-gal) Staining
2.7. Oxidative Stress
2.8. RNA Purification and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
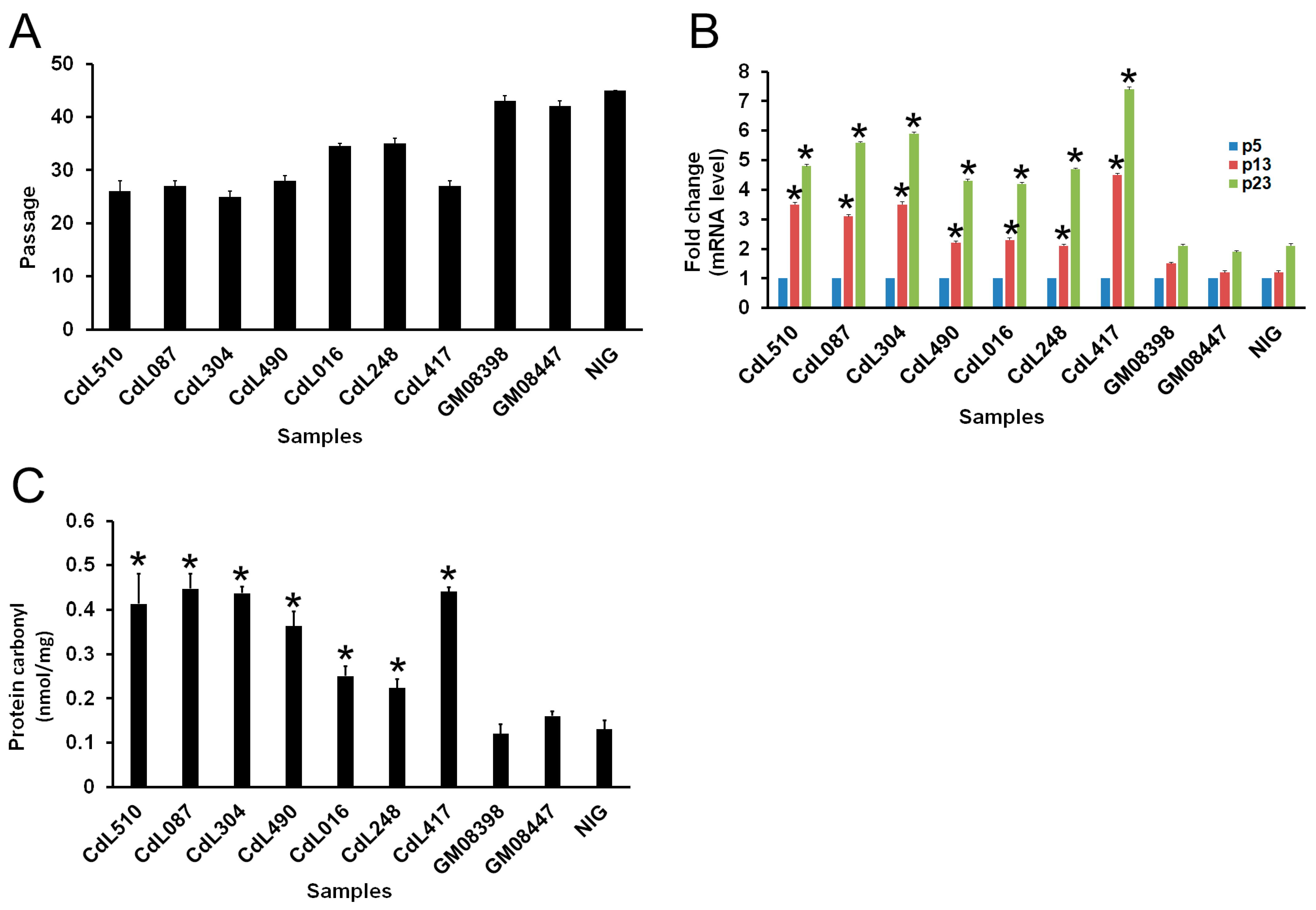
3.1. CdLS Cells Display Reduced In Vitro Lifespan
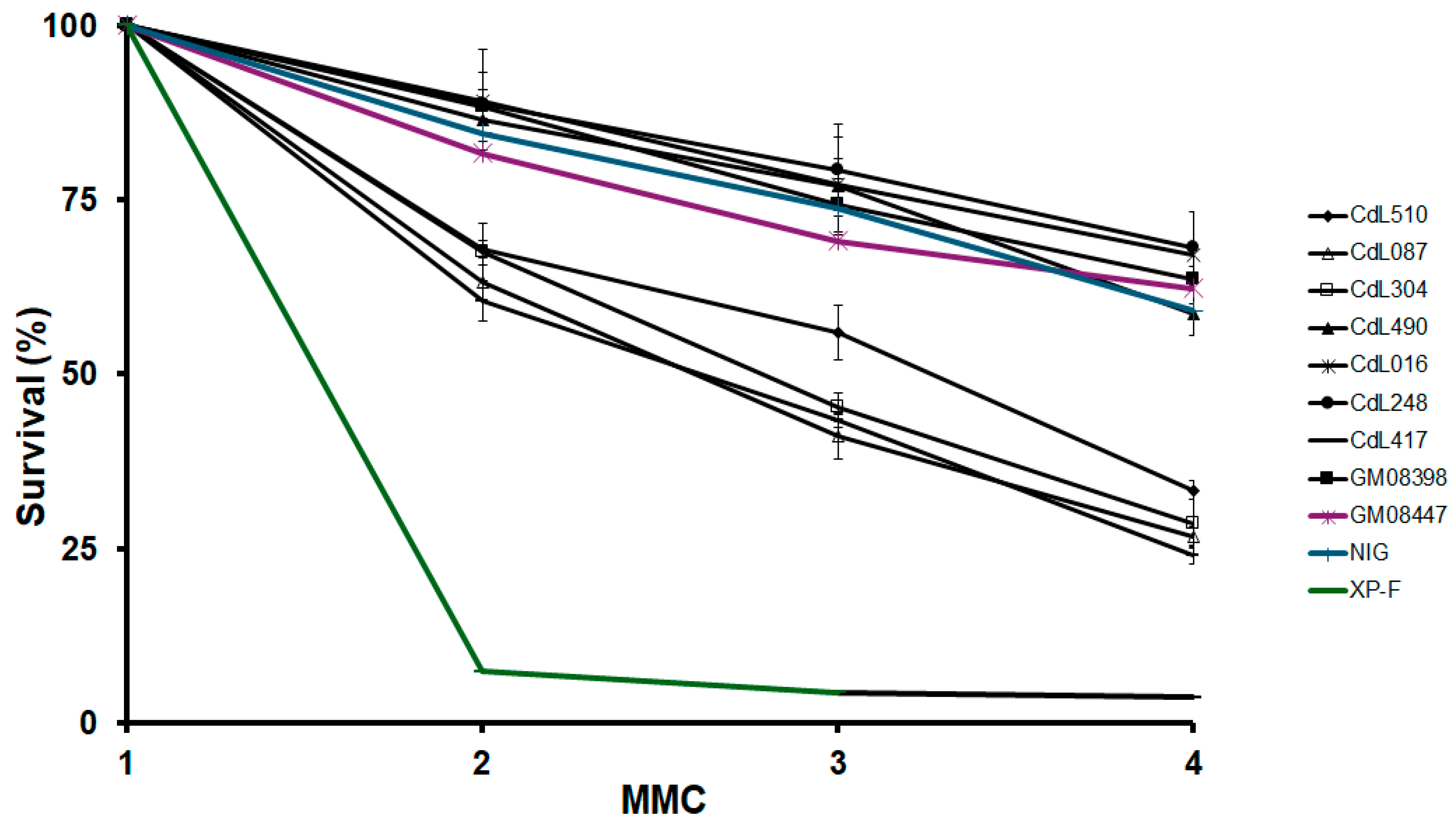
3.2. CdLS-Causative Genes Are Associated with Increased Sensitivity to Genotoxic Agents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yatskevich, S.; Rhodes, J.; Nasmyth, K. Organization of Chromosomal DNA by SMC Complexes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 445–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, T. Cohesion and cohesin-dependent chromatin organization. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 58, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsfield, J.A. Full circle: A brief history of cohesin and the regulation of gene expression. FEBS J. 2022, 290, 1670–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, M.; Pallotta, M.M.; Musio, A. The multifaceted roles of cohesin in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ruiten, M.S.; Rowland, B.D. SMC Complexes: Universal DNA Looping Machines with Distinct Regulators. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoth, C.; McLellan, M.D.; Vandin, F.; Ye, K.; Niu, B.; Lu, C.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; McMichael, J.F.; Wyczalkowski, M.A.; et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature 2013, 502, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Mermel, C.H.; Robinson, J.T.; Garraway, L.A.; Golub, T.R.; Meyerson, M.; Gabriel, S.B.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature 2014, 505, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiserson, M.D.; Vandin, F.; Wu, H.T.; Dobson, J.R.; Eldridge, J.V.; Thomas, J.L.; Papoutsaki, A.; Kim, Y.; Niu, B.; McLellan, M.; et al. Pan-cancer network analysis identifies combinations of rare somatic mutations across pathways and protein complexes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.E.; Li, T.; Shi, S.; Chen, D.X.; Chen, W.; Chen, H. ESCO2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating hnRNPA1 acetylation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.A.; Kim, J.S.; Bondaruk, J.; Shariat, S.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Ozawa, T.; Gerard, J.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, S.; et al. Frequent truncating mutations of STAG2 in bladder cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1428–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, B.D.; Stewart, C.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Alexe, G.; Kurek, K.C.; Calicchio, M.L.; Kiezun, A.; Carter, S.L.; Shukla, S.A.; Mehta, S.S.; et al. The genomic landscape of pediatric Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirode, F.; Surdez, D.; Ma, X.; Parker, M.; Le Deley, M.C.; Bahrami, A.; Zhang, Z.; Lapouble, E.; Grossetete-Lalami, S.; Rusch, M.; et al. Genomic landscape of Ewing sarcoma defines an aggressive subtype with co-association of STAG2 and TP53 mutations. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, A.; Shih, L.Y.; Minamino, M.; Sanada, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Okuno, Y.; Bando, M.; Nakato, R.; et al. Recurrent mutations in multiple components of the cohesin complex in myeloid neoplasms. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, M.; Astigiano, S.; Baldari, S.; Pallotta, M.M.; Porta, G.; Pigozzi, S.; Antonini, A.; Emionite, L.; Frattini, A.; Valli, R.; et al. The synergism of SMC1A cohesin gene silencing and bevacizumab against colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, K. Disorders of Transcriptional Regulation: An Emerging Category of Multiple Malformation Syndromes. Mol. Syndr. Syndromol. 2016, 7, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, A.D.; Moss, J.F.; Selicorni, A.; Bisgaard, A.M.; Deardorff, M.A.; Gillett, P.M.; Ishman, S.L.; Kerr, L.M.; Levin, A.V.; Mulder, P.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Cornelia de Lange syndrome: First international consensus statement. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deardorff, M.A.; Wilde, J.J.; Albrecht, M.; Dickinson, E.; Tennstedt, S.; Braunholz, D.; Monnich, M.; Yan, Y.; Xu, W.; Gil-Rodriguez, M.C.; et al. RAD21 mutations cause a human cohesinopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, M.A.; Kaur, M.; Yaeger, D.; Rampuria, A.; Korolev, S.; Pie, J.; Gil-Rodriguez, C.; Arnedo, M.; Loeys, B.; Kline, A.D.; et al. Mutations in cohesin complex members SMC3 and SMC1A cause a mild variant of cornelia de Lange syndrome with predominant mental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, M.A.; Bando, M.; Nakato, R.; Watrin, E.; Itoh, T.; Minamino, M.; Saitoh, K.; Komata, M.; Katou, Y.; Clark, D.; et al. HDAC8 mutations in Cornelia de Lange syndrome affect the cohesin acetylation cycle. Nature 2012, 489, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, E.T.; Wang, T.J.; Lisgo, S.; Bamshad, M.J.; Strachan, T. NIPBL, encoding a homolog of fungal Scc2-type sister chromatid cohesion proteins and fly Nipped-B, is mutated in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chea, S.; Kreger, J.; Lopez-Burks, M.E.; MacLean, A.L.; Lander, A.D.; Calof, A.L. Gastrulation-stage gene expression in Nipbl (+/−) mouse embryos foreshadows the development of syndromic birth defects. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadl4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, A.; Calof, A.L.; Lander, A.D.; Schilling, T.F. Multifactorial Origins of Heart and Gut Defects in nipbl-Deficient Zebrafish, a Model of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, S.; Calof, A.L.; Santos, R.; Lopez-Burks, M.E.; Young, C.M.; Hoang, M.P.; Chua, A.; Lao, T.; Lechner, M.S.; Daniel, J.A.; et al. Multiple organ system defects and transcriptional dysregulation in the Nipbl(+/-) mouse, a model of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bando, M.; Itoh, T.; Deardorff, M.A.; Clark, D.; Kaur, M.; Tandy, S.; Kondoh, T.; Rappaport, E.; et al. Transcriptional dysregulation in NIPBL and cohesin mutant human cells. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimenez, G.; Kalev-Zylinska, M.L.; Morison, I.; Bohlander, S.K.; Horsfield, J.A.; Antony, J. Cohesin rad21 mutation dysregulates erythropoiesis and granulopoiesis output within the whole kidney marrow of adult zebrafish. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Fernandez-Hernandez, R.; Cuadrado, A.; Coca, I.; Gomez, A.; Maqueda, M.; Latorre-Pellicer, A.; Puisac, B.; Ramos, F.J.; Sandoval, J.; et al. Disruption of NIPBL/Scc2 in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome provokes cohesin genome-wide redistribution with an impact in the transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olley, G.; Pradeepa, M.M.; Grimes, G.R.; Piquet, S.; Polo, S.E.; FitzPatrick, D.R.; Bickmore, W.A.; Boumendil, C. Cornelia de Lange syndrome-associated mutations cause a DNA damage signalling and repair defect. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrouwe, M.G.; Elghalbzouri-Maghrani, E.; Meijers, M.; Schouten, P.; Godthelp, B.C.; Bhuiyan, Z.A.; Redeker, E.J.; Mannens, M.M.; Mullenders, L.H.; Pastink, A.; et al. Increased DNA damage sensitivity of Cornelia de Lange syndrome cells: Evidence for impaired recombinational repair. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, M.; Musio, A. Cohesin—Bridging the gap among gene transcription, genome stability, and human diseases. FEBS Lett. 2024, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revenkova, E.; Focarelli, M.L.; Susani, L.; Paulis, M.; Bassi, M.T.; Mannini, L.; Frattini, A.; Delia, D.; Krantz, I.; Vezzoni, P.; et al. Cornelia de Lange syndrome mutations in SMC1A or SMC3 affect binding to DNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plesser Duvdevani, M.; Pettersson, M.; Eisfeldt, J.; Avraham, O.; Dagan, J.; Frumkin, A.; Lupski, J.R.; Lindstrand, A.; Harel, T. Whole-genome sequencing reveals complex chromosome rearrangement disrupting NIPBL in infant with Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervasini, C.; Picinelli, C.; Azzollini, J.; Rusconi, D.; Masciadri, M.; Cereda, A.; Marzocchi, C.; Zampino, G.; Selicorni, A.; Tenconi, R.; et al. Genomic imbalances in patients with a clinical presentation in the spectrum of Cornelia de Lange syndrome. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cukrov, D.; Newman, T.A.C.; Leask, M.; Leeke, B.; Sarogni, P.; Patimo, A.; Kline, A.D.; Krantz, I.D.; Horsfield, J.A.; Musio, A. Antioxidant treatment ameliorates phenotypic features of SMC1A-mutated Cornelia de Lange syndrome in vitro and in vivo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3002–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnden, D.G.; Klinger, H.P. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (1985) ISCN 1985. Report of the Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser. 1985, 21, 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, A.D.; Grados, M.; Sponseller, P.; Levy, H.P.; Blagowidow, N.; Schoedel, C.; Rampolla, J.; Clemens, D.K.; Krantz, I.; Kimball, A.; et al. Natural history of aging in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2007, 145, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Blair, J.; Devkota, B.; Fortunato, S.; Clark, D.; Lawrence, A.; Kim, J.; Do, W.; Semeo, B.; Katz, O.; et al. Genomic analyses in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome and related diagnoses: Novel candidate genes, genotype-phenotype correlations and common mechanisms. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2023, 191, 2113–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimigliano, A.; Mannini, L.; Bianchi, L.; Puglia, M.; Deardorff, M.A.; Menga, S.; Krantz, I.D.; Musio, A.; Bini, L. Proteomic profile identifies dysregulated pathways in Cornelia de Lange syndrome cells with distinct mutations in SMC1A and SMC3 genes. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 6111–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, L.; Lindroos, H.B.; Shirahige, K.; Sjogren, C. Postreplicative recruitment of cohesin to double-strand breaks is required for DNA repair. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, E.; Arbel-Eden, A.; Sattler, U.; Shroff, R.; Lichten, M.; Haber, J.E.; Koshland, D. DNA damage response pathway uses histone modification to assemble a double-strand break-specific cohesin domain. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ying, Y.; Shan, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Mao, W. Enhanced expression of cohesin loading factor NIPBL confers poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Beckouet, F.; Hu, B.; Roig, M.B.; Sutani, T.; Komata, M.; Uluocak, P.; Katis, V.L.; Shirahige, K.; Nasmyth, K. An Smc3 acetylation cycle is essential for establishment of sister chromatid cohesion. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, R.; Bakkenist, C.J.; McKinnon, P.J.; Kastan, M.B. Phosphorylation of SMC1 is a critical downstream event in the ATM-NBS1-BRCA1 pathway. Genes. Dev. 2004, 18, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, P.T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Patel, N.; Lee, E.Y.; Qin, J. SMC1 is a downstream effector in the ATM/NBS1 branch of the human S-phase checkpoint. Genes. Dev. 2002, 16, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Xu, B.; Kastan, M.B. Involvement of the cohesin protein, Smc1, in Atm-dependent and independent responses to DNA damage. Genes. Dev. 2002, 16, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.D.; McManus, K.; Yuen, K.W.; Reis, M.; Parmigiani, G.; Shen, D.; Barrett, I.; Nouhi, Y.; Spencer, F.; Markowitz, S.; et al. Chromatid cohesion defects may underlie chromosome instability in human colorectal cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3443–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, F.; Servadio, A.; Gatti, V.; Bianchi, P.; Mannini, L.; Prodosmo, A.; De Vitis, E.; Basso, G.; Friuli, A.; Laghi, L.; et al. Mutant cohesin drives chromosomal instability in early colorectal adenomas. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, M.M.; Di Nardo, M.; Musio, A. Synthetic Lethality between Cohesin and WNT Signaling Pathways in Diverse Cancer Contexts. Cells 2024, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarogni, P.; Palumbo, O.; Servadio, A.; Astigiano, S.; D’Alessio, B.; Gatti, V.; Cukrov, D.; Baldari, S.; Pallotta, M.M.; Aretini, P.; et al. Overexpression of the cohesin-core subunit SMC1A contributes to colorectal cancer development. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, M.M.; Di Nardo, M.; Hennekam, R.C.M.; Kaiser, F.J.; Parenti, I.; Pie, J.; Ramos, F.J.; Kline, A.D.; Musio, A. Cornelia de Lange syndrome and cancer: An open question. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2023, 191, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.A.; Ebens, C. Fanconi Anemia. In GeneReviews((R)); Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; McKinney, S.; Gerton, J.L. Persistent DNA Damage and Senescence in the Placenta Impacts Developmental Outcomes of Embryos. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cell Line | Gene | Gene Variation | Amino Acid Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| CdL510 | NIPBL | c.1372 C>T | p.Q458X |
| CdL087 | NIPBL | c.2479_2480del AG | p.R827gfsX2 |
| CdL304 | NIPBL | c.2479_2480del AG | p.R827gfsX2 |
| CdL490 | NIPBL | c.6893G>A | p.R2298H |
| CdL016 | HDAC8 | c.539A>G | p.H180R |
| CdL248 | HDAC8 | c.1001A>G | p.H334R |
| CdL417 | SMC1A | c.3146G>A | p.R1049Q |
| GM08398 | Control | ||
| GM08447 | Control | ||
| NIG | Control |
| Cell Line | Chromosome Aberrations | Metaphases |
|---|---|---|
| CdL510a | 15 | 100 |
| CdL510b | 13 | 100 |
| CdL087a | 12 | 100 |
| CdL087b | 14 | 100 |
| CdL304a | 13 | 100 |
| CdL304b | 11 | 100 |
| CdL490a | 9 | 100 |
| CdL490b | 7 | 100 |
| CdL016a | 7 | 100 |
| CdL016b | 6 | 100 |
| CdL248a | 6 | 100 |
| CdL248b | 6 | 100 |
| CdL417a | 23 | 100 |
| CdL417b | 25 | 100 |
| GM08398a | 3 | 100 |
| GM08398b | 4 | 100 |
| GM08447a | 2 | 100 |
| GM08447b | 4 | 100 |
| NIGa | 2 | 100 |
| NIGb | 3 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Nardo, M.; Krantz, I.D.; Musio, A. Genome Instability and Senescence Are Markers of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232025
Di Nardo M, Krantz ID, Musio A. Genome Instability and Senescence Are Markers of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Cells. Cells. 2024; 13(23):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232025
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Nardo, Maddalena, Ian D. Krantz, and Antonio Musio. 2024. "Genome Instability and Senescence Are Markers of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Cells" Cells 13, no. 23: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232025
APA StyleDi Nardo, M., Krantz, I. D., & Musio, A. (2024). Genome Instability and Senescence Are Markers of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Cells. Cells, 13(23), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232025








